Блог
3 ноября 2022 г.
IELTS и TOEFL по-прежнему можно сдать студентам из России, но для этого придется устроить целое путешествие в Казахстан, Азербайджан и другие страны, в которых можно пройти тестирование. Однако есть альтернативный способ подтвердить свои знания языка — экзамен Duolingo. Из чего он состоит, как его сдать и какие вузы принимают результаты — в нашей статье.
ACT — American College Testing — экзамен, который сдается большинством учащихся США для того, чтобы поступить в высшие учебные заведения этой страны. Некоторые университеты требуют результаты American College Testing и от иностранных абитуриентов. Часто они используются как дополнение к выписке школьных оценок. C 2020 года многие университеты США, включая Лигу плюща, отказываются от стандартизированных тестов ACT и SAT. Требования к наличию результатов этих экзаменов следует уточнять на сайте вуза.
Подготовка к экзаменам с UniPage
Мы поможем вам подготовиться к экзамену. Команда UniPage оценит вашу ситуацию, выслушает все пожелания и подберет лучшего преподавателя.
Подписывайтесь на наш YouTube-канал! Скоро новые выпуски про Британию, Германию, Францию и другие страны.
Перейти на канал
| Язык | английский |
| Стоимость экзамена | 150без части Writing-166.5с частью Writing USD |
| Частота проведения | 6 раз в год |
| Время проверки | 2-3 недели |
| Срок действия | 3 года |
| Место проведения | 150 стран |
| Сдать в России |
|
| Мин.-макс. балл | 1-36 |
| Альтернативный экзамен | SAT |
| Официальный сайт | ACT |
| Организатор | ACT, Inc. |
| Дата основания | 1959 год |
История теста ACT
Тест был придуман Эвереттом Франклином Линдквистом, профессором исследовательского Университета Айовы. Прототип ACT появился еще в 1929 году, когда исследователь разработал набор тестов для учеников средней и старшей школы, участвующих в олимпиаде. Официально ACT был впервые представлен в 1959 году.
С 2005 года в American College Testing появилась письменная часть. Сдавать ее необязательно, но многие крупные вузы требуют результаты Writing при поступлении. С 2015 года ACT доступен в электронном формате.
Материалы для самоподготовки к ACT
| Сайт | Описание |
| ACT | Официальный сайт ACT с примерами заданий и рекомендованными учебными пособиями |
| 4tests | Бесплатный онлайн-тест ACT |
| Varsitytutors | Бесплатные онлайн-тесты для каждой секции экзамена |
| Testverbal | Список слов для теста ACT |
| Testpreppractice | Список книг для подготовки к ACT |
Чем ACT отличается от SAT?
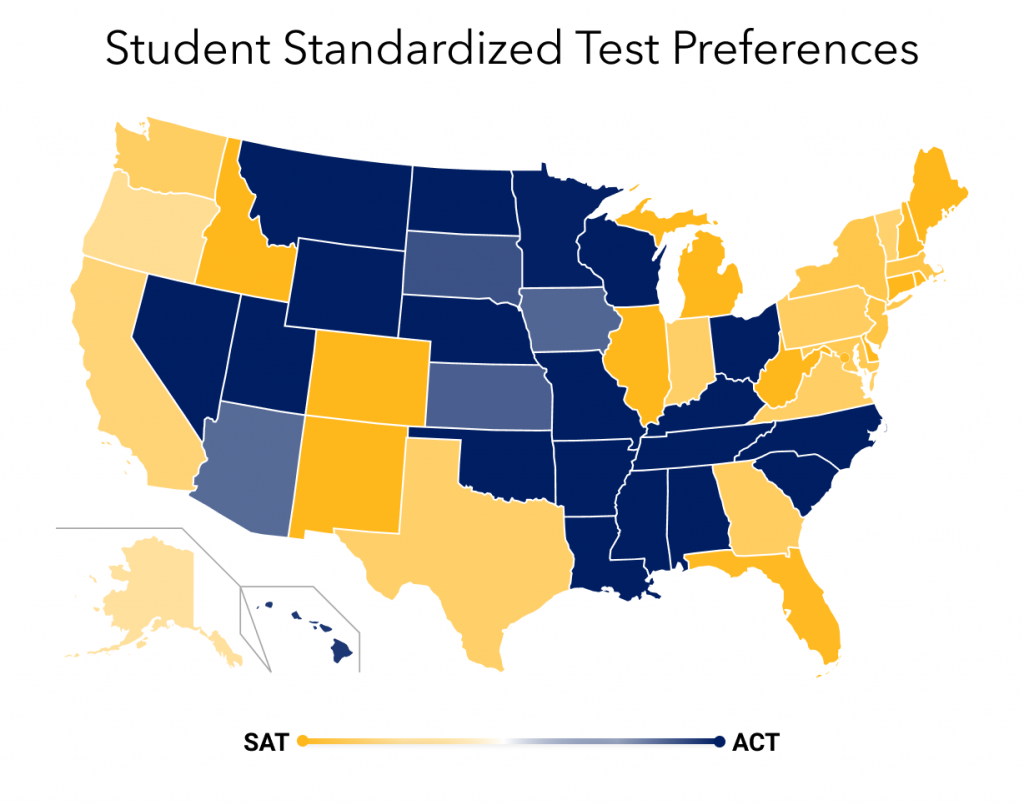
Часто ACT противопоставляется тесту SAT, который также нужен абитуриентам для поступления в вузы США. Считается, что American College Testing больше ориентирован на практические знания учащегося. ACT дает общую картину знаний школьника, а SAT показывает умения в конкретных дисциплинах. SAT более популярен на периферии США: на обоих побережьях страны и в штате Техас. ACT, напротив, в основном сдают будущие студенты на юге Соединенных Штатов, на Среднем Западе страны, а также в регионе Скалистых гор. Большинство колледжей и университетов США принимают результаты обоих экзаменов.
Также тест ACT отличается от SAT более простой формулировкой вопросов. Для того, чтобы успешно сдать ACT, необязательно обладать высоким словарным запасом, именно поэтому ACT часто выбирают иностранные абитуриенты.

Карта популярности ACT и SAT среди американских выпускников (ACT — синим, SAT — желтым цветом)
Структура ACT
Тест включает в себя 4 основных секции:
- English (английский);
- Mathematics (математика);
- Reading (чтение);
- Science (наука, умение рассуждать).
Существует также часть Writing (письмо), но она сдается отдельно от основных секций экзамена. Результаты Writing требуют некоторые учебные заведения США.
Каждая часть теста оценивается по шкале от 1 до 36 баллов. Общая оценка экзамена ACT — среднее арифметическое всех четырех тестов. Части English, Mathematics и Reading могут дать дополнительные баллыот 1 до 18, при этом общая оценка не меняется.
Часть Writing оценивается по шкале от 2 до 12 баллов и выносится на отдельный лист. Если вас не устраивает результат, тест ACT можно пересдать. Наивысший достижимый балл — 36.
Подробнее о содержании частей ACT
- Блок English состоит из 75 заданий. Его продолжительность составляет 45 минут. За это время нужно ответить на все вопросы: исправить ошибки, добавить необходимые знаки препинания. Часть English направлена на проверку знаний пунктуации и грамматики, риторических навыков, способности стилистической организации текста.
- Блок Mathematics длится один час, в течение которого необходимо справиться с 60 заданиями. Они дают представление о знаниях учащегося в нескольких дисциплинах: алгебра, геометрия, тригонометрия и теория вероятности. Каждое задание имеет 5 вариантов ответов. На математике можно использовать простой (непрограммируемый) калькулятор.
- Блок Reading состоит из 40 вопросов, которые относятся к четырем текстам на разные темы. Как правило, это отрывки из различных произведений. Первый текст представляет собой часть художественного произведения, второй касается социальных наук, третий — гуманитарных наук или рассказывает об искусстве, четвертый затрагивает знания о естественных дисциплинах. Эта часть экзамена рассчитана на 35 минут, за отведенное время необходимо ответить на вопросы об этих отрывках.
- Блок Science рассчитан на 35 минут. Это тест, состоящий из 40 вопросов. Экзаменуемому будут предложены семь отрывков из научных трудов по естественным предметам. К каждому тексту прилагаются вопросы. Во время сдачи этой части тестируемый должен проявить свои аналитические способности, умение решать задачи и рассуждать.
- Блок Writing длится 40 минут. За это время нужно написать эссе на социальную тему. Необходимо учитывать, что результат Writing не суммируется с общим баллом и не влияет на него. Но существует результат English+Writing, на который обращают внимание приемные комиссии некоторых вузов.
Сколько стоит сдать ACT?
| Услуга | Цена[1] |
|---|---|
| Регистрация на сдачу ACT without Writing |
|
| Регистрация на сдачу ACT with Writing |
|
| Отправка результатов в 5-6 вузов | 13 USDза каждый |
| Возврат средств в случае неявки | Нет |
ACT можно сдать в более чем 150 странах мира. В Австралии, России, Сингапуре и Франции организованы 4 центра приема экзамена. В Гонконге, где сдача ACT достаточно популярна, работает 6 центров приема теста.
На экзамен ACT необходимо зарегистрироваться. Это можно сделать по телефону, e-mail или на официальном сайте. На территории США экзамен проводится от 4 до 6 раз в год. Обычно тест можно сдать в сентябре, октябре, декабре, феврале, апреле и июне. Результаты ACT можно увидеть через 2-3 недели на официальном сайте. Чтобы получить официальный сертификат, придется подождать около двух месяцев.
Какой балл по ACT нужен для поступления в университет?
- Наиболее престижные вузы принимают абитуриентов с общим результатом по ACT в 30-36 баллов.
- Университеты из первой сотни рейтинга берут с баллами на уровне 25-27.
- Большинство вузов готовы рассмотреть кандидатов с баллами в диапазоне от 22 до 24.
- Существуют университеты и колледжи с либеральными взглядами на экзамен ACT, где достаточно иметь всего 17-21 баллов для поступления.
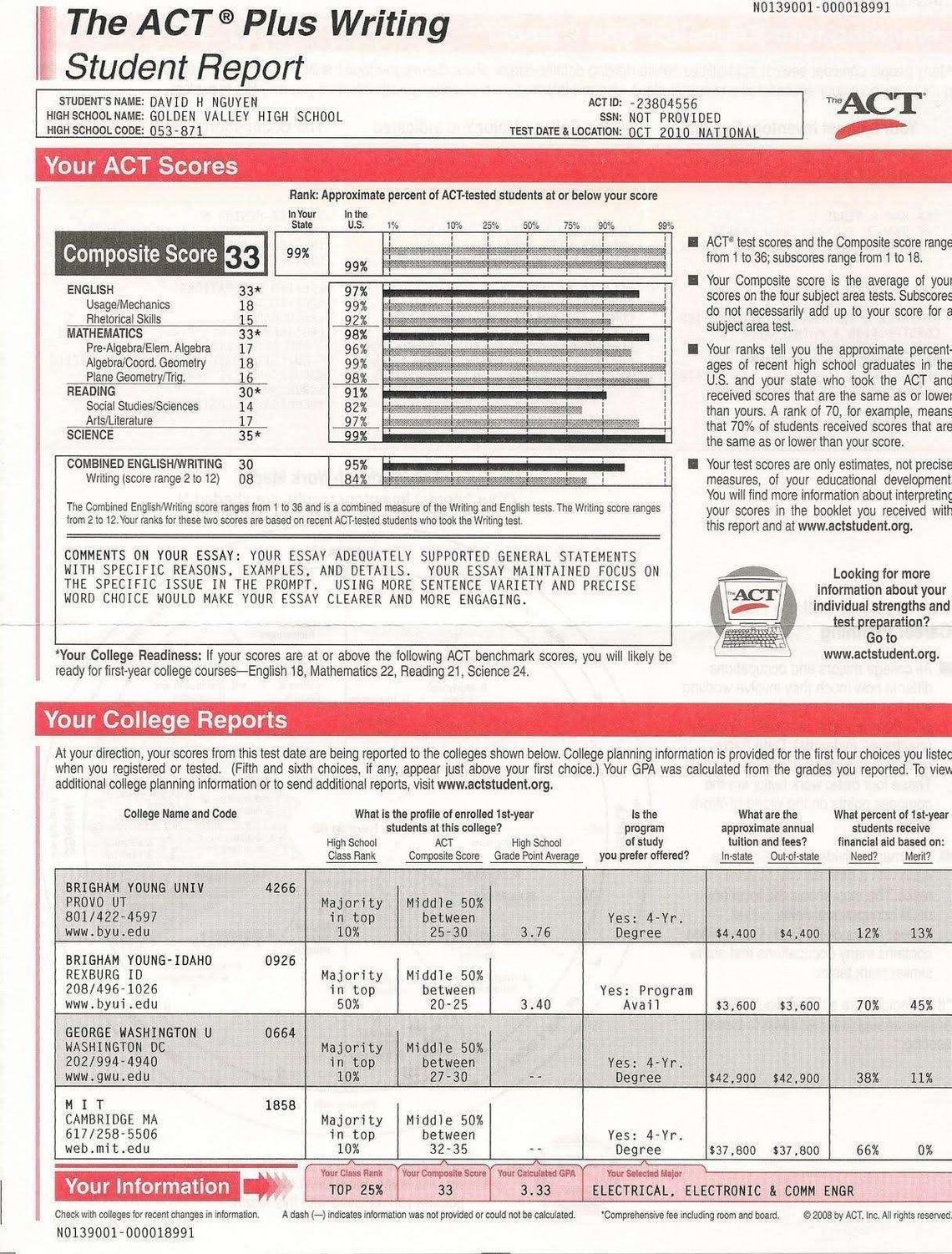
Образец сертификата ACT
Как сдать ACT на высокий балл?
- Следовать правилам. В случае нарушения дисциплины экзаменатор может удалить испытуемого из кабинета с последующим аннулированием работы. Не стоит приносить с собой шпаргалки, записывающие устройства или другие запрещенные предметы. Даже если кандидату не удалось воспользоваться шпаргалкой, но она была замечена инспектором, это уже веская причина для аннулирования работы. После окончания времени и слова «СТОП» нужно тут же закончить работу. В противном случае экзаменатор имеет право аннулировать результаты теста.
- Использовать правильные материалы для подготовки. Готовиться к тестированию следует только по официальным учебным пособиям, поскольку в них доступно описана структура экзамена и наилучшим образом подобраны задания. Лучше приобрести Real ACT Official Guide или учебные пособия других американских издательств — Barron’s, Kaplan, Princeton Review.
- Научиться распределять время. Экзамен ACT изобилует заданиями разной сложности, поэтому времени на их решение практически всегда недостаточно. Только правильное его распределение поможет справиться со всеми секциями и сэкономить пару минут для проверки ответов. Нужно не просто разобраться в структуре теста, но научиться находить правильный ответ максимально быстро. Для решения простых заданий достаточно быть предельно внимательным, поскольку нужный ответ находится прямо на поверхности. Желательно решить как можно больше пробных тестов на время, отводя для каждой секции определенное количество минут. Например, если в блоке представлено 60 вопросов, решить которые нужно за 60 минут, логично, что на каждое задание нужно потратить не более одной минуты.
- Готовиться заранее. Отличное знание предмета еще не является гарантией успешной сдачи экзамена. Помимо самого вопроса, немало времени занимает чтение разнообразных инструкций. Чтобы сэкономить лишние пару минут, следует заблаговременно ознакомиться с ними на официальном сайте экзамена ACT. После изучения инструкций можно закрепить результат, решив полноценный тест на время. На сайте экзамена предлагаются пробные варианты тестов.
- Тренировать внимательность. Предыдущий пункт ни в коем случае не призывает игнорировать инструкции. Их нужно читать и на экзамене. Важно быть максимально внимательным, особенно пристально стоит следить за словом «not». Часто испытуемые просто пропускают его, что становится причиной ошибки. Создатели экзамена прекрасно знают эту особенность, поэтому часто используют данный трюк в тесте.
- Учиться писать эссе. Академическая культура написания сочинений в американских учебных заведениях сильно отличается от того, как учат писать эссе в отечественных школах. Американцы особое значение придают наличию собственного мнения и умению аргументировать свою позицию. Не менее важны простота и ясность изложения, отсутствие путаницы, структурированность и логичность текста. На экзамене, как правило, предлагаются дискуссионные темы, но комиссия не требует от кандидата единственно правильного ответа на поставленный вопрос. Цель письменной секции заключается в оценке умений испытуемого сформулировать мысль и отстоять свою точку зрения. Чтобы справиться с этим заданием, важно наметить краткий план изложения. Это не займет много времени, но поможет логично составить и структурировать текст.
Ночь перед сдачей теста следует посвятить отдыху и сну. Не нужно доучивать материал, поскольку толку от этого будет действительно мало. Мозг должен расслабиться и отдохнуть, чтобы на следующий день быть во всеоружии. Недосып и повышенная возбудимость приводят к потери концентрации, забывчивости и неуверенности в собственных силах. Только полноценный отдых поможет побороть стресс и сосредоточиться на выполнении заданий теста.
Что еще нужно знать об ACT?
- В день тестирования обязательно нужно взять с собой приглашение на экзамен. Без этого документа и паспорта (или другого удостоверяющего личность документа) кандидата не допустят к прохождению теста.
- На экзамен необходимо взять пару простых карандашей, ластик, обычный калькулятор, аналоговые часы, безалкогольные напитки и легкие закуски.
- С собой запрещено брать маркеры, книги, словари, ручки, программируемые калькуляторы, любые записывающие устройства.
- Во время тестирования нельзя распивать принесенные напитки или поедать бутерброды и легкие закуски. Подкрепиться можно будет на перерыве (за время экзамена их будет несколько).
- Во всех аттестационных центрах тестирование ACT начинается в 8:00, но испытуемым необходимо прибыть на экзамен за 30 минут до его начала. Как правило, тест заканчивается в 12:15, а с письменной секцией — в 13:15.
- После прохождения теста каждый кандидат имеет возможность за отдельную плату воспользоваться дополнительной услугой — Test Information Release (TIR). Компания-организатор экзамена ACT в течение 3-5 недель после анонсирования официальных результатов тестирования предлагает выслать экзаменационные материалы желающим разобрать свои ошибки.
- Лишь 0,1% тестируемых на территории США сдают ACT на 36 баллов. В других странах сдающих на максимально возможный балл — единицы. Средняя общая оценка ACT составляет 21,1 балл.
Средние проходные баллы SAT и ACT в университетах США
Обновлено:
26 февраля 2021 г.
Ваша оценка сохранена.
Расскажите нам, что мы можем улучшить.
Ваша оценка сохранена.
Расскажите нам, что мы можем улучшить.
Подготовка к экзаменам с UniPage
Специалисты UniPage помогут найти опытного репетитора, который подготовит вас к важному экзамену. Занимайтесь:
- с носителем языка или преподавателем из России;
- очно в Москве или онлайн из любой точки мира;
- в группах или один на один.
Мы оценим вашу ситуацию, выслушаем все пожелания и подберем лучшего преподавателя.
Register for the ACT Test!
Next Test Date: April 15
Registration Deadline: March 10
Not quite ready to register? Sign up for a reminder alert so you don’t miss the deadline!
When it Comes to Test Prep, We’ve Got You Covered
Delivered by the experts, designed to fit your study preferences and your budget.
Your ACT Score
Viewing, sending, and understanding your score.
View and Send Your Score
You can have your ACT scores sent to other colleges and scholarship agencies even after you test.
When is Your Score Ready?
Learn more about when scores are ready, some within two weeks.
Understanding Your Score
Learn what goes into your composite score, how to use it, and more!
The ACT Test Overview
The ACT contains multiple-choice tests in four areas: English, mathematics, reading and science. ACT’s writing test is optional and will not affect your composite score.
Measures:
Your ability to make decisions to revise and edit short texts and essays in different genres.
Measures:
The mathematical skills you have typically acquired in courses up to the beginning of grade 12.
Measures:
Your ability to read closely, reason logically about texts using evidence, and integrate information from multiple resources.
Measures:
The interpretation, analysis, evaluation, reasoning and problem-solving skills required in biology, chemistry, Earth/space sciences and physics.
Measures:
The optional writing section measures writing skills taught in high school English classes and in entry-level college composition courses.
Test Day Checklist
Know what to expect on test day.
American College Testing – стандартизированный тест, чьи результаты требуются при поступлении в большинство колледжей и университетов США. ACT проводится на территории Соединенных Штатов и в официальных тестовых центрах мира, оценивает академическую готовность к колледжу местных/иностранных студентов.
Тест ACT определяет готовность по 5 блокам: английский, математика, чтение, естествознание, письмо (по желанию) + оценивает знания, навыки, приобретенные соискателями в школе. Это отличает ACT от теста Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT), ориентированного на проверку способностей учеников.
Для кого предназначен ACT?
Частные университеты и государственные вузы США предъявляют строгие академические требования к местным и зарубежным соискателям, но все они включают результаты стандартных тестов для оценки знаний, способностей будущих учеников. Колледжи и университеты США, предлагающие четырехлетние программы обучения – бакалавриат — принимают ACT и SAT: некоторые один из них, другие оба, поэтому при выборе вуза тщательно проверяйте список требований. Сегодня ACT остается наиболее востребованным приемными комиссиями вузов США.
Кто имеет право сдавать экзамен ACT, сроки проведения
Экзамен сдают ученики старших классов: чаще его выбирают учащиеся, готовящиеся к сдаче выпускных экзаменов после завершения среднего образования, которые хотят подать заявку на программы бакалавриата США. Ученики могут сдать тест до фактического сезона поступления: баллы остаются действительными на протяжении 5 лет после даты проведения испытания.
Разновидности American College Testing
Существует две разновидности тестирования: традиционный ACT без письменной части и ACT Plus Writing с дополнительным письменным тестом. При подаче заявок абитуриенты проверяют, требует ли выбранный колледж письменный модуль.
Стандартный тест включает 4 раздела, все вопросы сопровождаются несколькими вариантами ответов:
- Английский (75 вопросов, 45 минут): оценка письменного английского и риторических навыков
- Математика (60 вопросов, 60 минут): оценка математических навыков до уровня 10+1
- Чтение (40 вопросов, 35 минут): измерение прочитанного
- Наука (40 вопросов; 35 минут): измеряет навыки рассуждения, анализа, решения проблем и интерпретации в естественных науках.
Дополнительный письменный тест – 30-минутное эссе, позволяющее оценить навыки письма на английском.
Продолжительность теста – 2 ч. 55 мин., 3 ч. 25 мин. для письма ACT Plus, но он может занять и от 4 до 5 часов, включая перерывы и административные инструкции. Экзамен проводится письменно, но в ближайшее время планируется перевод в компьютерный или онлайн-формат.
Методика подсчета ACT
Методика начисления баллов используется для разделов с множественным выбором (математика, английский, чтение и наука): за каждый правильный ответ ученик получает 1 балл; для каждого раздела генерируется оценка, основанная на количестве правильных ответов. Баллы для каждого раздела преобразуются в общий балл от 1 до 36. Итоговый балл ACT – комбинированная оценка, которая рассчитывается как среднее значение по результатам выполнения заданий по всем четырем разделам.
Письменный тест ACT оценивают два экзаменатора по шкале от 1 до 6, где 6 баллов – максимально возможный. Обе оценки добавляются к подсчету.
Составной балл не включает оценку за письменную часть. Ученики могут узнать свои результаты онлайн через 2,5 недели после даты тестирования, но официальные отчеты об оценках публикуются через 3-8 недель после даты экзамена. Результаты письменного теста публикуются только после того, как все тесты были оценены, то есть через 5-8 недель после даты тестирования.
Ученик может отправить результаты теста ACT в любые колледжи кроме тех, которые вы выбрали во время регистрации, за дополнительную плату. Можно выполнить тест ACT несколько раз и подать в колледжи лучшие результаты.
Расписание экзаменов ACT
American College Testing проводится 6 раз за год: в сентябре, октябре, декабре, феврале, апреле, июне. Даты испытаний и соответствующие им сроки регистрации устанавливают международные испытательные центры: узнать адреса центров, даты проведения можно на официальном сайте ACT или у наших менеджеров. Регистрация участников теста на следующий учебный год начинается в июле.
Процедура подачи заявления ACT
Иностранные студенты регистрируются для участия в ACT онлайн: создают бесплатную учетную запись ACT, предоставляют персональные данные, информацию о плате за экзамен. В ближайшее время к общим требованиям прибавится подача фотографии: снимок можно будет загрузить через веб-сайт ACT, почту или мобильное устройство.
Учетная запись на веб-сайте ACT позволит студентам получать доступ и к другим возможностям: просмотр результатов, отчеты, изменения в предоставленную информацию при регистрации.
Экзаменационный сбор
Плата за экзамен для иностранных студентов составляет 65$ (без письменной части) и 80,5$ за тест с выполнением письменной работы. Стоимость оплаты включает отчеты, которые будут отправлены испытуемому, средней школе и четырем колледжам по выбору. Дополнительные сборы взимаются за добавление колледжа. Оплата за экзамен производится с помощью банковской карты и завершается в процессе регистрации ученика в центре.
Подготовка к тестированию
Перед участием в тестовых испытаниях ученики знакомятся с различными этапами теста, форматом проведения. На что стоит обратить внимание?
- Официальный орган тестирования публикует буклет материалов для подготовки к экзаменам под названием «Подготовка к ACT», который включает в себя практические тесты и стратегии подготовки и руководства для студентов.
- Знакомство с инструкциями отдельных разделов теста до экзамена позволит сэкономить время в день проведения испытаний.
- Результаты тестов с множественным выбором основаны на правильных ответах: оценки за неправильные ответы не начисляются, баллы не снимаются.
- Все вопросы одного раздела имеют одинаковый вес, поэтому сначала предпочтительнее ответить на простые и средние по сложности вопросы, прежде чем тратить время на трудные.
- Использование буклета «Письменный тест» для письменных заметок позволит подготовиться к началу написания эссе в папке ответов.
Различие между ACT и SAT
Оба теста – общепризнанные стандартизированные испытания, их сдача – общее требование к поступлению в американские высшие школы. Предназначенные главным образом для старшеклассников тесты измеряют мастерство при решении задач, понимании прочитанного.
Поскольку все американские колледжи и университеты принимают баллы по ACT или SAT, нет смысла сдавать оба теста. Содержание испытаний не идентично, но ACT и SAT во многом схожи:
Краткий обзор основных различий между ACT и SAT
|
Параметры |
ACT |
SAT |
|
Общее время |
2 часа 55 минут без письма 3 часа 35 минут с письмом 3 часа без эссе |
3 часа 50 минут с эссе |
|
Порядок разделов |
|
|
|
Время на раздел |
|
|
|
Количество вопросов |
|
|
|
Подсчет баллов |
Общая оценка – от 1 до 36. Каждый раздел использует шкалу от 1 до 36. Общий балл – средний из 4 баллов по разделам. В дополнительном разделе «Письмо» используется шкала от 2 до 12, баллы не засчитываются в окончательный счет. |
Общая оценка – 400-1600 В разделах «Основанное на фактах чтение и письмо» (EBRW) и «Математика» используется шкала 200-800, которые объединяются для получения общего балла. В дополнительном эссе используются три отдельные шкалы от 1 до 8, эти баллы не учитываются при подсчете окончательного результата. |
|
Стоимость |
50,5$ без письменного блока 67$ с письменным блоком |
47,5$ без эссе 64,5$ с эссе |
|
Кто принимает результаты |
Все колледжи и университеты США |
Все колледжи и университеты США |
Еще несколько отличий между двумя самыми популярными тестами, результаты которых принимают американские вузы:
- Научный раздел: ACT содержит раздел, полностью посвященный науке, SAT – нет. SAT предлагает вопросы, касающиеся научных аспектов в разделах «Чтение», «Письмо» и «Математика».
- Использование калькулятора: правила ACT разрешают использовать калькулятор для всех вопросов по математике, SAT содержит подраздел Math No Calculator, для которого нельзя использовать калькулятор.
- Акцент на геометрии: задания по геометрии составляют около 35-45% от ACT Math, от SAT – менее 10%. Тригонометрия составляет около 7% от ACT, от SAT – менее 5%.
- Варианты ответов — тесты различаются по количеству вариантов ответов по математике: ACT Math даёт 5 возможных вариантов ответа, SAT Math – 4 (AD).
- В разделе по чтению SAT все вопросы следуют в хронологическом порядке, в ACT Reading вопросы задаются случайным образом и не всегда следуют порядку содержания в отрывке.
- ACT Writing включает чтение короткого отрывка, анализ различных точек зрения на обсуждаемую проблему, после чего ученики высказывают свое мнение по этому вопросу. Соискатели, сдающие тест SAT, читают и анализируют эссе, используют доказательства, аргументацию автора, не высказывая собственное мнение.
Человек уже работает в выбранной сфере, но понимает, что на самом деле хочет сменить специальность или же углубить свои знания и экспертизу в своей области.Вне зависимости от цели обучения самые амбициозные абитуриенты зачастую видят своей целью поступление в университеты США.
И это абсолютно закономерно: взгляните на любой авторитетный рейтинг высших учебных заведений мира – например, QS или Times Higher Education – и вы увидите в числе лидеров огромное количество американских университетов.
Высшее образование в США ассоциируется с престижем, высочайшим качеством, инновациями, современным подходом к обучению, активным вовлечением студентов в практическую и исследовательскую деятельность.
Как часто мы слышим истории успеха, как еще во время учебы студенты, к примеру, Стэнфордского университета начинают собственный бизнес, и впоследствии становятся резидентами Кремниевой долины. Все это привлекает самых талантливых, самых упорных и целеустремленных абитуриентов со всего мира.
Не важно, студентом какого именно ВУЗа в США вы мечтаете стать, большинство университетов в Штатах для поступления на программы бакалавриата требуют от абитуриентов сертификат экзамена SAT или ACT. Именно об этих двух экзаменах пойдет речь в нашем материале. Рассмотрим, что это такое, в чем отличия, и как сдать экзамены SAT и ACT.
Итак, начать следует с того, что и SAT, и ACT – это американские стандартизированные экзамены, которые сдают выпускники школ для получения аттестата о среднем образовании и поступления в высшие учебные заведения. Основной целью данных тестов является оценка знаний студента по школьной программе, его готовности к учебе на программе высшего образования.
В целом, американские университеты не отдают однозначное предпочтение какому-то одному тесту, и абитуриент сам решает, какой экзамен он будет сдавать. Некоторые предпочитают сдавать оба – и SAT, и ACT. Однако мы советуем уточнить, какой из тестов предпочтительнее, на сайте выбранного университета.
Важно учитывать свои потребности, запросы, возможности и уровень подготовки, чтобы принять верное решение. Кому-то имеет смысл сдать именно SAT, кому-то – ACT, а для кого-то лучшим решением будет сдать оба теста. На личной консультации с нашим специалистом по высшему образованию за рубежом вы сможете задать все интересующие вас вопросы и узнать об особенностях поступления в университеты США – нажимайте на кнопку ниже и оставляйте заявку:
Получить персональную консультацию
А теперь давайте подробнее остановимся на каждом из экзаменов по-отдельности.
Содержание
Что такое SAT
Срок действия SAT
Структура теста
Оценка результатов
Проходной балл
Где сдавать?
Срок действия ACT
#Структура теста
Оценка результатов
Проходной балл
Где сдавать?
Основные отличия SAT и ACT
Что выбрать иностранному студенту – SAT или ACT?
Что такое SAT
Итак, экзамен SAT – что это? SAT Reasoning Test (Scholastic Aptitude Test или Scholastic Assessment Test) дословно расшифровывается как «Академический оценочный тест». Это стандартизированный тест, который необходим для поступления в высшие учебные заведения и колледжи США как для американских абитуриентов, так и для иностранных. При этом иностранным студентам помимо теста SAT необходимо сдать экзамен на уровень английского — TOEFL или IELTS.
SAT разрабатывается неправительственной организацией College Board и проводится уже более 120 лет — с 1901 года. Цель тестирования – проверить уровень подготовки студента по математике, оценить его аналитические и вербальные навыки. Для поступления на некоторые специальности может потребоваться сдача специализированного экзамена по предмету SAT Subject Test.
Срок действия SAT
После прохождения тестирования выдается сертификат сроком действия 5 лет. Таким образом, после того, как вы сдаете SAT экзамен, у вас есть 5 лет, в течение которых вы можете поступить в университет.
Структура теста
На сдачу экзамена SAT отводится 3 часа, и тестирование состоит из двух обязательных разделов, каждый из которых разделен еще на две части:
Английский язык и работа с текстом:
-
Задание на чтение (Reading Test). На выполнение этой части экзамена дается 65 минут. Обычно студентам предлагается прочитать 5 научно-познавательных текстов на разные темы, и затем на их остове необходимо ответить на 52 тестовых вопроса. Эта часть экзамена призвана оценить словарный запас студента и его способность анализировать тексты.
- Письмо и грамматика (Writing and Language Test). Эта часть длится 35 минут и состоит из 44 вопросов с вариантами ответов. Студенту даются отрывки из текстов, в которых нужно найти стилистические, орфографические и пунктуационные ошибки.
Математика:
-
Задания без калькулятора (The Math Test – No Calculator section). Первые 25 минут математического раздела отводятся на решение 20 заданий без использования калькулятора. 15 из них – с выбором ответа, и 5 – без выбора.
- Задания с калькулятором (The Math Test – Calculator). На эту часть дается 55 минут: студентам предстоит справиться с 38 задачами, для выполнения которых разрешается пользоваться калькулятором: 30 с выбором ответа и еще 8 – без выбора.
Также экзамен SAT включает раздел эссе, который до июня 2021 года являлся обязательным, а теперь — по выбору. Если вы пишете эссе, то к основному времени на экзамен добавляется еще 50 минут. Студенту предлагается тема — какое-либо утверждение (Statement), которое необходимо подтвердить или опровергнуть в своей работе.
Темы могут быть самыми разными, например, касаться значения работы и семьи в жизни человека, главное – все темы подбираются таким образом, чтобы они были понятны абитуриенту вне зависимости от его образования и социального положения. Работу проверяют два эксперта, каждый из которых ставит свои баллы, а целью данного раздела является оценка способности поступающего четко и грамотно выражать свои мысли.
Оценка результатов
На протяжении 120 лет проведения экзамена SAT и структура, и система оценки результатов претерпевали изменения. На сегодняшний день, как мы уже говорили, экзамен состоит из двух обязательных разделов – языкового и математического. Оценка SAT складывается из количества баллов за каждый раздел. За каждый из разделов можно получить от 200 до 800 баллов, а за весь экзамен – от 400 до 1600 баллов.
Все вопросы по сложности можно разделить на простые, средние и сложные, и, как правило, в начале раздела идут простые вопросы, постепенно становясь все сложнее к концу. При подсчете результата учитываются только правильные ответы, а за неправильные ответы или вопросы без ответа балл не снижается. Поэтому имеет смысл отвечать на все вопросы теста, даже если вы не уверены в ответе.
Поскольку эссе не является обязательной частью экзамена SAT, за этот раздел оценка выставляется отдельно. Эксперты оценивают работу по трем критериям:
- Понимание темы;
- Критический анализ;
- Техника написания эссе
Каждый из этих критериев оценивается по шкале от 2 до 8 баллов, то есть максимально за раздел эссе можно заработать 24 балла.
Проходной балл
Каждый университет устанавливает свой проходной балл экзамена SAT для зачисления на программы, и проходной балл варьируется в зависимости от выбранной программы. Ниже несколько примеров средних проходных баллов в университетах США:
|
ВУЗ |
Средний проходной балл SAT |
|
Калифорнийский технологический институт |
1530-1600 |
|
Гарвардский университет |
1480-1600 |
|
Йельский университет |
1480-1600 |
|
Массачусетский технологический институт (MIT) |
1480-1580 |
|
Стэнфордский университет |
1460-1590 |
Где сдавать?
Сдать SAT можно в экзаменационных центрах как на территории США, так и за ее пределами – 4 раза в год в октябре, декабре, марте и мае. К примеру, в России в 2021-2022 учебном году тест SAT можно сдать в экзаменационном центре в Москве и Сыктывкаре.
Для студентов из России стоимость сдачи SAT составляет 101 USD без раздела эссе и 117 USD с разделом эссе. Результаты теста публикуются на официальном сайте College Board – организации, которая проводит экзамен – примерно через 2 недели после сдачи. А через 6 недель студент получает печатный сертификат.
Что такое ACT
Еще один стандартизированный тест, который может потребоваться для поступления на программы бакалавриата в университеты и колледжи США – это ACT или «Американское тестирование» (American College Testing).
Прототип теста был разработан в 1929 году профессором Эвереттом Франклином Линдквистом, и первое официальное тестирование ACT состоялось в 1959 году. Сейчас тест сдают как американские, так и иностранные абитуриенты, и университеты обычно запрашивают сертификат ACT в дополнение к выписке школьных оценок.
Цель тестирования – определить уровень подготовки абитуриента к обучению на программе высшего образования, оценить его математические и языковые знания, способность грамотно излагать свои мысли на английском языке, умение анализировать художественные и научные тексты.
Иностранным студентам, которые поступают в американский ВУЗ с результатами ACT экзамена, обязательно нужно предоставить еще и сертификат международного тестирования по английскому языку (как правило, TOEFL или IELTS), чтобы подтвердить свой уровень владения английским.
Срок действия ACT
С сертификатом о результате экзамена ACT можно поступить в колледж или университет США в течение трех лет после сдачи.
Структура теста
Экзамен ACT состоит из четырех обязательных разделов:
- Английский язык (English)
Данный раздел включает 75 заданий, на выполнение которых отводится 45 минут. Здесь оцениваются знания грамматики и пунктуации, стилистики и орфографии.
- Математика (Mathematics)
На выполнение 60-ти заданий по математике дается 60 минут. Студенту предлагаются вопросы с вариантами ответов на проверку его знаний по алгебре, геометрии, тригонометрии и теории вероятности. Во время работы над этой частью экзамена разрешается пользоваться калькулятором.
- Чтение (Reading)
Эта часть экзамена рассчитана на 35 минут, в течение которых абитуриенту предлагается ознакомиться с четырьмя текстами на разные темы, а затем на их основе ответить на 40 вопросов. Как правило, первый текст является отрывком из художественного произведения, второй посвящен социальным наукам, третий касается гуманитарных наук или искусства, а в четвертом речь идет о естественнонаучных дисциплинах.
- Наука (Science)
Данный блок продолжительностью 35 минут призван оценить навыки аналитического мышления и умение решать задачи. Студенту предстоит ответить на 40 вопросов на основе семи отрывков из научных работ по естественным наукам.
Также в экзамене есть необязательный раздел эссе (Writing) – он оценивается отдельно от основных секций ACT. На этот блок отводится 40 минут, в течение которых необходимо написать эссе, как правило, на социальную тему. Эту часть экзамена проверяют двое экспертов, каждый из которых ставит свою оценку – от 2 до 12 баллов.
Важно, что оценка за раздел эссе не суммируется с баллами за остальные разделы и не влияет на общий результат экзамена. Однако приемные комиссии некоторых университетов обращают внимание на совместный результат английский + эссе (English+Writing).
Всего на сдачу теста ACT выделяется 2 часа 55 минут или 3 часа 35 минут, в том случае, если вы выбираете вариант экзамена с разделом эссе.
Оценка результатов
Каждая из четырех обязательных частей теста ACT оценивается по шкале от 1 до 36 баллов, а для определения результата всего экзамена баллы за каждый раздел не суммируются. Вместо этого вычисляется среднее арифметическое баллов за все четыре раздела.
При подсчете результатов учитываются только правильные ответы, и за неправильные ответы или вопросы, оставленные без ответа, общий балл не снижается. Поэтому, как и на экзамене SAT, стоит испытать удачу, и отвечать на все вопросы, включая и те, в которых абитуриент не уверен.
Как мы уже упоминали, в общем результате не учитывается балл за необязательный раздел эссе – эта оценка выносится на отдельный лист. А максимально высокий общий результат экзамена ACT составляет 36 баллов. Результаты публикуются на официальном сайте экзамена через 2 – 2 с половиной недели после сдачи, а официальный печатный сертификат можно получить, как правило, через 8 недель.
Проходной балл
С какими баллами за экзамен ACT принимают университеты США? Все зависит от конкретного выбранного ВУЗа. Логично, что самые престижные университеты, такие как MIT или Стэнфорд, принимают студентов с самыми лучшими результатами по экзамену ACT — в среднем 30-36 баллов. В то же время в США, есть университеты, в которых проходной балл гораздо ниже и составляет, к примеру, 17-21 балл.
Рассмотрим средние проходные баллы некоторых известных ВУЗов США:
|
ВУЗ |
Средний проходной балл ACT |
|
Калифорнийский технологический институт |
34-35 |
|
Массачусетский технологический институт (MIT) |
33-35 |
|
Гарвардский университет |
32-35 |
|
Принстонский университет |
32-35 |
|
Стэнфордский университет |
31-35 |
Где сдавать?
Помимо США тест ACT можно сдать более чем в 150 странах по всей планете. Например, в России действует экзаменационные центры в Москве, Санкт-Петербурге, Владивостоке и Екатеринбурге. Экзамен, как правило, проводится от четырех до шести раз в год в сентябре, октябре, декабре, феврале, апреле и июне.
Стоимость сдачи ACT без раздела эссе для иностранных студентов составляет 168,50 USD. Если экзамен включает раздел эссе, то стоимость сдачи составит 188,50 USD. Результаты можно увидеть на официальном сайте экзамена ACT через 2 – 2 с половиной недели, а печать официального сертификата обычно занимает примерно два месяца.
Основные отличия SAT и ACT
Итак, мы разобрались с деталями каждого экзамена по-отдельности. Так есть ли между ними какая-то разница, и если отличия есть, то в чем они заключаются? Как определить, какой из экзаменов целесообразнее сдавать для поступления в американский университет?
Сразу оговоримся: общих правил нет, и большинство высших учебных заведений США принимают во внимание результаты и SAT, и ACT. Некоторые, к слову, и вовсе отказываются от правила, что абитуриент должен предоставить сертификат какого-либо из этих тестов: с 2020 года наличие сертификата стандартизированного теста не является обязательным при приеме в ряд университетов, включая Стэнфордский, Йельский и MIT.
Однако для поступления на некоторые программы какого-либо университета может потребоваться не просто сертификат SAT, а SAT с частью эссе или специализированный Subject SAT по нескольким предметам. Или не просто сертификат ACT, а ACT с частью эссе. Поэтому смысл в том, чтобы разобраться, какой же из тестов будет более подходящим в вашем конкретном случае, все же есть.
Чтобы не запутаться в требованиях и правилах университетов, не тратить огромное количество времени на самостоятельное изучение тонкостей каждого экзамена, рекомендуем сэкономить свое время и нервы, которые еще пригодятся в процессе поступления, и получить профессиональный совет от эксперта по обучению за рубежом.
Вы можете записаться на бесплатную консультацию с нашим специалистом, нажав на кнопку ниже:
Получить персональную консультацию
Для удобства мы представили основные отличия между тестами SAT и ACT в виде сводной таблицы:
|
SAT |
ACT |
|
|
Продолжительность |
3 часа без раздела эссе 3 часа 50 минут с разделом эссе |
2 часа 55 минут без раздела эссе 3 часа 35 минут с разделом эссе |
|
Количество вопросов |
154 |
215 |
|
Срок действия сертификата |
5 лет |
3 года |
|
Структура |
Английский язык:
Математика:
Эссе (опционально) |
|
|
Максимально возможный балл |
1600 (сумма баллов за каждый раздел) |
36 (среднее арифметическое баллов за каждый раздел) |
|
Неправильные ответы |
не снижают общий балл |
не снижают общий балл |
|
Стоимость |
101 USD без раздела эссе; 117 USD с разделом эссе |
168,50 USD без раздела эссе; 188,50 USD с разделом эссе |
|
Где сдать тест в России |
Москва, Сыктывкар |
Москва, Санкт-Петербург, Владивосток, Екатеринбург |
А теперь подробнее остановимся на этих различиях.
Принято считать, что SAT больше ориентирован на логику и математику, в то время как ACT – на гуманитарные науки. SAT в большей степени оценивает логические, языковые, математические, аналитические навыки, а ACT – проверяет уровень знаний по школьной программе в целом. Поэтому, если вы считаете себя гуманитарием, возможно, вам будет более комфортно сдавать именно ACT. Однако стоит учитывать, что на выполнение заданий в SAT дается больше времени, чем на экзамене ACT.
Что касается структуры экзаменов, то раздел чтения в SAT в большей степени оценивает словарный запас студента, поэтому, если вы не уверены в своем уровне английского, лучше выбрать ACT. Хотя на выполнение этого раздела в ACT дается намного меньше времени, и есть риск просто не успеть проанализировать все тексты.
Раздел математики в обоих тестах включает задания по алгебре, геометрии, арифметике и тригонометрии. Помимо них в SAT включены вопросы по статистике и теории вероятности. Еще одно отличие состоит в том, что все математические задания на экзамене ACT можно выполнять с помощью калькулятора, а на SAT – только часть.
Оценка знаний по естественным наукам выделяется в отдельный блок только в экзамене ACT. Однако задания на проверку этих знаний есть и в SAT – они связаны с отрывками научных текстов, которые встречаются в остальных разделах экзамена.
Что выбрать иностранному студенту – SAT или ACT?
Считается, что тем абитуриентам, для которых английский язык не является родным, легче даются задания теста ACT. Они, как правило, отличаются более простыми формулировками, нежели в экзамене SAT.
Также мы уже упоминали, к примеру, раздел чтения – задания SAT этого блока направлены на то, чтобы оценить, насколько богатым словарным запасом владеет студент. Поэтому, если вы не можете похвастаться изысканностью речевых оборотов на английском и не привыкли читать большое количество иностранной литературы, стоит отдать предпочтение ACT.
Но выбирать экзамен, основываясь только на этом критерии, все же будет не лучшим решением. Очень важно учесть особенности своего характера, способность выполнять задания в сжатые сроки, уровень подготовки по предметам. И, конечно же, для начала стоит ознакомиться с требованиями того университета, где вы мечтаете учиться.
Узнать об особенностях поступления в лучшие университеты США, определиться, стоит ли сдавать экзамен SAT или ACT, и если стоит, то какой именно тест выбрать, когда начинать подготовку и как именно готовиться к сдаче – все это вы сможете узнать при личной беседе с нашим экспертом по зачислению в американские ВУЗы.
Консультация бесплатна, и мы с удовольствием проведем ее в удаленном формате или в нашем офисе в историческом центре Санкт-Петербурга. Сделайте первый шаг к мечте и оставьте заявку, заполнив форму:
Получить персональную консультацию
This article is about the college admission test in the United States. For the company which administers this test, see ACT (nonprofit organization).
|
|
This article needs to be updated. Please help update this to reflect recent events or newly available information. |
 |
|
| Type | Paper-based and computer-based standardized test |
|---|---|
| Developer / administrator | ACT, Inc. |
| Knowledge / skills tested | English, math, reading, science, writing (optional). |
| Purpose | Undergraduate admissions (mostly in the US and Canadian universities or colleges). |
| Year started | 1959 |
| Duration | English: 45 minutes, Math: 60 minutes, Reading: 35 minutes, Science: 35 minutes, Non-Graded Test: 20 minutes, Optional writing test: 40 minutes. Total: 3 hours and 55 minutes (excluding breaks).[1] |
| Score / grade range | Composite score: 1 to 36, Subscore (for each of the four subject areas): 1 to 36. (All in 1-point increments.)[2] Optional Writing Score: 2 to 12. (Sum of two graders’ scoring from 1-6) |
| Offered | US and Canada: 7 times a year.[3] Other countries: 5 times a year.[4] |
| Countries / regions | Worldwide[5][6] |
| Languages | English |
| Annual number of test takers | |
| Prerequisites / eligibility criteria | No official prerequisite. Intended for high school students. Fluency in English assumed. |
| Fee | Without writing: US$63.00 as of 2022. With writing: US$88.00 as of 2022. Outside US: $108.50 surcharge as of 2021 in addition to the above amounts.[8] (Fee waivers are available for 11th or 12th grade students who are US citizens or testing in the US or US territories, and have demonstrated financial need.[9]) |
| Scores / grades used by | Colleges or universities offering undergraduate programs (mostly in the US and Canada). |
| Website | www.act.org |
The ACT (; originally an abbreviation of American College Testing)[10] is a standardized test used for college admissions in the United States. It is currently administered by ACT, a nonprofit organization of the same name.[10] The ACT test covers four academic skill areas: English, mathematics, reading, and scientific reasoning. It also offers an optional direct writing test. It is accepted by all four-year colleges and universities in the United States as well as more than 225 universities outside of the U.S.
The main four ACT test sections are individually scored on a scale of 1–36, and a composite score (the rounded whole number average of the four sections) is provided.
The ACT was first introduced in November of 1959 by University of Iowa professor Everett Franklin Lindquist as a competitor to the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT).[11] The ACT originally consisted of four tests: English, Mathematics, Social Studies, and Natural Sciences. In 1989, however, the Social Studies test was changed into a Reading section (which included a social sciences subsection), and the Natural Sciences test was renamed the Science Reasoning test, with more emphasis on problem-solving skills as opposed to memorizing scientific facts.[12] In February 2005, an optional Writing Test was added to the ACT. By the fall of 2017, computer-based ACT tests were available for school-day testing in limited school districts of the US, with greater availability expected in fall of 2018.[13]
Historical Number of SAT and ACT Test Takers
The ACT has seen a gradual increase in the number of test takers since its inception, and in 2012 the ACT surpassed the SAT for the first time in total test takers; that year, 1,666,017 students took the ACT and 1,664,479 students took the SAT.[14]
Function[edit]
ACT, Inc., says that the ACT assessment measures high school students’ general educational development and their capability to complete college-level work with the multiple choice tests covering four skill areas: English, mathematics, reading, and science. The optional Writing Test measures skill in planning and writing a short essay.[15] Specifically, ACT states that its scores provide an indicator of «college readiness», and that scores in each of the subtests correspond to skills in entry-level college courses in English, algebra, social science, humanities, and biology.[16] According to a research study conducted by ACT, Inc. in 2003, there was a relationship between a student’s ACT composite score and the probability of that student earning a college degree.[17]
To develop the test, ACT incorporates the objectives for instruction from middle and high schools throughout the United States, reviews approved textbooks for subjects taught in Grades 7–12, and surveys educators on which knowledge skills are relevant to success in postsecondary education. ACT publishes a technical manual that summarizes studies conducted on its validity in predicting freshman GPA, equating different high school GPAs, and measuring educational achievement.[18]
Colleges use the ACT and the SAT because there are substantial differences in funding, curricula, grading, and difficulty among U.S. secondary schools due to American federalism, local control, the prevalence of private, distance, homeschooled students, and lack of a rigorous college entrance examination system similar those used in some other countries. ACT scores are used to supplement the secondary school record and help admission officers put local data—such as coursework, grades, and class rank—in a national perspective.[19][citation needed]
The majority of colleges do not indicate a preference for the SAT or ACT exams and accept both, being treated equally by most admissions officers.[20] According to «Uni in the USA,» colleges that also require students to take the SAT Subject Tests do so regardless of whether the candidate took the SAT or ACT;[20] however, some colleges accept the ACT in place of the SAT subject tests[21] and some accept the optional ACT Writing section in place of an SAT Subject Test.[22]
Most colleges use ACT scores as only one factor in the admission process. A sampling of ACT admissions scores shows that the 75th percentile composite score was 24.1 at public four-year institutions and 25.3 at private four-year institutions.
In addition, some states and individual school districts have used the ACT to assess student learning and/or the performance of schools, requiring all high school students to take the ACT, regardless of whether they are college bound. Colorado and Illinois were the first to incorporate the ACT as part of their mandatory testing program in 2001. Other states followed suit in subsequent years. During the 2018–2019 school year, 13 states will administer the ACT test to all public school 11th graders, and another six states will fund ACT test administration as an option or choice for districts.
While the exact manner in which ACT scores will help to determine admission of a student at American institutions of higher learning is generally a matter decided by the individual institution, some foreign countries have made ACT (and SAT) scores a legal criterion in deciding whether holders of American high school diplomas will be admitted at their public universities.
This map of the United States shows the states in which more seniors in the class of 2022 took the SAT than the ACT (colored in blue), and the states in which more seniors took the ACT than the SAT (colored in red).
The ACT is more widely used in the Midwestern, Rocky Mountain, and Southern United States, whereas the SAT is more popular on the East and West coasts. Recently, however, the ACT is being used more on the East Coast.[23] Use of the ACT by colleges has risen as a result of various criticisms of the effectiveness and fairness of the SAT.
Format[edit]
The required portion of the ACT is divided into four multiple-choice subject tests: English, mathematics, reading, and science reasoning. Subject test scores range from 1 to 36; all scores are integers. The English, mathematics, and reading tests also have subscores ranging from 1 to 18 (the subject score is not the sum of the subscores). In addition, students taking the optional writing test receive a writing score ranging from 2 to 12 (this is a change from the previous 1–36 score range); the writing score does not affect the composite score. Prior to September 2015, there was a Combined English/Writing score, which was a 36-point combination of the 36-point English Test score and the 12-point Writing subscore.[24] The ACT has eliminated the Combined English/writing score and has added two new combined scores: ELA (an average of the English, Reading, and Writing scores) and STEM (an average of the Math and Science scores).[25][26] These changes for the writing, ELA, and STEM scores were effective starting with the September 2015 test.[27]
Each question answered correctly is worth one raw point, and there is no penalty for marking incorrect answers on the multiple-choice parts of the test; a student can answer all questions without a decrease in their score due to incorrect answers. This is parallel to several AP Tests eliminating the penalties for incorrect answers. To improve the result, students can retake the test: 55% of students who retake the ACT improve their scores, 22% score the same, and 23% see their scores decrease.[28]
English[edit]
The first section is the 45-minute English test covering usage/mechanics, sentence structure, and rhetorical skills. The 75-question test consists of five passages with various sections underlined on one side of the page and options to correct the underlined portions on the other side of the page. Specifically, questions focus on usage and mechanics – issues such as commas, apostrophes, (misplaced/dangling) modifiers, colons, and fragments and run-ons – as well as on rhetorical skills – style (clarity and brevity), strategy, transitions, and organization (sentences in a paragraph and paragraphs in a passage) – and sentence structure – constructing sentences in a stylistically and grammatically correct manner.
Math[edit]
The second section is a 60-minute, 60-question math test with the usual distribution of questions being approximately 14 covering pre-algebra, 10 elementary algebra, 9 intermediate algebra, 14 plane geometry, 9 coordinate geometry, and 4 elementary trigonometry questions.[29] However, the distribution of question topics varies from test to test. The difficulty of questions usually increases as you get to higher question numbers. Calculators are permitted in this section only. The calculator requirements are stricter than the SAT’s in that computer algebra systems (such as the TI-89) are not allowed; however, the ACT permits calculators with paper tapes, that make noise (but must be disabled), or that have power cords with certain «modifications» (i.e., disabling the mentioned features), which the SAT does not allow.[30] Standard graphing calculators, such as the TI-83 and TI-84, are allowed. Within the TI-Nspire family, the standard and CX versions are allowed while the CX CAS is not. This is the only section that has five answer choices per question instead of four.
Reading[edit]
The reading section is a 35-minute, 40-question test that consists of four sections, three of which contain one long prose passage and one which contains two shorter prose passages. The passages are representative of the levels and kinds of text commonly encountered in first-year college curriculum. This reading test assesses skills in three general categories: key ideas and details, craft and structure, and integration of knowledge and ideas. Test questions will usually ask students to derive meaning from texts referring to what is explicitly stated or by reasoning to determine implicit meanings. Specifically, questions will ask you to use referring and reasoning skills to determine main ideas; locate and interpret significant details; understand sequences of events; make comparisons; comprehend cause-effect relationships; determine the meaning of context-dependent words, phrases, and statements; draw generalizations; and analyze the author’s or narrator’s voice and method.[31]
Science[edit]
The science test is a 35-minute, 40-question test. There are seven passages each followed by five to seven questions. The passages have three different formats: Data Representation, Research Summary, and Conflicting Viewpoints. While the format used to be very predictable (i.e. there were always three Data Representation passages with 5 questions following each, 3 Research Summary passages with six questions each, and one Conflicting Viewpoints passage with 7 questions),[32] when the number of passages was reduced from 7 to 6, more variability in the number of each passage type started to appear. But so far, there is still always only one Conflicting Viewpoints passage. These changes are very recent, and the only reference to them so far is in the recently released practice test on the ACT website.[33]
Writing[edit]
The optional writing section, which is always administered at the end of the test, is 40 minutes (increasing from the original 30-minute time limit on the September 2015 test). While no particular essay structure is required, the essays must be in response to a given prompt; the prompts are about broad social issues (changing from the old prompts which were directly applicable to teenagers), and students must analyze three different perspectives given and show how their opinion relates to these perspectives. The essay does not affect the composite score or the English section score; it is only given as a separate writing score and is included in the ELA score. Two trained readers assign each essay subscores between 1 and 6 in four different categories: Ideas and Analysis, Development and Support, Organization, Language Use and Conventions. Scores of 0 are reserved for essays that are blank, off-topic, non-English, not written with a no. 2 pencil, or considered illegible after several attempts at reading. The subscores from the two different readers are summed to produce final domain scores from 2 to 12 (or 0) in each of the four categories. If the two readers’ subscores differ by more than one point, then a senior third reader makes the final decision on the score. The four domain scores are combined through a process that has not been described to create a writing section score between 1 and 36. Note that the domain scores are not added to create the writing section score.[26][34]
Although the writing section is optional, many colleges require an essay score and will factor it into the admissions decision (but fewer than half of all colleges have this requirement).[35]
Averages[edit]
Historical average ACT scores of college-bound seniors.
This map shows the mean ACT composite scores of students within the United States in 2014
For the «enhanced» version of the ACT introduced in 1989, the mean score of each of the four tests, as well as the mean composite score, was scaled to be 18, with an intended standard error of measurement of 2 for the four test scores and 1 for the composite score.[36] These statistics vary from year to year for current populations of ACT takers.
The chart below summarizes each section and the average test score based on graduating high school seniors in 2022.[7][37]
| Section | Number of questions | Time (minutes) | Score Range | Average score (2022) | College Readiness Benchmark | Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | 75 | 45 | 1–36 | 19.0 | 18 | Usage/mechanics and rhetorical skills |
| Mathematics | 60 | 60 | 1–36 | 19.3 | 22 | Pre-algebra, elementary algebra, intermediate algebra, coordinate geometry, geometry, elementary trigonometry, reasoning, and problem-solving |
| Reading | 40 | 35 | 1–36 | 20.4 | 22 | Reading comprehension |
| Science | 40 | 35 | 1–36 | 19.9 | 23 | Interpretation, analysis, evaluation, reasoning, and problem-solving |
| Optional Writing Test (not included in composite score) | 1 essay prompt | 40 | 1–12 | 6.2 | Writing skills | |
| Composite | 1–36 | 19.8 | Average (mean) of all section scores except Writing |
Highest score[edit]
Percent of test takers achieving a 36 on the ACT from 1997 to 2022.[38][39][40][7]
The table below summarizes how many students achieved a composite score of 36 on the ACT between the years of 1997 and 2021.[38][40][39][7]
| Year | Number of students who achieved a composite score of 36 | Number of students overall | % of students who achieved a 36 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 3,376 | 1,349,644 | 0.2501 |
| 2021 | 4,055 | 1,295,349 | 0.3130 |
| 2020 | 5,579 | 1,670,497 | 0.3340 |
| 2019 | 4,879 | 1,782,820 | 0.2737 |
| 2018 | 3,741 | 1,914,817 | 0.1954 |
| 2017 | 2,760 | 2,030,038 | 0.1359 |
| 2016 | 2,235 | 2,090,342 | 0.1069 |
| 2015 | 1,598 | 1,924,436 | 0.0830 |
| 2014 | 1,407 | 1,845,787 | 0.07622 |
| 2013 | 1,162 | 1,799,243 | 0.06458 |
| 2012 | 781 | 1,666,017 | 0.04687 |
| 2011 | 704 | 1,623,112 | 0.04337 |
| 2010 | 588 | 1,568,835 | 0.03748 |
| 2009 | 638 | 1,480,469 | 0.04309 |
| 2008 | 428 | 1,421,941 | 0.03010 |
| 2007 | 314 | 1,300,599 | 0.02414 |
| 2006 | 216 | 1,206,455 | 0.01790 |
| 2005 | 193 | 1,186,251 | 0.01627 |
| 2004 | 224 | 1,171,460 | 0.01912 |
| 2003 | 195 | 1,175,059 | 0.01659 |
| 2002 | 134 | 1,116,082 | 0.01201 |
| 2001 | 89 | 1,069,772 | 0.00832 |
| 2000 | 131 | 1,065,138 | 0.01230 |
| 1999 | 85 | 1,019,053 | 0.00834 |
| 1998 | 71 | 995,039 | 0.00714 |
| 1997 | 74 | 959,301 | 0.00771 |
College admissions[edit]
The ACT Assessment Student Report, at ACT.org, provides the typical ACT Composite averages for college and universities admission policies. They caution that «because admission policies vary across colleges, the score ranges should be considered rough guidelines.» Following is a list of the average composite scores that typically are accepted at colleges or universities.[41]
- Ivy Caliber (Schools that as a rule of thumb have below a 1 in 8 acceptance rate): scores 32–36
- Highly selective (majority of accepted freshmen in top 10% of high school graduating class): scores 27–31
- Selective (majority of accepted freshmen in top 25% of high school graduating class): scores 24–26
- Traditional (majority of accepted freshmen in top 50% of high school graduating class): scores 21–23
- Liberal (some freshmen from lower half of high school graduating class): scores 18–20
- Open (all high school graduates accepted, to limit of capacity): scores 17–20 Any score is likely accepted.
Test availability[edit]
The ACT is offered seven times a year in the United States and its territories, Puerto Rico, and Canada: in September, October, December, February, April, June, and July. (In New York State, the test is not offered in July.) In other locations, the ACT is offered five times a year: in September, October, December, April, and June.[42] The ACT is offered only on Saturdays except for those with credible religious obligations, who may take the test on another day.[43]
The ACT is designed, administered, and scored so that there is no advantage to testing on one particular date.[44]
Candidates may choose either the ACT assessment ($63.00), or the ACT assessment plus writing ($88.00).[45]
Students with verifiable disabilities, including physical and learning disabilities, are eligible to take the test with accommodations. The standard time increase for students requiring additional time due to disabilities is 50%.[46] Originally, the score sheet was labeled that additional time was granted due to a learning disability; however, this was ultimately dropped because it was deemed illegal under the Americans with Disabilities Act and could be perceived as an unfair designator of disability.
Scores are sent to the student, their high school, and up to four colleges of the student’s choice (optional).[47]
Test section durations[edit]
Time is a major factor to consider in testing.
The ACT is generally regarded as being composed of somewhat easier questions versus the SAT[48][citation needed], but the shorter time allotted to complete each section increases difficulty. The ACT allows:
- 45 minutes for a 75-question English section
- 60 minutes for a 60-question Mathematics section
- 35 minutes for a 40-question Reading section
- 35 minutes for a 40-question Science section
Comparatively, the SAT is structured such that the test taker is allowed at least one minute per question, on generally shorter sections (25 or fewer questions). Times may be adjusted as a matter of accommodation for certain disabilities or other impairments.
National ranks (score cumulative percentages)[edit]
Score reports provided to students taking the ACT test include the ranks (or cumulative percents) for each score and subscore received by the student. Each rank gives the percentage of recently tested students in the U.S. who scored at or below the given student’s score.[49] The following table shows the ACT national ranks as of the 2020-21 school year.[50]
| ACT Score | English Rank | Math Rank | Reading Rank | Science Rank | Composite Rank | STEM Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 35 | 99 | 99 | 98 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| 34 | 96 | 99 | 96 | 98 | 99 | 99 |
| 33 | 94 | 98 | 94 | 97 | 98 | 98 |
| 32 | 92 | 97 | 91 | 96 | 96 | 97 |
| 31 | 91 | 96 | 89 | 95 | 95 | 96 |
| 30 | 89 | 94 | 86 | 93 | 93 | 94 |
| 29 | 88 | 93 | 84 | 92 | 90 | 92 |
| 28 | 86 | 91 | 82 | 90 | 88 | 90 |
| 27 | 84 | 88 | 80 | 88 | 85 | 87 |
| 26 | 82 | 84 | 77 | 85 | 82 | 84 |
| 25 | 79 | 79 | 74 | 82 | 78 | 80 |
| 24 | 75 | 74 | 71 | 77 | 74 | 75 |
| 23 | 71 | 70 | 66 | 71 | 70 | 70 |
| 22 | 65 | 65 | 61 | 64 | 64 | 65 |
| 21 | 60 | 61 | 55 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 20 | 55 | 58 | 50 | 51 | 53 | 54 |
| 19 | 49 | 54 | 44 | 45 | 47 | 48 |
| 18 | 45 | 49 | 39 | 39 | 41 | 41 |
| 17 | 41 | 42 | 34 | 32 | 35 | 33 |
| 16 | 37 | 33 | 29 | 26 | 28 | 26 |
| 15 | 32 | 21 | 24 | 19 | 22 | 18 |
| 14 | 25 | 11 | 19 | 14 | 16 | 11 |
| 13 | 19 | 4 | 14 | 10 | 10 | 5 |
| 12 | 15 | 1 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| 11 | 11 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 10 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Concordance of ACT Scores and SAT Scores[edit]
The College Board (the developer of the SAT) and ACT, Inc. compared scores from about 600,000 students who were graduating in 2017 and who took both the SAT (2016 revision) and the ACT in 2016 and 2017. The following table shows, for each ACT composite score in the data set, the corresponding range of SAT total scores for students with the same percentile rank on each test. The most appropriate corresponding SAT score point for the given ACT score is also shown in the table.[51]
| ACT Composite Score | SAT Total Score Range | SAT Total Score |
|---|---|---|
| 36 | 1570–1600 | 1590 |
| 35 | 1530–1560 | 1540 |
| 34 | 1490–1520 | 1500 |
| 33 | 1450–1480 | 1460 |
| 32 | 1420–1440 | 1430 |
| 31 | 1390–1410 | 1400 |
| 30 | 1360–1380 | 1370 |
| 29 | 1330–1350 | 1340 |
| 28 | 1300–1320 | 1310 |
| 27 | 1260–1290 | 1280 |
| 26 | 1230–1250 | 1240 |
| 25 | 1200–1220 | 1210 |
| 24 | 1160–1190 | 1180 |
| 23 | 1130–1150 | 1140 |
| 22 | 1100–1120 | 1110 |
| 21 | 1060–1090 | 1080 |
| 20 | 1030–1050 | 1040 |
| 19 | 990–1020 | 1010 |
| 18 | 960–980 | 970 |
| 17 | 920–950 | 930 |
| 16 | 880–910 | 890 |
| 15 | 830–870 | 850 |
| 14 | 780–820 | 800 |
| 13 | 730–770 | 760 |
| 12 | 690–720 | 710 |
| 11 | 650–680 | 670 |
| 10 | 620–640 | 630 |
| 9 | 590–610 | 590 |
Score cumulative percentages and comparison with pre-2016 SAT[edit]
The data in this section pertains to the SAT prior to the 2016 redesign. Comparisons to SAT scores are not valid after the 2017 graduating class.
Sixty percent—about 2.03 million students—of the 2017 high school graduating class took the ACT. For the graduating class of 2017, the average composite score was a 21.0. Of these test-takers, 46% were male and 52% were female, with 2% not reporting a gender. 2,760 students in the graduating class of 2017 received the highest ACT composite score of 36.[52]
2005 distribution of ACT scores
The following chart shows, for each ACT score from 11 to 36, the corresponding ACT percentile and equivalent total SAT score or score range.[53][failed verification] (Concordance data for ACT scores less than 11 is not yet available for the current version of the SAT.) Note that ACT percentiles are defined as the percentage of test takers scoring at or below the given score.
| SAT combined score (Math + Reading/Writing) | ACT composite score | The percentile of students at or below this score for the ACT (not SAT) |
|---|---|---|
| 1600 | 36 | 100% |
| 1560–1590 | 35 | 99.9% |
| 1520–1550 | 34 | 99% |
| 1490–1510 | 33 | 98% |
| 1450–1480 | 32 | 97% |
| 1420–1440 | 31 | 96% |
| 1390–1410 | 30 | 94% |
| 1350–1380 | 29 | 92% |
| 1310–1340 | 28 | 89% |
| 1280–1300 | 27 | 86% |
| 1240–1270 | 26 | 82% |
| 1200–1230 | 25 | 78% |
| 1160–1190 | 24 | 74% |
| 1130–1150 | 23 | 69% |
| 1100–1120 | 22 | 63% |
| 1060–1090 | 21 | 57% |
| 1020–1050 | 20 | 51% |
| 980–1010 | 19 | 44% |
| 940–970 | 18 | 38% |
| 900–930 | 17 | 31% |
| 860–890 | 16 | 25% |
| 810–850 | 15 | 19% |
| 760–800 | 14 | 13% |
| 720–750 | 13 | 8% |
| 630–710 | 12 | 4% |
| 560–620 | 11 | 1% |
Score vs Percentile for English Section[edit]
| Score | The percentile of students
at or below this score |
|---|---|
| 36 | 100% |
| 35 | 99% |
| 34 | 99% |
| 33 | 97% |
| 32 | 96% |
| 31 | 94% |
| 30 | 93% |
| 29 | 91% |
| 28 | 88% |
| 27 | 85% |
| 26 | 82% |
| 25 | 78% |
| 24 | 73% |
| 23 | 68% |
| 22 | 63% |
| 21 | 57% |
| 20 | 50% |
| 19 | 43% |
| 18 | 38% |
| 17 | 33% |
| 16 | 29% |
| 15 | 24% |
| 14 | 18% |
| 13 | 14% |
| 12 | 11% |
| 11 | 9% |
Score vs Percentile for Mathematics Section[edit]
| Score | The percentile of students
at or below this score |
|---|---|
| 36 | 99% |
| 35 | 99% |
| 34 | 99% |
| 33 | 98% |
| 32 | 97% |
| 31 | 96% |
| 30 | 94% |
| 29 | 93% |
| 28 | 91% |
| 27 | 88% |
| 26 | 84% |
| 25 | 79% |
| 24 | 74% |
| 23 | 67% |
| 22 | 61% |
| 21 | 57% |
| 20 | 52% |
| 19 | 47% |
| 18 | 41% |
| 17 | 34% |
| 16 | 26% |
| 15 | 14% |
| 14 | 6% |
| 13 | 2% |
| 12 | 1% |
| 11 | 1% |
Score vs Percentile for Reading Section[edit]
| Score | The percentile of students
at or below this score |
|---|---|
| 36 | 99% |
| 35 | 99% |
| 34 | 99% |
| 33 | 97% |
| 32 | 95% |
| 31 | 93% |
| 30 | 91% |
| 29 | 87% |
| 28 | 85% |
| 27 | 82% |
| 26 | 78% |
| 25 | 75% |
| 24 | 71% |
| 23 | 66% |
| 22 | 60% |
| 21 | 54% |
| 20 | 48% |
| 19 | 42% |
| 18 | 39% |
| 17 | 30% |
| 16 | 25% |
| 15 | 19% |
| 14 | 15% |
| 13 | 10% |
| 12 | 6% |
| 11 | 3% |
Score vs Percentile for Science Section[edit]
| Score | The percentile of students
at or below this score |
|---|---|
| 36 | 99% |
| 35 | 99% |
| 34 | 99% |
| 33 | 99% |
| 32 | 98% |
| 31 | 97% |
| 30 | 96% |
| 29 | 95% |
| 28 | 93% |
| 27 | 91% |
| 26 | 87% |
| 25 | 83% |
| 24 | 77% |
| 23 | 70% |
| 22 | 62% |
| 21 | 56% |
| 20 | 47% |
| 19 | 38% |
| 18 | 34% |
| 17 | 21% |
| 16 | 19% |
| 15 | 15% |
| 14 | 11% |
| 13 | 8% |
| 12 | 5% |
| 11 | 3% |
Sources:[54][failed verification]
See also[edit]
- ACT (nonprofit organization)#Other ACT programs
- College admissions in the United States
- Global Assessment Certificate
- List of admission tests to colleges and universities
- Math–verbal achievement gap
- PLAN (test)
- SAT
- 2019 college admissions bribery scandal
References[edit]
- ^ «Test Descriptions – ACT Student». ACT, Inc. Retrieved September 13, 2015.
- ^ «Understand Your Scores – Sample Student Report – ACT Student». ACT, Inc. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «Registration – Test Dates in the U.S., U.S. Territories, and Canada – ACT Student». ACT, Inc. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «Registration – Test Dates in Other Countries – ACT Student». ACT, Inc. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «Test Center Locations, Dates, and Codes». ACT, Inc. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «Test Center Codes – International – ACT Student». ACT Inc. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ a b c d «The ACT Profile Report – National, Graduating Class 2022» (PDF). ACT, Inc. Retrieved October 29, 2022.
- ^ «Current ACT Fees and Services». ACT, Inc. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ «The ACT Test Help and Frequently Asked Questions – Am I eligible for a fee waiver?». ACT, Inc. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ a b «About ACT: History». Archived from the original on October 8, 2006. Retrieved October 25, 2006. Name changed in 1996.
- ^ «ACT Assessment», Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2007. Archived August 29, 2009, at the Wayback Machine October 31, 2009.
- ^ «A (Mostly) Brief History Of The SAT and ACTs». Erik the Red. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «When Will the ACT Start Computer-Based Testing?». Magoosh. Retrieved February 16, 2018.
- ^ Pope, Justin (September 24, 2012). «SAT scores edge down; ACT now more popular exam». Associated Press. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ^ The Test Archived August 28, 2006, at the Wayback Machine. (URL accessed June 5, 2007).
- ^ «The ACT-Measure High School Student Readiness for College» (PDF).
- ^ Radunzal, J., Noble, J. (2003, April). «Tracking 2003 act-tested high school graduates: College readiness, enrollment, and long-term success.» Retrieved from: http://www.act.org/research/researchers/reports/pdf/ACT_RR2012-2.pdf Archived March 16, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- ^
The ACT Technical Manual - ^ SCHOOL, CENTURY ACADEMY HIGH. «SAT/ACT Information». www.conejousd.org. Retrieved June 2, 2017.
- ^ a b «Entrance Exam For College – College Entrance Exams – University In The USA». Uni in the USA. Archived from the original on October 20, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «ACT? SAT? Subject Tests? No Tests? Holy Moly! Who Is Requiring What These Days?». Huffington Post. August 11, 2014.
- ^ «SAT vs. ACT – Test Prep Tutoring & Classes – NYC, NY». CATES Tutoring and Educational Services. Archived from the original on October 16, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ Honawar, Vaishali; Alyson Klein (August 30, 2006). «ACT Scores Improve; More on East Coast Taking the SAT’s Rival». Education Week. 26 (1): 16. ISSN 0277-4232. Retrieved July 6, 2007.
Beginning in 2013, all freshman entering high school in the state of Ohio must take the test in order to graduate.
- ^ «Writing Test Scores». ACT. Retrieved May 3, 2021.
- ^ «What’s Next for the ACT – Test Updates and Enhancements». Archived from the original on July 29, 2015. Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ^ a b «The ACT Test for Students». ACT. Archived from the original on February 17, 2016.
- ^ «Newsroom – Press Kit, Digital Media Library, and Press Releases». Archived from the original on July 29, 2015. Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ^ «The ACT-Getting Ready for Test Day».
- ^ Geoff Martz; Kim Magloire; Theodore Silver. (2007). «Chapter 10». Cracking The ACT (2007 ed.). The Princeton Review. p. 94. ISBN 978-0-375-76585-8.
- ^ «ACT FAQ: Can I use a calculator?». ACT Inc. Archived from the original on August 20, 2007. Retrieved September 8, 2007.
- ^ «Description of Reading Test». ACT. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- ^ Geoff Martz; Kim Magloire; Theodore Silver. (2007). «Chapter 20». Cracking The ACT (2007 ed.). The Princeton Review. p. 307. ISBN 978-0-375-76585-8.
- ^ «Preparing for the ACT Test» (PDF). ACT, Inc. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 11, 2022. Retrieved March 18, 2022.
- ^ «The ACT Test for Students». ACT. Archived from the original on August 9, 2015. Retrieved July 27, 2015.
- ^ Cavner, Brian. «Comparison Between the SAT and ACT: Requirements differences between the two college admissions standardized tests». Archived from the original on February 15, 2008. Retrieved February 3, 2008.
- ^ «Preliminary Technical Manual for the Enhanced ACT Assessment» (PDF). Education Resources Information Center. ACT, Inc. October 1989. p. 28. Retrieved June 27, 2021.
- ^ «ACT Prep:Description of the ACT Assessment». ACT Inc. Archived from the original on June 30, 2007. Retrieved June 29, 2007.
- ^ a b «The ACT® Data». ACT Inc. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ a b «University School student receives perfect ACT score». WJHL News Channel 11. Nextstar Media. Retrieved December 19, 2021.
- ^ a b «ACT Research Publications». ACT, Inc. Retrieved December 19, 2021.
- ^ American College Test INC. (ACT). Research and Policy Issues-Information Brief 2002–1. (n.d.). «Interpreting act assessment scores: College admissions.» Retrieved October 8, 2012, from http://www.act.org/research/researchers/briefs/2002-1.html#UItAIYq5fw Archived January 20, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Registration – The ACT Test». ACT, Inc. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ «The ACT Test Help and Frequently Asked Questions – Is Non-Saturday Testing Available?». ACT, Inc. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ American College Test INC. (ACT), Research and Policy Issues-Information Brief (2001). «Facts about scoring the act assessment». Retrieved October 8, 2012, from http://www.act.org/research/researchers/briefs/2001-1.html#UIX3TYYq5fw Archived January 20, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Current ACT Fees and Services». Retrieved December 2, 2022.
- ^ «ACT Services for Students with Disabilities». ACT Inc. Archived from the original on August 22, 2007. Retrieved September 8, 2007.
- ^ «ACT Score Information: ACT Score Report Descriptions». ACT Inc. Archived from the original on July 11, 2007. Retrieved June 29, 2007.
- ^ «ACT Versus SAT: Popular Doesn’t Mean Better». www.icon-plus.com. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
- ^ «ACT National Ranks». ACT, Inc. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ «National Norms for ACT Test Scores» (PDF). ACT, Inc. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ «Guide to the 2018 ACT/SAT Concordance» (PDF). College Board and ACT, Inc. Retrieved November 26, 2021.
- ^ «Condition of College and Career Readiness 2017». ACT Inc. Retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ «Higher Ed Brief: SAT Concordance» (PDF). College Board. Retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ «UC Admissions». Archived from the original on April 20, 2009. Retrieved May 17, 2009. Univ. of California Eligibility by Examination Alone
External links[edit]
- ACT Taker’s Site
- ACT Corporate Site
This article is about the college admission test in the United States. For the company which administers this test, see ACT (nonprofit organization).
|
|
This article needs to be updated. Please help update this to reflect recent events or newly available information. |
 |
|
| Type | Paper-based and computer-based standardized test |
|---|---|
| Developer / administrator | ACT, Inc. |
| Knowledge / skills tested | English, math, reading, science, writing (optional). |
| Purpose | Undergraduate admissions (mostly in the US and Canadian universities or colleges). |
| Year started | 1959 |
| Duration | English: 45 minutes, Math: 60 minutes, Reading: 35 minutes, Science: 35 minutes, Non-Graded Test: 20 minutes, Optional writing test: 40 minutes. Total: 3 hours and 55 minutes (excluding breaks).[1] |
| Score / grade range | Composite score: 1 to 36, Subscore (for each of the four subject areas): 1 to 36. (All in 1-point increments.)[2] Optional Writing Score: 2 to 12. (Sum of two graders’ scoring from 1-6) |
| Offered | US and Canada: 7 times a year.[3] Other countries: 5 times a year.[4] |
| Countries / regions | Worldwide[5][6] |
| Languages | English |
| Annual number of test takers | |
| Prerequisites / eligibility criteria | No official prerequisite. Intended for high school students. Fluency in English assumed. |
| Fee | Without writing: US$63.00 as of 2022. With writing: US$88.00 as of 2022. Outside US: $108.50 surcharge as of 2021 in addition to the above amounts.[8] (Fee waivers are available for 11th or 12th grade students who are US citizens or testing in the US or US territories, and have demonstrated financial need.[9]) |
| Scores / grades used by | Colleges or universities offering undergraduate programs (mostly in the US and Canada). |
| Website | www.act.org |
The ACT (; originally an abbreviation of American College Testing)[10] is a standardized test used for college admissions in the United States. It is currently administered by ACT, a nonprofit organization of the same name.[10] The ACT test covers four academic skill areas: English, mathematics, reading, and scientific reasoning. It also offers an optional direct writing test. It is accepted by all four-year colleges and universities in the United States as well as more than 225 universities outside of the U.S.
The main four ACT test sections are individually scored on a scale of 1–36, and a composite score (the rounded whole number average of the four sections) is provided.
The ACT was first introduced in November of 1959 by University of Iowa professor Everett Franklin Lindquist as a competitor to the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT).[11] The ACT originally consisted of four tests: English, Mathematics, Social Studies, and Natural Sciences. In 1989, however, the Social Studies test was changed into a Reading section (which included a social sciences subsection), and the Natural Sciences test was renamed the Science Reasoning test, with more emphasis on problem-solving skills as opposed to memorizing scientific facts.[12] In February 2005, an optional Writing Test was added to the ACT. By the fall of 2017, computer-based ACT tests were available for school-day testing in limited school districts of the US, with greater availability expected in fall of 2018.[13]
Historical Number of SAT and ACT Test Takers
The ACT has seen a gradual increase in the number of test takers since its inception, and in 2012 the ACT surpassed the SAT for the first time in total test takers; that year, 1,666,017 students took the ACT and 1,664,479 students took the SAT.[14]
Function[edit]
ACT, Inc., says that the ACT assessment measures high school students’ general educational development and their capability to complete college-level work with the multiple choice tests covering four skill areas: English, mathematics, reading, and science. The optional Writing Test measures skill in planning and writing a short essay.[15] Specifically, ACT states that its scores provide an indicator of «college readiness», and that scores in each of the subtests correspond to skills in entry-level college courses in English, algebra, social science, humanities, and biology.[16] According to a research study conducted by ACT, Inc. in 2003, there was a relationship between a student’s ACT composite score and the probability of that student earning a college degree.[17]
To develop the test, ACT incorporates the objectives for instruction from middle and high schools throughout the United States, reviews approved textbooks for subjects taught in Grades 7–12, and surveys educators on which knowledge skills are relevant to success in postsecondary education. ACT publishes a technical manual that summarizes studies conducted on its validity in predicting freshman GPA, equating different high school GPAs, and measuring educational achievement.[18]
Colleges use the ACT and the SAT because there are substantial differences in funding, curricula, grading, and difficulty among U.S. secondary schools due to American federalism, local control, the prevalence of private, distance, homeschooled students, and lack of a rigorous college entrance examination system similar those used in some other countries. ACT scores are used to supplement the secondary school record and help admission officers put local data—such as coursework, grades, and class rank—in a national perspective.[19][citation needed]
The majority of colleges do not indicate a preference for the SAT or ACT exams and accept both, being treated equally by most admissions officers.[20] According to «Uni in the USA,» colleges that also require students to take the SAT Subject Tests do so regardless of whether the candidate took the SAT or ACT;[20] however, some colleges accept the ACT in place of the SAT subject tests[21] and some accept the optional ACT Writing section in place of an SAT Subject Test.[22]
Most colleges use ACT scores as only one factor in the admission process. A sampling of ACT admissions scores shows that the 75th percentile composite score was 24.1 at public four-year institutions and 25.3 at private four-year institutions.
In addition, some states and individual school districts have used the ACT to assess student learning and/or the performance of schools, requiring all high school students to take the ACT, regardless of whether they are college bound. Colorado and Illinois were the first to incorporate the ACT as part of their mandatory testing program in 2001. Other states followed suit in subsequent years. During the 2018–2019 school year, 13 states will administer the ACT test to all public school 11th graders, and another six states will fund ACT test administration as an option or choice for districts.
While the exact manner in which ACT scores will help to determine admission of a student at American institutions of higher learning is generally a matter decided by the individual institution, some foreign countries have made ACT (and SAT) scores a legal criterion in deciding whether holders of American high school diplomas will be admitted at their public universities.
This map of the United States shows the states in which more seniors in the class of 2022 took the SAT than the ACT (colored in blue), and the states in which more seniors took the ACT than the SAT (colored in red).
The ACT is more widely used in the Midwestern, Rocky Mountain, and Southern United States, whereas the SAT is more popular on the East and West coasts. Recently, however, the ACT is being used more on the East Coast.[23] Use of the ACT by colleges has risen as a result of various criticisms of the effectiveness and fairness of the SAT.
Format[edit]
The required portion of the ACT is divided into four multiple-choice subject tests: English, mathematics, reading, and science reasoning. Subject test scores range from 1 to 36; all scores are integers. The English, mathematics, and reading tests also have subscores ranging from 1 to 18 (the subject score is not the sum of the subscores). In addition, students taking the optional writing test receive a writing score ranging from 2 to 12 (this is a change from the previous 1–36 score range); the writing score does not affect the composite score. Prior to September 2015, there was a Combined English/Writing score, which was a 36-point combination of the 36-point English Test score and the 12-point Writing subscore.[24] The ACT has eliminated the Combined English/writing score and has added two new combined scores: ELA (an average of the English, Reading, and Writing scores) and STEM (an average of the Math and Science scores).[25][26] These changes for the writing, ELA, and STEM scores were effective starting with the September 2015 test.[27]
Each question answered correctly is worth one raw point, and there is no penalty for marking incorrect answers on the multiple-choice parts of the test; a student can answer all questions without a decrease in their score due to incorrect answers. This is parallel to several AP Tests eliminating the penalties for incorrect answers. To improve the result, students can retake the test: 55% of students who retake the ACT improve their scores, 22% score the same, and 23% see their scores decrease.[28]
English[edit]
The first section is the 45-minute English test covering usage/mechanics, sentence structure, and rhetorical skills. The 75-question test consists of five passages with various sections underlined on one side of the page and options to correct the underlined portions on the other side of the page. Specifically, questions focus on usage and mechanics – issues such as commas, apostrophes, (misplaced/dangling) modifiers, colons, and fragments and run-ons – as well as on rhetorical skills – style (clarity and brevity), strategy, transitions, and organization (sentences in a paragraph and paragraphs in a passage) – and sentence structure – constructing sentences in a stylistically and grammatically correct manner.
Math[edit]
The second section is a 60-minute, 60-question math test with the usual distribution of questions being approximately 14 covering pre-algebra, 10 elementary algebra, 9 intermediate algebra, 14 plane geometry, 9 coordinate geometry, and 4 elementary trigonometry questions.[29] However, the distribution of question topics varies from test to test. The difficulty of questions usually increases as you get to higher question numbers. Calculators are permitted in this section only. The calculator requirements are stricter than the SAT’s in that computer algebra systems (such as the TI-89) are not allowed; however, the ACT permits calculators with paper tapes, that make noise (but must be disabled), or that have power cords with certain «modifications» (i.e., disabling the mentioned features), which the SAT does not allow.[30] Standard graphing calculators, such as the TI-83 and TI-84, are allowed. Within the TI-Nspire family, the standard and CX versions are allowed while the CX CAS is not. This is the only section that has five answer choices per question instead of four.
Reading[edit]
The reading section is a 35-minute, 40-question test that consists of four sections, three of which contain one long prose passage and one which contains two shorter prose passages. The passages are representative of the levels and kinds of text commonly encountered in first-year college curriculum. This reading test assesses skills in three general categories: key ideas and details, craft and structure, and integration of knowledge and ideas. Test questions will usually ask students to derive meaning from texts referring to what is explicitly stated or by reasoning to determine implicit meanings. Specifically, questions will ask you to use referring and reasoning skills to determine main ideas; locate and interpret significant details; understand sequences of events; make comparisons; comprehend cause-effect relationships; determine the meaning of context-dependent words, phrases, and statements; draw generalizations; and analyze the author’s or narrator’s voice and method.[31]
Science[edit]
The science test is a 35-minute, 40-question test. There are seven passages each followed by five to seven questions. The passages have three different formats: Data Representation, Research Summary, and Conflicting Viewpoints. While the format used to be very predictable (i.e. there were always three Data Representation passages with 5 questions following each, 3 Research Summary passages with six questions each, and one Conflicting Viewpoints passage with 7 questions),[32] when the number of passages was reduced from 7 to 6, more variability in the number of each passage type started to appear. But so far, there is still always only one Conflicting Viewpoints passage. These changes are very recent, and the only reference to them so far is in the recently released practice test on the ACT website.[33]
Writing[edit]
The optional writing section, which is always administered at the end of the test, is 40 minutes (increasing from the original 30-minute time limit on the September 2015 test). While no particular essay structure is required, the essays must be in response to a given prompt; the prompts are about broad social issues (changing from the old prompts which were directly applicable to teenagers), and students must analyze three different perspectives given and show how their opinion relates to these perspectives. The essay does not affect the composite score or the English section score; it is only given as a separate writing score and is included in the ELA score. Two trained readers assign each essay subscores between 1 and 6 in four different categories: Ideas and Analysis, Development and Support, Organization, Language Use and Conventions. Scores of 0 are reserved for essays that are blank, off-topic, non-English, not written with a no. 2 pencil, or considered illegible after several attempts at reading. The subscores from the two different readers are summed to produce final domain scores from 2 to 12 (or 0) in each of the four categories. If the two readers’ subscores differ by more than one point, then a senior third reader makes the final decision on the score. The four domain scores are combined through a process that has not been described to create a writing section score between 1 and 36. Note that the domain scores are not added to create the writing section score.[26][34]
Although the writing section is optional, many colleges require an essay score and will factor it into the admissions decision (but fewer than half of all colleges have this requirement).[35]
Averages[edit]
Historical average ACT scores of college-bound seniors.
This map shows the mean ACT composite scores of students within the United States in 2014
For the «enhanced» version of the ACT introduced in 1989, the mean score of each of the four tests, as well as the mean composite score, was scaled to be 18, with an intended standard error of measurement of 2 for the four test scores and 1 for the composite score.[36] These statistics vary from year to year for current populations of ACT takers.
The chart below summarizes each section and the average test score based on graduating high school seniors in 2022.[7][37]
| Section | Number of questions | Time (minutes) | Score Range | Average score (2022) | College Readiness Benchmark | Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | 75 | 45 | 1–36 | 19.0 | 18 | Usage/mechanics and rhetorical skills |
| Mathematics | 60 | 60 | 1–36 | 19.3 | 22 | Pre-algebra, elementary algebra, intermediate algebra, coordinate geometry, geometry, elementary trigonometry, reasoning, and problem-solving |
| Reading | 40 | 35 | 1–36 | 20.4 | 22 | Reading comprehension |
| Science | 40 | 35 | 1–36 | 19.9 | 23 | Interpretation, analysis, evaluation, reasoning, and problem-solving |
| Optional Writing Test (not included in composite score) | 1 essay prompt | 40 | 1–12 | 6.2 | Writing skills | |
| Composite | 1–36 | 19.8 | Average (mean) of all section scores except Writing |
Highest score[edit]
Percent of test takers achieving a 36 on the ACT from 1997 to 2022.[38][39][40][7]
The table below summarizes how many students achieved a composite score of 36 on the ACT between the years of 1997 and 2021.[38][40][39][7]
| Year | Number of students who achieved a composite score of 36 | Number of students overall | % of students who achieved a 36 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 3,376 | 1,349,644 | 0.2501 |
| 2021 | 4,055 | 1,295,349 | 0.3130 |
| 2020 | 5,579 | 1,670,497 | 0.3340 |
| 2019 | 4,879 | 1,782,820 | 0.2737 |
| 2018 | 3,741 | 1,914,817 | 0.1954 |
| 2017 | 2,760 | 2,030,038 | 0.1359 |
| 2016 | 2,235 | 2,090,342 | 0.1069 |
| 2015 | 1,598 | 1,924,436 | 0.0830 |
| 2014 | 1,407 | 1,845,787 | 0.07622 |
| 2013 | 1,162 | 1,799,243 | 0.06458 |
| 2012 | 781 | 1,666,017 | 0.04687 |
| 2011 | 704 | 1,623,112 | 0.04337 |
| 2010 | 588 | 1,568,835 | 0.03748 |
| 2009 | 638 | 1,480,469 | 0.04309 |
| 2008 | 428 | 1,421,941 | 0.03010 |
| 2007 | 314 | 1,300,599 | 0.02414 |
| 2006 | 216 | 1,206,455 | 0.01790 |
| 2005 | 193 | 1,186,251 | 0.01627 |
| 2004 | 224 | 1,171,460 | 0.01912 |
| 2003 | 195 | 1,175,059 | 0.01659 |
| 2002 | 134 | 1,116,082 | 0.01201 |
| 2001 | 89 | 1,069,772 | 0.00832 |
| 2000 | 131 | 1,065,138 | 0.01230 |
| 1999 | 85 | 1,019,053 | 0.00834 |
| 1998 | 71 | 995,039 | 0.00714 |
| 1997 | 74 | 959,301 | 0.00771 |
College admissions[edit]
The ACT Assessment Student Report, at ACT.org, provides the typical ACT Composite averages for college and universities admission policies. They caution that «because admission policies vary across colleges, the score ranges should be considered rough guidelines.» Following is a list of the average composite scores that typically are accepted at colleges or universities.[41]
- Ivy Caliber (Schools that as a rule of thumb have below a 1 in 8 acceptance rate): scores 32–36
- Highly selective (majority of accepted freshmen in top 10% of high school graduating class): scores 27–31
- Selective (majority of accepted freshmen in top 25% of high school graduating class): scores 24–26
- Traditional (majority of accepted freshmen in top 50% of high school graduating class): scores 21–23
- Liberal (some freshmen from lower half of high school graduating class): scores 18–20
- Open (all high school graduates accepted, to limit of capacity): scores 17–20 Any score is likely accepted.
Test availability[edit]
The ACT is offered seven times a year in the United States and its territories, Puerto Rico, and Canada: in September, October, December, February, April, June, and July. (In New York State, the test is not offered in July.) In other locations, the ACT is offered five times a year: in September, October, December, April, and June.[42] The ACT is offered only on Saturdays except for those with credible religious obligations, who may take the test on another day.[43]
The ACT is designed, administered, and scored so that there is no advantage to testing on one particular date.[44]
Candidates may choose either the ACT assessment ($63.00), or the ACT assessment plus writing ($88.00).[45]
Students with verifiable disabilities, including physical and learning disabilities, are eligible to take the test with accommodations. The standard time increase for students requiring additional time due to disabilities is 50%.[46] Originally, the score sheet was labeled that additional time was granted due to a learning disability; however, this was ultimately dropped because it was deemed illegal under the Americans with Disabilities Act and could be perceived as an unfair designator of disability.
Scores are sent to the student, their high school, and up to four colleges of the student’s choice (optional).[47]
Test section durations[edit]
Time is a major factor to consider in testing.
The ACT is generally regarded as being composed of somewhat easier questions versus the SAT[48][citation needed], but the shorter time allotted to complete each section increases difficulty. The ACT allows:
- 45 minutes for a 75-question English section
- 60 minutes for a 60-question Mathematics section
- 35 minutes for a 40-question Reading section
- 35 minutes for a 40-question Science section
Comparatively, the SAT is structured such that the test taker is allowed at least one minute per question, on generally shorter sections (25 or fewer questions). Times may be adjusted as a matter of accommodation for certain disabilities or other impairments.
National ranks (score cumulative percentages)[edit]
Score reports provided to students taking the ACT test include the ranks (or cumulative percents) for each score and subscore received by the student. Each rank gives the percentage of recently tested students in the U.S. who scored at or below the given student’s score.[49] The following table shows the ACT national ranks as of the 2020-21 school year.[50]
| ACT Score | English Rank | Math Rank | Reading Rank | Science Rank | Composite Rank | STEM Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 35 | 99 | 99 | 98 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| 34 | 96 | 99 | 96 | 98 | 99 | 99 |
| 33 | 94 | 98 | 94 | 97 | 98 | 98 |
| 32 | 92 | 97 | 91 | 96 | 96 | 97 |
| 31 | 91 | 96 | 89 | 95 | 95 | 96 |
| 30 | 89 | 94 | 86 | 93 | 93 | 94 |
| 29 | 88 | 93 | 84 | 92 | 90 | 92 |
| 28 | 86 | 91 | 82 | 90 | 88 | 90 |
| 27 | 84 | 88 | 80 | 88 | 85 | 87 |
| 26 | 82 | 84 | 77 | 85 | 82 | 84 |
| 25 | 79 | 79 | 74 | 82 | 78 | 80 |
| 24 | 75 | 74 | 71 | 77 | 74 | 75 |
| 23 | 71 | 70 | 66 | 71 | 70 | 70 |
| 22 | 65 | 65 | 61 | 64 | 64 | 65 |
| 21 | 60 | 61 | 55 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 20 | 55 | 58 | 50 | 51 | 53 | 54 |
| 19 | 49 | 54 | 44 | 45 | 47 | 48 |
| 18 | 45 | 49 | 39 | 39 | 41 | 41 |
| 17 | 41 | 42 | 34 | 32 | 35 | 33 |
| 16 | 37 | 33 | 29 | 26 | 28 | 26 |
| 15 | 32 | 21 | 24 | 19 | 22 | 18 |
| 14 | 25 | 11 | 19 | 14 | 16 | 11 |
| 13 | 19 | 4 | 14 | 10 | 10 | 5 |
| 12 | 15 | 1 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| 11 | 11 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 10 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Concordance of ACT Scores and SAT Scores[edit]
The College Board (the developer of the SAT) and ACT, Inc. compared scores from about 600,000 students who were graduating in 2017 and who took both the SAT (2016 revision) and the ACT in 2016 and 2017. The following table shows, for each ACT composite score in the data set, the corresponding range of SAT total scores for students with the same percentile rank on each test. The most appropriate corresponding SAT score point for the given ACT score is also shown in the table.[51]
| ACT Composite Score | SAT Total Score Range | SAT Total Score |
|---|---|---|
| 36 | 1570–1600 | 1590 |
| 35 | 1530–1560 | 1540 |
| 34 | 1490–1520 | 1500 |
| 33 | 1450–1480 | 1460 |
| 32 | 1420–1440 | 1430 |
| 31 | 1390–1410 | 1400 |
| 30 | 1360–1380 | 1370 |
| 29 | 1330–1350 | 1340 |
| 28 | 1300–1320 | 1310 |
| 27 | 1260–1290 | 1280 |
| 26 | 1230–1250 | 1240 |
| 25 | 1200–1220 | 1210 |
| 24 | 1160–1190 | 1180 |
| 23 | 1130–1150 | 1140 |
| 22 | 1100–1120 | 1110 |
| 21 | 1060–1090 | 1080 |
| 20 | 1030–1050 | 1040 |
| 19 | 990–1020 | 1010 |
| 18 | 960–980 | 970 |
| 17 | 920–950 | 930 |
| 16 | 880–910 | 890 |
| 15 | 830–870 | 850 |
| 14 | 780–820 | 800 |
| 13 | 730–770 | 760 |
| 12 | 690–720 | 710 |
| 11 | 650–680 | 670 |
| 10 | 620–640 | 630 |
| 9 | 590–610 | 590 |
Score cumulative percentages and comparison with pre-2016 SAT[edit]
The data in this section pertains to the SAT prior to the 2016 redesign. Comparisons to SAT scores are not valid after the 2017 graduating class.
Sixty percent—about 2.03 million students—of the 2017 high school graduating class took the ACT. For the graduating class of 2017, the average composite score was a 21.0. Of these test-takers, 46% were male and 52% were female, with 2% not reporting a gender. 2,760 students in the graduating class of 2017 received the highest ACT composite score of 36.[52]
2005 distribution of ACT scores
The following chart shows, for each ACT score from 11 to 36, the corresponding ACT percentile and equivalent total SAT score or score range.[53][failed verification] (Concordance data for ACT scores less than 11 is not yet available for the current version of the SAT.) Note that ACT percentiles are defined as the percentage of test takers scoring at or below the given score.
| SAT combined score (Math + Reading/Writing) | ACT composite score | The percentile of students at or below this score for the ACT (not SAT) |
|---|---|---|
| 1600 | 36 | 100% |
| 1560–1590 | 35 | 99.9% |
| 1520–1550 | 34 | 99% |
| 1490–1510 | 33 | 98% |
| 1450–1480 | 32 | 97% |
| 1420–1440 | 31 | 96% |
| 1390–1410 | 30 | 94% |
| 1350–1380 | 29 | 92% |
| 1310–1340 | 28 | 89% |
| 1280–1300 | 27 | 86% |
| 1240–1270 | 26 | 82% |
| 1200–1230 | 25 | 78% |
| 1160–1190 | 24 | 74% |
| 1130–1150 | 23 | 69% |
| 1100–1120 | 22 | 63% |
| 1060–1090 | 21 | 57% |
| 1020–1050 | 20 | 51% |
| 980–1010 | 19 | 44% |
| 940–970 | 18 | 38% |
| 900–930 | 17 | 31% |
| 860–890 | 16 | 25% |
| 810–850 | 15 | 19% |
| 760–800 | 14 | 13% |
| 720–750 | 13 | 8% |
| 630–710 | 12 | 4% |
| 560–620 | 11 | 1% |
Score vs Percentile for English Section[edit]
| Score | The percentile of students
at or below this score |
|---|---|
| 36 | 100% |
| 35 | 99% |
| 34 | 99% |
| 33 | 97% |
| 32 | 96% |
| 31 | 94% |
| 30 | 93% |
| 29 | 91% |
| 28 | 88% |
| 27 | 85% |
| 26 | 82% |
| 25 | 78% |
| 24 | 73% |
| 23 | 68% |
| 22 | 63% |
| 21 | 57% |
| 20 | 50% |
| 19 | 43% |
| 18 | 38% |
| 17 | 33% |
| 16 | 29% |
| 15 | 24% |
| 14 | 18% |
| 13 | 14% |
| 12 | 11% |
| 11 | 9% |
Score vs Percentile for Mathematics Section[edit]
| Score | The percentile of students
at or below this score |
|---|---|
| 36 | 99% |
| 35 | 99% |
| 34 | 99% |
| 33 | 98% |
| 32 | 97% |
| 31 | 96% |
| 30 | 94% |
| 29 | 93% |
| 28 | 91% |
| 27 | 88% |
| 26 | 84% |
| 25 | 79% |
| 24 | 74% |
| 23 | 67% |
| 22 | 61% |
| 21 | 57% |
| 20 | 52% |
| 19 | 47% |
| 18 | 41% |
| 17 | 34% |
| 16 | 26% |
| 15 | 14% |
| 14 | 6% |
| 13 | 2% |
| 12 | 1% |
| 11 | 1% |
Score vs Percentile for Reading Section[edit]
| Score | The percentile of students
at or below this score |
|---|---|
| 36 | 99% |
| 35 | 99% |
| 34 | 99% |
| 33 | 97% |
| 32 | 95% |
| 31 | 93% |
| 30 | 91% |
| 29 | 87% |
| 28 | 85% |
| 27 | 82% |
| 26 | 78% |
| 25 | 75% |
| 24 | 71% |
| 23 | 66% |
| 22 | 60% |
| 21 | 54% |
| 20 | 48% |
| 19 | 42% |
| 18 | 39% |
| 17 | 30% |
| 16 | 25% |
| 15 | 19% |
| 14 | 15% |
| 13 | 10% |
| 12 | 6% |
| 11 | 3% |
Score vs Percentile for Science Section[edit]
| Score | The percentile of students
at or below this score |
|---|---|
| 36 | 99% |
| 35 | 99% |
| 34 | 99% |
| 33 | 99% |
| 32 | 98% |
| 31 | 97% |
| 30 | 96% |
| 29 | 95% |
| 28 | 93% |
| 27 | 91% |
| 26 | 87% |
| 25 | 83% |
| 24 | 77% |
| 23 | 70% |
| 22 | 62% |
| 21 | 56% |
| 20 | 47% |
| 19 | 38% |
| 18 | 34% |
| 17 | 21% |
| 16 | 19% |
| 15 | 15% |
| 14 | 11% |
| 13 | 8% |
| 12 | 5% |
| 11 | 3% |
Sources:[54][failed verification]
See also[edit]
- ACT (nonprofit organization)#Other ACT programs
- College admissions in the United States
- Global Assessment Certificate
- List of admission tests to colleges and universities
- Math–verbal achievement gap
- PLAN (test)
- SAT
- 2019 college admissions bribery scandal
References[edit]
- ^ «Test Descriptions – ACT Student». ACT, Inc. Retrieved September 13, 2015.
- ^ «Understand Your Scores – Sample Student Report – ACT Student». ACT, Inc. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «Registration – Test Dates in the U.S., U.S. Territories, and Canada – ACT Student». ACT, Inc. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «Registration – Test Dates in Other Countries – ACT Student». ACT, Inc. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «Test Center Locations, Dates, and Codes». ACT, Inc. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «Test Center Codes – International – ACT Student». ACT Inc. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ a b c d «The ACT Profile Report – National, Graduating Class 2022» (PDF). ACT, Inc. Retrieved October 29, 2022.
- ^ «Current ACT Fees and Services». ACT, Inc. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ «The ACT Test Help and Frequently Asked Questions – Am I eligible for a fee waiver?». ACT, Inc. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ a b «About ACT: History». Archived from the original on October 8, 2006. Retrieved October 25, 2006. Name changed in 1996.
- ^ «ACT Assessment», Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2007. Archived August 29, 2009, at the Wayback Machine October 31, 2009.
- ^ «A (Mostly) Brief History Of The SAT and ACTs». Erik the Red. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «When Will the ACT Start Computer-Based Testing?». Magoosh. Retrieved February 16, 2018.
- ^ Pope, Justin (September 24, 2012). «SAT scores edge down; ACT now more popular exam». Associated Press. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ^ The Test Archived August 28, 2006, at the Wayback Machine. (URL accessed June 5, 2007).
- ^ «The ACT-Measure High School Student Readiness for College» (PDF).
- ^ Radunzal, J., Noble, J. (2003, April). «Tracking 2003 act-tested high school graduates: College readiness, enrollment, and long-term success.» Retrieved from: http://www.act.org/research/researchers/reports/pdf/ACT_RR2012-2.pdf Archived March 16, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- ^
The ACT Technical Manual - ^ SCHOOL, CENTURY ACADEMY HIGH. «SAT/ACT Information». www.conejousd.org. Retrieved June 2, 2017.
- ^ a b «Entrance Exam For College – College Entrance Exams – University In The USA». Uni in the USA. Archived from the original on October 20, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ «ACT? SAT? Subject Tests? No Tests? Holy Moly! Who Is Requiring What These Days?». Huffington Post. August 11, 2014.
- ^ «SAT vs. ACT – Test Prep Tutoring & Classes – NYC, NY». CATES Tutoring and Educational Services. Archived from the original on October 16, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2014.
- ^ Honawar, Vaishali; Alyson Klein (August 30, 2006). «ACT Scores Improve; More on East Coast Taking the SAT’s Rival». Education Week. 26 (1): 16. ISSN 0277-4232. Retrieved July 6, 2007.
Beginning in 2013, all freshman entering high school in the state of Ohio must take the test in order to graduate.
- ^ «Writing Test Scores». ACT. Retrieved May 3, 2021.
- ^ «What’s Next for the ACT – Test Updates and Enhancements». Archived from the original on July 29, 2015. Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ^ a b «The ACT Test for Students». ACT. Archived from the original on February 17, 2016.
- ^ «Newsroom – Press Kit, Digital Media Library, and Press Releases». Archived from the original on July 29, 2015. Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ^ «The ACT-Getting Ready for Test Day».
- ^ Geoff Martz; Kim Magloire; Theodore Silver. (2007). «Chapter 10». Cracking The ACT (2007 ed.). The Princeton Review. p. 94. ISBN 978-0-375-76585-8.
- ^ «ACT FAQ: Can I use a calculator?». ACT Inc. Archived from the original on August 20, 2007. Retrieved September 8, 2007.
- ^ «Description of Reading Test». ACT. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- ^ Geoff Martz; Kim Magloire; Theodore Silver. (2007). «Chapter 20». Cracking The ACT (2007 ed.). The Princeton Review. p. 307. ISBN 978-0-375-76585-8.
- ^ «Preparing for the ACT Test» (PDF). ACT, Inc. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 11, 2022. Retrieved March 18, 2022.
- ^ «The ACT Test for Students». ACT. Archived from the original on August 9, 2015. Retrieved July 27, 2015.
- ^ Cavner, Brian. «Comparison Between the SAT and ACT: Requirements differences between the two college admissions standardized tests». Archived from the original on February 15, 2008. Retrieved February 3, 2008.
- ^ «Preliminary Technical Manual for the Enhanced ACT Assessment» (PDF). Education Resources Information Center. ACT, Inc. October 1989. p. 28. Retrieved June 27, 2021.
- ^ «ACT Prep:Description of the ACT Assessment». ACT Inc. Archived from the original on June 30, 2007. Retrieved June 29, 2007.
- ^ a b «The ACT® Data». ACT Inc. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ a b «University School student receives perfect ACT score». WJHL News Channel 11. Nextstar Media. Retrieved December 19, 2021.
- ^ a b «ACT Research Publications». ACT, Inc. Retrieved December 19, 2021.
- ^ American College Test INC. (ACT). Research and Policy Issues-Information Brief 2002–1. (n.d.). «Interpreting act assessment scores: College admissions.» Retrieved October 8, 2012, from http://www.act.org/research/researchers/briefs/2002-1.html#UItAIYq5fw Archived January 20, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Registration – The ACT Test». ACT, Inc. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ «The ACT Test Help and Frequently Asked Questions – Is Non-Saturday Testing Available?». ACT, Inc. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ American College Test INC. (ACT), Research and Policy Issues-Information Brief (2001). «Facts about scoring the act assessment». Retrieved October 8, 2012, from http://www.act.org/research/researchers/briefs/2001-1.html#UIX3TYYq5fw Archived January 20, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Current ACT Fees and Services». Retrieved December 2, 2022.
- ^ «ACT Services for Students with Disabilities». ACT Inc. Archived from the original on August 22, 2007. Retrieved September 8, 2007.
- ^ «ACT Score Information: ACT Score Report Descriptions». ACT Inc. Archived from the original on July 11, 2007. Retrieved June 29, 2007.
- ^ «ACT Versus SAT: Popular Doesn’t Mean Better». www.icon-plus.com. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
- ^ «ACT National Ranks». ACT, Inc. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ «National Norms for ACT Test Scores» (PDF). ACT, Inc. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ «Guide to the 2018 ACT/SAT Concordance» (PDF). College Board and ACT, Inc. Retrieved November 26, 2021.
- ^ «Condition of College and Career Readiness 2017». ACT Inc. Retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ «Higher Ed Brief: SAT Concordance» (PDF). College Board. Retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ «UC Admissions». Archived from the original on April 20, 2009. Retrieved May 17, 2009. Univ. of California Eligibility by Examination Alone
External links[edit]
- ACT Taker’s Site
- ACT Corporate Site
Струкрура экзамена ACT
Экзамен ACT состоит из четырех обязательных частей (English, Mathematics, Reading, Science) и факультативной секции написания сочинения (Writing)
Все задания имеют пять вариантов ответов, (А) — (Е). Правильный ответы необходимо отметить в специальной экзаменационной форме.
На экзамене нельзя пользоваться учебниками, словарями или линейками. Калькуляторами разрешенных моделей разрешается пользоваться только при выполнении заданий математической секции.
Примеры заданий секции English (фрагмент)
Notes from Underground
A lot of people hate to ride the New York City subways, but I love them because ❶ I like to get places fast. A musician balancing a cello case, two Buddhist monks in saffron robes, and a group of stockbrokers in crisp, ❷ charcoal gray suits get on at Wall Street. A passenger placidly sews while the subway train flings and jolts. A teenager ❸ whose holding a shoebox containing a kitten as tiny as a gingersnap smiles ❹ even if a line of girls in frilly white communion dresses file by. About three and a half million people aday ride the ❺ subways I think maybe ❻ I might possibly have met them all.
1. At this point, the writer wants to provide one reason why she likes to ride the subways. Which choice is most relevant to the information provided in this first paragraph?
A. NO CHANGE
B. I never know what I’l see there.
C. they are so much cheaper than taxis
D. they are places of enorous quiet and calm.
2. F. NO CHANGE
G. charcoal gray suits,
H. charcoal, gray suits
J. charcoal gray, suits
3. A. NO CHANGE
B. thats
C. as
D. who’s
4. F. NO CHANGE
G. as
H. whereas
J. such that
5. A. NO CHANGE
B. subways, and
C. subways, which
D. subways actually
6. F. NO CHANGE
G. perhaps I’ve
H. I’ve possibly
J. I’ve
Примеры заданий секции Math (фрагмент)
1. To keep up with rising expenses, a motel manager needs to raise the $40.00 room rate by 22%. What will be the new rate?
A. $40.22
B. $42.20
C. $48.00
D. $48.80
E. $62.00
2. In a bag of 24 ballons, there is an equal nnumber of ballons of each color. WAs a salesperson, your commission is diretly proportional to the dollar amount of sales you make. .If your sales are $800, your comission is $112. How much comission would you earn if you had $1,400 in sales?
F. $210
G. $196
H. $175
J. $128
K. $64
3. If 7 + 3x = 32, then 2x = ?
A. 5
B. 10
C. 12
D. 14
E. 58/3
4. Carmen is playig with blocks. She arranges stacks of blocks so that each successive level of blocks has 1 few bock than the level below it and th etop level has 1 block. Such a stack with 3 levels is shown below. Carmen wants to make such a stack with 12 levels. How many blocks wuld she use to build this stack?
F. 66
G. 78
H. 132
J. 144
K. 156
Примеры заданий секции Reading (фрагмент)
My grandfather has made crutches for me. These are sturdy crutches, just the right size. I am delighted with them and launch myself around the house on them.
And I take a fall immediately. And continue falling several times a day, great splatting, knocking-into-furniture-and- breaking-things falls that cause everyone in the family to come running. My grandfather has forgotten to put rubber tips on the ends of my crutches. When we figure this out and buy the rubber tips and put them on the crutches, I stop falling. But by then the bone-set that was coming long nicely has slipped, and the doctor has ordered me back to the wheelchair.
The missing crutch-tips are the first clue I have to this peculiar family trait, one that for lack of any better term I must call «flawed competence.» We Bryants are a family of able and clever people, industrious, intelligent, determined, and of good will. We are careful in our work. After all, my grandfather measured me on two occasions before he made the crutches. But we usually do something wrong.
Four years later I become increasingly aware of «flawed competence» when I develop a plan for converting our old grown-over tennis court into a basketball court. My grandfather is always interested in plans, and in this planning session, we decide that he will make the hoops, and he will help me make the backboards. Clearing the ground and smoothing the surface will be my tasks. So I rip out honeysuckle and hatchet down a few little scrub cedars. We Bryants are known for setting our minds to things.
1. The passage is written from the point of view of:
A. an unidentified narrator observing the relationship over time between a boy and his grandfather.
B. two members of the same family discovering their shared trait through joint activities.
C. a grown man agonizing over the mixed messages he received as a child from older relatives.
D. a boy and the man he becomes considering incidents that illustrate a family trait.
2. Which of the following best describes the author’s approach to presenting the story of the narrator’s discovery about himself?
F. Revealing the narrator’s self-awareness about a trait through a blend of personal reflection and scenes from the narrator’s youth and adulthood
G. Starting immediately with a statement of the discovery in the narrator’s voice and continuing with scenes that reveal how the discovery came about
H. Describing the physical details of scenes and summarizing their significance in a concluding statement in the narrator’s voice
J. Using dialogue in the midst of scenes fraught with tension to indicate what the narrator is experiencing internally
3. Each of the three projects described in the passage reveals:
A. the increasing antagonism between the grandfather and grandson.
B. the errors the narrator makes and disapproval they bring from others.
C. that such incidents set the state for the Bryant family traits to emerge.
D. that the narrator is determined to avoid being ungrateful, hateful, or overly fastidious.
4. The boy’s approach to the task of converting the tennis court to a basketball court can best be described as:
F. reluctant until his grandfather’s plans inspire him.
G. enthusiastic until his grandfather’s error puts them both in an awkward position.
H. apprehensive until he discovers his error is not a devastating one.
J. thrilled until he remembers that his grandfather is a poor planner.
Примеры заданий секции Science (фрагмент)
Metamorphic rocks form when temperature and/or pressure cause changes in preexisting rock. Figure 1 shows the temperature and pressure conditions in which certain facies (categories of metamorphic rocks) are formed.
A rock’s metamorphic grade (a measure of the intensity of metamorphism) is classified on a scale of low (very similar to the original rock) to high (very different from the original rock). Table 1 lists the gradesof Facies A — G from Figure 1. Figure 2 shows characteristic minerals that may be present in rocks of a given grade.
1. According to Figure 2, which of the following minerals would most typically be found only in rocks of a medium grade?
A. Muscovite
B. Biotite
C. Kyanite
D. Plagioclase
2. Figure 1 indicates that as depth increases, preassure:
F. decreases only
G. remains the same
C. increases only
D. increases, then decreases
3. According to Figure 2, the presenceof which of the following minerals in a metamorphic rock would be least helpful in determining that rock’s grade?
A. Chloride
B. Muscovite
C. Staurolite
D. Plagiosclase
4. Herfels is metamorphic rock formed when magma (molten rock) heats sedimentary rocks on Earth’s surface. According to Figure 1, hornfels is most likely a member of which of the following facies?
A. Facies A
B. Facies C
C. Facies E
D. Facies G
Вопросы и ответы об ACT
Возможны изменения в порядке проведения экзамена, вызванные COVID-19. Информация об изменениях постоянно обновляется на официальном сайте ACT.
Кому нужен ACT?
Результаты ACT необходимо предоставить при подаче документов в приемные комиссии колледжей и университетов США и Канады при поступлении на обучение по программе бакалавриата. Вузы других стран, в которых обучение ведется на английском языке, также могут требовать результаты ACT.
Какую роль играют результаты ACT при поступлении в американские колледжи и университеты?
Решение о зачислении абитуриента в вуз принимается на основе результатов стандартизированных экзаменов (ACT или SAT), оценок в аттестате, мотивационного эссе, внеакадемических достижениях (волонтерская работа, участие в социально значимых проектах) и рекомендательных писем. Однако среди всех критериев отбора именно результаты экзамена ACT (или его аналога SAT) играют определяющее значение. Другими словами, высокий балл ACT – это не гарантия поступления, но необходимое условие.