1 year(s) ago
A negative form19 A professor was lecturing his class one day. He wanted to focus on negation one __________ time. MUCH20 “The ____________ example is English”, he said, “In English a double negative forms a positive. In some languages, though, such as Russian, a double negative is still a negative. ONE21 However, there ____________ a language wherein a double positive can form a negative. ”A loud voice from the back piped up, ‘Yeah, right. ‘ NOT BEA boot on the wrong foot22 Willy asked his teacher to help him get his shoes on at the end of a busy day. After quite a struggle, Tessa finally got them on. “They’re on the wrong ____________, Miss,” mumbled Willy. Staying calm she swapped them over for him. FOOT23 “They’re not my shoes, Miss,” Willy murmurs again. Tessa ____________ hard to keep her cool and asked Willy why he hadn’t told her before. FIGHT24 She then kneeled down again and helped him pull the shoes off. “These aren’t my shoes, they’re my brother’s and Mum told ______________ not to tell anyone. ” I25 Tessa helped him back into his shoes, got him into his coat, wrapped his scarf round his neck. When he ____________, she asked, “Where are your gloves, Willy?” “Oh, Miss, I always put them in my shoes ” DRESS26 The first form of cryptography was actually the simple writing of a message. Do you know why? Because most people were ____________ to read or write. ABLE27 In fact, the very word cryptography comes from the Greek words ‘kryptos’, which mean ‘hidden’, and ‘graphein’, which means ‘writing’. Cryptography, by its very nature, implies secrecy and ____________. DIRECTNESS28 Early cryptography included transforming messages into unreadable figures to protect the content of a message while it was carried from one ____________ to another. ADDRESS29 Nowadays, cryptography has evolved ____________ and today it includes such things as digital signatures, authentification of a sender or receiver and many more. GREAT30 People wanted to conceal messages since they moved out of caves and started living in groups. The earliest forms of cryptography were found in the cradle of ____________, Egypt, Greece and Rome. CIVILIZE31 The Greeks, for example, wrapped a tape around a stick, and then wrote the message on the wound tape. Unwinding the tape made the writing ____________. The receiver of the message had a stick of the same diameter and used it to decipher the message. MEANING
ответы: 1
Зарегистрируйтесь, чтобы добавить ответ
Ответ:
19. More
20. First
21. Is
22. Feet
23. Fought
24. Me
25. Was dressed
26. Not able/unable
27. Directness
28. Addressee/receiver
29. Greatly/a lot
30. Civilisation
31. Meaningful

Oct 31, 2021
Чтобы ответить необходимо зарегистрироваться.
This article was originally published on the Red Hat Customer Portal. The information may no longer be current.
Cryptology is a young science.
Though it has been used for thousands of years to hide secret messages, systematic study of cryptology as a science (and perhaps an art) just started around one hundred years ago.
The first known evidence of the use of cryptography (in some form) was found in an inscription carved around 1900 BC, in the main chamber of the tomb of the nobleman Khnumhotep II, in Egypt. The scribe used some unusual hieroglyphic symbols here and there in place of more ordinary ones. The purpose was not to hide the message but perhaps to change its form in a way which would make it appear dignified. Though the inscription was not a form of secret writing, but incorporated some sort of transformation of the original text, and is the oldest known text to do so. Evidence of some use of cryptography has been seen in most major early civilizations. «Arthshashtra», a classic work on statecraft written by Kautalya, describes the espionage service in India and mentions giving assignments to spies in «secret writing» — sounds like an ancient version of James Bond?
Fast forwarding to around 100 BC, Julius Caesar was known to use a form of encryption to convey secret messages to his army generals posted in the war front. This substitution cipher, known as Caesar cipher, is perhaps the most mentioned historic cipher in academic literature. (A cipher is an algorithm used for encryption or decryption.) In a substitution cipher, each character of the plain text (plain text is the message which has to be encrypted) is substituted by another character to form the cipher text (cipher text is the encrypted message). The variant used by Caesar was a shift by 3 cipher. Each character was shifted by 3 places, so the character ‘A’ was replaced by ‘D’, ‘B’ was replaced by ‘E’, and so on. The characters would wrap around at the end, so ‘X’ would be replaced by ‘A’.
During the 16th century, Vigenere designed a cipher that was supposedly the first cipher which used an encryption key. In one of his ciphers, the encryption key was repeated multiple times spanning the entire message, and then the cipher text was produced by adding the message character with the key character modulo 26. (Modulo, or mod, is a mathematical expression in which you calculate the remainder of a division when one number is divided by another.) As with the Caesar cipher, Vigenere’s cipher can also easily be broken; however, Vigenere’s cipher brought the very idea of introducing encryption keys into the picture, though it was poorly executed. Comparing this to Caesar cipher, the secrecy of the message depends on the secrecy of the encryption key, rather than the secrecy of the system.
At the start of the 19th century when everything became electric, Hebern designed an electro-mechanical contraption which was called the Hebern rotor machine. It uses a single rotor, in which the secret key is embedded in a rotating disc. The key encoded a substitution table and each key press from the keyboard resulted in the output of cipher text. This also rotated the disc by one notch and a different table would then be used for the next plain text character. This was again broken by using letter frequencies.
The Engima machine was invented by German engineer Arthur Scherbius at the end of World War I, and was heavily used by the German forces during the Second World War. The Enigma machine used 3 or 4 or even more rotors. The rotors rotate at different rates as you type on the keyboard and output appropriate letters of cipher text. In this case the key was the initial setting of the rotors.
The Enigma machine’s cipher was eventually broken by Poland and the technology was later transferred to the British cryptographers who designed a means for obtaining the daily key.
In the early 1970’s, IBM realized that their customers were demanding some form of encryption, so they formed a «crypto group» headed by Horst-Feistel. They designed a cipher called Lucifer. In 1973, the Nation Bureau of Standards (now called NIST) in the US put out a request for proposals for a block cipher which would become a national standard. They had obviously realized that they were buying a lot of commercial products without any good crypto support. Lucifer was eventually accepted and was called DES or the Data Encryption Standard. In 1997, and in the following years, DES was broken by an exhaustive search attack. The main problem with DES was the small size of the encryption key. As computing power increased it became easy to brute force all different combinations of the key to obtain a possible plain text message.
In 1997, NIST again put out a request for proposal for a new block cipher. It received 50 submissions. In 2000, it accepted Rijndael, and christened it as AES or the Advanced Encryption Standard.
To conclude, history teaches us:
-
The secrecy of your message should always depend on the secrecy of the key, and not on the secrecy of the encryption system. (This is known as Kerckhoffs’s principle.)
-
Related to the above, always use ciphers which have been publicly reviewed and have been established as a standard. Using «secret crypto» is bad, because just like the Caesar cipher, once the system is known, all messages can be decrypted. For example, if your key is compromised, an attacker could access your messages; however, if the attacker can compromise the crypto system itself, they can obtain the plain text of every message (not just for a single person) encrypted by that system.
Huzaifa Sidhpurwala is a principal Product Security Engineer, working for Red Hat Product Security Team.
Read full bio
Asked by: Kavon Heller
Score: 4.5/5
(18 votes)
If you can make sense of what is written, then it is in plaintext. Ciphertext, or encrypted text, is a series of randomized letters and numbers which humans cannot make any sense of. An encryption algorithm takes in a plaintext message, runs the algorithm on the plaintext, and produces a ciphertext.
What is a plaintext in cryptography?
Plaintext is what encryption algorithms, or ciphers, transform an encrypted message into. It is any readable data — including binary files — in a form that can be seen or utilized without the need for a decryption key or decryption device.
What do you mean by ciphertext?
Ciphertext. Cipher is an algorithm which is applied to plain text to get ciphertext. It is the unreadable output of an encryption algorithm. The term «cipher» is sometimes used as an alternative term for ciphertext. Ciphertext is not understandable until it has been converted into plain text using a key.
What is ciphertext with example?
Ciphertext example
The Caesar cipher is a substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is «shifted» a certain number of places down the alphabet. For example, with a shift of 1, A would be B, B would be replaced by C, etc.
What is the relationship between plaintext and ciphertext is called?
Theory. In Shannon’s original definitions, confusion refers to making the relationship between the ciphertext and the symmetric key as complex and involved as possible; diffusion refers to dissipating the statistical structure of plaintext over the bulk of ciphertext.
41 related questions found
What are the two main goals of cryptography?
The Main Goals of cryptography
- Data Privacy(confidentiality)
- Data Authenticity(it came from from where it claims)
- Data integrity(it has not been modified on the way) in the digital world.
Which two methods are used to frustrate cryptanalysis?
Shannon suggests two methods for frustrating statistical cryptanalysis, diffusion, and confusion. It means any of the characters in plaintext is changed then simultaneously several characters of the ciphertext should also be changed.
How do I decode ciphertext?
To decrypt, take the first letter of the ciphertext and the first letter of the key, and subtract their value (letters have a value equal to their position in the alphabet starting from 0). If the result is negative, add 26 (26=the number of letters in the alphabet), the result gives the rank of the plain letter.
What is plaintext and ciphertext explain with example?
An encryption algorithm takes in a plaintext message, runs the algorithm on the plaintext, and produces a ciphertext. The ciphertext can be reversed through the process of decryption, to produce the original plaintext. Example: We will encrypt a sentence using Caesar Cipher. … Plaintext: This is a plaintext.
How do you use ciphertext?
Have your child follow these easy steps to use the Caesar Cipher.
- Write out the entire alphabet in a line.
- Choose a number to be your «rotation» amount. …
- Under your first line, starting at the letter you «rotated» to, rewrite the alphabet. …
- Decide what your message is going to say and write it on a piece of paper.
How do I convert ciphertext to plaintext?
This part of the process is called encryption (sometimes encipherment ). The ciphertext is transmitted to the receiver. The receiver converts the ciphertext message back to its plaintext form. This part of the process is called decryption (sometimes decipherment ).
What are the types of cryptography?
Cryptography can be broken down into three different types:
- Secret Key Cryptography.
- Public Key Cryptography.
- Hash Functions.
Why is ciphertext important?
Ciphertext is what encryption algorithms, or ciphers, transform an original message into. Data is said to be encrypted when a person or device lacking the cipher is unable to read it. They, or it, would need the cipher to decrypt the information.
What is the difference between Cleartext and plaintext?
Cleartext has not been subject to encryption whatsoever, and there is no expectation that it has been. Plaintext, the latter, specifically refers to information that is inputted into a cipher, or encryption algorithm.
Is plaintext also called cleartext?
The unencrypted form of an encrypted message. Also called cleartext.
What is cryptanalysis technique?
Cryptanalysis is the study of ciphertext, ciphers and cryptosystems with the aim of understanding how they work and finding and improving techniques for defeating or weakening them.
What is the plaintext of the message?
Plaintext is a term used in cryptography that refers to a message before encryption or after decryption. That is, it is a message in a form that is easily readable by humans. Encryption is the process of obscuring messages to make them unreadable in the absence special knowledge.
What does PKI mean?
PKI is an acronym for public key infrastructure, which is the technology behind digital certificates.
What is vigenere Cipher example?
The Vigenère cipher is an example of a polyalphabetic substitution cipher. A polyalphabetic substitution cipher is similar to a monoalphabetic substitution except that the cipher alphabet is changed periodically while enciphering the message. … Blaise de Vigenère developed what is now called the Vigenère cipher in 1585.
What is Monoalphabetic cipher example?
Examples of monoalphabetic ciphers would include the Caesar-shift cipher, where each letter is shifted based on a numeric key, and the atbash cipher, where each letter is mapped to the letter symmetric to it about the center of the alphabet.
How is cryptography calculated?
The conversion formula is of the form c ≡ p + a mod 26. We know that when p = 5 (plaintext E), we have c = 10 (ciphertext J). Thus, 10 ≡ 5 + a mod 26. So a ≡ 5 37 Page 4 mod 26, and the encryption formula is c ≡ p + 5 mod 26.
Which cipher used the key only once?
The key used for a one-time pad cipher is called pad, as it is printed on pads of paper.
Which block is cipher?
A block cipher is an encryption method that applies a deterministic algorithm along with a symmetric key to encrypt a block of text, rather than encrypting one bit at a time as in stream ciphers. For example, a common block cipher, AES, encrypts 128 bit blocks with a key of predetermined length: 128, 192, or 256 bits.
What is cryptanalysis used for?
Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic security systems and gain access to the contents of encrypted messages, even if the cryptographic key is unknown.
What is the first goal of cryptography?
Confidentiality: First, cryptography protects the confidentiality (or secrecy) of information. Even when the transmission or storage medium has been compromised, the encrypted information is practically useless to unauthorized persons without the proper keys for decryption.
Сегодня 12.04.2022 09:49 свежие новости час назад
Прогноз на сегодня : The first form of cryptography . Развитие событий.
Актуально сегодня (12.04.2022 09:49): The first form of cryptography
..
1. The first form of cryptography was actually the simple writing of a message
2. The first form of cryptography was actually
3. The first form of cryptography was
4. The first form of cryptography
5. The first form of cryptography was actually the
6. The first form of cryptography was actually the simple
7. The first form of cryptography was actually the simple writing
8. The first form of cryptography was actually the simple writing of a message do you know why егэ
9. The first form of cryptography was actually the simple writing of a message егэ
10. The first form of cryptography was actually the simple writing of a message do you know why because
11. The first form of cryptography was actually the simple writing of a message do you know why
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
9041462618282665b80f0416d63c2cfc 4d082d431e1c1ec4f90cfb3588eab17b
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
The first form of cryptography
firmware of modem is mts 827f under all operators | 7 сезон игры престолов смерти | искусство тестирования программ 3-е издание koob | Боевой листок шаблон Скачать | игра престолов сериал 2 сезон 1 серия | презентации психика и сознание | firmware for xbox 360 freeboot download | прошивки для телефонов bqs-4700 | схема нумерации мест в вагоне 1 класса экспресса москва калуга | найти госпожу для раба г казань |
Invision Community © 2022 IPS, Inc.
Карта сайт Rss
s
p
In this first section of Cryptography & Network Security you will get to read about What is Cryptography, its process, What is Encryption, What is Decryption, Advantage, and Disadvantage and Application of Cryptography. So let’s start.
What is Cryptography
Cryptography is a subject that is used to protect the user’s data and increase the security of the network. Cryptography is mostly read and learn by students of information technology (I.T) or Computer Science & Engineering (CSE).
The word Cryptography is derived from the Greek word Krypto, which means Hidden or Secrets. That is, cryptography is the secret way to keep your data, cryptography means The Art of Protecting Data. That is how we have to keep our data secret so that no one else can read it. Our data can be of different types like a credit card, debit card information, any website login credential, etc.
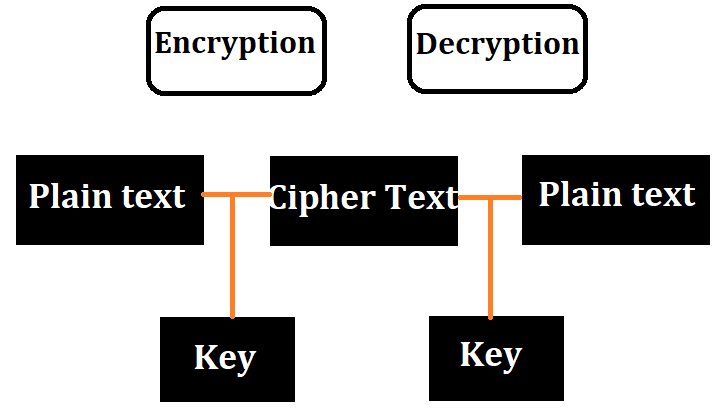
Through cryptography, we can convert our data into Unreadable Secret Codes, which no one can read, that Unreadable Secret Codes we call Cipher Text. But the person who has the secret key can read that data, the person can decrypt the data by that secret key, the decrypted data is called plain text. In this, there are two processes of Encryption and Decryption, which are used to protect the data. In Encryption, the data is converted from plain text to Cipher Text so that no one can read and in Decryption encryption causes the reverse process. In this, the data is converted from Cipher Text to Plain Text so that everyone can read.
The Process of Cryptography
There are two process –
- Encryption
- Decryption
What is Encryption
Encryption is a process of cryptography. It is used to keep user’s data secret. This is a method that is used to convert data and information into secret codes this is called cipher text. Cipher text is a text that no one can understand and the original data that we have is called plain text that everyone can read and understand.
- The main purpose of encryption is to keep the data secure.
- To read encrypted data you must have a public key.
Encryption basically consists of two types the first one is Asymmetric encryption and the second one is Symmetric encryption.
What is Decryption
Decryption is a process of cryptography. It is used to decrypt, encrypted data. Decrypted data or original data is called plain text. That is, converting Cipher text to plain text is called Decryption. To convert Cipher text to plain text we need a key so that we can convert the data into readable form.
Advantage of Cryptography
- Confidentiality – Cryptography techniques can keep any type of information confidentiality and protect it from unauthorized users.
- Authentication – This is a technique of cryptographic with the help of which we can protect the information of MAC and digital signatures.
- Data Integrity – The hash functions of cryptographic help in assuring the user’s data.
- Non-repudiation – Cryptography does not accept non-repudiation requests at the time of a digital signature.
Disadvantage of Cryptography
- A non-functional attack may be carried out by an intruder on a network or computer system.
- Through the use of cryptography, it cannot be ensured that the data used by the users are really secure.
- Cryptography does not provide security from threats arising from bad systems, protocols, and processes.
- Cryptography is a costly technology that is in terms of time and money.
Application of Cryptography
- Authentication/Digital Signatures – From Authentication and Digital Signatures though we can find out whether the data sent by the sender is authenticated or not.
- Time-stamping – This is a technique through which we can find out at what time an electronic document was distributed.
- Electronic Money – Electronic Money is a technique of cryptography that identifies money transactions by net transfer.
- Encryption/Decryption in email – Encryption, and Decryption are mostly used at the time of mailing so that the data of the users can remain secure.
- Encryption Social Media – In today’s time, every social media uses encryption techniques so that the user’s data can be kept secure.
1. What is Capstone?
It is known as «Corner Stone» It is the Jesus Christ.
He is “ the stone you builders rejected, which has become
the capstone.” Acts 4:11 (NIV)
History also refers this! B.C. & A.D. are cutting around
HIM, showing HIM as the Capstone. There are plenty to tell….no End.
2. What is Clipper?
Clipper is a compiler that was well known at the time of
80’s and early times of 90’s. We can build DOS based
applications (even large applications too) using clipper.
There is no seperate Database required to use
with clipper. It itself is having capacity to maintain data
in the form of tables and we can use it to write coding also.
3. What is quantum computing?
In quantum computing, we use the concept of qubits,
superposition and coherence. A normal bit can be in only
two states — 0 and 1. But a qubit it can be in 0, 1, or in
the superposition of 0 and 1.
Quantum computers, will be much much faster than
traditional silicon based compuers.
4. What is quantum cryptography?
The science of cryptography has existed in one form or
another for centuries.
Cryptography is the art of encoding and decoding messages
for transmission between two
parties, while keeping the message secret from unwanted
viewers. There are many common
implementations of cryptography in use today such as the
HTTPS protocol on the Internet. All
forms of data encryption and cryptography require a key in
some form or another for use in
encoding and decoding data. There are even some modern
methods of encryption that have been
mathematically proven to be unbreakable if they are
implemented properly.
The inherent problem with any form of cryptography is in
the method of key distribution.
To date, all forms of message encryption have possessed
this major vulnerability. As such, it
makes no difference whether a secret message is sent via
homing pigeon, a radio transmission, a
penciled message on a notepad, or whispering to another,
there is no physical way to get a
cryptographic key to another without running the risk of
the key being intercepted.
To solve this dilemma, a radical solution has been proposed
called quantum
cryptography. This method essentially uses photon light
particles to send a key to an intended
recipient. The difference with this method of key
distribution is that it implements quantum
mechanic’s uncertainty principle as a means to guarantee
the privacy of a key during
distribution. Practically, quantum cryptography has the
ability to afford complete privacy during
the entire broadcast of an encoded message.
5. What are biometric techniques?
those are technics like
face detection
Iris recognition
fingerprint recognition
palm vien recognition.
All these can be used for Authentication
6. What is tamper-resistant hardware?
Ensuring that various cryptographic keys are provided by
their intended users, and only for their intended purposes,
temper resistent hardware is introduced.
An example temper resistent device is your «SMART CARD».
You have to physically posess the device and also have to
possess the PIN or the password to use it.
8. (1/10)18 — (1/10)20 = ?
If it’s the Same Question:
Step 1. (0.1)/18-()/20
Step 2. (0.1)((1/18)-(1/20))
Step 3. 0.1 (10-9)/180 ————> LCM of 18 & 20 = 180
Step 4. 0.1/180
Step 5. 1/1800 is the Answer
Approx = 0.000557
10. How to Find the XP Lost Password?
Forgot XP Password
The other day I got a call from a friend who had managed to
remember his administrator password to his Windows XP
computer.
My heart sank as I told him it is almost impossible to
access hi PC now as this was the only account on the
machine, and with no password Windows XP was not going to
let him in!
Forgotten XP Password…
As I stared at my mates computer and asked if he had ever
made a Password Reset Disc I already knew what he was going
to say…
This situation reminded me of asking many friends for their
latest data backup CD/DVD when their computer crashed and
need a rebuild — they NEVER have one!!!
…well a quick check on Google and I found a great service
that could just help my mate out.
This site provides a tool to recover lost Windows XP
passwords — YEAH!
It works very prefect to regain your password .Also use to
bootable CD/DVD or usb
There is a free service as well as a priority service that
will retrieve your passwords within minutes. The fee for
the priority service is very cheap, and is really just to
cover server costs.
Download Interview PDF
- Подробности
-
42504
 |
||
| Прочитайте текст. Заполните пропуски в предложениях под номерами В4-В10 соответствующими формами слов, напечатанных заглавными буквами справа от каждого предложения. TEST 13 (part 1) |
Graffiti
|
B4 |
Graffiti is any type of public markings that may appear in the forms of simple written words to elaborate wall paintings. Graffiti has existed since ancient times. |
EXIST |
|
B5 |
The earliest forms of graffiti date back to 30, 000 BC in the form of prehistoric cave paintings and pictographs using tools such as animal bones and pigments. |
EARLY |
|
B6 |
The images drown on the walls showed scenes of animal wildlife and hunting expeditions. These illustrations were placed in ceremonial and sacred locations inside of the caves. |
PLACE |
|
B7 |
Modern graffiti comes in many different forms, from the scrawled message in a public bathroom stall to the spray-painted murals boasted on subway walls. |
COME |
|
B8 |
Nowadays, paint, particularly spray paint, and marker pens have become them most commonly used graffiti materials. |
COMMONLY |
|
B9 |
In most countries, marking or painting property without the property owner’s consent is considered to be vandalism, which is a punishable crime. |
OWNER |
|
B10 |
Because of the controversial material contained in many murals, graffiti is now considered to be a form of resistance art, in rebellion against common public beliefs and government laws. |
BELIEF |
1. Что такое шифрование?
а) способ изменения сообщения или другого документа, обеспечивающее искажение его содержимого+
б) совокупность тем или иным способом структурированных данных и комплексом аппаратно-программных средств
в) удобная среда для вычисления конечного пользователя
2. Что такое кодирование?
а) преобразование обычного, понятного текста в код+
б) преобразование
в) написание программы
3. Для восстановления защитного текста требуется:
а) ключ
б) матрица
в) вектор
4. Сколько лет назад появилось шифрование?
а) четыре тысячи лет назад+
б) две тысячи лет назад
в) пять тысяч лет назад
5. Первое известное применение шифра:
а) египетский текст+
б) русский
в) нет правильного ответа
6. Секретная информация, которая хранится вWindows:
а) пароли для доступа к сетевым ресурсам+
б) пароли для доступа в Интернет+
в) сертификаты для доступа к сетевым ресурсам и зашифрованным данным на самом компьютере+
7. Что такое алфавит?
а) конечное множество используемых для кодирования информации знаков+
б) буквы текста
в) нет правильного ответа
8. Что такое текст?
а) упорядоченный набор из элементов алфавита+
б) конечное множество используемых для кодирования информации знаков
в) все правильные
9. Выберите примеры алфавитов:
а) Z256 – символы, входящие в стандартные коды ASCII и КОИ-8+
б) восьмеричный и шестнадцатеричный алфавиты+
в) АЕЕ
10. Что такое шифрование?
а) преобразовательный процесс исходного текста в зашифрованный+
б) упорядоченный набор из элементов алфавита
в) нет правильного ответа
11. Что такое дешифрование?
а) на основе ключа шифрованный текст преобразуется в исходный+
б) пароли для доступа к сетевым ресурсам
в) сертификаты для доступа к сетевым ресурсам и зашифрованным данным на самом компьютере
12. Что представляет собой криптографическая система?
а) семейство Т преобразований открытого текста, члены его семейства индексируются символом k+
б) программу
в) систему
13. Что такое пространство ключей k?
а) набор возможных значений ключа+
б) длина ключа
в) нет правильного ответа
14. На какие виды подразделяют криптосистемы?
а) симметричные+
б) ассиметричные+
в) с открытым ключом+
15. Количество используемых ключей в симметричных криптосистемах для шифрования и дешифрования:
а) 1+
б) 2
в) 3
16. Количество используемых ключей в системах с открытым ключом:
а) 2+
б) 3
в) 1
17. Ключи, используемые в системах с открытым ключом:
а) открытый+
б) закрытый+
в) нет правильного ответа
18. Выберите то, как связаны ключи друг с другом в системе с открытым ключом:
а) математически+
б) логически
в) алгоритмически
19. Что принято называть электронной подписью?
а) присоединяемое к тексту его криптографическое преобразование+
б) текст
в) зашифрованный текст
20. Что такое криптостойкость?
а) характеристика шрифта, определяющая его стойкость к дешифрованию без знания ключа+
б) свойство гаммы
в) все ответы верны
21. Выберите то, что относится к показателям криптостойкости:
а) количество всех возможных ключей+
б) среднее время, необходимое для криптоанализа+
в) количество символов в ключе
22. Требования, предъявляемые к современным криптографическим системам защиты информации:
а) знание алгоритма шифрования не должно влиять на надежность защиты+
б) структурные элементы алгоритма шифрования должны быть неизменными+
в) не должно быть простых и легко устанавливаемых зависимостью между ключами +последовательно используемыми в процессе шифрования+
23. Для современных криптографических систем защиты информации сформулированы следующие общепринятые требования:
а) длина шифрованного текста должна быть равной лине исходного текста+
б) зашифрованное сообщение должно поддаваться чтению только при наличии ключа+
в) нет правильного ответа
24. Основными современными методами шифрования являются:
а) алгоритм гаммирования+
б) алгоритмы сложных математических преобразований+
в) алгоритм перестановки+
25. Чем являются символы исходного текста, складывающиеся с символами некой случайной последовательности?
а) алгоритмом гаммирования+
б) алгоритмом перестановки
в) алгоритмом аналитических преобразований
26. Чем являются символы оригинального текста, меняющиеся местами по определенному принципу, которые являются секретным ключом?
а) алгоритм перестановки+
б) алгоритм подстановки
в) алгоритм гаммирования
27. Самая простая разновидность подстановки:
а) простая замена+
б) перестановка
в) простая перестановка
28. Количество последовательностей, из которых состоит расшифровка текста по таблице Вижинера:
а) 3+
б) 4
в) 5
29. Таблицы Вижинера, применяемые для повышения стойкости шифрования:
а) во всех (кроме первой) строках таблицы буквы располагаются в произвольном порядке+
б) в качестве ключа используется случайность последовательных чисел+
в) нет правильного ответа
30. Суть метода перестановки:
а) символы шифруемого текста переставляются по определенным правилам внутри шифруемого блока символов+
б) замена алфавита
в) все правильные
31. Цель криптоанализа:
а) Определение стойкости алгоритма+
б) Увеличение количества функций замещения в криптографическом алгоритме
в) Уменьшение количества функций подстановок в криптографическом алгоритме
г) Определение использованных перестановок
32. По какой причине произойдет рост частоты применения брутфорс-атак?
а) Возросло используемое в алгоритмах количество перестановок и замещений
б) Алгоритмы по мере повышения стойкости становились менее сложными и более подверженными атакам
в) Мощность и скорость работы процессоров возросла+
г) Длина ключа со временем уменьшилась
33. Не будет являться свойством или характеристикой односторонней функции хэширования:
а) Она преобразует сообщение произвольной длины в значение фиксированной длины
б) Имея значение дайджеста сообщения, невозможно получить само сообщение
в) Получение одинакового дайджеста из двух различных сообщений невозможно, либо случается крайне редко
г) Она преобразует сообщение фиксированной длины в значение переменной длины+
34. Выберите то, что указывает на изменение сообщения:
а) Изменился открытый ключ
б) Изменился закрытый ключ
в) Изменился дайджест сообщения+
г) Сообщение было правильно зашифровано
35. Алгоритм американского правительства, который предназначен для создания безопасных дайджестов сообщений:
а) Data Encryption Algorithm
б) Digital Signature Standard
в) Secure Hash Algorithm+
г) Data Signature Algorithm
36. Выберите то, что лучшеописывает отличия между HMAC и CBC-MAC?
а) HMAC создает дайджест сообщения и применяется для контроля целостности; CBC-MAC используется для шифрования блоков данных с целью обеспечения конфиденциальности
б) HMAC использует симметричный ключ и алгоритм хэширования; CBC-MAC использует первый блок в качестве контрольной суммы
в) HMAC обеспечивает контроль целостности и аутентификацию источника данных; CBC-MAC использует блочный шифр в процессе создания MAC+
г) HMAC зашифровывает сообщение на симметричном ключе, а затем передает результат в алгоритм хэширования; CBC-MAC зашифровывает все сообщение целиком
37. Определите преимущество RSA над DSA?
а) Он может обеспечить функциональность цифровой подписи и шифрования+
б) Он использует меньше ресурсов и выполняет шифрование быстрее, поскольку использует симметричные ключи
в) Это блочный шифр и он лучше поточного
г) Он использует одноразовые шифровальные блокноты
38. С какой целью многими странами происходит ограничение использования и экспорта криптографических систем?
а) Без ограничений может возникнуть большое число проблем совместимости при попытке использовать различные алгоритмы в различных программах
б) Эти системы могут использоваться некоторыми странами против их местного населения
в) Криминальные элементы могут использовать шифрование, чтобы избежать обнаружения и преследования+
г) Законодательство сильно отстает, а создание новых типов шифрования еще больше усиливает эту проблему
39. Выберите то, что используют для создания цифровой подписи:
а) Закрытый ключ получателя
б) Открытый ключ отправителя
в) Закрытый ключ отправителя+
г) Открытый ключ получателя
40. Выберите то, что лучше всего описывает цифровую подпись:
а) Это метод переноса собственноручной подписи на электронный документ
б) Это метод шифрования конфиденциальной информации
в) Это метод, обеспечивающий электронную подпись и шифрование
г) Это метод, позволяющий получателю сообщения проверить его источник и убедиться в целостности сообщения+
41.Эффективная длина ключа в DES:
а) 56+
б) 64
в) 32
г) 16
42. Причина, по которой удостоверяющий центр отзывает сертификат:
а) Если открытый ключ пользователя скомпрометирован
б) Если пользователь переходит на использование модели PEM, которая использует сеть доверия
в) Если закрытый ключ пользователя скомпрометирован+
г) Если пользователь переходит работать в другой офис
43. Выберите то, что лучше всего описывает удостоверяющий центр?
а) Организация, которая выпускает закрытые ключи и соответствующие алгоритмы
б) Организация, которая проверяет процессы шифрования
в) Организация, которая проверяет ключи шифрования
г) Организация, которая выпускает сертификаты+
44. Расшифруйте аббревиатуру DEA:
а) Data Encoding Algorithm
б) Data Encoding Application
в) Data Encryption Algorithm+
г) Digital Encryption Algorithm
45. Разработчик первого алгоритма с открытыми ключами:
а) Ади Шамир
б) Росс Андерсон
в) Брюс Шнайер
г) Мартин Хеллман+
46. Процесс, выполняемый после создания сеансового ключа DES:
а) Подписание ключа
б) Передача ключа на хранение третьей стороне (key escrow)
в) Кластеризация ключа
г) Обмен ключом+
47. Количество циклов перестановки и замещения, выполняемый DES:
а) 16+
б) 32
в) 64
г) 56
48. Выберите правильное утверждение в отношении шифрования данных, выполняемого с целью их защиты:
а) Оно обеспечивает проверку целостности и правильности данных
б) Оно требует внимательного отношения к процессу управления ключами+
в) Оно не требует большого количества системных ресурсов
г) Оно требует передачи ключа на хранение третьей стороне (escrowed)
49. Название ситуации, в которой при использовании различных ключей для шифрования одного и того же сообщения в результате получается один и тот же шифротекст:
а) Коллизия
б) Хэширование
в) MAC
г) Кластеризация ключей+
50. Определение фактора трудозатрат для алгоритма:
а) Время зашифрования и расшифрования открытого текста
б) Время, которое займет взлом шифрования+
в)Время, которое занимает выполнение 16 циклов преобразований
г) Время, которое занимает выполнение функций подстановки
51. Основная цельиспользования одностороннего хэширования пароля пользователя:
а) Это снижает требуемый объем дискового пространства для хранения пароля пользователя
б) Это предотвращает ознакомление кого-либо с открытым текстом пароля+
в) Это позволяет избежать избыточной обработки, требуемой асимметричным алгоритмом
г) Это предотвращает атаки повтора (replay attack)
52. Алгоритм, основанный на сложности разложения больших чисел на два исходных простых сомножителя:
а) ECC
б) RSA+
в)DES
г) Диффи-Хеллман
53. Что является описанием разницы алгоритмов DES и RSA:
а) DES – это симметричный алгоритм, а RSA – асимметричный +
б) DES – это асимметричный алгоритм, а RSA – симметричный
в) Они оба являются алгоритмами хэширования, но RSA генерирует 160-битные значения хэша
г) DES генерирует открытый и закрытый ключи, а RSA выполняет шифрование сообщений
54. Алгоритм, использующий симметричный ключ и алгоритм хэширования:
а) HMAC+
б) 3DES
в) ISAKMP-OAKLEY
г) RSA
55. Количество способов гаммирования:
а) 2+
б) 5
в) 3
56. Показатель стойкости шифрования методом гаммирования:
а) свойство гаммы+
б) длина ключа
в) нет правильного ответа
57. То, что применяют в качестве гаммы:
а) любая последовательность случайных символов+
б) число
в) все ответы верны
58. Метод, который применяют при шифровании с помощью аналитических преобразований:
а) алгебры матриц+
б) матрица
в) факториал
59. То, что применяют в качестве ключа при шифровании с помощью аналитических преобразований:
а) матрица А+
б) вектор
в) обратная матрица
60. Способ осуществления дешифрования текста при аналитических преобразованиях:
а) умножение матрицы на вектор+
б) деление матрицы на вектор
в) перемножение матриц
1) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически соответствовало содержанию текста.
Graffiti
Graffiti is any type of public markings that may appear in the forms of simple written words to elaborate wall paintings. Graffiti ___ (EXIST) since ancient times.
2) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически соответствовало содержанию текста.
The ___ (EARLY) forms of graffiti date back to 30,000 BC in the form of prehistoric cave paintings and pictographs using tools such as animal bones and pigments.
3) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически соответствовало содержанию текста.
The images drawn on the walls showed scenes of animal wildlife and hunt ing expeditions. These illustrations ___ (PLACE) in ceremonial and sacred locations inside of the caves.
4) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически соответствовало содержанию текста.
Modern Graffiti ___ (COME) in many different forms, from the scrawled mes sage in a public bathroom stall to the spray painted murals boasted on subway walls.
5) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически соответствовало содержанию текста.
Nowadays, paint, particularly spray paint, and marker pens have become the ___ (COMMONLY) used graffiti materials.
6) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически соответствовало содержанию текста.
In most countries, marking or painting property without the property ___ (OWNER) consent is considered to be vandalism, which is a punishable crime.
7) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически соответствовало содержанию текста.
Because of the controversial material contained in many murals, graffiti is now considered to be a form of resistance art, in rebellion against common public ___ (BELIEF) and government laws.

Way to Success
Are you a talented actor or a popular singer? Have you got extraordinary leadership qualities or an ___ (ATTRACT) appearance? No? Don’t get upset because that doesn’t make any difference today.
9) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически и лексически соответствовало содержанию текста.
There is a great ___ (VARY) of other ways how to magically change your life.
10) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически и лексически соответствовало содержанию текста.
Firstly, you may get acquainted with a popular ___ (PRODUCE) and make him invite you to star in his new film.
11) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически и лексически соответствовало содержанию текста.
If you have ___ (DIFFICULT) in finding one, then try taking part in a reality show. Reality television has the potential to turn its participants into national celebrities.
12) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически и лексически соответствовало содержанию текста.
If you succeed in the show, you can ___ (EASY) become a superstar and your life will be full of excitement.
13) Вставьте слово, чтобы оно грамматически и лексически соответствовало содержанию текста.
In any case, you should take action now because ___ (LAZY) won’t make you successful.
14) Запишите в поле ответа цифру 1, 2, 3 или 4, соответствующую выбранному Вами варианту ответа.
The Phoenix Legend
This magical, mythical bird has long been a part of legends, dating ___ to an- cient civilizations.
1) from
2) back
3) away
4) through
15) Запишите в поле ответа цифру 1, 2, 3 или 4, соответствующую выбранному Вами варианту ответа.
In today’s culture, the phoenix’s legend is still going ___, with a major city in the United States named after the resurrecting beast and popular books and movies, including the phenomenally successful ‘Harry Potter’ series encompassing the bird into characters and plots.
1) healthy
2) strong
3) alive
4) fine
16) Запишите в поле ответа цифру 1, 2, 3 или 4, соответствующую выбранному Вами варианту ответа.
Since the story has come ___ to us through the oral tradition, there is no single version of it.
1) back
2) round
3) forward
4) down
17) Запишите в поле ответа цифру 1, 2, 3 или 4, соответствующую выбранному Вами варианту ответа.
It varies from teller to teller — each adding something of their own and changing tiny aspects of it. ___, the main facts of the legend of the Phoenix remain intact, even though the myth has been adulterated.
1) As a result
2) Therefore
3) Nonetheless
4) Regardless
18) Запишите в поле ответа цифру 1, 2, 3 или 4, соответствующую выбранному Вами варианту ответа.
According to the legend, the Phoenix is a supernatural creature that has an incredibly long ___, stretching to at least a thousand years. It cannot fall sick or get injured at any point in its lifetime. However, some believe that it does get affected by disease or drought, which leads it to prematurely enter the next phase of its life.
1) lifespan
2) lifespin
3) lifescan
4) lifespam
19) Запишите в поле ответа цифру 1, 2, 3 или 4, соответствующую выбранному Вами варианту ответа.
Once that time is over, the bird builds its own funeral pyre. The traditional story goes that the phoenix ignites himself, burns to ash, and then rises again from the ashes to live another thousand years. This triumph over adversity has caused the bird to become the ___ or symbol of many groups and organizations. Once the bird is born from ashes, the cycle begins anew.
1) pendant
2) anthem
3) mascot
4) amulet
20) Запишите в поле ответа цифру 1, 2, 3 или 4, соответствующую выбранному Вами варианту ответа.
Another version of the story is that before the fire consumes the bird, it lays an egg, which hatches a new phoenix. This phoenix will live to be a thousand years old before having an ___ in the same method. There is no way of ascertaining which version of the story is true, but all of them express the same theme: the triumph over adversity.
1) ancestor
2) offspring
3) predecessor
4) offcut
Урок посвящен тому, как решать 4 задание ЕГЭ по информатике
Содержание:
- Кодирование информации
- Кодирование и расшифровка сообщений
- Решение 4 заданий ЕГЭ
Кодирование информации
4-е задание: «Кодирование и декодирование информации»
Уровень сложности
— базовый,
Требуется использование специализированного программного обеспечения
— нет,
Максимальный балл
— 1,
Примерное время выполнения
— 2 минуты.
Проверяемые элементы содержания: Умение кодировать и декодировать информацию
До ЕГЭ 2021 года — это было задание № 5 ЕГЭ
Типичные ошибки и рекомендации по их предотвращению:
«Из-за невнимательного чтения условия задания экзаменуемые иногда не замечают, что требуется найти кодовое слово минимальной длины с максимальным (минимальным) числовым значением.
Кроме того, если в задании указано, что несколько букв остались без кодовых слов (как, например, в задании демоварианта), то кодовое слово для указанной буквы должно быть подобрано таким образом, чтобы осталась возможность найти кодовые слова, удовлетворяющие условию Фано, и для других букв. Так, например, если мы букву А закодируем нулём, а букву Б единицей, то букву В мы уже никак не сможем закодировать с соблюдением условия Фано, поэтому длину кодового слова для А или Б следует увеличить»
ФГБНУ «Федеральный институт педагогических измерений»
- Кодирование — это представление информации в форме, удобной для её хранения, передачи и обработки. Правило преобразования информации к такому представлению называется кодом.
- Кодирование бывает равномерным и неравномерным:
- при равномерном кодировании всем символам соответствуют коды одинаковой длины;
- при неравномерном кодировании разным символам соответствуют коды разной длины, это затрудняет декодирование.
Пример: Зашифруем буквы А, Б, В, Г при помощи двоичного кодирования равномерным кодом и посчитаем количество возможных сообщений:
Таким образом, мы получили равномерный код, т.к. длина каждого кодового слова одинакова для всех кодов (2).
Кодирование и расшифровка сообщений
Декодирование (расшифровка) — это восстановление сообщения из последовательности кодов.
Для решения задач с декодированием, необходимо знать условие Фано:
Условие Фано: ни одно кодовое слово не должно являться началом другого кодового слова (что обеспечивает однозначное декодирование сообщений с начала)
Префиксный код — это код, в котором ни одно кодовое слово не совпадает с началом другого кодового слова. Сообщения при использовании такого кода декодируются однозначно.
- если сообщение декодируется с конца, то его можно однозначно декодировать, если выполняется обратное условие Фано:
- условие Фано – это достаточное, но не необходимое условие однозначного декодирования.
Обратное условие Фано: никакое кодовое слово не является окончанием другого кодового слова
Постфиксный код — это код, в котором ни одно кодовое слово не совпадает с концом другого кодового слова. Сообщения при использовании такого кода декодируются однозначно и только с конца.
Однозначное декодирование обеспечивается:
Однозначное декодирование
Декодирование
Егифка ©:
Задание демонстрационного варианта 2022 года ФИПИ
Плейлист видеоразборов задания на YouTube:
ЕГЭ 4.1: Для кодирования букв О, В, Д, П, А решили использовать двоичное представление чисел 0, 1, 2, 3 и 4 соответственно (с сохранением одного незначащего нуля в случае одноразрядного представления).
Закодируйте последовательность букв ВОДОПАД таким способом и результат запишите восьмеричным кодом.
✍ Решение:
- Переведем числа в двоичные коды и поставим их в соответствие нашим буквам:
О -> 0 -> 00 В -> 1 -> 01 Д -> 2 -> 10 П -> 3 -> 11 А -> 4 -> 100
ВОДОПАД:010010001110010
010 010 001 110 010 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 2 2 1 6 2
Результат: 22162
Теоретическое решение ЕГЭ данного задания по информатике, видео:
📹 YouTube здесь
📹 Видеорешение на RuTube здесь
Рассмотрим еще разбор 4 задания ЕГЭ:
ЕГЭ 4.2: Для 5 букв латинского алфавита заданы их двоичные коды (для некоторых букв — из двух бит, для некоторых — из трех). Эти коды представлены в таблице:
| a | b | c | d | e |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 000 | 110 | 01 | 001 | 10 |
Какой набор букв закодирован двоичной строкой 1100000100110?
✍ Решение:
- Во-первых, проверяем условие Фано: никакое кодовое слово не является началом другого кодового слова. Условие верно.
- Код разбиваем слева направо согласно данным, представленным в таблице. Затем переведём его в буквы:
✎ 1 вариант решения:
110 000 01 001 10 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ b a c d e
Результат: b a c d e.
✎ 2 вариант решения:
-
Этот вариант решения 4 задания ЕГЭ более сложен, но тоже верен.
- Сделаем дерево, согласно кодам в таблице:
- Сопоставим закодированное сообщение с кодами в дереве:
110 000 01 001 10
Результат: b a c d e.
Кроме того, вы можете посмотреть видеорешение этого задания ЕГЭ по информатике (теоретическое решение):
📹 YouTube здесь
📹 Видеорешение на RuTube здесь
Решим следующее 4 задание:
ЕГЭ 4.3:
Для передачи чисел по каналу с помехами используется код проверки четности. Каждая его цифра записывается в двоичном представлении, с добавлением ведущих нулей до длины 4, и к получившейся последовательности дописывается сумма её элементов по модулю 2 (например, если передаём 23, то получим последовательность 0010100110).
Определите, какое число передавалось по каналу в виде 01100010100100100110.
✍ Решение:
- Рассмотрим пример из условия задачи:
Было2310 Стало00101001102
0010100110 (0010 - 2, 0011 - 3)
01100 01010 01001 00110
0110 0101 0100 0011
0110 0101 0100 0011 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 6 5 4 3
Ответ: 6 5 4 3
Вы можете посмотреть видеорешение этого задания ЕГЭ по информатике, теоретическое решение:
📹 YouTube здесь
📹 Видеорешение на RuTube здесь
ЕГЭ 4.4:
Для кодирования некоторой последовательности, состоящей из букв К, Л, М, Н решили использовать неравномерный двоичный код, удовлетворяющий условию Фано. Для буквы Н использовали кодовое слово 0, для буквы К — кодовое слово 10.
Какова наименьшая возможная суммарная длина всех четырёх кодовых слов?
Подобные задания для тренировки
✍ Решение:
✎
1 вариант решения
основан на логических умозаключениях:
- Найдём самые короткие возможные кодовые слова для всех букв.
- Кодовые слова 01 и 00 использовать нельзя, так как тогда нарушается условие Фано (начинаются с 0, а 0 — это Н).
- Начнем с двухразрядных кодовых слов. Возьмем для буквы Л кодовое слово 11. Тогда для четвёртой буквы нельзя подобрать кодовое слово, не нарушая условие Фано (если потом взять 110 или 111, то они начинаются с 11).
- Значит, надо использовать трёхзначные кодовые слова. Закодируем буквы Л и М кодовыми словами 110 и 111. Условие Фано соблюдается.
- Суммарная длина всех четырёх кодовых слов равна:
(Н)1 + (К)2 + (Л)3 + (М)3 = 9
✎ 2 вариант решения:
- Будем использовать дерево. Влево откладываем 0, вправо — 1:
- Теперь выпишем соответствие каждой буквы ее кодового слова согласно дереву:
(Н) -> 0 -> 1 символ (К) -> 10 -> 2 символа (Л) -> 110 -> 3 символа (М) -> 111 -> 3 символа
(Н)1 + (К)2 + (Л)3 + (М)3 = 9
Ответ: 9
4.5:
По каналу связи передаются сообщения, содержащие только 4 буквы: А, Б, В, Г; для передачи используется двоичный код, допускающий однозначное декодирование. Для букв А, Б, В используются такие кодовые слова:
А: 101010, Б: 011011, В: 01000
Укажите кратчайшее кодовое слово для буквы Г, при котором код будет допускать однозначное декодирование. Если таких кодов несколько, укажите код с наименьшим числовым значением.
Подобные задания для тренировки
✍ Решение:
- Наименьшие коды могли бы выглядеть, как 0 и 1 (одноразрядные). Но это не удовлетворяло бы условию Фано (А начинается с единицы — 101010, Б начинается с нуля — 011011).
- Следующим наименьшим кодом было бы двухбуквенное слово 00. Так как оно не является префиксом ни одного из представленных кодовых слов, то Г = 00.
Результат: 00
4.6:
Для кодирования некоторой последовательности, состоящей из букв А, Б, В, Г и Д, решили использовать неравномерный двоичный код, позволяющий однозначно декодировать двоичную последовательность, появляющуюся на приемной стороне канала связи. Использовали код:
А - 01 Б - 00 В - 11 Г - 100
Укажите, каким кодовым словом должна быть закодирована буква Д. Длина этого кодового слова должна быть наименьшей из всех возможных. Код должен удовлетворять свойству однозначного декодирования. Если таких кодов несколько, укажите код с наименьшим числовым значением.
✍ Решение:
- Так как необходимо найти кодовое слово наименьшей длины, воспользуемся деревом. Влево будем откладывать нули, а вправо — единицы:
- Поскольку у нас все ветви завершены листьями, т.е. буквами, кроме одной ветви, то остается единственный вариант, куда можно поставить букву Д:
- Перепишем сверху вниз получившееся кодовое слово для Д: 101
Результат: 101
Подробней разбор урока можно посмотреть на видео ЕГЭ по информатике 2017:
📹 YouTube здесь
📹 Видеорешение на RuTube здесь
4.7: Демоверсия ЕГЭ 2018 информатика (ФИПИ):
По каналу связи передаются шифрованные сообщения, содержащие только десять букв: А, Б, Е, И, К, Л, Р, С, Т, У. Для передачи используется неравномерный двоичный код. Для девяти букв используются кодовые слова.
Укажите кратчайшее кодовое слово для буквы Б, при котором код будет удовлетворять условию Фано. Если таких кодов несколько, укажите код с наименьшим числовым значением.
Подобные задания для тренировки
✍ Решение:
- Для решения будем использовать дерево. Ветви, соответствующие нулю, будем откладывать влево, единице — вправо.
- При рассмотрении дерева видим, что все ветви «закрыты» листьями, кроме одной ветви — 1100:

Результат: 1100
Подробное теоретическое решение данного 4 (раньше №5) задания из демоверсии ЕГЭ 2018 года смотрите на видео:
📹 Видеорешение на RuTube здесь
4.8:
По каналу связи передаются шифрованные сообщения, содержащие только четыре букв: А, Б, В, Г; для передачи используется двоичный код, допускающий однозначное декодирование. Для букв А, Б, В используются кодовые слова:
А: 00011 Б: 111 В: 1010
Укажите кратчайшее кодовое слово для буквы Г, при котором код будет допускать однозначное декодирование. Если таких кодов несколько, укажите код с наименьшим числовым значением.
✍ Решение:
- Для решения будем использовать дерево. Ветви, соответствующие нулю, будем откладывать влево, единице — вправо.
- Поскольку в задании явно не указано о том, что код должен удовлетворять условию Фано, то дерево нужно построить как с начала (по условию Фано), так и с конца (обратное условие Фано).
- Получившееся числовое значение кодового слова для буквы Г — 01.
- Получившееся числовое значение кодового слова для буквы Г — 00.
- После сравнения двух кодовых слов (01 и 00), код с наименьшим числовым значением — это 00.
Дерево по условию Фано (однозначно декодируется с начала):
Дерево по обратному условию Фано (однозначно декодируется с конца):
Результат: 00
4.9:
По каналу связи передаются сообщения, содержащие только буквы: А, Е, Д, К, М, Р; для передачи используется двоичный код, удовлетворяющий условию Фано. Известно, что используются следующие коды:
Е – 000 Д – 10 К – 111
Укажите наименьшую возможную длину закодированного сообщения ДЕДМАКАР.
В ответе напишите число – количество бит.
Подобные задания для тренировки
✍ Решение:
- С помощью дерева отобразим известные коды для букв:
- В результирующем слове — ДЕДМАКАР — вде буквы А. Значит, для получения наименьшей длины необходимо для буквы А выбрать наименьший код в дереве. Учтем это и достроим дерево для остальных трех букв А, М и Р:
- Расположим буквы в порядке их следования в слове и подставим их кодовые слова:
Д Е Д М А К А Р 10 000 10 001 01 111 01 110
Результат: 20
Смотрите виде решения задания:
📹 YouTube здесь
📹 Видеорешение на RuTube здесь
The earliest form of cryptography was the simple writing of a message, as most people could not read (New World, 2007). In fact, the very word cryptography comes from the Greek words kryptos and graphein, which mean hidden and writing, respectively (Pawlan, 1998).
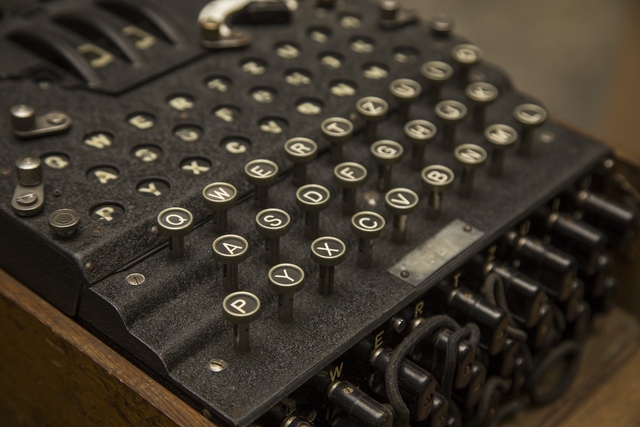
Above: The Enigma Machine, the German cipher machine utilzed during WWII.
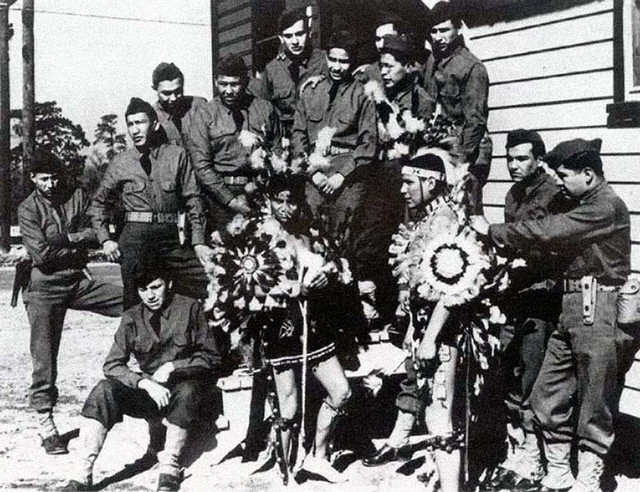
Below: Comanche code-talkers used words from their Native American language to help send secret messages for U.S. forces in the European theatre during WWII.
Early cryptography was solely concerned with converting messages into unreadable groups of figures to protect the message’s content during the time the message was being carried from one place to another. In the modern era, cryptography has grown from basic message confidentiality to include some phases of message integrity checking, sender/receiver identity authentication, and digital signatures, among other things (New World, 2007).
The need to conceal messages has been with us since we moved out of caves, started living in groups and decided to take this civilization idea seriously. As soon as there were different groups or tribes, the idea that we had to work against each other surfaced and was proliferated, along with rank violence, secrecy, and crowd manipulation. The earliest forms of cryptography were found in the cradle of civilization, which comes as no surprise, including the regions currently encompassed by Egypt, Greece and Rome.
As early as 1900 B.C., Egyptian scribes used hieroglyphs in a non-standard fashion, presumably to hide the meaning from those who did not know the meaning (Whitman, 2005). The Greek’s idea was to wrap a tape around a stick, and then write the message on the wound tape. When the tape was unwound, the writing would be meaningless. The receiver of the message would of course have a stick of the same diameter and use it to decipher the message. The Roman method of cryptography was known as the Caesar Shift Cipher. It utilized the idea of shifting letters by an agreed upon number (three was a common historical choice), and thus writing the message using the letter-shift. The receiving group would then shift the letters back by the same number and decipher the message (Taylor, 2002).
The Caesar Shift Cipher is an example of a Monoalphabetic Cipher. It is easy to see why this method of encryption is simple to break. All a person has to do is to go down the alphabet, juxtapositioning the start of the alphabet to each succeeding letter. At each iteration, the message is decrypted to see if it makes sense. When it does appear as a readable message, the code has been broken. Another way to break Monoalphabetic ciphers is by the use of what is known as frequency analysis, attributed to the Arabs circa 1000 C.E. (New World, 2007). This method utilizes the idea that certain letters, in English the letter «e,» for instance, are repeated more often than others. Armed with this knowledge, a person could go over a message and look for the repeated use, or frequency of use, of a particular letter and try to substitute known frequently used letters (Taylor, 2002).
As for the Greek method of using a stick, once the method was known, it was a simple matter of trying out sticks of different diameters until the message became readable.
The art and science of cryptography showed no major changes or advancements until the Middle Ages. By that time, all of the western European governments were utilizing cryptography in one form or another. Keeping in touch with ambassadors was the major use of cryptography. One Leon Battista Alberti was known as “The Father of Western Cryptology,” most notably due to his development of polyalphabetic substitution. His method was to use two copper disks that fit together. Each one of them had the alphabet inscribed on it. After every few words, the disks were rotated to change the encryption logic, thereby limiting the use of frequency analysis to crack the cipher (Cohen, 1990). Polyalphabetic substitution went through a variety of changes and is most notably attributed to Vigenere, although Rubin claims that he in fact had nothing to do with its creation. Rubin further points out that the use of the cipher disks continued in the Civil War, with the South using brass cipher disks, although the North regularly cracked the messages (2008).
Gilbert Vernam worked to improve the broken cipher, creating the Vernam-Vigenere cipher in 1918, but was unable to create one of significantly greater strength. His work did lead to the one time pad, which uses a key word only once, and it proved to be near unbreakable (Rubin, 2008). Whitman reports that criminals used cryptography during prohibition to communicate with each other.
Additionally, it is important to mention the recently popularized «windtalkers.» The Navajo’s used their own language as a basis for cryptography (2005). The code was never broken and was instrumental in the victory in the Pacific Theatre during WWII. An argument could be made that the spoken language was not technically cryptography, but it should be noted that at every communication, the message was written down as a matter of procedure.
In modern times, the public key method of cryptography has seen wide adoption. The use of a common public key and a private key held only by the sender is in use today as a form of asymmetric encryption; one of the uses of this method is for the sender to use the private key to encrypt the message and then anyone who receives the message uses the public key to decipher it. In this way, the receiver knows who the message had to come from.
This method makes up the backbone of the Digital Signature. Problems arise when communications between multiple organizations require the use of many public keys and knowing when to use which one. No matter which method is used, a combination of methods applied one after the other will give the best result (Whitman, 2005).
In conclusion, it is somewhat surprising how limited the history of this very important topic is. No doubt cryptography and in a greater sense, cryptology, has played an enormous role in the shaping and development of many societies and cultures. While history may paint a different picture, the fact that the winners often write history is worth noting. If an army has a strong weapon that was instrumental in providing information that led to success, how apt are they to reveal it in the records of the wars? Instead, it may seem better to have idolized heroes than to reveal the cloak and dagger methods that actually led to success. Crpytography, by its very nature, suggests secrecy and misdirection; therefore, the fact that the history of this topic is short and somewhat inaccessible is of no great surprise. Perhaps it is itself coded in what is has already been written.
Cohen, F (1990). A short history of cryptography. Retrieved May 4, 2009, from http://www.all.net/books/ip/Chap2-1.html New World Encyclopedia (2007).
Cryptography. Retrieved May 4, 2009, from http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Cryptography
Pawlan, M. (1998, February). Cryptography: the ancient art of secret messages. Retrieved May 4, 2009, from http://www.pawlan.com/Monica/crypto/
Rubin, J. (2008). Vigenere Cipher. Retrieved May 4, 2009, from http://www.juliantrubin.com/encyclopedia/mathematics/vigenere_cipher.html
Taylor, K. (2002, July 31). Number theory 1. Retrieved May 4, 2009, from http://math.usask.ca/encryption/lessons/lesson00/page1.html
Whitman, M. & Mattord, H. (2005). Principles of information security. [University of Phoenix Custom Edition e-text]. Canada, Thomson Learning, Inc. Retrieved May 4, 2009, from University of Phoenix, rEsource, CMGT/432