Last Updated on December 12, 2022 by
Cisco Netacad ITN Version 7.00 CCNA 1 v7 Final Exam Answers 2021 2022 2023 – Introduction to Networks
-
Recommend
ITN (Version 7.00 & v7.02) – ITNv7 Final Exam Answers 2021 2022 2023 Full 100%
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 143. What service is the client requesting?
- Telnet
- SSH
- IMAP
- FTP
-
Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.) —> Case A
-
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
- implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- applies delimiting of Ethernet frame fields to synchronize communication between nodes
-
Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.) —> Case B
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
-
Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.) —> Case C
- implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
- implements a process to delimit fields within an Ethernet 2 frame
-
-
A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
- Enter CTRL-Z at the privileged mode prompt.
- Power cycle the device.
- Exit privileged EXEC mode and press Enter.
- Exit global configuration mode.
- Reboot the device.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
While at the privileged mode prompt such as Router#, type exit ,press Enter , and the banner message appears. Power cycling a network device that has had the banner motd command issued will also display the banner message, but this is not a quick way to test the configuration.
-
What happens when the transport input ssh command is entered on the switch vty lines?
- The switch requires a username/password combination for remote access.
- The SSH client on the switch is enabled.
- Communication between the switch and remote users is encrypted.
- The switch requires remote connections via a proprietary client software.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The transport input ssh command when entered on the switch vty (virtual terminal lines) will encrypt all inbound controlled telnet connections.
-
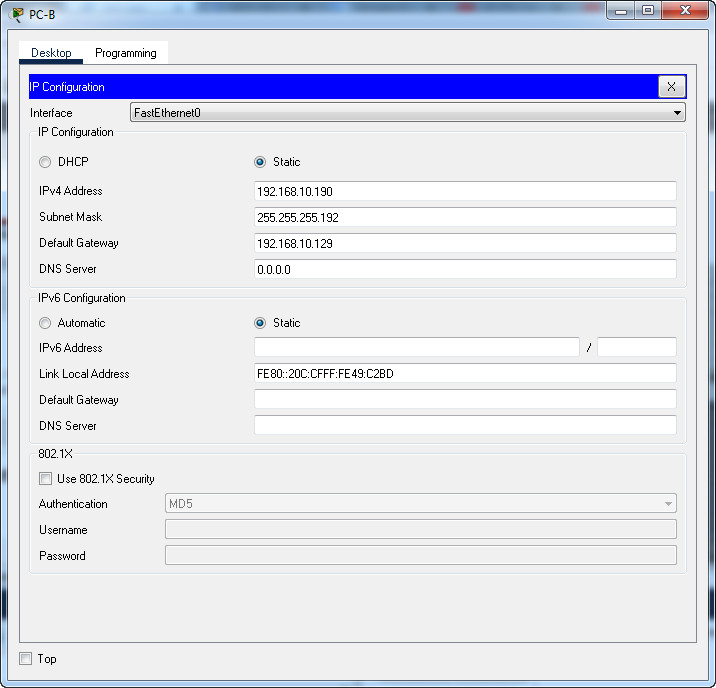
What is the subnet ID associated with the IPv6 address 2001:DA48:FC5:A4:3D1B::1/64?
- 2001:DA48::/64
- 2001::/64
- 2001:DA48:FC5:A4::/64
- 2001:DA48:FC5::A4:/64
Explanation:
-
A client is using SLAAC to obtain an IPv6 address for its interface. After an address has been generated and applied to the interface, what must the client do before it can begin to use this IPv6 address?
- It must send an ICMPv6 Router Solicitation message to determine what default gateway it should use.
- It must send a DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST message to request the address of the DNS server.
- It must send a DHCPv6 REQUEST message to the DHCPv6 server to request permission to use this address.
- It must send an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message to ensure that the address is not already in use on the network.
Explanation:
Stateless DHCPv6 or stateful DHCPv6 uses a DHCP server, but Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) does not. A SLAAC client can automatically generate an address that is based on information from local routers via Router Advertisement (RA) messages. Once an address has been assigned to an interface via SLAAC, the client must ensure via Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) that the address is not already in use. It does this by sending out an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message and listening for a response. If a response is received, then it means that another device is already using this address.
-
Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FE80::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FF00::/8
- FEC0::/10
Explanation:
Link-local addresses are in the range of FE80::/10 to FEBF::/10. The original IPv6 specification defined site-local addresses and used the prefix range FEC0::/10, but these addresses were deprecated by the IETF in favor of unique local addresses. FDEE::/7 is a unique local address because it is in the range of FC00::/7 to FDFF::/7. IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8.
-
What mechanism is used by a router to prevent a received IPv4 packet from traveling endlessly on a network?
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It increments the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Parameter Problem message to the source host.
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It decrements the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Time Exceeded message to the source host.
-
A network administrator is designing the layout of a new wireless network. Which three areas of concern should be accounted for when building a wireless network? (Choose three.)
- mobility options
- security
- interference
- coverage area
- packet collision
- extensive cabling
Explanation:
The three areas of concern for wireless networks focus on the size of the coverage area, any nearby interference, and providing network security. Extensive cabling is not a concern for wireless networks, as a wireless network will require minimal cabling for providing wireless access to hosts. Mobility options are not a component of the areas of concern for wireless networks.
-
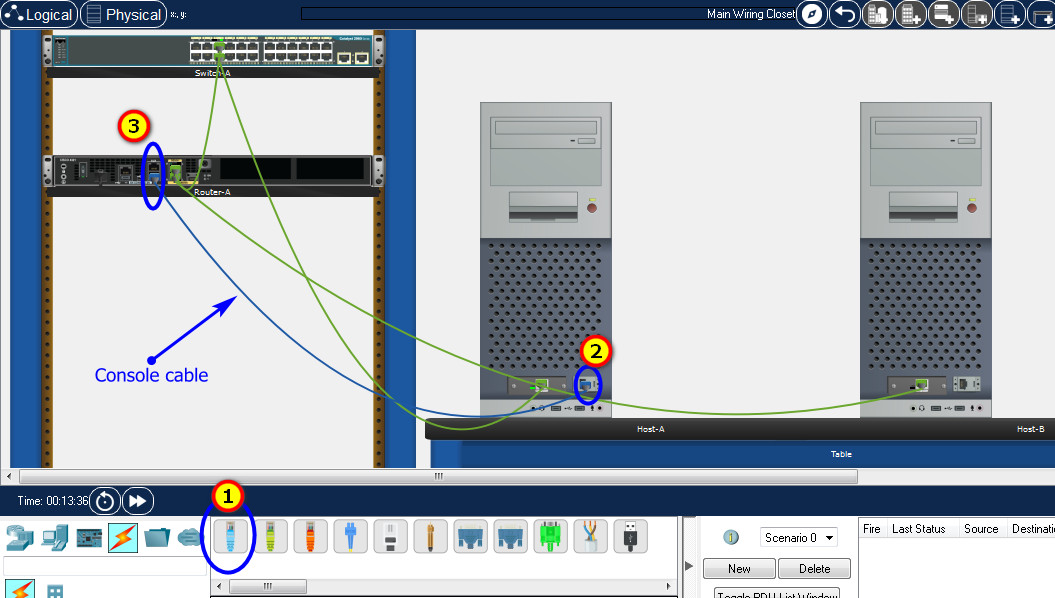
Refer to the exhibit. What is wrong with the displayed termination?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 07 - The untwisted length of each wire is too long.
- The woven copper braid should not have been removed.
- The wrong type of connector is being used.
- The wires are too thick for the connector that is used.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a cable to an RJ-45 connector is terminated, it is important to ensure that the untwisted wires are not too long and that the flexible plastic sheath surrounding the wires is crimped down and not the bare wires. None of the colored wires should be visible from the bottom of the jack.
-
A network administrator notices that some newly installed Ethernet cabling is carrying corrupt and distorted data signals. The new cabling was installed in the ceiling close to fluorescent lights and electrical equipment. Which two factors may interfere with the copper cabling and result in signal distortion and data corruption? (Choose two.)
- EMI
- signal attenuation
- crosstalk
- RFI
- extended length of cabling
Explanation:
EMI and RFI signals can distort and corrupt data signals that are carried by copper media. These distortions usually come from radio waves and electromagnetic devices such as motors and florescent lights. Crosstalk is a disturbance that is caused by adjacent wires bundled too close together with the magnetic field of one wire affecting another. Signal attenuation is caused when an electrical signal begins to deteriorate over the length of a copper cable.
-
Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function of TCP or UDP in this situation? (Choose three.)
- TCP is the preferred protocol when a function requires lower network overhead.
- The source port field identifies the running application or service that will handle data returning to the PC.
- The TCP source port number identifies the sending host on the network.
- UDP segments are encapsulated within IP packets for transport across the network.
- The UDP destination port number identifies the application or service on the server which will handle the data.
- The TCP process running on the PC randomly selects the destination port when establishing a session with the server.
Explanation:
Layer 4 port numbers identify the application or service which will handle the data. The source port number is added by the sending device and will be the destination port number when the requested information is returned. Layer 4 segments are encapsulated within IP packets. UDP, not TCP, is used when low overhead is needed. A source IP address, not a TCP source port number, identifies the sending host on the network. Destination port numbers are specific ports that a server application or service monitors for requests.
-
Match the application protocols to the correct transport protocols.
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 01 -
A group of Windows PCs in a new subnet has been added to an Ethernet network. When testing the connectivity, a technician finds that these PCs can access local network resources but not the Internet resources. To troubleshoot the problem, the technician wants to initially confirm the IP address and DNS configurations on the PCs, and also verify connectivity to the local router. Which three Windows CLI commands and utilities will provide the necessary information? (Choose three.)
- netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor
- arp -a
- tracert
- ping
- ipconfig
- nslookup
- telnet
Explanation:
The ipconfig and nslookup commands will provide initial IP address and DNS configuration information to the technicians and determine if DHCP is assigning correct information to the PCs. The ping utility would be used to verify, or not, connectivity to the default gateway (router) using the configured default gateway address, or using the known correct default gateway address if these are found to be different. The arp -a or netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor commands could be used if the problem is then suspected to be an IP address to MAC address mapping issue. The telnet and tracert utilities could be used to determine where the problem was located in the network if the default gateway configuration was found to be correct.
-
What two pieces of information are displayed in the output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose two.)
- speed and duplex settings
- MAC addresses
- next-hop addresses
- interface descriptions
- IP addresses
- Layer 1 statuses
Explanation:
The command show ip interface brief shows the IP address of each interface, as well as the operational status of the interfaces at both Layer 1 and Layer 2. In order to see interface descriptions and speed and duplex settings, use the command show running-config interface. Next-hop addresses are displayed in the routing table with the command show ip route, and the MAC address of an interface can be seen with the command show interfaces.
-
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 25 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.128
-
Which frame field is created by a source node and used by a destination node to ensure that a transmitted data signal has not been altered by interference, distortion, or signal loss?
- transport layer error check field
- error correction process field
- flow control field
- User Datagram Protocol field
- frame check sequence field
-
What is a function of the data link layer?
- provides delivery of data between two applications
- provides for the exchange of frames over a common local media
- provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
- provides the formatting of data
-
What are three characteristics of the CSMA/CD process? (Choose three.)
- After detecting a collision, hosts can attempt to resume transmission after a random time delay has expired.
- A jam signal indicates that the collision has cleared and the media is not busy.
- All of the devices on a segment see data that passes on the network medium.
- The device with the electronic token is the only one that can transmit after a collision.
- Devices can be configured with a higher transmission priority.
- A device listens and waits until the media is not busy before transmitting.
-
What characteristic describes a Trojan horse?
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- malicious software or code running on an end device
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
-
What three requirements are defined by the protocols used in network communcations to allow message transmission across a network? (Choose three.)
- end-device installation
- media selection
- message encoding
- delivery options
- connector specifications
- message size
-
What are two features of ARP? (Choose two.)
- If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.
- When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
- If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
- An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
- If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.
Explanation:
When a node encapsulates a data packet into a frame, it needs the destination MAC address. First it determines if the destination device is on the local network or on a remote network. Then it checks the ARP table (not the MAC table) to see if a pair of IP address and MAC address exists for either the destination IP address (if the destination host is on the local network) or the default gateway IP address (if the destination host is on a remote network). If the match does not exist, it generates an ARP broadcast to seek the IP address to MAC address resolution. Because the destination MAC address is unknown, the ARP request is broadcast with the MAC address FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. Either the destination device or the default gateway will respond with its MAC address, which enables the sending node to assemble the frame. If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will discard the packet because a frame cannot be created.
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 06 - The entire command, configure terminal , must be used.
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
In order to enter global configuration mode, the command configure terminal , or a shortened version such as config t , must be entered from privileged EXEC mode. In this scenario the administrator is in user EXEC mode, as indicated by the > symbol after the hostname. The administrator would need to use the enable command to move into privileged EXEC mode before entering the configure terminal command.
-
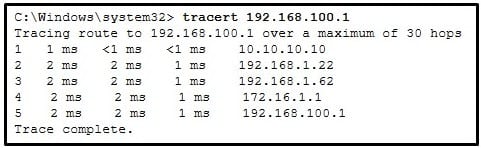
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 05 - This host does not have a default gateway configured.
- There are 4 hops between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
- There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
Explanation:
The output displays a successful Layer 3 connection between a host computer and a host at 19.168.100.1. It can be determined that 4 hops exist between them and the average transmission time is 1 milliseconds. Layer 3 connectivity does not necessarily mean that an application can run between the hosts.
-
What are two characteristics of IP? (Choose two.)
- retransmits packets if errors occur
- guarantees delivery of packets
- does not require a dedicated end-to-end connection
- operates independently of the network media
- re-assembles out of order packets into the correct order at the receiver end
Explanation:
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a connectionless, best effort protocol. This means that IP requires no end-to-end connection nor does it guarantee delivery of packets. IP is also media independent, which means it operates independently of the network media carrying the packets.
-
What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a host needs to send a message to another host located on the same network, it can forward the message directly. However, when a host needs to send a message to a remote network, it must use the router, also known as the default gateway. This is because the data link frame address of the remote destination host cannot be used directly. Instead, the IP packet has to be sent to the router (default gateway) and the router will forward the packet toward its destination. Therefore, if the default gateway is incorrectly configured, the host can communicate with other hosts on the same network, but not with hosts on remote networks.
-
Users report that the network access is slow. After questioning the employees, the network administrator learned that one employee downloaded a third-party scanning program for the printer. What type of malware might be introduced that causes slow performance of the network?
- spam
- virus
- worm
- phishing
Explanation:
-
A company has a file server that shares a folder named Public. The network security policy specifies that the Public folder is assigned Read-Only rights to anyone who can log into the server while the Edit rights are assigned only to the network admin group. Which component is addressed in the AAA network service framework?
- automation
- authorization
- accounting
- authentication
Explanation:
After a user is successfully authenticated (logged into the server), the authorization is the process of determining what network resources the user can access and what operations (such as read or edit) the user can perform.
-
What are two common causes of signal degradation when using UTP cabling? (Choose two.)
- loss of light over long distances
- low-quality cable or connectors
- low-quality shielding in cable
- installing cables in conduit
- improper termination
-
Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
Explanation:
The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
-
What is the consequence of configuring a router with the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command?
- Each router interface will generate an IPv6 link-local address.
- The IPv6 enabled router interfaces begin sending ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages.
- It statically creates a global unicast address on this router.
- All router interfaces will be automatically activated.
-
Which two protocols operate at the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose two.)
- POP
- DNS
- IP
- TCP
- Ethernet
- UDP
-
An employee of a large corporation remotely logs into the company using the appropriate username and password. The employee is attending an important video conference with a customer concerning a large sale. It is important for the video quality to be excellent during the meeting. The employee is unaware that after a successful login, the connection to the company ISP failed. The secondary connection, however, activated within seconds. The disruption was not noticed by the employee or other employees.
What three network characteristics are described in this scenario? (Choose three.)- integrity
- scalability
- quality of service
- fault tolerance
- powerline networking
- security
-
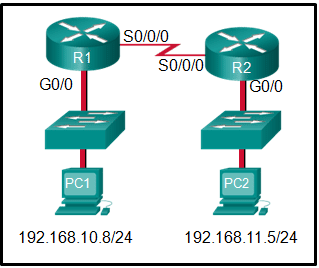
Refer to the exhibit. If PC1 is sending a packet to PC2 and routing has been configured between the two routers, what will R1 do with the Ethernet frame header attached by PC1?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 04 - open the header and use it to determine whether the data is to be sent out S0/0/0
- open the header and replace the destination MAC address with a new one
- nothing, because the router has a route to the destination network
- remove the Ethernet header and configure a new Layer 2 header before sending it out S0/0/0
Explanation:
When PC1 forms the various headers attached to the data one of those headers is the Layer 2 header. Because PC1 connects to an Ethernet network, an Ethernet header is used. The source MAC address will be the MAC address of PC1 and the destination MAC address will be that of G0/0 on R1. When R1 gets that information, the router removes the Layer 2 header and creates a new one for the type of network the data will be placed onto (the serial link).
-
Which three layers of the OSI model map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- transport
- application
- network
- session
- data link
- presentation
Explanation:
-
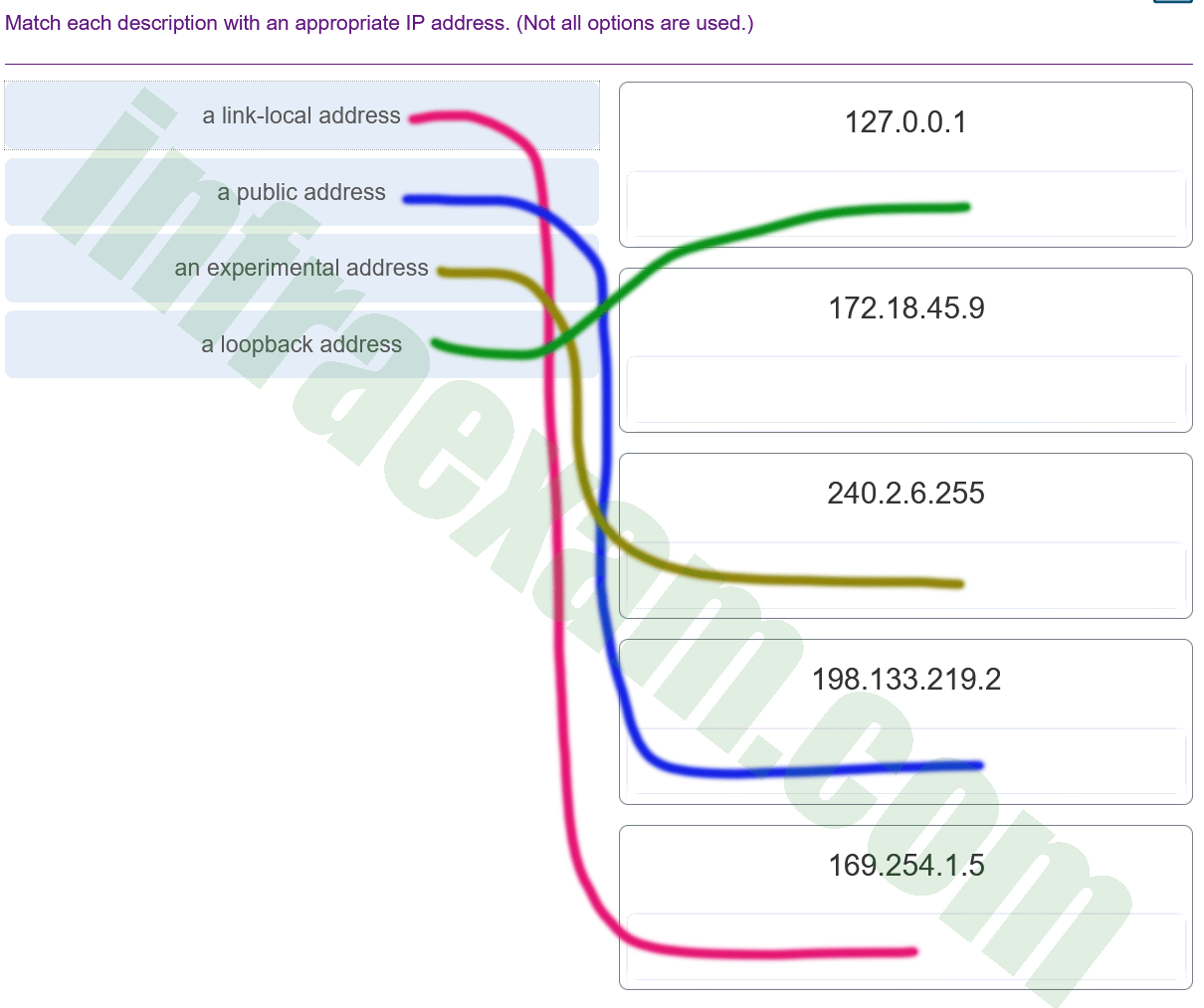
Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 02 Explanation:
Link-Local addresses are assigned automatically by the OS environment and are located in the block 169.254.0.0/16. The private addresses ranges are 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, and 192.168.0.0/16. TEST-NET addresses belong to the range 192.0.2.0/24. The addresses in the block 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.254 are reserved as experimental addresses. Loopback addresses belong to the block 127.0.0.0/8.
-
What does the term “attenuation” mean in data communication?
- strengthening of a signal by a networking device
- leakage of signals from one cable pair to another
- loss of signal strength as distance increases
- time for a signal to reach its destination
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Data is transmitted on copper cables as electrical pulses. A detector in the network interface of a destination device must receive a signal that can be successfully decoded to match the signal sent. However, the farther the signal travels, the more it deteriorates. This is referred to as signal attenuation.
-
Which two statements describe how to assess traffic flow patterns and network traffic types using a protocol analyzer? (Choose two.)
- Capture traffic during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types.
- Perform the capture on different network segments.
- Only capture WAN traffic because traffic to the web is responsible for the largest amount of traffic on a network.
- Only capture traffic in the areas of the network that receive most of the traffic such as the data center.
- Capture traffic on the weekends when most employees are off work.
Explanation:
Traffic flow patterns should be gathered during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types. The capture should also be performed on different network segments because some traffic will be local to a particular segment.
-
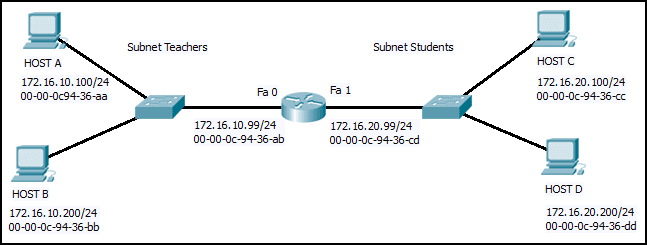
Refer to the exhibit. Host B on subnet Teachers transmits a packet to host D on subnet Students. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 addresses are contained in the PDUs that are transmitted from host B to the router?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 03 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-dd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.100.200 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-cd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.99
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
- Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-dd
-
Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
- 192.168.1.64/26
Explanation:
For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
-
What are two problems that can be caused by a large number of ARP request and reply messages? (Choose two.)
- A large number of ARP request and reply messages may slow down the switching process, leading the switch to make many changes in its MAC table.
- The ARP request is sent as a broadcast, and will flood the entire subnet.
- Switches become overloaded because they concentrate all the traffic from the attached subnets.
- All ARP request messages must be processed by all nodes on the local network.
- The network may become overloaded because ARP reply messages have a very large payload due to the 48-bit MAC address and 32-bit IP address that they contain.
-
Why would a Layer 2 switch need an IP address?
- to enable the switch to be managed remotely
- to enable the switch to receive frames from attached PCs
- to enable the switch to send broadcast frames to attached PCs
- to enable the switch to function as a default gateway
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A switch, as a Layer 2 device, does not need an IP address to transmit frames to attached devices. However, when a switch is accessed remotely through the network, it must have a Layer 3 address. The IP address must be applied to a virtual interface rather than to a physical interface. Routers, not switches, function as default gateways.
-
How does the service password-encryption command enhance password security on Cisco routers and switches?
- It requires encrypted passwords to be used when connecting remotely to a router or switch with Telnet.
- It encrypts passwords that are stored in router or switch configuration files.
- It requires that a user type encrypted passwords to gain console access to a router or switch.
- It encrypts passwords as they are sent across the network.
Explanation:
The service password-encryption command encrypts plaintext passwords in the configuration file so that they cannot be viewed by unauthorized users.
-
Which two statements are correct in a comparison of IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers? (Choose two.)
- The Destination Address field is new in IPv6.
- The Source Address field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
- The Version field from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6.
- The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6.
- The Header Checksum field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
-
Which two statements accurately describe an advantage or a disadvantage when deploying NAT for IPv4 in a network? (Choose two.)
- NAT will impact negatively on switch performance.
- NAT causes routing tables to include more information.
- NAT improves packet handling.
- NAT adds authentication capability to IPv4.
- NAT provides a solution to slow down the IPv4 address depletion.
- NAT introduces problems for some applications that require end-to-end connectivity.
-
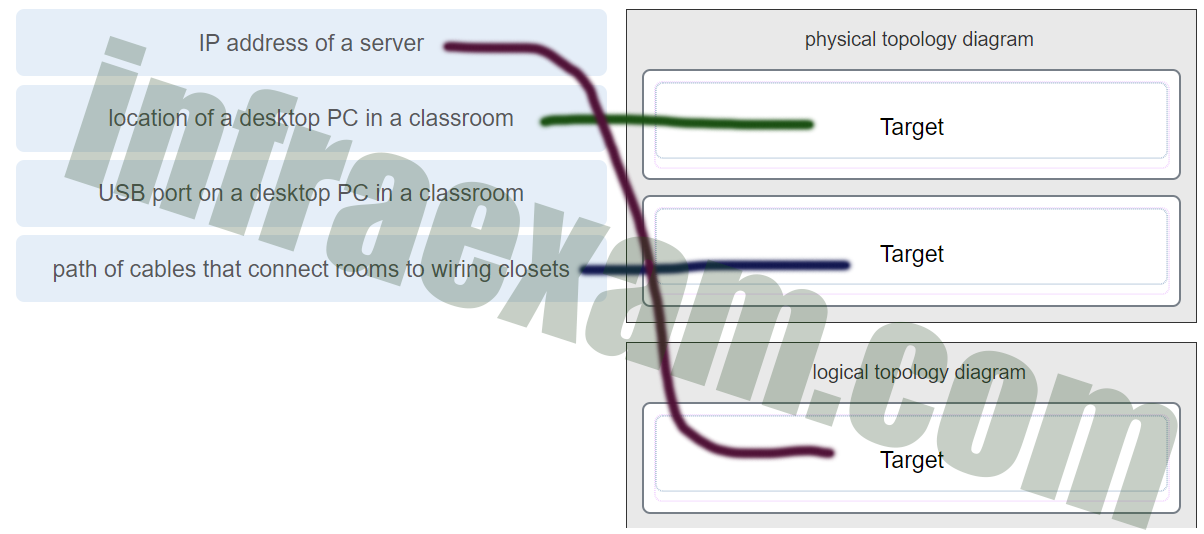
Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 003 Explanation:
A logical topology diagram typically depicts the IP addressing scheme and groupings of devices and ports. A physical topology diagram shows how those devices are connected to each other and the network, focusing on the physical locations of intermediary devices, configured ports, and cabling.
-
What service is provided by HTTP?
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 67. What service is the client requesting?
- Telnet
- FTP
- SSH
- DHCP
-
What are the two most effective ways to defend against malware? (Choose two.)
- Implement strong passwords.
- Update the operating system and other application software.
- Install and update antivirus software.
- Implement RAID.
- Implement a VPN.
- Implement network firewalls.
Explanation:
-
An administrator defined a local user account with a secret password on router R1 for use with SSH. Which three additional steps are required to configure R1 to accept only encrypted SSH connections? (Choose three.)
- Configure the IP domain name on the router.
- Enable inbound vty Telnet sessions.
- Configure DNS on the router.
- Generate the SSH keys.
- Generate two-way pre-shared keys.
- Enable inbound vty SSH sessions.
Explanation:
There are four steps to configure SSH support on a Cisco router:
Step 1: Set the domain name.
Step 2: Generate one-way secret keys.
Step 3: Create a local username and password.
Step 4: Enable SSH inbound on a vty line.
-
A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in its ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
- It will send the frame and use its own MAC address as the destination.
- It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
- It will send a request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.
-
Match the header field with the appropriate layer of the OSI model. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 03 -
When a switch configuration includes a user-defined error threshold on a per-port basis, to which switching method will the switch revert when the error threshold is reached?
- fast-forward
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
-
What are proprietary protocols?
- protocols that can be freely used by any organization or vendor
- protocols developed by private organizations to operate on any vendor hardware
- a collection of protocols known as the TCP/IP protocol suite
- protocols developed by organizations who have control over their definition and operation
Explanation:
Proprietary protocols have their definition and operation controlled by one company or vendor. Some of them can be used by different organizations with permission from the owner. The TCP/IP protocol suite is an open standard, not a proprietary protocol.
-
What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- A company can monopolize the market.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
Explanation:
A monopoly by one company is not a good idea from a user point of view. If a protocol can only be run on one brand, it makes it difficult to have mixed equipment in a network. A proprietary protocol is not free to use. An open standard protocol will in general be implemented by a wide range of vendors.
-
Which type of server relies on record types such as A, NS, AAAA, and MX in order to provide services?
- file
- web
- DNS
Explanation:
-
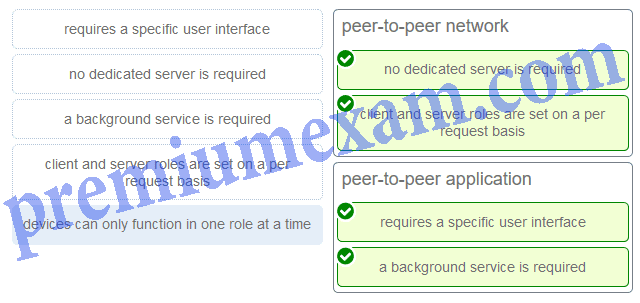
Match a statement to the related network model. (Not all options are used.)
ITN Chapter 10 Exam Answers 02 Explanation:
Peer-to-peer networks do not require the use of a dedicated server, and devices can assume both client and server roles simultaneously on a per request basis. Because they do not require formalized accounts or permissions, they are best used in limited situations. Peer-to-peer applications require a user interface and background service to be running, and can be used in more diverse situations.
-
A network administrator wants to have the same network mask for all networks at a particular small site. The site has the following networks and number of devices:
IP phones – 22 addresses
PCs – 20 addresses needed
Printers – 2 addresses needed
Scanners – 2 addresses neededThe network administrator has deemed that 192.168.10.0/24 is to be the network used at this site. Which single subnet mask would make the most efficient use of the available addresses to use for the four subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
-
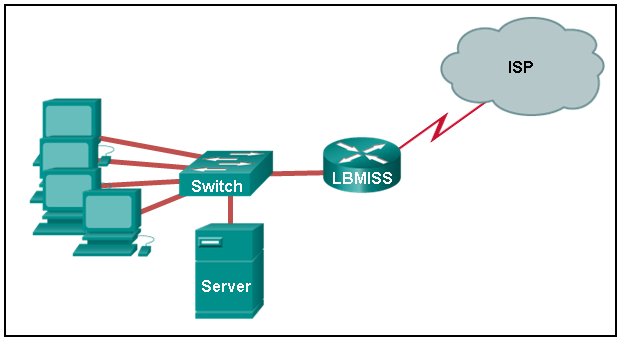
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has assigned the LAN of LBMISS an address range of 192.168.10.0. This address range has been subnetted using a /29 prefix. In order to accommodate a new building, the technician has decided to use the fifth subnet for configuring the new network (subnet zero is the first subnet). By company policies, the router interface is always assigned the first usable host address and the workgroup server is given the last usable host address. Which configuration should be entered into the properties of the workgroup server to allow connectivity to the Internet?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 02 - IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
- IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
- IP address: 192.168.10.254 subnet mask: 255.255.255.0, default gateway: 192.168.10.1
- IP address: 192.168.10.41 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.46
- IP address: 192.168.10.65 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.76
Explanation:
-
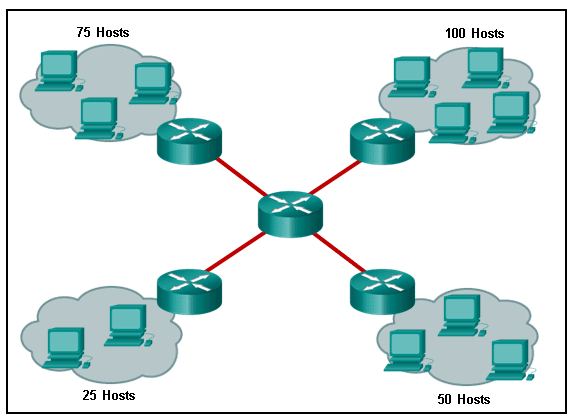
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer has been given the network address of 192.168.99.0 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192 to subnet across the four networks shown. How many total host addresses are unused across all four subnets?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 01 - 158
- 200
- 224
- 88
- 72
Explanation:
-
What would be the interface ID of an IPv6 enabled interface with a MAC address of 1C-6F-65-C2-BD-F8 when the interface ID is generated by using the EUI-64 process?
- 1E6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- C16F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 0C6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 106F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
-
Which information does the show startup-config command display?
- the IOS image copied into RAM
- the bootstrap program in the ROM
- the contents of the saved configuration file in the NVRAM
- the contents of the current running configuration file in the RAM
-
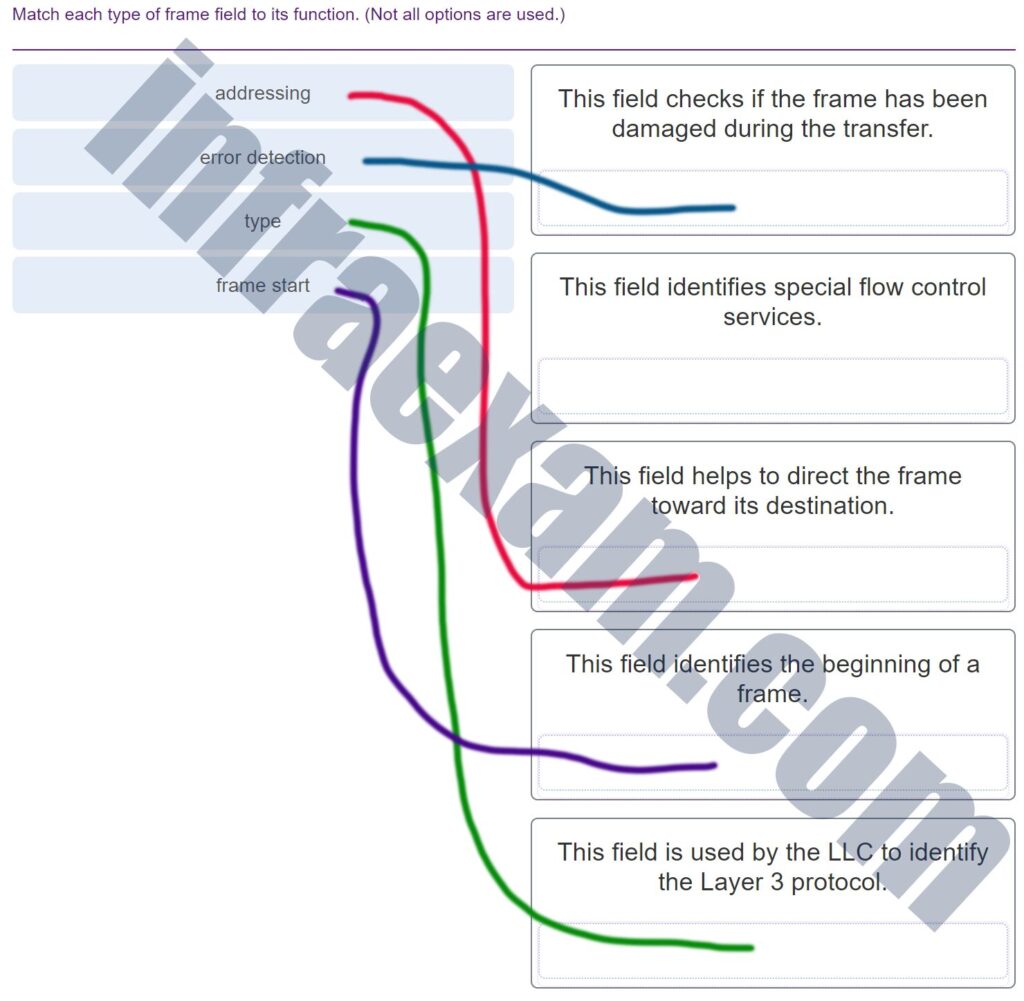
Match each type of frame field to its function. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 004 -
What are two primary responsibilities of the Ethernet MAC sublayer? (Choose two.)
- accessing the media
- data encapsulation
- logical addressing
- error detection
- frame delimiting
-
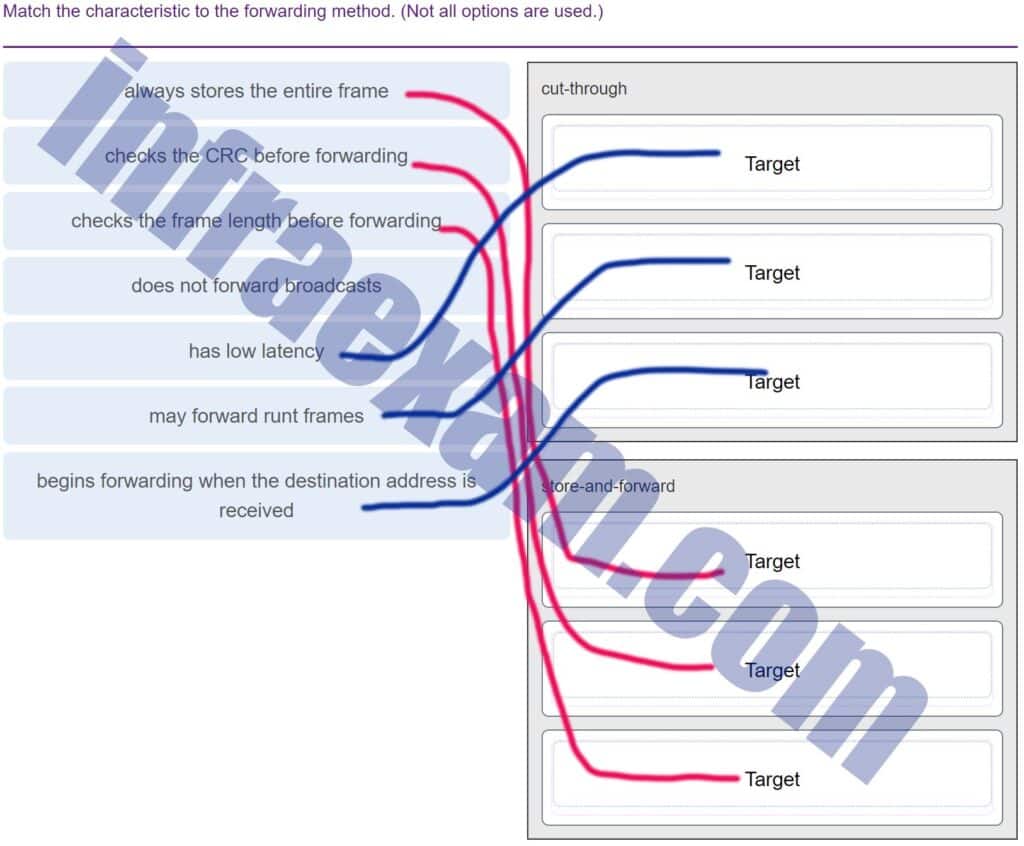
Match the characteristic to the forwarding method. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 005 -
Which switching method drops frames that fail the FCS check?
- store-and-forward switching
- ingress port buffering
- cut-through switching
- borderless switching
-
What is an advantage for small organizations of adopting IMAP instead of POP?
- IMAP sends and retrieves email, but POP only retrieves email.
- POP only allows the client to store messages in a centralized way, while IMAP allows distributed storage.
- Messages are kept in the mail servers until they are manually deleted from the email client.
- When the user connects to a POP server, copies of the messages are kept in the mail server for a short time, but IMAP keeps them for a long time.
Explanation:
-
A wired laser printer is attached to a home computer. That printer has been shared so that other computers on the home network can also use the printer. What networking model is in use?
- point-to-point
- client-based
- peer-to-peer (P2P)
- master-slave
Explanation:
-
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 200 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
-
Which wireless technology has low-power and data rate requirements making it popular in home automation applications?
- ZigBee
- 5G
- Wi-Fi
- LoRaWAN
-
What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- 3-way handshake
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering
- use of checksum
Explanation:
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 69. What service is the client requesting?
- DHCP
- SMTP
- TFTP
- DNS
-
What service is provided by Internet Messenger?
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
-
What characteristic describes antispyware?
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- applications that protect end devices from becoming infected with malicious software
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
-
A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses
Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses
Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
-
Refer to the exhibit. A company uses the address block of 128.107.0.0/16 for its network. What subnet mask would provide the maximum number of equal size subnets while providing enough host addresses for each subnet in the exhibit?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 08 - 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240
-
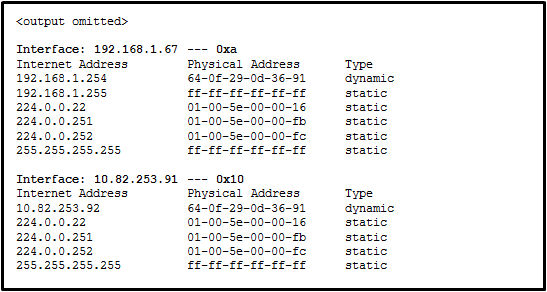
Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol was responsible for building the table that is shown?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 09 - ARP
- DNS
- DHCP
- ICMP
-
Which two traffic types use the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP)? (Choose two.)
- web
- peer to peer
- file transfer
- video
- voice
-
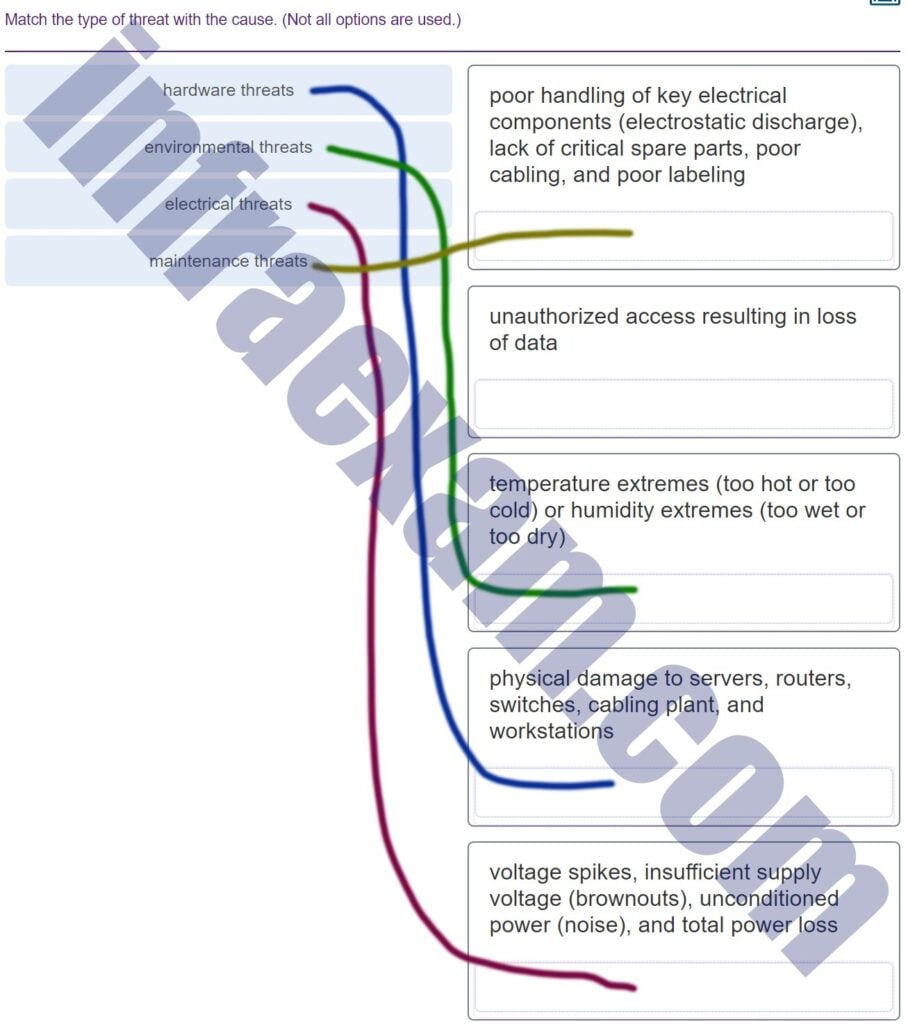
Match the type of threat with the cause. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 006 -
Refer to the exhibit. The switches are in their default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for its default gateway. Which network hosts will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 10 - only hosts A, B, C, and D
- only router R1
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only hosts B and C
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
- only host D
Explanation:
-
Which value, that is contained in an IPv4 header field, is decremented by each router that receives a packet?
- Differentiated Services
- Fragment Offset
- Header Length
- Time-to-Live
-
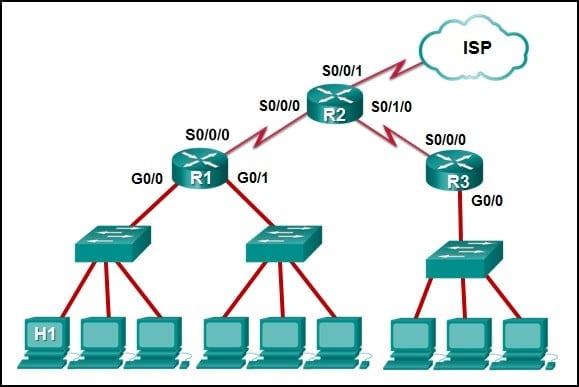
Refer to the exhibit. The IP address of which device interface should be used as the default gateway setting of host H1?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 11 - R2: S0/0/1
- R1: G0/0
- R2: S0/0/0
- R1: S0/0/0
-
Which two statements describe features of an IPv4 routing table on a router? (Choose two.)
- Directly connected interfaces will have two route source codes in the routing table: C and S .
- The netstat -r command can be used to display the routing table of a router.
- If there are two or more possible routes to the same destination, the route associated with the higher metric value is included in the routing table.
- The routing table lists the MAC addresses of each active interface.
- If a default static route is configured in the router, an entry will be included in the routing table with source code S .
- It stores information about routes derived from the active router interfaces.
-
Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
Explanation:
-
What is the consequence of configuring a router with the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command?
- All router interfaces will be automatically activated.
- Each router interface will generate an IPv6 link-local address.
- The IPv6 enabled router interfaces begin sending ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages.
- It statically creates a global unicast address on this router.
-
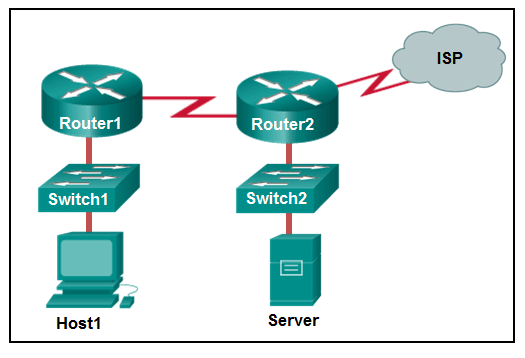
Refer to the exhibit. If Host1 were to transfer a file to the server, what layers of the TCP/IP model would be used?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 12 - only application, Internet, and network access layers
- only application, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
- application, session, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
- only application and Internet layers
- application, transport, Internet, and network access layers
- only Internet and network access layers
Explanation:
-
The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
Explanation:
-
What characteristic describes adware?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
-
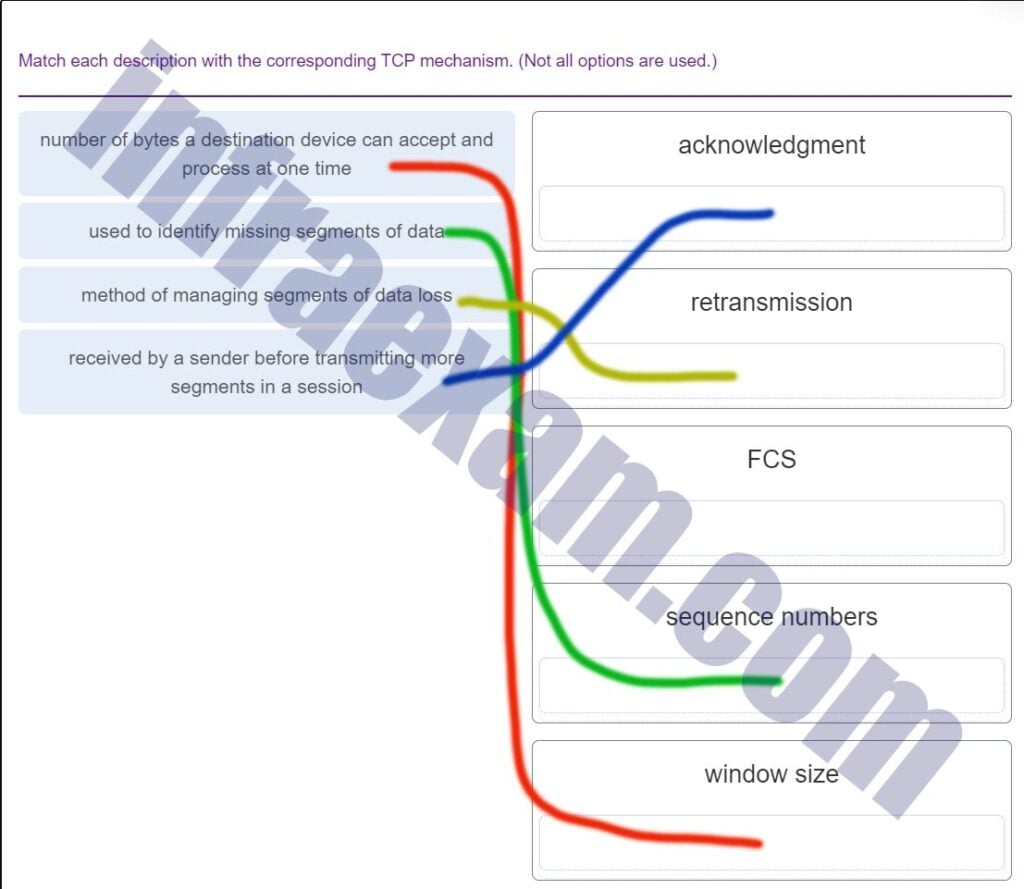
Match each description with the corresponding TCP mechanism. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 007 -
What is the purpose of the TCP sliding window?
- to ensure that segments arrive in order at the destination
- to request that a source decrease the rate at which it transmits data
- to inform a source to retransmit data from a specific point forward
- to end communication when data transmission is complete
-
What technique is used with UTP cable to help protect against signal interference from crosstalk?
- terminating the cable with special grounded connectors
- twisting the wires together into pairs
- wrapping a foil shield around the wire pairs
- encasing the cables within a flexible plastic sheath
Explanation:
To help prevent the effects of crosstalk, UTP cable wires are twisted together into pairs. Twisting the wires together causes the magnetic fields of each wire to cancel each other out.
-
A network technician is researching the use of fiber optic cabling in a new technology center. Which two issues should be considered before implementing fiber optic media? (Choose two.)
- Fiber optic cabling requires different termination and splicing expertise from what copper cabling requires.
- Fiber optic cabling requires specific grounding to be immune to EMI.
- Fiber optic cabling is susceptible to loss of signal due to RFI.
- Fiber optic provides higher data capacity but is more expensive than copper cabling.
- Fiber optic cable is able to withstand rough handling.
-
Users are reporting longer delays in authentication and in accessing network resources during certain time periods of the week. What kind of information should network engineers check to find out if this situation is part of a normal network behavior?
- syslog records and messages
- debug output and packet captures
- network configuration files
- the network performance baseline
-
A user is complaining that an external web page is taking longer than normal to load.The web page does eventually load on the user machine. Which tool should the technician use with administrator privileges in order to locate where the issue is in the network?
- ipconfig /displaydns
- nslookup
- tracert
- ping
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 53. What service is the client requesting?
- SSH
- FTP
- Telnet
- DNS
-
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 issues an ARP request because it needs to send a packet to PC2. In this scenario, what will happen next?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 13 - RT1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/0 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/1 MAC address.
- PC2 will send an ARP reply with its MAC address.
Explanation:
When a network device wants to communicate with another device on the same network, it sends a broadcast ARP request. In this case, the request will contain the IP address of PC2. The destination device (PC2) sends an ARP reply with its MAC address.
-
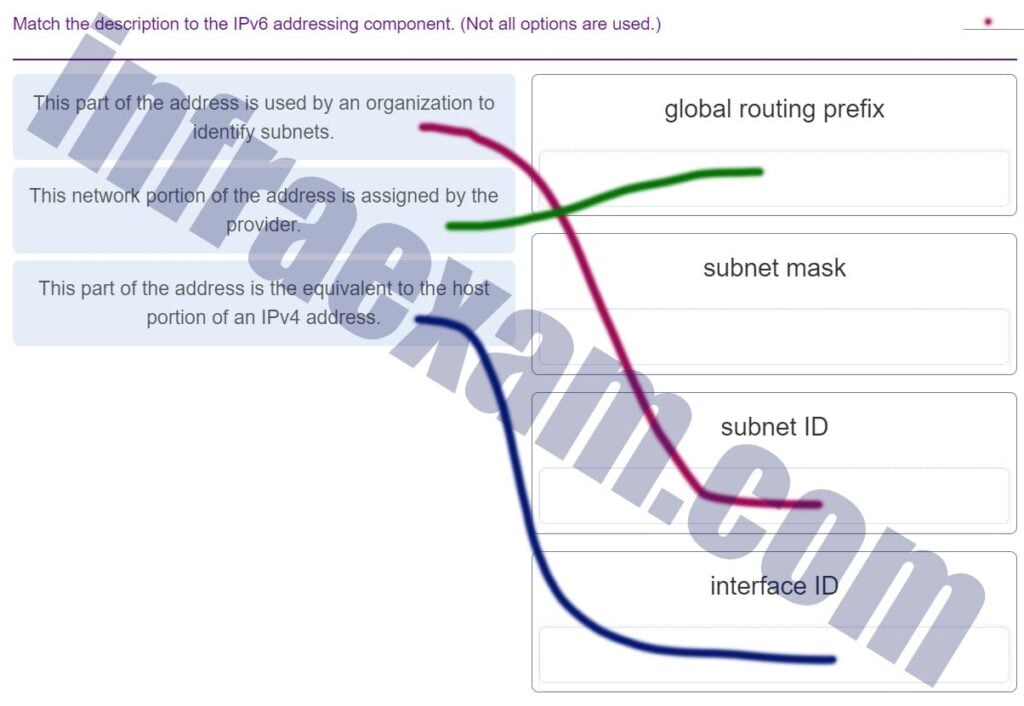
Match the description to the IPv6 addressing component. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 008 -
An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::2. What is the target of this packet?
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link
- all IPv6 DHCP servers
- all IPv6 enabled devices across the network
- all IPv6 configured routers on the local link
-
What are the three parts of an IPv6 global unicast address? (Choose three.)
- subnet ID
- global routing prefix
- interface ID
- subnet mask
- broadcast address
-
What is one main characteristic of the data link layer?
- It generates the electrical or optical signals that represent the 1 and 0 on the media.
- It converts a stream of data bits into a predefined code.
- It shields the upper layer protocol from being aware of the physical medium to be used in the communication.
- It accepts Layer 3 packets and decides the path by which to forward the packet to a remote network.
-
Which type of security threat would be responsible if a spreadsheet add-on disables the local software firewall?
- Trojan horse
- brute-force attack
- DoS
- buffer overflow
Explanation:
A Trojan horse is software that does something harmful, but is hidden in legitimate software code. A denial of service (DoS) attack results in interruption of network services to users, network devices, or applications. A brute-force attack commonly involves trying to access a network device. A buffer overflow occurs when a program attempts to store more data in a memory location than it can hold.
-
What service is provided by HTTPS?
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
-
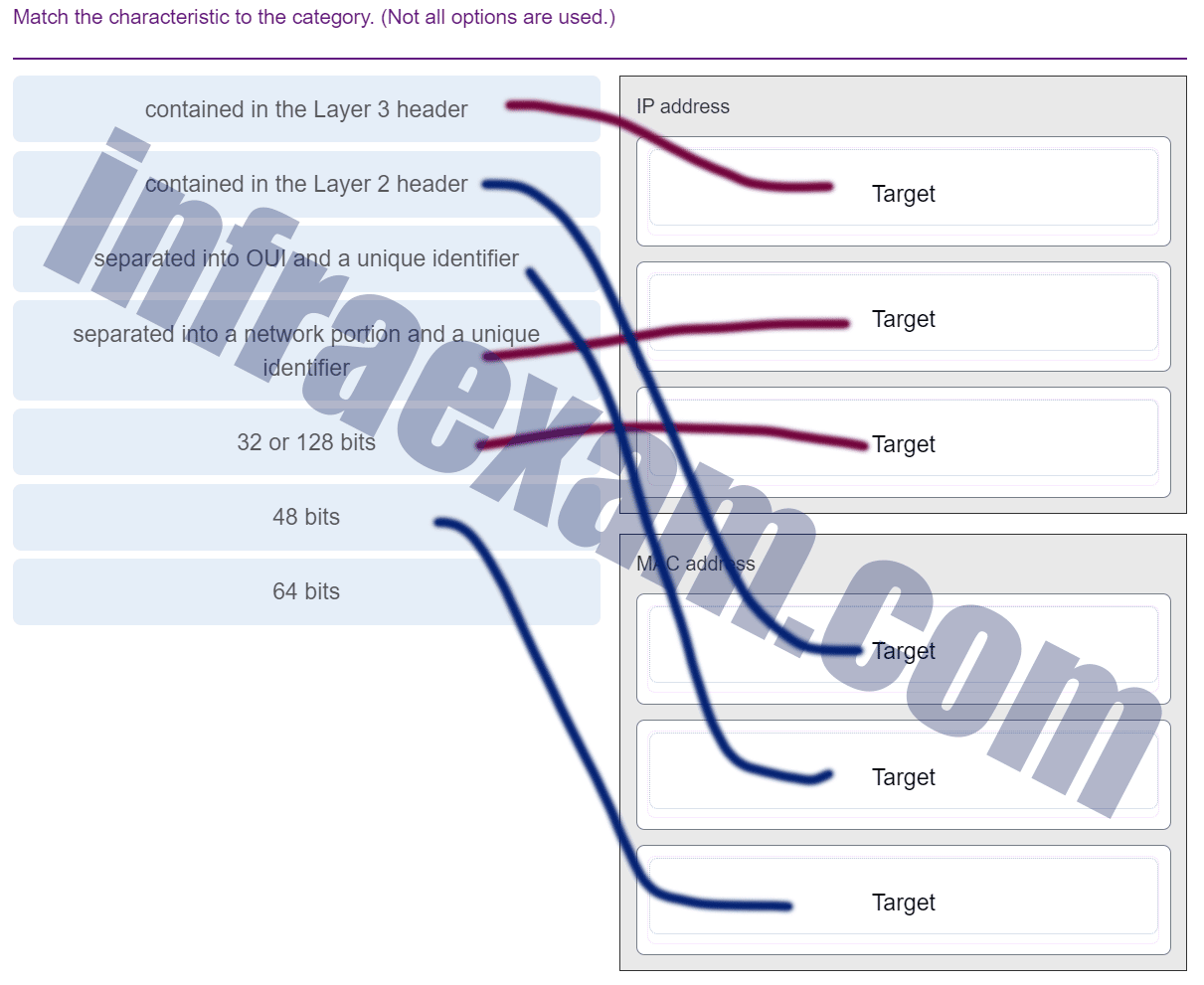
Match the characteristic to the category. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 009 -
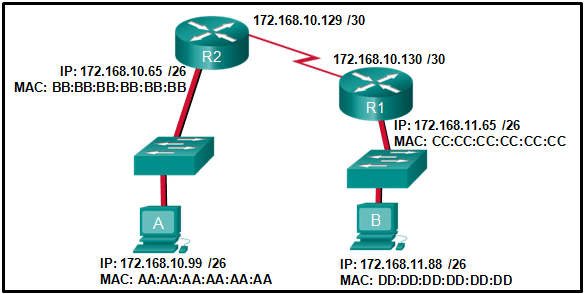
Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 14 - 172.168.10.65
- 172.168.10.99
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
-
Which two statements are correct about MAC and IP addresses during data transmission if NAT is not involved? (Choose two.)
- Destination MAC addresses will never change in a frame that goes across seven routers.
- A packet that has crossed four routers has changed the destination IP address four times.
- Every time a frame is encapsulated with a new destination MAC address, a new destination IP address is needed.
- Destination and source MAC addresses have local significance and change every time a frame goes from one LAN to another.
- Destination IP addresses in a packet header remain constant along the entire path to a target host.
-
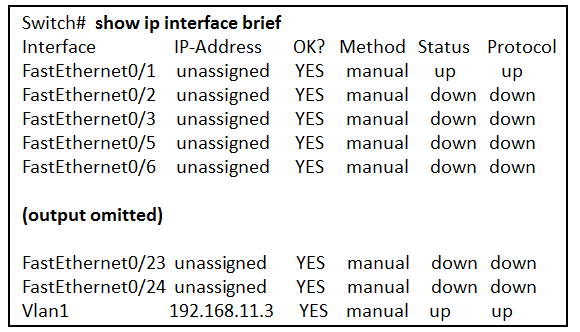
Refer to the exhibit. What three facts can be determined from the viewable output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose three.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 15 - Two devices are attached to the switch.
- The default SVI has been configured.
- The switch can be remotely managed.
- Two physical interfaces have been configured.
- Passwords have been configured on the switch.
- One device is attached to a physical interface.
-
A user is executing a tracert to a remote device. At what point would a router, which is in the path to the destination device, stop forwarding the packet?
- when the values of both the Echo Request and Echo Reply messages reach zero
- when the value in the TTL field reaches zero
- when the router receives an ICMP Time Exceeded message
- when the host responds with an ICMP Echo Reply message
- when the RTT value reaches zero
Explanation:
When a router receives a traceroute packet, the value in the TTL field is decremented by 1. When the value in the field reaches zero, the receiving router will not forward the packet, and will send an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source.
-
What are two functions that are provided by the network layer? (Choose two.)
- carrying data between processes that are running on source and destination hosts
- directing data packets to destination hosts on other networks
- providing dedicated end-to-end connections
- placing data on the network medium
- providing end devices with a unique network identifier
-
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 61 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.128
-
What characteristic describes spyware?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
-
What are three commonly followed standards for constructing and installing cabling? (Choose three.)
- pinouts
- tensile strength of plastic insulator
- cable lengths
- connector types
- cost per meter (foot)
- connector color
-
Which connector is used with twisted-pair cabling in an Ethernet LAN?
-
What attribute of a NIC would place it at the data link layer of the OSI model?
- attached Ethernet cable
- TCP/IP protocol stack
- IP address
- RJ-45 port
- MAC address
-
A network administrator needs to keep the user ID, password, and session contents private when establishing remote CLI connectivity with a switch to manage it. Which access method should be chosen?
- AUX
- Telnet
- SSH
- Console
-
A user sends an HTTP request to a web server on a remote network. During encapsulation for this request, what information is added to the address field of a frame to indicate the destination?
- the network domain of the destination host
- the MAC address of the default gateway
- the IP address of the default gateway
- the MAC address of the destination host
-
Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- route print
- show ip route
- netstat -r
- netstat -s
- tracert
Answers Explanation & Hints:
On a Windows host, the route print or netstat -r commands can be used to display the host routing table. Both commands generate the same output. On a router, the show ip route command is used to display the routing table. The netstat –s command is used to display per-protocol statistics. The tracert command is used to display the path that a packet travels to its destination.
-
Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 001 -
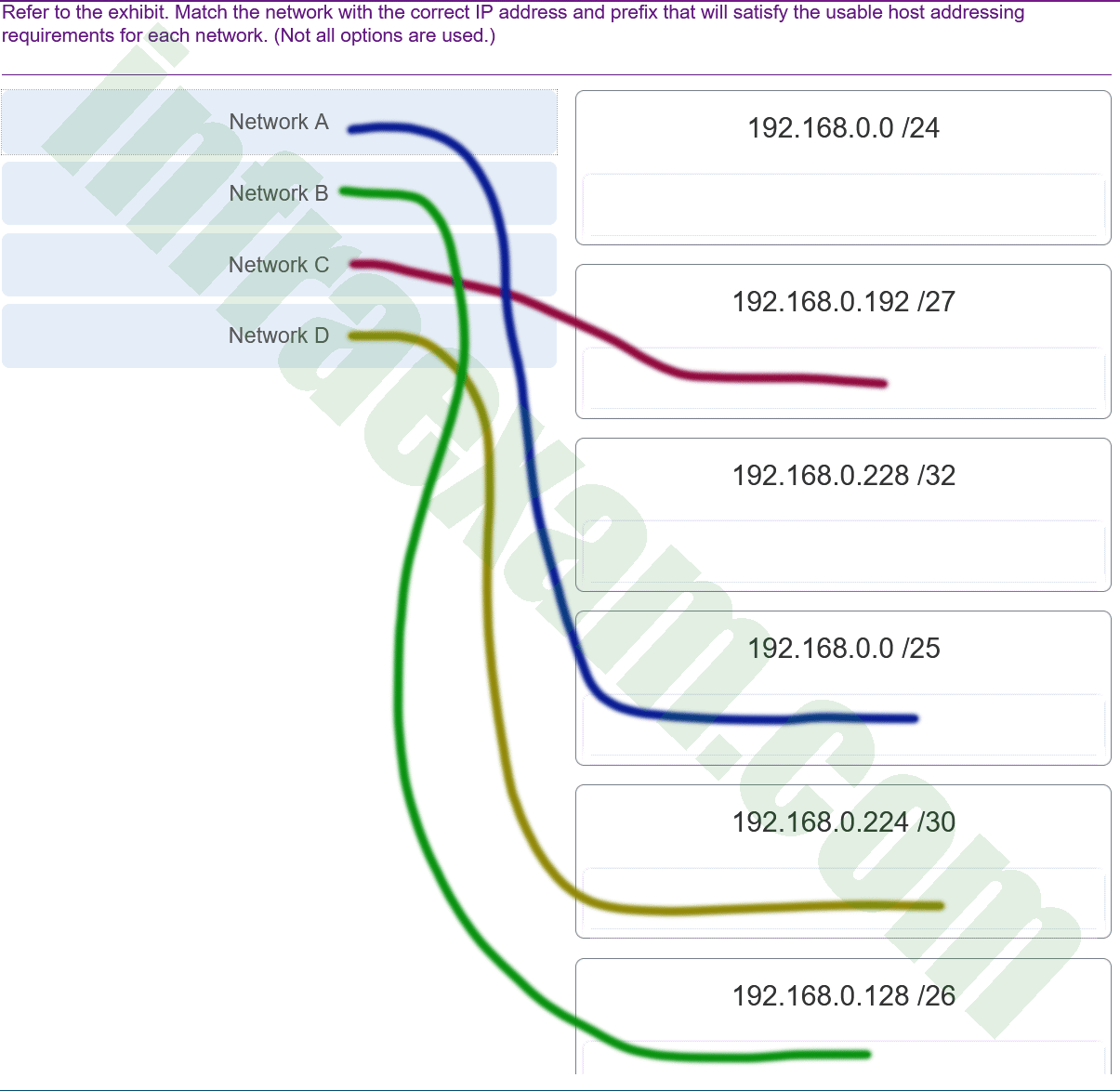
Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 01 CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 002 Explanation:
Network A needs to use 192.168.0.0 /25 which yields 128 host addresses.
Network B needs to use 192.168.0.128 /26 which yields 64 host addresses.
Network C needs to use 192.168.0.192 /27 which yields 32 host addresses.
Network D needs to use 192.168.0.224 /30 which yields 4 host addresses. -
A technician with a PC is using multiple applications while connected to the Internet. How is the PC able to keep track of the data flow between multiple application sessions and have each application receive the correct packet flows?
- The data flow is being tracked based on the source port number that is used by each application.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the destination IP address that is used by the PC of the technician.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the source IP address that is used by the PC of the technician.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the destination MAC address of the technician PC.
Explanation:
The source port number of an application is randomly generated and used to individually keep track of each session connecting out to the Internet. Each application will use a unique source port number to provide simultaneous communication from multiple applications through the Internet.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 80. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- HTTP
- DHCP
- SMTP
-
A user is attempting to access http://www.cisco.com/ without success. Which two configuration values must be set on the host to allow this access? (Choose two.)
- source port number
- HTTP server
- source MAC address
- DNS server
- default gateway
-
What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA
- token passing
-
What are two ICMPv6 messages that are not present in ICMP for IPv4? (Choose two.)
- Router Advertisement
- Destination Unreachable
- Neighbor Solicitation
- Route Redirection
- Host Confirmation
- Time Exceeded
-
An organization is assigned an IPv6 address block of 2001:db8:0:ca00::/56. How many subnets can be created without using bits in the interface ID space?
- 4096
- 256
- 512
- 1024
-
What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
-
A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in the ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
- It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
- It will send the frame and use the device MAC address as the destination.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.
- It will send an ARP request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
-
What characteristic describes a virus?
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- malicious software or code running on an end device
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
-
A disgruntled employee is using some free wireless networking tools to determine information about the enterprise wireless networks. This person is planning on using this information to hack the wireless network. What type of attack is this?
- access
- DoS
- Trojan horse
- reconnaissance
-
What service is provided by POP3?
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Retrieves email from the server by downloading the email to the local mail application of the client.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
-
What command can be used on a Windows PC to see the IP configuration of that computer?
- ipconfig
- show interfaces
- ping
- show ip interface brief
-
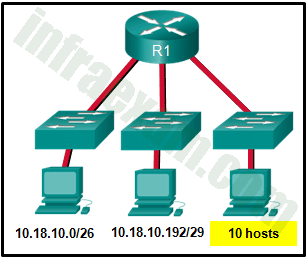
Refer to the exhibit. Which two network addresses can be assigned to the network containing 10 hosts? Your answers should waste the fewest addresses, not reuse addresses that are already assigned, and stay within the 10.18.10.0/24 range of addresses. (Choose two.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 02 - 10.18.10.224/27
- 10.18.10.208/28
- 10.18.10.200/27
- 10.18.10.200/28
- 10.18.10.224/28
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Addresses 10.18.10.0 through 10.18.10.63 are taken for the leftmost network. Addresses 192 through 199 are used by the center network. Because 4 host bits are needed to accommodate 10 hosts, a /28 mask is needed. 10.18.10.200/28 is not a valid network number. Two subnets that can be used are 10.18.10.208/28 and 10.18.10.224/28.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 110. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- DHCP
- POP3
- SMTP
-
Which layer of the TCP/IP model provides a route to forward messages through an internetwork?
- transport
- application
- network access
- internet
-
What characteristic describes identity theft?
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- software that identifies fast-spreading threats
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
-
What two security solutions are most likely to be used only in a corporate environment? (Choose two.)
- intrusion prevention systems
- antivirus software
- antispyware
- strong passwords
- virtual private networks
-
What service is provided by DNS?
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
-
Which wireless technology has low-power and low-data rate requirements making it popular in IoT environments?
- Bluetooth
- Zigbee
- WiMAX
- Wi-Fi
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Zigbee is a specification used for low-data rate, low-power communications. It is intended for applications that require short-range, low data-rates and long battery life. Zigbee is typically used for industrial and Internet of Things (IoT) environments such as wireless light switches and medical device data collection.
-
What characteristic describes a VPN?
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that identifies fast-spreading threats
-
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 4 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.224
-
During the process of forwarding traffic, what will the router do immediately after matching the destination IP address to a network on a directly connected routing table entry?
- switch the packet to the directly connected interface
- discard the traffic after consulting the route table
- look up the next-hop address for the packet
- analyze the destination IP address
-
What service is provided by BOOTP?
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- Legacy application that enables a diskless workstation to discover its own IP address and find a BOOTP server on the network.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 21. What service is the client requesting?
- DHCP
- FTP
- TFTP
- DNS
-
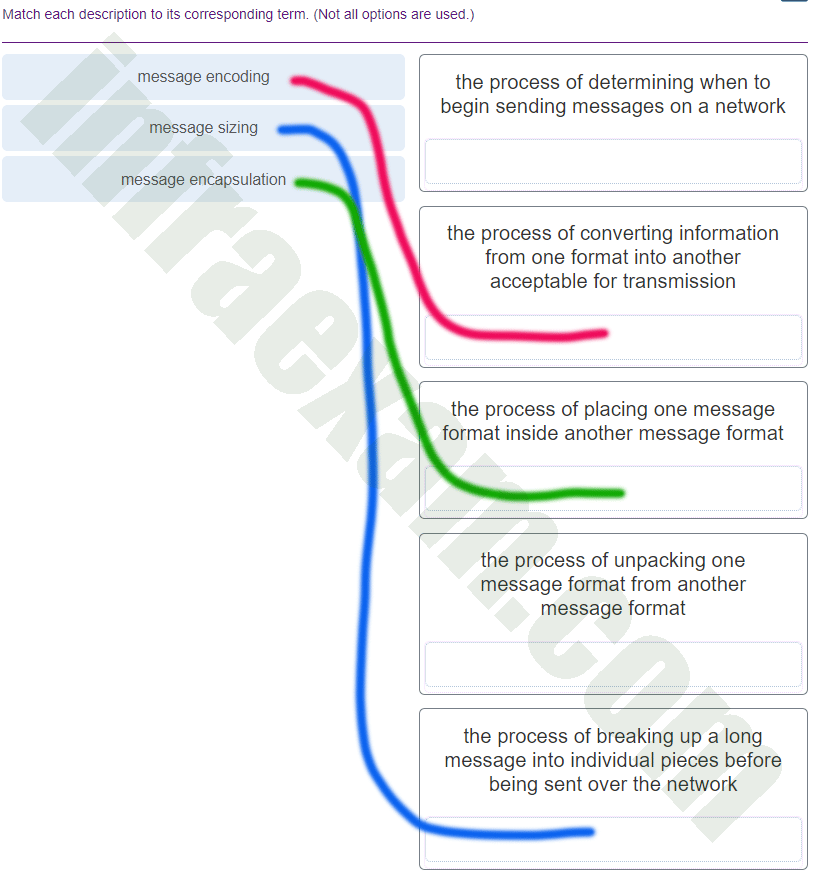
Match each description to its corresponding term. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 003 -
A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- netstat
- nslookup
- ipconfig
Explanation:
-
What two ICMPv6 message types must be permitted through IPv6 access control lists to allow resolution of Layer 3 addresses to Layer 2 MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
- echo requests
- router solicitations
- router advertisements
- neighbor advertisements
- echo replies
- neighbor solicitations
-
Refer to the exhibit. The switches have a default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for the default gateway. Which network devices will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 03 - only hosts A, B, C, and D
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only host D
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
- only router R1
- only hosts B and C
-
Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
- implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
- applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
-
Two pings were issued from a host on a local network. The first ping was issued to the IP address of the default gateway of the host and it failed. The second ping was issued to the IP address of a host outside the local network and it was successful. What is a possible cause for the failed ping?
- The default gateway is not operational.
- The default gateway device is configured with the wrong IP address.
- The TCP/IP stack on the default gateway is not working properly.
- Security rules are applied to the default gateway device, preventing it from processing ping requests.
-
What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
-
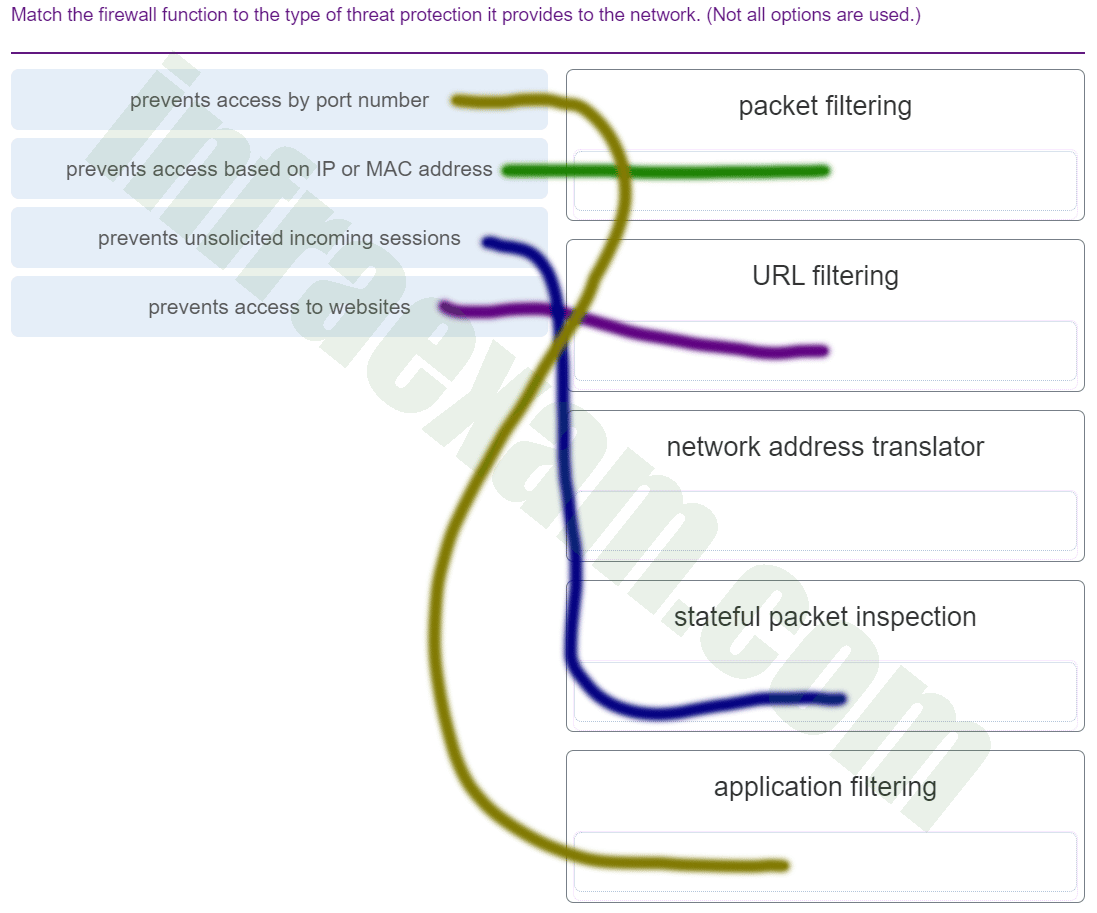
Match the firewall function to the type of threat protection it provides to the network. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 004 Answers Explanation & Hints:
Application filters prevent access based on Layer 4 port numbers.
Packet filters prevent access based on IP or MAC address.
URL filters prevent access to web site URLs or content.
Stateful packet inspection prevents unsolicited incoming sessions.
Network address translators translate internal IP addresses to to outside IP addresses and do not prevent network attacks. -
What service is provided by SMTP?
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Allows clients to send email to a mail server and the servers to send email to other servers.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 22. What service is the client requesting?
- SSH
- DNS
- DHCP
- TFTP
-
Recommend
4.4
43
votes
Article Rating
Network Essentials Final Exam Answers 100%
-
What is a disadvantage of deploying a peer-to-peer network model?
- difficulty of setup
- lack of centralized administration
- high degree of complexity
- high cost
Explanation:The simplest peer-to-peer network consists of two computers that are directly connected to each other through the use of a wired or wireless connection. The primary disadvantages of a peer-to-peer network are its lack of central administration, minimal security, and its lack of scalability.
-
What is a purpose of an IP address?
- It identifies the physical location of a data center.
- It identifies a location in memory from which a program runs.
- It identifies a return address for replying to email messages.
- It identifies the source and destination of data packets.
Explanation:Packets that are routed across the Internet contain source and destination IP addresses. These addresses are used to determine how the packets should be routed from source to destination by intermediate devices.
-
A consumer places a smartphone close to a pay terminal at a store and the shopping charge is successfully paid. Which type of wireless technology was used?
- Bluetooth
- NFC
- Wi-Fi
- 3G
Explanation:NFC is a wireless technology that allows data to be exchanged between devices that are in very close proximity to each other.
-
Which type of network cable is commonly used to connect office computers to the local network?
- coaxial cable
- twisted-pair cable
- glass fiber-optic cable
- plastic fiber-optic cable
Explanation:Twisted-pair is a type of copper cable used to interconnect devices on a local network.
-
What are two advantages of using fiber-optic cabling to interconnect devices? (Choose two.)
- Fiber-optic cable is immune from EMI and RFI.
- Fiber-optic cables can extend several miles.
- Fiber-optic cables use extra shielding to protect copper wires.
- Fiber-optic cables are easy to install..
- Fiber-optic cables are commonly found in both homes and small businesses.
Explanation:Fiber-optic cables provide immunity to both EMI and RFI and a single cable can extend for several miles before regeneration is needed.
-
The functions of which two layers of the OSI model are matched to the network access layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- application
- physical
- transport
- network
- data link
Explanation:The application layer of the TCP/IP model is composed of the application, presentation, and session layers of the OSI model and is used by network applications to complete specific tasks. The network access layer of the TCP/IP model is composed of the physical and data link layers of the OSI model and describes how a device accesses and sends data over the network media.
-
What is the minimum size of a valid Ethernet frame?
- 48 bytes
- 64 bytes
- 96 bytes
- 128 bytes
Explanation:Ethernet standards define a frame with a minimum of 64 bytes and a maximum of 1518 bytes including fields of destination MAC address, source MAC, Length/Type, data payload, and FCS.
-
A network design engineer has been asked to design the IP addressing scheme for a customer network. The network will use IP addresses from the 192.168.30.0/24 network. The engineer allocates 254 IP addresses for the hosts on the network but excludes 192.168.30.0/24 and 192.168.30.255/24 IP addresses. Why must the engineer exclude these two IP addresses?
- 192.168.30.0/24 and 192.168.30.255/24 IP addresses are reserved for the email and DNS servers.
- 192.168.30.0/24 and 192.168.30.255/24 IP addresses are reserved for outside Internet connectivity.
- 192.168.30.0/24 is the network IP address and 192.168.30.255/24 is the IP broadcast address.
- 192.168.30.0/24 is the IP address reserved for the default gateway, and 192.168.30.255/24 is the IP address reserved for the DHCP server.
Explanation:The IPv4 addressing system is a hierarchical addressing system. An IPv4 address is made up of two parts, the network address and the host address. When the host portion is all “0s” in binary, it is designated as a network address. When the host portion is all “1s” in binary, it is designated as a broadcast address. These two addresses cannot be assigned to individual hosts.
-
Which protocol is used to automatically assign IP addresses to hosts?
- DNS
- NAT
- DHCP
- HTTP
Explanation:DHCP, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is used to automatically assign IP addresses to hosts that are configured as DHCP clients.
-
What are three advantages of using private IP addresses and NAT? (Choose three.)
- conserves registered public IP addresses
- reduces CPU usage on customer routers
- creates multiple public IP addresses
- hides private LAN addressing from outside devices that are connected to the Internet
- permits LAN expansion without additional public IP addresses
- improves the performance of the router that is connected to the Internet
Explanation:Private IP addresses are designed to be exclusively used for internal networks and they cannot be used on the Internet. Thus they are not visible directly from the Internet and they can be used freely by network administrators for internal networks. In order for the internal hosts to access the Internet, NAT is used to translate between private and public IP addresses. NAT takes an internal private IP address and translates it to a global public IP address before the packet is forwarded.
-
What was the reason for the creation and implementation of IPv6?
- to make reading a 32-bit address easier
- to relieve IPv4 address depletion
- to provide more address space in the Internet Names Registry
- to allow NAT support for private addressing
Explanation:IPv4 addressing space is exhausted by the rapid growth of the Internet and the devices connected to the Internet. IPv6 expands the IP addressing space by increasing the address length from the 32 bits to 128 bits, which should provide sufficient addresses for future Internet growth needs for many years to come.
-
Which three pieces of information are identified by a URL? (Choose three.)
- the MAC address of the web server
- the protocol that is being used
- the domain name that is being accessed
- the IP address of the gateway
- the version of the browser
- the location of the resource
Explanation:URLs are used to access specific content on a web server through a web browser. The URL identifies the protocol that is being used such as HTTP or FTP, the domain of the server, and the location of the resource on the server.
-
Which protocol is used by web servers to serve up a web page?
- FTP
- HTTP
- IMAP
- POP
Explanation:Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a protocol that is used by web servers to serve up a web page.
-
Why do streaming audio and video applications use UDP instead of TCP?
- Streaming audio and video applications require receipt of all packets regardless of delay.
- The three-way handshake used in UDP speeds up the audio and video streams.
- Streaming audio and video applications cannot tolerate the delay caused by retransmission.
- UDP provides guaranteed segment delivery to provide reliable audio and video streams.
Explanation:UDP is a ‘best effort’ delivery system that does not require acknowledgment of receipt and is the preferred transport service for streaming audio and video. UDP provides low overhead and does not implement as much delay as TCP. Streaming audio and video cannot tolerate network traffic congestion and long delays.
-
At which layer of the TCP/IP model does TCP operate?
- transport
- application
- internetwork
- network access
Explanation:TCP is the Transmission Control Protocol and it operates at the transport layer of the TCP/IP model. TCP ensures that IP packets are delivered reliably.
-
Which protocol is used to transfer web pages from a server to a client device?
- HTML
- SMTP
- HTTP
- SSH
- POP
Explanation:The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) provides services between a web browser requesting web pages and a web server responding to the requests. HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is a markup language to instruct a web browser how to interpret and display a web page.
-
Which type of device filtering can be enabled on some wireless access points or wireless routers?
- authentication
- IP address
- user ID
- MAC address
Explanation:On wireless access points, MAC addresses can be manually entered to filter which devices are allowed on the wireless network.
-
Which technology is used to uniquely identify a WLAN network?
- MAC address table
- SSID
- WEP
- WPA
Explanation:When a wireless AP or router is being set up, an SSID is configured to uniquely identify the WLAN that is managed by the device.
-
What type of Internet connection would be best for a residence in a remote area without mobile phone coverage or wired connectivity?
- dial-up
- cellular
- satellite
- DSL
Explanation:Satellite Internet service provides the best option for a home user that would otherwise have no Internet connectivity at all. Cellular Internet is only available in areas with mobile phone coverage.
-
Which advanced wireless security measure allows a network administrator to keep sensitive data secure as it travels over the air in a wireless network?
- encryption
- authentication
- traffic filtering
- MAC address filtering
Explanation:Encryption is used to secure plaintext data that would be viewable traveling over a wireless network.
-
Which three steps must be completed to manually connect an Android or IOS device to a secured wireless network? (Choose three.)
- Input the authentication password.
- Enter the network SSID.
- Choose the correct security type.
- Set the IP address.
- Activate the Bluetooth antenna.
- Change the MAC address.
Explanation:In order to connect an Android or IOS device to a Wi-Fi network manually, perform these steps:
- Enter the network SSID of the wireless network.
- Choose the security type used by the wireless network.
- Input the password to authenticate successfully.
-
Which three attacks exploit human behavior? (Choose three.)
- pretexting
- brute force
- phishing
- zombies
- vishing
- malware
Explanation:Attacks aimed at exploiting human behavior such as pretexting, phishing, and vishing are commonly used by hackers to obtain information directly from authorized users.
-
Which address prefix range is reserved for IPv4 multicast?
- 240.0.0.0 – 254.255.255.255
- 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
- 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255
- 127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
Explanation:Multicast IPv4 addresses use the reserved class D address range of 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255.
-
An intruder tries a large number of possibilities in rapid succession to guess a password. As a result, other users on the network are locked out. What type of attack has occurred?
- DDoS
- brute force
- ping of death
- SYN flooding
Explanation:In a brute force attack, an unauthorized person will try to gain access to a system by sending as many passwords as possible as rapidly as possible.
-
What type of DoS attack originates from a malicious host that has an invalid source IP address and that requests a client connection?
- ping of death
- SYN flooding
- phishing
- brute force
Explanation:SYN flooding is a type of denial of services attack where the attacker sends fake session requests to a target host in an attempt to prevent the host from responding to legitimate session requests.
-
Which two ports can be used for the initial configuration of a Cisco router? (Choose two.)
- AUX
- console
- flash slot
- LAN interface
- WAN interface
Explanation:The AUX and console ports on a Cisco 1941 router can be used to perform initial setup. The initial setup does not require that the router be connected to a network. A network administrator uses a computer to connect to the console ports directly. A network administrator can also access the router remotely through a dialup phone line and a modem connected to the AUX port. LAN and WAN interfaces are used to connect to networks. The flash slots expand storage capability through the use of a compact flash card.
-
When is an IP address required to be configured on a Cisco LAN switch?
- when the switch is connected to another switch
- when the switch must forward LAN traffic
- when the switch needs to be managed through an in-band connection
- when the switch is configured from a computer connected to the console port
Explanation:A LAN switch uses Layer 2 addresses to determine how to forward packets. An IP address is only necessary if the switch needs to be remotely managed through an in-band connection on the network.
-
What advantage does SSH offer over Telnet?
- encryption
- more connection lines
- connection-oriented services
- username and password authentication
Explanation:Both Telnet and SSH are used to remotely connect to a network device for management tasks. However, Telnet uses plaintext communications, whereas SSH provides security for remote connections by providing encryption of all transmitted data between devices.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is statically assigning an IP address to a PC. The default gateway is correct. What would be a valid IP address to assign to the host?
Network Essentials Final Exam Answers 001
- 128.106.10.100
- 128.107.255.1
- 128.107.255.254
- 128.108.100.10
Explanation:In data communication, the default gateway device is involved only when a host needs to communicate with other hosts on another network. The default gateway address identifies a network device used by hosts to communicate with devices on remote networks. The IP address of the host and the default gateway address must be in the same network. With the default subnet mask, valid host IP addresses range from 128.107.0.1 to 128.107.255.254.
-
Which three items should be documented after troubleshooting an internal web server crash? (Choose three.)
- when the problem occurred
- the dialogue with the user
- the configuration of all networking devices on the LAN at the time of the crash
- the configuration of all hosts on the LAN at the time of the crash
- steps that were performed to identify the cause of the problem
- steps that were performed that failed to identify the cause of the problem
Explanation:Proper documentation is a very important step in troubleshooting. The proper documentation can help troubleshoot the same or similar problems in the future. The documentation should include as much information as possible about the following:
- the problem encountered
- steps taken to determine the cause of the problem
- steps to correct the problem and ensure that it will not reoccur
-
Which step should be taken next once a problem is resolved during a troubleshooting process?
- Consult an FAQ.
- Escalate the problem.
- Update the documentation.
- Run remote access software.
Explanation:Proper documentation can help troubleshoot the same or similar problems in the future. Proper documentation should include the type of error encountered, the steps taken to determine the cause of the problem, and the steps taken to correct the problem.
-
Which three pieces of information are revealed by the ipconfig command (without the /all switch)? (Choose three.)
- IP address
- DHCP server
- subnet mask
- default gateway
- DNS server
- MAC address
Explanation:The ipconfig command is used to display the current TCP/IP network configuration values of the device. This includes the IP address; the subnet mask and the default gateway addresses. Using the ipconfig /all switch displays additional information like the physical address of the device and the DHCP server address among other things.
-
Fill in the blank.
A zombie is a computer that is infected with malicious software and instructed to join a botnet.
Explanation:Zombies are computer systems that are infected with bot software which, once activated, instructs infected machines to function as a botnet.
-
Match the router prompt to the configuration task.
Network Essentials Final Exam Answers 001
-
Match the command to the function.
Network Essentials Final Exam Answers 002
Last Updated on May 20, 2021 by
Cisco CCNA 1 ITN v6.0 final Exam Answers Routing and Switching (R&S) Introduction to Networks (ITN) (Version 6.00) collection year 2017, 2018 and 2019 Full 100%. CCNA 1 has been know as ITN. The following are the questions exam answers. Guarantee Passed 100%. CCNA 1 v6.0 final exam answers has some new update from the old version 5.1. You can review all final Exam Answers. You will get passed scored 100% with this version 6.0. Good Luck for Cisco Netacad ITN v6.0 Exam!
Noted: There are 3 forms of Final Exam. In this page we have collected all 3 forms. You will random from these question which 55 to 60 questions.
-
Recommend
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to «Online Test» link below.
| Version 5.02 | Version 5.1 | Version 6.0 | Online Assessment |
| Final Exam | Final Exam | Final Exam | Online A, Online B, Online C |
| CCNA2 Pretest Exam | |||
| Pretest Exam | Pretest Exam | Pretest Exam | Online Test |
March, 2019 New Update for CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam
-
What is an example of a top-level domain?
- www.cisco.com
- cisco.com
- .com
- root.cisco.com
Explanation:
Top-level domains represent a country or type of organization, such as .com or .edu.
-
What is a characteristic of multicast messages?
- They are sent to a select group of hosts.
- They are sent to all hosts on a network.
- They must be acknowledged.
- They are sent to a single destination.
Explanation:
Multicast is a one-to-many type of communication. Multicast messages are addressed to a specific multicast group.
-
A network technician suspects that a particular network connection between two Cisco switches is having a duplex mismatch. Which command would the technician use to see the Layer 1 and Layer 2 details of a switch port?
- show interfaces
- show running-config
- show ip interface brief
- show mac-address-table
Explanation:
The show interfaces command can be used on both routers and switches to see speed, duplex, media type, MAC address, port type, and other Layer 1/Layer 2-related information.
-
Where are Cisco IOS debug output messages sent by default?
- memory buffers
- vty lines
- Syslog server
- console line
Explanation:
Debug messages, like other IOS log messages, are sent to the console line by default. Sending these messages to the terminal lines requires the terminal monitor command.
-
Which command can an administrator issue on a Cisco router to send debug messages to the vty lines?
- terminal monitor
- logging console
- logging buffered
- logging synchronous
Explanation:
Debug messages, like other IOS log messages, are sent to the console line by default. Sending these messages to the terminal lines requires the terminal monitor command.
-
What is one indication that a Windows computer did not receive an IPv4 address from a DHCP server?
- The computer cannot ping 127.0.0.1.
- Windows displays a DHCP timeout message.
- The computer receives an IP address that starts with 169.254.
- The computer cannot ping other devices on the same network with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 range.
Explanation:
When a Windows PC cannot communicate with an IPv4 DHCP server, the computer automatically assigns an IP address in the 169.254.0.0/16 range. Any other device on the same network that receives an address in the same range is reachable.
-
What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
Explanation:
When sending an echo request message, a router will use the IP address of the exit interface as the source IP address. This default behavior can be changed by using an extended ping and specifying a specific source IP address.
-
A user is unable to reach the web site when typing http://www.cisco.com in a web browser, but can reach the same site by typing http://72.163.4.161. What is the issue?
- default gateway
- DHCP
- DNS
- TCP/IP protocol stack
Explanation:
Domain Name Service (DNS) is used to translate a web address to an IP address. The address of the DNS server is provided via DHCP to host computers.
-
What is a characteristic of a fault tolerant network?
- a network that protects confidential information from unauthorized access
- a network that can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service delivered to existing users
- a network that supports a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users
- a network that recovers quickly when a failure occurs and depends on redundancy to limit the impact of a failure
Explanation:
Fault tolerant networks limit the impact of a failure because the networks are built in a way that allows for quick recovery when such a failure occurs. These networks depend on multiple or redundant paths between the source and destination of a message.
A scalable network can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users.
Quality of service (QoS) is a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users.
-
Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
Explanation:
QoS mechanisms enable the establishment of queue management strategies that enforce priorities for different categories of application data. Thus, this queuing enables voice data to have priority over transaction data, which has priority over web data.
-
What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
Explanation:
Cloud computing extends IT’s capabilities without requiring investment in new infrastructure, training new personnel, or licensing new software. These services are available on-demand and delivered economically to any device anywhere in the world without compromising security or function. BYOD is about end users having the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business or campus network. Smart home technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated. Powerline networking is a trend for home networking that uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
-
What is the function of the shell in an OS?
- It interacts with the device hardware.
- It interfaces between the users and the kernel.
- It provides dedicated firewall services.
- It provides the intrusion protection services for the device.
Explanation:
Most operating systems contain a shell and a kernel. The kernel interacts with the hardware and the shell interfaces between the kernel and the users.
-
Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco switch?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection
Explanation:
A CLI session using Secure Shell (SSH) provides enhanced security because SSH supports strong passwords and encryption during the transport of session data. The other methods support authentication but not encryption.
-
A network technician is attempting to configure an interface by entering the following command: SanJose(config)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0. The command is rejected by the device. What is the reason for this?
- The command is being entered from the wrong mode of operation.
- The command syntax is wrong.
- The subnet mask information is incorrect.
- The interface is shutdown and must be enabled before the switch will accept the IP address.
Explanation:
The wrong mode of operation is being used. The CLI prompt indicates that the mode of operation is global configuration. IP addresses must be configured from interface configuration mode, as indicated by the SanJose(config-if)# prompt.
-
An administrator uses the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination on a switch after issuing the ping command. What is the purpose of using these keystrokes?
- to restart the ping process
- to interrupt the ping process
- to exit to a different configuration mode
- to allow the user to complete the command
Explanation:
To interrupt an IOS process such as ping or traceroute, a user enters the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination. Tab completes the remainder of parameters or arguments within a command. To exit from configuration mode to privileged mode use the Ctrl-Z keystroke. CTRL-R will redisplay the line just typed, thus making it easier for the user to press Enter and reissue the ping command.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses a console connection to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 001 - letmein
- secretin
- lineconin
- linevtyin
Explanation:
Telnet accesses a network device through the virtual interface configured with the line VTY command. The password configured under this is required to access the user EXEC mode. The password configured under the line console 0 command is required to gain entry through the console port, and the enable and enable secret passwords are used to allow entry into the privileged EXEC mode.
-
On which switch interface would an administrator configure an IP address so that the switch can be managed remotely?
- FastEthernet0/1
- VLAN 1
- vty 0
- console 0
Explanation:
Interface VLAN 1 is a virtual interface on a switch, called SVI (switch virtual interface). Configuring an IP address on the default SVI, interface VLAN 1, will allow a switch to be accessed remotely. The VTY line must also be configured to allow remote access, but an IP address cannot be configured on this line.
-
What protocol is responsible for controlling the size of segments and the rate at which segments are exchanged between a web client and a web server?
- TCP
- IP
- HTTP
- Ethernet
Explanation:
TCP is a Layer 4 protocol of the OSI model. TCP has several responsibilities in the network communication process. It divides large messages into smaller segments which are more efficient to send across the network. It also controls the size and rate of segments exchanged between clients and servers.
-
What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- A company can monopolize the market.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.
Explanation:
A monopoly by one company is not a good idea from a user point of view. If a protocol can only be run on one brand, it makes it difficult to have mixed equipment in a network. A proprietary protocol is not free to use. An open standard protocol will in general be implemented by a wide range of vendors.
-
What are two benefits of using a layered network model? (Choose two.)
- It assists in protocol design.
- It speeds up packet delivery.
- It prevents designers from creating their own model.
- It prevents technology in one layer from affecting other layers.
- It ensures a device at one layer can function at the next higher layer.
Explanation:
Some vendors have developed their own reference models and protocols. Today, if a device is to communicate on the Internet, the device must use the TCP/IP model. The benefits of using a layered model are as follows:
- assists in protocol design
- fosters competition between vendors
- prevents a technology that functions at one layer from affecting any other layer
- provides a common language for describing network functionality
- helps in visualizing the interaction between each layer and protocols between each layer
-
Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- data link
- network
- physical
- session
- transport
Explanation:
The OSI transport layer is functionally equivalent to the TCP/IP transport layer, and the OSI network layer is equivalent to the TCP/IP internet layer. The OSI data link and physical layers together are equivalent to the TCP/IP network access layer. The OSI session layer (with the presentation layer) is included within the TCP/IP application layer.
-
Which name is assigned to the transport layer PDU?
- bits
- data
- frame
- packet
- segment
Explanation:
Application data is passed down the protocol stack on its way to be transmitted across the network media. During the process, various protocols add information to it at each level. At each stage of the process, a PDU (protocol data unit) has a different name to reflect its new functions. The PDUs are named according to the protocols of the TCP/IP suite:
- Data – The general term for the PDU used at the application layer.
- Segment – transport layer PDU
- Packet – network layer PDU
- Frame – data link layer PDU
- Bits – A physical layer PDU used when physically transmitting data over the medium
-
A network administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues on a server. Using a tester, the administrator notices that the signals generated by the server NIC are distorted and not usable. In which layer of the OSI model is the error categorized?
- presentation layer
- network layer
- physical layer
- data link layer
Explanation:
The NIC has responsibilities in both Layer 1 and Layer 2. The NIC encodes the frame as a series of signals that are transmitted onto the local media. This is the responsibility of the physical layer of the OSI model. The signal could be in the form of electrical, optical, or radio waves.
-
A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
Explanation:
Throughput usually does not match the specified bandwidth of physical links due to multiple factors. These factors include, the amount of traffic, type of traffic, and latency created by the network devices the data has to cross.
-
What is a characteristic of UTP cabling?
- cancellation
- cladding
- immunity to electrical hazards
- woven copper braid or metallic foil
Explanation:
Cladding and immunization from electrical hazards are characteristics for fiber-optic cabling. A woven copper braid or metallic foil is used as a shield for the inner coaxial cable conductor. Cancellation is a property of UTP cabling where two wires are located adjacent to one another so each magnetic field cancels out the adjacent magnetic field.
-
What are two characteristics of fiber-optic cable? (Choose two.)
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding, and twisting to protect data.
- It typically contains 4 pairs of fiber-optic wires.
- It is more expensive than UTP cabling is.
Explanation:
Fiber-optic cabling supports higher bandwidth than UTP for longer distances. Fiber is immune to EMI and RFI, but costs more, requires more skill to install, and requires more safety precautions.
-
What is a characteristic of the LLC sublayer?
- It provides the logical addressing required that identifies the device.
- It provides delimitation of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium.
- It places information in the frame allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to use the same network interface and media.
- It defines software processes that provide services to the physical layer.
Explanation:
The Logical Link Control (LLC) defines the software processes that provide services to the network layer protocols. The information is placed by LLC in the frame and identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame. This information allows multiple Layer 3 protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6, to utilize the same network interface and media.
-
A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies for connecting remote sites to a headquarters building. Which topology provides high availability and connects some, but not all, remote sites?
- mesh
- partial mesh
- hub and spoke
- point-to-point
Explanation:
Partial mesh topologies provide high availability by interconnecting multiple remote sites, but do not require a connection between all remote sites. A mesh topology requires point-to-point links with every system being connected to every other system. A point-to-point topology is where each device is connected to one other device. A hub and spoke uses a central device in a star topology that connects to other point-to-point devices.
-
What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA
- token passing
Explanation:
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) is used with wireless networking technology to mediate media contention. Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is used with wired Ethernet technology to mediate media contention. Priority ordering and token passing are not used (or not a method) for media access control.
-
What are the three primary functions provided by Layer 2 data encapsulation? (Choose three.)
- error correction through a collision detection method
- session control using port numbers
- data link layer addressing
- placement and removal of frames from the media
- detection of errors through CRC calculations
- delimiting groups of bits into frames
- conversion of bits into data signals
Explanation:
Through the framing process, delimiters are used to identify the start and end of the sequence of bits that make up a frame. Data link layer addressing is added to enable a frame to be delivered to a destination node. A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) field is calculated on every bit and added to the frame. If the CRC value contained in the arriving frame is the same as the one the receiving node creates, the frame will be processed.
-
What will a host on an Ethernet network do if it receives a frame with a destination MAC address that does not match its own MAC address?
- It will discard the frame.
- It will forward the frame to the next host.
- It will remove the frame from the media.
- It will strip off the data-link frame to check the destination IP address.
Explanation:
In an Ethernet network, each NIC in the network checks every arriving frame to see if the destination MAC address in the frame matches its own MAC address. If there is no match, the device discards the frame. If there is a match, the NIC passes the frame up to the next OSI layer.
-
Which frame forwarding method receives the entire frame and performs a CRC check to detect errors before forwarding the frame?
- cut-through switching
- store-and-forward switching
- fragment-free switching
- fast-forward switching
Explanation:
Fast-forward and fragment-free switching are variations of cut-through switching, which begins to forward the frame before the entire frame is received.
-
Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 002 - DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- 172.168.10.99
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- 172.168.10.65
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
Explanation:
When a host sends information to a distant network, the Layer 2 frame header will contain a source and destination MAC address. The source address will be the originating host device. The destination address will be the router interface that connects to the same network. In the case of host A sending information to host B, the source address is AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA and the destination address is the MAC address assigned to the R2 Ethernet interface, BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB.
-
What addresses are mapped by ARP?
- destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address
- destination IPv4 address to the source MAC address
- destination IPv4 address to the destination host name
- destination MAC address to the source IPv4 address
Explanation:
ARP, or the Address Resolution Protocol, works by mapping a destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address. The host knows the destination IPv4 address and uses ARP to resolve the corresponding destination MAC address.
-
What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
Explanation:
The OSI network layer provides several services to allow communication between devices:
- addressing
- encapsulation
- routing
- de-encapsulation
Error detection, placing frames on the media, and collision detection are all functions of the data ink layer.
-
What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed
- to store the startup configuration file
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
Explanation:
NVRAM is permanent memory storage, so the startup configuration file is preserved even if the router loses power.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What will be the result of entering this configuration the next time a network administrator connects a console cable to the router and no additional commands have been entered?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 003 - The administrator will be required to enter Cisco123.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco234.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco789.
- The administrator will be presented with the R1> prompt.
Explanation:
Until both the password password and the login commands are entered in console line configuration mode, no password is required to gain access to enable mode.
-
What is the dotted decimal representation of the IPv4 address 11001011.00000000.01110001.11010011?
- 192.0.2.199
- 198.51.100.201
- 203.0.113.211
- 209.165.201.223
Explanation:
Each section (octet) contains eight binary digits. Each digit represents a specific value (128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1). Everywhere there is a 1, the specific value is relevant. Add all relevant values in a particular octet to obtain the decimal value. For example binary 11001011 equals 203 in decimal.
-
What are three characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose three.)
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts.
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information.
- Routers will not forward multicast addresses in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses.
Explanation:
Broadcast messages consist of single packets that are sent to all hosts on a network segment. These types of messages are used to request IPv4 addresses, and map upper layer addresses to lower layer addresses. A multicast transmission is a single packet sent to a group of hosts and is used by routing protocols, such as OSPF and RIPv2, to exchange routes. The address range 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 is reserved for link-local addresses to reach multicast groups on a local network.
-
What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 127.16.0.0/12
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 192.168.0.0/16
Explanation:
The private IP address blocks that are used inside companies are as follows:
- 10.0.0.0 /8 (any address that starts with 10 in the first octet)
- 172.16.0.0 /12 (any address that starts with 172.16 in the first two octets through 172.31.255.255)
- 192.168.0.0 /16 (any address that starts with 192.168 in the first two octets)
-
What purpose does NAT64 serve in IPv6?
- It converts IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
- It translates private IPv6 addresses into public IPv6 addresses.
- It enables companies to use IPv6 unique local addresses in the network.
- It converts regular IPv6 addresses into 64-bit addresses that can be used on the Internet.
- It converts the 48-bit MAC address into a 64-bit host address that can be used for automatic host addressing.
Explanation:
NAT64 is typically used in IPv6 when networks are being transitioned from IPv4 to IPv6. It allows the IPv6 networks to connect to IPv4 networks (such as the Internet), and works by translating the IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
-
What is the most compressed representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001?
- 2001:0:abcd::1
- 2001:0:0:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd::1
- 2001:0000:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd:0:1
Explanation:
The IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001 in its most compressed format would be 2001:0:0:abcd::1. The first two hextets of zeros would each compress to a single zero. The three consecutive hextets of zeros can be compressed to a double colon ::. The three leading zeros in the last hextet can be removed. The double colon :: can only be used once in an address.
-
Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FEC0::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FE80::/10
- FF00::/8
Explanation:
Link-local addresses are in the range of FE80::/10 to FEBF::/10. The original IPv6 specification defined site-local addresses and used the prefix range FEC0::/10, but these addresses were deprecated by the IETF in favor of unique local addresses. FDEE::/7 is a unique local address because it is in the range of FC00::/7 to FDFF::/7. IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8.
-
How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
- 254
- 190
- 192
- 62
- 64
Explanation:
When a /26 mask is used, 6 bits are used as host bits. With 6 bits, 64 addresses are possible, but one address is for the subnet number and one address is for a broadcast. This leaves 62 addresses that can be assigned to network devices.
-
A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
Explanation:
The subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 has 8 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.128 results in 7 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.224 has 5 host bits. Finally, 255.255.255.240 represents 4 host bits.
-
Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
Explanation:
For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
-
Which statement is true about variable-length subnet masking?
- Each subnet is the same size.
- The size of each subnet may be different, depending on requirements.
- Subnets may only be subnetted one additional time.
- Bits are returned, rather than borrowed, to create additional subnets.
Explanation:
In variable-length subnet masking, bits are borrowed to create subnets. Additional bits may be borrowed to create additional subnets within the original subnets. This may continue until there are no bits available to borrow.
-
Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
Explanation:
The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
-
A user opens three browsers on the same PC to access www.cisco.com to search for certification course information. The Cisco web server sends a datagram as a reply to the request from one of the web browsers. Which information is used by the TCP/IP protocol stack in the PC to identify which of the three web browsers should receive the reply?
- the destination IP address
- the destination port number
- the source IP address
- the source port number
Explanation:
Each web browser client application opens a randomly generated port number in the range of the registered ports and uses this number as the source port number in the datagram that it sends to a server. The server then uses this port number as the destination port number in the reply datagram that it sends to the web browser. The PC that is running the web browser application receives the datagram and uses the destination port number that is contained in this datagram to identify the client application.
-
What are two ways that TCP uses the sequence numbers in a segment? (Choose two.)
- to identify missing segments at the destination
- to reassemble the segments at the remote location
- to specify the order in which the segments travel from source to destination
- to limit the number of segments that can be sent out of an interface at one time
- to determine if the packet changed during transit
-
Which two tasks are functions of the presentation layer? (Choose two.)
- compression
- addressing
- encryption
- session control
- authentication
Explanation:
The presentation layer deals with common data format. Encryption, formatting, and compression are some of the functions of the layer. Addressing occurs in the network layer, session control occurs in the session layer, and authentication takes place in the application or session layer.
-
What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
- wireless networking
- social networking without the Internet
- network printing using a print server
- resource sharing without a dedicated server
Explanation:
The peer-to-peer (P2P) networking model allows data, printer, and resource sharing without a dedicated server.
-
A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- ipconfig
- netstat
- nslookup
Explanation:
Traceroute (tracert) is a utility that generates a list of hops that were successfully reached along the path from source to destination.This list can provide important verification and troubleshooting information. The ipconfig utility is used to display the IP configuration settings on a Windows PC. The Netstat utility is used to identify which active TCP connections are open and running on a networked host. Nslookup is a utility that allows the user to manually query the name servers to resolve a given host name. This utility can also be used to troubleshoot name resolution issues and to verify the current status of the name servers.
-
Which domain name would be an example of a top-level domain?
- www.cisco.com
- cisco.com
- .com
- root.cisco.com
-
Explanation:
Top-level domains represent a country or type of organization, such as .com or .edu.
-
A PC obtains its IP address from a DHCP server. If the PC is taken off the network for repair, what happens to the IP address configuration?
- The configuration is permanent and nothing changes.
- The address lease is automatically renewed until the PC is returned.
- The address is returned to the pool for reuse when the lease expires.
- The configuration is held by the server to be reissued when the PC is returned.
Explanation:
When a DCHP address is issued to a host, it is for a specific lease time. Once the lease expires, the address is returned to the DHCP pool.
-
A wireless host needs to request an IP address. What protocol would be used to process the request?
- FTP
- HTTP
- DHCP
- ICMP
- SNMP
Explanation:
The DHCP protocol is used to request, issue, and manage IP addressing information. CSMA/CD is the access method used with wired Ethernet. ICMP is used to test connectivity. SNMP is used with network management and FTP is used for file transfer.
-
Which example of malicious code would be classified as a Trojan horse?
- malware that was written to look like a video game
- malware that requires manual user intervention to spread between systems
- malware that attaches itself to a legitimate program and spreads to other programs when launched
- malware that can automatically spread from one system to another by exploiting a vulnerability in the target
Explanation:
A Trojan horse is malicious code that has been written specifically to look like a legitimate program. This is in contrast to a virus, which simply attaches itself to an actual legitimate program. Viruses require manual intervention from a user to spread from one system to another, while a worm is able to spread automatically between systems by exploiting vulnerabilities on those devices.
-
When applied to a router, which command would help mitigate brute-force password attacks against the router?
- exec-timeout 30
- service password-encryption
- banner motd $Max failed logins = 5$
- login block-for 60 attempts 5 within 60
Explanation:
The login block-for command sets a limit on the maximum number of failed login attempts allowed within a defined period of time. If this limit is exceeded, no further logins are allowed for the specified period of time. This helps to mitigate brute-force password cracking since it will significantly increase the amount of time required to crack a password. The exec-timeout command specifies how long the session can be idle before the user is disconnected. The service password-encryption command encrypts the passwords in the running configuration. The banner motd command displays a message to users who are logging in to the device.
-
Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (not all options are used.)
- Question
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 004 - Answer
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 005
- Question
-
Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 006 - Question
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 007 - Answer
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 008 Explanation:
Packets with a destination of 172.17.6.15 are forwarded through Fa0/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.10.5 are forwarded through Fa1/1. Packets with a destination of 172.17.12.10 are forwarded through Fa1/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.14.8 are forwarded through Fa0/1. Because network 172.17.8.0 has no entry in the routing table, it will take the gateway of last resort, which means that packets with a destination of 172.17.8.20 are forwarded through Serial0/0/0. Because a gateway of last resort exists, no packets will be dropped.
- Question
-
A company is expanding its business to other countries. All branch offices must remain connected to corporate headquarters at all times. Which network technology is required to support this requirement?
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN
- WLAN
Explanation:
A local-area network (LAN) normally connects end users and network resources over a limited geographic area using Ethernet technology. A wireless LAN (WLAN) serves the same purpose as a LAN but uses wireless technologies. A metropolitan-area network (MAN) spans a larger geographic area such as a city, and a wide-area network (WAN) connects networks together over a large geographic area. WANs can span cities, countries, or the globe.
-
A home user is looking for an ISP connection that provides high speed digital transmission over regular phone lines. What ISP connection type should be used?
- DSL
- dial-up
- satellite
- cell modem
- cable modem
-
How does quality of service help a network support a wide range of applications and services?
- by limiting the impact of a network failure
- by allowing quick recovery from network failures
- by providing mechanisms to manage congested network traffic
- by providing the ability for the network to grow to accommodate new users
Explanation:
Quality of service (QoS), is a vital component of the architecture of a network. With QoS, network administrators can provide applications with predictable and measurable service guarantees through mechanisms that manage congested network traffic.
-
After making configuration changes on a Cisco switch, a network administrator issues a copy running-config startup-config command. What is the result of issuing this command?
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
Explanation:
With the copy running-config startup-config command, the content of the current operating configuration replaces the startup configuration file stored in NVRAM. The configuration file saved in NVRAM will be loaded when the device is restarted.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator has already logged into a Telnet session on the switch, which password is needed to access privileged EXEC mode?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 009 - letmein
- secretin
- lineconin
- linevtyin
Explanation:
Telnet accesses a network device through the virtual interface configured with the line VTY command. The password configured under this is required to access the user EXEC mode. The password configured under the line console 0 command is required to gain entry through the console port, and the enable and enable secret passwords are used to allow entry into the privileged EXEC mode.
- letmein
-
What function does pressing the Tab key have when entering a command in IOS?
- It aborts the current command and returns to configuration mode.
- It exits configuration mode and returns to user EXEC mode.
- It moves the cursor to the beginning of the next line.
- It completes the remainder of a partially typed word in a command.
Explanation:
Pressing the Tab key after a command has been partially typed will cause the IOS to complete the rest of the command.
-
What layer is responsible for routing messages through an internetwork in the TCP/IP model?
- internet
- transport
- network access
- session
Explanation:
The TCP/IP model consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and network access. Of these four layers, it is the internet layer that is responsible for routing messages. The session layer is not part of the TCP/IP model but is rather part of the OSI model.
-
Which statement accurately describes a TCP/IP encapsulation process when a PC is sending data to the network?
- Data is sent from the internet layer to the network access layer.
- Packets are sent from the network access layer to the transport layer.
- Segments are sent from the transport layer to the internet layer.
- Frames are sent from the network access layer to the internet layer.
Explanation:
When the data is traveling from the PC to the network, the transport layer sends segments to the internet layer. The internet layer sends packets to the network access layer, which creates frames and then converts the frames to bits. The bits are released to the network media.
-
What unique address is embedded in an Ethernet NIC and used for communication on an Ethernet network?
- host address
- IP address
- MAC address
- network address
Explanation:
The MAC address is a 48-bit address that is burned into every Ethernet NIC. Each MAC address is unique throughout the world.
-
Which procedure is used to reduce the effect of crosstalk in copper cables?
- requiring proper grounding connections
- twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together
- wrapping the bundle of wires with metallic shielding
- designing a cable infrastructure to avoid crosstalk interference
- avoiding sharp bends during installation
Explanation:
In copper cables, crosstalk is a disturbance caused by the electric or magnetic fields of a signal on one wire interfering with the signal in an adjacent wire. Twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together can effectively cancel the crosstalk. The other options are effective measures to counter the negative effects of EMI and RFI, but not crosstalk.
-
During the encapsulation process, what occurs at the data link layer for a PC connected to an Ethernet network?
- An IP address is added.
- The logical address is added.
- The physical address is added.
- The process port number is added.
Explanation:
The Ethernet frame includes the source and destination physical address. The trailer includes a CRC value in the Frame Check Sequence field to allow the receiving device to determine if the frame has been changed (has errors) during the transmission.
-
What are two characteristics of Ethernet MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
- They are globally unique.
- They are routable on the Internet.
- They are expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits.
- MAC addresses use a flexible hierarchical structure.
- MAC addresses must be unique for both Ethernet and serial interfaces on a device.
Explanation:
An Ethernet MAC address is a 48-bit binary value expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits. MAC addresses must be globally unique by design. MAC addresses are in flat structure and thus they are not routable on the Internet. Serial interfaces do not use MAC addresses.
-
If a device receives an Ethernet frame of 60 bytes, what will it do?
- drop the frame
- process the frame as it is
- send an error message to the sending device
- add random data bytes to make it 64 bytes long and then forward it
Explanation:
Ethernet standards define the minimum frame size as 64 bytes. A frame less than 64 bytes is considered a “collision fragment” or “runt frame” and is automatically discarded by receiving devices.
-
Under which two circumstances will a switch flood a frame out of every port except the port that the frame was received on? (Choose two.)
- The frame has the broadcast address as the destination address.
- The destination address is unknown to the switch.
- The source address in the frame header is the broadcast address.
- The source address in the frame is a multicast address.
- The destination address in the frame is a known unicast address.
Explanation:
A switch will flood a frame out of every port, except the one that the frame was received from, under two circumstances. Either the frame has the broadcast address as the destination address, or the destination address is unknown to the switch.
-
Which switching method has the lowest level of latency?
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
- fast-forward
Explanation:
Fast-forward switching begins to forward a frame after reading the destination MAC address, resulting in the lowest latency. Fragment-free reads the first 64 bytes before forwarding. Store-and-forward has the highest latency because it reads the entire frame before beginning to forward it. Both fragment-free and fast-forward are types of cut-through switching.
-
Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- netstat -s
- route print
- show ip route
- netstat -r
- tracert
Explanation:
On a Windows host, the route print or netstat -r commands can be used to display the host routing table. Both commands generate the same output. On a router, the show ip route command is used to display the routing table. The netstat –scommand is used to display per-protocol statistics. The tracert command is used to display the path that a packet travels to its destination.
-
Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet forwarding
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection
- flow control
-
What is the binary representation of 0xCA?
- 10111010
- 11010101
- 11001010
- 11011010
Explanation:
When converted, CA in hex is equivalent to 11011010 in binary. One way to do the conversion is one nibble at a time, C = 1100 and A = 1010. Combine the two nibbles gives 11001010.
-
At a minimum, which address is required on IPv6-enabled interfaces?
- link-local
- unique local
- site local
- global unicast
Explanation:
All IPv6 enabled interfaces must at minimum have a link-local address. Other IPv6 addresses can be assigned to the interface as required.
-
Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
Explanation:
Using stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC), a PC can solicit a router and receive the prefix length of the network. From this information the PC can then create its own IPv6 global unicast address.
-
What is the purpose of the command ping ::1?
- It tests the internal configuration of an IPv6 host.
- It tests the broadcast capability of all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the multicast connectivity to all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the reachability of the default gateway for the network.
Explanation:
The address ::1 is an IPv6 loopback address. Using the command ping ::1 tests the internal IP stack to ensure that it is configured and functioning correctly. It does not test reachability to any external device, nor does it confirm that IPv6 addresses are properly configured on the host.
-
How many usable IP addresses are available on the 192.168.1.0/27 network?
- 256
- 254
- 62
- 30
- 16
- 32
Explanation:
A /27 mask is the same as 255.255.255.224. This leaves 5 host bits. With 5 host bits, 32 IP addresses are possible, but one address represents the subnet number and one address represents the broadcast address. Thus, 30 addresses can then be used to assign to network devices.
-
A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses
Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses
Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addressesWhat single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
If the same mask is to be used, then the network with the most hosts must be examined for number of hosts. Because this is 10 hosts, 4 host bits are needed. The /28 or 255.255.255.240 subnet mask would be appropriate to use for these networks.
-
What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
Explanation:
In order to accommodate 40 devices, 6 host bits are needed. With 6 bits, 64 addresses are possible, but one address is for the subnet number and one address is for a broadcast. This leaves 62 addresses that can be assigned to network devices. The mask associated with leaving 6 host bits for addressing is 255.255.255.192.
-
What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering
- 3-way handshake
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- use of checksum
Explanation:
Both TCP and UDP use source and destination port numbers to distinguish different data streams and to forward the right data segments to the right applications. Error checking the header and data is done by both protocols by using a checksum calculation to determine the integrity of the data that is received. TCP is connection-oriented and uses a 3-way handshake to establish an initial connection. TCP also uses window to regulate the amount of traffic sent before receiving an acknowledgment. UDP is connectionless and is the best protocol for carry digitized VoIP signals.
-
Why are port numbers included in the TCP header of a segment?
- to indicate the correct router interface that should be used to forward a segment
- to identify which switch ports should receive or forward the segment
- to determine which Layer 3 protocol should be used to encapsulate the data
- to enable a receiving host to forward the data to the appropriate application
- to allow the receiving host to assemble the packet in the proper order
-
Which two protocols operate at the highest layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack? (Choose two.)
- DNS
- Ethernet
- IP
- POP
- TCP
- UDP
Explanation:
The application layer is the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack. Application layer protocols include HTTP, DNS, HTML, TFTP, POP, IMAP, FTP, and SMTP.
-
What is one difference between the client-server and peer-to-peer network models?
- Only in the client-server model can file transfers occur.
- Every device in a peer-to-peer network can function as a client or a server.
- A peer-to-peer network transfers data faster than a transfer using a client-server network.
- A data transfer that uses a device serving in a client role requires that a dedicated server be present.
Explanation:
Data transfer speeds depend on a number of factors including the amount of traffic, the quality of service imposed, and the network media. Transfer speeds are not dependent on the network model type. File transfers can occur using the client-server model or the peer-to-peer model. A data transfer between a device acting in the client role and a device acting in the server role can occur in both peer-to-peer and client-server networks.
-
Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
- peer-to-peer
- master-slave
- client/server
- point-to-point
Explanation:
In the client/server network model, a network device assumes the role of server in order to provide a particular service such as file transfer and storage. In the client/server network model, a dedicated server does not have to be used, but if one is present, the network model being used is the client/server model. In contrast, a peer-to-peer network does not have a dedicated server.
-
What network service resolves the URL entered on a PC to the IP address of the destination server?
- DNS
- DHCP
- FTP
- SNMP
Explanation:
When a client attempts to connect to a website, the destination URL must be resolved to an IP address. To do this the client queries a Domain Name System (DNS) server.
-
A network engineer is analyzing reports from a recently performed network baseline. Which situation would depict a possible latency issue?
- a change in the bandwidth according to the show interfaces output
- a next-hop timeout from a traceroute
- an increase in host-to-host ping response times
- a change in the amount of RAM according to the show version output
Explanation:
While analyzing historical reports an administrator can compare host-to-host timers from the ping command and depict possible latency issues.
-
Which firewall feature is used to ensure that packets coming into a network are legitimate responses to requests initiated from internal hosts?
- stateful packet inspection
- URL filtering
- application filtering
- packet filtering
Explanation:
Stateful packet inspection on a firewall checks that incoming packets are actually legitimate responses to requests originating from hosts inside the network. Packet filtering can be used to permit or deny access to resources based on IP or MAC address. Application filtering can permit or deny access based on port number. URL filtering is used to permit or deny access based on URL or on keywords.
-
Fill in the blank.
During data communications, a host may need to send a single message to a specific group of destination hosts simultaneously. This message is in the form of a Multicast message.
-
A medium-sized business is researching available options for connecting to the Internet. The company is looking for a high speed option with dedicated, symmetric access. Which connection type should the company choose?
- DSL
- dialup
- satellite
- leased line
- cable modem
-
What is the purpose of having a converged network?
- to provide high speed connectivity to all end devices
- to make sure that all types of data packets will be treated equally
- to achieve fault tolerance and high availability of data network infrastructure devices
- to reduce the cost of deploying and maintaining the communication infrastructure
Explanation:
With the development of technology, companies can now consolidate disparate networks onto one platform called a converged network. In a converged network, voice, video, and data travel over the same network, thus eliminating the need to create and maintain separate networks. This also reduces the costs associated with providing and maintaining the communication network infrastructure.
-
What characteristic of a network enables it to quickly grow to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users?
- reliability
- scalability
- quality of service
- accessibility
Explanation:
Networks must be able to quickly grow to support new users and services, without impacting existing users and services. This ability to grow is known as scalability.
-
After several configuration changes are made to a router, the copy running-configuration startup-configuration command is issued. Where will the changes be stored?
- flash
- ROM
- NVRAM
- RAM
- the configuration register
- a TFTP server
-
Refer to the exhibit. From global configuration mode, an administrator is attempting to create a message-of-the-day banner by using the command banner motd V Authorized access only! Violators will be prosecuted! V When users log in using Telnet, the banner does not appear correctly. What is the problem?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 015 - The banner message is too long.
- The delimiting character appears in the banner message.
- The symbol “!” signals the end of a banner message.
- Message-of-the-day banners will only appear when a user logs in through the console port.
-
What are three characteristics of an SVI? (Choose three.)
- It is designed as a security protocol to protect switch ports.
- It is not associated with any physical interface on a switch.
- It is a special interface that allows connectivity by different types of media.
- It is required to allow connectivity by any device at any location.
- It provides a means to remotely manage a switch.
- It is associated with VLAN1 by default.
Explanation:
Switches have one or more switch virtual interfaces (SVIs). SVIs are created in software since there is no physical hardware associated with them. Virtual interfaces provide a means to remotely manage a switch over a network that is using IP. Each switch comes with one SVI appearing in the default configuration “out-of-the-box.” The default SVI interface is VLAN1.
-
A technician configures a switch with these commands:SwitchA(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
SwitchA(config-if)# no shutdownWhat is the technician configuring?
- Telnet access
- SVI
- password encryption
- physical switchport access
Explanation:
For a switch to have an IP address, a switch virtual interface must be configured. This allows the switch to be managed remotely over the network.
-
In computer communication, what is the purpose of message encoding?
- to convert information to the appropriate form for transmission
- to interpret information
- to break large messages into smaller frames
- to negotiate correct timing for successful communication
Explanation:
Before a message is sent across a network it must first be encoded. Encoding is the process of converting the data message into another format suitable for transmission across the physical medium. Each bit of the message is encoded into a pattern of sounds, light waves, or electrical impulses depending on the network media over which the bits are transmitted. The destination host receives and decodes the signals in order to interpret the message.
-
What is the process of dividing a data stream into smaller pieces before transmission?
- segmentation
- encapsulation
- encoding
- flow control
Explanation:
Data streams would cause significant network congestion if they were transmitted as a single large stream of bits. To increase efficiency, data streams are segmented into smaller more manageable pieces which are then transmitted over the network.
-
When IPv4 addressing is manually configured on a web server, which property of the IPv4 configuration identifies the network and host portion for an IPv4 address?
- DNS server address
- subnet mask
- default gateway
- DHCP server address
Explanation:
There are several components that need to be entered when configuring IPv4 for an end device:
- IPv4 address – uniquely identifies an end device on the network
- Subnet mask – determines the network address portion and host portion for an IPv4 address
- Default gateway – the IP address of the router interface used for communicating with hosts in another network
- DNS server address – the IP address of the Domain Name System (DNS) server
DHCP server address (if DHCP is used) is not configured manually on end devices. It will be provided by a DHCP server when an end device requests an IP address.
-
A network engineer is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical database application. The engineer notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
Explanation:
Throughput usually does not match the specified bandwidth of physical links due to multiple factors. These factors include, the amount of traffic, type of traffic, and latency created by the network devices the data has to cross.
-
Which type of UTP cable is used to connect a PC to a switch port?
- console
- rollover
- crossover
- straight-through
Explanation:
A rollover cable is a Cisco proprietary cable used to connect to a router or switch console port. A straight-through (also called patch) cable is usually used to interconnect a host to a switch and a switch to a router. A crossover cable is used to interconnect similar devices together, for example, between two switches, two routers, and two hosts.
-
What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
Explanation:
Important actions that a switch performs are as follows:
- When a frame comes in, the switch examines the Layer 2 source address to build and maintain the Layer 2 MAC address table.
- It examines the Layer 2 destination address to determine how to forward the frame. When the destination address is in the MAC address table, then the frame is sent out a particular port. When the address is unknown, the frame is sent to all ports that have devices connected to that network.
-
What are two examples of the cut-through switching method? (Choose two.)
- store-and-forward switching
- fast-forward switching
- CRC switching
- fragment-free switching
- QOS switching
Explanation:
Store-and forward switching accepts the entire frame and performs error checking using CRC before forwarding the frame. Store-and-forward is often required for QOS analysis. Fast-forward and fragment-free are both variations of the cut-through switching method where only part of the frame is received before the switch begins to forward it.
-
What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
- source and destination MAC
- source and destination application protocol
- source and destination port number
- source and destination IP address
Explanation:
IP is a Layer 3 protocol. Layer 3 devices can open the Layer 3 header to inspect the Layer 3 header which contains IP-related information including the source and destination IP addresses.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 016 - subnet mask
- DNS address
- host IP address
- default gateway address
Explanation:
When a 255.255.255.224 subnet mask is used, the first three bits of the last octet are part of the network portion for an IPv4 address in the subnet. For the 192.168.5.96/27 network, valid host addresses are 192.168.5.97 through 192.168.5.126. The default gateway address is for the Layer 3 device on the same network and it must contain an IP address within the valid IP address range.
-
Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
- to identify the broadcast address of the destination network
- to identify the host address of the destination host
- to identify faulty frames
- to identify the network address of the destination network
Explanation:
ANDing allows us to identify the network address from the IP address and the network mask.
-
Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117
- 192.15.301.240
- 64.104.78.227
-
What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local
- multicast
- global unicast
Explanation:
Link-local IPv6 addresses start with FE80::/10, which is any address from FE80:: to FEBF::. Link-local addresses are used extensively in IPv6 and allow directly connected devices to communicate with each other on the link they share.
-
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 017 - There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
- There are 4 hops between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
- This host does not have a default gateway configured.
Explanation:
The output displays a successful Layer 3 connection between a host computer and a host at 19.168.100.1. It can be determined that 4 hops exist between them and the average transmission time is 1 milliseconds. Layer 3 connectivity does not necessarily mean that an application can run between the hosts.
-
How many hosts are addressable on a network that has a mask of 255.255.255.248?
- 2
- 6
- 8
- 14
- 16
- 254
Explanation:
The subnet mask of 255.255.255.248 is the same as /29. This means the network portion of the address is 29 of the 32 bits in the address. Only 3 bits remain for host bits. 2^3 = 8, but one of these addresses has to be used for the network number and one address must be used as the broadcast address to reach all of the hosts on this network. That leaves only 6 usable IP addresses that can be assigned to hosts in this network. Don’t forget that the default gateway must be one of these devices if this network is to communicate with other networks.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address of 192.168.10.0/24 that has been assigned to a high school building. The largest network in this building has 100 devices. If 192.168.10.0 is the network number for the largest network, what would be the network number for the next largest network, which has 40 devices?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 018 - 192.168.10.0
- 192.168.10.128
- 192.168.10.192
- 192.168.10.224
- 192.168.10.240
Explanation:
The first thing to calculate is what IP addresses are used by the largest LAN. Because the LAN has 100 hosts, 7 bits must be left for host bits. This would be a subnet mask of 255.255.255.128 for the largest LAN (192.168.10.0/25). The IP addresses range from 192.168.10.0 through 192.168.10.127. 192.168.10.0 is the network number (all 0s in the host bits) and 192.168.10.127 is the broadcast for this Ethernet LAN (all 1s in the host bits). The next available IP address is the next network number – 192.168.10.128.
-
In what two situations would UDP be the preferred transport protocol over TCP? (Choose two.)
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
Explanation:
UDP is a stateless protocol, which means that neither device on either end of the conversation must keep track of the conversation. As a stateless protocol, UDP is used as the Layer 4 protocol for applications that need speedy (best-effort) delivery. An example of such traffic is the transport of digitized voice or video.
-
What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
- timing and synchronization
- destination and source port numbers
- destination and source physical addresses
- destination and source logical network addresses
Explanation:
The destination and source port numbers are used to identify exactly which protocol and process is requesting or responding to a request.
-
What is the TCP mechanism used in congestion avoidance?
- three-way handshake
- socket pair
- two-way handshake
- sliding window
Explanation:
TCP uses windows to attempt to manage the rate of transmission to the maximum flow that the network and destination device can support while minimizing loss and retransmissions. When overwhelmed with data, the destination can send a request to reduce the of the window. This congestion avoidance is called sliding windows.
-
Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
- UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.
- UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
- UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection.
- UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.
- UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
- UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
Explanation:
UDP is a simple protocol that provides the basic transport layer functions. It has much lower overhead than TCP because it is not connection-oriented and does not offer the sophisticated retransmission, sequencing, and flow control mechanisms that provide reliability.
-
Which two roles can a computer assume in a peer-to-peer network where a file is being shared between two computers? (Choose two.)
- client
- master
- server
- slave
- transient
Explanation:
In a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, two or more computers are connected and can share resources without the use of a dedicated server. The computer that has the file acts as a server for the device (the client) that requests the file.
-
What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
- to request an HTML page from a web server
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
Explanation:
There are three common HTTP message types:
- GET – used by clients to request data from the web server
- POST – used by clients to upload data to a web server
- PUT – used by clients to upload data to a web server
-
When planning for network growth, where in the network should packet captures take place to assess network traffic?
- on as many different network segments as possible
- only at the edge of the network
- between hosts and the default gateway
- only on the busiest network segment
Explanation:
Because some types of traffic will be only on specific network segments, packet captures for analysis should be performed on as many segments as possible.
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is testing connectivity to a remote device with the IP address 10.1.1.1. What does the output of this command indicate?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 019 - Connectivity to the remote device was successful.
- A router along the path did not have a route to the destination.
- A ping packet is being blocked by a security device along the path.
- The connection timed out while waiting for a reply from the remote device.
Explanation:
In the output of the ping command, an exclamation mark (!) indicates a response was successfully received, a period (.) indicates that the connection timed out while waiting for a reply, and the letter “U” indicates that a router along the path did not have a route to the destination and sent an ICMP destination unreachable message back to the source.
-
Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
- Question
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 020 - Answer
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 021 Explanation:A logical topology diagram typically depicts the IP addressing scheme and groupings of devices and ports. A physical topology diagram shows how those devices are connected to each other and the network, focusing on the physical locations of intermediary devices, configured ports, and cabling.
- Question
-
Match the situation with the appropriate use of network media.
- Question
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 024 - Answer
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 025 Explanation:Copper Cables – horizontal cabling structure and desktop PCs in offices in an enterprise
Fiber optic – backbone cabling in an enterprise and long-haul networks
Wireless – coffee shops and waiting rooms in a hospital
- Question
-
Recommend
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to «Online Test» link below.
| Version 5.02 | Version 5.1 | Version 6.0 | Online Assessment |
| Final Exam | Final Exam | Final Exam | Online A, Online B, Online C |
| CCNA2 Pretest Exam | |||
| Pretest Exam | Pretest Exam | Pretest Exam | Online Test |
ITN Final Skills Exam (PTSA) — ID: 002 — Last Updated: Aug 2021
ITN (Version 7.00) Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Exam Answers
Topology
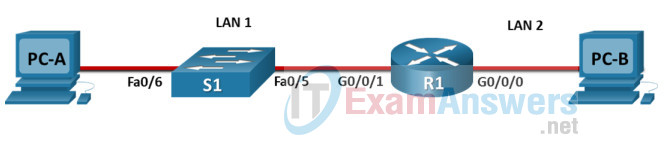
ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Device Names Table
You will receive one of three possible scenarios. In order to use the logical topology diagram that is provided with the instructions, use the device names in the Device Names Table.
| Topology Diagram Name | Your Scenario Name |
|---|---|
| R1 | R1 |
| S1 | S1 |
| PC-A | PC-A |
| PC-B | PC-B |
Addressing Requirements Table
| Item | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Network Address | 192.168.10.0/24 |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 100 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 50 |
| R1 G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| R1 G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet |
| S1 SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| PC-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| PC-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet |
ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
- Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
- Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
- Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Assessment Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network
- Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
- Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 4: Configure Security Settings on R1 and S1
- Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Instructions
In this assessment you will configure the R1 router and S1 switch, as you have done in the activities in this course. You will also connect two PCs using a switch and a router that are in the main wiring closet. You will subnet the 192.168.10.0/24 network to provide IPv4 addresses for two subnets that will support the required number of hosts. The larger subnet (LAN 1) requires 100 hosts and the smaller subnet (LAN 2) requires 50 hosts.
No subnet calculators may be used.
Part 1: Build the Network
a. Build the network according to the logical topology by placing the required equipment in the wiring closet equipment rack.
b. Cable the network devices in the closet as shown in the topology diagram.
c. Connect the hosts as shown in the topology diagram.
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
In this part of the assessment you will develop an IP addressing scheme. You will subnet an IPv4 network to create two subnets with the required number of hosts. You will also subnet an IPv6 network. You will then assign the addresses according to the requirements below.
Work with the following information:
- IPv4 Network: 192.168.10.0/24
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 1: 100
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 2: 50
a. Record your subnet assignments according to the following requirements.
1) Assign the first IPv4 address of each subnet to a router interface
- LAN 1 is hosted on R1 G0/0/1
- LAN 2 is hosted on R1 G0/0/0
2) Assign the last IPv4 address of each subnet to the PC NIC.
3) Assign the second IPv4 address of LAN 1 to S1 SVI.
Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
Network devices must be configured over a direct console connection.
Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
a. Disable DNS lookup on R1 and S1
b. Configure router hostname using the name R1.
c. Configure switch hostname using the name S1.
d. Configure an appropriate banner on R1 and S1.
e. Allow console logins with the password [email protected]!
Step 2: Configure Interfaces
a. Configure R1 G0/0/0 and G0/0/1 interfaces using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
b. Configure the S1 VLAN 1 SVI interface using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
- The switch should be reachable from devices on other networks.
Part 4: Configure Security Settings on R1 and S1
Step 1: Configure enhanced password security
a. Configure NoOneShouldKnow as the encrypted privileged EXEC password
b. Encrypt all plaintext passwords
c. Set minimum password length to 10 on R1.
Step 2: Configure SSH on R1 and S1
a. Configure netsec.com as the domain name
b. Configure a local user netadmin with the encrypted password Ci$co12345
c. Set login on vty lines to use local database.
d. Configure the vty lines to accept SSH access only.
e. Generate an RSA crypto key using 1024 bits modulus.
Step 3: Secure switch ports on S1
a. Shut down all unused ports on S1.
b. Enter descriptions for all unused switch ports to indicate that they are intentionally shutdown.
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Configure both hosts with the IPv4 addresses that were assigned in Part 2 of this assessment.
ID: 002
Answers Key — 100% Score
Part 1: Build the Network
Placing Switch S1 and Router R1 to wiring closet equipment rack.
Using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect PC-A (FastEthernet0 port) and S1 (FastEthernet0/6 port)
Same as above, using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect all devices as shown in the topology diagram.

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Turn-on PCs and Router R1
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
| Item | Requirements | IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|
| Network Address | 192.168.10.0/24 | |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 100 | 192.168.10.0/25 SM: 255.255.255.128 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 50 | 192.168.10.128/26 SM: 255.255.255.192 |
| R1 G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.1 |
| R1 G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet | 192.168.10.129 |
| S1 SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.2 |
| PC-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.126 |
| PC-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet | 192.168.10.190 |
Configuration for router R1
Using line console to connect PC-A and Router R1
Click to PC-A —> Terminal app —> click OK
Router R1 configuration script
enable configure terminal no ip domain-lookup hostname R1 banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!# interface g0/0/0 description Connect to Subnet B ip address 192.168.10.129 255.255.255.192 no shutdown exit interface g0/0/1 description Connect to Subnet A ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.128 no shutdown exit enable secret NoOneShouldKnow service password-encryption security passwords min-length 10 ip domain-name netsec.com username netadmin secret Ci$co12345 line console 0 password [email protected]! login exit line vty 0 15 transport input ssh login local exit crypto key generate rsa 1024 exit copy running-config startup-config
Configuration for Switch S1
Then, using Console cable to connect User-B and Switch
To show Console port on Switch, Right click Switch —> Inspect Rear —> Console port
Switch S1 configuration script
enable configure terminal no ip domain-lookup hostname S1 banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!# interface vlan 1 description Switch Subnet A ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.128 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.10.1 enable secret NoOneShouldKnow service password-encryption ip domain-name netsec.com username netadmin secret Ci$co12345 line console 0 password [email protected]! login exit line vty 0 15 transport input ssh login local exit crypto key generate rsa 1024 int range f0/1 - 4, f0/7 - 24, g0/1 - 2 description Unused switch ports shutdown end copy running-config startup-config
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
On PCs, go to Desktop tab —> IP Configuration menu
| PC-A Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 192.168.10.126 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.128 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 192.168.10.1 |
| PC-B Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 192.168.10.190 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.192 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 192.168.10.129 |
Download PDF & Packet Tracer files:
[sociallocker id=»57850″]
[/sociallocker]
ITN Final Skills Exam (PTSA)
ITN (Version 7.00) Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Exam Answers
Topology

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Device Names Table
You will receive one of three possible scenarios. In order to use the logical topology diagram that is provided with the instructions, use the device names in the Device Names Table.
| Topology Diagram Name | Your Scenario Name |
|---|---|
| R1 | Central-RT |
| S1 | Central-SW |
| PC-A | User-A |
| PC-B | User-B |
Addressing Requirements Table
| Item | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Network Address | 192.168.10.0/24 |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 100 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 50 |
| Central-RT G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| Central-RT G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet |
| Central-SW SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet |
ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
- Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
- Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
- Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Assessment Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network
- Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
- Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Central-RT and Central-SW
- Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Instructions
In this assessment you will configure the Central-RT router and Central-SW switch, as you have done in the activities in this course. You will also connect two PCs using a switch and a router that are in the main wiring closet. You will subnet the 192.168.10.0/24 network to provide IPv4 addresses for two subnets that will support the required number of hosts. The larger subnet (LAN 1) requires 100 hosts and the smaller subnet (LAN 2) requires 50 hosts.
No subnet calculators may be used.
Part 1: Build the Network
a. Build the network according to the logical topology by placing the required equipment in the wiring closet equipment rack.
b. Cable the network devices in the closet as shown in the topology diagram.
c. Connect the hosts as shown in the topology diagram.
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
In this part of the assessment you will develop an IP addressing scheme. You will subnet an IPv4 network to create two subnets with the required number of hosts. You will also subnet an IPv6 network. You will then assign the addresses according to the requirements below.
Work with the following information:
- IPv4 Network: 192.168.10.0/24
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 1: 100
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 2: 50
a. Record your subnet assignments according to the following requirements.
1) Assign the first IPv4 address of each subnet to a router interface
- LAN 1 is hosted on Central-RT G0/0/1
- LAN 2 is hosted on Central-RT G0/0/0
2) Assign the last IPv4 address of each subnet to the PC NIC.
3) Assign the second IPv4 address of LAN 1 to Central-SW SVI.
Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
Network devices must be configured over a direct console connection.
Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
a. Disable DNS lookup on Central-RT and Central-SW
b. Configure router hostname using the name Central-RT.
c. Configure switch hostname using the name Central-SW.
d. Configure an appropriate banner on Central-RT and Central-SW.
e. Allow console logins with the password [email protected]!
Step 2: Configure Interfaces
a. Configure Central-RT G0/0/0 and G0/0/1 interfaces using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
b. Configure the Central-SW VLAN 1 SVI interface using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
- The switch should be reachable from devices on other networks.
Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Central-RT and Central-SW
Step 1: Configure enhanced password security
a. Configure NoOneShouldKnow as the encrypted privileged EXEC password
b. Encrypt all plaintext passwords
c. Set minimum password length to 10 on Central-RT.
Step 2: Configure SSH on Central-RT and Central-SW
a. Configure netsec.com as the domain name
b. Configure a local user netadmin with the encrypted password Ci$co12345
c. Set login on vty lines to use local database.
d. Configure the vty lines to accept SSH access only.
e. Generate an RSA crypto key using 1024 bits modulus.
Step 3: Secure switch ports on Central-SW
a. Shut down all unused ports on Central-SW.
b. Enter descriptions for all unused switch ports to indicate that they are intentionally shutdown.
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Configure both hosts with the IPv4 addresses that were assigned in Part 2 of this assessment.
ID: 012
Answers Key
Part 1: Build the Network
Placing Switch Central-SW and Router Central-RT to wiring closet equipment rack.
Using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect User-A (FastEthernet0 port) and Central-SW (FastEthernet0/6 port)
Same as above, using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect all devices as shown in the topology diagram.

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Turn-on PCs and Router Central-RT
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
| Item | Requirements | IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|
| Network Address | 192.168.10.0/24 | |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 100 | 192.168.10.0/25 SM: 255.255.255.128 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 50 | 192.168.10.128/26 SM: 255.255.255.192 |
| Central-RT G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.1 |
| Central-RT G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet | 192.168.10.129 |
| Central-SW SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.2 |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.126 |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet | 192.168.10.190 |
Using line console to connect User-A and Router
Click to User-A —> Terminal app —> click OK
Router Central-RT configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Central-RT
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface g0/0/0
description Connect to Subnet B
ip address 192.168.10.129 255.255.255.192
no shutdown
exit
interface g0/0/1
description Connect to Subnet A
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.128
no shutdown
exit
enable secret NoOneShouldKnow
service password-encryption
security passwords min-length 10
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
exit
copy running-config startup-config
Configuration for Switch Central-SW
Then, using Console cable to connect User-B and Switch
To show Console port on Switch, Right click Switch —> Inspect Rear —> Console port
Switch Central-SW configuration script
enable configure terminal no ip domain-lookup hostname Central-SW banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!# interface vlan 1 description Switch Subnet A ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.128 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.10.1 enable secret NoOneShouldKnow service password-encryption ip domain-name netsec.com username netadmin secret Ci$co12345 line console 0 password [email protected]! login exit line vty 0 15 transport input ssh login local exit crypto key generate rsa 1024 int range f0/1 - 4, f0/7 - 24, g0/1 - 2 description Unused switch ports shutdown end copy running-config startup-config
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
On PCs, go to Desktop tab —> IP Configuration menu
| PC-A Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 192.168.10.126 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.128 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 192.168.10.1 |
| PC-B Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 192.168.10.190 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.192 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 192.168.10.129 |
Download PDF & Packet Tracer files:
[sociallocker id=»57850″]
[/sociallocker]
ITN Final Skills Exam (PTSA)
ITN (Version 7.00) Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Exam Answers
Topology

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Device Names Table
You will receive one of three possible scenarios. In order to use the logical topology diagram that is provided with the instructions, use the device names in the Device Names Table.
| Topology Diagram Name | Your Scenario Name |
|---|---|
| R1 | Central-RT |
| S1 | Central-SW |
| PC-A | User-A |
| PC-B | User-B |
Addressing Requirements Table
| Item | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Network Address | 209.165.201.0/24 |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 29 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 17 |
| Central-RT G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| Central-RT G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet |
| Central-SW SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet |
ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
- Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
- Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
- Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Assessment Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network
- Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
- Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Central-RT and Central-SW
- Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Instructions
In this assessment you will configure the Central-RT router and Central-SW switch, as you have done in the activities in this course. You will also connect two PCs using a switch and a router that are in the main wiring closet. You will subnet the 209.165.201.0/24 network to provide IPv4 addresses for two subnets that will support the required number of hosts. The larger subnet (LAN 1) requires 29 hosts and the smaller subnet (LAN 2) requires 17 hosts.
No subnet calculators may be used.
Part 1: Build the Network
a. Build the network according to the logical topology by placing the required equipment in the wiring closet equipment rack.
b. Cable the network devices in the closet as shown in the topology diagram.
c. Connect the hosts as shown in the topology diagram.
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
In this part of the assessment you will develop an IP addressing scheme. You will subnet an IPv4 network to create two subnets with the required number of hosts. You will also subnet an IPv6 network. You will then assign the addresses according to the requirements below.
Work with the following information:
- IPv4 Network: 209.165.201.0/24
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 1: 29
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 2: 17
a. Record your subnet assignments according to the following requirements.
1) Assign the first IPv4 address of each subnet to a router interface
- LAN 1 is hosted on Central-RT G0/0/1
- LAN 2 is hosted on Central-RT G0/0/0
2) Assign the last IPv4 address of each subnet to the PC NIC.
3) Assign the second IPv4 address of LAN 1 to Central-SW SVI.
Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
Network devices must be configured over a direct console connection.
Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
a. Disable DNS lookup on Central-RT and Central-SW
b. Configure router hostname using the name Central-RT.
c. Configure switch hostname using the name Central-SW.
d. Configure an appropriate banner on Central-RT and Central-SW.
e. Allow console logins with the password [email protected]!
Step 2: Configure Interfaces
a. Configure Central-RT G0/0/0 and G0/0/1 interfaces using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
b. Configure the Central-SW VLAN 1 SVI interface using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
- The switch should be reachable from devices on other networks.
Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Central-RT and Central-SW
Step 1: Configure enhanced password security
a. Configure NoOneShouldKnow as the encrypted privileged EXEC password
b. Encrypt all plaintext passwords
c. Set minimum password length to 10 on Central-RT.
Step 2: Configure SSH on Central-RT and Central-SW
a. Configure netsec.com as the domain name
b. Configure a local user netadmin with the encrypted password Ci$co12345
c. Set login on vty lines to use local database.
d. Configure the vty lines to accept SSH access only.
e. Generate an RSA crypto key using 1024 bits modulus.
Step 3: Secure switch ports on Central-SW
a. Shut down all unused ports on Central-SW.
b. Enter descriptions for all unused switch ports to indicate that they are intentionally shutdown.
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Configure both hosts with the IPv4 addresses that were assigned in Part 2 of this assessment.
ID: 211
Answers Key — 100% Score
Part 1: Build the Network
Placing Switch Central-SW and Router Central-RT to wiring closet equipment rack.
Using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect User-A (FastEthernet0 port) and Central-SW (FastEthernet0/6 port)
Same as above, using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect all devices as shown in the topology diagram.

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Turn-on PCs and Router Central-RT
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
| Item | Requirements | IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|
| Network Address | 209.165.201.0/24 | |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 29 | 209.165.201.0/27 SM: 255.255.255.224 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 17 | 209.165.201.32/27 SM: 255.255.255.224 |
| Central-RT G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet | 209.165.201.1 |
| Central-RT G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet | 209.165.201.33 |
| Central-SW SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet | 209.165.201.2 |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet | 209.165.201.30 |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet | 209.165.201.62 |
Using line console to connect User-A and Router
Click to User-A —> Terminal app —> click OK
Router Central-RT configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Central-RT
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface g0/0/0
description Connect to Subnet B
ip address 209.165.201.33 255.255.255.224
no shutdown
exit
interface g0/0/1
description Connect to Subnet A
ip address 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.224
no shutdown
exit
enable secret NoOneShouldKnow
service password-encryption
security passwords min-length 10
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
exit
copy running-config startup-config
Configuration for Switch Central-SW
Then, using Console cable to connect User-B and Switch
To show Console port on Switch, Right click Switch —> Inspect Rear —> Console port
Switch Central-SW configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Central-SW
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface vlan 1
description Switch Subnet A
ip address 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.224
no shutdown
exit
ip default-gateway 209.165.201.1
enable secret NoOneShouldKnow
service password-encryption
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
int range f0/1 - 4, f0/7 - 24, g0/1 - 2
description Unused switch ports
shutdown
end
copy running-config startup-config
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
On PCs, go to Desktop tab —> IP Configuration menu
| PC-A Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 209.165.201.30 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.224 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 209.165.201.1 |
| PC-B Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 209.165.201.62 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.224 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 209.165.201.33 |
Download PDF & Packet Tracer files:
[sociallocker id=»57850″]
[/sociallocker]
ITN Final Skills Exam (PTSA)
ITN (Version 7.00) Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Exam Answers
Topology

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Device Names Table
You will receive one of three possible scenarios. In order to use the logical topology diagram that is provided with the instructions, use the device names in the Device Names Table.
| Topology Diagram Name | Your Scenario Name |
|---|---|
| R1 | Router-A |
| S1 | Switch-A |
| PC-A | Host-A |
| PC-B | Host-B |
Addressing Requirements Table
| Item | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Network Address | 172.16.1.0/24 |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 60 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 20 |
| Router-A G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| Router-A G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet |
| Switch-A SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet |
ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
- Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
- Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
- Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Assessment Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network
- Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
- Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Router-A and Switch-A
- Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Instructions
In this assessment you will configure the Router-A router and Switch-A switch, as you have done in the activities in this course. You will also connect two PCs using a switch and a router that are in the main wiring closet. You will subnet the 172.16.1.0/24 network to provide IPv4 addresses for two subnets that will support the required number of hosts. The larger subnet (LAN 1) requires 60 hosts and the smaller subnet (LAN 2) requires 20 hosts.
No subnet calculators may be used.
Part 1: Build the Network
a. Build the network according to the logical topology by placing the required equipment in the wiring closet equipment rack.
b. Cable the network devices in the closet as shown in the topology diagram.
c. Connect the hosts as shown in the topology diagram.
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
In this part of the assessment you will develop an IP addressing scheme. You will subnet an IPv4 network to create two subnets with the required number of hosts. You will also subnet an IPv6 network. You will then assign the addresses according to the requirements below.
Work with the following information:
- IPv4 Network: 172.16.1.0/24
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 1: 60
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 2: 20
a. Record your subnet assignments according to the following requirements.
1) Assign the first IPv4 address of each subnet to a router interface
- LAN 1 is hosted on Router-A G0/0/1
- LAN 2 is hosted on Router-A G0/0/0
2) Assign the last IPv4 address of each subnet to the PC NIC.
3) Assign the second IPv4 address of LAN 1 to Switch-A SVI.
Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
Network devices must be configured over a direct console connection.
Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
a. Disable DNS lookup on Router-A and Switch-A
b. Configure router hostname using the name Router-A.
c. Configure switch hostname using the name Switch-A.
d. Configure an appropriate banner on Router-A and Switch-A.
e. Allow console logins with the password [email protected]!
Step 2: Configure Interfaces
a. Configure Router-A G0/0/0 and G0/0/1 interfaces using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
b. Configure the Switch-A VLAN 1 SVI interface using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
- The switch should be reachable from devices on other networks.
Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Router-A and Switch-A
Step 1: Configure enhanced password security
a. Configure NoOneShouldKnow as the encrypted privileged EXEC password
b. Encrypt all plaintext passwords
c. Set minimum password length to 10 on Router-A.
Step 2: Configure SSH on Router-A and Switch-A
a. Configure netsec.com as the domain name
b. Configure a local user netadmin with the encrypted password Ci$co12345
c. Set login on vty lines to use local database.
d. Configure the vty lines to accept SSH access only.
e. Generate an RSA crypto key using 1024 bits modulus.
Step 3: Secure switch ports on Switch-A
a. Shut down all unused ports on Switch-A.
b. Enter descriptions for all unused switch ports to indicate that they are intentionally shutdown.
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Configure both hosts with the IPv4 addresses that were assigned in Part 2 of this assessment.
ID: 120
Answers Key — 100% Score
Part 1: Build the Network
Placing Switch Switch-A and Router Router-A to wiring closet equipment rack.
Using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect User-A (FastEthernet0 port) and Switch-A (FastEthernet0/6 port)
Same as above, using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect all devices as shown in the topology diagram.

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Turn-on PCs and Router Router-A
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
| Item | Requirements | IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|
| Network Address | 172.16.1.0/24 | |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 60 | 172.16.1.0/26 SM: 255.255.255.192 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 20 | 172.16.1.64/27 SM: 255.255.255.224 |
| Router-A G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet | 172.16.1.1 |
| Router-A G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet | 172.16.1.65 |
| Switch-A SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet | 172.16.1.2 |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet | 172.16.1.62 |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet | 172.16.1.94 |
Using line console to connect User-A and Router
Click to User-A —> Terminal app —> click OK
Router Router-A configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Router-A
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface g0/0/0
description Connect to Subnet B
ip address 172.16.1.65 255.255.255.224
no shutdown
exit
interface g0/0/1
description Connect to Subnet A
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.192
no shutdown
exit
enable secret NoOneShouldKnow
service password-encryption
security passwords min-length 10
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
exit
copy running-config startup-config
Configuration for Switch-A
Then, using Console cable to connect User-B and Switch
To show Console port on Switch, Right click Switch —> Inspect Rear —> Console port
Switch Switch-A configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Switch-A
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface vlan 1
description Switch Subnet A
ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.192
no shutdown
exit
ip default-gateway 172.16.1.1
enable secret NoOneShouldKnow
service password-encryption
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
int range f0/1 - 4, f0/7 - 24, g0/1 - 2
description Unused switch ports
shutdown
end
copy running-config startup-config
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
On PCs, go to Desktop tab —> IP Configuration menu
| PC-A Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 172.16.1.62 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.192 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 172.16.1.1 |
| PC-B Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 172.16.1.94 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.224 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 172.16.1.65 |
Download PDF & Packet Tracer files:
[sociallocker id=»57850″]
[/sociallocker]
ITN Final Skills Exam (PTSA)
ITN (Version 7.00) Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Exam Answers
Topology

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Device Names Table
You will receive one of three possible scenarios. In order to use the logical topology diagram that is provided with the instructions, use the device names in the Device Names Table.
| Topology Diagram Name | Your Scenario Name |
|---|---|
| R1 | Central-RT |
| S1 | Central-SW |
| PC-A | User-A |
| PC-B | User-B |
Addressing Requirements Table
| Item | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Network Address | 192.168.10.0/24 |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 100 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 50 |
| Central-RT G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| Central-RT G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet |
| Central-SW SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet |
ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
- Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
- Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
- Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Assessment Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network
- Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
- Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Central-RT and Central-SW
- Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Instructions
In this assessment you will configure the Central-RT router and Central-SW switch, as you have done in the activities in this course. You will also connect two PCs using a switch and a router that are in the main wiring closet. You will subnet the 192.168.10.0/24 network to provide IPv4 addresses for two subnets that will support the required number of hosts. The larger subnet (LAN 1) requires 100 hosts and the smaller subnet (LAN 2) requires 50 hosts.
No subnet calculators may be used.
Part 1: Build the Network
a. Build the network according to the logical topology by placing the required equipment in the wiring closet equipment rack.
b. Cable the network devices in the closet as shown in the topology diagram.
c. Connect the hosts as shown in the topology diagram.
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
In this part of the assessment you will develop an IP addressing scheme. You will subnet an IPv4 network to create two subnets with the required number of hosts. You will also subnet an IPv6 network. You will then assign the addresses according to the requirements below.
Work with the following information:
- IPv4 Network: 192.168.10.0/24
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 1: 100
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 2: 50
a. Record your subnet assignments according to the following requirements.
1) Assign the first IPv4 address of each subnet to a router interface
- LAN 1 is hosted on Central-RT G0/0/1
- LAN 2 is hosted on Central-RT G0/0/0
2) Assign the last IPv4 address of each subnet to the PC NIC.
3) Assign the second IPv4 address of LAN 1 to Central-SW SVI.
Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
Network devices must be configured over a direct console connection.
Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
a. Disable DNS lookup on Central-RT and Central-SW
b. Configure router hostname using the name Central-RT.
c. Configure switch hostname using the name Central-SW.
d. Configure an appropriate banner on Central-RT and Central-SW.
e. Allow console logins with the password [email protected]!
Step 2: Configure Interfaces
a. Configure Central-RT G0/0/0 and G0/0/1 interfaces using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
b. Configure the Central-SW VLAN 1 SVI interface using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
- The switch should be reachable from devices on other networks.
Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Central-RT and Central-SW
Step 1: Configure enhanced password security
a. Configure DontTellAnyone as the encrypted privileged EXEC password
b. Encrypt all plaintext passwords
c. Set minimum password length to 10 on Central-RT.
Step 2: Configure SSH on Central-RT and Central-SW
a. Configure netsec.com as the domain name
b. Configure a local user netadmin with the encrypted password Ci$co12345
c. Set login on vty lines to use local database.
d. Configure the vty lines to accept SSH access only.
e. Generate an RSA crypto key using 1024 bits modulus.
Step 3: Secure switch ports on Central-SW
a. Shut down all unused ports on Central-SW.
b. Enter descriptions for all unused switch ports to indicate that they are intentionally shutdown.
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Configure both hosts with the IPv4 addresses that were assigned in Part 2 of this assessment.
ID: 011
Answers Key
Part 1: Build the Network
Placing Switch Central-SW and Router Central-RT to wiring closet equipment rack.
Using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect User-A (FastEthernet0 port) and Central-SW (FastEthernet0/6 port)
Same as above, using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect all devices as shown in the topology diagram.

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Turn-on PCs and Router Central-RT
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
| Item | Requirements | IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|
| Network Address | 192.168.10.0/24 | |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 100 | 192.168.10.0/25 SM: 255.255.255.128 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 50 | 192.168.10.128/26 SM: 255.255.255.192 |
| Central-RT G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.1 |
| Central-RT G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet | 192.168.10.129 |
| Central-SW SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.2 |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.126 |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet | 192.168.10.190 |
Using line console to connect User-A and Router
Click to User-A —> Terminal app —> click OK
Router Central-RT configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Central-RT
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface g0/0/0
description Connect to Subnet B
ip address 192.168.10.129 255.255.255.192
no shutdown
exit
interface g0/0/1
description Connect to Subnet A
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.128
no shutdown
exit
enable secret DontTellAnyone
service password-encryption
security passwords min-length 10
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
exit
copy running-config startup-config
Configuration for Switch Central-SW
Then, using Console cable to connect User-B and Switch
To show Console port on Switch, Right click Switch —> Inspect Rear —> Console port
Switch Central-SW configuration script
enable configure terminal no ip domain-lookup hostname Central-SW banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!# interface vlan 1 description Switch Subnet A ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.128 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.10.1 enable secret DontTellAnyone service password-encryption ip domain-name netsec.com username netadmin secret Ci$co12345 line console 0 password [email protected]! login exit line vty 0 15 transport input ssh login local exit crypto key generate rsa 1024 int range f0/1 - 4, f0/7 - 24, g0/1 - 2 description Unused switch ports shutdown end copy running-config startup-config
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
On PCs, go to Desktop tab —> IP Configuration menu
| PC-A Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 192.168.10.126 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.128 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 192.168.10.1 |
| PC-B Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 192.168.10.190 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.192 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 192.168.10.129 |
Download PDF & Packet Tracer files:
[sociallocker id=»57850″]
[/sociallocker]
ITN Final Skills Exam (PTSA)
ITN (Version 7.00) Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Exam Answers
Topology

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Device Names Table
You will receive one of three possible scenarios. In order to use the logical topology diagram that is provided with the instructions, use the device names in the Device Names Table.
| Topology Diagram Name | Your Scenario Name |
|---|---|
| R1 | Router-A |
| S1 | Switch-A |
| PC-A | Host-A |
| PC-B | Host-B |
Addressing Requirements Table
| Item | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Network Address | 192.168.10.0/24 |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 100 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 50 |
| Router-A G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| Router-A G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet |
| Switch-A SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| Host-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| Host-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet |
ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
- Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
- Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
- Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Assessment Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network
- Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
- Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Router-A and Switch-A
- Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Instructions
In this assessment you will configure the Router-A router and Switch-A switch, as you have done in the activities in this course. You will also connect two PCs using a switch and a router that are in the main wiring closet. You will subnet the 192.168.10.0/24 network to provide IPv4 addresses for two subnets that will support the required number of hosts. The larger subnet (LAN 1) requires 100 hosts and the smaller subnet (LAN 2) requires 50 hosts.
No subnet calculators may be used.
Part 1: Build the Network
a. Build the network according to the logical topology by placing the required equipment in the wiring closet equipment rack.
b. Cable the network devices in the closet as shown in the topology diagram.
c. Connect the hosts as shown in the topology diagram.
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
In this part of the assessment you will develop an IP addressing scheme. You will subnet an IPv4 network to create two subnets with the required number of hosts. You will also subnet an IPv6 network. You will then assign the addresses according to the requirements below.
Work with the following information:
- IPv4 Network: 192.168.10.0/24
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 1: 100
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 2: 50
a. Record your subnet assignments according to the following requirements.
1) Assign the first IPv4 address of each subnet to a router interface
- LAN 1 is hosted on Router-A G0/0/1
- LAN 2 is hosted on Router-A G0/0/0
2) Assign the last IPv4 address of each subnet to the PC NIC.
3) Assign the second IPv4 address of LAN 1 to Switch-A SVI.
Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
Network devices must be configured over a direct console connection.
Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
a. Disable DNS lookup on Router-A and Switch-A
b. Configure router hostname using the name Router-A.
c. Configure switch hostname using the name Switch-A.
d. Configure an appropriate banner on Router-A and Switch-A.
e. Allow console logins with the password [email protected]!
Step 2: Configure Interfaces
a. Configure Router-A G0/0/0 and G0/0/1 interfaces using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
b. Configure the Switch-A VLAN 1 SVI interface using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
- The switch should be reachable from devices on other networks.
Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Router-A and Switch-A
Step 1: Configure enhanced password security
a. Configure DontTellAnyone as the encrypted privileged EXEC password
b. Encrypt all plaintext passwords
c. Set minimum password length to 10 on Router-A.
Step 2: Configure SSH on Router-A and Switch-A
a. Configure netsec.com as the domain name
b. Configure a local user netadmin with the encrypted password Ci$co12345
c. Set login on vty lines to use local database.
d. Configure the vty lines to accept SSH access only.
e. Generate an RSA crypto key using 1024 bits modulus.
Step 3: Secure switch ports on Switch-A
a. Shut down all unused ports on Switch-A.
b. Enter descriptions for all unused switch ports to indicate that they are intentionally shutdown.
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Configure both hosts with the IPv4 addresses that were assigned in Part 2 of this assessment.
ID: 021
Answers Key
Part 1: Build the Network
Placing Switch Switch-A and Router Router-A to wiring closet equipment rack.
Using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect Host-A (FastEthernet0 port) and Switch-A (FastEthernet0/6 port)
Same as above, using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect all devices as shown in the topology diagram.

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Turn-on PCs and Router Router-A
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
| Item | Requirements | IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|
| Network Address | 192.168.10.0/24 | |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 100 | 192.168.10.0/25 SM: 255.255.255.128 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 50 | 192.168.10.128/26 SM: 255.255.255.192 |
| Router-A G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.1 |
| Router-A G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet | 192.168.10.129 |
| Switch-A SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.2 |
| Host-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet | 192.168.10.126 |
| Host-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet | 192.168.10.190 |
Using line console to connect Host-A and Router
Click to Host-A —> Terminal app —> click OK
Router Router-A configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Router-A
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface g0/0/0
description Connect to Subnet B
ip address 192.168.10.129 255.255.255.192
no shutdown
exit
interface g0/0/1
description Connect to Subnet A
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.128
no shutdown
exit
enable secret DontTellAnyone
service password-encryption
security passwords min-length 10
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
exit
copy running-config startup-config
Configuration for Switch Switch-A
Then, using Console cable to connect Host-B and Switch
To show Console port on Switch, Right click Switch —> Inspect Rear —> Console port
Switch Switch-A configuration script
enable configure terminal no ip domain-lookup hostname Switch-A banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!# interface vlan 1 description Switch Subnet A ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.128 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.10.1 enable secret DontTellAnyone service password-encryption ip domain-name netsec.com username netadmin secret Ci$co12345 line console 0 password [email protected]! login exit line vty 0 15 transport input ssh login local exit crypto key generate rsa 1024 int range f0/1 - 4, f0/7 - 24, g0/1 - 2 description Unused switch ports shutdown end copy running-config startup-config
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
On PCs, go to Desktop tab —> IP Configuration menu
| PC-A Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 192.168.10.126 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.128 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 192.168.10.1 |
| PC-B Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 192.168.10.190 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.192 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 192.168.10.129 |
Download PDF & Packet Tracer files:
[sociallocker id=»57850″]
[/sociallocker]
ITN Final Skills Exam (PTSA)
ITN (Version 7.00) Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Exam Answers
Topology

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Device Names Table
You will receive one of three possible scenarios. In order to use the logical topology diagram that is provided with the instructions, use the device names in the Device Names Table.
| Topology Diagram Name | Your Scenario Name |
|---|---|
| R1 | Central-RT |
| S1 | Central-SW |
| PC-A | User-A |
| PC-B | User-B |
Addressing Requirements Table
| Item | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Network Address | 209.165.201.0/24 |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 29 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 17 |
| Central-RT G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| Central-RT G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet |
| Central-SW SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet |
ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
- Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
- Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
- Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Assessment Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network
- Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
- Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Central-RT and Central-SW
- Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Instructions
In this assessment you will configure the Central-RT router and Central-SW switch, as you have done in the activities in this course. You will also connect two PCs using a switch and a router that are in the main wiring closet. You will subnet the 209.165.201.0/24 network to provide IPv4 addresses for two subnets that will support the required number of hosts. The larger subnet (LAN 1) requires 29 hosts and the smaller subnet (LAN 2) requires 17 hosts.
No subnet calculators may be used.
Part 1: Build the Network
a. Build the network according to the logical topology by placing the required equipment in the wiring closet equipment rack.
b. Cable the network devices in the closet as shown in the topology diagram.
c. Connect the hosts as shown in the topology diagram.
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
In this part of the assessment you will develop an IP addressing scheme. You will subnet an IPv4 network to create two subnets with the required number of hosts. You will also subnet an IPv6 network. You will then assign the addresses according to the requirements below.
Work with the following information:
- IPv4 Network: 209.165.201.0/24
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 1: 29
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 2: 17
a. Record your subnet assignments according to the following requirements.
1) Assign the first IPv4 address of each subnet to a router interface
- LAN 1 is hosted on Central-RT G0/0/1
- LAN 2 is hosted on Central-RT G0/0/0
2) Assign the last IPv4 address of each subnet to the PC NIC.
3) Assign the second IPv4 address of LAN 1 to Central-SW SVI.
Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
Network devices must be configured over a direct console connection.
Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
a. Disable DNS lookup on Central-RT and Central-SW
b. Configure router hostname using the name Central-RT.
c. Configure switch hostname using the name Central-SW.
d. Configure an appropriate banner on Central-RT and Central-SW.
e. Allow console logins with the password [email protected]!
Step 2: Configure Interfaces
a. Configure Central-RT G0/0/0 and G0/0/1 interfaces using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
b. Configure the Central-SW VLAN 1 SVI interface using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
- The switch should be reachable from devices on other networks.
Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Central-RT and Central-SW
Step 1: Configure enhanced password security
a. Configure ThisisaSecret as the encrypted privileged EXEC password
b. Encrypt all plaintext passwords
c. Set minimum password length to 10 on Central-RT.
Step 2: Configure SSH on Central-RT and Central-SW
a. Configure netsec.com as the domain name
b. Configure a local user netadmin with the encrypted password Ci$co12345
c. Set login on vty lines to use local database.
d. Configure the vty lines to accept SSH access only.
e. Generate an RSA crypto key using 1024 bits modulus.
Step 3: Secure switch ports on Central-SW
a. Shut down all unused ports on Central-SW.
b. Enter descriptions for all unused switch ports to indicate that they are intentionally shutdown.
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Configure both hosts with the IPv4 addresses that were assigned in Part 2 of this assessment.
ID: 210
Answers Key — 100% Score
Part 1: Build the Network
Placing Switch Central-SW and Router Central-RT to wiring closet equipment rack.
Using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect User-A (FastEthernet0 port) and Central-SW (FastEthernet0/6 port)
Same as above, using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect all devices as shown in the topology diagram.

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Turn-on PCs and Router Central-RT
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
| Item | Requirements | IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|
| Network Address | 209.165.201.0/24 | |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 29 | 209.165.201.0/27 SM: 255.255.255.224 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 17 | 209.165.201.32/27 SM: 255.255.255.224 |
| Central-RT G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet | 209.165.201.1 |
| Central-RT G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet | 209.165.201.33 |
| Central-SW SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet | 209.165.201.2 |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet | 209.165.201.30 |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet | 209.165.201.62 |
Using line console to connect User-A and Router
Click to User-A —> Terminal app —> click OK
Router Central-RT configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Central-RT
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface g0/0/0
description Connect to Subnet B
ip address 209.165.201.33 255.255.255.224
no shutdown
exit
interface g0/0/1
description Connect to Subnet A
ip address 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.224
no shutdown
exit
enable secret ThisisaSecret
service password-encryption
security passwords min-length 10
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
exit
copy running-config startup-config
Configuration for Switch Central-SW
Then, using Console cable to connect User-B and Switch
To show Console port on Switch, Right click Switch —> Inspect Rear —> Console port
Switch Central-SW configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Central-SW
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface vlan 1
description Switch Subnet A
ip address 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.224
no shutdown
exit
ip default-gateway 209.165.201.1
enable secret ThisisaSecret
service password-encryption
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
int range f0/1 - 4, f0/7 - 24, g0/1 - 2
description Unused switch ports
shutdown
end
copy running-config startup-config
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
On PCs, go to Desktop tab —> IP Configuration menu
| PC-A Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 209.165.201.30 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.224 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 209.165.201.1 |
| PC-B Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 209.165.201.62 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.224 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 209.165.201.33 |
Download PDF & Packet Tracer files:
[sociallocker id=»57850″]
[/sociallocker]
ITN Final Skills Exam (PTSA)
ITN (Version 7.00) Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Exam Answers
Topology

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Device Names Table
You will receive one of three possible scenarios. In order to use the logical topology diagram that is provided with the instructions, use the device names in the Device Names Table.
| Topology Diagram Name | Your Scenario Name |
|---|---|
| R1 | Central-RT |
| S1 | Central-SW |
| PC-A | User-A |
| PC-B | User-B |
Addressing Requirements Table
| Item | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Network Address | 172.16.1.0/24 |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 60 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 20 |
| Central-RT G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| Central-RT G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet |
| Central-SW SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet |
ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
- Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
- Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
- Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Assessment Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network
- Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
- Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Central-RT and Central-SW
- Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Instructions
In this assessment you will configure the Central-RT router and Central-SW switch, as you have done in the activities in this course. You will also connect two PCs using a switch and a router that are in the main wiring closet. You will subnet the 172.16.1.0/24 network to provide IPv4 addresses for two subnets that will support the required number of hosts. The larger subnet (LAN 1) requires 60 hosts and the smaller subnet (LAN 2) requires 20 hosts.
No subnet calculators may be used.
Part 1: Build the Network
a. Build the network according to the logical topology by placing the required equipment in the wiring closet equipment rack.
b. Cable the network devices in the closet as shown in the topology diagram.
c. Connect the hosts as shown in the topology diagram.
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
In this part of the assessment you will develop an IP addressing scheme. You will subnet an IPv4 network to create two subnets with the required number of hosts. You will also subnet an IPv6 network. You will then assign the addresses according to the requirements below.
Work with the following information:
- IPv4 Network: 172.16.1.0/24
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 1: 60
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 2: 20
a. Record your subnet assignments according to the following requirements.
1) Assign the first IPv4 address of each subnet to a router interface
- LAN 1 is hosted on Central-RT G0/0/1
- LAN 2 is hosted on Central-RT G0/0/0
2) Assign the last IPv4 address of each subnet to the PC NIC.
3) Assign the second IPv4 address of LAN 1 to Central-SW SVI.
Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
Network devices must be configured over a direct console connection.
Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
a. Disable DNS lookup on Central-RT and Central-SW
b. Configure router hostname using the name Central-RT.
c. Configure switch hostname using the name Central-SW.
d. Configure an appropriate banner on Central-RT and Central-SW.
e. Allow console logins with the password [email protected]!
Step 2: Configure Interfaces
a. Configure Central-RT G0/0/0 and G0/0/1 interfaces using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
b. Configure the Central-SW VLAN 1 SVI interface using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
- The switch should be reachable from devices on other networks.
Part 4: Configure Security Settings on Central-RT and Central-SW
Step 1: Configure enhanced password security
a. Configure DontTellAnyone as the encrypted privileged EXEC password
b. Encrypt all plaintext passwords
c. Set minimum password length to 10 on Central-RT.
Step 2: Configure SSH on Central-RT and Central-SW
a. Configure netsec.com as the domain name
b. Configure a local user netadmin with the encrypted password Ci$co12345
c. Set login on vty lines to use local database.
d. Configure the vty lines to accept SSH access only.
e. Generate an RSA crypto key using 1024 bits modulus.
Step 3: Secure switch ports on Central-SW
a. Shut down all unused ports on Central-SW.
b. Enter descriptions for all unused switch ports to indicate that they are intentionally shutdown.
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Configure both hosts with the IPv4 addresses that were assigned in Part 2 of this assessment.
ID: 111
Answers Key — 100% Score
Part 1: Build the Network
Placing Switch Central-SW and Router Central-RT to wiring closet equipment rack.
Using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect User-A (FastEthernet0 port) and Central-SW (FastEthernet0/6 port)
Same as above, using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect all devices as shown in the topology diagram.

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Turn-on PCs and Router Central-RT
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
| Item | Requirements | IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|
| Network Address | 172.16.1.0/24 | |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 60 | 172.16.1.0/26 SM: 255.255.255.192 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 20 | 172.16.1.64/27 SM: 255.255.255.224 |
| Central-RT G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet | 172.16.1.1 |
| Central-RT G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet | 172.16.1.65 |
| Central-SW SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet | 172.16.1.2 |
| User-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet | 172.16.1.62 |
| User-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet | 172.16.1.94 |
Using line console to connect User-A and Router
Click to User-A —> Terminal app —> click OK
Router Central-RT configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Central-RT
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface g0/0/0
description Connect to Subnet B
ip address 172.16.1.65 255.255.255.224
no shutdown
exit
interface g0/0/1
description Connect to Subnet A
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.192
no shutdown
exit
enable secret DontTellAnyone
service password-encryption
security passwords min-length 10
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
exit
copy running-config startup-config
Configuration for Central-SW
Then, using Console cable to connect User-B and Switch
To show Console port on Switch, Right click Switch —> Inspect Rear —> Console port
Switch Central-SW configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname Central-SW
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface vlan 1
description Switch Subnet A
ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.192
no shutdown
exit
ip default-gateway 172.16.1.1
enable secret DontTellAnyone
service password-encryption
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
int range f0/1 - 4, f0/7 - 24, g0/1 - 2
description Unused switch ports
shutdown
end
copy running-config startup-config
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
On PCs, go to Desktop tab —> IP Configuration menu
| PC-A Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 172.16.1.62 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.192 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 172.16.1.1 |
| PC-B Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 172.16.1.94 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.224 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 172.16.1.65 |
Download PDF & Packet Tracer files:
[sociallocker id=»57850″]
[/sociallocker]
ITN Final Skills Exam (PTSA)
ITN (Version 7.00) Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Exam Answers
Topology

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Device Names Table
You will receive one of three possible scenarios. In order to use the logical topology diagram that is provided with the instructions, use the device names in the Device Names Table.
| Topology Diagram Name | Your Scenario Name |
|---|---|
| R1 | R1 |
| S1 | S1 |
| PC-A | PC-A |
| PC-B | PC-B |
Addressing Requirements Table
| Item | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Network Address | 172.16.1.0/24 |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 60 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 20 |
| R1 G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| R1 G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet |
| S1 SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| PC-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet |
| PC-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet |
ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
- Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
- Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
- Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Assessment Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network
- Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
- Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 4: Configure Security Settings on R1 and S1
- Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Instructions
In this assessment you will configure the R1 router and S1 switch, as you have done in the activities in this course. You will also connect two PCs using a switch and a router that are in the main wiring closet. You will subnet the 172.16.1.0/24 network to provide IPv4 addresses for two subnets that will support the required number of hosts. The larger subnet (LAN 1) requires 60 hosts and the smaller subnet (LAN 2) requires 20 hosts.
No subnet calculators may be used.
Part 1: Build the Network
a. Build the network according to the logical topology by placing the required equipment in the wiring closet equipment rack.
b. Cable the network devices in the closet as shown in the topology diagram.
c. Connect the hosts as shown in the topology diagram.
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
In this part of the assessment you will develop an IP addressing scheme. You will subnet an IPv4 network to create two subnets with the required number of hosts. You will also subnet an IPv6 network. You will then assign the addresses according to the requirements below.
Work with the following information:
- IPv4 Network: 172.16.1.0/24
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 1: 60
- Required number of hosts in IPv4 LAN 2: 20
a. Record your subnet assignments according to the following requirements.
1) Assign the first IPv4 address of each subnet to a router interface
- LAN 1 is hosted on R1 G0/0/1
- LAN 2 is hosted on R1 G0/0/0
2) Assign the last IPv4 address of each subnet to the PC NIC.
3) Assign the second IPv4 address of LAN 1 to S1 SVI.
Part 3: Configure Basic Device Settings
Network devices must be configured over a direct console connection.
Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
a. Disable DNS lookup on R1 and S1
b. Configure router hostname using the name R1.
c. Configure switch hostname using the name S1.
d. Configure an appropriate banner on R1 and S1.
e. Allow console logins with the password [email protected]!
Step 2: Configure Interfaces
a. Configure R1 G0/0/0 and G0/0/1 interfaces using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
b. Configure the S1 VLAN 1 SVI interface using the addressing from the previous part of this assessment:
- Interface description
- IPv4 address / subnet mask
- The switch should be reachable from devices on other networks.
Part 4: Configure Security Settings on R1 and S1
Step 1: Configure enhanced password security
a. Configure DontTellAnyone as the encrypted privileged EXEC password
b. Encrypt all plaintext passwords
c. Set minimum password length to 10 on R1.
Step 2: Configure SSH on R1 and S1
a. Configure netsec.com as the domain name
b. Configure a local user netadmin with the encrypted password Ci$co12345
c. Set login on vty lines to use local database.
d. Configure the vty lines to accept SSH access only.
e. Generate an RSA crypto key using 1024 bits modulus.
Step 3: Secure switch ports on S1
a. Shut down all unused ports on S1.
b. Enter descriptions for all unused switch ports to indicate that they are intentionally shutdown.
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
Configure both hosts with the IPv4 addresses that were assigned in Part 2 of this assessment.
ID: 101
Answers Key — 100% Score
Part 1: Build the Network
Placing Switch S1 and Router R1 to wiring closet equipment rack.
Using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect PC-A (FastEthernet0 port) and S1 (FastEthernet0/6 port)
Same as above, using Copper Straight-Through cable to connect all devices as shown in the topology diagram.

ITN Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA)
Turn-on PCs and Router R1
Part 2: Develop an IP Addressing Scheme
| Item | Requirements | IPv4 Address |
|---|---|---|
| Network Address | 172.16.1.0/24 | |
| LAN 1 subnet host requirements | 60 | 172.16.1.0/26 SM: 255.255.255.192 |
| LAN 2 subnet host requirements | 20 | 172.16.1.64/27 SM: 255.255.255.224 |
| R1 G0/0/1 | First host address in LAN 1 subnet | 172.16.1.1 |
| R1 G0/0/0 | First host address in LAN 2 subnet | 172.16.1.65 |
| S1 SVI | Second host address in LAN 1 subnet | 172.16.1.2 |
| PC-A | Last host address in LAN 1 subnet | 172.16.1.62 |
| PC-B | Last host address in LAN 2 subnet | 172.16.1.94 |
Using line console to connect PC-A and Router
Click to PC-A —> Terminal app —> click OK
Router R1 configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname R1
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface g0/0/0
description Connect to Subnet B
ip address 172.16.1.65 255.255.255.224
no shutdown
exit
interface g0/0/1
description Connect to Subnet A
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.192
no shutdown
exit
enable secret DontTellAnyone
service password-encryption
security passwords min-length 10
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
exit
copy running-config startup-config
Configuration for S1
Then, using Console cable to connect PC-B and Switch
To show Console port on Switch, Right click Switch —> Inspect Rear —> Console port
Switch S1 configuration script
enable
configure terminal
no ip domain-lookup
hostname S1
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
interface vlan 1
description Switch Subnet A
ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.192
no shutdown
exit
ip default-gateway 172.16.1.1
enable secret DontTellAnyone
service password-encryption
ip domain-name netsec.com
username netadmin secret Ci$co12345
line console 0
password [email protected]!
login
exit
line vty 0 15
transport input ssh
login local
exit
crypto key generate rsa
1024
int range f0/1 - 4, f0/7 - 24, g0/1 - 2
description Unused switch ports
shutdown
end
copy running-config startup-config
Part 5: Configure the Hosts and Verify Connectivity
On PCs, go to Desktop tab —> IP Configuration menu
| PC-A Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 172.16.1.62 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.192 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 172.16.1.1 |
| PC-B Network Configuration | |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | 172.16.1.94 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.224 |
| IPv4 Default Gateway | 172.16.1.65 |
Download PDF & Packet Tracer files:
[sociallocker id=»57850″]
[/sociallocker]
What two ICMPv6 message types must be permitted through IPV6 access control lists to allow resolution of layer 3 addresses to layer 2 MAC addresses?
Click the card to flip 👆
Students also viewed
Recent flashcard sets
Sets found in the same folder
Other sets by this creator
Verified questions
Other Quizlet sets
What two ICMPv6 message types must be permitted through IPV6 access control lists to allow resolution of layer 3 addresses to layer 2 MAC addresses?
Click the card to flip 👆
Students also viewed
Recent flashcard sets
Sets found in the same folder
Other sets by this creator
Verified questions
Other Quizlet sets
Время на прочтение
15 мин
Количество просмотров 43K
Приветствую, аудитория Хабра. За отсутствием комплексного материала по теме Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) , хочу поделиться опытом освоения профессии сетевого инженера. Если кому-то опыт окажется полезным, значит я старался не зря.
Цель статьи: актуализация информации по текущему треку CCNA 200-301, как подготовиться и на чем учиться, а так же подсказать вектор развития будущему инженеру и попробовать ответить на вопрос: Нужен ли тебе CCNA?
Статья будет активно обновляться. Проверяйте раздел Обновления.
Немного о том, кто я такой. Работаю сетевым инженером в государственной компании. Наша сеть построена на коммутаторах Cisco. Пришел на позицию младшего админа из инженера проектировщика. За четыре года поднабрался опыта и определился с вектором развития. Пройти именно CCNA меня побудило любопытство, отсутствие базового каркаса по сетевым технологиям и текущие рабочие задачи.
За время подготовки к экзамену у меня накопилась некоторая экспертиза, как сейчас модно говорить, посему, хочу поделиться ей с вами и разжечь потухшее пламя обозначенной темы.
Текст навеян мыслями «вдруг это еще кому-то пригодится и человеку не придется тратить кучу времени, чтобы собрать все кусочки информации в одно целое» ,а так же благодаря заметке Дмитрия Бубнова.
В чем отличия моего взгляда на тему:
-
Дмитрий уже имел опыт работы с сетями (5+ лет и являлся тренером Mikrotik)
-
Сдавал CCNA до обновления трека в 2020 г.
Я сетями увлекся не так давно (около года назад), поэтому статья может помочь тем, кто еще в самом начале пути и не успел понять за что хвататься и в каком порядке.
Оглавление
-
О чем
-
Как готовиться
-
Как учиться
-
-
Что учить
-
Англоязычные ресурсы
-
Русскоязычные ресурсы
-
Где брать материалы
-
Как попробовать экзамен
-
-
Как поднять лабораторию
-
Как сдаваться
-
После сертификации
-
Повторная сертификация
-
-
Реалии РФ
-
Итоги и размышления
-
Обновления
-
Благодарности
О чем
Историческая справка: Раньше CCNA делился на два трека, ICND1 и ICND2. Экзамен назывался: CCNA Routing&Switching 200-125. Не стану углубляться в старый экзамен, сразу перейдем в настоящее. В 2020 году Cisco выкатила глобальный апдейт экзаменационного трека, взяв основные темы из старого трека, кое-что выкинула, кое-что добавила и мы получили единый CCNA 200-301.
Прежде чем мы рассмотрим основные изменения, позволю себе еще одно лирическое отступление. Новый CCNA позиционируется как фундамент или ступенька, если хотите, с которой вы выйдите на Professional Level (CCNP etc.), имея представление о широком спектре концепций и технологий. Ниже таблица с официального сайта Cisco, иллюстрирующая все имеющиеся сертификации.
Лайфхак: Теперь не обязательно сдавать CCNA, чтобы сдать CCNP. Если чувствуете потребность прыгнуть сразу в CCNP, вы можете без проблем это сделать.
С лирикой точно закончили, теперь пройдемся по изменениям:
Экзамен Cisco 200-125 длился 90 минут и включал от 60 до 70 вопросов. Что касается Cisco 200-301, нам дают 150 минут (в них входит +30 мин. за неродной английский), чтобы осилить около 100 вопросов.
Форматы вопросов:
-
multiple-choice single answer – you need to choose only a single correct answer:
-
multiple-choice multiple answer – you need to choose multiple answers:
-
drag-and-drop – you need to drag and drop items to the proper categories:
Лабораторные сценарии из экзамена убрали. Максимум, с чем придется встретиться, это описание сценария + пример топологии, но это будет вопрос из разряда multiple-choice multiple/single answer.
Проходной балл составляет от 800 до 850 баллов из 1000.
Стоимость экзамена — 300$ (при переводе на текущий курс ~ 26тыс руб.)
Заметка: Подсчет баллов не так прост, каждый вопрос имеет разный вес, что, в конечном итоге, определяет процент, отведенный на каждый из них. Подвох в том, что вы никогда не узнаете сколько баллов приносит тот или иной вопрос. Поэтому готовиться надо ко всему и сразу.
Так же, с недавних пор, Cisco не показывает вам полученный балл, все, что вы увидите после завершения экзамена в графе «Grade», это: Pass/Fail.
Теперь к вопросам: перелопатили экзаменационные блоки, что было раньше:
-
15% Network Fundamentals
-
21% LAN Switching Technologies
-
23% Routing Technologies
-
10% WAN Technologies
-
10% Infrastructure Services
-
11% Infrastructure Security
-
10% Infrastructure Mgt
Как это выглядит сейчас:
-
20% Network Fundamentals
-
20% Network Access
-
25% IP Connectivity
-
10% IP Services
-
15% Security Fundamentals
-
10% Automation and Programmability
Добавленные темы
-
Основы работы с сетью — маршрутизаторы, кабели, коммутаторы IPv4 и IPv6, TCP и UDP
-
Подключение по IP — OSPFv2, IP-маршрутизация
-
IP-службы — SNMP, NTP, DHCP, QoS
-
Безопасность Основы — беспроводная безопасность, VPN, безопасность портов
-
Доступ к сети — сети VLAN, а также транкинг, EtherChannel
-
Автоматизация и программируемость — Chef, Puppet, REST API, JSON, SDN
Удаленные темы
-
Основы сети — модель OSI
-
Коммутация LAN — VTP, кадр, стек коммутатора
-
Маршрутизация — EIGRP, OSPFv3, RIPv2, маршрутизация между VLAN
-
WAN — PPP, PPPoE, MLPPP , GRE, BGP, доступ к WAN
Полный список тем можно посмотреть на оф. сайте Cisco, тут
Как готовиться
Тут все и просто и сложно одновременно. Я пошел простым путем и заплатил учебному центру за дипломную программу. Поступил я так из собственных соображений, а именно:
-
Пришел в IT из инженера проектировщика, хотелось иметь на руках некоторые бумажные «пруфы», что я перепрофилировался.
-
Было плохо с общим пониманием происходящего, нужна была структурированная подача материала.
-
Давали аккаунт в Netacad Cisco на все треки курса (их три части)
-
Ваучер на сдачу CCNA
Для начала, необходимо понять с чем предстоит столкнуться. Советую пройти вот этот короткий курс с канала NetSkills Курс молодого бойца. Окунуться сразу в практику. Каждое видео начинается с небольшой вводной теории, затем практическая лабораторная. Курс покрывает основные технологии, которые вы точно встретите в CCNA и в дальнейшей практике. Как дополнительный плюс, познакомитесь с IOS Cisco, посмотрите на разные типы устройств, как выглядит основной инструмент — симулятор Packet Tracer (PT).
Лайфхак: Packet Tracer бесплатен, предоставляется в рамках бесплатного курса (нужно предварительно пройти регистрацию аккаунта в netacad) https://www.netacad.com/courses/packet-tracer/introduction-packet-tracer
Я придерживался следующей стратегии при подготовке:
-
Учить английский в процессе, у меня он был весьма слаб, а экзамен полностью англоязычный.
-
Использовать несколько ресурсов для подготовки, чтобы перекрывать максимум деталей по темам.
-
Packet Tracer, в нем удобный модуль симуляции трафика и приличный набор симулированного функционала реальных железок (с недостатками, но несущественными на старте), начать можно с него, проще для освоения и понимания базовых вещей.
-
eve-ng/pnet эмулятор для создания более сложных топологий, на него можно пересесть когда поймете базу в PT + попробуете базово разобраться с linux.
-
Флеш-карточки Anki на разные темы экзамена. Помогает освежить в памяти более точную инфу, такую как «виртуальный MAC HSRP».
Как учиться
Перед тем как мы продолжим, хочу затронуть важную тему в самостоятельном обучении — подходы к обучению.
Вам придется сохранять мотивацию на протяжении всего времени (от 2 до 6 месяцев), которое уйдет на подготовку. Подключим к нашему обучению элемент планирования.
-
оцените сколько времени вы готовы потратить на подготовку
-
когда вы будете учиться
-
где вам комфортней учиться
-
что нужно для учебы/выполнения лабораторных. (Скачать Packet Tracer, подобрать литературу и т.п)
-
подумать о своих целях: зачем Вам это нужно и что это Вам даст. Это позволит не терять мотивацию по ходу подготовки
Обязательно попробуйте найти группы единомышленников, где люди проходят тот же путь. Так же есть группы, где вам, в свободное время, могут помочь действующие инструктора или люди, кто уже прошли этот путь. Готовиться в подходящем окружении поможет быстрее пройти сложные моменты и поддержать вашу мотивацию. Иначе это можно назвать активным обучением. Подробнее можно почитать тут. (Обратите внимание на блок-схему в конце)
Каждый человек учится по своему, вместо пассивного изучения материала, рекомендую попробовать делать заметки. Подробнее об этом можно почитать тут.
Если заметки не ваше, попробуйте делать короткие ревью в блоге, вести список задач (по типу ToDo), делать mindmap, если захотите совместить подходы, попробуйте Notion или, если важен момент self-hosted, Obsidian.
Я делал несколько постов в блоге на тему тайм-менеджмента и обучения: часть 1, часть 2, часть 3.
Правильного пути «как правильно учиться» нет, ищите тот вариант, который подходит именно вам.
Что учить
Тут хочу выделить две основные категории: русскоязычный контент и зарубежный.
Первый подойдет тем, кто еще не совсем подружился с английским языком, второй, соответственно, тем, кто уже понял, что информации на русском катастрофически мало.
Совет: Крайне рекомендую отринуть страх и сомнения на счет языкового барьера, даже если вы будете работать только на отечественном рынке, лучше не отказываться от идеи сделать английский язык своим другом.
Англоязычные ресурсы
Хорошим выбором может стать курс от Нила Андерсона, так же на Udemy
В статье Дмитрия есть ссылка на книгу от того же автора, где подробно описаны лабораторные, которые можно собрать в PT. Можно попробовать в связке с курсом.
Если в каких-то темах не хватит информации, можно обратиться за курсами к CBT Nuggets, много хвалебных отзывов. Я целиком не впитывал, оттуда знаю только Кейта Баркера, его youtube канал — кладезь информации. Интересная подача, квизы, лабораторные. Уже должно хватить с головой.
Если считаете, что все еще мало информации (в рамках CCNA само собой) то вам прямо в CCNA 200-301 Official Cert Guide, Volume 1/2 by Wendell Odom
Лайфхак: Если с английским, на текущий момент, плохо, можете брать Official Cert Guide предыдущей редакции (есть на русском) и читать их параллельно с новым. Различия есть, но основной текст идентичен в большинстве тем, не считая добавленных новых. Заодно поймете, почему готовиться только по переведенным книгам — плохо.
Если и там что-то осталось непонятно, то предпоследняя остановка перед страшными RFC — CCNA Certification Study Guide Volume 2 Exam 200 301 by Todd Lammle
Совет: RFC (Request for Comments) — ваш постоянный спутник в мире сетевых технологий. Советую начать к нему привыкать. RFC содержит технические спецификации и стандарты по различным технологиям широко применяемых в Интернете.
Выше я писал про flash карточки Anki, их можно найти на канале Jeremy подписавшись на рассылку. Карточки + лабораторные придут на почту. Так же можно обратиться к его видео по CCNA, сухие факты, минимум воды, в конце каждого видео закрепляющие вопросы. (курс в процессе написания)
Русскоязычные ресурсы
Проект Иннокентия Солнцева — NetworkEducation, о котором писал Дмитрий, все еще полезен и актуален. Материалы все так же предоставляются по месячной подписке. Однозначно стоят своих денег.
Лайфхак: Чат внизу страницы очень даже рабочий, вы можете задать вопрос (слишком уж простых задавать не стоит, много информации можно найти за пару минут в любом удобном поисковике) и вам обязательно ответят.
Сети для самых маленьких, куда ж без них. Лучший способ понять, как же все может строиться в реальном мире (или достаточно близко к нему). К ним подходите осторожно, сложность материала растет постепенно, но не заметите как уже зависли на задачках по OSPF от Наташи Самойленко 
Блог сетевика Андрея, неожиданная находка, помогло с освоением EVE-NG, советую изучить подробнее, есть не только выкладки по CCNA (пусть и старой редакции) но и по другим вещам. Большое спасибо, Андрей, за блог. Надеюсь, ты не забросишь свое дело.
Бонус: Отдельно хочу познакомить вас с циклом «Собес» от команды linkmeup, мне помогло прогнать несколько поведенческих страхов и понять концепцию собеседования с технической стороны.
Ну и ознакомьтесь с остальными подкастами. Много полезного и интересного.
Где брать материалы
Есть много вариантов, все перечислять, пожалуй, не этично. Самый простой — купить. Вариант попроще — пользоваться сообществами в Telegram. Можете сходить в библиотеку Дмитрия. Все необходимое для подготовки, можно найти в моей группе в телеграм, по хэштегу #ccna и #eve_ng.
Как попробовать экзамен
Элемент подготовки к экзаменационному окружению так же имеет некоторый вес, что греха таить, экзамен, который нас ждет, это тест. Если вы давно не сдавали подобного рода экзамены, то словите некоторый стресс, к этому нужно быть готовым. В наших силах несколько нивелировать этот элемент экзамена. Есть следующие варианты:
-
Тестовый экзамен Cisco, стоит 79$, посоветовать не могу, не пробовал проходить
-
Примеры тестов по экзаменационным вопросам на Udemy, один из примеров.
-
Поискать в интернете подборки вопросов и попробовать отвечать в рамках определенного таймера. (Подробнее ниже в цитате из комментариев)
-
И последний пункт, который я вам не рекомендую, но должен о нем упомянуть, чтобы предостеречь от возможных последствий. Так называемые «дампы», сборники вопросов с реального экзамена. За определенную цену вам скидывают банк вопросов с ответами.
Важно: Если, со стороны Cisco, вы будете уличены в использовании «дампов», ваш экзамен аннулируют и вы попадете в черный список, что закроет вам пути по сертификационным трекам Cisco насовсем.
Насильно никто вычислять не станет, конечно, таких, как вы, тысячи. Но если решились, то на свой страх и риск.
Со свой стороны добавлю, важно усвоить материал, а не просто получить лычку. Не создавайте проблем себе будущему. Ему не понравится, поверьте.
@zipo
Со своей стороны могу посоветовать достаточно хороший тестовый движек, для проверки своих знаний и «погружению» в атмосферу экзамена: https://loorex.com/Для него можно много разных тестов найти, профильных и не только, для 200-301 тоже находится: https://onlinetestcentre.com/200-301.html
Как поднять лабораторию
Заметка: Для сдачи CCNA вполне достаточно и Packet Tracer, лабораторные в VIRL/GNS3/EVE-NG etc, будут более актуальны в треке CCNP и выше. Поэтому данный раздел рекомендуется к ознакомлению только при наличии желания и времени.
Вопрос комплексный, есть несколько ресурсов, которые помогут это сделать from zero to hero, я использовал два: первый и второй. Даже при наличии более простого способа, о котором ниже, с первым ресурсом настоятельно рекомендую ознакомиться перед стартом, а второй использовать уже по ходу работы.
Со своей стороны хочу предложить вариант, как я уже сказал выше, попроще, который не потребует особого знания Linux на старте и позволит вам сразу начать строить вещи посложнее, чем в PT.
Речь пойдет о PnetLab, собранном на основе eve-ng. Инструкцию и образ забираем тут
Материалы по подготовке лабораторного стена выложил в своем небольшом канале в Телеграм, искать по хэштеку #ccna.
Коротко, что такое PNETLab (Packet Network Emulator Tool Lab) — платформа, позволяющая загружать и делиться лабораториями с сообществом. Включает в себя PNETLab Box и PNETLab Store.
-
PNETLab Box (с двумя режимами: Offline и Online) — виртуальная машина в которой мы строим и используем свои топологии, храним лабы и образы.
-
PNETLab Store — это веб-платформа с сотнями бесплатных лабораторий по сетям, базам данных и т.п. Все, что вам нужно сделать, это загрузить лабораторную и посмотреть образы, которые в ней используются.
После установки, открываем лабу и работаем, ничего дополнительно делать не нужно, в большинстве случаем, все работает «из коробки».
Лайфхак: Отдельно хочу отметить темы экзамена, связанные с DNA центром. По ссылке ниже вы найдете полностью функциональную лабораторную, можно воочию посмотреть, что такое DNA от Cisco.
DNA Center Always On Lab
https://sandboxdnac.cisco.com/
Username: devnetuser
Password: Cisco123!
Как сдаваться
Экзамен сдается в авторизованных центрах Pearson VUE. Они есть в каждом крупном городе. В условиях COVID-19 активно продвигается возможность сдать дома или в офисе. Нужна веб-камера, подготовленный компьютер и помещение, а так же, вам будет предоставлен специальный человек — проктор. Он будет с вами на протяжении всего экзамена.
Вне зависимости от выбранного способа, оформляетесь на сайте Pearson VUE, экзамен оплачиваете и применяете ваучер (если есть) там же. Место, где сдается экзамен, не должно с вас брать ни копейки.
Пара слов о регистрации на Pearson VUE, она там не совсем очевидна.
Создаем аккаунт на Pearson VUE
Заходит на сайт по ссылке выше и в указанном поле ищем Cisco Systems
Далее, Create account
Соглашаемся с политикой конфиденциальности и попадаем в следующее окно, далее следует пояснить пару важных моментов:
-
Пункты 1, 3, 5 можно не заполнять
-
Важно заполнить пункт 2 и 4 в точности как в вашем втором документе, который планируете брать (подробнее об этом ниже)
-
Пункт 6 просто указываете и подтверждаете свою почту. Небольшое НО для тех, у кого будет в наличии ваучер со скидкой. В пункт 6 вы должны указать ту почту, на которую привязан аккаунт Cisco с ваучером.
Дальше не должно быть каких-то нюансов, просто завершаем процедуру регистрации.
Регистрируемся на экзамен
Все в том же окне, где создавали аккаунт, теперь нажимаем Sign in и заходим в, созданный выше, аккаунт.
Попадаем в Dashboard, выбираем View exams
Выбираем Proctored Exams -> CCNA -> 200-301
Далее процедура простая, выбираем где сдавать (в центре или дома/офисе), выбираем ближайший центр (в моем случае), выбираем день и время экзамена, не забываем применить ваучер (если есть) и оплачиваем. Там же попутно можно почитать, что можно брать с собой на экзамен, если у вас есть что-то по здоровью (например очки или ингалятор).
Пара слов о документах, в авторизованном центре с вас потребуют два документа, удостоверяющих личность. Паспорт РФ и водительские права — самый распространенный вариант. Можно использовать загран. паспорт, главное, чтобы на втором документе было продублировано ваше ФИО на английском языке.
Экзамен я сдал, поэтому могу поделиться парой советов, который помогли мне, чтобы все прошло максимально спокойно.
-
В день перед экзаменом постарайтесь себя вообще ничем не грузить. (я после работы сел проходить ремастер Medievil, расслабляет)
-
Обязательно выспитесь, 7-ми часового сна должно хватить.
-
Далее зависит от того, на какое время у вас экзамен, я сдавал утром, поэтому хороший завтрак перед 2-х часовым экзаменом — хорошее решение.
-
Берите с собой по минимуму личных вещей, рюкзак может не влезть в ячейку для личных вещей.
-
Приезжайте не за 15 минут, а хотя бы за 30, этого с головой достаточно, чтобы найти нужный этаж, кабинет и пройти формальности.
-
Туалет. Тут все понятно, сидеть 2.5 часа, лучше этот вопрос сразу закрыть.
-
Вам дадут черновик, советую сразу сделать шаблон по двоичной системе и маскам подсети. Для понимания, рекомендую ознакомиться с этим плейлистом.
-
В экзамене нет возможности вернуться к предыдущим вопросам, поэтому внимательно читайте вопрос и все варианты ответов.
-
Времени много, на все вопросы точно хватит, используете его правильно, у вас оно будет перед глазами. (я сдал ~1ч 30мин)
-
И самое банальное, не нервничайте, важно, какие навыки вы приобрели за время подготовки, сертификат это всего лишь электронная бумажка.
После сертификации
После того как Вы сдали экзамен и получили распечатку с процентами по блокам от экзаменатора, можно попробовать угадать, где Вы были не так сильны. После этого останется решить еще один вопрос — где взять сам сертификат?
Вообще, Cisco дает всю информацию о том, что делать после сдачи. (где регистрироваться, как проверить сертификат, как получить pdf сертификата и т.д), но если вдруг потерялись, то Вам пригодится эта справка с сайта Cisco.
Там ничего сложного, в течении 24 часов Вам на почту (которую указывали при регистрации на экзамен) придет инструкция как зарегистрироваться на CiscoMetrics. Там вы найдете свой сертификат (Cisco просит еще несколько дней, чтобы закончить все формальности, сразу его может там не оказаться, не пугайтесь).
Проверить сертификат можно по ссылке, она ведет на оф. сайт Cisco с формой верификации.
Повторная сертификация
Сертификаты Cisco имеют срок годности. Для CCNA/CCNP — 3 года. Для повторной сертификации необходимо сдать один из следующих экзаменов до истечения срока действия сертификата:
-
повторный экзамен CCNA
-
любой один экзамен Professional
-
один из линейки Core экзаменов по технологиям
-
один лабораторный экзамен CCIE
-
также можно пройти ресертификацию, заработав 30 кредитов CE (Continuing Education). Вы можете получать кредиты CE, посещая учебные сессии Cisco Live или проходя онлайн-курсы.
Реалии РФ
Что касается отечественного рынка, со стороны государственных структур уже не только прослеживаются тревожные звоночки по импортозамещению но и предпринимаются активные действия.
Что имею на это сказать. Основным регулятором у нас выступает ФСТЭК, на их сайте есть список оборудования, которое получило сертификат соответствия. Cisco там еще присутствует. Линейка коммутаторов 9300 туда тоже попала. Государственным компаниям рекомендуется ориентироваться на данный список при планировании закупок. С коммерческими структурами все проще, на сколько мне известно. О чем это нам говорит как специалистам? Тут я нагло использую цитату из комментариев:
vvpoloskin
Тут много факторов. Раньше сертификация на ту же циску требовалась рынку. Сейчас требования по импортозамещению, регулирование безопасности (та же сертифицированная криптография и файрволлы) и санкционное давление убирают ее оборудование из российского энтерпрайза, а «долларовые» цены убирают из операторов. Раньше было множество интеграторов, которым нужны были сертифицированные кадры для приобретения партнёрских статусов для продажи оборудования, сейчас их скупили и объединили в рамках крупных закупочных альянсов. Опять же раньше был бум автоматизации, множество организаций подключали компьютеры и телефоны к сети, для этого требовались поставки огромного количества коммутаторов, VoIP телефонов и другого сетевого оборудования. Нужны были люди, которые могут это продавать и обслуживать. Сейчас же оборудование есть у всех.
Не всегда будет так, что вы придете в компанию и там вас будет ждать Cisco инфраструктура. Важно после CCNA попробовать поработать и с другими вендорами. Развернуть RouterOS например, от mikrotik или на том же сайте Network Education посмотреть ознакомительный курс по Juniper.
Другие вендоры так же имеют свои сертификации и материалы для подготовки. На хабре точно найдется пара тройка статей на эти темы.
Итоги и размышления
Важно понимать, привязка к конкретному вендору на ранних этапах вашего развития — не лучший путь, если хотите стать востребованным специалистом в будущем. Важно разобраться в технологиях. CCNA был для меня хорош тем, что Cisco, хоть и делает упор на свои протоколы, но так же подробно рассказывает про аналогичные, на базе открытых стандартов.
Karroplan
Но не забывайте, что ccna это только первая ступенька и лестница растет не только вверх, но и в стороны (в смысле, стоит и смежные темы изучать — сторейдж, виртуализацию, операционки, автоматизацию, программирование).
Что касается изучения темы в горизонтальной плоскости. Тут три основных момента с которых можно начать
-
Освоить linux, сетевику без него никак. Хороший канал от автора книги Внутренне устройство Linux, Дмитрия Кетова, и плейлист по подготовке к сертификации Red Hat RHCSA, так же много моментов объясняется достаточно подробно и последовательно.
-
Виртуализация. Virtual BOX, VMWare Player, Hyper V — это то, что можно потрогать бесплатно.
-
Программирование и автоматизация. Это то, чем сейчас живет мир сетевых технологий. В CCNA затрагивается данная тема, советую ее не обходить, а попробовать погрузиться чуть глубже, чем это есть на уровне CCNA.
В дополнение приведу статью на хабре, которая, возможно, уже начинает потихоньку устаревать, но там достаточно подробно расписаны пункты по всестороннему развитию сетевого инженера. Рекомендую ознакомиться.
Отвечая на поставленный в начале вопрос, нет, не каждому нужно сдавать CCNA. Можно расти и развиваться вне рамок сертификаций. Как верно написал в своей заметке Дмитрий, если вы не хотите все это сдавать, просто прочитайте книжки и поделайте лабораторные + сети для самых маленьких. Если вы встали на путь сетевика, это даст вам первоначальный запал.
Сертификация, на мой взгляд, дело личного вызова. Увы, в современных реалиях сертификатом CCNA вы не сможете впечатлить работодателя. Главная идея — получить от этого процесса максимум. Все остальное, это опыт и практика. И точно не стоит останавливаться на темах, представленных в CCNA.
Успехов в подготовке и на экзамене! Дорогу осилит идущий.
Обновления
upd1: Причесал текст, добавил информацию по баллам и типам вопросов. Добавил ссылку на получение Packet Tracer, добавил раздел Реалии РФ, добавил бонус-ссылку на цикл подкастов «Собес»
upd2: Спасибо vvpoloskin за наводку на тему импортозамещения и использования Cisco в РФ
upd3: Спасибо Karroplan за совет раскрыть тему становления сетевого инженера не только в рамках CCNA.
upd4: Добавил таблицу по сертификациям с пояснениями
upd5: Добавил подраздел Как поднять лабораторию
upd6: Сдал CCNA, дополнил раздел Как сдаваться и добавил раздел Повторная сертификация»
upd7: Добавил в раздел Как поднять лабораторию информацию по материалам для подготовки лабораторного стенда. Добавил оглавление в начале статьи с «кликабельными» заголовками
upd8: Добавил подраздел Как учиться, идею подсмотрел на курсе Наташи Самойленко, вспомнил, как это помогло мне. Так же добавил подраздел Как попробовать экзамен, спасибо за наводку @zipo
upd9: Добавил ссылки на посты в блоге про тайм-менеджмент, поправил ссылку на материалы.
upd10: Добавил мини-раздел После сертификации, где искать сертификат после сдачи
Благодарности
Сказать «спасибы» я обязан следующим людям, значительно повлиявшим на мое восприятие профессии сетевика и всего, что с ней связано.
Иннокентий, если Вы это прочитали, спасибо Вам большое за труды. Лучшие материалы в .ру сегменте.
Марат aka @eucariot, не хочется повторяться за Дмитрием, но аналогично, лови мои восхищения за вклад становления сетевиков. Ждем еще линкмитапов в Москве!
Всей команде подкастов linkmeup.ru за мотивацию в трудные минуты.
Огромные спасибы любимой девушке, за терпение и поддержку. Тебе еще со мной CCNP проходить 
И, конечно, спасибы начальнику моего отдела, за поддержку в начинаниях и помощи в понимании технологий.