How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
Introduction to Networks ( Version 7.00) – Modules 8 – 10: Communicating Between Networks Exam
1. Which information is used by routers to forward a data packet toward its destination?
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- source data-link address
- destination data-link address
2. A computer has to send a packet to a destination host in the same LAN. How will the packet be sent?
- The packet will be sent to the default gateway first, and then, depending on the response from the gateway, it may be sent to the destination host.
- The packet will be sent directly to the destination host.
- The packet will first be sent to the default gateway, and then from the default gateway it will be sent directly to the destination host.
- The packet will be sent only to the default gateway.
3. A router receives a packet from the Gigabit 0/0 interface and determines that the packet needs to be forwarded out the Gigabit 0/1 interface. What will the router do next?
- route the packet out the Gigabit 0/1 interface
- create a new Layer 2 Ethernet frame to be sent to the destination
- look into the ARP cache to determine the destination IP address
- look into the routing table to determine if the destination network is in the routing table
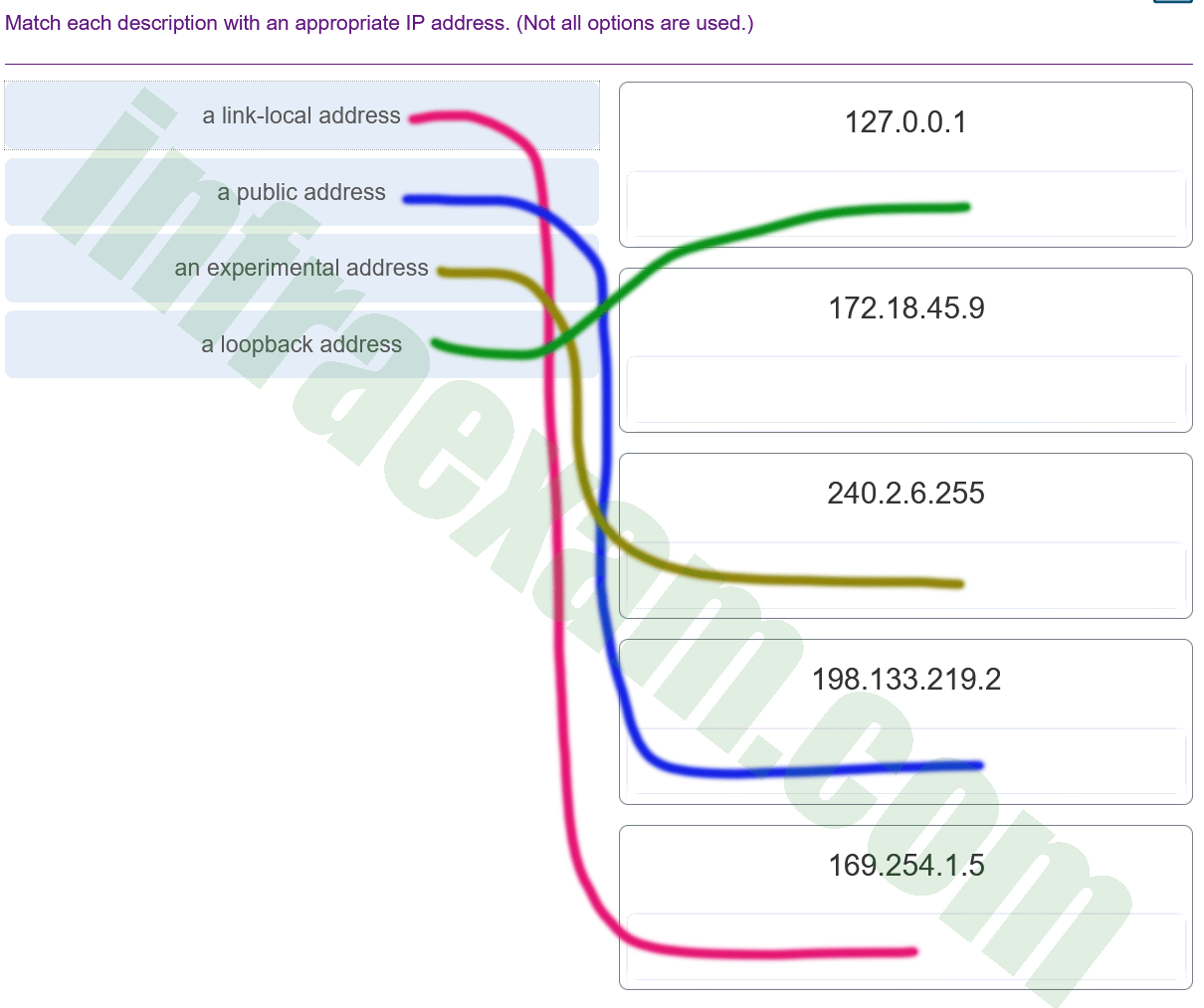
4. Which IPv4 address can a host use to ping the loopback interface?
- 126.0.0.1
- 127.0.0.0
- 126.0.0.0
- 127.0.0.1
5. A computer can access devices on the same network but cannot access devices on other networks. What is the probable cause of this problem?
- The cable is not connected properly to the NIC.
- The computer has an invalid IP address.
- The computer has an incorrect subnet mask.
- The computer has an invalid default gateway address.
6. Which statement describes a feature of the IP protocol?
- IP encapsulation is modified based on network media.
- IP relies on Layer 2 protocols for transmission error control.
- MAC addresses are used during the IP packet encapsulation.
- IP relies on upper layer services to handle situations of missing or out-of-order packets.
Explanation: IP protocol is a connection-less protocol, considered unreliable in terms of end-to-end delivery. It does not provide error control in the cases where receiving packets are out-of-order or in cases of missing packets. It relies on upper layer services, such as TCP, to resolve these issues.
7. Why is NAT not needed in IPv6?
- Because IPv6 has integrated security, there is no need to hide the IPv6 addresses of internal networks.
- Any host or user can get a public IPv6 network address because the number of available IPv6 addresses is extremely large.
- The problems that are induced by NAT applications are solved because the IPv6 header improves packet handling by intermediate routers.
- The end-to-end connectivity problems that are caused by NAT are solved because the number of routes increases with the number of nodes that are connected to the Internet.
Explanation: The large number of public IPv6 addresses eliminates the need for NAT. Sites from the largest enterprises to single households can get public IPv6 network addresses. This avoids some of the NAT-induced application problems that are experienced by applications that require end-to-end connectivity.
8. Which parameter does the router use to choose the path to the destination when there are multiple routes available?
- the lower metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the lower gateway IP address to get to the destination network
- the higher metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the higher gateway IP address to get to the destination network
9. What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
Explanation: The OSI network layer provides several services to allow communication between devices:
- addressing
- encapsulation
- routing
- de-encapsulation
Error detection, placing frames on the media, and collision detection are all functions of the data ink layer.
10. Within a production network, what is the purpose of configuring a switch with a default gateway address?
- Hosts that are connected to the switch can use the switch default gateway address to forward packets to a remote destination.
- A switch must have a default gateway to be accessible by Telnet and SSH.
- The default gateway address is used to forward packets originating from the switch to remote networks.
- It provides a next-hop address for all traffic that flows through the switch.
Explanation: A default gateway address allows a switch to forward packets that originate on the switch to remote networks. A default gateway address on a switch does not provide Layer 3 routing for PCs that are connected on that switch. A switch can still be accessible from Telnet as long as the source of the Telnet connection is on the local network.
11. What is a basic characteristic of the IP protocol?
- connectionless
- media dependent
- user data segmentation
- reliable end-to-end delivery
Explanation: Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer protocol that does not require initial exchange of control information to establish an end-to-end connection before packets are forwarded. Thus, IP is connectionless and does not provide reliable end-to-end delivery by itself. IP is media independent. User data segmentation is a service provided at the transport layer.
12. Which field in the IPv4 header is used to prevent a packet from traversing a network endlessly?
- Time-to-Live
- Sequence Number
- Acknowledgment Number
- Differentiated Services
Explanation: The value of the Time-to-Live (TTL) field in the IPv4 header is used to limit the lifetime of a packet. The sending host sets the initial TTL value; which is decreased by one each time the packet is processed by a router. If the TTL field decrements to zero, the router discards the packet and sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Time Exceeded message to the source IP address. The Differentiated Services (DS) field is used to determine the priority of each packet. Sequence Number and Acknowledgment Number are two fields in the TCP header.
13. What is one advantage that the IPv6 simplified header offers over IPv4?
- smaller-sized header
- little requirement for processing checksums
- smaller-sized source and destination IP addresses
- efficient packet handling
Explanation: The IPv6 simplified header offers several advantages over IPv4:
- Better routing efficiency and efficient packet handling for performance and forwarding-rate scalability
- No requirement for processing checksums
- Simplified and more efficient extension header mechanisms (as opposed to the IPv4 Options field)
- A Flow Label field for per-flow processing with no need to open the transport inner packet to identify the various traffic flows
14. What IPv4 header field identifies the upper layer protocol carried in the packet?
- Protocol
- Identification
- Version
- Differentiated Services
Explanation: It is the Protocol field in the IP header that identifies the upper-layer protocol the packet is carrying. The Version field identifies the IP version. The Differential Services field is used for setting packet priority. The Identification field is used to reorder fragmented packets.
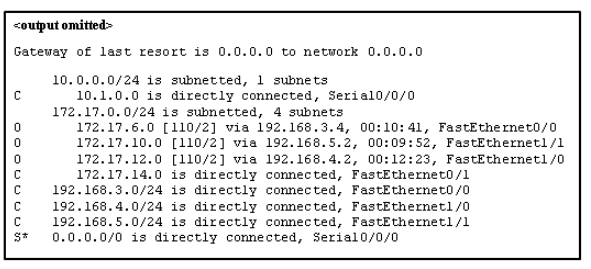
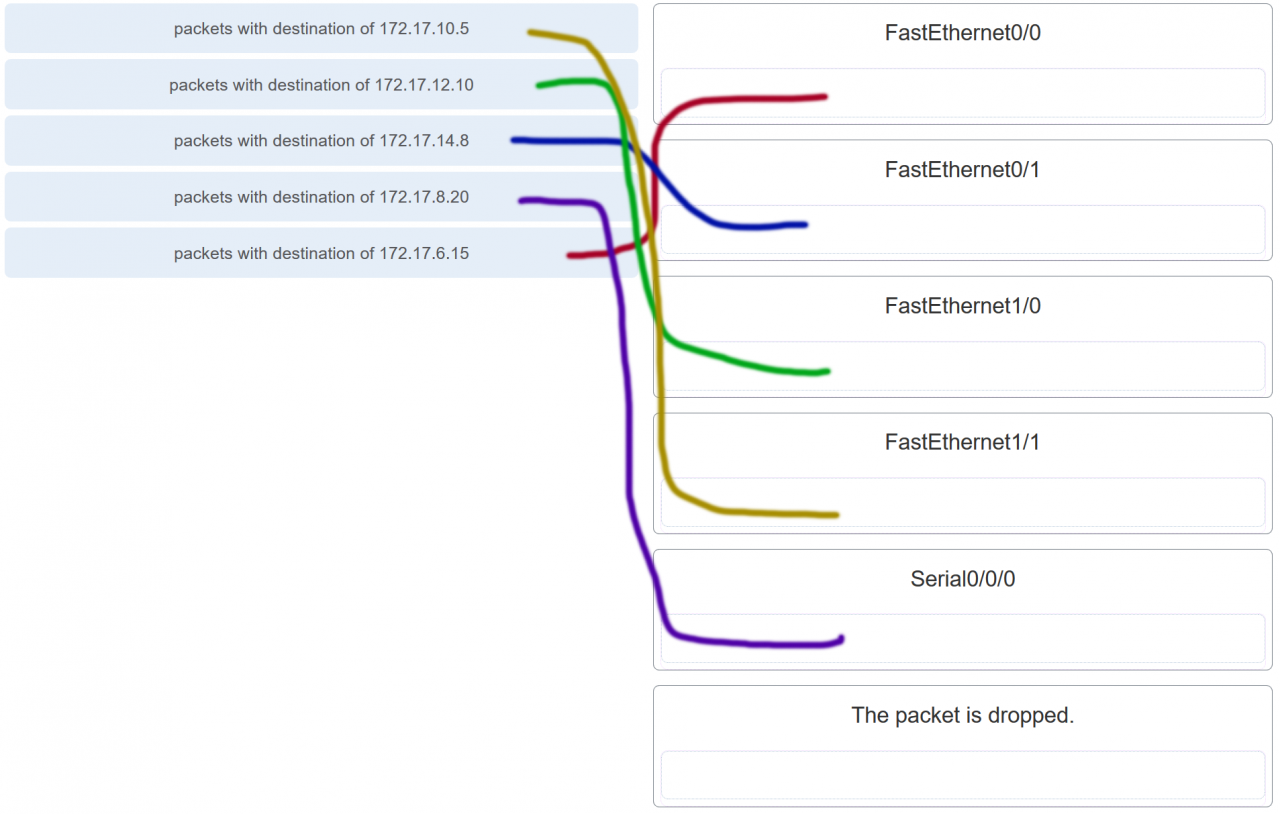
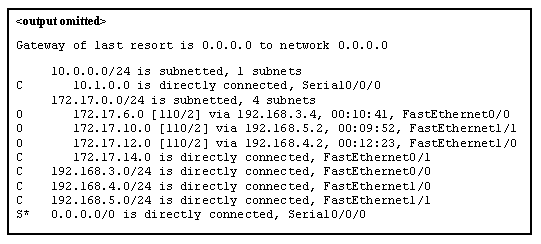
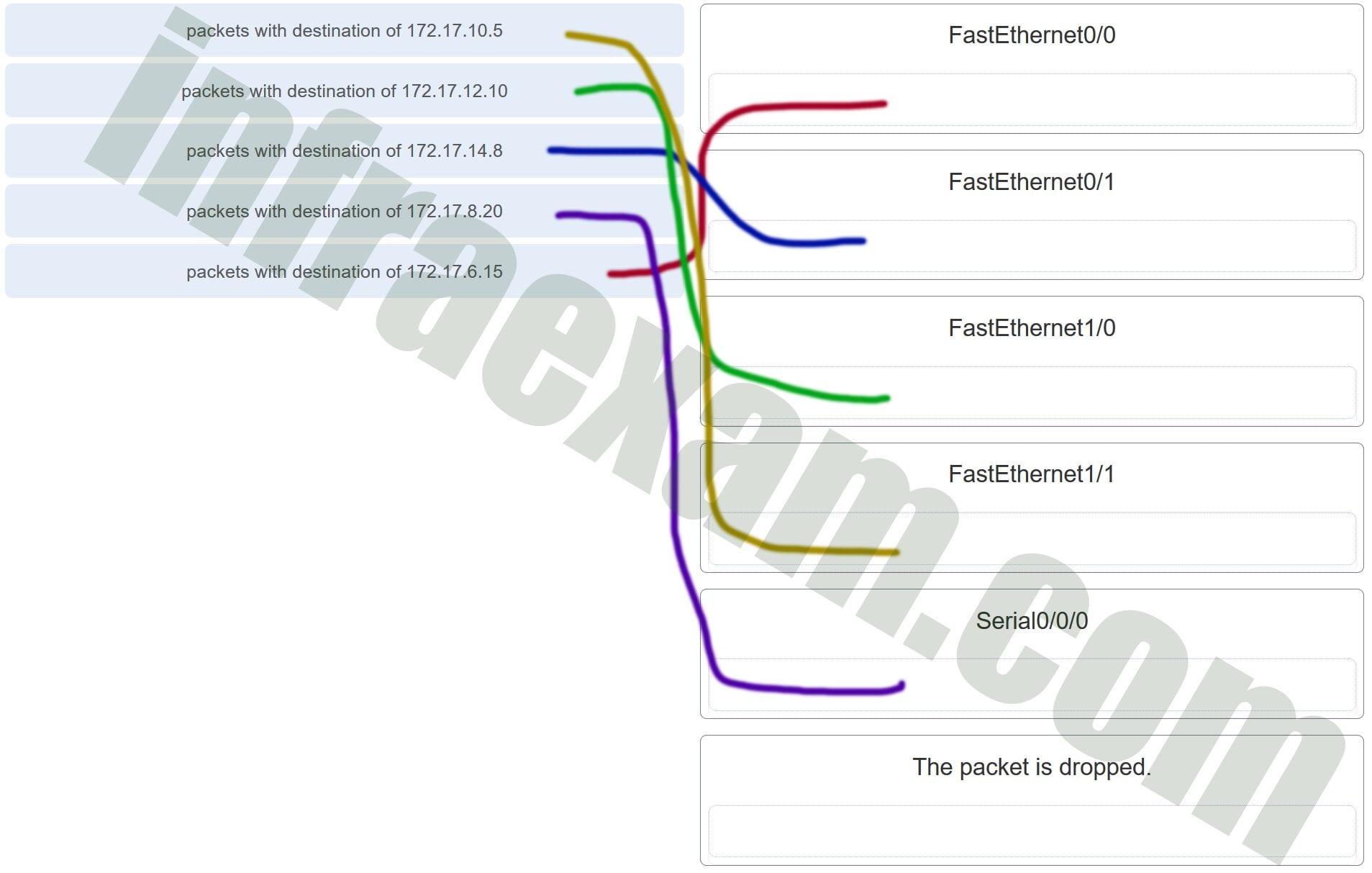
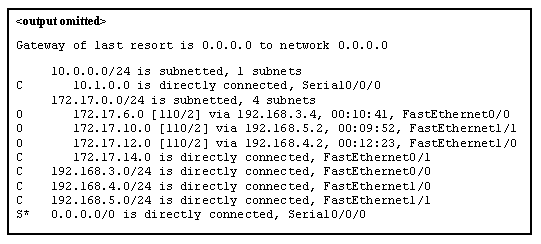
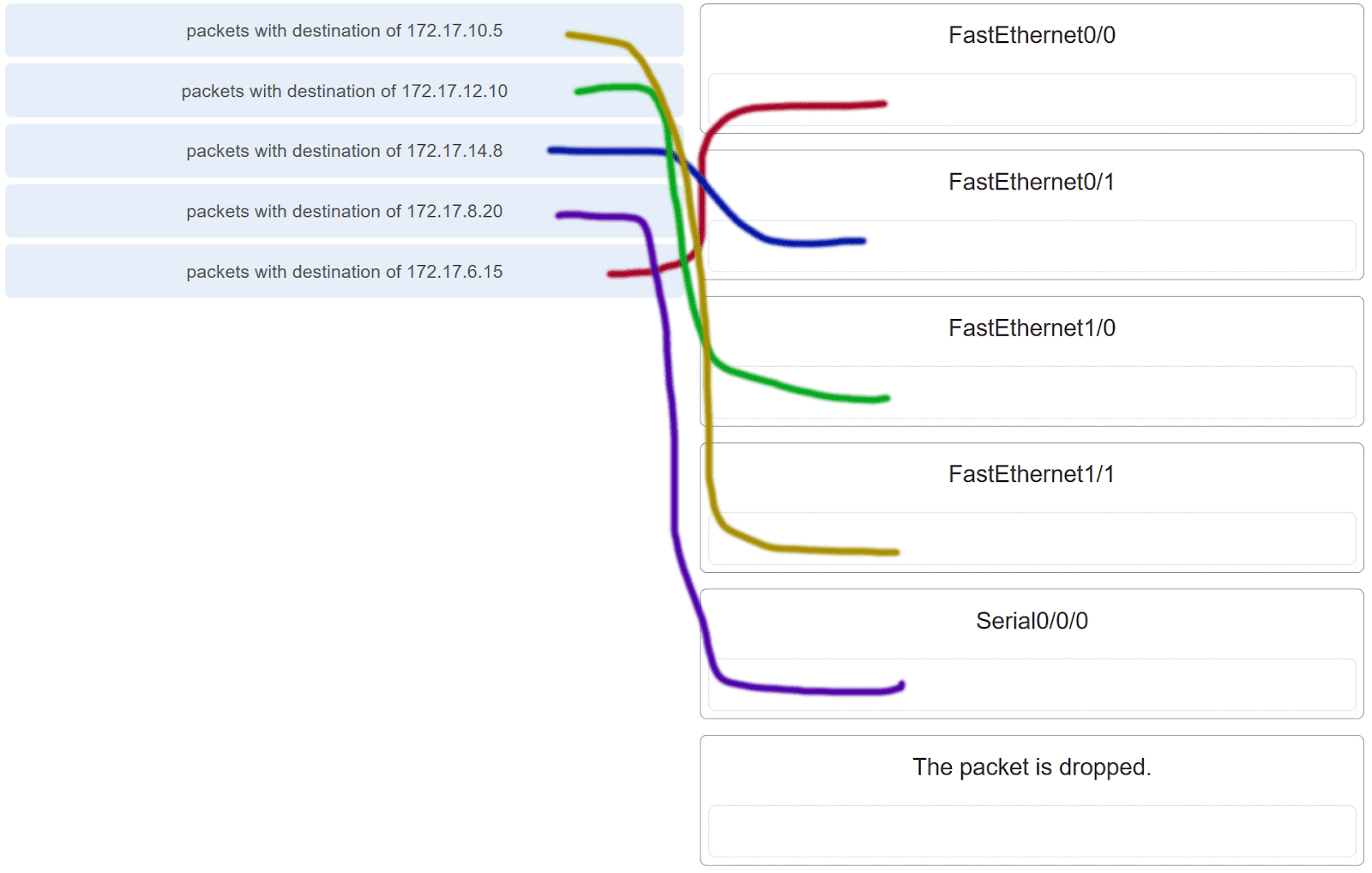
15. Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
Explanation: Packets with a destination of 172.17.6.15 are forwarded through Fa0/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.10.5 are forwarded through Fa1/1. Packets with a destination of 172.17.12.10 are forwarded through Fa1/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.14.8 are forwarded through Fa0/1. Because network 172.17.8.0 has no entry in the routing table, it will take the gateway of last resort, which means that packets with a destination of 172.17.8.20 are forwarded through Serial0/0/0. Because a gateway of last resort exists, no packets will be dropped.
16. What information does the loopback test provide?
- The TCP/IP stack on the device is working correctly.
- The device has end-to-end connectivity.
- DHCP is working correctly.
- The Ethernet cable is working correctly.
- The device has the correct IP address on the network.
Explanation: Because the loopback test sends packets back to the host device, it does not provide information about network connectivity to other hosts. The loopback test verifies that the host NIC, drivers, and TCP/IP stack are functioning.
17. What routing table entry has a next hop address associated with a destination network?
- directly-connected routes
- local routes
- remote routes
- C and L source routes
Explanation: Routing table entries for remote routes will have a next hop IP address. The next hop IP address is the address of the router interface of the next device to be used to reach the destination network. Directly-connected and local routes have no next hop, because they do not require going through another router to be reached.
18. How do hosts ensure that their packets are directed to the correct network destination?
- They have to keep their own local routing table that contains a route to the loopback interface, a local network route, and a remote default route.
- They always direct their packets to the default gateway, which will be responsible for the packet delivery.
- They search in their own local routing table for a route to the network destination address and pass this information to the default gateway.
- They send a query packet to the default gateway asking for the best route.
Explanation: Hosts must maintain their own local routing table to ensure that network layer packets are directed to the correct destination network. This local table typically contains a route to the loopback interface, a route to the network that the host is connected to, and a local default route, which represents the route that packets must take to reach all remote network addresses.
19. When transporting data from real-time applications, such as streaming audio and video, which field in the IPv6 header can be used to inform the routers and switches to maintain the same path for the packets in the same conversation?
- Next Header
- Flow Label
- Traffic Class
- Differentiated Services
Explanation: The Flow Label in IPv6 header is a 20-bit field that provides a special service for real-time applications. This field can be used to inform routers and switches to maintain the same path for the packet flow so that packets will not be reordered.
20. What statement describes the function of the Address Resolution Protocol?
- ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on a different network.
- ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on the local network.
- ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on a different network.
- ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on the local network.
Explanation: When a PC wants to send data on the network, it always knows the IP address of the destination. However, it also needs to discover the MAC address of the destination. ARP is the protocol that is used to discover the MAC address of a host that belongs to the same network.
21. Under which two circumstances will a switch flood a frame out of every port except the port that the frame was received on? (Choose two.)
- The frame has the broadcast address as the destination address.
- The destination address is unknown to the switch.
- The source address in the frame header is the broadcast address.
- The source address in the frame is a multicast address.
- The destination address in the frame is a known unicast address.
Explanation: A switch will flood a frame out of every port, except the one that the frame was received from, under two circumstances. Either the frame has the broadcast address as the destination address, or the destination address is unknown to the switch.
22. Which statement describes the treatment of ARP requests on the local link?
- They must be forwarded by all routers on the local network.
- They are received and processed by every device on the local network.
- They are dropped by all switches on the local network.
- They are received and processed only by the target device.
Explanation: One of the negative issues with ARP requests is that they are sent as a broadcast. This means all devices on the local link must receive and process the request.
23. Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame?
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF
- AAAA.AAAA.AAAA
- the physical address of the destination host
Explanation: The purpose of an ARP request is to find the MAC address of the destination host on an Ethernet LAN. The ARP process sends a Layer 2 broadcast to all devices on the Ethernet LAN. The frame contains the IP address of the destination and the broadcast MAC address, FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. The host with the IP address that matches the IP address in the ARP request will reply with a unicast frame that includes the MAC address of the host. Thus the original sending host will obtain the destination IP and MAC address pair to continue the encapsulation process for data transmission.
24. A network technician issues the arp -d * command on a PC after the router that is connected to the LAN is reconfigured. What is the result after this command is issued?
- The ARP cache is cleared.
- The current content of the ARP cache is displayed.
- The detailed information of the ARP cache is displayed.
- The ARP cache is synchronized with the router interface.
Explanation: Issuing the arp –d * command on a PC will clear the ARP cache content. This is helpful when a network technician wants to ensure the cache is populated with updated information.
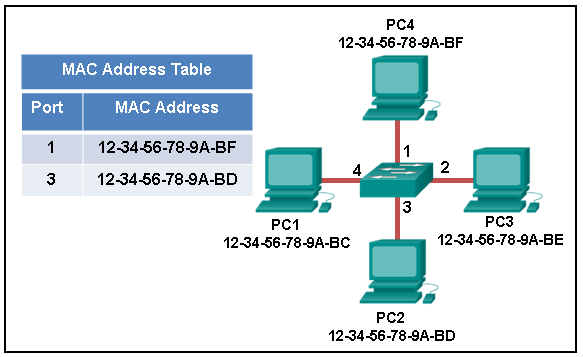
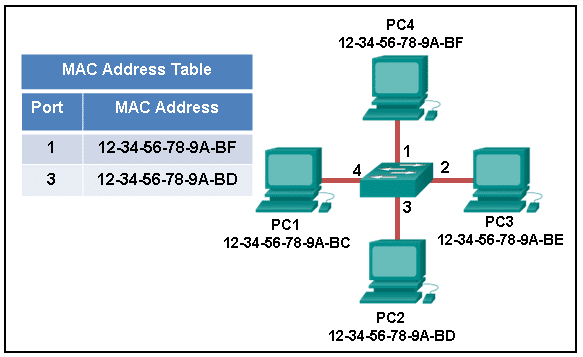
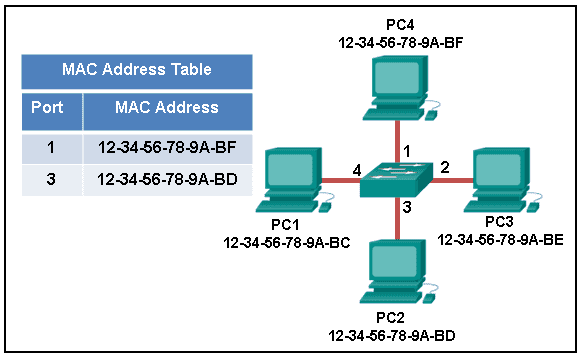
25. Refer to the exhibit. The exhibit shows a small switched network and the contents of the MAC address table of the switch. PC1 has sent a frame addressed to PC3. What will the switch do with the frame?
- The switch will discard the frame.
- The switch will forward the frame only to port 2.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports except port 4.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports.
- The switch will forward the frame only to ports 1 and 3.
Explanation: The MAC address of PC3 is not present in the MAC table of the switch. Because the switch does not know where to send the frame that is addressed to PC3, it will forward the frame to all the switch ports, except for port 4, which is the incoming port.
26. Which two types of IPv6 messages are used in place of ARP for address resolution?
- anycast
- broadcast
- echo reply
- echo request
- neighbor solicitation
- neighbor advertisement
Explanation: IPv6 does not use ARP. Instead, ICMPv6 neighbor discovery is used by sending neighbor solicitation and neighbor advertisement messages.
27. What is the aim of an ARP spoofing attack?
- to flood the network with ARP reply broadcasts
- to fill switch MAC address tables with bogus addresses
- to associate IP addresses to the wrong MAC address
- to overwhelm network hosts with ARP requests
Explanation: In an ARP spoofing attack, a malicious host intercepts ARP requests and replies to them so that network hosts will map an IP address to the MAC address of the malicious host.
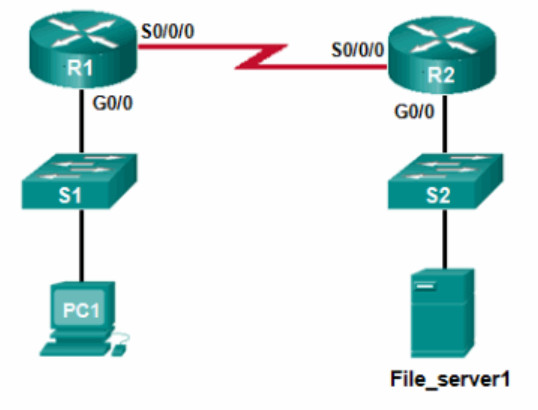
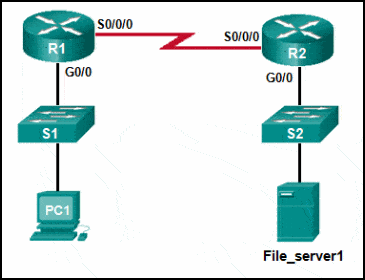
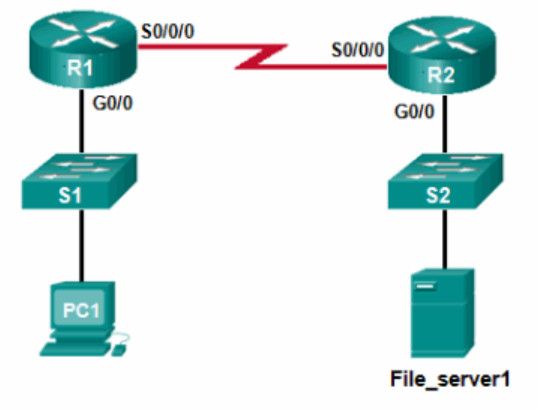
28. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 attempts to connect to File_server1 and sends an ARP request to obtain a destination MAC address. Which MAC address will PC1 receive in the ARP reply?
- the MAC address of S1
- the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R1
- the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R2
- the MAC address of S2
- the MAC address of File_server1
Explanation: PC1 must have a MAC address to use as a destination Layer 2 address. PC1 will send an ARP request as a broadcast and R1 will send back an ARP reply with its G0/0 interface MAC address. PC1 can then forward the packet to the MAC address of the default gateway, R1.
29. Where are IPv4 address to Layer 2 Ethernet address mappings maintained on a host computer?
- neighbor table
- ARP cache
- routing table
- MAC address table
Explanation: The ARP cache is used to store IPv4 addresses and the Ethernet physical addresses or MAC addresses to which the IPv4 addresses are mapped. Incorrect mappings of IP addresses to MAC addresses can result in loss of end-to-end connectivity.
30. What important information is examined in the Ethernet frame header by a Layer 2 device in order to forward the data onward?
- source MAC address
- source IP address
- destination MAC address
- Ethernet type
- destination IP address
Explanation: The Layer 2 device, such as a switch, uses the destination MAC address to determine which path (interface or port) should be used to send the data onward to the destination device.
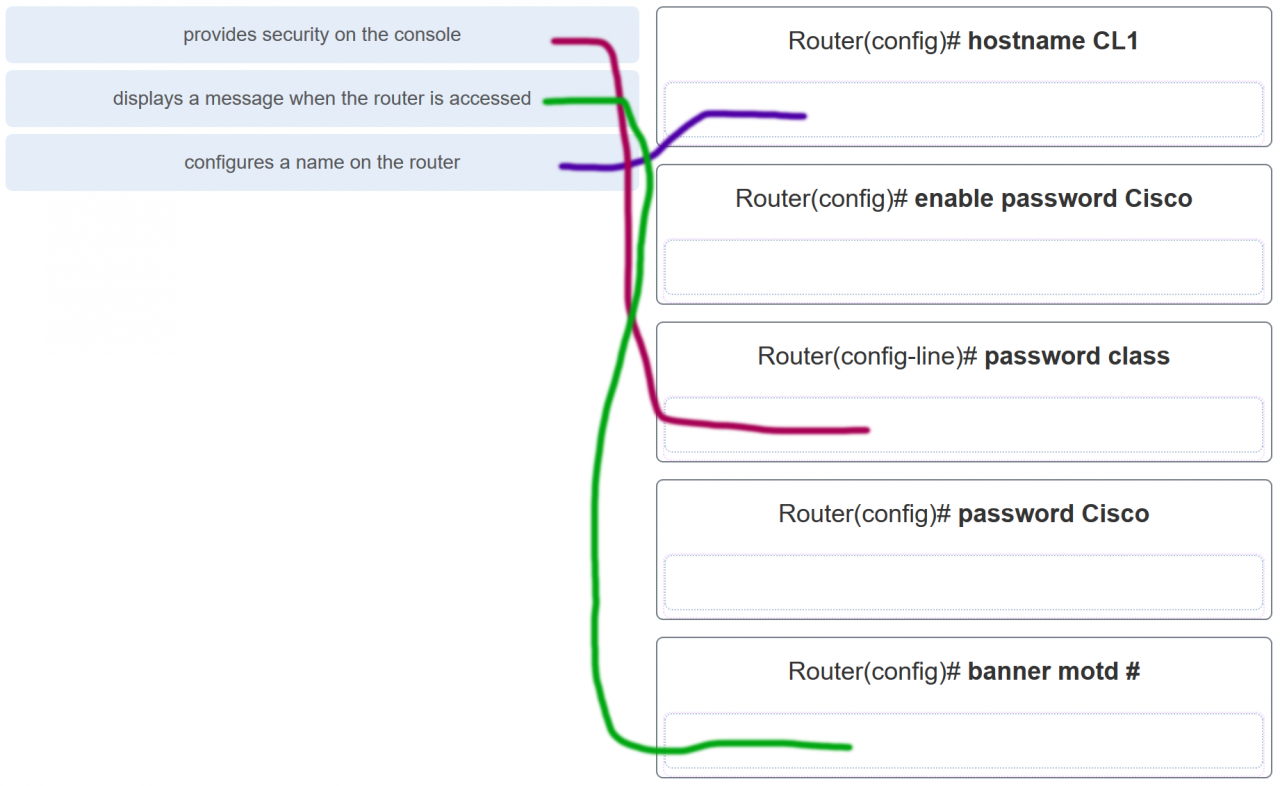
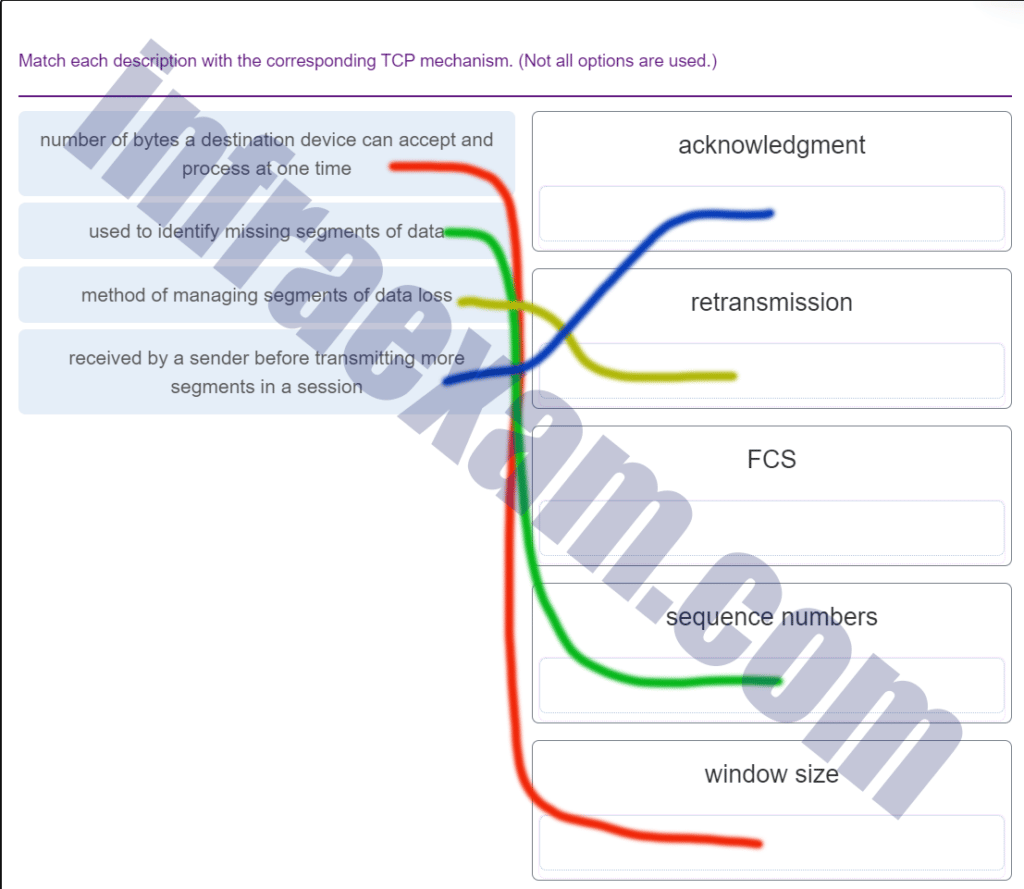
31. Match the commands to the correct actions. (Not all options are used.)
32. A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
- Reboot the device.
- Enter CTRL-Z at the privileged mode prompt.
- Exit global configuration mode.
- Power cycle the device.
- Exit privileged EXEC mode and press Enter.
Explanation: While at the privileged mode prompt such as Router#, type exit,press Enter, and the banner message appears. Power cycling a network device that has had the banner motd command issued will also display the banner message, but this is not a quick way to test the configuration.
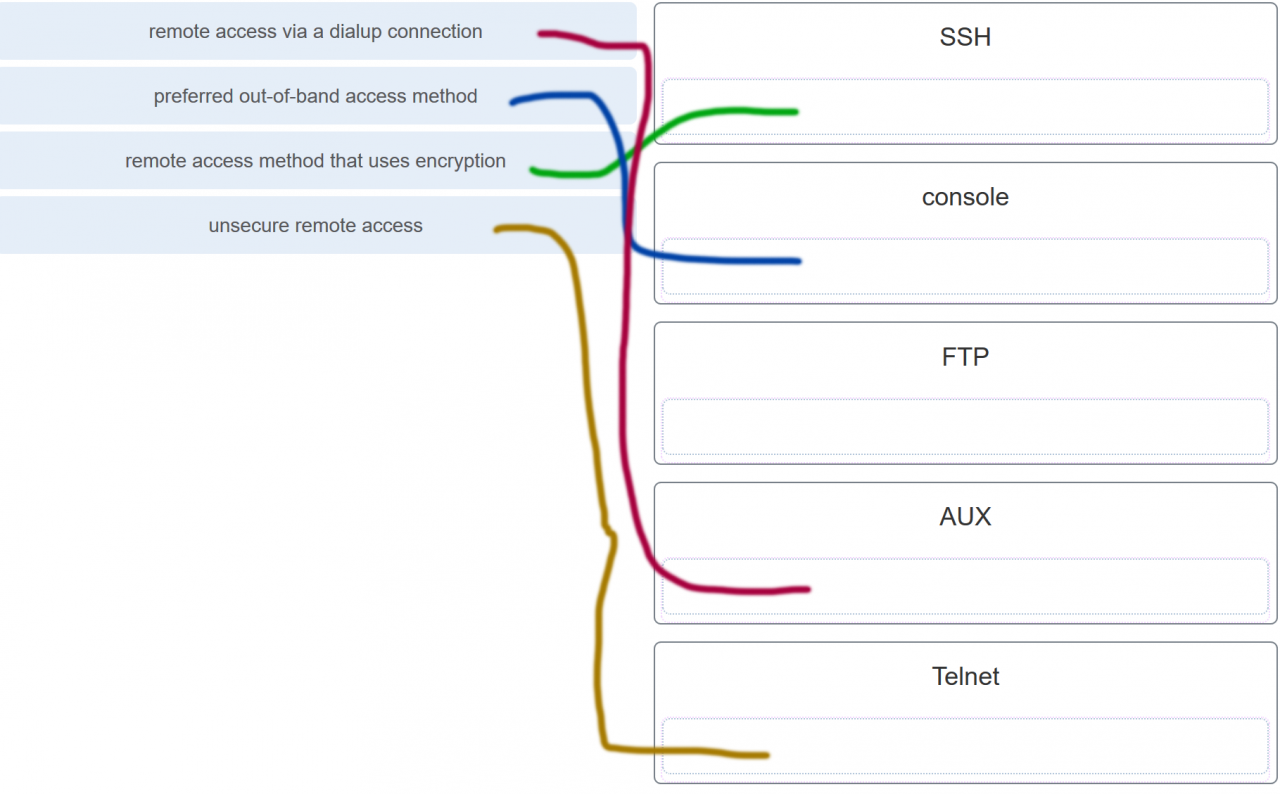
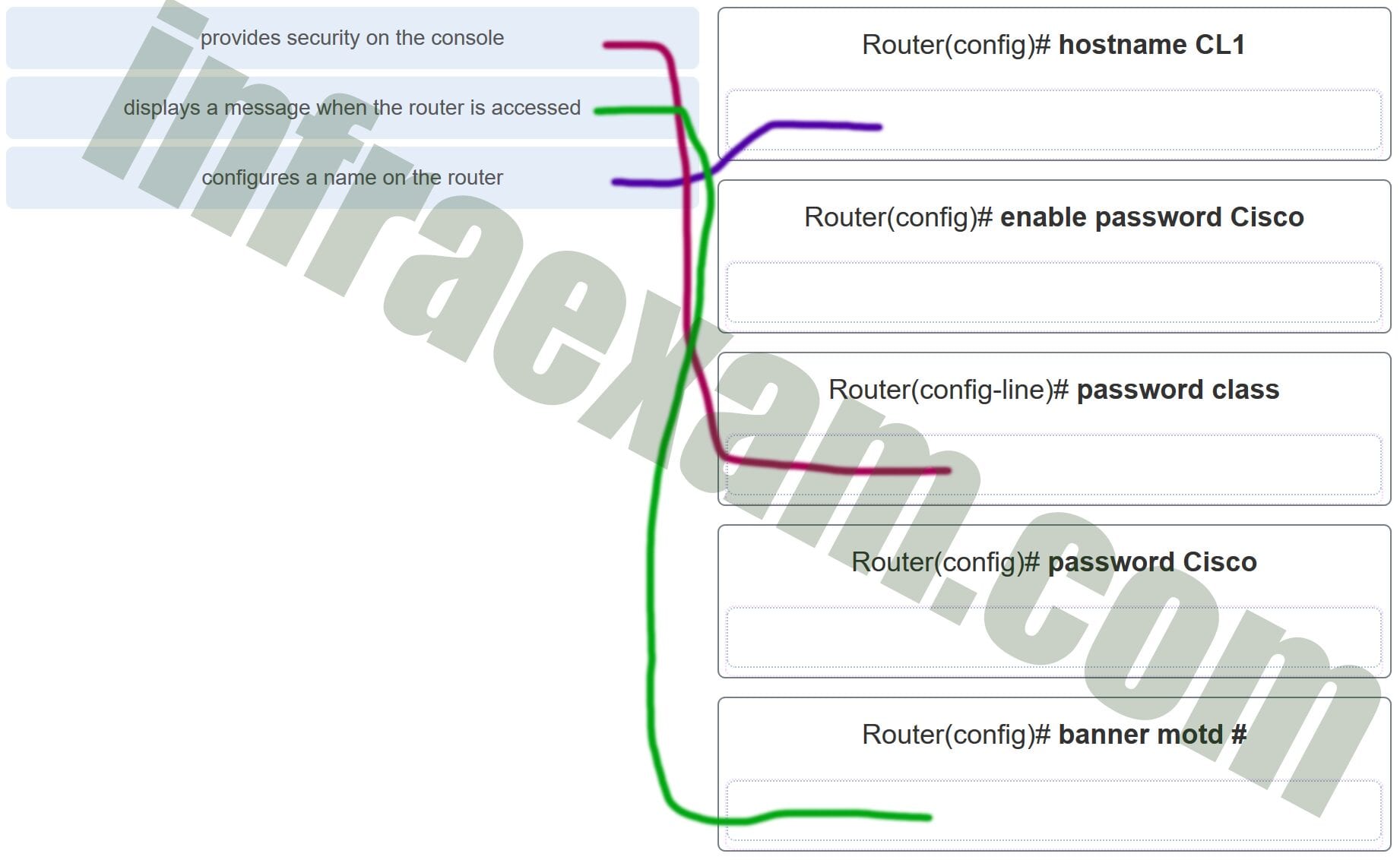
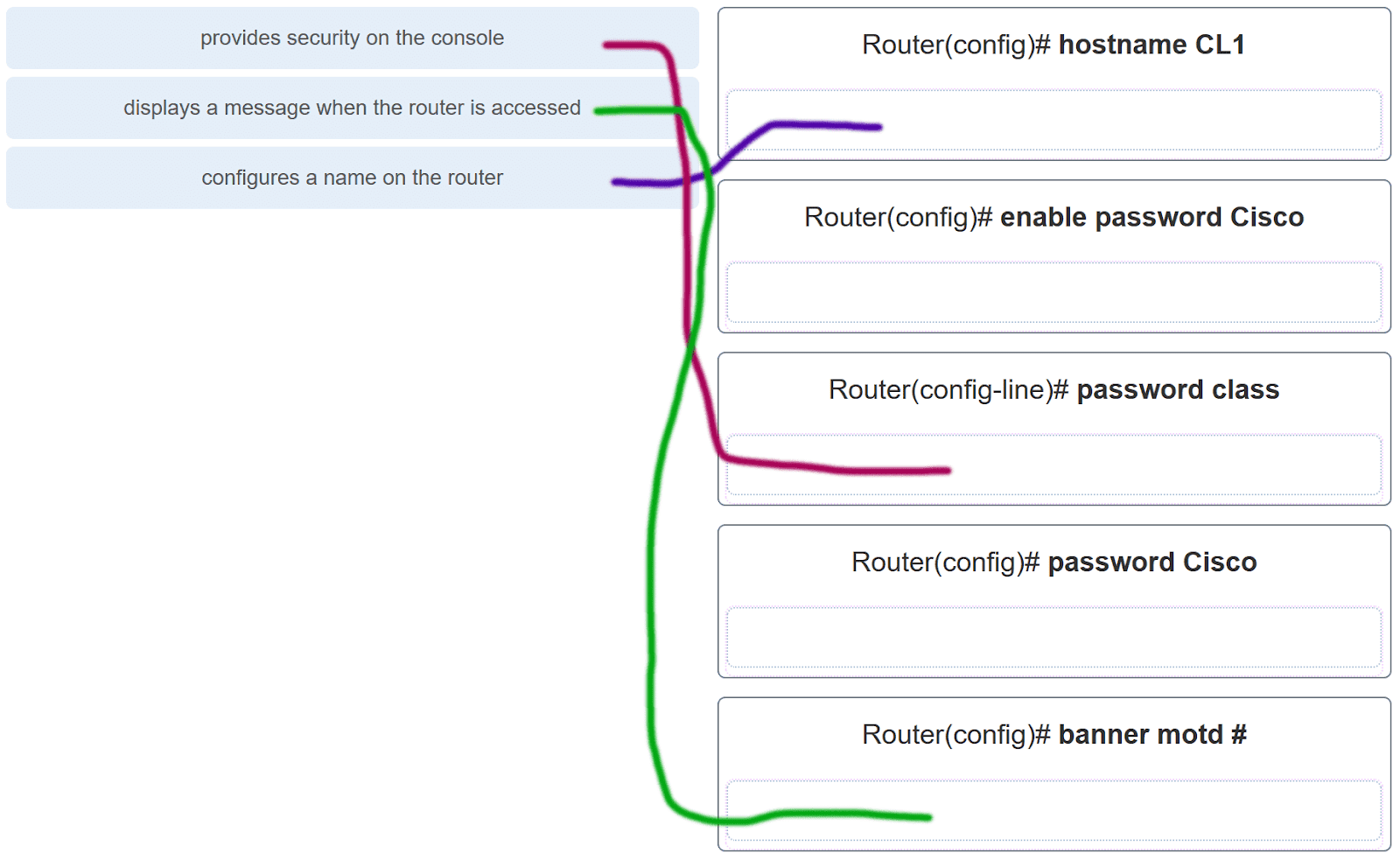
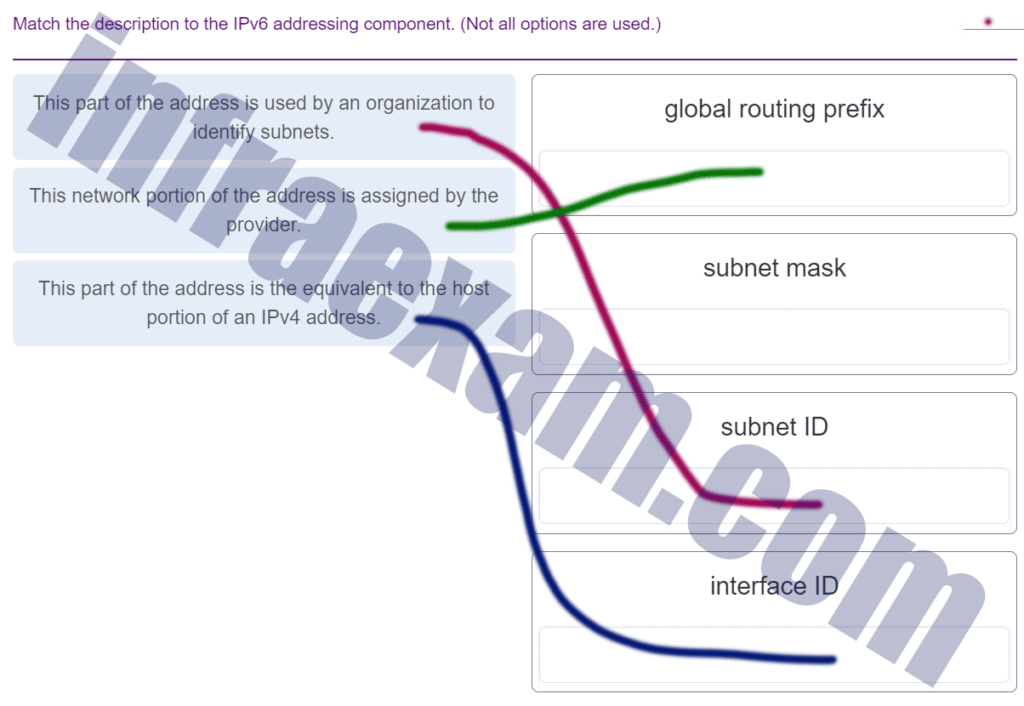
33. A network administrator requires access to manage routers and switches locally and remotely. Match the description to the access method. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: Both the console and AUX ports can be used to directly connect to a Cisco network device for management purposes. However, it is more common to use the console port. The AUX port is more often used for remote access via a dial up connection. SSH and Telnet are both remote access methods that depend on an active network connection. SSH uses a stronger password authentication than Telnet uses and also uses encryption on transmitted data.
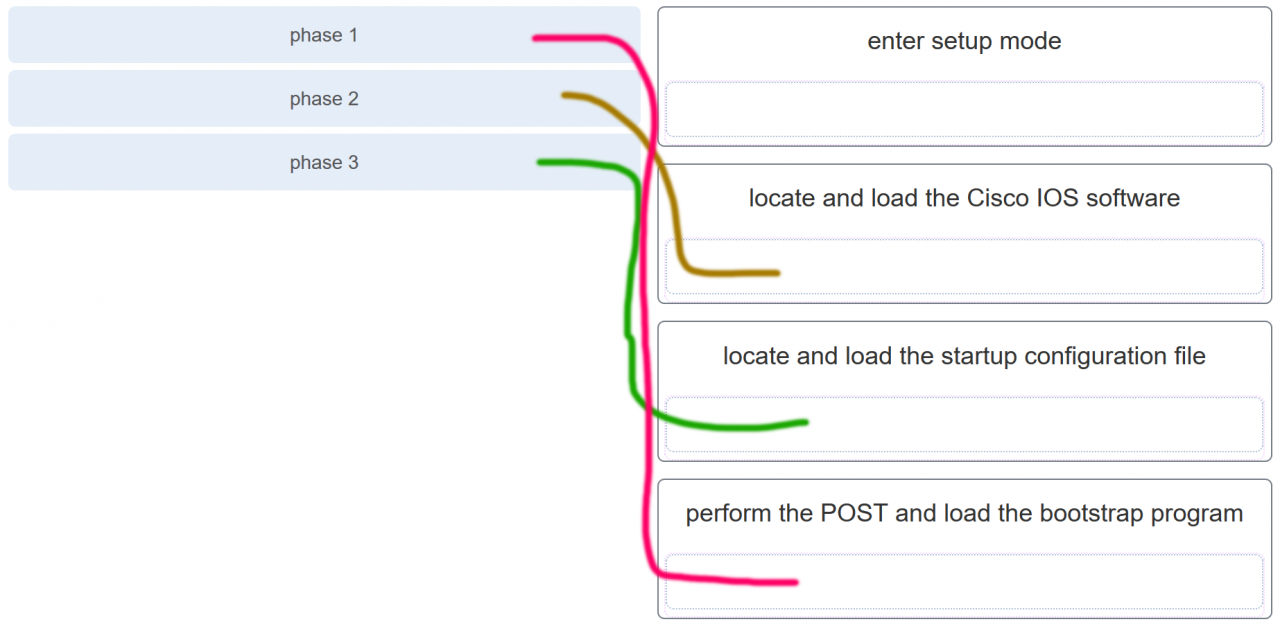
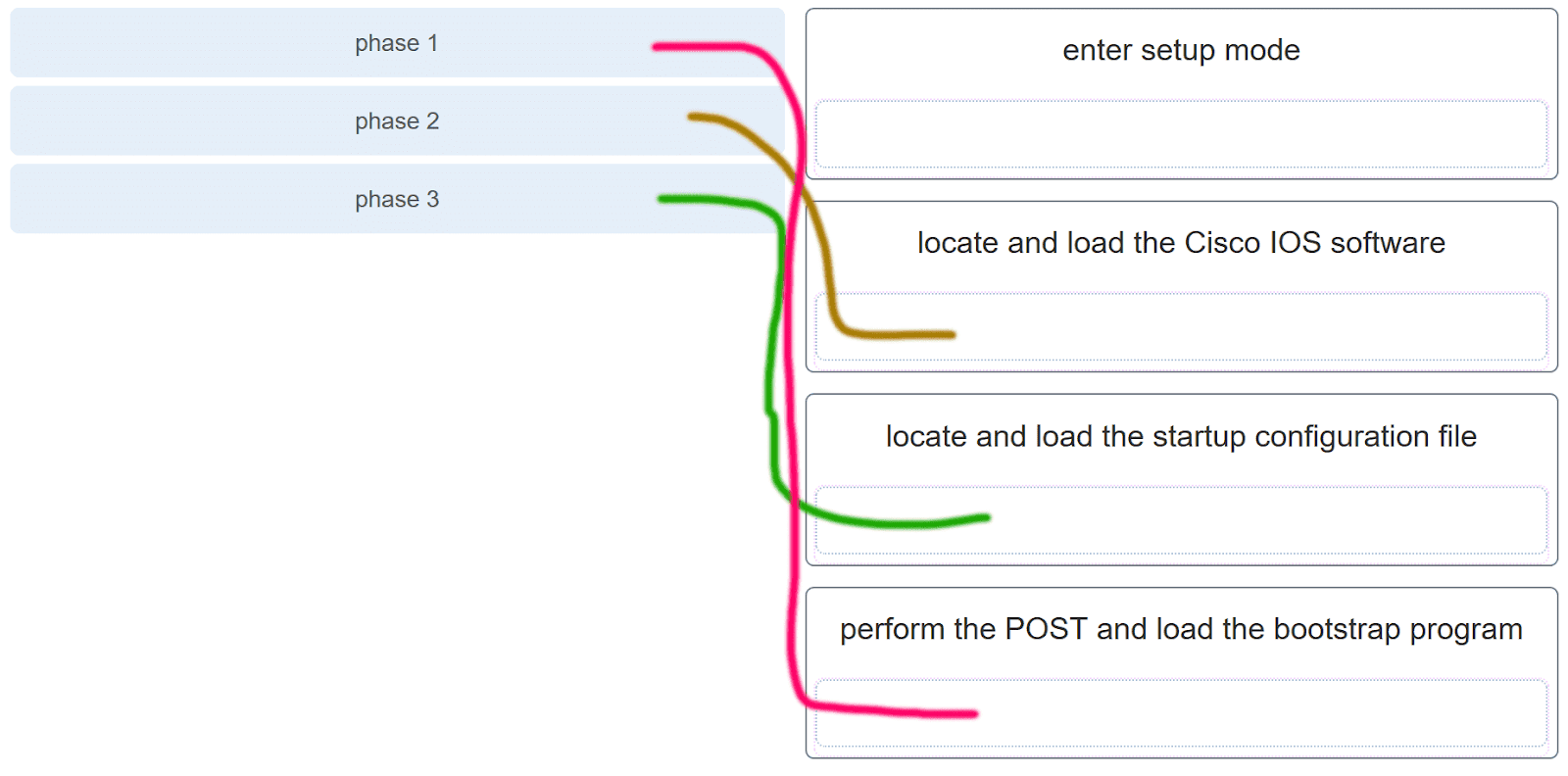
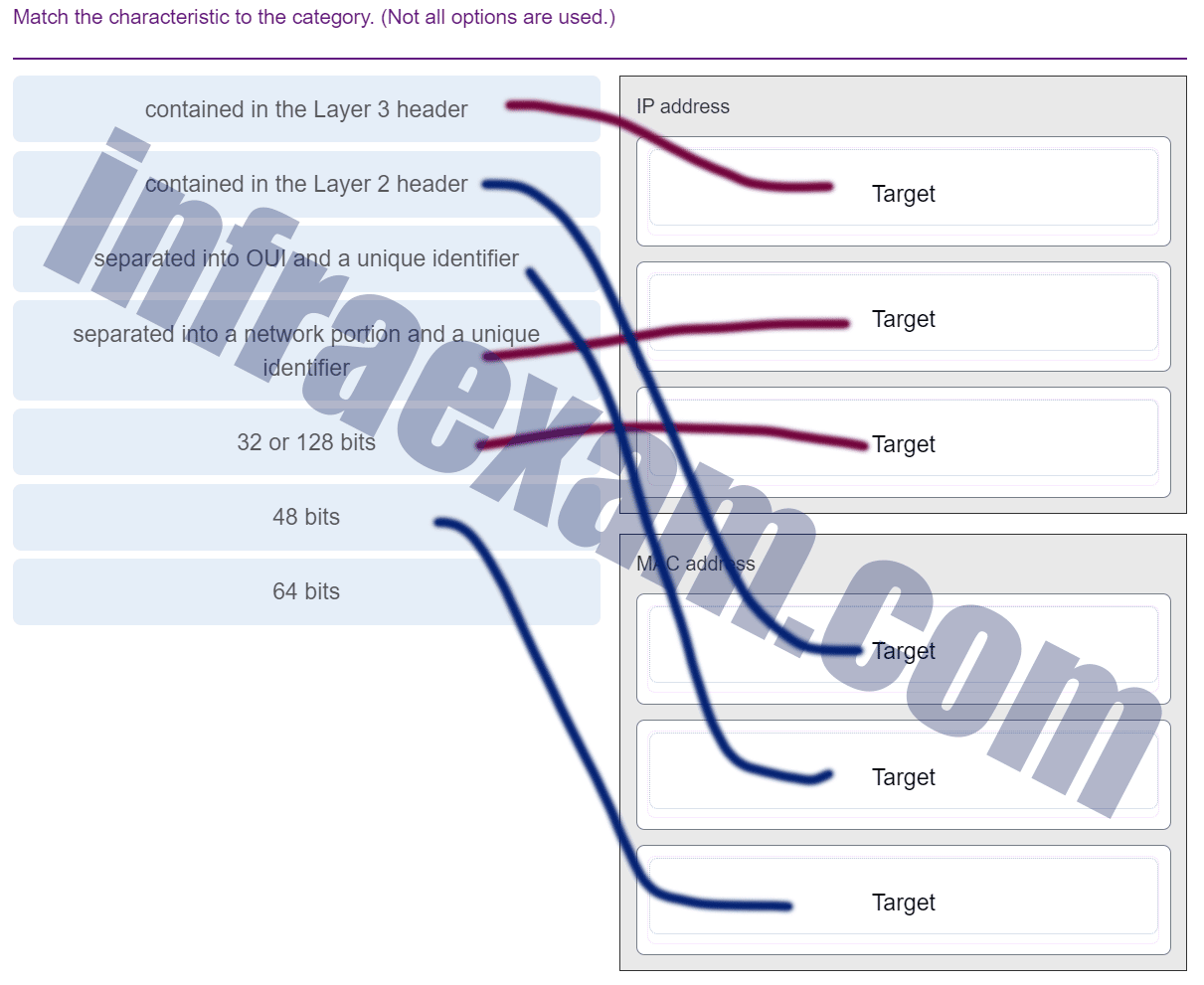
34. Match the phases to the functions during the boot up process of a Cisco router. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: There are three major phases to the bootup process of a Cisco router:
- Perform the POST and load the bootstrap program.
- Locate and load the Cisco IOS software.
- Locate and load the startup configuration file
If a startup configuration file cannot be located, the router will enter setup mode by displaying the setup mode prompt.
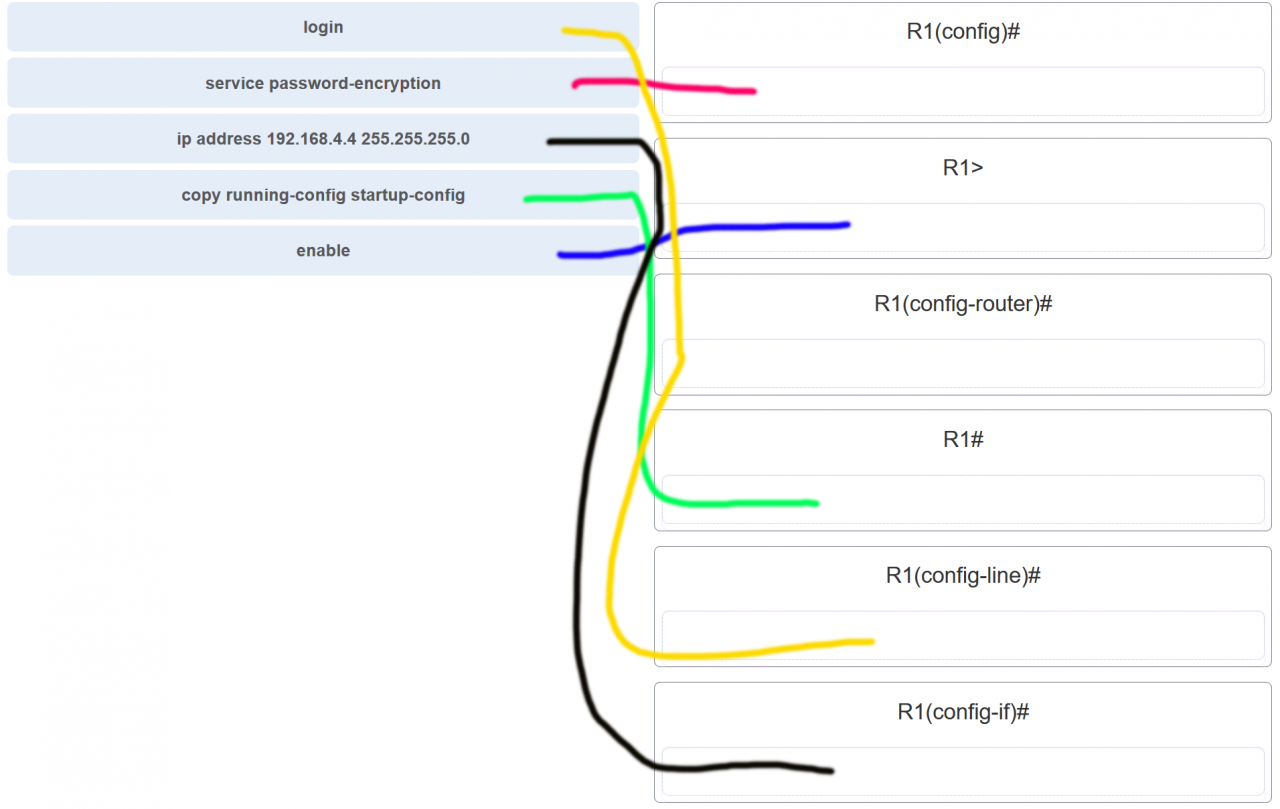
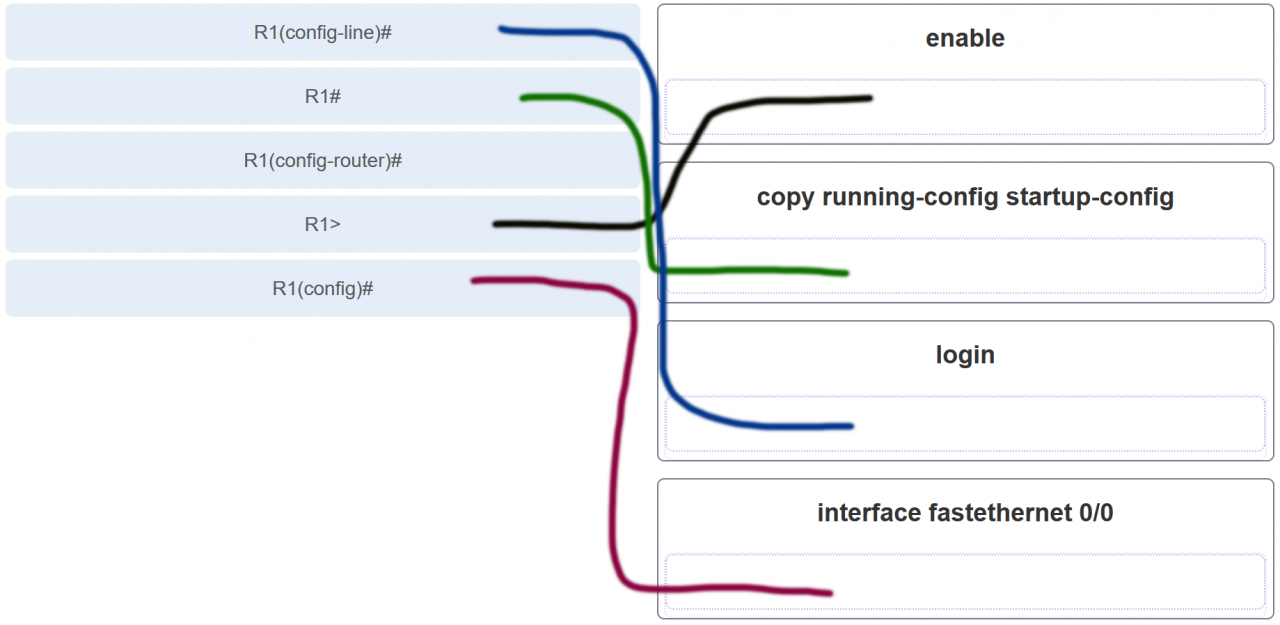
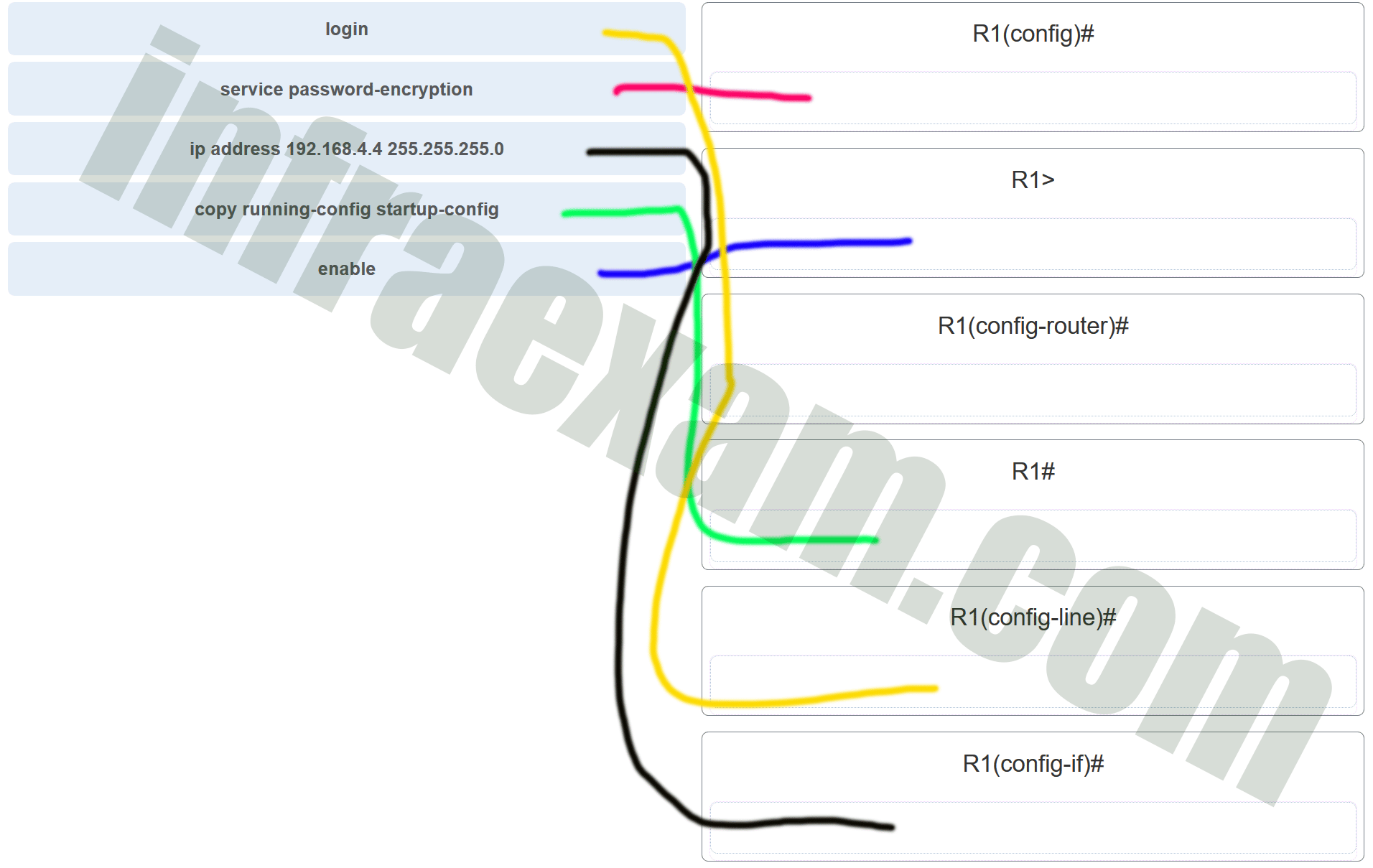
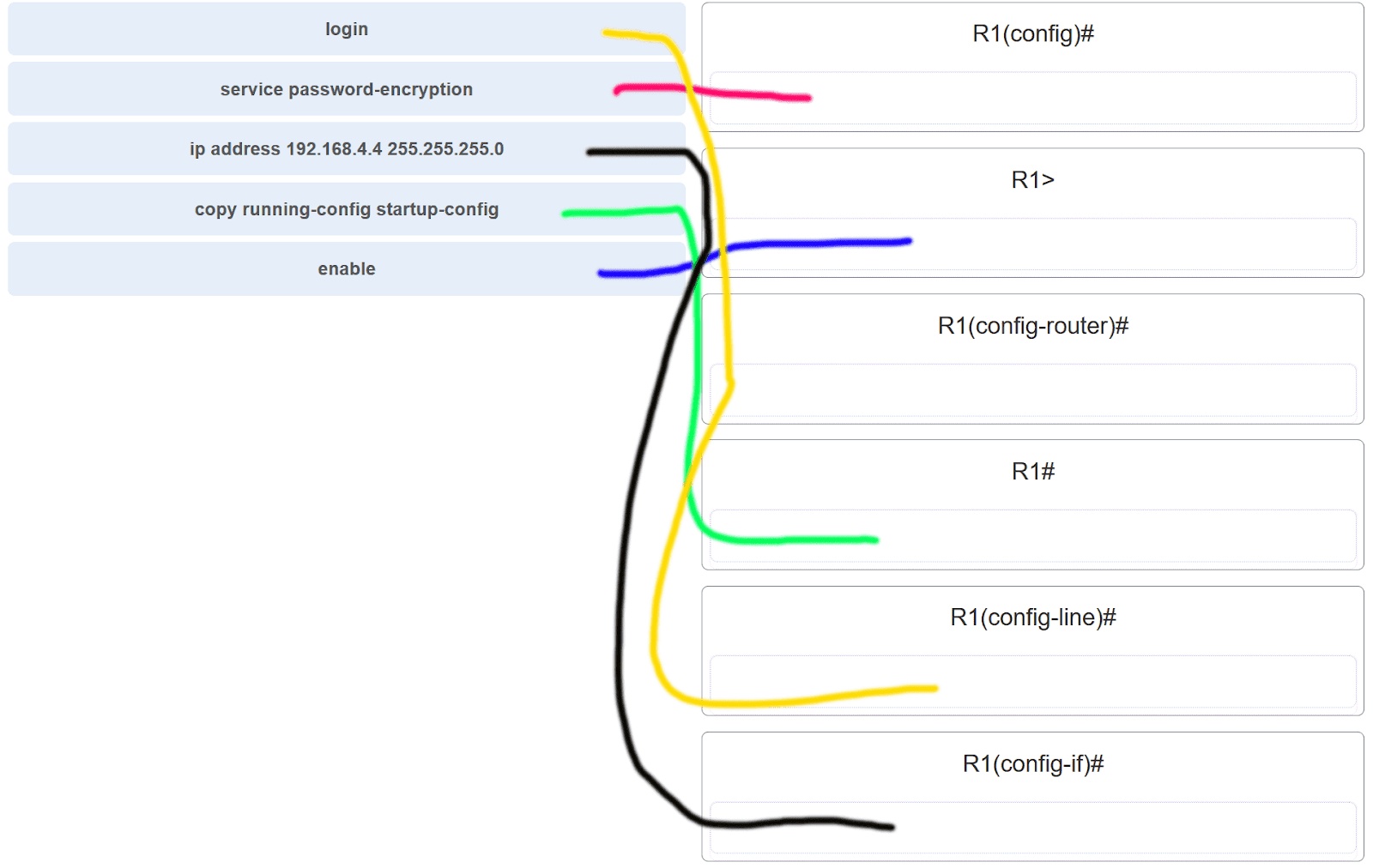
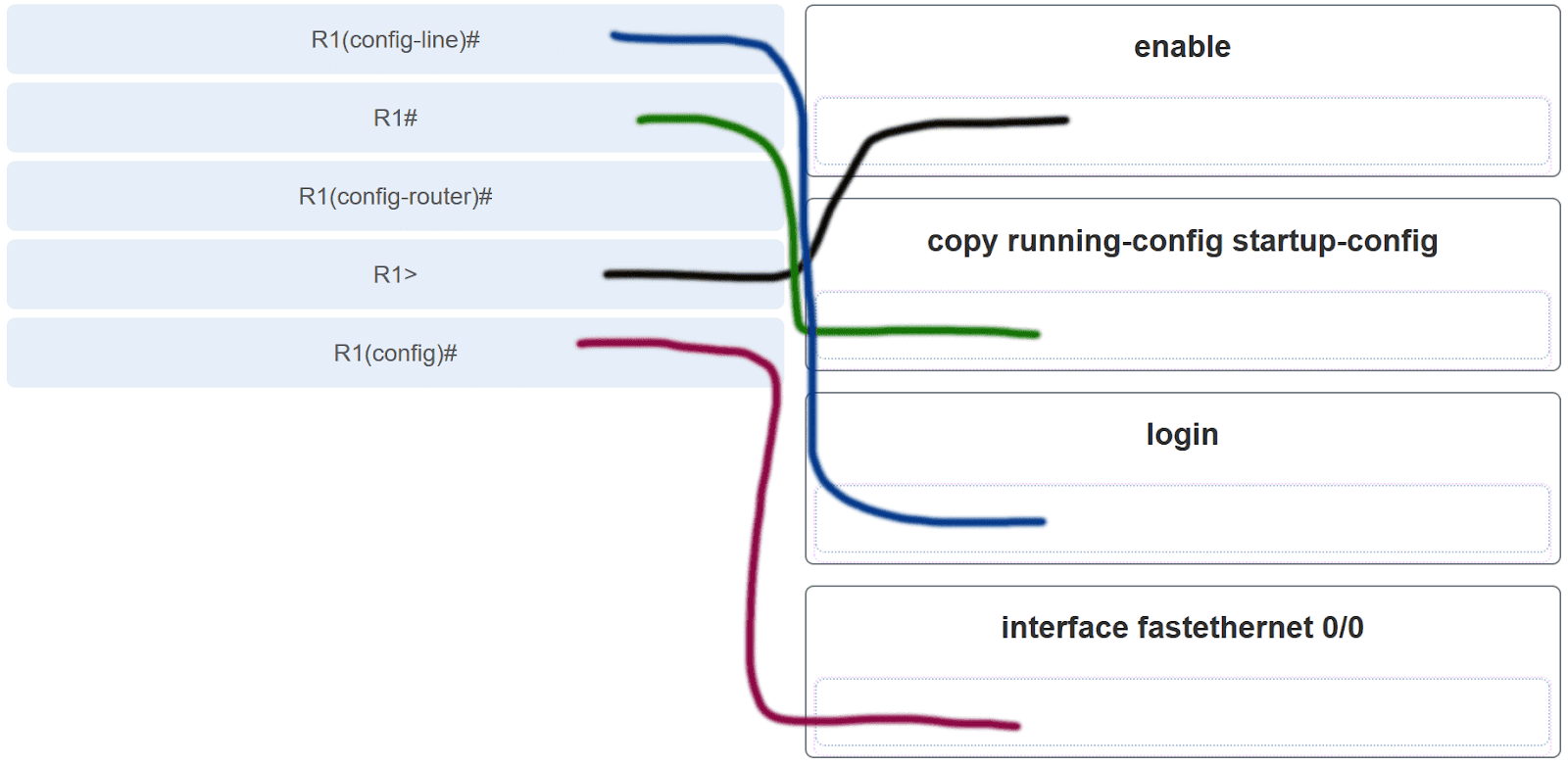
35. Match the command with the device mode at which the command is entered. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: The enable command is entered in R1> mode. The login command is entered in R1(config-line)# mode. The copy running-config startup-config command is entered in R1# mode. The ip address 192.168.4.4 255.255.255.0 command is entered in R1(config-if)# mode. The service password-encryption command is entered in global configuration mode.
36. What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed
- to store the startup configuration file
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
Explanation: NVRAM is permanent memory storage, so the startup configuration file is preserved even if the router loses power.
37. A router boots and enters setup mode. What is the reason for this?
- The IOS image is corrupt.
- Cisco IOS is missing from flash memory.
- The configuration file is missing from NVRAM.
- The POST process has detected hardware failure.
Explanation: If a router cannot locate the startup-config file in NVRAM, it will enter setup mode to allow the configuration to be entered from the console device.
38. The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
Explanation: A default gateway address is typically configured on all devices to allow them to communicate beyond just their local network.In a switch this is achieved using the command ip default-gateway <ip address>.
39. What happens when the transport input ssh command is entered on the switch vty lines?
- The SSH client on the switch is enabled.
- Communication between the switch and remote users is encrypted.
- The switch requires a username/password combination for remote access.
- The switch requires remote connections via a proprietary client software.
Explanation: The transport input ssh command when entered on the switch vty (virtual terminal lines) will encrypt all inbound controlled telnet connections.
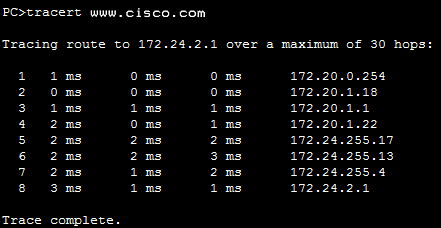
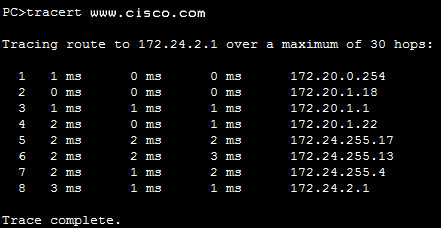
40. Refer to the exhibit. A user PC has successfully transmitted packets to www.cisco.com. Which IP address does the user PC target in order to forward its data off the local network?
- 172.24.255.17
- 172.24.1.22
- 172.20.0.254
- 172.24.255.4
- 172.20.1.18
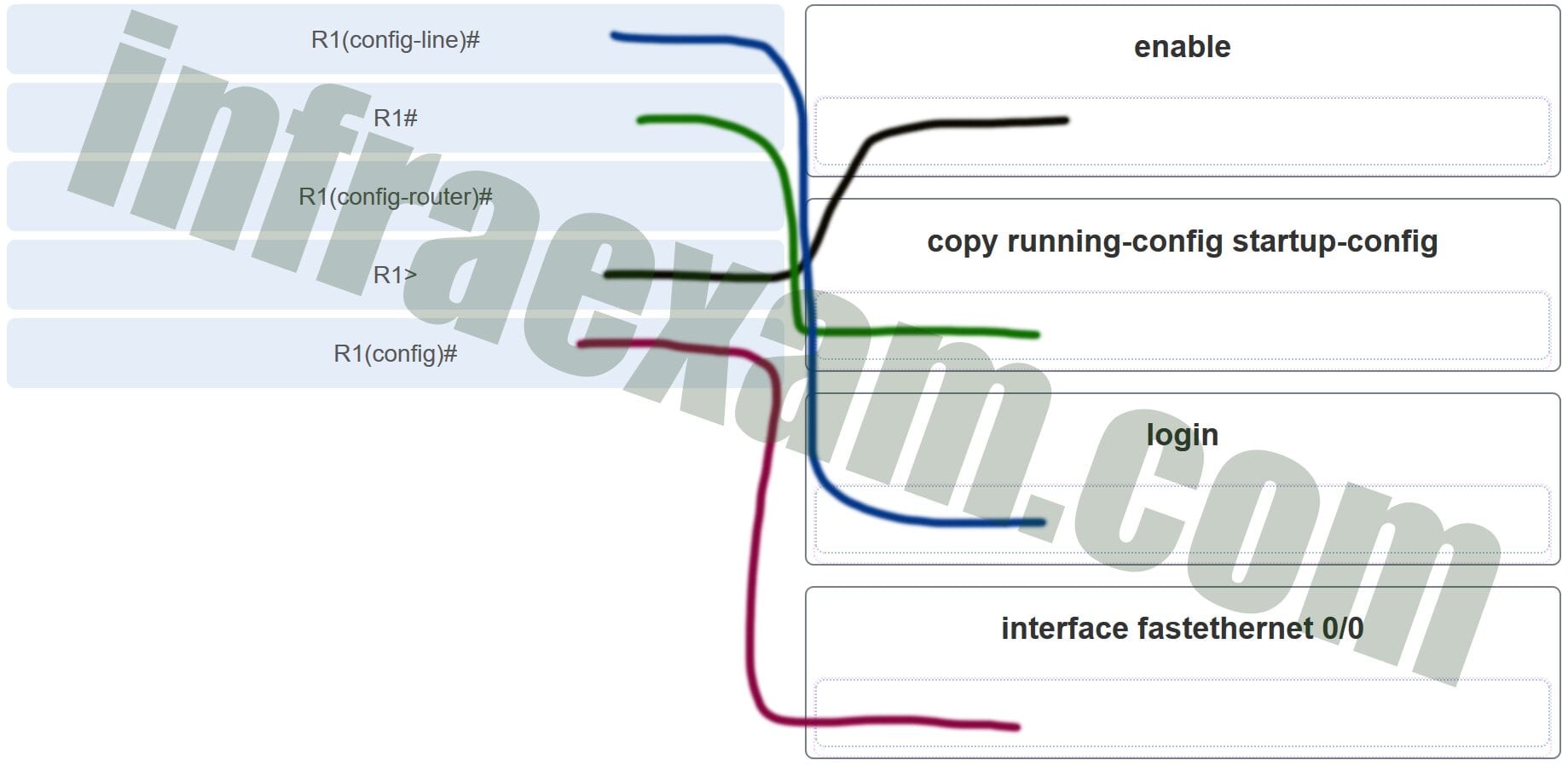
41. Match the configuration mode with the command that is available in that mode. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: The enable command is entered at the R1> prompt. The login command is entered at the R1(config-line)# prompt. The copy running-config startup-config command is entered at the R1# prompt. The interface fastethernet 0/0 command is entered at the R1(config)# prompt.
42. Which three commands are used to set up secure access to a router through a connection to the console interface? (Choose three.)
- interface fastethernet 0/0
- line vty 0 4
- line console 0
- enable secret cisco
- login
- password cisco
Explanation: The three commands needed to password protect the console port are as follows:
- line console 0
- password cisco
- login
The interface fastethernet 0/0 command is commonly used to access the configuration mode used to apply specific parameters such as the IP address to the Fa0/0 port. The line vty 0 4 command is used to access the configuration mode for Telnet. The0and 4 parameters specify ports 0 through 4, or a maximum of five simultaneous Telnet connections. The enable secret command is used to apply a password used on the router to access the privileged mode.
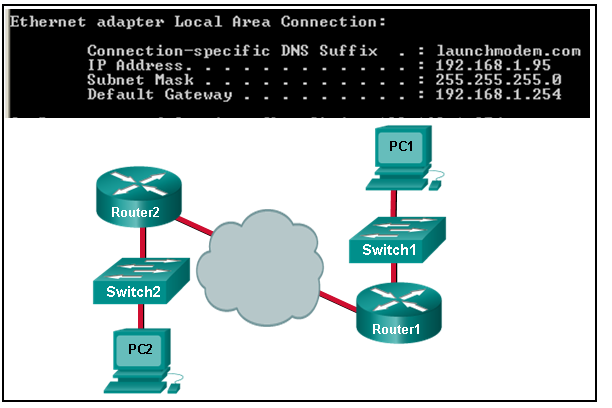
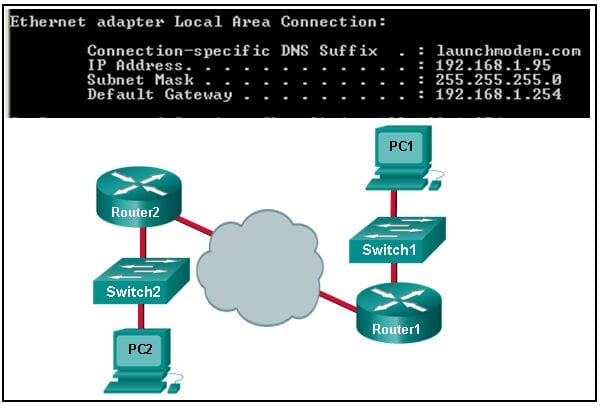
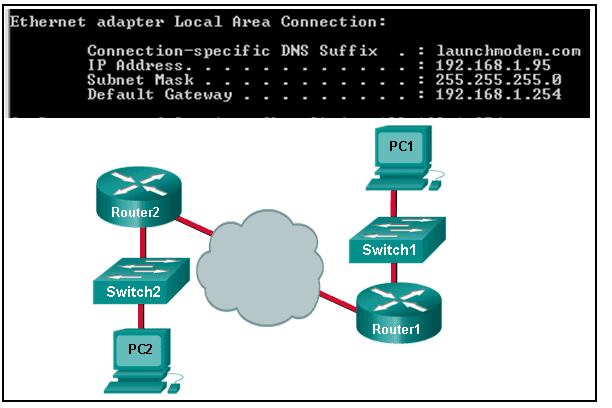
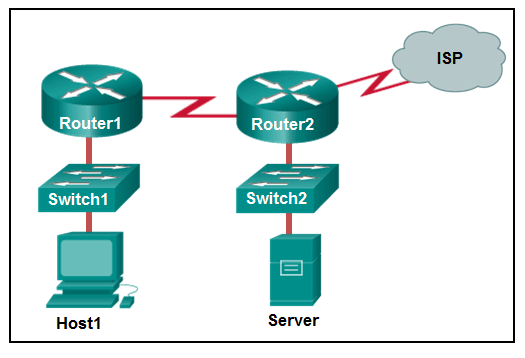
43. Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address configuration shown from PC1. What is a description of the default gateway address?
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the company to the Internet.
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the PC1 LAN to Router1.
- It is the IP address of Switch1 that connects PC1 to other devices on the same LAN.
- It is the IP address of the ISP network device located in the cloud.
Explanation: The default gateway is used to route packets destined for remote networks. The default gateway IP address is the address of the first Layer 3 device (the router interface) that connects to the same network.
44. Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet forwarding
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection
- flow control
Explanation: A router accepts a packet and accesses its routing table to determine the appropriate exit interface based on the destination address. The router then forwards the packet out of that interface.
45. What is the effect of using the Router# copy running-config startup-config command on a router?
- The contents of ROM will change.
- The contents of RAM will change.
- The contents of NVRAM will change.
- The contents of flash will change.
Explanation: The command copy running-config startup-config copies the running-configuration file from RAM into NVRAM and saves it as the startup-configuration file. Since NVRAM is none-volatile memory it will be able to retain the configuration details when the router is powered off.
46. What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
Explanation: When a host needs to send a message to another host located on the same network, it can forward the message directly. However, when a host needs to send a message to a remote network, it must use the router, also known as the default gateway. This is because the data link frame address of the remote destination host cannot be used directly. Instead, the IP packet has to be sent to the router (default gateway) and the router will forward the packet toward its destination. Therefore, if the default gateway is incorrectly configured, the host can communicate with other hosts on the same network, but not with hosts on remote networks.
47. What are two potential network problems that can result from ARP operation? (Choose two.)
- Manually configuring static ARP associations could facilitate ARP poisoning or MAC address spoofing.
- On large networks with low bandwidth, multiple ARP broadcasts could cause data communication delays.
- Network attackers could manipulate MAC address and IP address mappings in ARP messages with the intent of intercepting network traffic.
- Large numbers of ARP request broadcasts could cause the host MAC address table to overflow and prevent the host from communicating on the network.
- Multiple ARP replies result in the switch MAC address table containing entries that match the MAC addresses of hosts that are connected to the relevant switch port.
Explanation: Large numbers of ARP broadcast messages could cause momentary data communications delays. Network attackers could manipulate MAC address and IP address mappings in ARP messages with the intent to intercept network traffic. ARP requests and replies cause entries to be made into the ARP table, not the MAC address table. ARP table overflows are very unlikely. Manually configuring static ARP associations is a way to prevent, not facilitate, ARP poisoning and MAC address spoofing. Multiple ARP replies resulting in the switch MAC address table containing entries that match the MAC addresses of connected nodes and are associated with the relevant switch port are required for normal switch frame forwarding operations. It is not an ARP caused network problem.
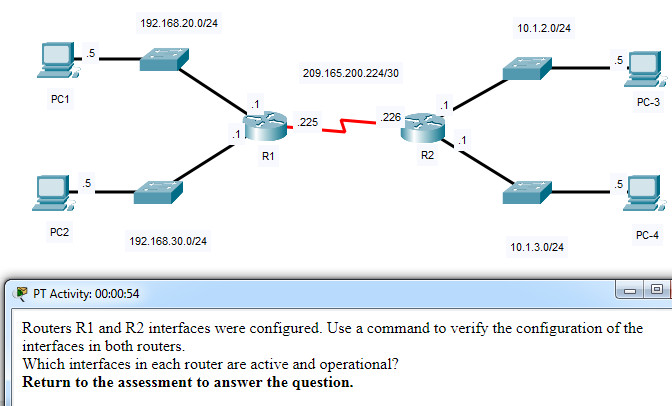
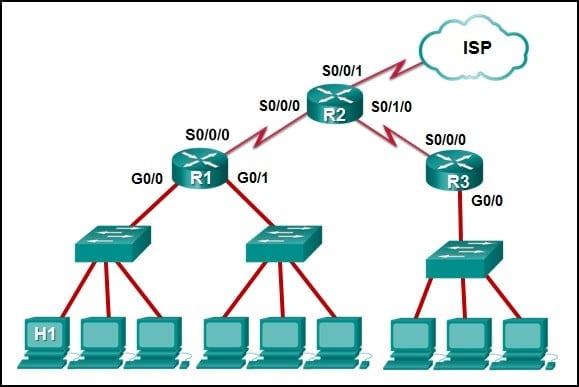
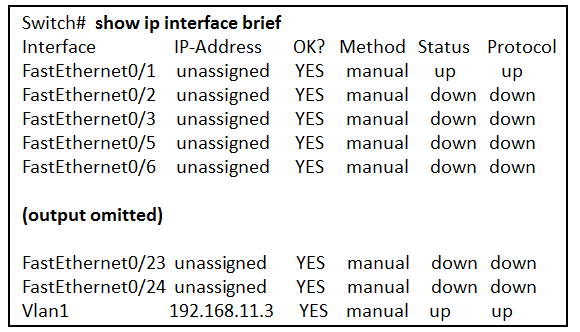
48. Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
CCNA 1 v7 Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam
[sociallocker id=”54558″]
[/sociallocker]
Which interfaces in each router are active and operational?
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R1: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/0
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/1
Explanation: The command to use for this activity is show ip interface brief in each router. The active and operational interfaces are represented by the value “up” in the “Status” and “Protocol” columns. The interfaces in R1 with these characteristics are G0/0 and S0/0/0. In R2 they are G0/1 and S0/0/0.
49. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to identify the next level protocol?
- protocol
- destination IPv4 address
- source IPv4 address
- TTL
50. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains an 8-bit binary value used to determine the priority of each packet?
- differentiated services
- destination IPv4 address
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
51. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a 32-bit binary value associated with an interface on the sending device?
- source IPv4 address
- destination IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
52. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to detect corruption in the IPv4 header?
- header checksum
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
Explanation: The header checksum is used to determine if any errors have been introduced during transmission.
53.
RTR1(config)# interface gi0/1 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Marketing LAN RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.27.15.17 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# interface gi0/0 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Payroll LAN RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.27.14.148 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.14.15.254 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN RTR1(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.39 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Payroll LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 10.27.14.148
- 10.27.14.1
- 10.14.15.254
- 203.0.113.39
- 10.27.15.17
54. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a unicast, multicast, or broadcast address?
- destination IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
- header checksum
55. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to limit the lifetime of a packet?
- TTL
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- header checksum
56. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a 4-bit binary value set to 0100?
- version
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
57. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to identify the next level protocol?
- protocol
- version
- differentiated services
- header checksum
58. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a 4-bit binary value set to 0100?
- version
- differentiated services
- header checksum
- TTL
59. What property of ARP causes cached IP-to-MAC mappings to remain in memory longer?
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
60. What property of ARP allows MAC addresses of frequently used servers to be fixed in the ARP table?
- A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
62. What property of ARP allows hosts on a LAN to send traffic to remote networks?
- Local hosts learn the MAC address of the default gateway.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
63.
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.235.234 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.234.114 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.234.235.254 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.3 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Registrar LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.235.234
- 192.168.235.1
- 10.234.235.254
- 203.0.113.3
- 192.168.234.114
64. What property of ARP forces all Ethernet NICs to process an ARP request?
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
65. What property of ARP causes a reply only to the source sending an ARP request?
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
66. What property of ARP causes the request to be flooded out all ports of a switch except for the port receiving the ARP request?
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
67. What property of ARP causes the NICs receiving an ARP request to pass the data portion of the Ethernet frame to the ARP process?
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
68. What property of ARP causes the NICs receiving an ARP request to pass the data portion of the Ethernet frame to the ARP process?
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
69.
Main(config)# interface gi0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Service LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 172.29.157.156 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Engineering LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 172.29.156.36 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Main(config-if)# ip address 10.156.157.254 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Main(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.177 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Service LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 172.29.157.156
- 172.29.157.1
- 10.156.157.254
- 198.51.100.177
- 172.29.156.36
70.
BldgA(config)# interface gi0/1
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Medical LAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.191.189 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface gi0/0
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Client LAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.190.70 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 10.190.191.254 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.213 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Medical LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.191.189
- 192.168.191.1
- 10.190.191.254
- 198.51.100.213
- 192.168.190.70
71.
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.225.223 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.224.103 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.224.225.254 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.246 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Registrar LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.225.223
- 192.168.225.1
- 10.224.225.254
- 203.0.113.246
- 192.168.224.103
72.
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.118.63.65 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.118.62.196 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.62.63.254 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.87 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Manager LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 10.118.62.196
- 10.118.62.1
- 10.62.63.254
- 209.165.200.87
- 10.118.63.65
73.
HQ(config)# interface gi0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Branch LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.19.99.99 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface gi0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Store LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.19.98.230 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP HQ(config-if)# ip address 10.98.99.254 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.120 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Store LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 172.19.98.230
- 172.19.98.1
- 10.98.99.254
- 209.165.200.120
- 172.19.99.99
74.
HQ(config)# interface gi0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Branch LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.20.133.132 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface gi0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Store LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.20.132.13 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP HQ(config-if)# ip address 10.132.133.254 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.156 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Store LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 172.20.132.13
- 172.20.132.1
- 10.132.133.254
- 198.51.100.156
- 172.20.133.132
75.
Main(config)# interface gi0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Service LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 192.168.167.166 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Engineering LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 192.168.166.46 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Main(config-if)# ip address 10.166.167.254 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Main(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.189 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Service LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.167.166
- 192.168.167.1
- 10.166.167.254
- 198.51.100.189
- 192.168.166.46
76.
BldgA(config)# interface gi0/1
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Medical LAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.201.200 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface gi0/0
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Client LAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.200.80 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 10.200.201.254 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.222 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Medical LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.201.200
- 192.168.201.1
- 10.200.201.254
- 203.0.113.222
- 192.168.200.80
Last Updated on February 1, 2021 by
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10: Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 2020 Correct 100%
Cisco Netacad ITN Version 7.00 CCNA 1 v7 Modules 8 – 10: Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 2020 2021 – Introduction to Networks
-
A computer can access devices on the same network but cannot access devices on other networks. What is the probable cause of this problem?
- The cable is not connected properly to the NIC.
- The computer has an invalid IP address.
- The computer has an incorrect subnet mask.
- The computer has an invalid default gateway address.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The default gateway is the address of the device a host uses to access the Internet or another network. If the default gateway is missing or incorrect, that host will not be able to communicate outside the local network. Because the host can access other hosts on the local network, the network cable and the other parts of the IP configuration are working.
-
Which statement describes a feature of the IP protocol?
- IP encapsulation is modified based on network media.
- IP relies on Layer 2 protocols for transmission error control.
- MAC addresses are used during the IP packet encapsulation.
- IP relies on upper layer services to handle situations of missing or out-of-order packets.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
IP protocol is a connection-less protocol, considered unreliable in terms of end-to-end delivery. It does not provide error control in the cases where receiving packets are out-of-order or in cases of missing packets. It relies on upper layer services, such as TCP, to resolve these issues.
-
Why is NAT not needed in IPv6?
- Because IPv6 has integrated security, there is no need to hide the IPv6 addresses of internal networks.
- Any host or user can get a public IPv6 network address because the number of available IPv6 addresses is extremely large.
- The problems that are induced by NAT applications are solved because the IPv6 header improves packet handling by intermediate routers.
- The end-to-end connectivity problems that are caused by NAT are solved because the number of routes increases with the number of nodes that are connected to the Internet.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The large number of public IPv6 addresses eliminates the need for NAT. Sites from the largest enterprises to single households can get public IPv6 network addresses. This avoids some of the NAT-induced application problems that are experienced by applications that require end-to-end connectivity.
-
Which parameter does the router use to choose the path to the destination when there are multiple routes available?
- the lower metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the lower gateway IP address to get to the destination network
- the higher metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the higher gateway IP address to get to the destination network
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a packet arrives at the router interface, the router examines its header to determine the destination network. If there is a route for the destination network in the routing table, the router forwards the packet using that information. If there are two or more possible routes to the same destination, the metric is used to decide which route appears on the routing table. The lower the metric, the better the route.
-
What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The OSI network layer provides several services to allow communication between devices:addressing
encapsulation
routing
de-encapsulation
Error detection, placing frames on the media, and collision detection are all functions of the data ink layer.
-
Within a production network, what is the purpose of configuring a switch with a default gateway address?
- Hosts that are connected to the switch can use the switch default gateway address to forward packets to a remote destination.
- A switch must have a default gateway to be accessible by Telnet and SSH.
- The default gateway address is used to forward packets originating from the switch to remote networks.
- It provides a next-hop address for all traffic that flows through the switch.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A default gateway address allows a switch to forward packets that originate on the switch to remote networks. A default gateway address on a switch does not provide Layer 3 routing for PCs that are connected on that switch. A switch can still be accessible from Telnet as long as the source of the Telnet connection is on the local network.
-
What is a basic characteristic of the IP protocol?
- connectionless
- media dependent
- user data segmentation
- reliable end-to-end delivery
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer protocol that does not require initial exchange of control information to establish an end-to-end connection before packets are forwarded. Thus, IP is connectionless and does not provide reliable end-to-end delivery by itself. IP is media independent. User data segmentation is a service provided at the transport layer.
-
Which field in the IPv4 header is used to prevent a packet from traversing a network endlessly?
- Time-to-Live
- Sequence Number
- Acknowledgment Number
- Differentiated Services
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The value of the Time-to-Live (TTL) field in the IPv4 header is used to limit the lifetime of a packet. The sending host sets the initial TTL value; which is decreased by one each time the packet is processed by a router. If the TTL field decrements to zero, the router discards the packet and sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Time Exceeded message to the source IP address. The Differentiated Services (DS) field is used to determine the priority of each packet. Sequence Number and Acknowledgment Number are two fields in the TCP header.
-
What is one advantage that the IPv6 simplified header offers over IPv4?
- smaller-sized header
- little requirement for processing checksums
- smaller-sized source and destination IP addresses
- efficient packet handling
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The IPv6 simplified header offers several advantages over IPv4:
· Better routing efficiency and efficient packet handling for performance and forwarding-rate scalability
· No requirement for processing checksums
· Simplified and more efficient extension header mechanisms (as opposed to the IPv4 Options field)
· A Flow Label field for per-flow processing with no need to open the transport inner packet to identify the various traffic flows
-
What IPv4 header field identifies the upper layer protocol carried in the packet?
- Protocol
- Identification
- Version
- Differentiated Services
Answers Explanation & Hints:
It is the Protocol field in the IP header that identifies the upper-layer protocol the packet is carrying. The Version field identifies the IP version. The Differential Services field is used for setting packet priority. The Identification field is used to reorder fragmented packets.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 02
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 001
Answers Explanation & Hints:Packets with a destination of 172.17.6.15 are forwarded through Fa0/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.10.5 are forwarded through Fa1/1. Packets with a destination of 172.17.12.10 are forwarded through Fa1/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.14.8 are forwarded through Fa0/1. Because network 172.17.8.0 has no entry in the routing table, it will take the gateway of last resort, which means that packets with a destination of 172.17.8.20 are forwarded through Serial0/0/0. Because a gateway of last resort exists, no packets will be dropped.
-
What information does the loopback test provide?
- The TCP/IP stack on the device is working correctly.
- The device has end-to-end connectivity.
- DHCP is working correctly.
- The Ethernet cable is working correctly.
- The device has the correct IP address on the network.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Because the loopback test sends packets back to the host device, it does not provide information about network connectivity to other hosts. The loopback test verifies that the host NIC, drivers, and TCP/IP stack are functioning.
-
What routing table entry has a next hop address associated with a destination network?
- directly-connected routes
- local routes
- remote routes
- C and L source routes
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Routing table entries for remote routes will have a next hop IP address. The next hop IP address is the address of the router interface of the next device to be used to reach the destination network. Directly-connected and local routes have no next hop, because they do not require going through another router to be reached.
-
How do hosts ensure that their packets are directed to the correct network destination?
- They have to keep their own local routing table that contains a route to the loopback interface, a local network route, and a remote default route.
- They always direct their packets to the default gateway, which will be responsible for the packet delivery.
- They search in their own local routing table for a route to the network destination address and pass this information to the default gateway.
- They send a query packet to the default gateway asking for the best route.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Hosts must maintain their own local routing table to ensure that network layer packets are directed to the correct destination network. This local table typically contains a route to the loopback interface, a route to the network that the host is connected to, and a local default route, which represents the route that packets must take to reach all remote network addresses.
-
When transporting data from real-time applications, such as streaming audio and video, which field in the IPv6 header can be used to inform the routers and switches to maintain the same path for the packets in the same conversation?
- Next Header
- Flow Label
- Traffic Class
- Differentiated Services
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The Flow Label in IPv6 header is a 20-bit field that provides a special service for real-time applications. This field can be used to inform routers and switches to maintain the same path for the packet flow so that packets will not be reordered.
-
What statement describes the function of the Address Resolution Protocol?
- ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on a different network.
- ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on the local network.
- ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on a different network.
- ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on the local network.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a PC wants to send data on the network, it always knows the IP address of the destination. However, it also needs to discover the MAC address of the destination. ARP is the protocol that is used to discover the MAC address of a host that belongs to the same network.
-
Under which two circumstances will a switch flood a frame out of every port except the port that the frame was received on? (Choose two.)
- The frame has the broadcast address as the destination address.
- The destination address is unknown to the switch.
- The source address in the frame header is the broadcast address.
- The source address in the frame is a multicast address.
- The destination address in the frame is a known unicast address.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A switch will flood a frame out of every port, except the one that the frame was received from, under two circumstances. Either the frame has the broadcast address as the destination address, or the destination address is unknown to the switch.
-
Which statement describes the treatment of ARP requests on the local link?
- They must be forwarded by all routers on the local network.
- They are received and processed by every device on the local network.
- They are dropped by all switches on the local network.
- They are received and processed only by the target device.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
One of the negative issues with ARP requests is that they are sent as a broadcast. This means all devices on the local link must receive and process the request.
-
Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame?
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF
- AAAA.AAAA.AAAA
- the physical address of the destination host
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The purpose of an ARP request is to find the MAC address of the destination host on an Ethernet LAN. The ARP process sends a Layer 2 broadcast to all devices on the Ethernet LAN. The frame contains the IP address of the destination and the broadcast MAC address, FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. The host with the IP address that matches the IP address in the ARP request will reply with a unicast frame that includes the MAC address of the host. Thus the original sending host will obtain the destination IP and MAC address pair to continue the encapsulation process for data transmission.
-
A network technician issues the arp -d * command on a PC after the router that is connected to the LAN is reconfigured. What is the result after this command is issued?
- The ARP cache is cleared.
- The current content of the ARP cache is displayed.
- The detailed information of the ARP cache is displayed.
- The ARP cache is synchronized with the router interface.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Issuing the arp –d * command on a PC will clear the ARP cache content. This is helpful when a network technician wants to ensure the cache is populated with updated information.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The exhibit shows a small switched network and the contents of the MAC address table of the switch. PC1 has sent a frame addressed to PC3. What will the switch do with the frame?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 04
- The switch will discard the frame.
- The switch will forward the frame only to port 2.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports except port 4.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports.
- The switch will forward the frame only to ports 1 and 3.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The MAC address of PC3 is not present in the MAC table of the switch. Because the switch does not know where to send the frame that is addressed to PC3, it will forward the frame to all the switch ports, except for port 4, which is the incoming port.
-
Which two types of IPv6 messages are used in place of ARP for address resolution?
- anycast
- broadcast
- echo reply
- echo request
- neighbor solicitation
- neighbor advertisement
Answers Explanation & Hints:
IPv6 does not use ARP. Instead, ICMPv6 neighbor discovery is used by sending neighbor solicitation and neighbor advertisement messages.
-
What is the aim of an ARP spoofing attack?
- to flood the network with ARP reply broadcasts
- to fill switch MAC address tables with bogus addresses
- to associate IP addresses to the wrong MAC address
- to overwhelm network hosts with ARP requests
Answers Explanation & Hints:
In an ARP spoofing attack, a malicious host intercepts ARP requests and replies to them so that network hosts will map an IP address to the MAC address of the malicious host.
-
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 attempts to connect to File_server1 and sends an ARP request to obtain a destination MAC address. Which MAC address will PC1 receive in the ARP reply?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 03
- the MAC address of S1
- the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R1
- the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R2
- the MAC address of S2
- the MAC address of File_server1
Answers Explanation & Hints:
PC1 must have a MAC address to use as a destination Layer 2 address. PC1 will send an ARP request as a broadcast and R1 will send back an ARP reply with its G0/0 interface MAC address. PC1 can then forward the packet to the MAC address of the default gateway, R1.
-
Where are IPv4 address to Layer 2 Ethernet address mappings maintained on a host computer?
- neighbor table
- ARP cache
- routing table
- MAC address table
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The ARP cache is used to store IPv4 addresses and the Ethernet physical addresses or MAC addresses to which the IPv4 addresses are mapped. Incorrect mappings of IP addresses to MAC addresses can result in loss of end-to-end connectivity.
-
What important information is examined in the Ethernet frame header by a Layer 2 device in order to forward the data onward?
- source MAC address
- source IP address
- destination MAC address
- Ethernet type
- destination IP address
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The Layer 2 device, such as a switch, uses the destination MAC address to determine which path (interface or port) should be used to send the data onward to the destination device.
-
Match the commands to the correct actions. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 002
-
A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
- Reboot the device.
- Enter CTRL-Z at the privileged mode prompt.
- Exit global configuration mode.
- Power cycle the device.
- Exit privileged EXEC mode and press Enter.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
While at the privileged mode prompt such as Router#, type exit ,press Enter , and the banner message appears. Power cycling a network device that has had the banner motd command issued will also display the banner message, but this is not a quick way to test the configuration.
-
A network administrator requires access to manage routers and switches locally and remotely. Match the description to the access method. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 003
Answers Explanation & Hints:Both the console and AUX ports can be used to directly connect to a Cisco network device for management purposes. However, it is more common to use the console port. The AUX port is more often used for remote access via a dial up connection. SSH and Telnet are both remote access methods that depend on an active network connection. SSH uses a stronger password authentication than Telnet uses and also uses encryption on transmitted data.
-
Match the phases to the functions during the boot up process of a Cisco router. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 004
Answers Explanation & Hints:There are three major phases to the bootup process of a Cisco router:
- Perform the POST and load the bootstrap program.
- Locate and load the Cisco IOS software.
- Locate and load the startup configuration file
If a startup configuration file cannot be located, the router will enter setup mode by displaying the setup mode prompt.
-
Match the command with the device mode at which the command is entered. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 005
Answers Explanation & Hints:The enable command is entered in R1> mode. The login command is entered in R1(config-line)# mode. The copy running-config startup-config command is entered in R1# mode. The ip address 192.168.4.4 255.255.255.0 command is entered in R1(config-if)# mode. The service password-encryption command is entered in global configuration mode.
-
What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed
- to store the startup configuration file
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
Answers Explanation & Hints:
NVRAM is permanent memory storage, so the startup configuration file is preserved even if the router loses power.
-
A router boots and enters setup mode. What is the reason for this?
- The IOS image is corrupt.
- Cisco IOS is missing from flash memory.
- The configuration file is missing from NVRAM.
- The POST process has detected hardware failure.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
If a router cannot locate the startup-config file in NVRAM, it will enter setup mode to allow the configuration to be entered from the console device.
-
The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A default gateway address is typically configured on all devices to allow them to communicate beyond just their local network.In a switch this is achieved using the command ip default-gateway <ip address>.
-
What happens when the transport input ssh command is entered on the switch vty lines?
- The SSH client on the switch is enabled.
- Communication between the switch and remote users is encrypted.
- The switch requires a username/password combination for remote access.
- The switch requires remote connections via a proprietary client software.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The transport input ssh command when entered on the switch vty (virtual terminal lines) will encrypt all inbound controlled telnet connections.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A user PC has successfully transmitted packets to www.cisco.com. Which IP address does the user PC target in order to forward its data off the local network?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 03
- 172.24.255.17
- 172.24.1.22
- 172.20.0.254
- 172.24.255.4
- 172.20.1.18
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a host sends packets to a destination outside of its local network, the first hop IP address encountered is the default gateway.
-
Match the configuration mode with the command that is available in that mode. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 006
Answers Explanation & Hints:The enable command is entered at the R1> prompt. The login command is entered at the R1(config-line)# prompt. The copy running-config startup-config command is entered at the R1# prompt. The interface fastethernet 0/0 command is entered at the R1(config)# prompt.
-
Which three commands are used to set up secure access to a router through a connection to the console interface? (Choose three.)
- interface fastethernet 0/0
- line vty 0 4
- line console 0
- enable secret cisco
- login
- password cisco
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The three commands needed to password protect the console port are as follows:
line console 0
password cisco
login
The interface fastethernet 0/0 command is commonly used to access the configuration mode used to apply specific parameters such as the IP address to the Fa0/0 port. The line vty 0 4 command is used to access the configuration mode for Telnet. The 0 and 4 parameters specify ports 0 through 4, or a maximum of five simultaneous Telnet connections. The enable secret command is used to apply a password used on the router to access the privileged mode.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address configuration shown from PC1. What is a description of the default gateway address?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 8 – 10 Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 01
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the company to the Internet.
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the PC1 LAN to Router1.
- It is the IP address of Switch1 that connects PC1 to other devices on the same LAN.
- It is the IP address of the ISP network device located in the cloud.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The default gateway is used to route packets destined for remote networks. The default gateway IP address is the address of the first Layer 3 device (the router interface) that connects to the same network.
-
Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet forwarding
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection
- flow control
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A router accepts a packet and accesses its routing table to determine the appropriate exit interface based on the destination address. The router then forwards the packet out of that interface.
-
What is the effect of using the Router# copy running-config startup-config command on a router?
- The contents of ROM will change.
- The contents of RAM will change.
- The contents of NVRAM will change.
- The contents of flash will change.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The command copy running-config startup-config copies the running-configuration file from RAM into NVRAM and saves it as the startup-configuration file. Since NVRAM is none-volatile memory it will be able to retain the configuration details when the router is powered off.
-
What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a host needs to send a message to another host located on the same network, it can forward the message directly. However, when a host needs to send a message to a remote network, it must use the router, also known as the default gateway. This is because the data link frame address of the remote destination host cannot be used directly. Instead, the IP packet has to be sent to the router (default gateway) and the router will forward the packet toward its destination. Therefore, if the default gateway is incorrectly configured, the host can communicate with other hosts on the same network, but not with hosts on remote networks.
-
What are two potential network problems that can result from ARP operation? (Choose two.)
- Manually configuring static ARP associations could facilitate ARP poisoning or MAC address spoofing.
- On large networks with low bandwidth, multiple ARP broadcasts could cause data communication delays.
- Network attackers could manipulate MAC address and IP address mappings in ARP messages with the intent of intercepting network traffic.
- Large numbers of ARP request broadcasts could cause the host MAC address table to overflow and prevent the host from communicating on the network.
- Multiple ARP replies result in the switch MAC address table containing entries that match the MAC addresses of hosts that are connected to the relevant switch port.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Large numbers of ARP broadcast messages could cause momentary data communications delays. Network attackers could manipulate MAC address and IP address mappings in ARP messages with the intent to intercept network traffic. ARP requests and replies cause entries to be made into the ARP table, not the MAC address table. ARP table overflows are very unlikely. Manually configuring static ARP associations is a way to prevent, not facilitate, ARP poisoning and MAC address spoofing. Multiple ARP replies resulting in the switch MAC address table containing entries that match the MAC addresses of connected nodes and are associated with the relevant switch port are required for normal switch frame forwarding operations. It is not an ARP caused network problem.
-
Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which interfaces in each router are active and operational?
- R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/0 - R1: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/1 - R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/0 - R1: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/1Answers Explanation & Hints:The command to use for this activity is show ip interface brief in each router. The active and operational interfaces are represented by the value “up” in the “Status” and “Protocol” columns. The interfaces in R1 with these characteristics are G0/0 and S0/0/0. In R2 they are G0/1 and S0/0/0.
- R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
-
Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to identify the next level protocol?
- protocol
- destination IPv4 address
- source IPv4 address
- TTL
-
Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains an 8-bit binary value used to determine the priority of each packet?
- differentiated services
- destination IPv4 address
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
-
Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a 32-bit binary value associated with an interface on the sending device?
- source IPv4 address
- destination IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
-
Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to detect corruption in the IPv4 header?
- header checksum
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
-
Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a 32-bit binary value associated with an interface on the sending device?
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
- header checksum
-
Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a unicast, multicast, or broadcast address?
- destination IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
- header checksum
-
Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to limit the lifetime of a packet?
- TTL
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- header checksum
-
Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a 4-bit binary value set to 0100?
- version
- source IPv4 address
- protocol
- TTL
-
Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to identify the next level protocol?
- protocol
- version
- differentiated services
- header checksum
-
Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a 4-bit binary value set to 0100?
- version
- differentiated services
- header checksum
- TTL
-
What property of ARP causes cached IP-to-MAC mappings to remain in memory longer?
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
-
What property of ARP allows MAC addresses of frequently used servers to be fixed in the ARP table?
- A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
-
What property of ARP allows MAC addresses of frequently used servers to be fixed in the ARP table?
- A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
-
What property of ARP allows hosts on a LAN to send traffic to remote networks?
- Local hosts learn the MAC address of the default gateway.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
-
What property of ARP allows hosts on a LAN to send traffic to remote networks?
- Local hosts learn the MAC address of the default gateway.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
-
What property of ARP forces all Ethernet NICs to process an ARP request?
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
-
What property of ARP causes a reply only to the source sending an ARP request?
- The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
-
What property of ARP causes the request to be flooded out all ports of a switch except for the port receiving the ARP request?
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
-
What property of ARP causes the NICs receiving an ARP request to pass the data portion of the Ethernet frame to the ARP process?
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
-
What property of ARP causes the NICs receiving an ARP request to pass the data portion of the Ethernet frame to the ARP process?
- The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
-
Main(config)# interface gi0/1
Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Service LAN
Main(config-if)# ip address 172.29.157.156 255.255.255.0
Main(config-if)# no shutdown
Main(config-if)# interface gi0/0
Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Engineering LAN
Main(config-if)# ip address 172.29.156.36 255.255.255.0
Main(config-if)# no shutdown
Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
Main(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
Main(config-if)# ip address 10.156.157.254 255.255.255.0
Main(config-if)# no shutdown
Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
Main(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.177 255.255.255.0
Main(config-if)# no shutdown
Main(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Service LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 172.29.157.156
- 172.29.157.1
- 10.156.157.254
- 198.51.100.177
- 172.29.156.36
-
BldgA(config)# interface gi0/1
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Medical LAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.191.189 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface gi0/0
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Client LAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.190.70 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 10.190.191.254 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.213 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Medical LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.191.189
- 192.168.191.1
- 10.190.191.254
- 198.51.100.213
- 192.168.190.70
-
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN
Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.225.223 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN
Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.224.103 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.224.225.254 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
Floor(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.246 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Registrar LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.225.223
- 192.168.225.1
- 10.224.225.254
- 203.0.113.246
- 192.168.224.103
-
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN
Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.118.63.65 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN
Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.118.62.196 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.62.63.254 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
Floor(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.87 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Manager LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 10.118.62.196
- 10.118.62.1
- 10.62.63.254
- 209.165.200.87
- 10.118.63.65
-
HQ(config)# interface gi0/1
HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Branch LAN
HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.19.99.99 255.255.255.0
HQ(config-if)# no shutdown
HQ(config-if)# interface gi0/0
HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Store LAN
HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.19.98.230 255.255.255.0
HQ(config-if)# no shutdown
HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
HQ(config-if)# ip address 10.98.99.254 255.255.255.0
HQ(config-if)# no shutdown
HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
HQ(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.120 255.255.255.0
HQ(config-if)# no shutdown
HQ(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Store LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 172.19.98.230
- 172.19.98.1
- 10.98.99.254
- 209.165.200.120
- 172.19.99.99
-
HQ(config)# interface gi0/1
HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Branch LAN
HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.20.133.132 255.255.255.0
HQ(config-if)# no shutdown
HQ(config-if)# interface gi0/0
HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Store LAN
HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.20.132.13 255.255.255.0
HQ(config-if)# no shutdown
HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
HQ(config-if)# ip address 10.132.133.254 255.255.255.0
HQ(config-if)# no shutdown
HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
HQ(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.156 255.255.255.0
HQ(config-if)# no shutdown
HQ(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Store LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 172.20.132.13
- 172.20.132.1
- 10.132.133.254
- 198.51.100.156
- 172.20.133.132
-
Main(config)# interface gi0/1
Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Service LAN
Main(config-if)# ip address 192.168.167.166 255.255.255.0
Main(config-if)# no shutdown
Main(config-if)# interface gi0/0
Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Engineering LAN
Main(config-if)# ip address 192.168.166.46 255.255.255.0
Main(config-if)# no shutdown
Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
Main(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
Main(config-if)# ip address 10.166.167.254 255.255.255.0
Main(config-if)# no shutdown
Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
Main(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.189 255.255.255.0
Main(config-if)# no shutdown
Main(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Service LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.167.166
- 192.168.167.1
- 10.166.167.254
- 198.51.100.189
- 192.168.166.46
-
BldgA(config)# interface gi0/1
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Medical LAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.201.200 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface gi0/0
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Client LAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.200.80 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 10.200.201.254 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
BldgA(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.222 255.255.255.0
BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown
BldgA(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Medical LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.201.200
- 192.168.201.1
- 10.200.201.254
- 203.0.113.222
- 192.168.200.80
-
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN
Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.235.234 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN
Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.234.114 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.234.235.254 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
Floor(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.3 255.255.255.0
Floor(config-if)# no shutdown
Floor(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Registrar LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 192.168.235.234
- 192.168.235.1
- 10.234.235.254
- 203.0.113.3
- 192.168.234.114
-
RTR1(config)# interface gi0/1
RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Marketing LAN
RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.27.15.17 255.255.255.0
RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown
RTR1(config-if)# interface gi0/0
RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Payroll LAN
RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.27.14.148 255.255.255.0
RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown
RTR1(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP
RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.14.15.254 255.255.255.0
RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown
RTR1(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN
RTR1(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.39 255.255.255.0
RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown
RTR1(config-if)# endRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Payroll LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
- 10.27.14.148
- 10.27.14.1
- 10.14.15.254
- 203.0.113.39
- 10.27.15.17
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10: Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers 2020
1. Which information is used by routers to forward a data packet toward its destination?
source IP address
destination IP address*
source data-link address
destination data-link address
2. A computer has to send a packet to a destination host in the same LAN. How will the packet be sent?
The packet will be sent to the default gateway first, and then, depending on the response from the gateway, it may be sent to the destination host.
The packet will be sent directly to the destination host.*
The packet will first be sent to the default gateway, and then from the default gateway it will be sent directly to the destination host.
The packet will be sent only to the default gateway.
3. A router receives a packet from the Gigabit 0/0 interface and determines that the packet needs to be forwarded out the Gigabit 0/1 interface. What
will the router do next?
route the packet out the Gigabit 0/1 interface
create a new Layer 2 Ethernet frame to be sent to the destination*
look into the ARP cache to determine the destination IP address
look into the routing table to determine if the destination network is in the routing table
4. Which IPv4 address can a host use to ping the loopback interface?
126.0.0.1
127.0.0.0
126.0.0.0
127.0.0.1*
5. A computer can access devices on the same network but cannot access devices on other networks. What is the probable cause of this problem?
The cable is not connected properly to the NIC.
The computer has an invalid IP address.
The computer has an incorrect subnet mask.
The computer has an invalid default gateway address.*
6. Which statement describes a feature of the IP protocol?
IP encapsulation is modified based on network media.
IP relies on Layer 2 protocols for transmission error control.
MAC addresses are used during the IP packet encapsulation.
IP relies on upper layer services to handle situations of missing or out-of-order packets.*
Explanation: IP protocol is a connection-less protocol, considered unreliable in terms of end-to-end delivery. It does not provide error control in the cases where receiving packets are out-of-order or in cases of missing packets. It relies on upper layer services, such as TCP, to resolve these issues.
7. Why is NAT not needed in IPv6?
Because IPv6 has integrated security, there is no need to hide the IPv6 addresses of internal networks.
Any host or user can get a public IPv6 network address because the number of available IPv6 addresses is extremely large.*
The problems that are induced by NAT applications are solved because the IPv6 header improves packet handling by intermediate routers.
The end-to-end connectivity problems that are caused by NAT are solved because the number of routes increases with the number of nodes that are connected to the Internet.
8. Which parameter does the router use to choose the path to the destination when there are multiple routes available?
the lower metric value that is associated with the destination network*
the lower gateway IP address to get to the destination network
the higher metric value that is associated with the destination network
the higher gateway IP address to get to the destination network
9. What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
performing error detection
routing packets toward the destination*
encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer*
placement of frames on the media
collision detection
Explanation: The OSI network layer provides several services to allow communication between devices:
addressing
encapsulation
routing
de-encapsulation
Error detection, placing frames on the media, and collision detection are all functions of the data ink layer.
10. Within a production network, what is the purpose of configuring a switch with a default gateway address?
Hosts that are connected to the switch can use the switch default gateway address to forward packets to a remote destination.
A switch must have a default gateway to be accessible by Telnet and SSH.
The default gateway address is used to forward packets originating from the switch to remote networks.*
It provides a next-hop address for all traffic that flows through the switch.
Explanation: A default gateway address allows a switch to forward packets that originate on the switch to remote networks. A default gateway address on a switch does not provide Layer 3 routing for PCs that are connected on that switch. A switch can still be accessible from Telnet as long as the source of the Telnet connection is on the local network.
11. What is a basic characteristic of the IP protocol?
Connectionless*
media dependent
user data segmentation
reliable end-to-end delivery
Explanation: Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer protocol that does not require initial exchange of control information to establish an end-to-end connection before packets are forwarded. Thus, IP is connectionless and does not provide reliable end-to-end delivery by itself. IP is media independent. User data segmentation is a service provided at the transport layer.
12. Which field in the IPv4 header is used to prevent a packet from traversing a network endlessly?
Time-to-Live*
Sequence Number
Acknowledgment Number
Differentiated Services
Explanation: The value of the Time-to-Live (TTL) field in the IPv4 header is used to limit the lifetime of a packet. The sending host sets the initial TTL value; which is decreased by one each time the packet is processed by a router. If the TTL field decrements to zero, the router discards the packet and sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Time Exceeded message to the source IP address. The Differentiated Services (DS) field is used to determine the priority of each packet. Sequence Number and Acknowledgment Number are two fields in the TCP header.
13. What is one advantage that the IPv6 simplified header offers over IPv4?
smaller-sized header
little requirement for processing checksums
smaller-sized source and destination IP addresses
efficient packet handling*
Explanation: The IPv6 simplified header offers several advantages over IPv4:
Better routing efficiency and efficient packet handling for performance and forwarding-rate scalability
No requirement for processing checksums
Simplified and more efficient extension header mechanisms (as opposed to the IPv4 Options field)
A Flow Label field for per-flow processing with no need to open the transport inner packet to identify the various traffic flows
14. What IPv4 header field identifies the upper layer protocol carried in the packet?
Protocol*
Identification
Version
Differentiated Services
Explanation: It is the Protocol field in the IP header that identifies the upper-layer protocol the packet is carrying. The Version field identifies the IP version. The Differential Services field is used for setting packet priority. The Identification field is used to reorder fragmented packets.
15. Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p15-1
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p15-2
Explanation: Packets with a destination of 172.17.6.15 are forwarded through Fa0/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.10.5 are forwarded through Fa1/1. Packets with a destination of 172.17.12.10 are forwarded through Fa1/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.14.8 are forwarded through Fa0/1. Because network 172.17.8.0 has no entry in the routing table, it will take the gateway of last resort, which means that packets with a destination of 172.17.8.20 are forwarded through Serial0/0/0. Because a gateway of last resort exists, no packets will be dropped.
16. What information does the loopback test provide?
The TCP/IP stack on the device is working correctly.*
The device has end-to-end connectivity.
DHCP is working correctly.
The Ethernet cable is working correctly.
The device has the correct IP address on the network.
17. What routing table entry has a next hop address associated with a destination network?
directly-connected routes
local routes
remote routes*
C and L source routes
18. How do hosts ensure that their packets are directed to the correct network destination?
They have to keep their own local routing table that contains a route to the loopback interface, a local network route, and a remote default route.*
They always direct their packets to the default gateway, which will be responsible for the packet delivery.
They search in their own local routing table for a route to the network destination address and pass this information to the default gateway.
They send a query packet to the default gateway asking for the best route.
19. When transporting data from real-time applications, such as streaming audio and video, which field in the IPv6 header can be used to inform the routers and switches to maintain the same path for the packets in the same conversation?
Next Header
Flow Label*
Traffic Class
Differentiated Services
Explanation: The Flow Label in IPv6 header is a 20-bit field that provides a special service for real-time applications. This field can be used to inform routers and switches to maintain the same path for the packet flow so that packets will not be reordered.
20. What statement describes the function of the Address Resolution Protocol?
ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on a different network.
ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on the local network.
ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on a different network.
ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on the local network.*
21. Under which two circumstances will a switch flood a frame out of every port except the port that the frame was received on? (Choose two.)
The frame has the broadcast address as the destination address.*
The destination address is unknown to the switch.*
The source address in the frame header is the broadcast address.
The source address in the frame is a multicast address.
The destination address in the frame is a known unicast address.
Explanation: A switch will flood a frame out of every port, except the one that the frame was received from, under two circumstances. Either the frame has the broadcast address as the destination address, or the destination address is unknown to the switch.
22. Which statement describes the treatment of ARP requests on the local link?
They must be forwarded by all routers on the local network.
They are received and processed by every device on the local network.*
They are dropped by all switches on the local network.
They are received and processed only by the target device.
Explanation: One of the negative issues with ARP requests is that they are sent as a broadcast. This means all devices on the local link must receive and process the request.
23. Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame?
0.0.0.0
255.255.255.255
FFFF.FFFF.FFFF*
AAAA.AAAA.AAAA
the physical address of the destination host
Explanation: The purpose of an ARP request is to find the MAC address of the destination host on an Ethernet LAN. The ARP process sends a Layer 2 broadcast to all devices on the Ethernet LAN. The frame contains the IP address of the destination and the broadcast MAC address, FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. The host with the IP address that matches the IP address in the ARP request will reply with a unicast frame that includes the MAC address of the host. Thus the original sending host will obtain the destination IP and MAC address pair to continue the encapsulation process for data transmission.
24. A network technician issues the arp -d * command on a PC after the router that is connected to the LAN is reconfigured. What is the result after this command is issued?
The ARP cache is cleared.*
The current content of the ARP cache is displayed.
The detailed information of the ARP cache is displayed.
The ARP cache is synchronized with the router interface.
Explanation: Issuing the arp –d * command on a PC will clear the ARP cache content. This is helpful when a network technician wants to ensure the cache is populated with updated information.
25. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p25
The exhibit shows a small switched network and the contents of the MAC address table of the switch. PC1 has sent a frame addressed to PC3. What will the switch do with the frame?
The switch will discard the frame.
The switch will forward the frame only to port 2.
The switch will forward the frame to all ports except port 4.*
The switch will forward the frame to all ports.
The switch will forward the frame only to ports 1 and 3.
Explanation: The MAC address of PC3 is not present in the MAC table of the switch. Because the switch does not know where to send the frame that is addressed to PC3, it will forward the frame to all the switch ports, except for port 4, which is the incoming port.
26. Which two types of IPv6 messages are used in place of ARP for address resolution?
anycast
broadcast
echo reply
echo request
neighbor solicitation*
neighbor advertisement*
Explanation: IPv6 does not use ARP. Instead, ICMPv6 neighbor discovery is used by sending neighbor solicitation and neighbor advertisement messages.
27. What is the aim of an ARP spoofing attack?
to flood the network with ARP reply broadcasts
to fill switch MAC address tables with bogus addresses
to associate IP addresses to the wrong MAC address*
to overwhelm network hosts with ARP requests
28. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p28
PC1 attempts to connect to File_server1 and sends an ARP request to obtain a destination MAC address. Which MAC address will PC1 receive in the ARP reply?
the MAC address of S1
the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R1*
the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R2
the MAC address of S2
the MAC address of File_server1
29. Where are IPv4 address to Layer 2 Ethernet address mappings maintained on a host computer?
neighbor table
ARP cache*
routing table
MAC address table
30. What important information is examined in the Ethernet frame header by a Layer 2 device in order to forward the data onward?
source MAC address
source IP address
destination MAC address*
Ethernet type
destination IP address
Explanation: The Layer 2 device, such as a switch, uses the destination MAC address to determine which path (interface or port) should be used to send the data onward to the destination device.
31. Match the commands to the correct actions. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p31
32. A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
Reboot the device.
Enter CTRL-Z at the privileged mode prompt.
Exit global configuration mode.
Power cycle the device.
Exit privileged EXEC mode and press Enter.*
Explanation: While at the privileged mode prompt such as Router#, type exit,press Enter, and the banner message appears. Power cycling a network device that has had the banner motd command issued will also display the banner message, but this is not a quick way to test the configuration.
33. A network administrator requires access to manage routers and switches locally and remotely. Match the description to the access method. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p33
Explanation: Both the console and AUX ports can be used to directly connect to a Cisco network device for management purposes. However, it is more common to use the console port. The AUX port is more often used for remote access via a dial up connection. SSH and Telnet are both remote access methods that depend on an active network connection. SSH uses a stronger password authentication than Telnet uses and also uses encryption on transmitted data.
34. Match the phases to the functions during the boot up process of a Cisco router. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p34
Explanation: There are three major phases to the bootup process of a Cisco router:
1. Perform the POST and load the bootstrap program.
2. Locate and load the Cisco IOS software.
3. Locate and load the startup configuration file
If a startup configuration file cannot be located, the router will enter setup mode by displaying the setup mode prompt.
35. Match the command with the device mode at which the command is entered. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p35
Explanation: The enable command is entered in R1> mode. The login command is entered in R1(config-line)# mode. The copy running-config startup-config command is entered in R1# mode. The ip address 192.168.4.4 255.255.255.0 command is entered in R1(config-if)# mode. The service password-encryption command is entered in global configuration mode.
36. What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
to store the routing table
to retain contents when power is removed*
to store the startup configuration file*
to contain the running configuration file
to store the ARP table
Explanation: NVRAM is permanent memory storage, so the startup configuration file is preserved even if the router loses power.
37. A router boots and enters setup mode. What is the reason for this?
The IOS image is corrupt.
Cisco IOS is missing from flash memory.
The configuration file is missing from NVRAM.*
The POST process has detected hardware failure.
38. The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.*
The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
Explanation: A default gateway address is typically configured on all devices to allow them to communicate beyond just their local network.In a switch this is achieved using the command ip default-gateway .
39. What happens when the transport input ssh command is entered on the switch vty lines?
The SSH client on the switch is enabled.
Communication between the switch and remote users is encrypted.*
The switch requires a username/password combination for remote access.
The switch requires remote connections via a proprietary client software.
Explanation: The transport input ssh command when entered on the switch vty (virtual terminal lines) will encrypt all inbound controlled telnet connections.
40. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p40
A user PC has successfully transmitted packets to www.cisco.com. Which IP address does the user PC target in order to forward its data off the local network?
172.24.255.17
172.24.1.22
172.20.0.254*
172.24.255.4
172.20.1.18
41. Match the configuration mode with the command that is available in that mode. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p41
Explanation: The enable command is entered at the R1> prompt. The login command is entered at the R1(config-line)# prompt. The copy running-config startup-config command is entered at the R1# prompt. The interface fastethernet 0/0 command is entered at the R1(config)# prompt.
42. Which three commands are used to set up secure access to a router through a connection to the console interface? (Choose three.)
interface fastethernet 0/0
line vty 0 4
line console 0*
enable secret cisco
login*
password cisco*
Explanation: The three commands needed to password protect the console port are as follows:
line console 0
password cisco
login
The interface fastethernet 0/0 command is commonly used to access the configuration mode used to apply specific parameters such as the IP address to the Fa0/0 port. The line vty 0 4 command is used to access the configuration mode for Telnet. The0and 4 parameters specify ports 0 through 4, or a maximum of five simultaneous Telnet connections. The enable secret command is used to apply a password used on the router to access the privileged mode.
43. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p43
Consider the IP address configuration shown from PC1. What is a description of the default gateway address?
It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the company to the Internet.
It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the PC1 LAN to Router1.*
It is the IP address of Switch1 that connects PC1 to other devices on the same LAN.
It is the IP address of the ISP network device located in the cloud.
44. Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
packet forwarding*
microsegmentation
domain name resolution
path selection*
flow control
Explanation: A router accepts a packet and accesses its routing table to determine the appropriate exit interface based on the destination address. The router then forwards the packet out of that interface.
45. What is the effect of using the Router# copy running-config startup-config command on a router?
The contents of ROM will change.
The contents of RAM will change.
The contents of NVRAM will change.*
The contents of flash will change.
Explanation: The command copy running-config startup-config copies the running-configuration file from RAM into NVRAM and saves it as the startup-configuration file. Since NVRAM is none-volatile memory it will be able to retain the configuration details when the router is powered off.
46. What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.*
A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
Explanation: When a host needs to send a message to another host located on the same network, it can forward the message directly. However, when a host needs to send a message to a remote network, it must use the router, also known as the default gateway. This is because the data link frame address of the remote destination host cannot be used directly. Instead, the IP packet has to be sent to the router (default gateway) and the router will forward the packet toward its destination. Therefore, if the default gateway is incorrectly configured, the host can communicate with other hosts on the same network, but not with hosts on remote networks.
47. What are two potential network problems that can result from ARP operation? (Choose two.)
Manually configuring static ARP associations could facilitate ARP poisoning or MAC address spoofing.
On large networks with low bandwidth, multiple ARP broadcasts could cause data communication delays.*
Network attackers could manipulate MAC address and IP address mappings in ARP messages with the intent of intercepting network traffic.*
Large numbers of ARP request broadcasts could cause the host MAC address table to overflow and prevent the host from communicating on the network.
Multiple ARP replies result in the switch MAC address table containing entries that match the MAC addresses of hosts that are connected to the relevant switch port.
Explanation: Large numbers of ARP broadcast messages could cause momentary data communications delays. Network attackers could manipulate MAC address and IP address mappings in ARP messages with the intent to intercept network traffic. ARP requests and replies cause entries to be made into the ARP table, not the MAC address table. ARP table overflows are very unlikely. Manually configuring static ARP associations is a way to prevent, not facilitate, ARP poisoning and MAC address spoofing. Multiple ARP replies resulting in the switch MAC address table containing entries that match the MAC addresses of connected nodes and are associated with the relevant switch port are required for normal switch frame forwarding operations. It is not an ARP caused network problem.
48. Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which interfaces in each router are active and operational?
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R1: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/0**
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/1
Explanation: The command to use for this activity is show ip interface brief in each router. The active and operational interfaces are represented by the value “up” in the “Status” and “Protocol” columns. The interfaces in R1 with these characteristics are G0/0 and S0/0/0. In R2 they are G0/1 and S0/0/0.
49. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to identify the next level protocol?
Protocol*
destination IPv4 address
source IPv4 address
TTL
50. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains an 8-bit binary value used to determine the priority of each packet?
differentiated services*
destination IPv4 address
source IPv4 address
protocol
51. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a 32-bit binary value associated with an interface on the sending device?
source IPv4 address*
destination IPv4 address
protocol
TTL
52. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to detect corruption in the IPv4 header?
header checksum*
source IPv4 address
protocol
TTL
53.
RTR1(config)# interface gi0/1 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Marketing LAN RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.27.15.17 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# interface gi0/0 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Payroll LAN RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.27.14.148 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP RTR1(config-if)# ip address 10.14.15.254 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 RTR1(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN RTR1(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.39 255.255.255.0 RTR1(config-if)# no shutdown RTR1(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Payroll LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
10.27.14.148*
10.27.14.1
10.14.15.254
203.0.113.39
10.27.15.17
54. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a unicast, multicast, or broadcast address?
destination IPv4 address*
protocol
TTL
header checksum
55. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to limit the lifetime of a packet?
TTL*
source IPv4 address
protocol
header checksum
56. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a 4-bit binary value set to 0100?
Versión*
source IPv4 address
protocol
TTL
57. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header used to identify the next level protocol?
Protocol*
version
differentiated services
header checksum
58. Which term describes a field in the IPv4 packet header that contains a 4-bit binary value set to 0100?
Versión*
differentiated services
header checksum
TTL
59. What property of ARP causes cached IP-to-MAC mappings to remain in memory longer?
Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.*
A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.
The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
60. What property of ARP allows MAC addresses of frequently used servers to be fixed in the ARP table?
A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.*
Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
61. What property of ARP allows MAC addresses of frequently used servers to be fixed in the ARP table?
A static IP-to-MAC address entry can be entered manually into an ARP table.*
The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
62. What property of ARP allows hosts on a LAN to send traffic to remote networks?
Local hosts learn the MAC address of the default gateway.*
The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
63.
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.235.234 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.234.114 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.234.235.254 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.3 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Registrar LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
192.168.235.234*
192.168.235.1
10.234.235.254
203.0.113.3
192.168.234.114
64. What property of ARP forces all Ethernet NICs to process an ARP request?
The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.*
The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
65. What property of ARP causes a reply only to the source sending an ARP request?
The source MAC address appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.*
The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
66. What property of ARP causes the request to be flooded out all ports of a switch except for the port receiving the ARP request?
The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.*
The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
67. What property of ARP causes the NICs receiving an ARP request to pass the data portion of the Ethernet frame to the ARP process?
The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.*
The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
ARP replies are broadcast on the network when a host receives an ARP request.
68. What property of ARP causes the NICs receiving an ARP request to pass the data portion of the Ethernet frame to the ARP process?
The type field 0x806 appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.*
The destination MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF appears in the header of the Ethernet frame.
Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
The port-to-MAC address table on a switch has the same entries as the ARP table on the switch.
69.
Main(config)# interface gi0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Service LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 172.29.157.156 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Engineering LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 172.29.156.36 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Main(config-if)# ip address 10.156.157.254 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Main(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.177 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Service LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
172.29.157.156*
172.29.157.1
10.156.157.254
198.51.100.177
172.29.156.36
70.
BldgA(config)# interface gi0/1 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Medical LAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.191.189 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface gi0/0 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Client LAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.190.70 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP BldgA(config-if)# ip address 10.190.191.254 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.213 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Medical LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
192.168.191.189*
192.168.191.1
10.190.191.254
198.51.100.213
192.168.190.70
71.
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.225.223 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 192.168.224.103 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.224.225.254 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.246 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Registrar LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
192.168.225.223*
192.168.225.1
10.224.225.254
203.0.113.246
192.168.224.103
72.
Floor(config)# interface gi0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Registrar LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.118.63.65 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Manager LAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.118.62.196 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Floor(config-if)# ip address 10.62.63.254 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Floor(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Floor(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.87 255.255.255.0 Floor(config-if)# no shutdown Floor(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Manager LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
10.118.62.196*
10.118.62.1
10.62.63.254
209.165.200.87
10.118.63.65
73.
HQ(config)# interface gi0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Branch LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.19.99.99 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface gi0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Store LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.19.98.230 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP HQ(config-if)# ip address 10.98.99.254 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.120 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Store LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
172.19.98.230*
172.19.98.1
10.98.99.254
209.165.200.120
172.19.99.99
74.
HQ(config)# interface gi0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Branch LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.20.133.132 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface gi0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Store LAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 172.20.132.13 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP HQ(config-if)# ip address 10.132.133.254 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 HQ(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN HQ(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.156 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Store LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
172.20.132.13*
172.20.132.1
10.132.133.254
198.51.100.156
172.20.133.132
75.
Main(config)# interface gi0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Service LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 192.168.167.166 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface gi0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Engineering LAN Main(config-if)# ip address 192.168.166.46 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP Main(config-if)# ip address 10.166.167.254 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 Main(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN Main(config-if)# ip address 198.51.100.189 255.255.255.0 Main(config-if)# no shutdown Main(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Service LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
192.168.167.166*
192.168.167.1
10.166.167.254
198.51.100.189
192.168.166.46
76.
BldgA(config)# interface gi0/1 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Medical LAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.201.200 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface gi0/0 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Client LAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.200.80 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/0 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the ISP BldgA(config-if)# ip address 10.200.201.254 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 BldgA(config-if)# description Connects to the Head Office WAN BldgA(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.222 255.255.255.0 BldgA(config-if)# no shutdown BldgA(config-if)# end
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is connecting a new host to the Medical LAN. The host needs to communicate with remote networks. What IP address would be configured as the default gateway on the new host?
192.168.201.200*
192.168.201.1
10.200.201.254
203.0.113.222
192.168.200.80
77. Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
CCNA 1 v7.0 Modules 8 – 10 Exam Answers p77
Which interfaces in each router are active and operational?
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R1: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/1**
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/0
R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/0
CCNA1 v7 – ITN – Modules 8 – 10: Communicating Between Networks Exam Answers (Additional)
1. Which information is used by routers to forward a data packet toward its destination?
source IP address
destination IP address*
source data-link address
destination data-link address
2. A computer has to send a packet to a destination host in the same LAN. How will the packet be sent?
The packet will be sent to the default gateway first, and then, depending on the response from the gateway, it may be sent to the destination host.
The packet will be sent directly to the destination host.*
The packet will first be sent to the default gateway, and then from the default gateway it will be sent directly to the destination host.
The packet will be sent only to the default gateway.
3. A router receives a packet from the Gigabit 0/0 interface and determines that the packet needs to be forwarded out the Gigabit 0/1 interface. What will the router do next?
route the packet out the Gigabit 0/1 interface
create a new Layer 2 Ethernet frame to be sent to the destination*
look into the ARP cache to determine the destination IP address
look into the routing table to determine if the destination network is in the routing table
4. Which IPv4 address can a host use to ping the loopback interface?
126.0.0.1
127.0.0.0
126.0.0.0
127.0.0.1*
5. When a connectionless protocol is in use at a lower layer of the OSI model, how is missing data detected and retransmitted if necessary?
Connectionless acknowledgements are used to request retransmission.
Upper-layer connection-oriented protocols keep track of the data received and can request retransmission from the upper-level protocols on the sending host.*
Network layer IP protocols manage the communication sessions if connection-oriented transport services are not available.
The best-effort delivery process guarantees that all packets that are sent are received.
6. What was the reason for the creation and implementation of IPv6?
to make reading a 32-bit address easier
to relieve IPv4 address depletion*
to provide more address space in the Internet Names Registry
to allow NAT support for private addressing
7. Which statement accurately describes a characteristic of IPv4?
All IPv4 addresses are assignable to hosts.
IPv4 has a 32-bit address space.*
An IPv4 header has fewer fields than an IPv6 header has.
IPv4 natively supports IPsec.
8. Which field in an IPv4 packet header will typically stay the same during its transmission?
Flag
Time-to-Live
Packet Length
Destination Address*
9. When a router receives a packet, what information must be examined in order for the packet to be forwarded to a remote destination?
destination MAC address
source IP address
destination IP address*
source MAC address
10. Which field in an IPv6 packet is used by the router to determine if a packet has expired and should be dropped?
TTL
Hop Limit*
Address Unreachable
No Route to Destination
11. Which command can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table?
netstat –s
show ip route
netstat –r*
tracert
12. What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
source and destination MAC
source and destination application protocol
source and destination port number
source and destination IP address*
13. How does the network layer use the MTU value?
The network layer depends on the higher level layers to determine the MTU.
The network layer depends on the data link layer to set the MTU, and adjusts the speed of transmission to accommodate it.
The MTU is passed to the network layer by the data link layer.*
To increase speed of delivery, the network layer ignores the MTU.
14. Which characteristic describes an IPv6 enhancement over IPv4?
IPv6 addresses are based on 128-bit flat addressing as opposed to IPv4 which is based on 32-bit hierarchical addressing.
The IPv6 header is simpler than the IPv4 header is, which improves packet handling.*
Both IPv4 and IPv6 support authentication, but only IPv6 supports privacy capabilities.
The IPv6 address space is four times bigger than the IPv4 address space.
15. When an IP packet is sent to a host on a remote network, what information is provided by ARP?
the IP address of the destination host
the IP address of the default gateway
the MAC address of the router interface closest to the sending host*
the MAC address of the switch port that connects to the sending host
16. How does the ARP process use an IP address?
to determine the MAC address of the remote destination host
to determine the MAC address of a device on the same network*
to determine the amount of time a packet takes when traveling from source to destination
to determine the network number based on the number of bits in the IP address
17. The ARP table in a switch maps which two types of address together?
Layer 3 address to a Layer 2 address*
Layer 3 address to a Layer 4 address
Layer 4 address to a Layer 2 address
Layer 2 address to a Layer 4 address
18. What is one function of the ARP protocol?
obtaining an IPv4 address automatically
mapping a domain name to its IP address
resolving an IPv4 address to a MAC address*
maintaining a table of domain names with their resolved IP addresses
19. Which router component holds the routing table, ARP cache, and running configuration file?
RAM*
Flash
NVRAM
ROM
20. What type of information is contained in an ARP table?
switch ports associated with destination MAC addresses
domain name to IP address mappings
routes to reach destination networks
IP address to MAC address mappings*
21. A PC is configured to obtain an IP address automatically from network 192.168.1.0/24. The network administrator issues the arp –a command and notices an entry of 192.168.1.255 ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff. Which statement describes this entry?
This is a static map entry.*
This is a dynamic map entry.
This entry refers to the PC itself.
This entry maps to the default gateway.
22. A cybersecurity analyst believes an attacker is spoofing the MAC address of the default gateway to perform a man-in-the-middle attack. Which command should the analyst use to view the MAC address a host is using to reach the default gateway?
ipconfig /all
route print
netstat -r
arp –a*
23. What is a function of ARP?
resolving MAC addresses to IPv4 addresses
resolving port addresses to MAC addresses
resolving MAC addresses to port addresses
resolving IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses*
24. What is the purpose of ARP in an IPv4 network?
to forward data onward based on the destination IP address
to obtain a specific MAC address when an IP address is known*
to forward data onward based on the destination MAC address.
to build the MAC address table in a switch from the information that is gathered
25. Which action is taken by a Layer 2 switch when it receives a Layer 2 broadcast frame?
It drops the frame.
It sends the frame to all ports except the port on which it received the frame.*
It sends the frame to all ports that are registered to forward broadcasts.
It sends the frame to all ports.
26. Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame?
0.0.0.0
255.255.255.255
FFFF.FFFF.FFFF*
127.0.0.1
01-00-5E-00-AA-23
27. What addresses are mapped by ARP?
destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address*
destination IPv4 address to the source MAC address
destination IPv4 address to the destination host name
destination MAC address to the source IPv4 address
28. What will a Layer 2 switch do when the destination MAC address of a received frame is not in the MAC table?
It initiates an ARP request.
It broadcasts the frame out of all ports on the switch.
It notifies the sending host that the frame cannot be delivered.
It forwards the frame out of all ports except for the port at which the frame was received.*
29. Which two ICMPv6 messages are used during the Ethernet MAC address resolution process? (Choose two.)
router solicitation
router advertisement
neighbor solicitation*
neighbor advertisement*
echo request
30. A router boots and enters setup mode. What is the reason for this?
The IOS image is corrupt.
Cisco IOS is missing from flash memory.
The configuration file is missing from NVRAM.*
The POST process has detected hardware failure.
31. Which command is used to encrypt all passwords in a router configuration file?
Router_A (config) # enable secret
Router_A (config) # service password-encryption*
Router_A (config) # enable password
Router_A (config) # encrypt password
32. Company policy requires using the most secure method to safeguard access to the privileged exec and configuration mode on the routers. The privileged exec password is trustknow1. Which of the following router commands achieves the goal of providing the highest level of security?
secret password trustknow1
enable password trustknow1
service password-encryption
enable secret trustknow1*
33. What will be the response from the router after the command, “router(config)# hostname portsmouth” is entered?
portsmouth#
portsmouth(config)#*
invalid input detected
router(config-host)#
hostname = portsmouth
portsmouth#
? command not recognized
router(config)#
34. An administrator is configuring a new router to permit out-of-band management access. Which set of commands will allow the required login using a password of cisco?
Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)# password manage
Router(config-line)# exit
Router(config)# enable password cisco
Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)# password cisco
Router(config-line)# login
Router(config)# line console 0
Router(config-line)# password cisco
Router(config-line)# login***
Router(config)# line console 0
Router(config-line)# password cisco
Router(config-line)# exit
Router(config)# service password-encryption
35. Which command can be used on a Cisco router to display all interfaces, the IPv4 address assigned, and the current status?
show ip interface brief*
ping
show ip route
show interface fa0/1
36. Which CLI mode allows users to access all device commands, such as those used for configuration, management, and troubleshooting?
user EXEC mode
privileged EXEC mode*
global configuration mode
interface configuration mode
37. What is the purpose of the startup configuration file on a Cisco router?
to facilitate the basic operation of the hardware components of a device
to contain the commands that are used to initially configure a router on startup*
to contain the configuration commands that the router IOS is currently using
to provide a limited backup version of the IOS, in case the router cannot load the full featured IOS
38. Which characteristic describes the default gateway of a host computer?
the logical address of the router interface on the same network as the host computer*
the physical address of the switch interface connected to the host computer
the physical address of the router interface on the same network as the host computer
the logical address assigned to the switch interface connected to the router
39. What is the purpose of the banner motd command?
It configures a message that will identify printed documents to LAN users.
It is a way that routers communicate the status of their links with one another.
It provides an easy way of communicating with any user attached to a router’s LANs.
It provides a way to make announcements to those who log in to a router.*
40. A technician is configuring a router to allow for all forms of management access. As part of each different type of access, the technician is trying to type the command login. Which configuration mode should be entered to do this task?
user executive mode
global configuration mode
any line configuration mode*
privileged EXEC mode
41. What is stored in the NVRAM of a Cisco router?
the Cisco IOS
the running configuration
the bootup instructions
the startup configuration*
42. Which statement regarding the service password-encryption command is true?
It is configured in privileged EXEC mode.
It encrypts only line mode passwords.
As soon as the service password-encryption command is entered, all currently set passwords formerly displayed in plain text are encrypted.*
To see the passwords encrypted by the service password-encryption command in plain text, issue the no service password-encryption command.
Подборка по базе: Контрольная работа _Разделительные вопросы_ (1).doc, Самые популярные вопросы о Чичикове из поэмы.docx, Примерные вопросы к дифференцированному зачету_Психология общени, Политология. Ответы на тест 1.pdf, Тестовые вопросы к разделу 5_ просмотр попытки.pdf, ОИ рк1 ответы.pdf, Тестовые вопросы к разделу 8_ просмотр попытки.pdf, Экзамен вопросы СП ОМ_англ_ok.docx, 2.2 Вопросы к экзамену Смета+Финансы.docx, РК-1 вопросы каз, русс 1 курс.docx
Обратитесь к выставке.Сопоставьте пакеты с их IP-адресом назначения с выходными интерфейсами на маршрутизаторе. (Не все мишени используются.)


| Ответы, объяснения и подсказки:
Пакеты с адресом 172.17.6.15 пересылаются через Fa0 / 0. Пакеты с адресатом 172.17.10.5 пересылаются через Fa1 / 1. Пакеты с адресом 172.17.12.10 пересылаются через Fa1 / 0. Пакеты с адресом 172.17.14.8 пересылаются через Fa0 / 1. Поскольку сеть 172.17.8.0 не имеет записи в таблице маршрутизации, она будет использовать шлюз последней инстанции, что означает, что пакеты с адресом 172.17.8.20 пересылаются через Serial0 / 0/0. Поскольку существует шлюз последней инстанции, пакеты не отбрасываются. |
- Какую информацию предоставляет петлевой тест?
- Стек TCP / IP на устройстве работает правильно.
- Устройство имеет сквозное соединение.
- DHCP работает правильно.
- Кабель Ethernet работает правильно.
- Устройство имеет правильный IP-адрес в сети.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Поскольку тест обратной связи отправляет пакеты обратно на хост-устройство, он не предоставляет информацию о сетевом подключении к другим хостам. Тест обратной петли проверяет, что сетевая карта хоста, драйверы и стек TCP / IP работают.
- Какая запись таблицы маршрутизации имеет адрес следующего перехода, связанный с сетью назначения?
- маршруты с прямым подключением
- местные маршруты
- удаленные маршруты
- Исходные маршруты C и L
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Записи таблицы маршрутизации для удаленных маршрутов будут иметь IP-адрес следующего перехода. IP-адрес следующего перехода — это адрес интерфейса маршрутизатора следующего устройства, которое будет использоваться для доступа к сети назначения. Прямые и локальные маршруты не имеют следующего перехода, потому что для их достижения не требуется прохождение через другой маршрутизатор.
- Как хосты гарантируют, что их пакеты направляются в правильное сетевое назначение?
- Они должны вести свою собственную локальную таблицу маршрутизации, которая содержит маршрут к интерфейсу обратной связи, локальный сетевой маршрут и удаленный маршрут по умолчанию.
- Они всегда направляют свои пакеты на шлюз по умолчанию, который будет отвечать за доставку пакетов.
- Они ищут в своей локальной таблице маршрутизации маршрут к сетевому адресу назначения и передают эту информацию на шлюз по умолчанию.
- Они отправляют пакет запроса на шлюз по умолчанию, запрашивая лучший маршрут.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Хосты должны поддерживать свою собственную локальную таблицу маршрутизации, чтобы гарантировать, что пакеты сетевого уровня направляются в правильную сеть назначения. Эта локальная таблица обычно содержит маршрут к интерфейсу обратной связи, маршрут к сети, к которой подключен хост, и локальный маршрут по умолчанию, который представляет маршрут, по которому пакеты должны достичь всех удаленных сетевых адресов.
- При транспортировке данных из приложений реального времени, таких как потоковое аудио и видео, какое поле в заголовке IPv6 можно использовать для информирования маршрутизаторов и коммутаторов, чтобы они поддерживали один и тот же путь для пакетов в одном разговоре?
- Следующий заголовок
- Этикетка потока
- Класс трафика
- Дифференцированные услуги
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Метка потока в заголовке IPv6 — это 20-битное поле, которое предоставляет специальный сервис для приложений реального времени. Это поле можно использовать для информирования маршрутизаторов и коммутаторов, чтобы они поддерживали один и тот же путь для потока пакетов, чтобы пакеты не переупорядочивались.
- Какое утверждение описывает функцию протокола разрешения адресов?
- ARP используется для обнаружения IP-адреса любого хоста в другой сети.
- ARP используется для обнаружения IP-адреса любого хоста в локальной сети.
- ARP используется для обнаружения MAC-адреса любого хоста в другой сети.
- ARP используется для обнаружения MAC-адреса любого хоста в локальной сети.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Когда ПК хочет отправить данные по сети, он всегда знает IP-адрес места назначения. Однако ему также необходимо узнать MAC-адрес места назначения. ARP — это протокол, который используется для обнаружения MAC-адреса хоста, принадлежащего той же сети.
- При каких двух обстоятельствах коммутатор будет рассылать фрейм из каждого порта, кроме порта, на который фрейм был получен? (Выберите два.)
- Кадр имеет широковещательный адрес в качестве адреса назначения.
- Адрес назначения неизвестен коммутатору.
- Исходный адрес в заголовке кадра — это широковещательный адрес.
- Исходный адрес в кадре — это адрес многоадресной рассылки.
- Адрес назначения в кадре — это известный одноадресный адрес.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Коммутатор будет рассылать фрейм из каждого порта, кроме того, от которого фрейм был получен, в двух случаях. Либо кадр имеет широковещательный адрес в качестве адреса назначения, либо адрес назначения неизвестен коммутатору.
- В каком утверждении описывается обработка запросов ARP по локальной ссылке?
- Они должны пересылаться всеми маршрутизаторами в локальной сети.
- Они принимаются и обрабатываются каждым устройством в локальной сети.
- Они сбрасываются всеми коммутаторами в локальной сети.
- Их принимает и обрабатывает только целевое устройство.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Одна из отрицательных проблем с запросами ARP заключается в том, что они отправляются в виде широковещательной рассылки. Это означает, что все устройства на локальном канале должны получить и обработать запрос.
- Какой адрес назначения используется в кадре запроса ARP?
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF
- AAAA.AAAA.AAAA
- физический адрес хоста назначения
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Цель запроса ARP — найти MAC-адрес целевого хоста в локальной сети Ethernet. Процесс ARP отправляет широковещательную рассылку уровня 2 всем устройствам в локальной сети Ethernet. Кадр содержит IP-адрес пункта назначения и широковещательный MAC-адрес FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. Хост с IP-адресом, который соответствует IP-адресу в запросе ARP, ответит одноадресным кадром, который включает MAC-адрес хоста. Таким образом, исходный хост-отправитель получит пару IP-адресов и MAC-адресов назначения, чтобы продолжить процесс инкапсуляции для передачи данных.
- Сетевой специалист вводит команду arp —d * на ПК после перенастройки маршрутизатора, подключенного к локальной сети. Каков результат после выполнения этой команды?
- Кэш ARP очищен.
- Отображается текущее содержимое кэша ARP.
- Отображается подробная информация о кэше ARP.
- Кэш ARP синхронизируется с интерфейсом маршрутизатора.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Выполнение команды arp –d * на ПК очистит содержимое кэша ARP. Это полезно, когда технический специалист по сети хочет убедиться, что кэш заполнен обновленной информацией.
- Обратитесь к выставке.На выставке показана небольшая коммутируемая сеть и содержимое таблицы MAC-адресов коммутатора.ПК1 отправил кадр, адресованный ПК3.Что переключатель будет делать с рамкой?

- Коммутатор отбросит рамку.
- Коммутатор будет пересылать кадр только на порт 2.
- Коммутатор перенаправит кадр на все порты, кроме порта 4.
- Коммутатор направит кадр на все порты.
- Коммутатор будет пересылать фрейм только на порты 1 и 3.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: MAC-адрес ПК3 отсутствует в таблице MAC-адресов коммутатора. Поскольку коммутатор не знает, куда отправить кадр, адресованный ПК3, он пересылает кадр на все порты коммутатора, за исключением порта 4, который является входящим портом.
- Какие два типа сообщений IPv6 используются вместо ARP для разрешения адресов?
- Anycast
- транслировать
- эхо-ответ
- эхо-запрос
- ходатайство соседа
- реклама соседа
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: IPv6 не использует ARP. Вместо этого используется обнаружение соседей ICMPv6 путем отправки сообщений запроса соседей и объявления соседей.
- Какова цель атаки с подменой ARP?
- залить сеть ответными широковещательными сообщениями ARP
- для заполнения таблиц MAC-адресов коммутатора фиктивными адресами
- связать IP-адреса с неправильным MAC-адресом
- чтобы завалить сетевые узлы запросами ARP
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: При атаке с подменой ARP злонамеренный хост перехватывает запросы ARP и отвечает на них, чтобы сетевые хосты сопоставляли IP-адрес с MAC-адресом вредоносного хоста.
- Обратитесь к выставке.ПК1 пытается подключиться к File_server1 и отправляет запрос ARP для получения MAC-адреса назначения. Какой MAC-адрес получит ПК1 в ответе ARP?

- MAC-адрес S1
- MAC-адрес интерфейса G0 / 0 на R1
- MAC-адрес интерфейса G0 / 0 на R2
- MAC-адрес S2
- MAC-адрес File_server1
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: ПК1 должен иметь MAC-адрес для использования в качестве адреса назначения уровня 2. ПК1 отправит запрос ARP в виде широковещательной рассылки, а маршрутизатор R1 отправит обратно ответ ARP со своим MAC-адресом интерфейса G0 / 0. Затем ПК1 может переслать пакет на MAC-адрес шлюза по умолчанию, R1.
- Где на главном компьютере поддерживаются сопоставления адресов IPv4 и Ethernet уровня 2?
- таблица соседей
- Кеш ARP
- таблица маршрутизации
- Таблица MAC-адресов
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Кэш ARP используется для хранения адресов IPv4 и физических адресов Ethernet или MAC-адресов, которым сопоставлены адреса IPv4. Неправильное сопоставление IP-адресов с MAC-адресами может привести к потере сквозного подключения.
- Какая важная информация проверяется в заголовке кадра Ethernet устройством уровня 2 для пересылки данных вперед?
- исходный MAC-адрес
- исходный IP-адрес
- MAC-адрес назначения
- Тип Ethernet
- IP-адрес получателя
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Устройство уровня 2, такое как коммутатор, использует MAC-адрес назначения, чтобы определить, какой путь (интерфейс или порт) следует использовать для отправки данных на устройство назначения.
- Сопоставьте команды с правильными действиями. (Не все варианты используются.)

- Нового сетевого администратора попросили ввести баннерное сообщение на устройстве Cisco.Как сетевой администратор может быстрее всего проверить, правильно ли настроен баннер?
- Перезагрузите устройство.
- Введите CTRL-Z в приглашении привилегированного режима.
- Выйдите из режима глобальной конфигурации.
- Выключите и снова включите устройство.
- Выйдите из привилегированного режима EXEC и нажмите Enter.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: В приглашении привилегированного режима, таком как Router #, введите exit, нажмите Enter, появится баннерное сообщение. При включении и выключении питания сетевого устройства, для которого была введена команда banner motd, также будет отображаться баннерное сообщение, но это не быстрый способ проверить конфигурацию.
- Сетевому администратору требуется доступ для управления маршрутизаторами и коммутаторами локально и удаленно. Сопоставьте описание с методом доступа. (Не все варианты используются.)

| Ответы, объяснения и подсказки:
И консоль, и порты AUX могут использоваться для прямого подключения к сетевому устройству Cisco в целях управления. Однако чаще используется консольный порт. Порт AUX чаще используется для удаленного доступа через коммутируемое соединение. SSH и Telnet — это методы удаленного доступа, зависящие от активного сетевого подключения. SSH использует более надежную парольную аутентификацию, чем Telnet, а также использует шифрование передаваемых данных. |
- Сопоставьте фазы с функциями во время процесса загрузки маршрутизатора Cisco. (Не все варианты используются.)

| Ответы, объяснения и подсказки:
Процесс загрузки маршрутизатора Cisco состоит из трех основных этапов:
Если не удается найти файл начальной конфигурации, маршрутизатор перейдет в режим настройки, отобразив запрос режима настройки. |
На чтение 6 мин. Просмотров 579 Опубликовано 18.03.2014
Ответы на на все вопросы (все модули) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
Ответы на 1 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 1) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Какие три утверждения относительно протокола IP являются верными? (Выберите три варианта.)
IP является протоколом без установления соединения.
Протокол IP не предлагает функции восстановления.
Протокол IP осуществляет негарантированную доставку данных
2) Какие компоненты модели OSI и стека протоколов TCP/IP расходятся сильнее всего?
Канальный уровень
3) Сколько бит содержит IPv4 адрес?
32
4) Каково назначение маршрутизатора?
соединение сетей между собой и выбор наилучшего пути между ними
5) Какие два утверждения о цели модели OSI являются верными? (Выберите два варианта.)
Эталонная модель OSI определяет функции сети, реализуемые на каждом уровне.
Модель OSI облегчает понимание передачи данных по сети.
6) Укажите неправильную характеристику сети с коммутацией пакетов
Трафик реального времени передается без задержек
7) Какое утверждение относительно логических топологий сети является верным?
Логическая топология описывает пути, по которым сигналы передаются из одной точки сети в другую.

Физическая топология определяет способ соединения компьютеров, принтеров, сетевых и прочих устройств.
9) Какое из этих событий произошло позже других:
изобретение Web;
10) Каково назначение коммутатора?
подключение сети к конечным системам и интеллектуальная коммутация данных внутри локальной сети
Ответы на 2 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 2) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Укажите неправильное описание методов кодирования
метод NRZ обладает свойством самосинхронизации
2) Какой принцип лежит в основе методов обнаружения и коррекции ошибок?
избыточность
3) Укажите правильный вариант
Символьное подавление — способ сжатия информации, при котором длинные последовательности из идентичных данных заменяются более короткими.
4) Укажите неправильный вариант ответа
Кодовое расстояние в коде Хемминга dmin = 2
5) Укажите неправильный ответ о преимуществах синхронных каналов передачи данных
Невысокая цена оборудования
6) Во сколько раз увеличится ширина спектра кода NRZ при увеличении тактовой частоты передатчика в 2 раза?
2
7) Какой из вариантов является признаком синхронного канала в отличие от асинхронного
данные передаются блоками. Для синхронизации работы приемника и передатчика в начале блока передаются биты синхронизации

B8ZC используется в потоках E1 (2.044 Мбит/с)
9) Укажите неправильный вариант ответа
Текстовые документы, базы данных, принято сжимать с потерей качества
10) Укажите неправильный вариант скорости COM порта в компьютере
2048000
Ответы на 3 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 3) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Каковы два главных преимущества добавления моста к сети? (Выберите два варианта.)
расширение ЛВС для охвата больших расстояний путем соединения нескольких сегментов
изоляция потенциальных проблем сети в отдельных сегментах
2) Какой разъем не используется для подключения сетевой платы к локальной сети
DB -9
3) Укажите неправильный вариант ответа
Хаб может проверить физический адрес (источник и пункт назначения), содержащиеся в пакете.
4) Какова максимальная длина сегмента 10BASE-2 в метрах
185
5) Какой стандарт не предусматривает использование витой пары?
10BASE-2
6) На каком уровне OSI работают мост и коммутатор
2
7) Какой стандарт не предусматривает использование разделяемой среды:
10GBASE-T

мосты ведут таблицу маршрутизации, что позволяет им передавать выбрать оптимальный путь из одной сети в другую.
9) Укажите неверную запись стандарта
1GBACE –T
10) На каком уровне OSI работают репитер и хаб
1
Ответы на 4 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 4) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Укажите неправильный вариант – размер поля Data (данные) в кадре Ethernet 802.3
1530
2) Чем объясняется, что минимальный размер поля данных кадра Ethernet выбран равным 46 байт?
для устойчивого распознавания коллизий;
3) На какой скорости работает Fast Ethetnet
100М
4) Как скорость передачи данных технологии Ethernet на разделяемой среде влияет на максимальный диаметр сети?
чем выше скорость передачи, тем меньше максимальный диаметр сети;
5) В каких средах не работает Ethernet на физическом уровне
Акустический канал
6) К какому типу относится МАС-адрес 01:С2:00:00:08?
индивидуальный
7) Из каких соображений выбирается длительность слота в режиме DCF?
длительность слота должна превосходить время распространения сигнала между любыми станциями сети плюс время, затрачиваемое станцией на распознавание

OUI
9) Выберите утверждения, корректно описывающие особенности метода доступа технологии Ethernet:
если в течение времени передачи кадра коллизия не произошла, то кадр считается переданным успешно.
10) Какое количество бит в MAC адресе
48
Ответы на 5 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 5) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Как вы считаете, протоколы транспортного уровня устанавливаются
и там, и там.
2) Какие параметры сети учитывают метрики, поддерживаемые протоколом OSPF
пропускная способность
3) Данные каких трех типов предоставляются DHCP-клиенту сервером DHCP? (Выберите три варианта.)
IP-адреса DNS-серверов
маска подсети
основной шлюз
4) Какое утверждение наилучшим образом описывает статические и динамические маршруты
Статические маршруты вручную задаются администратором сети, динамические маршруты автоматически добавляются и настраиваются протоколом маршрутизации.
5) Какие три утверждения относительно протокола IP являются верными? (Выберите три варианта.)
IP является протоколом без установления соединения.
Протокол IP осуществляет негарантированную доставку данных.
Протокол IP не предлагает функции восстановления.
6) В студенческом общежитии живет 200 студентов и каждый из них имеет собственный ноутбук. В общежитии оборудована специальная комната, в которой развернута компьютерная сеть, имеющая 25 коннекторов для подключения компьютеров. Время от времени студенты работают в этом компьютерном классе, подключая свои ноутбуки к сети. Каким количеством IP-адресов должен располагать администратор этой компьютерной сети, чтобы все студенты могли подключаться к сети, не выполняя процедуру конфигурирования своих ноутбуков при каждом посещении компьютерного класса не используя DHCP?
254
7) К какому типу стандартов могут относиться современные документы RFC
к международным стандартам.

решение проблемы дефицита адресов в протоколе IPv4;
Ответы на 6 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 6) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Какой из протоколов предназначен для пересылки электронной почты
SMTP
2) Какие три утверждения точно описывают распределенные сети WAN ? (Выберите три варианта)
В распределенных сетях последовательные соединения различных типов используются для предоставления доступа к полосе пропускания.
В распределенных сетях используются услуги таких операторов, как телефонные компании, компании, предоставляющие услуги кабельной связи, спутниковые системы и поставщики сетевых услуг.
Распределенные сети связывают устройства, разделенные обширными географическими областями.
3) Каков размер ячейки ATM
53
4) Какая из атак осуществляется отправкой подложного ARP ответа?
Перенаправление трафика
5) Какая из функций IPsec может выполняться алгоритмом AES?
Конфиденциальность
6) Какая из сетевых технологий появилась раньше?
X.25
7) В чем заключаются преимущества услуг виртуальных частных сетей по сравнению с услугами выделенных каналов с точки зрения поставщика этих услуг?
можно обслужить большее число клиентов, имея ту же инфраструктуру физических каналов связи

21
9) Какая разновидность облачных технологий предоставляет программное обеспечение как услугу
SaaS
10) Укажите назначение сервера DNS
Преобразует имя компьютера или домена в ассоциированный IP-адрес.
A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
- Enter CTRL-Z at the privileged mode prompt.
- Power cycle the device.
- Exit privileged EXEC mode and press Enter.
- Exit global configuration mode.
- Reboot the device.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
While at the privileged mode prompt such as Router#, type exit ,press Enter , and the banner message appears. Power cycling a network device that has had the banner motd command issued will also display the banner message, but this is not a quick way to test the configuration.
What happens when the transport input ssh command is entered on the switch vty lines?
- The switch requires a username/password combination for remote access.
- The SSH client on the switch is enabled.
- Communication between the switch and remote users is encrypted.
- The switch requires remote connections via a proprietary client software.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The transport input ssh command when entered on the switch vty (virtual terminal lines) will encrypt all inbound controlled telnet connections.
What is the subnet ID associated with the IPv6 address 2001:DA48:FC5:A4:3D1B::1/64?
- 2001:DA48::/64
- 2001::/64
- 2001:DA48:FC5:A4::/64
- 2001:DA48:FC5::A4:/64
Explanation:
A client is using SLAAC to obtain an IPv6 address for its interface. After an address has been generated and applied to the interface, what must the client do before it can begin to use this IPv6 address?
- It must send an ICMPv6 Router Solicitation message to determine what default gateway it should use.
- It must send a DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST message to request the address of the DNS server.
- It must send a DHCPv6 REQUEST message to the DHCPv6 server to request permission to use this address.
- It must send an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message to ensure that the address is not already in use on the network.
Explanation:
Stateless DHCPv6 or stateful DHCPv6 uses a DHCP server, but Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) does not. A SLAAC client can automatically generate an address that is based on information from local routers via Router Advertisement (RA) messages. Once an address has been assigned to an interface via SLAAC, the client must ensure via Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) that the address is not already in use. It does this by sending out an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message and listening for a response. If a response is received, then it means that another device is already using this address.
Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FE80::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FF00::/8
- FEC0::/10
Explanation:
Link-local addresses are in the range of FE80::/10 to FEBF::/10. The original IPv6 specification defined site-local addresses and used the prefix range FEC0::/10, but these addresses were deprecated by the IETF in favor of unique local addresses. FDEE::/7 is a unique local address because it is in the range of FC00::/7 to FDFF::/7. IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8.
What mechanism is used by a router to prevent a received IPv4 packet from traveling endlessly on a network?
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It increments the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Parameter Problem message to the source host.
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It decrements the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Time Exceeded message to the source host.
A network administrator is designing the layout of a new wireless network. Which three areas of concern should be accounted for when building a wireless network? (Choose three.)
- mobility options
- security
- interference
- coverage area
- packet collision
- extensive cabling
Explanation:
The three areas of concern for wireless networks focus on the size of the coverage area, any nearby interference, and providing network security. Extensive cabling is not a concern for wireless networks, as a wireless network will require minimal cabling for providing wireless access to hosts. Mobility options are not a component of the areas of concern for wireless networks.
Refer to the exhibit. What is wrong with the displayed termination?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 07
- The untwisted length of each wire is too long.
- The woven copper braid should not have been removed.
- The wrong type of connector is being used.
- The wires are too thick for the connector that is used.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a cable to an RJ-45 connector is terminated, it is important to ensure that the untwisted wires are not too long and that the flexible plastic sheath surrounding the wires is crimped down and not the bare wires. None of the colored wires should be visible from the bottom of the jack.
A network administrator notices that some newly installed Ethernet cabling is carrying corrupt and distorted data signals. The new cabling was installed in the ceiling close to fluorescent lights and electrical equipment. Which two factors may interfere with the copper cabling and result in signal distortion and data corruption? (Choose two.)
- EMI
- signal attenuation
- crosstalk
- RFI
- extended length of cabling
Explanation:
EMI and RFI signals can distort and corrupt data signals that are carried by copper media. These distortions usually come from radio waves and electromagnetic devices such as motors and florescent lights. Crosstalk is a disturbance that is caused by adjacent wires bundled too close together with the magnetic field of one wire affecting another. Signal attenuation is caused when an electrical signal begins to deteriorate over the length of a copper cable.
Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function of TCP or UDP in this situation? (Choose three.)
- TCP is the preferred protocol when a function requires lower network overhead.
- The source port field identifies the running application or service that will handle data returning to the PC.
- The TCP source port number identifies the sending host on the network.
- UDP segments are encapsulated within IP packets for transport across the network.
- The UDP destination port number identifies the application or service on the server which will handle the data.
- The TCP process running on the PC randomly selects the destination port when establishing a session with the server.
Explanation:
Layer 4 port numbers identify the application or service which will handle the data. The source port number is added by the sending device and will be the destination port number when the requested information is returned. Layer 4 segments are encapsulated within IP packets. UDP, not TCP, is used when low overhead is needed. A source IP address, not a TCP source port number, identifies the sending host on the network. Destination port numbers are specific ports that a server application or service monitors for requests.
Match the application protocols to the correct transport protocols.
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 01
A group of Windows PCs in a new subnet has been added to an Ethernet network. When testing the connectivity, a technician finds that these PCs can access local network resources but not the Internet resources. To troubleshoot the problem, the technician wants to initially confirm the IP address and DNS configurations on the PCs, and also verify connectivity to the local router. Which three Windows CLI commands and utilities will provide the necessary information? (Choose three.)
- netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor
- arp -a
- tracert
- ping
- ipconfig
- nslookup
- telnet
Explanation:
The ipconfig and nslookup commands will provide initial IP address and DNS configuration information to the technicians and determine if DHCP is assigning correct information to the PCs. The ping utility would be used to verify, or not, connectivity to the default gateway (router) using the configured default gateway address, or using the known correct default gateway address if these are found to be different. The arp -a or netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor commands could be used if the problem is then suspected to be an IP address to MAC address mapping issue. The telnet and tracert utilities could be used to determine where the problem was located in the network if the default gateway configuration was found to be correct.
What two pieces of information are displayed in the output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose two.)
- speed and duplex settings
- MAC addresses
- next-hop addresses
- interface descriptions
- IP addresses
- Layer 1 statuses
Explanation:
The command show ip interface brief shows the IP address of each interface, as well as the operational status of the interfaces at both Layer 1 and Layer 2. In order to see interface descriptions and speed and duplex settings, use the command show running-config interface. Next-hop addresses are displayed in the routing table with the command show ip route, and the MAC address of an interface can be seen with the command show interfaces.
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 25 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.128
Which frame field is created by a source node and used by a destination node to ensure that a transmitted data signal has not been altered by interference, distortion, or signal loss?
- transport layer error check field
- error correction process field
- flow control field
- User Datagram Protocol field
- frame check sequence field
What is a function of the data link layer?
- provides delivery of data between two applications
- provides for the exchange of frames over a common local media
- provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
- provides the formatting of data
What are three characteristics of the CSMA/CD process? (Choose three.)
- After detecting a collision, hosts can attempt to resume transmission after a random time delay has expired.
- A jam signal indicates that the collision has cleared and the media is not busy.
- All of the devices on a segment see data that passes on the network medium.
- The device with the electronic token is the only one that can transmit after a collision.
- Devices can be configured with a higher transmission priority.
- A device listens and waits until the media is not busy before transmitting.
What characteristic describes a Trojan horse?
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- malicious software or code running on an end device
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
What three requirements are defined by the protocols used in network communcations to allow message transmission across a network? (Choose three.)
- end-device installation
- media selection
- message encoding
- delivery options
- connector specifications
- message size
What are two features of ARP? (Choose two.)
- If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.
- When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
- If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
- An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
- If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.
Explanation:
When a node encapsulates a data packet into a frame, it needs the destination MAC address. First it determines if the destination device is on the local network or on a remote network. Then it checks the ARP table (not the MAC table) to see if a pair of IP address and MAC address exists for either the destination IP address (if the destination host is on the local network) or the default gateway IP address (if the destination host is on a remote network). If the match does not exist, it generates an ARP broadcast to seek the IP address to MAC address resolution. Because the destination MAC address is unknown, the ARP request is broadcast with the MAC address FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. Either the destination device or the default gateway will respond with its MAC address, which enables the sending node to assemble the frame. If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will discard the packet because a frame cannot be created.
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 06
- The entire command, configure terminal , must be used.
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
In order to enter global configuration mode, the command configure terminal , or a shortened version such as config t , must be entered from privileged EXEC mode. In this scenario the administrator is in user EXEC mode, as indicated by the > symbol after the hostname. The administrator would need to use the enable command to move into privileged EXEC mode before entering the configure terminal command.
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 05
- This host does not have a default gateway configured.
- There are 4 hops between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
- There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
Explanation:
The output displays a successful Layer 3 connection between a host computer and a host at 19.168.100.1. It can be determined that 4 hops exist between them and the average transmission time is 1 milliseconds. Layer 3 connectivity does not necessarily mean that an application can run between the hosts.
What are two characteristics of IP? (Choose two.)
- retransmits packets if errors occur
- guarantees delivery of packets
- does not require a dedicated end-to-end connection
- operates independently of the network media
- re-assembles out of order packets into the correct order at the receiver end
Explanation:
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a connectionless, best effort protocol. This means that IP requires no end-to-end connection nor does it guarantee delivery of packets. IP is also media independent, which means it operates independently of the network media carrying the packets.
What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a host needs to send a message to another host located on the same network, it can forward the message directly. However, when a host needs to send a message to a remote network, it must use the router, also known as the default gateway. This is because the data link frame address of the remote destination host cannot be used directly. Instead, the IP packet has to be sent to the router (default gateway) and the router will forward the packet toward its destination. Therefore, if the default gateway is incorrectly configured, the host can communicate with other hosts on the same network, but not with hosts on remote networks.
Users report that the network access is slow. After questioning the employees, the network administrator learned that one employee downloaded a third-party scanning program for the printer. What type of malware might be introduced that causes slow performance of the network?
- spam
- virus
- worm
- phishing
Explanation:
A company has a file server that shares a folder named Public. The network security policy specifies that the Public folder is assigned Read-Only rights to anyone who can log into the server while the Edit rights are assigned only to the network admin group. Which component is addressed in the AAA network service framework?
- automation
- authorization
- accounting
- authentication
Explanation:
After a user is successfully authenticated (logged into the server), the authorization is the process of determining what network resources the user can access and what operations (such as read or edit) the user can perform.
What are two common causes of signal degradation when using UTP cabling? (Choose two.)
- loss of light over long distances
- low-quality cable or connectors
- low-quality shielding in cable
- installing cables in conduit
- improper termination
Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
Explanation:
The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
What is the consequence of configuring a router with the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command?
- Each router interface will generate an IPv6 link-local address.
- The IPv6 enabled router interfaces begin sending ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages.
- It statically creates a global unicast address on this router.
- All router interfaces will be automatically activated.
Which two protocols operate at the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose two.)
- POP
- DNS
- IP
- TCP
- Ethernet
- UDP
An employee of a large corporation remotely logs into the company using the appropriate username and password. The employee is attending an important video conference with a customer concerning a large sale. It is important for the video quality to be excellent during the meeting. The employee is unaware that after a successful login, the connection to the company ISP failed. The secondary connection, however, activated within seconds. The disruption was not noticed by the employee or other employees.
What three network characteristics are described in this scenario? (Choose three.)
- integrity
- scalability
- quality of service
- fault tolerance
- powerline networking
- security
Refer to the exhibit. If PC1 is sending a packet to PC2 and routing has been configured between the two routers, what will R1 do with the Ethernet frame header attached by PC1?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 04
- open the header and use it to determine whether the data is to be sent out S0/0/0
- open the header and replace the destination MAC address with a new one
- nothing, because the router has a route to the destination network
- remove the Ethernet header and configure a new Layer 2 header before sending it out S0/0/0
Explanation:
When PC1 forms the various headers attached to the data one of those headers is the Layer 2 header. Because PC1 connects to an Ethernet network, an Ethernet header is used. The source MAC address will be the MAC address of PC1 and the destination MAC address will be that of G0/0 on R1. When R1 gets that information, the router removes the Layer 2 header and creates a new one for the type of network the data will be placed onto (the serial link).
Which three layers of the OSI model map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- transport
- application
- network
- session
- data link
- presentation
Explanation:
Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 02
Link-Local addresses are assigned automatically by the OS environment and are located in the block 169.254.0.0/16. The private addresses ranges are 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, and 192.168.0.0/16. TEST-NET addresses belong to the range 192.0.2.0/24. The addresses in the block 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.254 are reserved as experimental addresses. Loopback addresses belong to the block 127.0.0.0/8.
What does the term “attenuation” mean in data communication?
- strengthening of a signal by a networking device
- leakage of signals from one cable pair to another
- loss of signal strength as distance increases
- time for a signal to reach its destination
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Data is transmitted on copper cables as electrical pulses. A detector in the network interface of a destination device must receive a signal that can be successfully decoded to match the signal sent. However, the farther the signal travels, the more it deteriorates. This is referred to as signal attenuation.
Which two statements describe how to assess traffic flow patterns and network traffic types using a protocol analyzer? (Choose two.)
- Capture traffic during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types.
- Perform the capture on different network segments.
- Only capture WAN traffic because traffic to the web is responsible for the largest amount of traffic on a network.
- Only capture traffic in the areas of the network that receive most of the traffic such as the data center.
- Capture traffic on the weekends when most employees are off work.
Explanation:
Traffic flow patterns should be gathered during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types. The capture should also be performed on different network segments because some traffic will be local to a particular segment.
Refer to the exhibit. Host B on subnet Teachers transmits a packet to host D on subnet Students. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 addresses are contained in the PDUs that are transmitted from host B to the router?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 03
- Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-dd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.100.200 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-cd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.99
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
- 192.168.1.64/26
Explanation:
For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
What are two problems that can be caused by a large number of ARP request and reply messages? (Choose two.)
- A large number of ARP request and reply messages may slow down the switching process, leading the switch to make many changes in its MAC table.
- The ARP request is sent as a broadcast, and will flood the entire subnet.
- Switches become overloaded because they concentrate all the traffic from the attached subnets.
- All ARP request messages must be processed by all nodes on the local network.
- The network may become overloaded because ARP reply messages have a very large payload due to the 48-bit MAC address and 32-bit IP address that they contain.
Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
Why would a Layer 2 switch need an IP address?
- to enable the switch to be managed remotely
- to enable the switch to receive frames from attached PCs
- to enable the switch to send broadcast frames to attached PCs
- to enable the switch to function as a default gateway
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A switch, as a Layer 2 device, does not need an IP address to transmit frames to attached devices. However, when a switch is accessed remotely through the network, it must have a Layer 3 address. The IP address must be applied to a virtual interface rather than to a physical interface. Routers, not switches, function as default gateways.
How does the service password-encryption command enhance password security on Cisco routers and switches?
- It requires encrypted passwords to be used when connecting remotely to a router or switch with Telnet.
- It encrypts passwords that are stored in router or switch configuration files.
- It requires that a user type encrypted passwords to gain console access to a router or switch.
- It encrypts passwords as they are sent across the network.
Explanation:
The service password-encryption command encrypts plaintext passwords in the configuration file so that they cannot be viewed by unauthorized users.
Which two statements are correct in a comparison of IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers? (Choose two.)
- The Destination Address field is new in IPv6.
- The Source Address field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
- The Version field from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6.
- The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6.
- The Header Checksum field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
Which two statements accurately describe an advantage or a disadvantage when deploying NAT for IPv4 in a network? (Choose two.)
- NAT will impact negatively on switch performance.
- NAT causes routing tables to include more information.
- NAT improves packet handling.
- NAT adds authentication capability to IPv4.
- NAT provides a solution to slow down the IPv4 address depletion.
- NAT introduces problems for some applications that require end-to-end connectivity.
Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 003
A logical topology diagram typically depicts the IP addressing scheme and groupings of devices and ports. A physical topology diagram shows how those devices are connected to each other and the network, focusing on the physical locations of intermediary devices, configured ports, and cabling.
What service is provided by HTTP?
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 67. What service is the client requesting?
- Telnet
- FTP
- SSH
- DHCP
What are the two most effective ways to defend against malware? (Choose two.)
- Implement strong passwords.
- Update the operating system and other application software.
- Install and update antivirus software.
- Implement RAID.
- Implement a VPN.
- Implement network firewalls.
Explanation:
An administrator defined a local user account with a secret password on router R1 for use with SSH. Which three additional steps are required to configure R1 to accept only encrypted SSH connections? (Choose three.)
- Configure the IP domain name on the router.
- Enable inbound vty Telnet sessions.
- Configure DNS on the router.
- Generate the SSH keys.
- Generate two-way pre-shared keys.
- Enable inbound vty SSH sessions.
Explanation:
There are four steps to configure SSH support on a Cisco router:
Step 1: Set the domain name.
Step 2: Generate one-way secret keys.
Step 3: Create a local username and password.
Step 4: Enable SSH inbound on a vty line.
A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in its ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
- It will send the frame and use its own MAC address as the destination.
- It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
- It will send a request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.
Match the header field with the appropriate layer of the OSI model. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 03
When a switch configuration includes a user-defined error threshold on a per-port basis, to which switching method will the switch revert when the error threshold is reached?
- fast-forward
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
What are proprietary protocols?
- protocols that can be freely used by any organization or vendor
- protocols developed by private organizations to operate on any vendor hardware
- a collection of protocols known as the TCP/IP protocol suite
- protocols developed by organizations who have control over their definition and operation
Explanation:
Proprietary protocols have their definition and operation controlled by one company or vendor. Some of them can be used by different organizations with permission from the owner. The TCP/IP protocol suite is an open standard, not a proprietary protocol.
What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- A company can monopolize the market.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
Explanation:
A monopoly by one company is not a good idea from a user point of view. If a protocol can only be run on one brand, it makes it difficult to have mixed equipment in a network. A proprietary protocol is not free to use. An open standard protocol will in general be implemented by a wide range of vendors.
Which type of server relies on record types such as A, NS, AAAA, and MX in order to provide services?
- file
- web
- DNS
Explanation:
Match a statement to the related network model. (Not all options are used.)
ITN Chapter 10 Exam Answers 02
Peer-to-peer networks do not require the use of a dedicated server, and devices can assume both client and server roles simultaneously on a per request basis. Because they do not require formalized accounts or permissions, they are best used in limited situations. Peer-to-peer applications require a user interface and background service to be running, and can be used in more diverse situations.
A network administrator wants to have the same network mask for all networks at a particular small site. The site has the following networks and number of devices:
IP phones – 22 addresses
PCs – 20 addresses needed
Printers – 2 addresses needed
Scanners – 2 addresses needed
The network administrator has deemed that 192.168.10.0/24 is to be the network used at this site. Which single subnet mask would make the most efficient use of the available addresses to use for the four subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has assigned the LAN of LBMISS an address range of 192.168.10.0. This address range has been subnetted using a /29 prefix. In order to accommodate a new building, the technician has decided to use the fifth subnet for configuring the new network (subnet zero is the first subnet). By company policies, the router interface is always assigned the first usable host address and the workgroup server is given the last usable host address. Which configuration should be entered into the properties of the workgroup server to allow connectivity to the Internet?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 02
- IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
- IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
- IP address: 192.168.10.254 subnet mask: 255.255.255.0, default gateway: 192.168.10.1
- IP address: 192.168.10.41 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.46
- IP address: 192.168.10.65 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.76
Explanation:
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer has been given the network address of 192.168.99.0 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192 to subnet across the four networks shown. How many total host addresses are unused across all four subnets?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 01
- 158
- 200
- 224
- 88
- 72
Explanation:
What would be the interface ID of an IPv6 enabled interface with a MAC address of 1C-6F-65-C2-BD-F8 when the interface ID is generated by using the EUI-64 process?
- 1E6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- C16F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 0C6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 106F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
Which information does the show startup-config command display?
- the IOS image copied into RAM
- the bootstrap program in the ROM
- the contents of the saved configuration file in the NVRAM
- the contents of the current running configuration file in the RAM
Match each type of frame field to its function. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 004
What are two primary responsibilities of the Ethernet MAC sublayer? (Choose two.)
- accessing the media
- data encapsulation
- logical addressing
- error detection
- frame delimiting
Match the characteristic to the forwarding method. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 005
Which switching method drops frames that fail the FCS check?
- store-and-forward switching
- ingress port buffering
- cut-through switching
- borderless switching
What is an advantage for small organizations of adopting IMAP instead of POP?
- IMAP sends and retrieves email, but POP only retrieves email.
- POP only allows the client to store messages in a centralized way, while IMAP allows distributed storage.
- Messages are kept in the mail servers until they are manually deleted from the email client.
- When the user connects to a POP server, copies of the messages are kept in the mail server for a short time, but IMAP keeps them for a long time.
Explanation:
A wired laser printer is attached to a home computer. That printer has been shared so that other computers on the home network can also use the printer. What networking model is in use?
- point-to-point
- client-based
- peer-to-peer (P2P)
- master-slave
Explanation:
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 200 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
Which wireless technology has low-power and data rate requirements making it popular in home automation applications?
- ZigBee
- 5G
- Wi-Fi
- LoRaWAN
What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- 3-way handshake
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering
- use of checksum
Explanation:
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 69. What service is the client requesting?
- DHCP
- SMTP
- TFTP
- DNS
What service is provided by Internet Messenger?
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
What characteristic describes antispyware?
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- applications that protect end devices from becoming infected with malicious software
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses
Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses
Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
Refer to the exhibit. A company uses the address block of 128.107.0.0/16 for its network. What subnet mask would provide the maximum number of equal size subnets while providing enough host addresses for each subnet in the exhibit?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 08
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240
Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol was responsible for building the table that is shown?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 09
- ARP
- DNS
- DHCP
- ICMP
Which two traffic types use the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP)? (Choose two.)
- web
- peer to peer
- file transfer
- video
- voice
Match the type of threat with the cause. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 006
Refer to the exhibit. The switches are in their default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for its default gateway. Which network hosts will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 10
- only hosts A, B, C, and D
- only router R1
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only hosts B and C
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
- only host D
Explanation:
Which value, that is contained in an IPv4 header field, is decremented by each router that receives a packet?
- Differentiated Services
- Fragment Offset
- Header Length
- Time-to-Live
Refer to the exhibit. The IP address of which device interface should be used as the default gateway setting of host H1?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 11
- R2: S0/0/1
- R1: G0/0
- R2: S0/0/0
- R1: S0/0/0
Which two statements describe features of an IPv4 routing table on a router? (Choose two.)
- Directly connected interfaces will have two route source codes in the routing table: C and S .
- The netstat -r command can be used to display the routing table of a router.
- If there are two or more possible routes to the same destination, the route associated with the higher metric value is included in the routing table.
- The routing table lists the MAC addresses of each active interface.
- If a default static route is configured in the router, an entry will be included in the routing table with source code S .
- It stores information about routes derived from the active router interfaces.
Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
Explanation:
What is the consequence of configuring a router with the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command?
- All router interfaces will be automatically activated.
- Each router interface will generate an IPv6 link-local address.
- The IPv6 enabled router interfaces begin sending ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages.
- It statically creates a global unicast address on this router.
Refer to the exhibit. If Host1 were to transfer a file to the server, what layers of the TCP/IP model would be used?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 12
- only application, Internet, and network access layers
- only application, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
- application, session, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
- only application and Internet layers
- application, transport, Internet, and network access layers
- only Internet and network access layers
Explanation:
The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
Explanation:
What characteristic describes adware?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
Match each description with the corresponding TCP mechanism. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 007
What is the purpose of the TCP sliding window?
- to ensure that segments arrive in order at the destination
- to request that a source decrease the rate at which it transmits data
- to inform a source to retransmit data from a specific point forward
- to end communication when data transmission is complete
What technique is used with UTP cable to help protect against signal interference from crosstalk?
- terminating the cable with special grounded connectors
- twisting the wires together into pairs
- wrapping a foil shield around the wire pairs
- encasing the cables within a flexible plastic sheath
Explanation:
To help prevent the effects of crosstalk, UTP cable wires are twisted together into pairs. Twisting the wires together causes the magnetic fields of each wire to cancel each other out.
A network technician is researching the use of fiber optic cabling in a new technology center. Which two issues should be considered before implementing fiber optic media? (Choose two.)
- Fiber optic cabling requires different termination and splicing expertise from what copper cabling requires.
- Fiber optic cabling requires specific grounding to be immune to EMI.
- Fiber optic cabling is susceptible to loss of signal due to RFI.
- Fiber optic provides higher data capacity but is more expensive than copper cabling.
- Fiber optic cable is able to withstand rough handling.
Users are reporting longer delays in authentication and in accessing network resources during certain time periods of the week. What kind of information should network engineers check to find out if this situation is part of a normal network behavior?
- syslog records and messages
- debug output and packet captures
- network configuration files
- the network performance baseline
A user is complaining that an external web page is taking longer than normal to load.The web page does eventually load on the user machine. Which tool should the technician use with administrator privileges in order to locate where the issue is in the network?
- ipconfig /displaydns
- nslookup
- tracert
- ping
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 53. What service is the client requesting?
- SSH
- FTP
- Telnet
- DNS
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 issues an ARP request because it needs to send a packet to PC2. In this scenario, what will happen next?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 13
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/0 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/1 MAC address.
- PC2 will send an ARP reply with its MAC address.
Explanation:
When a network device wants to communicate with another device on the same network, it sends a broadcast ARP request. In this case, the request will contain the IP address of PC2. The destination device (PC2) sends an ARP reply with its MAC address.
Match the description to the IPv6 addressing component. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 008
An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::2. What is the target of this packet?
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link
- all IPv6 DHCP servers
- all IPv6 enabled devices across the network
- all IPv6 configured routers on the local link
What are the three parts of an IPv6 global unicast address? (Choose three.)
- subnet ID
- global routing prefix
- interface ID
- subnet mask
- broadcast address
What is one main characteristic of the data link layer?
- It generates the electrical or optical signals that represent the 1 and 0 on the media.
- It converts a stream of data bits into a predefined code.
- It shields the upper layer protocol from being aware of the physical medium to be used in the communication.
- It accepts Layer 3 packets and decides the path by which to forward the packet to a remote network.
Which type of security threat would be responsible if a spreadsheet add-on disables the local software firewall?
- Trojan horse
- brute-force attack
- DoS
- buffer overflow
Explanation:
A Trojan horse is software that does something harmful, but is hidden in legitimate software code. A denial of service (DoS) attack results in interruption of network services to users, network devices, or applications. A brute-force attack commonly involves trying to access a network device. A buffer overflow occurs when a program attempts to store more data in a memory location than it can hold.
What service is provided by HTTPS?
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
Match the characteristic to the category. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 009
Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 14
- 172.168.10.65
- 172.168.10.99
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
Which two statements are correct about MAC and IP addresses during data transmission if NAT is not involved? (Choose two.)
- Destination MAC addresses will never change in a frame that goes across seven routers.
- A packet that has crossed four routers has changed the destination IP address four times.
- Every time a frame is encapsulated with a new destination MAC address, a new destination IP address is needed.
- Destination and source MAC addresses have local significance and change every time a frame goes from one LAN to another.
- Destination IP addresses in a packet header remain constant along the entire path to a target host.
Refer to the exhibit. What three facts can be determined from the viewable output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose three.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 15
- Two devices are attached to the switch.
- The default SVI has been configured.
- The switch can be remotely managed.
- Two physical interfaces have been configured.
- Passwords have been configured on the switch.
- One device is attached to a physical interface.
A user is executing a tracert to a remote device. At what point would a router, which is in the path to the destination device, stop forwarding the packet?
- when the values of both the Echo Request and Echo Reply messages reach zero
- when the value in the TTL field reaches zero
- when the router receives an ICMP Time Exceeded message
- when the host responds with an ICMP Echo Reply message
- when the RTT value reaches zero
Explanation:
When a router receives a traceroute packet, the value in the TTL field is decremented by 1. When the value in the field reaches zero, the receiving router will not forward the packet, and will send an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source.
What are two functions that are provided by the network layer? (Choose two.)
- carrying data between processes that are running on source and destination hosts
- directing data packets to destination hosts on other networks
- providing dedicated end-to-end connections
- placing data on the network medium
- providing end devices with a unique network identifier
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 61 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.128
What characteristic describes spyware?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
What are three commonly followed standards for constructing and installing cabling? (Choose three.)
- pinouts
- tensile strength of plastic insulator
- cable lengths
- connector types
- cost per meter (foot)
- connector color
Which connector is used with twisted-pair cabling in an Ethernet LAN?
What attribute of a NIC would place it at the data link layer of the OSI model?
- attached Ethernet cable
- TCP/IP protocol stack
- IP address
- RJ-45 port
- MAC address
A network administrator needs to keep the user ID, password, and session contents private when establishing remote CLI connectivity with a switch to manage it. Which access method should be chosen?
- AUX
- Telnet
- SSH
- Console
A user sends an HTTP request to a web server on a remote network. During encapsulation for this request, what information is added to the address field of a frame to indicate the destination?
- the network domain of the destination host
- the MAC address of the default gateway
- the IP address of the default gateway
- the MAC address of the destination host
Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- route print
- show ip route
- netstat -r
- netstat -s
- tracert
Answers Explanation & Hints:
On a Windows host, the route print or netstat -r commands can be used to display the host routing table. Both commands generate the same output. On a router, the show ip route command is used to display the routing table. The netstat –s command is used to display per-protocol statistics. The tracert command is used to display the path that a packet travels to its destination.
Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 001
Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 01
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 002
Network A needs to use 192.168.0.0 /25 which yields 128 host addresses.
Network B needs to use 192.168.0.128 /26 which yields 64 host addresses.
Network C needs to use 192.168.0.192 /27 which yields 32 host addresses.
Network D needs to use 192.168.0.224 /30 which yields 4 host addresses.
A technician with a PC is using multiple applications while connected to the Internet. How is the PC able to keep track of the data flow between multiple application sessions and have each application receive the correct packet flows?
- The data flow is being tracked based on the source port number that is used by each application.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the destination IP address that is used by the PC of the technician.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the source IP address that is used by the PC of the technician.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the destination MAC address of the technician PC.
Explanation:
The source port number of an application is randomly generated and used to individually keep track of each session connecting out to the Internet. Each application will use a unique source port number to provide simultaneous communication from multiple applications through the Internet.
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 80. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- HTTP
- DHCP
- SMTP
A user is attempting to access http://www.cisco.com/ without success. Which two configuration values must be set on the host to allow this access? (Choose two.)
- source port number
- HTTP server
- source MAC address
- DNS server
- default gateway
What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA
- token passing
What are two ICMPv6 messages that are not present in ICMP for IPv4? (Choose two.)
- Router Advertisement
- Destination Unreachable
- Neighbor Solicitation
- Route Redirection
- Host Confirmation
- Time Exceeded
An organization is assigned an IPv6 address block of 2001:db8:0:ca00::/56. How many subnets can be created without using bits in the interface ID space?
- 4096
- 256
- 512
- 1024
What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in the ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
- It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
- It will send the frame and use the device MAC address as the destination.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.
- It will send an ARP request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
What characteristic describes a virus?
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- malicious software or code running on an end device
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
A disgruntled employee is using some free wireless networking tools to determine information about the enterprise wireless networks. This person is planning on using this information to hack the wireless network. What type of attack is this?
- access
- DoS
- Trojan horse
- reconnaissance
What service is provided by POP3?
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Retrieves email from the server by downloading the email to the local mail application of the client.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
What command can be used on a Windows PC to see the IP configuration of that computer?
- ipconfig
- show interfaces
- ping
- show ip interface brief
Refer to the exhibit. Which two network addresses can be assigned to the network containing 10 hosts? Your answers should waste the fewest addresses, not reuse addresses that are already assigned, and stay within the 10.18.10.0/24 range of addresses. (Choose two.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 02
- 10.18.10.224/27
- 10.18.10.208/28
- 10.18.10.200/27
- 10.18.10.200/28
- 10.18.10.224/28
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Addresses 10.18.10.0 through 10.18.10.63 are taken for the leftmost network. Addresses 192 through 199 are used by the center network. Because 4 host bits are needed to accommodate 10 hosts, a /28 mask is needed. 10.18.10.200/28 is not a valid network number. Two subnets that can be used are 10.18.10.208/28 and 10.18.10.224/28.
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 110. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- DHCP
- POP3
- SMTP
Which layer of the TCP/IP model provides a route to forward messages through an internetwork?
- transport
- application
- network access
- internet
What characteristic describes identity theft?
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- software that identifies fast-spreading threats
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications

1. Cтруктура глобальной вычислительной сети. Два типа вычислительных машин и их функции
Типичный пример структуры глобальной компьютерной сети приведен на рис. 6.2. Здесь используются следующие обозначения: S (switch) — коммутаторы, К — компьютеры, R (router) —
маршрутизаторы, MUX (multiplexor)- мультиплексор, UNI (User-Network Interface) — интерфейс пользователь — сеть и NNI (Network-Network Interface) — интерфейс сеть — сеть
Рис. 6.2. Пример структуры глобальной сети
Сеть строится на основе некоммутируемых (выделенных) каналов связи, которые соединяют коммутаторы глобальной сети между собой. Коммутаторы называют такжецентрами коммутации пакетов (ЦКП), то есть они являются коммутаторами пакетов, которые в разных технологиях глобальных сетей могут иметь и другие названия — кадры, ячейки cellКоммутаторы устанавливаются в тех географических пунктах, в которых требуется ответвление или слияние потоков данных конечных абонентов или магистральных каналов, переносящих данные многих абонентов. Естественно, выбор мест расположения коммутаторов определяется многими соображениями, в которые включается также возможность обслуживания коммутаторов квалифицированным персоналом, наличие выделенных каналов связи в данном пункте, надежность сети, определяемая избыточными связями между коммутаторами.
Абоненты сети подключаются к коммутаторам в общем случае также с помощью выделенных каналов связи. Эти каналы связи имеют более низкую пропускную способность, чем магистральные каналы, объединяющие коммутаторы, иначе сеть бы не справилась с потоками данных своих многочисленных пользователей. Для подключения конечных пользователей допускается использование коммутируемых каналов, то есть каналов телефонных сетей, хотя в таком случае качество транспортных услуг обычно ухудшается.
На рис. 6.2. показаны основные типы конечных узлов глобальной сети: отдельные компьютеры К, локальные сети, маршрутизаторы R и мультиплексоры MUX, которые используются для одновременной передачи по компьютерной сети данных и голоса (или изображения). Все эти устройства вырабатывают данные для передачи в глобальной сети, поэтому являются для нее устройствами типа DTE (Data Terminal Equipment). Локальная сеть отделена от глобальной маршрутизатором или удаленным мостом (который на рисунке не показан), поэтому для глобальной сети она представлена единым устройством DTE — портом маршрутизатора или моста.
При передаче данных через глобальную сеть мосты и маршрутизаторы,работают в соответствии с той же логикой, что и при соединении локальных сетей. Мосты, которые в этом случае
называются удаленными мостами (remote bridges), строят таблицу МАС — адресов на основании проходящего через них трафика, и по данным этой таблицы принимают решение — передавать кадры в удаленную сеть или нет.
. Маршрутизаторы принимают решение на основании номера сети пакета какого-либо протокола сетевого уровня (например, IP или IPX) и, если пакет нужно переправить следующему маршрутизатору по глобальной сети, например frame relay, упаковывают его в кадр этой сети, снабжают соответствующим аппаратным адресом следующего маршрутизатора и отправляют в глобальную сеть.
Мультиплексоры «голос — данные» предназначены для совмещения в рамках одной территориальной сети компьютерного и голосового трафиков.
Типы ВМ
Существуют 2 типа ВМ: аналоговые и цифровые. В АВМ для представления информации используются непрерывные физические величины, чаще всего напряжение.В ЦВМ информация представленна двоичными кодами. При этом каждый разряд принимает два значения из набора{1;0}.Для представления двоичной переменной используется дискретный сигнал.ЦВМ являются более универсальным средством обработки информации и по ряду наиболее важных общетехнических показателей превосходят АВМ.
В электронных машинах непрерывного действия отдельные операции над величинами выполняются
при помощи специальных электрических схем, каждая из которых предназначена для выполнения
только одной операции. Типовыми операциями являются: сложение, вычитание, умножение, деление,
дефференцирование, интегрирование, получение тригонометрических, логарифмических и
экспоненциальных зависимостей
2. Вычислительные сети с коммутацией каналов и сообщений. Область применения. Достоинства и недостатки этих сетей.

Между АМ2 и АМ6 существуют группы каналов:
1{1, 2, 4, 6} , 2{1, 2, 5, 7}, 3{3, 4, 6}, 4{3, 5, 7};
Коммуникационная сеть — множество коммуникационных машин, соединённых физическими магистральными каналами.
Физический канал — это среда и аппаратура передачи и приема данных (коаксиальные, оптоволоконные и т.п. проводные среды).
Терминал — устройство ввода вывода информации.
Вычислительные машины: абонентские (обеспечивают ввод/вывод информации в вычислительной сети при отсутствии терминалов); вспомогательные или коммуникационные (осуществляют преобразование и передачу информации от одной абонентской машины к другой).
По способу работы вычислительные сети подразделяются на: (1)Сети коммутации каналов; (2)Cети коммутации сообщений; (3)Сети коммутации пакетов;
1.Сети коммутации каналов. Первыми появились сети коммутации каналов. Между АМ2 и АМ6 должно быть прямое соединение, включающее одну из четырех групп магистральных каналов. Каналы фиксируется за АМ2 и АМ6, каналами не могут воспользоваться другие АМ в течении всего взаимодействия. Это соединение должно оставаться неизменным в течение всего сеанса. Легкость реализации такого способа передачи информации влечет за собой и его недостатки: низкий коэффициент использования каналов, высокую стоимость передачи данных, увеличение времени ожидания других клиентов.
Сети коммутации каналов обеспечивают возможность коммутации потоков данных постоянной интенсивности, например разговаривающими по телефону собеседниками.
(+) Возможность диалогового режима между АМ.
(-) Необходимость большого числа магистральных каналов.
2. Cети коммутации сообщений . При коммутации сообщений, информация передается порциями, называемыми сообщениями. Прямое соединение обычно не устанавливается, а передача сообщения начинается после освобождения первого канала и так далее, пока сообщение не дойдет до адресата. Каждым сервером осуществляются прием информации, ее сборка, проверка, маршрутизация и передача сообщения. Недостатками коммутации сообщений являются низкая скорость передачи данных и невозможность проведения диалога между клиентами, хотя стоимость передачи и уменьшается.
Сообщение — логически завершенная порция данных, произвольной длины. Передача информации может начаться после освобождения 1-ого или 3-его канала. Далее сообщение оседает во внешней памяти (жесткий диск) коммуникационной машины. По мере освобождения каналов информация будет передаваться дальше и дублироваться во внешней памяти коммуникационных машин, пока не достигнет АМ получателя. Особенности: коммуникация сообщений потребовала создания специальных коммуникационных машин, способных запоминать и обрабатывать значительное число сообщений. Оказалось целесообразным использования таких машин — длительное время хранения
сообщений, изготовление их дубликатов и рассылка по нужным адресам. Постепенно объем памяти таких машин возрос и они стали ЦКС (Центрами Коммутации Сообщений).
(+) Длительное хранение сообщений.
(-) Значительное время доставки сообщений, не позволяющее осуществить диалог между абонентскими машинами.
3. Вычислительные сети с коммутацией пакетов. Принципы функционирования. Область применения. Достоинства и недостатки этих сетей.
При коммутации пакетов все передаваемые сообщения разбиваются в исходной абонентской машине (АМ) на сравнительно небольшие части, определенной длины, называемые пакетами. Каждый пакет снабжается заголовком, в котором указывается адресная информация, необходимая для доставки пакета АМ назначения. А также номером пакета, который будет использоваться АМ назначения для сборки сообщения. Пакеты транспортируются в коммуникационной сети как независимые информационные блоки. Коммуникационные машины принимают пакеты от конечных АМ и на основании адресной информации передают их друг другу, а в конечном итоге — АМ назначения.Если коммуникационная машина занята передачей другого пакета, то пакет записывается во внутреннюю оперативную память (ОП), для временного хранения. Пакет будет извлечен и передан следующей коммуникационной машине в порядке очереди. Сети с коммутацией пакетов были разработаны для сетей с пульсирующей нагрузкой.
При коммутации пакетов обмен производится короткими пакетами фиксированной структуры. Пакет — часть сообщения, удовлетворяющая некоторому стандарту. Малая длина пакетов предотвращает блокировку линий связи, не дает расти очереди в узлах коммутации. Это обеспечивает быстрое соединение, низкий уровень ошибок, надежность и эффективность использования сети. Но при передаче пакета возникает проблема маршрутизации, которая решается программно-аппаратными методами. Наиболее распространенными способами являются фиксированная маршрутизация и маршрутизация способом кратчайшей очереди. Фиксированная маршрутизация предполагает наличие таблицы маршрутов, в которой закрепляется маршрут от одного клиента к другому, что обеспечивает простоту реализации, но одновременно и неравномерную загрузку сети. В методе кратчайшей очереди используется несколько таблиц, в которых каналы расставлены по приоритетам. Приоритетфункция, обратная расстоянию до адресата. Передача начинается по первому свободному каналу с высшим приоритетом. При использовании этого метода задержка передачи пакета минимальная.
(+) Резко уменьшился объем памяти, необходимый для коммуникационных машин.
(+) Стало ненужным использование внешней памяти, что дало возможность резко сократить время доставки.
(-)Пришлось отказаться от длительного хранения и дублирования сообщений.
(+) Сети с коммутацией пакетов получили ряд преимуществ: быстрое соединение; низкий уровень ошибок; надежность функционирования; стойкость к высоким нагрузкам сети. На всплески нагрузки, такая сеть отвечает небольшим снижением скорости передачи.
4. 7-уровневая эталонная модель взаимодействия открытых систем. Назначение уровней.
МОС/ISO (Международная Организация по Стандартизации/International Organization for Standardization) разработала эталонную модель ВОС (Взаимосвязи Открытых Систем). ВОС определяет различные уровни взаимодействия систем, дает им стандартные имена и указывает, какие функции должен выполнять каждый уровень. Модель не включает средства взаимодействия приложений конечных пользователей. Свои собственные протоколы взаимодействия приложения реализуют, обращаясь к системным средствам. ВОС предусматривает сложную 7-уровневую архитектуру.
|
Область действия операционной |
7 |
Прикладной |
Определяет для |
Процесс или |
|
|
системы |
пользовательских приложений |
прикладной |
|||
|
программный интерфейс. |
процесс |
||||
|
6 |
Представительский |
Управление представлением |
|||
|
(Отвечает за кодирование |
|||||
|
данных, полученных от |
|||||
|
прикладного уровня, в |
|||||
|
представление, готовое к |
|||||
|
передаче по сети, и наоборот). |
|||||
|
5 |
Сеансовый |
Управляет соединениями |
|||
|
(Сеансами связи). |
|||||
|
Порт |
|||||
|
4 |
Транспортный |
Обеспечивает заданную |
Транспортная |
||
|
надежность передачи. |
сеть |
||||
|
Управление логическими |
|||||
|
каналами. |
|||||
|
3 |
Сетевой |
Управляет сетью |
|||
|
(Маршрутизацией). |
|||||
|
Транспортный |
2 |
Канальный |
Управление информационным |
||
|
канал |
каналом. |
||||
|
Информационный |
1 |
Физический |
Управление физическим |
||
|
канал |
каналом. |
||||
|
Физический канал |
|||||
Уровни 1 и 2 определяют функции, описывающие передачу информации между двумя вычислительными машинами, соединенными физическим каналом.
Уровни 3 и 4 осуществляют передачу информации от порта одной абонентской машины до порта другой абонентской машины.
Уровни 5, 6, 7 описывают взаимодействие операционных систем абонентских машин.
Порт – адресуемый участок оперативной памяти абонентской машины, предназначенный для сетевого взаимодействия.
Транспортная сеть – логическая система, обеспечивающая передачу информации от процесса в одной абонентской машине к процессу в другой абонентской машине.
Информационный канал – логическая система, состоящая из 2х программ управления физическим каналом, которые связаны этим физическим каналом.
Транспортный канал (логический канал) – логическая система, предназначенная для передачи информации между двумя смежными вычислительными машинами, состоящая из 2х связанных физическим каналом логических модулей, каждый из которых включает управление информационным и физическим каналами.
Соединение абонентских машин в вычислительной сети происходит посредством создания логических каналов. Жизненный цикл логического канала: канал создается, поддерживается и уничтожается.
(-) Сложность программной структуры вычислительной сети.
(+)Обеспечивает относительную программную независимость.
(+)Между уровнями определены однозначно интерфейсы, изменение одного из уровней не влечет за собой необходимости внесения изменений в другие уровни. Таким образом, существует относительная независимость уровней друг от друга.
В различных вычислительных сетях используется разное число уровней (от 4 до 7). чем больше число уровней, тем легче совершенствовать один из уровней, Однако, с увеличением числа уровней увеличивается сложность программного обеспечения.
Первый уровень, физический , определяет некоторые физические характеристики канала. Сюда относятся типы кабелей, разъёмов, электрические характеристики сигнала. По типу характеристик сети делятся на аналоговые и цифровые. Единицей обмена является бит.
Второй уровень, канальный , управляет передачей данных между двумя узлами сети. Он обеспечивает контроль корректности передачи сблокированной информации посредством проверки контрольной суммы блока. Для повышения скорости обмена осуществляется сжатие данных. При получении сообщение разворачивается. Единицей обмена является пакет.
Третий уровень, сетевой , обеспечивает управление маршрутизацией пакетов. Он распространяется на соглашение о блокировании данных и их адресов. По одному каналу может передаваться информация с нескольких модемов для увеличения его загрузки. Используются сетевые протоколы IPX и SPX и др. (в
локальных сетях), IP ( Internet Protocol – интернет протокол) и TCP ( Transmission Control Protocol – протокол управления передачей) и др. – в сетях интернета. Единицей обмена является, также пакет.
Четвёртый уровень, транспортный , отвечает за стандартизацию обмена данных между портами разных ЭВМ сети. Используются протоколы TP 0. TP 1. Единицей обмена является сеансовое сообщение.
Пятый уровень, сеансовый , определяет правила диалога прикладных программ, рестарта, проверки прав доступа к сетевым ресурсам. Единицей обмена этого и следующих уровней является пользовательское сообщение.
Шестой уровень, представления , определяет форматы данных, алфавиты, коды, представления специальных и графических символов. Здесь же определяется стандарт на форму передаваемых документов. В банковской системе распространён стандарт Swift . Он определяет расположение и назначение полей документа.
Седьмой уровень, прикладной , управляет выполнением прикладной программы.
Каждый уровень решает свои задачи, и обеспечивает сервисом расположенный над ним уровень. Правила взаимодействия соседних уровней в одной системе называют интерфейсом.
5.Прикладной, представительский и сеансовый уровни модели МОС. Их функции и назначение.
Прикладной уровень (7ой уровень эталонной модели ВОС (Взаимосвязи открытых систем) разработанной МОС (Международной организацией по стандартизации)) – это просто набор разнообразных протоколов, с помощью которых пользователи сети получают доступ к разделяемым ресурсам, таким как файлы, принтеры или гипертекстовые Web-страницы, а также организуют свою совместную работу, например, с помощью протокола электронной почты. Единица данных, которой оперирует прикладной уровень, обычно называется сообщением. Самый верхний уровень модели OSI. Он представляет собой окно для доступа прикладных процессов к сетевым услугам. Этот уровень обеспечивает услуги, напрямую поддерживающие приложения пользователя, такие как программное обеспечение для передачи файлов, доступа к базам данных и электронная почта. Нижележащие уровни поддерживают задачи, выполняемые на прикладном уровне. Прикладной уровень управляет общим доступом к сети, потоком данных и обработкой ошибок.
Протоколы: FTP (File Transfer Protocol/Протокол Передачи Файлов), HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol/Протокол Передачи Гипертекста), SIP (Session Initiation Protocol/Протокол Установления Сеанса Связи для обмена мультимедийными данными).
Представительный уровень – 6ой уровень. Сообщения, полученные с прикладного уровня, на уровне представления преобразуются в формат для передачи по сети, а полученные из сети данные преобразуются в формат приложений. Этот уровень имеет дело с формой представления передаваемой по сети информации, не меняя при этом ее содержания. За счет уровня представления информация, передаваемая прикладным уровнем одной системы, всегда понятна прикладному уровню другой системы. С помощью средств данного уровня протоколы прикладных уровней могут преодолеть синтаксические различия в представлении данных или же различия в кодах символов, например кодов ASCII и EBCDIC. На этом уровне может выполняться шифрование и дешифрование данных, благодаря которому секретность обмена данными обеспечивается сразу для всех прикладных служб. Примером такого протокола является протокол Secure Socket Layer (SSL), который обеспечивает секретный обмен сообщениями для протоколов прикладного уровня стека TCP/IP.
Сеансовый уровень обеспечивает управление диалогом: фиксирует, какая из сторон является активной в настоящий момент, предоставляет средства синхронизации. Последние позволяют вставлять контрольные точки в длинные передачи, чтобы в случае отказа можно было вернуться назад к последней контрольной точке, а не начинать все с начала. На практике немногие приложения используют сеансовый уровень, и он редко реализуется в виде отдельных протоколов, хотя функции этого уровня часто объединяют с функциями прикладного уровня и реализуют в одном протоколе.
Сеансовый уровень (5ый уровень) обеспечивает поддержание сеанса связи, позволяя приложениям взаимодействовать между собой длительное время. Уровень управляет созданием/завершением сеанса, обменом информацией, синхронизацией процессов, определением права на передачу данных и поддержанием сеанса в периоды неактивности приложений. В задачи пятого уровня входит периодическая проверка соединения, восстановление соединения в случае его разрушения, либо рестарт, если восстановление не возможно. Можно выделить 3 основных типа соединений:
— Симплексное соединение – предусматривает одностороннюю передачу данных, без отправки ответных сообщений. Примером использования такого типа соединений может служить отправка информации от различных датчиков (температуры, давления, дыма и т.п.);
—Полудуплексное соединение – предусматривает двусторонний обмен данными, но данные в текущий момент времени могут передаваться только в одну сторону. Поэтому доступ к каналу связи должен быть разграничен по какому-либо принципу. Ярким примером полудуплексного режима может служить голосовая радиосвязь, когда один из участников только говорит, а другой — только слушает. После окончания реплики первого участника, очередь предоставляется второму и т.д.
—Полный дуплекс – предусматривает установление двух независимых каналов связи между участниками обмена. Это позволяет вести прием и передачу информации одновременно. Наиболее знакомым нам типом полнодуплексных соединений является телефонная связь.
6.Транспортный уровень модели МОС.
Транспортный уровень (Transport Layer) служит для организации гарантированной доставки данных, для чего используется подготовленный канал связи. При этом отслеживается правильная последовательность передачи и приема пакетов, восстанавливаются потерянные или отсеиваются дублирующие. При необходимости данные фрагментируются (разбиваются на более мелкие пакеты) или дефрагментируются (объединяются в большой пакет), что повышает надежность доставки данных и их целостность.
Транспортный уровень (4-ый уровень эталонной модели ВОС (Взаимосвязи открытых систем) разработанной МОС (Международной организацией по стандартизации)) обеспечивает интерфейс между процессами и сетью. Он устанавливает логические каналы между процессами и обеспечивает передачу по этим каналам информационных пакетов, которыми обмениваются процессы. Логические каналы, устанавливаемые транспортным уровнем, называются транспортными каналами.Так же транспортный уровень обеспечивает приложениям или верхним уровням стека (прикладной или сеансовый уровни) передачу данных с требуемой степенью надежности. Международная организация по стандартизации (МОС) определяет 5 классов сервиса, предоставляемых транспортным уровнем, которые отличаются качеством услуг:
-срочностью;
-возможность восстановления прерванной связи ;
— способностью к обнаружению и исправлению ошибок передачи, а именно искажению, потере, дублированию пакетов.
Выбор класса определяется двумя факторами:
-какой степенью обеспечивается надежность самими приложениями и протоколами более высокого уровня, чем транспортный.
-насколько надежна система транспортировки, обеспечиваемая более низкими уровнями (сетевой, канальный, физический), чем транспортный.
Так, например, если качество каналов передачи связи очень высокое и вероятность возникновения ошибок, не обнаруженных протоколами более низких уровней, невелика, то разумно воспользоваться одним из облегченных сервисов транспортного уровня, не обремененных многочисленными проверками, квитированием и другими приемами повышения надежности. Если же транспортные средства нижних уровней изначально очень ненадежны, то целесообразно обратиться к наиболее развитому сервису транспортного уровня, который работает, используя максимум средств для
обнаружения и устранения ошибок, — с помощью предварительного установления логического соединения, контроля доставки сообщений по контрольным суммам и циклической нумерации пакетов, установления тайм-аутов доставки и т. п.
Все протоколы, начиная с транспортного уровня и выше, реализуются программными средствами конечных узлов сети, т.е. абонентскими машинамиВ качестве примера транспортных протоколов можно привести протоколы: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) и UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
7. Сетевой уровень модели МОС, как средство для маршрутизации пакетов данных.
Сетевой уровень (3ий уровень эталонной модели ВОС (Взаимосвязи открытых систем) разработанной МОС (Международной организацией по стандартизации)). Сетевой уровень служит для образования единой транспортной системы, объединяющей несколько сетей, причем эти сети могут использовать совершенно различные принципы передачи сообщений между конечными узлами и обладать произвольной структурой связей.
Протоколы канального уровня локальных сетей обеспечивают доставку данных между любыми узлами только в сети с соответствующей типовой топологией. Можно было бы усложнять протоколы канального уровня для поддержания петлевидных избыточных связей, но принцип разделения обязанностей между уровнями приводит к другому решению. Чтобы с одной стороны сохранить простоту процедур передачи данных для типовых топологий, а с другой допустить использование произвольных топологий, вводится дополнительный сетевой уровень.Под сетью понимается совокупность компьютеров, соединенных между собой в соответствии с одной из стандартных типовых топологий и использующих для передачи данных один из протоколов канального уровня, определенный для этой топологии.Внутри сети доставка данных обеспечивается соответствующим канальным уровнем, а вот доставкой данных между сетями занимается сетевой уровень, который и поддерживает возможность правильного выбора маршрута передачи сообщения даже в том случае, когда структура связей между составляющими сетями имеет характер, отличный от принятого в протоколах канального уровня.Сети соединяются между собой специальными устройствами, называемыми маршрутизаторами. Маршрутизаторэто устройство, которое собирает информацию о топологии межсетевых соединений и на ее основании пересылает пакеты сетевого уровня в сеть назначения.Чтобы передать сообщение от отправителя, находящегося в одной сети, получателю, находящемуся в другой сети, нужно совершить некоторое количество транзитных передач, каждый раз выбирая подходящий маршрут. Таким образом, маршрут представляет собой последовательность маршрутизаторов, через которые проходит пакет.
Проблема выбора наилучшего пути называется маршрутизацией, и ее решение является одной из главных задач сетевого уровня. Критерием при выборе маршрута является время передачи данных по этому маршруту; оно зависит от пропускной способности каналов связи и интенсивности трафика, которая может изменяться с течением времени. Выбор маршрута может осуществляться и по другим критериям, например надежности передачи.
Сетевой уровень решает также задачи согласования разных технологий, упрощения адресации в крупных сетях и создания барьеров на пути нежелательного трафика между сетями.
Сообщения сетевого уровня принято называть пакетами. При организации доставки пакетов на сетевом уровне используется понятие «номер сети». В этом случае адрес получателя состоит из
старшей части — номера сети и младшей — номера узла в этой сети. Все узлы одной сети должны иметь одну и ту же старшую часть адреса, поэтому сеть — это совокупность узлов, сетевой адрес которых содержит один и тот же номер сети.
На сетевом уровне определяются следующие протоколы. Первый вид -сетевые протоколы — реализуют продвижение пакетов через сеть. Второй вид протоколы маршрутизации. С помощью этих протоколов маршрутизаторы собирают информацию о топологии межсетевых соединений. Третий вид — протоколы, которые отвечают за отображение адреса узла, используемого на сетевом уровне, в локальный адрес сети. Такие протоколы часто называют протоколами разрешения адресов. Протоколы сетевого уровня реализуются программными модулями операционной системы, а также программными и аппаратными средствами маршрутизаторов.Примерами протоколов сетевого уровня являются протокол межсетевого взаимодействия IP стека TCP/IP и протокол межсетевого обмена пакетами IPX стека Novell.
8. Канальный и физический уровни модели МОС. Их функции.
Физический уровень — (1ый уровень эталонной модели ВОС (Взаимосвязи открытых систем) разработанной МОС (Международной организацией по стандартизации)). Физический уровень имеет дело с передачей битов по физическим каналам связи, таким, например, как коаксиальный кабель, витая пара, оптоволоконный кабель или цифровой территориальный канал. К этому уровню имеют отношение характеристики физических сред передачи данных, такие как полоса пропускания, помехозащищенность, волновое сопротивление и другие. На этом же уровне определяются характеристики электрических сигналов, передающих дискретную информацию, например, крутизна фронтов импульсов, уровни напряжения или тока передаваемого сигнала, тип кодирования, скорость передачи сигналов.
Передача сигналов в физической среде осуществляется в виде прямого манчестерского кода.
При манчестерском кодировании каждый такт делится на две части. Информация
кодируется перепадами потенциала в середине каждого такта. Единица кодируется перепадом от низкого уровня сигнала к высокому, а ноль — обратным перепадом. В начале каждого такта может происходить служебный перепад сигнала, если нужно представить несколько единиц или нулей подряд. Так как сигнал изменяется по крайней мере один раз за такт передачи одного бита данных, то манчестерский код обладает хорошими самосинхронизирующими свойствами и повышенной помехоустойчивостью.
Для физического уровня стандартизированы типы разъемов и назначение каждого контакта.
Функции физического уровня реализуются во всех устройствах, подключенных к сети. Со стороны компьютера функции физического уровня выполняются сетевым адаптером или последовательным портом.