How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
Introduction to Networks ( Version 7.00) – Modules 11 – 13: IP Addressing Exam
1. What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
- /25
- /26
- /27
- /28
Explanation: The binary format for 255.255.255.224 is 11111111.11111111.11111111.11100000. The prefix length is the number of consecutive 1s in the subnet mask. Therefore, the prefix length is /27.
2. How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
- 254
- 190
- 192
- 62
- 64
3. Which subnet mask would be used if 5 host bits are available?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
4. A network administrator subnets the 192.168.10.0/24 network into subnets with /26 masks. How many equal-sized subnets are created?
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 64
5. Match the subnetwork to a host address that would be included within the subnetwork. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: Subnet 192.168.1.32/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.33 – 192.168.1.62 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.63
Subnet 192.168.1.64/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.65 – 192.168.1.94 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.95
Subnet 192.168.1.96/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.97 – 192.168.1.126 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.127
6. An administrator wants to create four subnetworks from the network address 192.168.1.0/24. What is the network address and subnet mask of the second useable subnet?
- subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.32
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.128
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.8
subnet mask 255.255.255.224
Explanation: The number of bits that are borrowed would be two, thus giving a total of 4 useable subnets:
192.168.1.0
192.168.1.64
192.168.1.128
192.168.1.192
Because 2 bits are borrowed, the new subnet mask would be /26 or 255.255.255.192
7. How many bits must be borrowed from the host portion of an address to accommodate a router with five connected networks?
- two
- three
- four
- five
Explanation: Each network that is directly connected to an interface on a router requires its own subnet. The formula 2n, where n is the number of bits borrowed, is used to calculate the available number of subnets when borrowing a specific number of bits.
8. How many host addresses are available on the 192.168.10.128/26 network?
- 30
- 32
- 60
- 62
- 64
Explanation: A /26 prefix gives 6 host bits, which provides a total of 64 addresses, because 26 = 64. Subtracting the network and broadcast addresses leaves 62 usable host addresses.
9. How many host addresses are available on the network 172.16.128.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.252.0?
- 510
- 512
- 1022
- 1024
- 2046
- 2048
Explanation: A mask of 255.255.252.0 is equal to a prefix of /22. A /22 prefix provides 22 bits for the network portion and leaves 10 bits for the host portion. The 10 bits in the host portion will provide 1022 usable IP addresses (210 – 2 = 1022).
10. Match each IPv4 address to the appropriate address category. (Not all options are used.)
11. What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 100.64.0.0/14
- 169.254.0.0/16
- 239.0.0.0/8
Explanation: RFC 1918, Address Allocation for Private Internets, defines three blocks of IPv4 address for private networks that should not be routable on the public Internet.
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
12. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator must send a message to everyone on the router A network. What is the broadcast address for network 172.16.16.0/22?
- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
Explanation: The 172.16.16.0/22 network has 22 bits in the network portion and 10 bits in the host portion. Converting the network address to binary yields a subnet mask of 255.255.252.0. The range of addresses in this network will end with the last address available before 172.16.20.0. Valid host addresses for this network range from 172.16.16.1-172.16.19.254, making 172.16.19.255 the broadcast address.
13. A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
Explanation: The subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 has 8 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.128 results in 7 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.224 has 5 host bits. Finally, 255.255.255.240 represents 4 host bits.
14. Refer to the exhibit. Considering the addresses already used and having to remain within the 10.16.10.0/24 network range, which subnet address could be assigned to the network containing 25 hosts?
- 10.16.10.160/26
- 10.16.10.128/28
- 10.16.10.64/27
- 10.16.10.224/26
- 10.16.10.240/27
- 10.16.10.240/28
Explanation: Addresses 10.16.10.0 through 10.16.10.63 are taken for the leftmost network. Addresses 10.16.10.192 through 10.16.10.207 are used by the center network.The address space from 208-255 assumes a /28 mask, which does not allow enough host bits to accommodate 25 host addresses.The address ranges that are available include 10.16.10.64/26 and10.16.10.128/26. To accommodate 25 hosts, 5 host bits are needed, so a /27 mask is necessary. Four possible /27 subnets could be created from the available addresses between 10.16.10.64 and 10.16.10.191:
10.16.10.64/27
10.16.10.96/27
10.16.10.128/27
10.16.10.160/27
15. What is the usable number of host IP addresses on a network that has a /26 mask?
- 256
- 254
- 64
- 62
- 32
- 16
Explanation: A /26 mask is the same as 255.255.255.192. The mask leaves 6 host bits. With 6 host bits, 64 IP addresses are possible. One address represents the subnet number and one address represents the broadcast address, which means that 62 addresses can then be used to assign to network devices.
16. Which address prefix range is reserved for IPv4 multicast?
- 240.0.0.0 – 254.255.255.255
- 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
- 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255
- 127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
Explanation: Multicast IPv4 addresses use the reserved class D address range of 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255.
17. Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network.
Explanation: Network A needs to use 192.168.0.128 /25, which yields 128 host addresses.
Network B needs to use 192.168.0.0 /26, which yields 64 host addresses.
Network C needs to use 192.168.0.96 /27, which yields 32 host addresses.
Network D needs to use 192.168.0.80/30, which yields 4 host addresses.
18. A high school in New York (school A) is using videoconferencing technology to establish student interactions with another high school (school B) in Russia. The videoconferencing is conducted between two end devices through the Internet. The network administrator of school A configures the end device with the IP address 209.165.201.10. The administrator sends a request for the IP address for the end device in school B and the response is 192.168.25.10. Neither school is using a VPN. The administrator knows immediately that this IP will not work. Why?
- This is a loopback address.
- This is a link-local address.
- This is a private IP address.
- There is an IP address conflict.
19. Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117
- 172.31.1.25
- 64.104.78.227
Explanation: The ranges of private IPv4 addresses are as folllows:
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
20. A message is sent to all hosts on a remote network. Which type of message is it?
- limited broadcast
- multicast
- directed broadcast
- unicast
Explanation: A directed broadcast is a message sent to all hosts on a specific network. It is useful for sending a broadcast to all hosts on a nonlocal network. A multicast message is a message sent to a selected group of hosts that are part of a subscribing multicast group. A limited broadcast is used for a communication that is limited to the hosts on the local network. A unicast message is a message sent from one host to another.
21. A company has a network address of 192.168.1.64 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192. The company wants to create two subnetworks that would contain 10 hosts and 18 hosts respectively. Which two networks would achieve that? (Choose two.)
- 192.168.1.16/28
- 192.168.1.64/27
- 192.168.1.128/27
- 192.168.1.96/28
- 192.168.1.192/28
Explanation: Subnet 192.168.1.64 /27 has 5 bits that are allocated for host addresses and therefore will be able to support 32 addresses, but only 30 valid host IP addresses. Subnet 192.168.1.96/28 has 4 bits for host addresses and will be able to support 16 addresses, but only 14 valid host IP addresses.
22. Which address is a valid IPv6 link-local unicast address?
- FEC8:1::FFFF
- FD80::1:1234
- FE80::1:4545:6578:ABC1
- FE0A::100:7788:998F
- FC90:5678:4251:FFFF
Explanation: IPv6 LLAs are in the fe80::/10 range. The /10 indicates that the first 10 bits are 1111 1110 10xx xxxx. The first hextet has a range of 1111 1110 1000 0000 (fe80) to 1111 1110 1011 1111 (febf).
23. Which of these addresses is the shortest abbreviation for the IP address: 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB:0000:0000:0057?
- 3FFE:1044::AB::57
- 3FFE:1044::00AB::0057
- 3FFE:1044:0:0:AB::57
- 3FFE:1044:0:0:00AB::0057
- 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::57
- 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::0057
Explanation: The rules for reducing the notation of IPv6 addresses are:
1. Omit any leading 0s (zeros) in any hextet.
2. Replace any single, contiguous string of one or more 16-bit hextets consisting of all zeros with a double colon (::) .
3. The double colon (::) can only be used once within an address.
24. A network administrator has received the IPv6 prefix 2001:DB8::/48 for subnetting. Assuming the administrator does not subnet into the interface ID portion of the address space, how many subnets can the administrator create from the /48 prefix?
- 16
- 256
- 4096
- 65536
Explanation: With a network prefix of 48, there will be 16 bits available for subnetting because the interface ID starts at bit 64. Sixteen bits will yield 65536 subnets.
25. Given IPv6 address prefix 2001:db8::/48, what will be the last subnet that is created if the subnet prefix is changed to /52?
- 2001:db8:0:f00::/52
- 2001:db8:0:8000::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f000::/52
Explanation: Prefix 2001:db8::/48 has 48 network bits. If we subnet to a /52, we are moving the network boundary four bits to the right and creating 16 subnets. The first subnet is 2001:db8::/52 the last subnet is 2001:db8:0:f000::/52.
26. Consider the following range of addresses:
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000::
…
2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::
The prefix-length for the range of addresses is /60 .
Explanation: All the addresses have the part 2001:0DB8:BC15:00A in common. Each number or letter in the address represents 4 bits, so the prefix-length is /60.
27. What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local
- multicast
- global unicast
Explanation: Link-local IPv6 addresses start with FE80::/10, which is any address from FE80:: to FEBF::. Link-local addresses are used extensively in IPv6 and allow directly connected devices to communicate with each other on the link they share.
28. Refer to the exhibit. A company is deploying an IPv6 addressing scheme for its network. The company design document indicates that the subnet portion of the IPv6 addresses is used for the new hierarchical network design, with the site subsection to represent multiple geographical sites of the company, the sub-site section to represent multiple campuses at each site, and the subnet section to indicate each network segment separated by routers. With such a scheme, what is the maximum number of subnets achieved per sub-site?
Refer to the exhibit. A company is deploying an IPv6 addressing scheme for its network. The company design document indicates that the subnet portion of the IPv6 addresses is used for the new hierarchical network design, with the s ite subsection to represent multiple geographical sites of the company, the s ub-site section to represent multiple campuses at each site, and the s ubnet section to indicate each network segment separated by routers. With such a scheme, what is the maximum number of subnets achieved per sub-site ?
- 0
- 4
- 16
- 256
Explanation: Because only one hexadecimal character is used to represent the subnet, that one character can represent 16 different values 0 through F.
29. What is used in the EUI-64 process to create an IPv6 interface ID on an IPv6 enabled interface?
- the MAC address of the IPv6 enabled interface
- a randomly generated 64-bit hexadecimal address
- an IPv6 address that is provided by a DHCPv6 server
- an IPv4 address that is configured on the interface
Explanation: The EUI-64 process uses the MAC address of an interface to construct an interface ID (IID). Because the MAC address is only 48 bits in length, 16 additional bits (FF:FE) must be added to the MAC address to create the full 64-bit interface ID.
30. What is the prefix for the host address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
- 2001:DB8:BC15
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12
Explanation: The network portion, or prefix, of an IPv6 address is identified through the prefix length. A /64 prefix length indicates that the first 64 bits of the IPv6 address is the network portion. Hence the prefix is 2001:DB8:BC15:A.
31. An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::1. What is the target of this packet?
- the one IPv6 device on the link that has been uniquely configured with this address
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link or network
- only IPv6 DHCP servers
- only IPv6 configured routers
Explanation: This address is one of the assigned IPv6 multicast addresses. Packets addressed to FF02::1 are for all IPv6 enabled devices on the link or network. FF02::2 is for all IPv6 routers that exist on the network.
32. Match the IPv6 address with the IPv6 address type. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: FF02::1:FFAE:F85F is a solicited node multicast address.
2001:DB8::BAF:3F57:FE94 is a global unicast address.
FF02::1 is the all node multicast address. Packets sent to this address will be received by all IPv6 hosts on the local link.
::1 is the IPv6 loopback address.
There are no examples of link local or unique local addresses provided.
33. Which IPv6 prefix is reserved for communication between devices on the same link?
- FC00::/7
- 2001::/32
- FE80::/10
- FDFF::/7
Explanation: IPv6 link-local unicast addresses are in the FE80::/10 prefix range and are not routable. They are used only for communications between devices on the same link.
34. Which type of IPv6 address refers to any unicast address that is assigned to multiple hosts?
- unique local
- global unicast
- link-local
- anycast
Explanation: The IPv6 specifications include anycast addresses. An anycast address is any unicast IPv6 address that is assigned to multiple devices.
35. What are two types of IPv6 unicast addresses? (Choose two.)
- multicast
- loopback
- link-local
- anycast
- broadcast
Explanation: Multicast, anycast, and unicast are types of IPv6 addresses. There is no broadcast address in IPv6. Loopback and link-local are specific types of unicast addresses.
36. Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
Explanation: Using stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC), a PC can solicit a router and receive the prefix length of the network. From this information the PC can then create its own IPv6 global unicast address.
37. Which protocol supports Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) for dynamic assignment of IPv6 addresses to a host?
- ARPv6
- DHCPv6
- ICMPv6
- UDP
Explanation: SLAAC uses ICMPv6 messages when dynamically assigning an IPv6 address to a host. DHCPv6 is an alternate method of assigning an IPv6 addresses to a host. ARPv6 does not exist. Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) provides the functionality of ARP for IPv6 networks. UDP is the transport layer protocol used by DHCPv6.
38. Three methods allow IPv6 and IPv4 to co-exist. Match each method with its description. (Not all options are used.)
39. A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?
- the TCP/IP stack on a network host
- connectivity between two adjacent Cisco devices
- connectivity between a PC and the default gateway
- connectivity between two PCs on the same network
- physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network
40. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to troubleshoot connectivity between PC1 and PC2 and uses the tracert command from PC1 to do it. Based on the displayed output, where should the administrator begin troubleshooting?
- PC2
- R1
- SW2
- R2
- SW1
41. Which protocol is used by the traceroute command to send and receive echo-requests and echo-replies?
- SNMP
- ICMP
- Telnet
- TCP
Explanation: Traceroute uses the ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to send and receive echo-request and echo-reply messages.
42. Which ICMPv6 message is sent when the IPv6 hop limit field of a packet is decremented to zero and the packet cannot be forwarded?
- network unreachable
- time exceeded
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
Explanation: ICMPv6 uses the hop limit field in the IPv6 packet header to determine if the packet has expired. If the hop limit field has reached zero, a router will send a time exceeded message back towards the source indicating that the router cannot forward the packet.
43. A user executes a traceroute over IPv6. At what point would a router in the path to the destination device drop the packet?
- when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches 255
- when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches zero
- when the router receives an ICMP time exceeded message
- when the target host responds with an ICMP echo reply message
Explanation: When a traceroute is performed, the value in the Hop Limit field of an IPv6 packet determines how many router hops the packet can travel. Once the Hop Limit field reaches a value of zero, it can no longer be forwarded and the receiving router will drop the packet.
44. What is the purpose of ICMP messages?
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
Explanation: The purpose of ICMP messages is to provide feedback about issues that are related to the processing of IP packets.
45. What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
Explanation: When sending an echo request message, a router will use the IP address of the exit interface as the source IP address. This default behavior can be changed by using an extended ping and specifying a specific source IP address.
46. Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: Link-Local addresses are assigned automatically by the OS environment and are located in the block 169.254.0.0/16. The private addresses ranges are 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, and 192.168.0.0/16. TEST-NET addresses belong to the range 192.0.2.0/24. The addresses in the block 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.254 are reserved as experimental addresses. Loopback addresses belong to the block 127.0.0.0/8.
47. A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1. What does this code represent?
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- network unreachable
48. Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
Explanation: For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
49. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
CCNA 1 v7 Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers Full
What are the three IPv6 addresses displayed when the route from PC1 to PC2 is traced? (Choose three.)
- 2001:DB8:1:1::1
- 2001:DB8:1:1::A
- 2001:DB8:1:2::2
- 2001:DB8:1:2::1
- 2001:DB8:1:3::1
- 2001:DB8:1:3::2
- 2001:DB8:1:4::1
Explanation: Using the ipv6config command on PC2 displays the IPv6 address of PC2, which is 2001:DB8:1:4::A. The IPV6 link-local address, FE80::260:70FF:FE34:6930, is not used in route tracing. Using the tracert 2001:DB8:1:4::A command on PC1 displays four addresses: 2001:DB8:1:1::1, 2001:DB8:1:2::1 , 2001:DB8:1:3::2, and 2001:DB8:1:4::A.
50. A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- all hosts in the same subnet
- a specially defined group of hosts
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- all hosts on the Internet
Explanation: A broadcast is delivered to every host that has an IP address within the same network.
51. A host is transmitting a unicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- one specific host
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts on the Internet
- the closest neighbor on the same network
52. A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 3. What does this code represent?
- address unreachable
- network unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
53. A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- one specific host
- directly connected network devices
60. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db80:::1::80:1
61. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9:20::b000:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
62. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909?
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 200:420:110:c4b::910:0:90
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
63. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0ab8:0001:0000:1000?
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
64. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0420:00c4:1008:0025:0190:0000:0990?
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
65. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
66. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:0000:0000:0000:0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029?
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
67. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
68. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909?
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
69. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80::0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029
70. A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 2 . What does this code represent?
- beyond scope of the source address
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- address unreachable
- no route to destination
71. A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1 . What does this code represent?
- host unreachable
- beyond scope of the source address
- address unreachable
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
72. A user issues a ping fe80:65ab:dcc1::100 command and receives a response that includes a code of 3. What does this code represent?
- address unreachable
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- beyond scope of the source address
- no route to destination
73. A user issues a ping 10.10.14.67 command and receives a response that includes a code of 0 . What does this code represent?
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
74. A user issues a ping fe80:65ab:dcc1::100 command and receives a response that includes a code of 4. What does this code represent?
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
75. A user issues a ping 198.133.219.8 command and receives a response that includes a code of 0 . What does this code represent?
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
76. A user issues a ping 2001:db8:3040:114::88 command and receives a response that includes a code of 4 . What does this code represent?
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
77. A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 2. What does this code represent?
- beyond scope of the source address
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
Last Updated on February 1, 2021 by
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13: IP Addressing Exam Answers 2020 Correct 100%
Cisco Netacad ITN Version 7.00 CCNA 1 v7 Modules 11 – 13: IP Addressing Exam Answers 2020 2021 – Introduction to Networks
-
Match the subnetwork to a host address that would be included within the subnetwork. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 001
Answers Explanation & Hints:Subnet 192.168.1.32/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.33 – 192.168.1.62 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.63
Subnet 192.168.1.64/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.65 – 192.168.1.94 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.95
Subnet 192.168.1.96/27 will have a valid host range from 192.168.1.97 – 192.168.1.126 with the broadcast address as 192.168.1.127 -
An administrator wants to create four subnetworks from the network address 192.168.1.0/24. What is the network address and subnet mask of the second useable subnet?
- subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.32
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.128
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.8
subnet mask 255.255.255.224Answers Explanation & Hints:The number of bits that are borrowed would be two, thus giving a total of 4 useable subnets:
192.168.1.0
192.168.1.64
192.168.1.128
192.168.1.192
Because 2 bits are borrowed, the new subnet mask would be /26 or 255.255.255.192
- subnetwork 192.168.1.64
-
How many bits must be borrowed from the host portion of an address to accommodate a router with five connected networks?
- two
- three
- four
- five
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Each network that is directly connected to an interface on a router requires its own subnet. The formula 2 n , where n is the number of bits borrowed, is used to calculate the available number of subnets when borrowing a specific number of bits.
-
How many host addresses are available on the 192.168.10.128/26 network?
- 30
- 32
- 60
- 62
- 64
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A /26 prefix gives 6 host bits, which provides a total of 64 addresses, because 2 6 = 64. Subtracting the network and broadcast addresses leaves 62 usable host addresses.
-
How many host addresses are available on the network 172.16.128.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.252.0?
- 510
- 512
- 1022
- 1024
- 2046
- 2048
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A mask of 255.255.252.0 is equal to a prefix of /22. A /22 prefix provides 22 bits for the network portion and leaves 10 bits for the host portion. The 10 bits in the host portion will provide 1022 usable IP addresses (2 10 – 2 = 1022).
-
Match each IPv4 address to the appropriate address category. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 002
Answers Explanation & Hints:To determine whether a given IPv4 address is a network, host, or broadcast address, first determine the address space based on the subnet mask. Convert the address and mask to binary values, then perform the ANDing function to determine the network address. To calculate the of the address space, use the number of host bits in the subnet mask as an exponent of 2. The number of valid host addresses in the space is that number minus 2. The network address will have all zeroes in the host portion, and the broadcast address will have all ones. For example, 10.0.50.10/30 yields a network IP address of 10.0.50.8 when the mask is ANDed with the given address. Because there are only 2 host bits in the mask, there are only 2 valid host addresses (4-2). 10.0.50.10 is one of the two valid host IP addresses.
-
What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 100.64.0.0/14
- 169.254.0.0/16
- 239.0.0.0/8
Answers Explanation & Hints:
RFC 1918, Address Allocation for Private Internets, defines three blocks of IPv4 address for private networks that should not be routable on the public Internet.10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0/12
192.168.0.0/16
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator must send a message to everyone on the router A network. What is the broadcast address for network 172.16.16.0/22?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 03
- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The 172.16.16.0/22 network has 22 bits in the network portion and 10 bits in the host portion. Converting the network address to binary yields a subnet mask of 255.255.252.0. The range of addresses in this network will end with the last address available before 172.16.20.0. Valid host addresses for this network range from 172.16.16.1-172.16.19.254, making 172.16.19.255 the broadcast address.
-
A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 has 8 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.128 results in 7 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.224 has 5 host bits. Finally, 255.255.255.240 represents 4 host bits.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Considering the addresses already used and having to remain within the 10.16.10.0/24 network range, which subnet address could be assigned to the network containing 25 hosts?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 04
- 10.16.10.160/26
- 10.16.10.128/28
- 10.16.10.64/27
- 10.16.10.224/26
- 10.16.10.240/27
- 10.16.10.240/28
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Addresses 10.16.10.0 through 10.16.10.63 are taken for the leftmost network. Addresses 10.16.10.192 through 10.16.10.207 are used by the center network.The address space from 208-255 assumes a /28 mask, which does not allow enough host bits to accommodate 25 host addresses.The address ranges that are available include 10.16.10.64/26 and10.16.10.128/26. To accommodate 25 hosts, 5 host bits are needed, so a /27 mask is necessary. Four possible /27 subnets could be created from the available addresses between 10.16.10.64 and 10.16.10.191:
10.16.10.64/27
10.16.10.96/27
10.16.10.128/27
10.16.10.160/27
-
What is the usable number of host IP addresses on a network that has a /26 mask?
- 256
- 254
- 64
- 62
- 32
- 16
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A /26 mask is the same as 255.255.255.192. The mask leaves 6 host bits. With 6 host bits, 64 IP addresses are possible. One address represents the subnet number and one address represents the broadcast address, which means that 62 addresses can then be used to assign to network devices.
-
Which address prefix range is reserved for IPv4 multicast?
- 240.0.0.0 – 254.255.255.255
- 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
- 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255
- 127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Multicast IPv4 addresses use the reserved class D address range of 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network.
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 05
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 003
Answers Explanation & Hints:Network A needs to use 192.168.0.128 /25, which yields 128 host addresses.
Network B needs to use 192.168.0.0 /26, which yields 64 host addresses.
Network C needs to use 192.168.0.96 /27, which yields 32 host addresses.
Network D needs to use 192.168.0.80/30, which yields 4 host addresses. -
A high school in New York (school A) is using videoconferencing technology to establish student interactions with another high school (school B) in Russia. The videoconferencing is conducted between two end devices through the Internet. The network administrator of school A configures the end device with the IP address 209.165.201.10. The administrator sends a request for the IP address for the end device in school B and the response is 192.168.25.10. Neither school is using a VPN. The administrator knows immediately that this IP will not work. Why?
- This is a loopback address.
- This is a link-local address.
- This is a private IP address.
- There is an IP address conflict.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The IP address 192.168.25.10 is an IPv4 private address. This address will not be routed over the Internet, so school A will not be able to reach school B. Because the address is a private one, it can be used freely on an internal network. As long as no two devices on the internal network are assigned the same private IP, there is no IP conflict issue. Devices that are assigned a private IP will need to use NAT in order to communicate over the Internet.
-
Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117
- 172.31.1.25
- 64.104.78.227
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The ranges of private IPv4 addresses are as folllows:
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
-
A message is sent to all hosts on a remote network. Which type of message is it?
- limited broadcast
- multicast
- directed broadcast
- unicast
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A directed broadcast is a message sent to all hosts on a specific network. It is useful for sending a broadcast to all hosts on a nonlocal network. A multicast message is a message sent to a selected group of hosts that are part of a subscribing multicast group. A limited broadcast is used for a communication that is limited to the hosts on the local network. A unicast message is a message sent from one host to another.
-
A company has a network address of 192.168.1.64 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192. The company wants to create two subnetworks that would contain 10 hosts and 18 hosts respectively. Which two networks would achieve that? (Choose two.)
- 192.168.1.16/28
- 192.168.1.64/27
- 192.168.1.128/27
- 192.168.1.96/28
- 192.168.1.192/28
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Subnet 192.168.1.64 /27 has 5 bits that are allocated for host addresses and therefore will be able to support 32 addresses, but only 30 valid host IP addresses. Subnet 192.168.1.96/28 has 4 bits for host addresses and will be able to support 16 addresses, but only 14 valid host IP addresses.
-
Which address is a valid IPv6 link-local unicast address?
- FEC8:1::FFFF
- FD80::1:1234
- FE80::1:4545:6578:ABC1
- FE0A::100:7788:998F
- FC90:5678:4251:FFFF
Answers Explanation & Hints:
IPv6 LLAs are in the fe80::/10 range. The /10 indicates that the first 10 bits are 1111 1110 10xx xxxx. The first hextet has a range of 1111 1110 1000 0000 (fe80) to 1111 1110 1011 1111 (febf).
-
Which of these addresses is the shortest abbreviation for the IP address:
3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB:0000:0000:0057?
- 3FFE:1044::AB::57
- 3FFE:1044::00AB::0057
- 3FFE:1044:0:0:AB::57
- 3FFE:1044:0:0:00AB::0057
- 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::57
- 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::0057
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The rules for reducing the notation of IPv6 addresses are:
1. Omit any leading 0s (zeros) in any hextet.
2. Replace any single, contiguous string of one or more 16-bit hextets consisting of all zeros with a double colon (::) .
3. The double colon (::) can only be used once within an address.
-
A network administrator has received the IPv6 prefix 2001:DB8::/48 for subnetting. Assuming the administrator does not subnet into the interface ID portion of the address space, how many subnets can the administrator create from the /48 prefix?
- 16
- 256
- 4096
- 65536
Answers Explanation & Hints:
With a network prefix of 48, there will be 16 bits available for subnetting because the interface ID starts at bit 64. Sixteen bits will yield 65536 subnets.
-
Given IPv6 address prefix 2001:db8::/48, what will be the last subnet that is created if the subnet prefix is changed to /52?
- 2001:db8:0:f00::/52
- 2001:db8:0:8000::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f000::/52
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Prefix 2001:db8::/48 has 48 network bits. If we subnet to a /52, we are moving the network boundary four bits to the right and creating 16 subnets. The first subnet is 2001:db8::/52 the last subnet is 2001:db8:0:f000::/52.
-
Consider the following range of addresses:
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000::
…
2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::
The prefix-length for the range of addresses is /60 .
Answers Explanation & Hints:All the addresses have the part 2001:0DB8:BC15:00A in common. Each number or letter in the address represents 4 bits, so the prefix-length is /60.
-
What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local
- multicast
- global unicast
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Link-local IPv6 addresses start with FE80::/10, which is any address from FE80:: to FEBF::. Link-local addresses are used extensively in IPv6 and allow directly connected devices to communicate with each other on the link they share.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A company is deploying an IPv6 addressing scheme for its network. The company design document indicates that the subnet portion of the IPv6 addresses is used for the new hierarchical network design, with the site subsection to represent multiple geographical sites of the company, the sub-site section to represent multiple campuses at each site, and the subnet section to indicate each network segment separated by routers. With such a scheme, what is the maximum number of subnets achieved per sub-site?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 02
- 0
- 4
- 16
- 256
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Because only one hexadecimal character is used to represent the subnet, that one character can represent 16 different values 0 through F.
-
What is used in the EUI-64 process to create an IPv6 interface ID on an IPv6 enabled interface?
- the MAC address of the IPv6 enabled interface
- a randomly generated 64-bit hexadecimal address
- an IPv6 address that is provided by a DHCPv6 server
- an IPv4 address that is configured on the interface
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The EUI-64 process uses the MAC address of an interface to construct an interface ID (IID). Because the MAC address is only 48 bits in length, 16 additional bits (FF:FE) must be added to the MAC address to create the full 64-bit interface ID.
-
What is the prefix for the host address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
- 2001:DB8:BC15
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The network portion, or prefix, of an IPv6 address is identified through the prefix length. A /64 prefix length indicates that the first 64 bits of the IPv6 address is the network portion. Hence the prefix is 2001:DB8:BC15:A.
-
An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::1. What is the target of this packet?
- the one IPv6 device on the link that has been uniquely configured with this address
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link or network
- only IPv6 DHCP servers
- only IPv6 configured routers
Answers Explanation & Hints:
This address is one of the assigned IPv6 multicast addresses. Packets addressed to FF02::1 are for all IPv6 enabled devices on the link or network. FF02::2 is for all IPv6 routers that exist on the network.
-
Match the IPv6 address with the IPv6 address type. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 004
Answers Explanation & Hints:FF02::1:FFAE:F85F is a solicited node multicast address.
2001:DB8::BAF:3F57:FE94 is a global unicast address.
FF02::1 is the all node multicast address. Packets sent to this address will be received by all IPv6 hosts on the local link.
::1 is the IPv6 loopback address.
There are no examples of link local or unique local addresses provided. -
Which IPv6 prefix is reserved for communication between devices on the same link?
- FC00::/7
- 2001::/32
- FE80::/10
- FDFF::/7
Answers Explanation & Hints:
IPv6 link-local unicast addresses are in the FE80::/10 prefix range and are not routable. They are used only for communications between devices on the same link.
-
Which type of IPv6 address refers to any unicast address that is assigned to multiple hosts?
- unique local
- global unicast
- link-local
- anycast
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The IPv6 specifications include anycast addresses. An anycast address is any unicast IPv6 address that is assigned to multiple devices.
-
What are two types of IPv6 unicast addresses? (Choose two.)
- multicast
- loopback
- link-local
- anycast
- broadcast
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Multicast, anycast, and unicast are types of IPv6 addresses. There is no broadcast address in IPv6. Loopback and link-local are specific types of unicast addresses.
-
Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Using stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC), a PC can solicit a router and receive the prefix length of the network. From this information the PC can then create its own IPv6 global unicast address.
-
Which protocol supports Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) for dynamic assignment of IPv6 addresses to a host?
- ARPv6
- DHCPv6
- ICMPv6
- UDP
Answers Explanation & Hints:
SLAAC uses ICMPv6 messages when dynamically assigning an IPv6 address to a host. DHCPv6 is an alternate method of assigning an IPv6 addresses to a host. ARPv6 does not exist. Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) provides the functionality of ARP for IPv6 networks. UDP is the transport layer protocol used by DHCPv6.
-
Three methods allow IPv6 and IPv4 to co-exist. Match each method with its description. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 005
Answers Explanation & Hints:The term for the method that allows for the coexistence of the two types of packets on a single network is dual-stack. Tunneling allows for the IPv6 packet to be transported inside IPv4 packets. An IP packet can also be converted from version 6 to version 4 and vice versa. DHCP is a protocol that is used for allocating network parameters to hosts on an IP network.
-
A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?
- the TCP/IP stack on a network host
- connectivity between two adjacent Cisco devices
- connectivity between a PC and the default gateway
- connectivity between two PCs on the same network
- physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network
Answers Explanation & Hints:
127.0.0.1 is the local loopback address on any TCP/IP network device. By pinging this address, the technician is verifying the TCP/IP protocol stack on that particular device.
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to troubleshoot connectivity between PC1 and PC2 and uses the tracert command from PC1 to do it. Based on the displayed output, where should the administrator begin troubleshooting?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 01
- PC2
- R1
- SW2
- R2
- SW1
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Tracert is used to trace the path a packet takes. The only successful response was from the first device along the path on the same LAN as the sending host. The first device is the default gateway on router R1. The administrator should therefore start troubleshooting at R1.
-
Which protocol is used by the traceroute command to send and receive echo-requests and echo-replies?
- SNMP
- ICMP
- Telnet
- TCP
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Traceroute uses the ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to send and receive echo-request and echo-reply messages.
-
Which ICMPv6 message is sent when the IPv6 hop limit field of a packet is decremented to zero and the packet cannot be forwarded?
- network unreachable
- time exceeded
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
Answers Explanation & Hints:
ICMPv6 uses the hop limit field in the IPv6 packet header to determine if the packet has expired. If the hop limit field has reached zero, a router will send a time exceeded message back towards the source indicating that the router cannot forward the packet.
-
A user executes a traceroute over IPv6. At what point would a router in the path to the destination device drop the packet?
- when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches 255
- when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches zero
- when the router receives an ICMP time exceeded message
- when the target host responds with an ICMP echo reply message
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a traceroute is performed, the value in the Hop Limit field of an IPv6 packet determines how many router hops the packet can travel. Once the Hop Limit field reaches a value of zero, it can no longer be forwarded and the receiving router will drop the packet.
-
What is the purpose of ICMP messages?
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The purpose of ICMP messages is to provide feedback about issues that are related to the processing of IP packets.
-
What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When sending an echo request message, a router will use the IP address of the exit interface as the source IP address. This default behavior can be changed by using an extended ping and specifying a specific source IP address.
-
Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 11 – 13 IP Addressing Exam Answers 006
Answers Explanation & Hints:Link-Local addresses are assigned automatically by the OS environment and are located in the block 169.254.0.0/16. The private addresses ranges are 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, and 192.168.0.0/16. TEST-NET addresses belong to the range 192.0.2.0/24. The addresses in the block 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.254 are reserved as experimental addresses. Loopback addresses belong to the block 127.0.0.0/8.
-
What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
- /25
- /26
- /27
- /28
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The binary format for 255.255.255.224 is 11111111.11111111.11111111.11100000. The prefix length is the number of consecutive 1s in the subnet mask. Therefore, the prefix length is /27.
-
Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
Answers Explanation & Hints:
For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
-
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
What are the three IPv6 addresses displayed when the route from PC1 to PC2 is traced? (Choose three.)
- 2001:DB8:1:1::1
- 2001:DB8:1:1::A
- 2001:DB8:1:2::2
- 2001:DB8:1:2::1
- 2001:DB8:1:3::1
- 2001:DB8:1:3::2
- 2001:DB8:1:4::1
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Using the ipv6config command on PC2 displays the IPv6 address of PC2, which is 2001:DB8:1:4::A. The IPV6 link-local address, FE80::260:70FF:FE34:6930, is not used in route tracing. Using the tracert 2001:DB8:1:4::A command on PC1 displays four addresses: 2001:DB8:1:1::1, 2001:DB8:1:2::1 , 2001:DB8:1:3::2, and 2001:DB8:1:4::A.
-
A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- all hosts in the same subnet
- a specially defined group of hosts
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- all hosts on the Internet
-
A host is transmitting a unicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- one specific host
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts on the Internet
- the closest neighbor on the same network
-
A host is transmitting a unicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- one specific host
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts with the same IP address
- the closest neighbor on the same network
-
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- all hosts with the same IP address
- the closest neighbor on the same network
-
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- directly connected network devices
- the closest neighbor on the same network
-
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- all hosts with the same IP address
- all hosts on the Internet
-
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- directly connected network devices
- all hosts on the Internet
-
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts in the same subnet
- directly connected network devices
- the closest neighbor on the same network
-
A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- all hosts in the same subnet
- one specific host
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- directly connected network devices
-
A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- all hosts in the same subnet
- one specific host
- all hosts on the Internet
- directly connected network devices
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db80:::1::80:1
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9:20::b000:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909?
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 200:420:110:c4b::910:0:90
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0ab8:0001:0000:1000?
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0420:00c4:1008:0025:0190:0000:0990?
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:0000:0000:0000:0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029?
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909?
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80::0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029
-
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 2. What does this code represent?
- beyond scope of the source address
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- address unreachable
- no route to destination
-
A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1. What does this code represent?
- host unreachable
- beyond scope of the source address
- address unreachable
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
-
A user issues a ping fe80:65ab:dcc1::100 command and receives a response that includes a code of 3. What does this code represent?
- address unreachable
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- beyond scope of the source address
- no route to destination
-
A user issues a ping 10.10.14.67 command and receives a response that includes a code of 0. What does this code represent?
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
-
A user issues a ping fe80:65ab:dcc1::100 command and receives a response that includes a code of 4. What does this code represent?
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
-
A user issues a ping 198.133.219.8 command and receives a response that includes a code of 0. What does this code represent?
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
-
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:3040:114::88 command and receives a response that includes a code of 4. What does this code represent?
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
-
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 2. What does this code represent?
- beyond scope of the source address
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
-
A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1. What does this code represent?
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- network unreachable
-
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 3. What does this code represent?
- address unreachable
- network unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
Home
Expert solutions
4.5 (2 reviews)
Term
What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
Click the card to flip 👆
Created by
bryankeller39202Teacher
Terms in this set (116)
What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
/27
How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
62
Which subnet mask would be used if 5 host bits are available?
255.255.255.224
A network administrator subnets the 192.168.10.0/24 network into subnets with /26 masks. How many equal-sized subnets are created?
4
An administrator wants to create four subnetworks from the network address 192.168.1.0/24. What is the network address and subnet mask of the second useable subnet?
subnetwork 192.168.1.64subnet mask 255.255.255.192
How many bits must be borrowed from the host portion of an address to accommodate a router with five connected networks?
3
How many host addresses are available on the 192.168.10.128/26 network?
62
How many host addresses are available on the network 172.16.128.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.252.0?
1022
What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
10.0.0.0/8 172.16.0.0/12
192.168.0.0/16
An administrator must send a message to everyone on the router A network. What is the broadcast address for network 172.16.16.0/22?
172.16.19.255
Students also viewed
CCNA 1 v7 Modules 11 — 13: IP Addressing Exam
66 termsImages
sarabblair
Intro Network v7 module 14-15
57 terms
Falcon87
CNA 101 — Modules 14-15 Network Application C…
32 terms
Jesse_Withrow
11-13
51 terms
Chris_Dritmanis
Recent flashcard sets
Livsstil og helse
23 terms
kevin_t28
Spartans
31 terms
sofiacsullice
ENGLISH 10 — Q1
27 terms
lapenamayyy23
connecteurs espagnol
20 terms
Julio-Dev
Sets found in the same folder
Modules 8 — 10 Communicating Between Networks…
107 terms
bryankeller39202Teacher
Modules 14 — 15: Network Application Communic…
102 terms
bryankeller39202Teacher
Modules 4-7 Ethernet Concepts
133 terms
bryankeller39202Teacher
Modules 1 -3 Basic Network Connectivity and C…
123 terms
bryankeller39202Teacher
Verified questions
other
Leaking purple fluid indicates that you should check your
Verified answer
other
How might an entrepreneur finance a business?
Verified answer
other
Describe three basic sleeves.
Verified answer
other
Describe four other laundering products beside detergents
Verified answer
Other Quizlet sets
Ag Marketing Final Exam
156 terms
Bailey_Downing1
Systems of Microbiology
15 terms
Sabrine_Mahmoud
Foundations of Business Thought Midterm (borr…
54 terms
lisasponaugle
Chapter 13 Heart Disease, Hypertension, Strok…
74 terms
diandra98
1
/
5
Home
Expert solutions
4.5 (2 reviews)
Term
What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
Click the card to flip 👆
Created by
bryankeller39202Teacher
Terms in this set (116)
What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
/27
How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
62
Which subnet mask would be used if 5 host bits are available?
255.255.255.224
A network administrator subnets the 192.168.10.0/24 network into subnets with /26 masks. How many equal-sized subnets are created?
4
An administrator wants to create four subnetworks from the network address 192.168.1.0/24. What is the network address and subnet mask of the second useable subnet?
subnetwork 192.168.1.64subnet mask 255.255.255.192
How many bits must be borrowed from the host portion of an address to accommodate a router with five connected networks?
3
How many host addresses are available on the 192.168.10.128/26 network?
62
How many host addresses are available on the network 172.16.128.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.252.0?
1022
What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
10.0.0.0/8 172.16.0.0/12
192.168.0.0/16
An administrator must send a message to everyone on the router A network. What is the broadcast address for network 172.16.16.0/22?
172.16.19.255
Students also viewed
CCNA 1 v7 Modules 11 — 13: IP Addressing Exam
66 termsImages
sarabblair
Intro Network v7 module 14-15
57 terms
Falcon87
CNA 101 — Modules 14-15 Network Application C…
32 terms
Jesse_Withrow
11-13
51 terms
Chris_Dritmanis
Recent flashcard sets
Livsstil og helse
23 terms
kevin_t28
Spartans
31 terms
sofiacsullice
ENGLISH 10 — Q1
27 terms
lapenamayyy23
connecteurs espagnol
20 terms
Julio-Dev
Sets found in the same folder
Modules 8 — 10 Communicating Between Networks…
107 terms
bryankeller39202Teacher
Modules 14 — 15: Network Application Communic…
102 terms
bryankeller39202Teacher
Modules 4-7 Ethernet Concepts
133 terms
bryankeller39202Teacher
Modules 1 -3 Basic Network Connectivity and C…
123 terms
bryankeller39202Teacher
Verified questions
other
Leaking purple fluid indicates that you should check your
Verified answer
other
How might an entrepreneur finance a business?
Verified answer
other
Describe three basic sleeves.
Verified answer
other
Describe four other laundering products beside detergents
Verified answer
Other Quizlet sets
Ag Marketing Final Exam
156 terms
Bailey_Downing1
Systems of Microbiology
15 terms
Sabrine_Mahmoud
Foundations of Business Thought Midterm (borr…
54 terms
lisasponaugle
Chapter 13 Heart Disease, Hypertension, Strok…
74 terms
diandra98
1
/
5
Last Updated on December 24, 2020 by
-
An administrator wants to create four subnetworks from the network address 192.168.1.0/24. What is the network address and subnet mask of the second useable subnet?
- subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.32
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.128
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.8
subnet mask 255.255.255.224
- subnetwork 192.168.1.64
-
How many bits must be borrowed from the host portion of an address to accommodate a router with five connected networks?
- two
- three
- four
- five
-
How many host addresses are available on the 192.168.10.128/26 network?
- 30
- 32
- 60
- 62
- 64
-
How many host addresses are available on the network 172.16.128.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.252.0?
- 510
- 512
- 1022
- 1024
- 2046
- 2048
-
Match the subnetwork to a host address that would be included within the subnetwork. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 001
-
Match each IPv4 address to the appropriate address category. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 002
-
What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 100.64.0.0/14
- 169.254.0.0/16
- 239.0.0.0/8
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator must send a message to everyone on the router A network. What is the broadcast address for network 172.16.16.0/22?
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 03
- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
-
A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
-
Refer to the exhibit. Considering the addresses already used and having to remain within the 10.16.10.0/24 network range, which subnet address could be assigned to the network containing 25 hosts?
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 02
- 10.16.10.160/26
- 10.16.10.128/28
- 10.16.10.64/27
- 10.16.10.224/26
- 10.16.10.240/27
- 10.16.10.240/28
-
What is the usable number of host IP addresses on a network that has a /26 mask?
- 256
- 254
- 64
- 62
- 32
- 16
-
Which address prefix range is reserved for IPv4 multicast?
- 240.0.0.0 – 254.255.255.255
- 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
- 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255
- 127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
-
Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network.
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 01
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 003
-
A high school in New York (school A) is using videoconferencing technology to establish student interactions with another high school (school B) in Russia. The videoconferencing is conducted between two end devices through the Internet. The network administrator of school A configures the end device with the IP address 209.165.201.10. The administrator sends a request for the IP address for the end device in school B and the response is 192.168.25.10. Neither school is using a VPN. The administrator knows immediately that this IP will not work. Why?
- This is a loopback address.
- This is a link-local address.
- This is a private IP address.
- There is an IP address conflict.
-
Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117
- 172.31.1.25
- 64.104.78.227
-
A message is sent to all hosts on a remote network. Which type of message is it?
- limited broadcast
- multicast
- directed broadcast
- unicast
-
A company has a network address of 192.168.1.64 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192. The company wants to create two subnetworks that would contain 10 hosts and 18 hosts respectively. Which two networks would achieve that? (Choose two.)
- 192.168.1.16/28
- 192.168.1.64/27
- 192.168.1.128/27
- 192.168.1.96/28
- 192.168.1.192/28
-
Which address is a valid IPv6 link-local unicast address?
- FEC8:1::FFFF
- FD80::1:1234
- FE80::1:4545:6578:ABC1
- FE0A::100:7788:998F
- FC90:5678:4251:FFFF
-
Which of these addresses is the shortest abbreviation for the IP address:
3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB:0000:0000:0057?
- 3FFE:1044::AB::57
- 3FFE:1044::00AB::0057
- 3FFE:1044:0:0:AB::57
- 3FFE:1044:0:0:00AB::0057
- 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::57
- 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::0057
-
A network administrator has received the IPv6 prefix 2001:DB8::/48 for subnetting. Assuming the administrator does not subnet into the interface ID portion of the address space, how many subnets can the administrator create from the /48 prefix?
- 16
- 256
- 4096
- 65536
-
Given IPv6 address prefix 2001:db8::/48, what will be the last subnet that is created if the subnet prefix is changed to /52?
- 2001:db8:0:f00::/52
- 2001:db8:0:8000::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f000::/52
-
Consider the following range of addresses:
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000::
…
2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::
The prefix-length for the range of addresses is /60 .
-
What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local
- multicast
- global unicast
-
Refer to the exhibit. A company is deploying an IPv6 addressing scheme for its network. The company design document indicates that the subnet portion of the IPv6 addresses is used for the new hierarchical network design, with the site subsection to represent multiple geographical sites of the company, the sub-site section to represent multiple campuses at each site, and the subnet section to indicate each network segment separated by routers. With such a scheme, what is the maximum number of subnets achieved per sub-site?
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 04
- 0
- 4
- 16
- 256
-
What is used in the EUI-64 process to create an IPv6 interface ID on an IPv6 enabled interface?
- the MAC address of the IPv6 enabled interface
- a randomly generated 64-bit hexadecimal address
- an IPv6 address that is provided by a DHCPv6 server
- an IPv4 address that is configured on the interface
-
What is the prefix for the host address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
- 2001:DB8:BC15
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12
-
An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::1. What is the target of this packet?
- the one IPv6 device on the link that has been uniquely configured with this address
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link or network
- only IPv6 DHCP servers
- only IPv6 configured routers
-
Match the IPv6 address with the IPv6 address type. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 004
-
Which IPv6 prefix is reserved for communication between devices on the same link?
- FC00::/7
- 2001::/32
- FE80::/10
- FDFF::/7
-
Which type of IPv6 address refers to any unicast address that is assigned to multiple hosts?
- unique local
- global unicast
- link-local
- anycast
-
What are two types of IPv6 unicast addresses? (Choose two.)
- multicast
- loopback
- link-local
- anycast
- broadcast
-
Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
-
Which protocol supports Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) for dynamic assignment of IPv6 addresses to a host?
- ARPv6
- DHCPv6
- ICMPv6
- UDP
-
Three methods allow IPv6 and IPv4 to co-exist. Match each method with its description. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 005
-
A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?
- the TCP/IP stack on a network host
- connectivity between two adjacent Cisco devices
- connectivity between a PC and the default gateway
- connectivity between two PCs on the same network
- physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to troubleshoot connectivity between PC1 and PC2 and uses the tracert command from PC1 to do it. Based on the displayed output, where should the administrator begin troubleshooting?
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 05
- PC2
- R1
- SW2
- R2
- SW1
-
Which protocol is used by the traceroute command to send and receive echo-requests and echo-replies?
- SNMP
- ICMP
- Telnet
- TCP
-
Which ICMPv6 message is sent when the IPv6 hop limit field of a packet is decremented to zero and the packet cannot be forwarded?
- network unreachable
- time exceeded
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
-
A user executes a traceroute over IPv6. At what point would a router in the path to the destination device drop the packet?
- when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches 255
- when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches zero
- when the router receives an ICMP time exceeded message
- when the target host responds with an ICMP echo reply message
-
What is the purpose of ICMP messages?
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
-
What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
-
Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 ITN – IP Addressing Exam Answers 006
-
What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
- /25
- /26
- /27
- /28
-
Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
-
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
What are the three IPv6 addresses displayed when the route from PC1 to PC2 is traced? (Choose three.)
- 2001:DB8:1:1::1
- 2001:DB8:1:1::A
- 2001:DB8:1:2::2
- 2001:DB8:1:2::1
- 2001:DB8:1:3::1
- 2001:DB8:1:3::2
- 2001:DB8:1:4::1
-
A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- all hosts in the same subnet
- a specially defined group of hosts
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- all hosts on the Internet
-
A host is transmitting a unicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- one specific host
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts on the Internet
- the closest neighbor on the same network
-
A host is transmitting a unicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- one specific host
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts with the same IP address
- the closest neighbor on the same network
-
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- all hosts with the same IP address
- the closest neighbor on the same network
-
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- directly connected network devices
- the closest neighbor on the same network
-
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- all hosts with the same IP address
- all hosts on the Internet
-
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- directly connected network devices
- all hosts on the Internet
-
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts in the same subnet
- directly connected network devices
- the closest neighbor on the same network
-
A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- all hosts in the same subnet
- one specific host
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- directly connected network devices
-
A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- all hosts in the same subnet
- one specific host
- all hosts on the Internet
- directly connected network devices
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db80:::1::80:1
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9:20::b000:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909?
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 200:420:110:c4b::910:0:90
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0ab8:0001:0000:1000?
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0420:00c4:1008:0025:0190:0000:0990?
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:0000:0000:0000:0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029?
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909?
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80::0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029
-
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 2. What does this code represent?
- beyond scope of the source address
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- address unreachable
- no route to destination
-
A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1. What does this code represent?
- host unreachable
- beyond scope of the source address
- address unreachable
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
-
A user issues a ping fe80:65ab:dcc1::100 command and receives a response that includes a code of 3. What does this code represent?
- address unreachable
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- beyond scope of the source address
- no route to destination
-
A user issues a ping 10.10.14.67 command and receives a response that includes a code of 0. What does this code represent?
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
-
A user issues a ping fe80:65ab:dcc1::100 command and receives a response that includes a code of 4. What does this code represent?
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
-
A user issues a ping 198.133.219.8 command and receives a response that includes a code of 0. What does this code represent?
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
-
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:3040:114::88 command and receives a response that includes a code of 4. What does this code represent?
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
-
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 2. What does this code represent?
- beyond scope of the source address
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
-
A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1. What does this code represent?
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- network unreachable
-
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 3. What does this code represent?
- address unreachable
- network unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
a specially defined group of hosts
the closest neighbor on the same network
all hosts on the Internet
all hosts in the same subnet
What are three parts of an IPv6 global unicast address? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
a global routing prefix that is used to identify the portion of the network address provided by a local administrator
an interface ID that is used to identify the local host on the network
an interface ID that is used to identify the local network for a particular host
a subnet ID that is used to identify networks inside of the local enterprise site
a global routing prefix that is used to identify the network portion of the address that has been provided by an ISP
If a network device has a mask of /28, how many IP addresses are available for hosts on this network?
What is the interface ID of the IPv6 address 2001:DB8::1000:A9CD:47FF:FE57:FE94/64?
FE57:FE94
1000:A9CD:47FF:FE57:FE94
47FF:FE57:FE94
FE94
A9CD:47FF:FE57:FE94
Which utility uses the Internet Control Messaging Protocol (ICMP)?
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909?
2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
2002:42::25:1090:0:99
2002:42:10:c400::909
200:420:110:c4b::910:0:90
What subnet mask is represented by the slash notation /20?
255.255.255.192
255.255.255.0
255.255.240.0
255.255.255.248
255.255.224.0
A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?
connectivity between two adjacent Cisco devices
connectivity between a PC and the default gateway
physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network
the TCP/IP stack on a network host
connectivity between two PCs on the same network
What is the purpose of ICMP messages?
to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions
to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
to inform routers about network topology changes
A user issues a ping fe80:65ab:dcc1::100 command and receives a response that includes a code of 3. What does this code represent?
beyond scope of the source address
no route to destination
address unreachable
communication with the destination administratively prohibited
Which address prefix range is reserved for IPv4 multicast?
240.0.0.0 – 254.255.255.255
169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255
224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:3040:114::88 command and receives a response that includes a code of 4. What does this code represent?
network unreachable
port unreachable
protocol unreachable
host unreachable
Which type of IPv6 address refers to any unicast address that is assigned to multiple hosts?
unique local
link-local
anycast
global unicast
Your organization is issued the IPv6 prefix of 2001:0000:130F::/48 by your service provider. With this prefix, how many bits are available for your organization to create subnetworks if interface ID bits are not borrowed?
A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.224
255.255.255.128
What does the IP address 172.17.4.250/24 represent?
multicast address
broadcast address
host address
network address
Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
192.168.1.245
172.31.1.25
128.107.12.117
10.15.250.5
198.133.219.17
64.104.78.227
A user issues a ping 10.10.14.67 command and receives a response that includes a code of 0. What does this code represent?
host unreachable
port unreachable
network unreachable
protocol unreachable
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 2. What does this code represent?
address unreachable
beyond scope of the source address
no route to destination
communication with the destination administratively prohibited
What message is sent by a host to check the uniqueness of an IPv6 address before using that address?
ARP request
neighbor solicitation
router solicitation
echo request
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0ab8:0001:0000:1000?
2001:db8:0:1::8:1
2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
What type of address is automatically assigned to an interface when IPv6 is enabled on that interface?
global unicast
unique local
loopback
link-local
A network administrator has received the IPv6 prefix 2001:DB8::/48 for subnetting. Assuming the administrator does not subnet into the interface ID portion of the address space, how many subnets can the administrator create from the /48 prefix?
How many host addresses are available on the 192.168.10.128/26 network?
An administrator wants to create four subnetworks from the network address 192.168.1.0/24. What is the network address and subnet mask of the second useable subnet?
subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.192
subnetwork 192.168.1.32
subnet mask 255.255.255.240
subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.240
subnetwork 192.168.1.8
subnet mask 255.255.255.224
subnetwork 192.168.1.128
subnet mask 255.255.255.192
What are two types of IPv6 unicast addresses? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
broadcast
anycast
link-local
loopback
multicast
Which address type is not supported in IPv6?
private
unicast
broadcast
multicast
A network administrator can successfully ping the server at www.cisco.com, but cannot ping the company web server located at an ISP in another city. Which tool or command would help identify the specific router where the packet was lost or delayed?
netstat
ipconfig
telnet
traceroute
Consider the following range of addresses:
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000::
…
2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::
The prefix-length for the range of addresses is
A user who is unable to connect to the file server contacts the help desk. The helpdesk technician asks the user to ping the IP address of the default gateway that is configured on the workstation. What is the purpose for this ping command?
to obtain a dynamic IP address from the server
to test that the host has the capability to reach hosts on other networks
to resolve the domain name of the file server to its IP address
to request that gateway forward the connection request to the file server
Which two things can be determined by using the ping command? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
the IP address of the router nearest the destination device
the destination device is reachable through the network
the average time it takes a packet to reach the destination and for the response to return to the source
the number of routers between the source and destination device
the average time it takes each router in the path between source and destination to respond
Which protocol supports Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) for dynamic assignment of IPv6 addresses to a host?
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
fe80:9:20::b000:290
fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
A message is sent to all hosts on a remote network. Which type of message is it?
limited broadcast
multicast
directed broadcast
unicast
Which ICMPv6 message is sent when the IPv6 hop limit field of a packet is decremented to zero and the packet cannot be forwarded?
time exceeded
port unreachable
network unreachable
protocol unreachable
A network administrator subnets the 192.168.10.0/24 network into subnets with /26 masks. How many equal-sized subnets are created?
Which type of IPv6 address is not routable and used only for communication on a single subnet?
loopback address
unspecified address
link-local address
unique local address
global unicast address
Given IPv6 address prefix 2001:db8::/48, what will be the last subnet that is created if the subnet prefix is changed to /52?
2001:db8:0:f00::/52
2001:db8:0:f000::/52
2001:db8:0:f::/52
2001:db8:0:8000::/52
Which protocol is used by IPv4 and IPv6 to provide error messaging?
How many bits must be borrowed from the host portion of an address to accommodate a router with five connected networks?
Which IPv6 prefix is reserved for communication between devices on the same link?
2001::/32
FE80::/10
FC00::/7
FDFF::/7
What is the valid most compressed format possible of the IPv6 address 2001:0DB8:0000:AB00:0000:0000:0000:1234?
2001:DB8:0:AB00::1234
2001:DB8:0:AB::1234
2001:DB8::AB00::1234
2001:DB8:0:AB:0:1234
What is the prefix associated with the IPv6 address 2001:CA48:D15:EA:CC44::1/64?
2001:CA48:D15:EA:CC44::/64
2001:CA48:D15:EA::/64
2001:CA48::/64
2001::/64
Which statement describes a characteristic of the traceroute utility?
It identifies the routers in the path from a source host to a destination host.
It sends four Echo Request messages.
It utilizes the ICMP Source Quench messages.
It is primarily used to test connectivity between two hosts.
How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
If a network device has a mask of /26, how many IP addresses are available for hosts on this network?
What is a function of the tracert command that differs from the ping command when they are used on a workstation?
The tracert command sends one ICMP message to each hop in the path.
The tracert command is used to test the connectivity between two devices.
The tracert command reaches the destination faster.
The tracert command shows the information of routers in the path.
Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
192.168.1.32/27
192.168.1.64/29
192.168.1.32/28
192.168.1.64/26
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0420:00c4:1008:0025:0190:0000:0990?
2002:42::25:1090:0:99
2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
2002:42:10:c400::909
2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
Which IPv6 network prefix is only intended for local links and can not be routed?
FC00::/7
2001::/3
FEC0::/10
FE80::/10
How many host addresses are available on the network 172.16.128.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.252.0?
1024
1022
2048
510
512
2046
How many usable IP addresses are available on the 192.168.1.0/27 network?
What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
loopback
multicast
global unicast
link-local
A user issues a ping fe80:65ab:dcc1::100 command and receives a response that includes a code of 4. What does this code represent?
protocol unreachable
network unreachable
host unreachable
port unreachable
Which address is a valid IPv6 link-local unicast address?
FEC8:1::FFFF
FE80::1:4545:6578:ABC1
FC90:5678:4251:FFFF
FE0A::100:7788:998F
FD80::1:1234
A technician is troubleshooting a network where it is suspected that a defective node in the network path is causing packets to be dropped. The technician only has the IP address of the end point device and does not have any details of the intermediate devices. What command can the technician use to identify the faulty node?
ipconfig /flushdns
tracert
ipconfig /displaydns
ping
Which subnet mask would be used if 5 host bits are available?
255.255.255.128
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.224
What is the most compressed representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001?
2001:0:0:abcd::1
2001:0000:abcd::1
2001::abcd:0:1
2001:0:abcd::1
2001::abcd::1
What is used in the EUI-64 process to create an IPv6 interface ID on an IPv6 enabled interface?
an IPv6 address that is provided by a DHCPv6 server
a randomly generated 64-bit hexadecimal address
an IPv4 address that is configured on the interface
the MAC address of the IPv6 enabled interface
At a minimum, which address is required on IPv6-enabled interfaces?
site local
unique local
link-local
global unicast
What is the usable number of host IP addresses on a network that has a /26 mask?
Which subnet mask would be used if exactly 4 host bits are available?
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.248
255.255.255.128
255.255.255.224
Which of these addresses is the shortest abbreviation for the IP address:
3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB:0000:0000:0057?
3FFE:1044::00AB::0057
3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::57
3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::0057
3FFE:1044:0:0:00AB::0057
3FFE:1044::AB::57
3FFE:1044:0:0:AB::57
A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1. What does this code represent?
host unreachable
communication with the destination administratively prohibited
beyond scope of the source address
address unreachable
A user calls to report that a PC cannot access the internet. The network technician asks the user to issue the command ping 127.0.0.1 in a command prompt window. The user reports that the result is four positive replies. What conclusion can be drawn based on this connectivity test?
The TCP/IP implementation is functional.
The PC can access the network. The problem exists beyond the local network.
The IP address obtained from the DHCP server is correct.
The PC can access the Internet. However, the web browser may not work.
An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::1. What is the target of this packet?
only IPv6 configured routers
only IPv6 DHCP servers
all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link or network
Which command can be used to test connectivity between two devices using echo request and echo reply messages?
netstat
ICMP
ping
traceroute
Which ICMP message is used by the traceroute utility during the process of finding the path between two end hosts?
ping
time exceeded
destination unreachable
redirect
A user issues a ping 198.133.219.8 command and receives a response that includes a code of 0. What does this code represent?
protocol unreachable
host unreachable
network unreachable
port unreachable
A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 3. What does this code represent?
address unreachable
network unreachable
host unreachable
protocol unreachable
Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
stateful DHCPv6
SLAAC
stateless DHCPv6
static IPv6 addressing
What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
a loopback IP address
the highest configured IP address on the router
the IP address of the outbound interface
the lowest configured IP address on the router
A user executes a traceroute over IPv6. At what point would a router in the path to the destination device drop the packet?
when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches zero
when the router receives an ICMP time exceeded message
when the target host responds with an ICMP echo reply message
when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches 255
Which two parts are components of an IPv4 address? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
network portion
logical portion
subnet portion
host portion
physical portion
A high school in New York (school A) is using videoconferencing technology to establish student interactions with another high school (school B) in Russia. The videoconferencing is conducted between two end devices through the Internet. The network administrator of school A configures the end device with the IP address 209.165.201.10. The administrator sends a request for the IP address for the end device in school B and the response is 192.168.25.10. Neither school is using a VPN. The administrator knows immediately that this IP will not work. Why?
This is a link-local address.
This is a loopback address.
This is a private IP address.
There is an IP address conflict.
A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
a specially defined group of hosts
one specific host
all hosts with the same IP address
the closest neighbor on the same network
What is the purpose of the command ping ::1?
It tests the internal configuration of an IPv6 host.
It tests the multicast connectivity to all hosts on the subnet.
It tests the reachability of the default gateway for the network.
It tests the broadcast capability of all hosts on the subnet.
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
2001:db80:0:1::80:1
2001:db80:::1::80:1
2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
What is the subnet address for the IPv6 address 2001:D12:AA04:B5::1/64?
2001:D12::/64
2001:D12:AA04::/64
2001::/64
2001:D12:AA04:B5::/64
What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
What is the prefix for the host address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
2001:DB8:BC15:A:12
2001:DB8:BC15
2001:DB8:BC15:A:1
2001:DB8:BC15:A
A company has a network address of 192.168.1.64 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192. The company wants to create two subnetworks that would contain 10 hosts and 18 hosts respectively. Which two networks would achieve that? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
192.168.1.96/28
192.168.1.16/28
192.168.1.192/28
192.168.1.64/27
192.168.1.128/27
A network administrator is variably subnetting a network. The smallest subnet has a mask of 255.255.255.224. How many usable host addresses will this subnet provide?
What is the minimum configuration for a router interface that is participating in IPv6 routing?
to have only an automatically generated multicast IPv6 address
to have both an IPv4 and an IPv6 address
to have both a link-local and a global unicast IPv6 address
to have a self-generated loopback address
to have only a link-local IPv6 address
Which protocol is used by the traceroute command to send and receive echo-requests and echo-replies?
Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
to identify faulty frames
to identify the broadcast address of the destination network
to identify the network address of the destination network
to identify the host address of the destination host
What is indicated by a successful ping to the ::1 IPv6 address?
IP is properly installed on the host.
All hosts on the local link are available.
The default gateway address is correctly configured.
The link-local address is correctly configured.
The host is cabled properly.
What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
169.254.0.0/16
172.16.0.0/12
100.64.0.0/14
239.0.0.0/8
10.0.0.0/8
192.168.0.0/16
Which protocol provides feedback from the destination host to the source host about errors in packet delivery?
A host is transmitting a unicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
the closest neighbor on the same network
one specific host
a specially defined group of hosts
all hosts on the Internet
What is the purpose of the subnet mask in conjunction with an IP address?
to determine the subnet to which the host belongs
to uniquely identify a host on a network
to mask the IP address to outsiders
to identify whether the address is public or private
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:0000:0000:0000:0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029?
fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
What field content is used by ICMPv6 to determine that a packet has expired?
Hop Limit field
TTL field
CRC field
Time Exceeded field
Which statement is true about variable-length subnet masking?
Subnets may only be subnetted one additional time.
The size of each subnet may be different, depending on requirements.
Bits are returned, rather than borrowed, to create additional subnets.
Each subnet is the same size.
Подборка по базе: Контрольная работа _Разделительные вопросы_ (1).doc, Самые популярные вопросы о Чичикове из поэмы.docx, Примерные вопросы к дифференцированному зачету_Психология общени, Политология. Ответы на тест 1.pdf, Тестовые вопросы к разделу 5_ просмотр попытки.pdf, ОИ рк1 ответы.pdf, Тестовые вопросы к разделу 8_ просмотр попытки.pdf, Экзамен вопросы СП ОМ_англ_ok.docx, 2.2 Вопросы к экзамену Смета+Финансы.docx, РК-1 вопросы каз, русс 1 курс.docx
Сколько адресов хостов доступно в сети 172.16.128.0 с маской подсети 255.255.252.0?
- 510
- 512
- 1022
- 1024
- 2046
- 2048
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Маска 255.255.252.0 равна префиксу / 22. Префикс A / 22 предоставляет 22 бита для сетевой части и оставляет 10 бит для хост-части. 10 бит в части хоста предоставят 1022 используемых IP-адреса (2 10 — 2 = 1022).

| Ответы, объяснения и подсказки:
Чтобы определить, является ли данный IPv4-адрес сетевым, хост-адресом или широковещательным адресом, сначала определите адресное пространство на основе маски подсети. Преобразуйте адрес и маску в двоичные значения, затем выполните функцию И для определения сетевого адреса. Чтобы вычислить адресное пространство, используйте количество битов хоста в маске подсети как показатель степени 2. Количество действительных адресов хоста в пространстве равно этому числу минус 2. Сетевой адрес будет иметь все нули в части хоста. , а широковещательный адрес будет содержать все единицы. Например, 10.0.50.10/30 дает сетевой IP-адрес 10.0.50.8, когда маска соединена оператором AND с заданным адресом. Поскольку в маске всего 2 бита хоста, есть только 2 действительных адреса хоста (4–2). 10.0.50.10 — один из двух допустимых IP-адресов хоста. |
- Какие три блока адресов определены RFC 1918 для использования в частной сети? (Выберите три.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 100.64.0.0/14
- 169.254.0.0/16
- 239.0.0.0/8
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: RFC 1918, Распределение адресов для частных сетей, определяет три блока IPv4-адресов для частных сетей, которые не должны маршрутизироваться в общедоступном Интернете.
10.0.0.0 / 8 172.16.0.0/12
192.168.0.0/16
- Обратитесь к выставке.Администратор должен отправить сообщение всем в сети маршрутизатора A.Какой широковещательный адрес для сети 172.16.16.0/22?

- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Сеть 172.16.16.0/22 имеет 22 бита в сетевой части и 10 бит в хостовой части. Преобразование сетевого адреса в двоичный дает маску подсети 255.255.252.0. Диапазон адресов в этой сети будет заканчиваться последним адресом, доступным до 172.16.20.0. Допустимые адреса узлов для этой сети находятся в диапазоне от 172.16.16.1-172.16.19.254, что делает 172.16.19.255 широковещательным адресом.
- Администратору сайта сказали, что в конкретной сети на сайте должно быть 126 хостов.Какая маска подсети будет использоваться, содержащая необходимое количество бит хоста?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Маска подсети 255.255.255.0 имеет 8 бит хоста. Маска 255.255.255.128 дает 7 бит хоста. Маска 255.255.255.224 имеет 5 бит хоста. Наконец, 255.255.255.240 представляет 4 бита хоста.
- Обратитесь к выставке.Учитывая уже используемые адреса и необходимость оставаться в пределах диапазона сети 10.16.10.0/24, какой адрес подсети можно назначить сети, содержащей 25 хостов?

- 10.16.10.160/26
- 10.16.10.128/28
- 10.16.10.64/27
- 10.16.10.224/26
- 10.16.10.240/27
- 10.16.10.240/28
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Адреса с 10.16.10.0 по 10.16.10.63 берутся для самой левой сети. Адреса с 10.16.10.192 по 10.16.10.207 используются центральной сетью. Адресное пространство от 208 до 255 предполагает маску / 28, которая не позволяет разместить достаточно битов хоста для размещения 25 адресов хоста. Доступные диапазоны адресов включают 10.16. 10.64 / 26 и 10.16.10.128 / 26. Для размещения 25 хостов необходимо 5 бит хостов, поэтому необходима маска / 27. Четыре возможных подсети / 27 могут быть созданы из доступных адресов между 10.16.10.64 и 10.16.10.191:
10.16.10.64/27
10.16.10.96/27
10.16.10.128/27
10.16.10.160/27 - Какое количество IP-адресов хоста можно использовать в сети с маской / 26?
- 256
- 254
- 64
- 62
- 32
- 16
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Маска A / 26 такая же, как 255.255.255.192. В маске остается 6 бит хоста. С 6 битами хоста возможно 64 IP-адреса. Один адрес представляет номер подсети, а один адрес представляет широковещательный адрес, что означает, что 62 адреса могут быть использованы для назначения сетевым устройствам.
- Какой диапазон префиксов адресов зарезервирован для многоадресной рассылки IPv4?
- 240.0.0.0 — 254.255.255.255
- 224.0.0.0 — 239.255.255.255
- 169.254.0.0 — 169.254.255.255
- 127.0.0.0–127.255.255.255
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Многоадресные IPv4-адреса используют зарезервированный диапазон адресов класса D от 224.0.0.0 до 239.255.255.255.
- Обратитесь к выставке.Сопоставьте сеть с правильным IP-адресом и префиксом, которые будут удовлетворять требованиям к пригодной адресации хоста для каждой сети.


| Ответы, объяснения и подсказки:
Сеть A должна использовать 192.168.0.128 / 25, что дает 128 адресов хостов. |
- Средняя школа в Нью-Йорке (школа A) использует технологию видеоконференцсвязи для установления взаимодействия учащихся с другой средней школой (школа B) в России.Видеоконференцсвязь осуществляется между двумя конечными устройствами через Интернет.Сетевой администратор школы A настраивает конечное устройство с IP-адресом 209.165.201.10.Администратор отправляет запрос IP-адреса для конечного устройства в школе B, и в ответ он получает 192.168.25.10.Ни одна из школ не использует VPN.Администратор сразу знает, что этот IP работать не будет. Почему?
- Это адрес обратной связи.
- Это локальный адрес ссылки.
- Это частный IP-адрес.
- Конфликт IP-адресов.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: IP-адрес 192.168.25.10 является частным адресом IPv4. Этот адрес не будет маршрутизироваться через Интернет, поэтому школа A не сможет связаться со школой B. Поскольку адрес является частным, его можно свободно использовать во внутренней сети. Пока никаким двум устройствам во внутренней сети не назначен один и тот же частный IP-адрес, проблема конфликта IP-адресов отсутствует. Устройства, которым назначен частный IP-адрес, должны будут использовать NAT для связи через Интернет.
- Какие три адреса являются действительными общедоступными адресами? (Выберите три.)
- 198.133.219.17
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117
- 172.31.1.25
- 64.104.78.227
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Диапазоны частных IPv4-адресов следующие:
10.0.0.0 — 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 — 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 — 192.168.255.255
- Сообщение отправляется на все хосты в удаленной сети.Что это за тип сообщения?
- ограниченная трансляция
- многоадресная передача
- направленная трансляция
- одноадресная передача
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Направленная трансляция — это сообщение, отправляемое всем хостам в определенной сети. Это полезно для отправки широковещательной рассылки на все хосты в нелокальной сети. Многоадресное сообщение — это сообщение, отправленное выбранной группе хостов, которые являются частью подписывающейся группы многоадресной рассылки. Ограниченная широковещательная передача используется для связи, которая ограничена узлами в локальной сети. Одноадресное сообщение — это сообщение, отправленное с одного хоста на другой.
- Компания имеет сетевой адрес 192.168.1.64 с маской подсети 255.255.255.192.Компания хочет создать две подсети, которые будут содержать 10 и 18 хостов соответственно. Какие две сети смогли бы этого достичь? (Выберите два.)
- 192.168.1.16/28
- 192.168.1.64/27
- 192.168.1.128/27
- 192.168.1.96/28
- 192.168.1.192/28
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Подсеть 192.168.1.64 / 27 имеет 5 бит, которые выделены для адресов хоста, и поэтому она сможет поддерживать 32 адреса, но только 30 действительных IP-адресов хоста. Подсеть 192.168.1.96/28 имеет 4 бита для адресов хоста и может поддерживать 16 адресов, но только 14 действительных IP-адресов хоста.
- Какой адрес является допустимым IPv6-адресом для локальной одноадресной рассылки?
- FEC8: 1 :: FFFF
- FD80 :: 1: 1234
- FE80 :: 1: 4545: 6578: ABC1
- FE0A :: 100: 7788: 998F
- FC90: 5678: 4251: FFFF
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: LLA IPv6 находятся в диапазоне fe80 :: / 10. / 10 указывает, что первые 10 бит — это 1111 1110 10xx xxxx. Первый гекстет имеет диапазон от 1111 1110 1000 0000 (fe80) до 1111 1110 1011 1111 (febf).
- Какой из этих адресов является кратчайшим сокращением IP-адреса:
3FFE: 1044: 0000: 0000: 00AB: 0000: 0000: 0057?
- 3FFE: 1044 :: AB :: 57
- 3FFE: 1044 :: 00AB :: 0057
- 3FFE: 1044: 0: 0: AB :: 57
- 3FFE: 1044: 0: 0: 00AB :: 0057
- 3FFE: 1044: 0000: 0000: 00AB :: 57
- 3FFE: 1044: 0000: 0000: 00AB :: 0057
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Правила сокращения записи адресов IPv6 следующие:
1. Пропускайте любые ведущие нули (нули) в любом гекстете.
2. Замените любую непрерывную строку из одного или нескольких 16-битных гекстетов, состоящих из всех нулей, двойным двоеточием (: :).
3. Двойное двоеточие (:можно использовать в адресе только один раз.
- Сетевой администратор получил префикс IPv6 2001: DB8 :: / 48 для разделения на подсети.Предполагая, что администратор не выполняет подсети в части идентификатора интерфейса адресного пространства, сколько подсетей может создать администратор с префиксом / 48?
- 16
- 256
- 4096
- 65536
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: При сетевом префиксе 48 будет доступно 16 бит для разделения на подсети, потому что идентификатор интерфейса начинается с 64 бита. Шестнадцать бит дают 65536 подсетей.
- Учитывая префикс IPv6-адреса 2001: db8 :: / 48, какая подсеть будет создана последней, если префикс подсети будет изменен на / 52?
- 2001: db8: 0: f00 :: / 52
- 2001: db8: 0: 8000 :: / 52
- 2001: db8: 0: f :: / 52
- 2001: db8: 0: f000 :: / 52
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Префикс 2001: db8 :: / 48 имеет 48 сетевых битов. Если мы подсеть к / 52, мы перемещаем границу сети на четыре бита вправо и создаем 16 подсетей. Первая подсеть — 2001: db8 :: / 52, последняя подсеть — 2001: db8: 0: f000 :: / 52.
- Рассмотрим следующий диапазон адресов:
2001: 0DB8: BC15: 00A0: 0000 ::
2001: 0DB8: BC15: 00A1: 0000 ::
2001: 0DB8: BC15: 00A2: 0000 ::
…
2001: 0DB8: BC15: 00AF: 0000 ::
Длина префикса для диапазона адресов — / 60 .
| Ответы, объяснения и подсказки:
Все адреса имеют общую часть 2001: 0DB8: BC15: 00A. Каждая цифра или буква в адресе представляют 4 бита, поэтому длина префикса составляет / 60. |
- Какой тип IPv6-адреса FE80 :: 1?
- петля
- link-local
- многоадресная передача
- глобальная одноадресная передача
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Локальные для канала IPv6-адреса начинаются с FE80 :: / 10, что является любым адресом от FE80 :: до FEBF ::. Адреса локальной связи широко используются в IPv6 и позволяют напрямую подключенным устройствам обмениваться данными друг с другом по общей ссылке.
- Обратитесь к выставке.Компания развертывает схему адресации IPv6 для своей сети.В проектном документе компании указано, что часть подсети адресов IPv6 используется для нового иерархического дизайна сети, при этом подраздел сайта представляет несколько географических сайтов компании, раздел дочерних сайтов представляет несколько кампусов на каждом сайте, а подраздел сайта — это несколько кампусов на каждом сайте. раздел подсети, чтобы указать каждый сегмент сети, разделенный маршрутизаторами.Какое максимальное количество подсетей достигается при такой схеме на подузел?

- 0
- 4
- 16
- 256
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Поскольку для представления подсети используется только один шестнадцатеричный символ, этот один символ может представлять 16 различных значений от 0 до F.

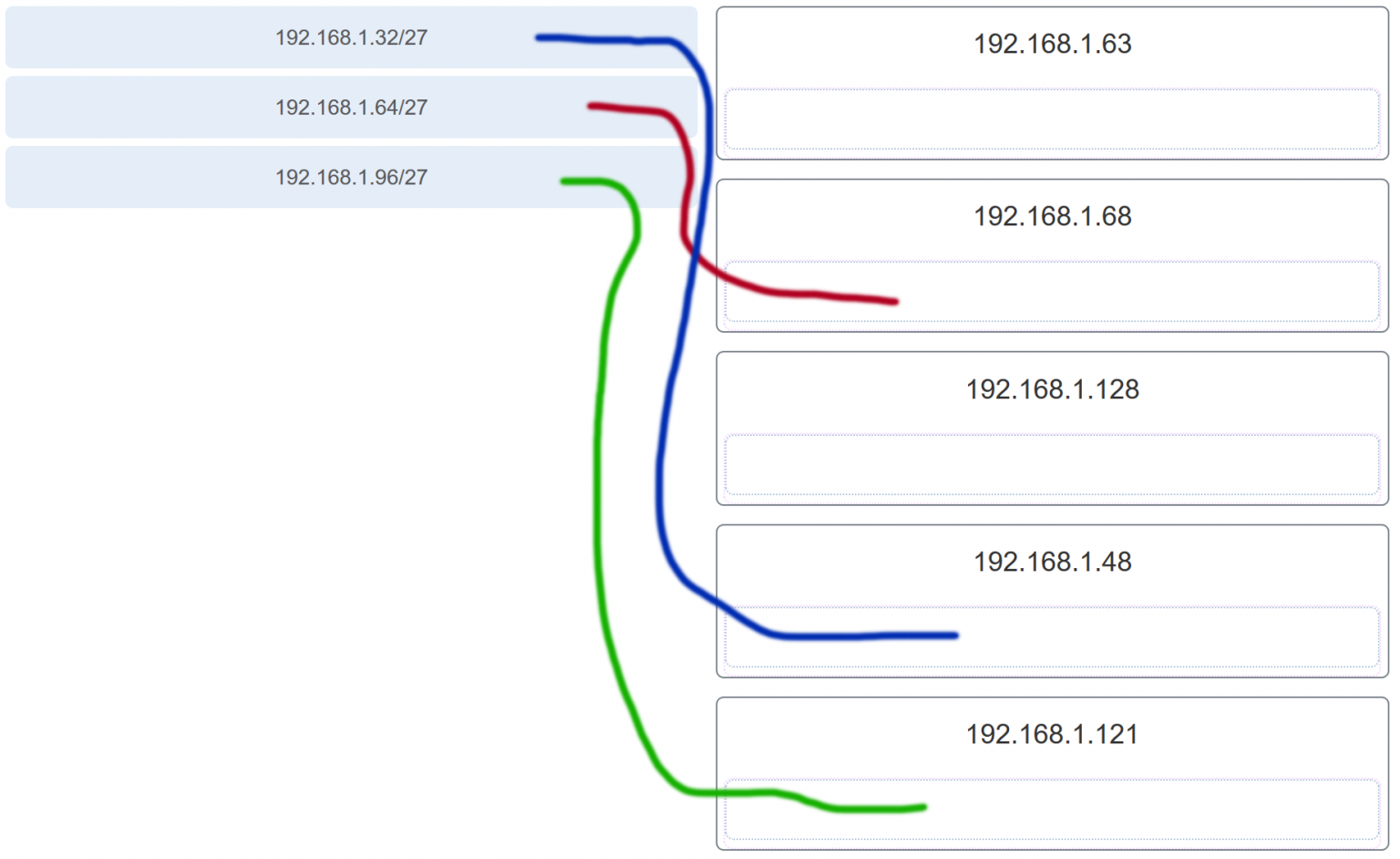
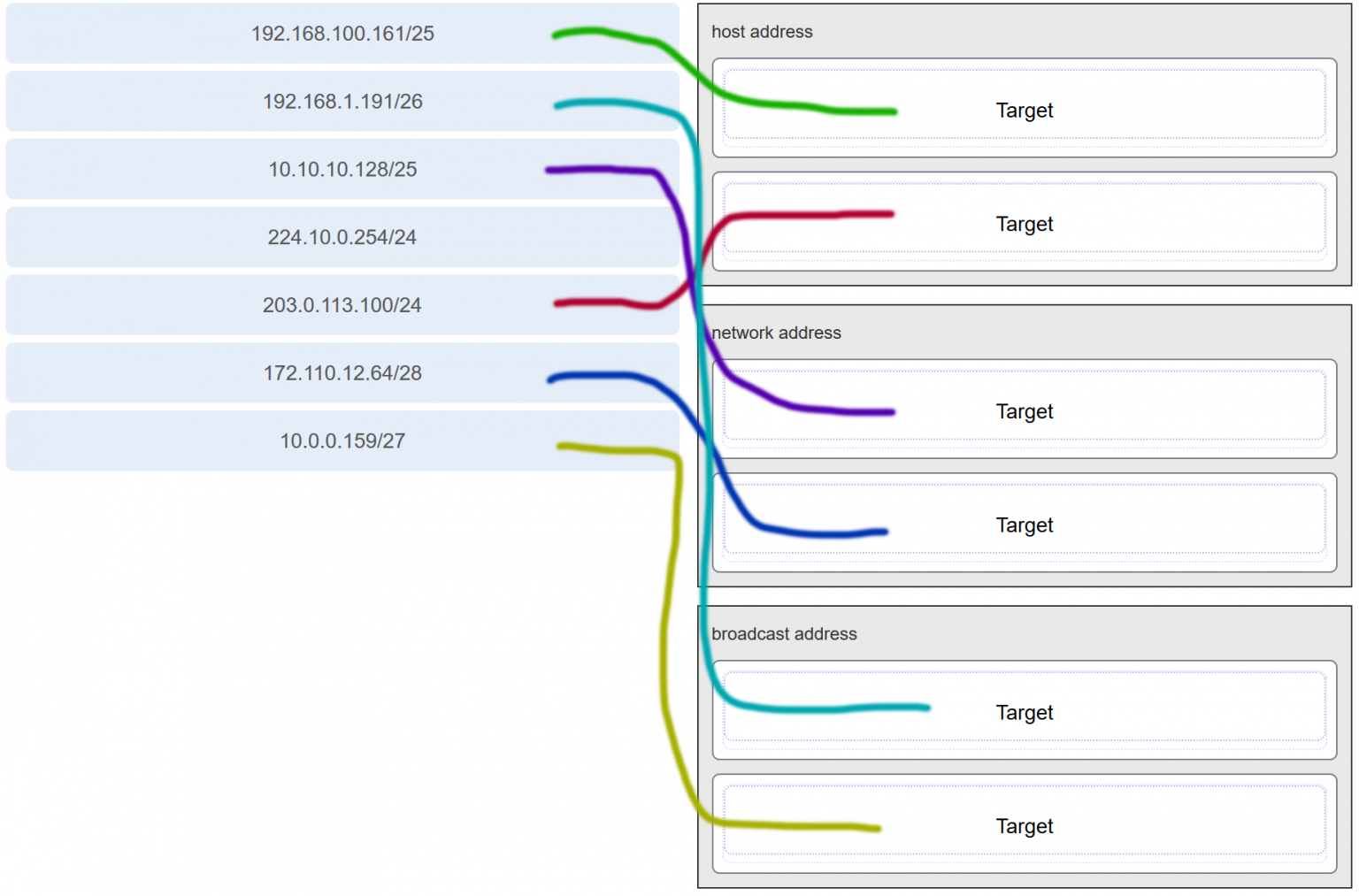
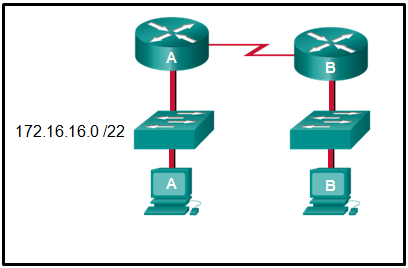
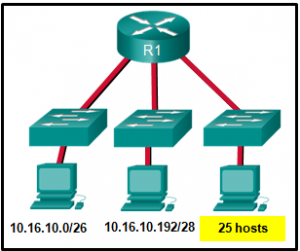
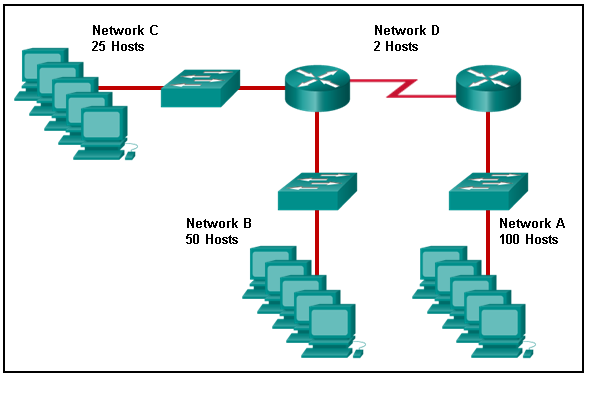
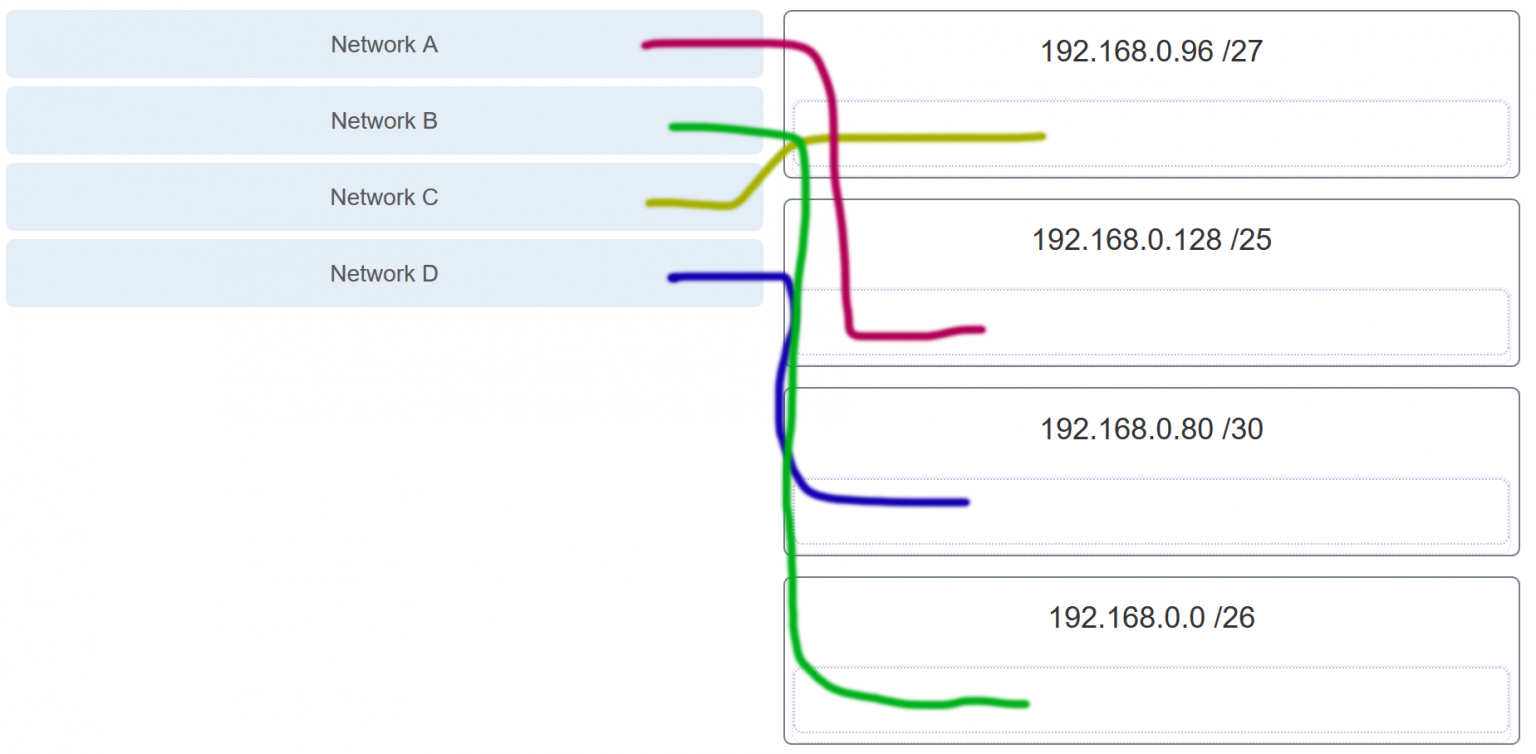
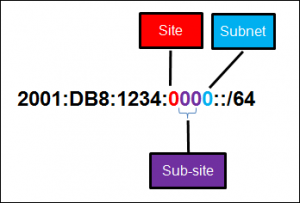

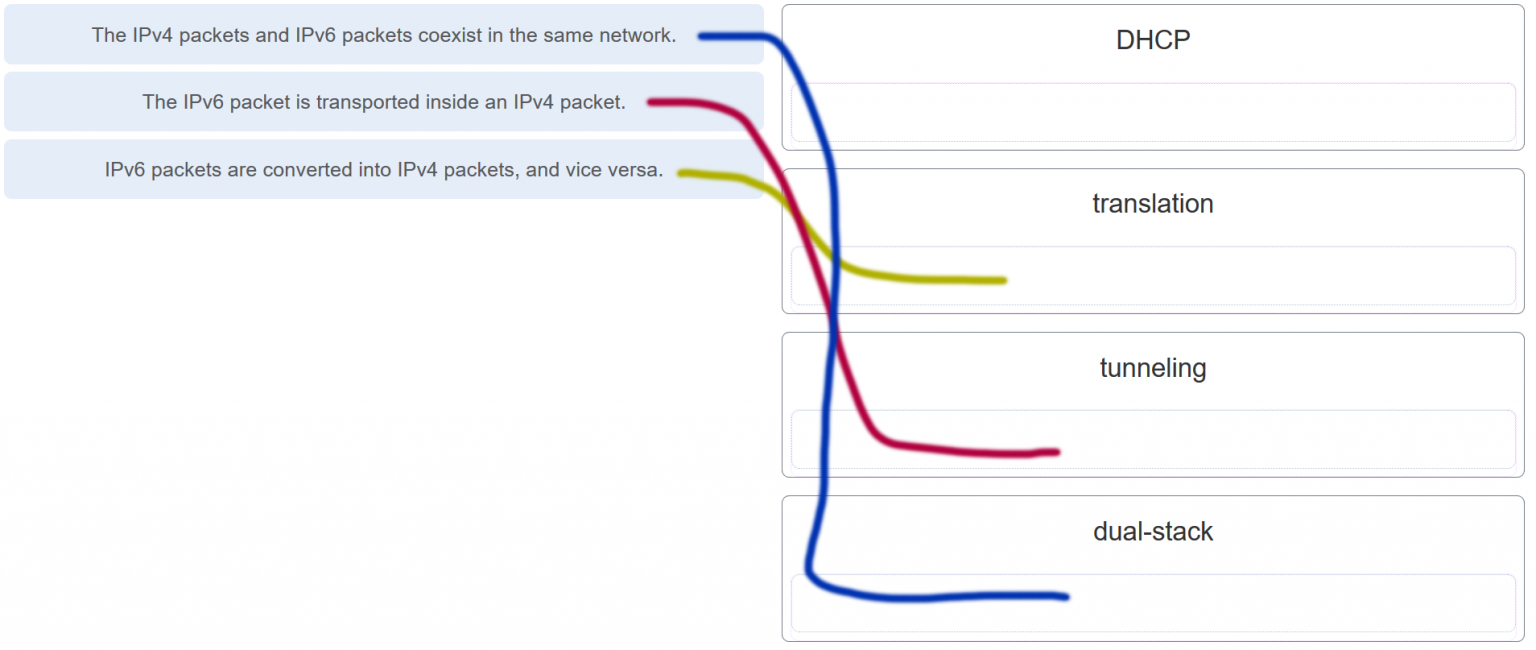
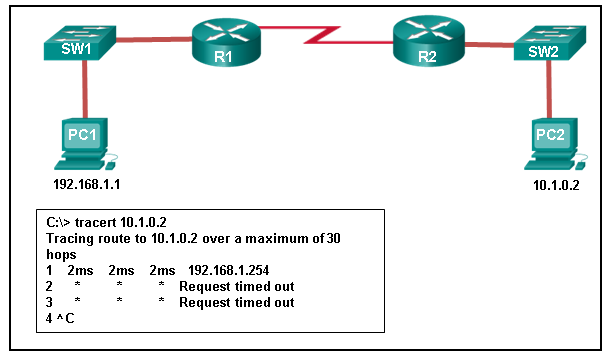
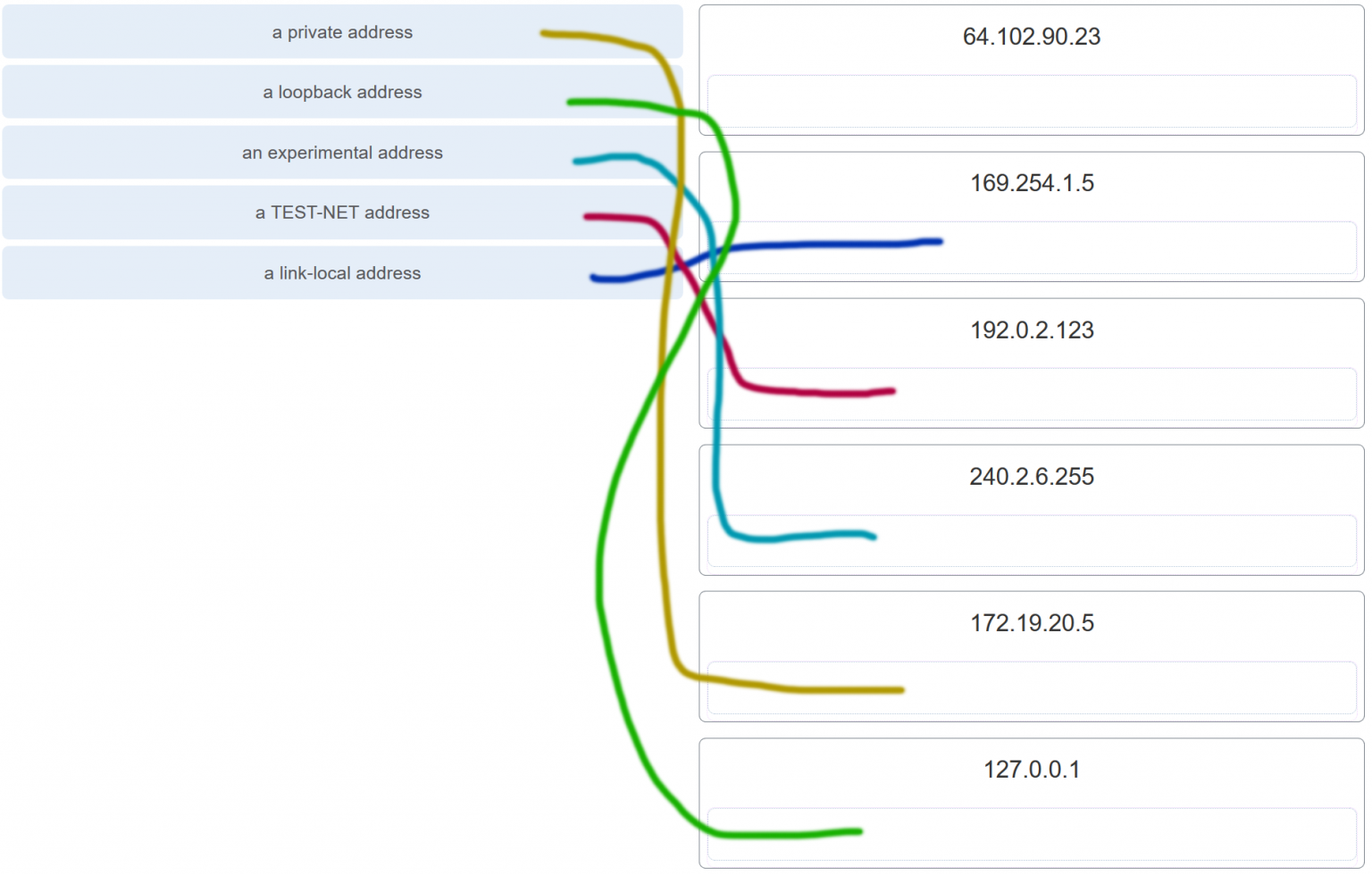
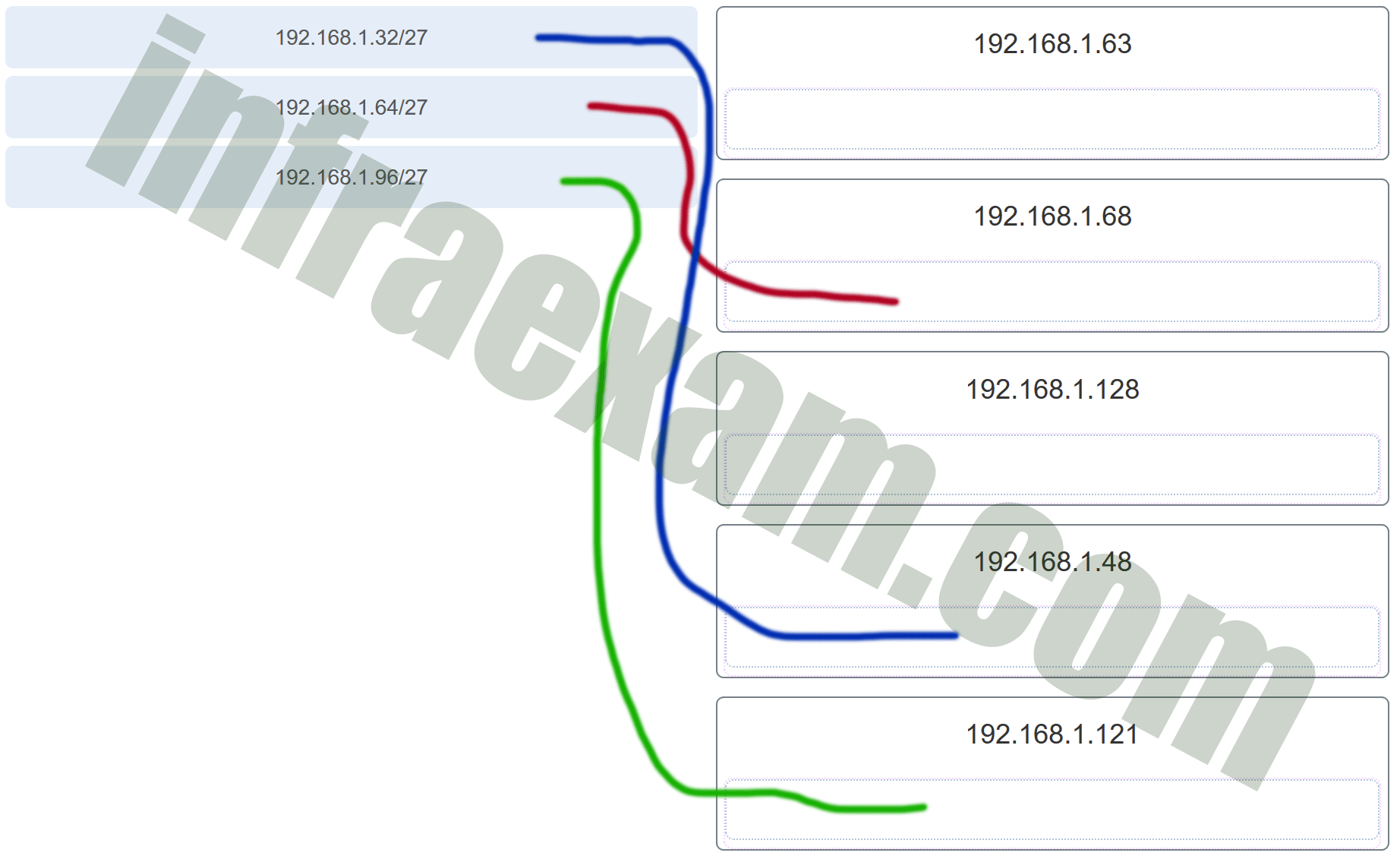
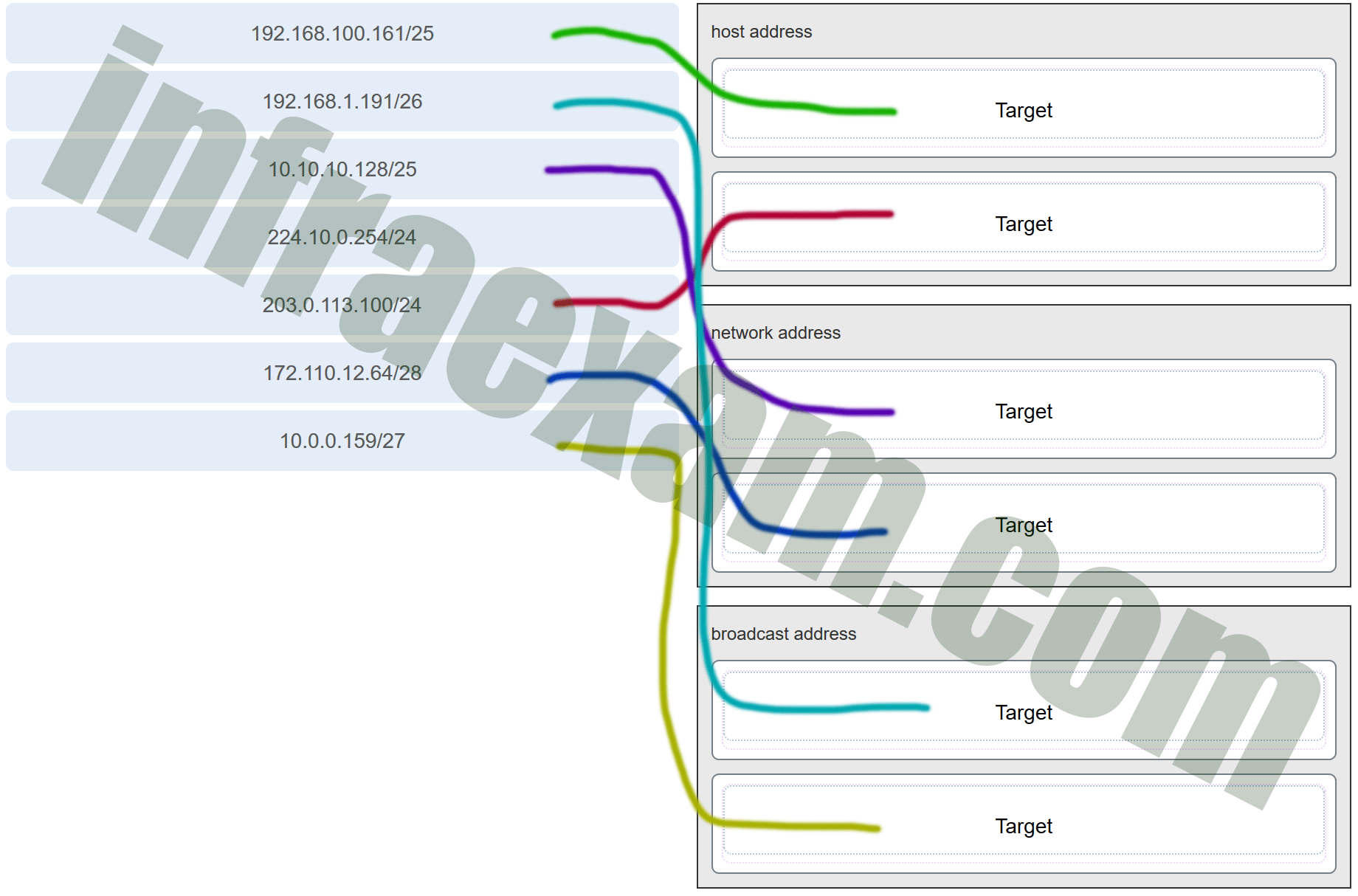
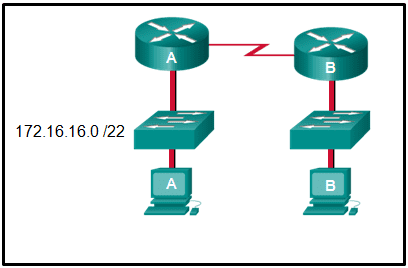
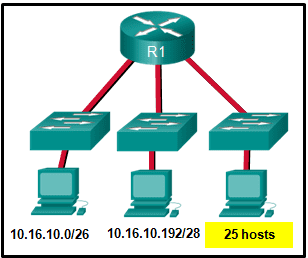
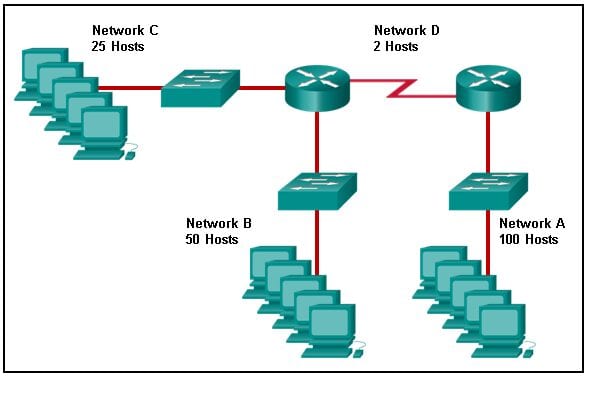
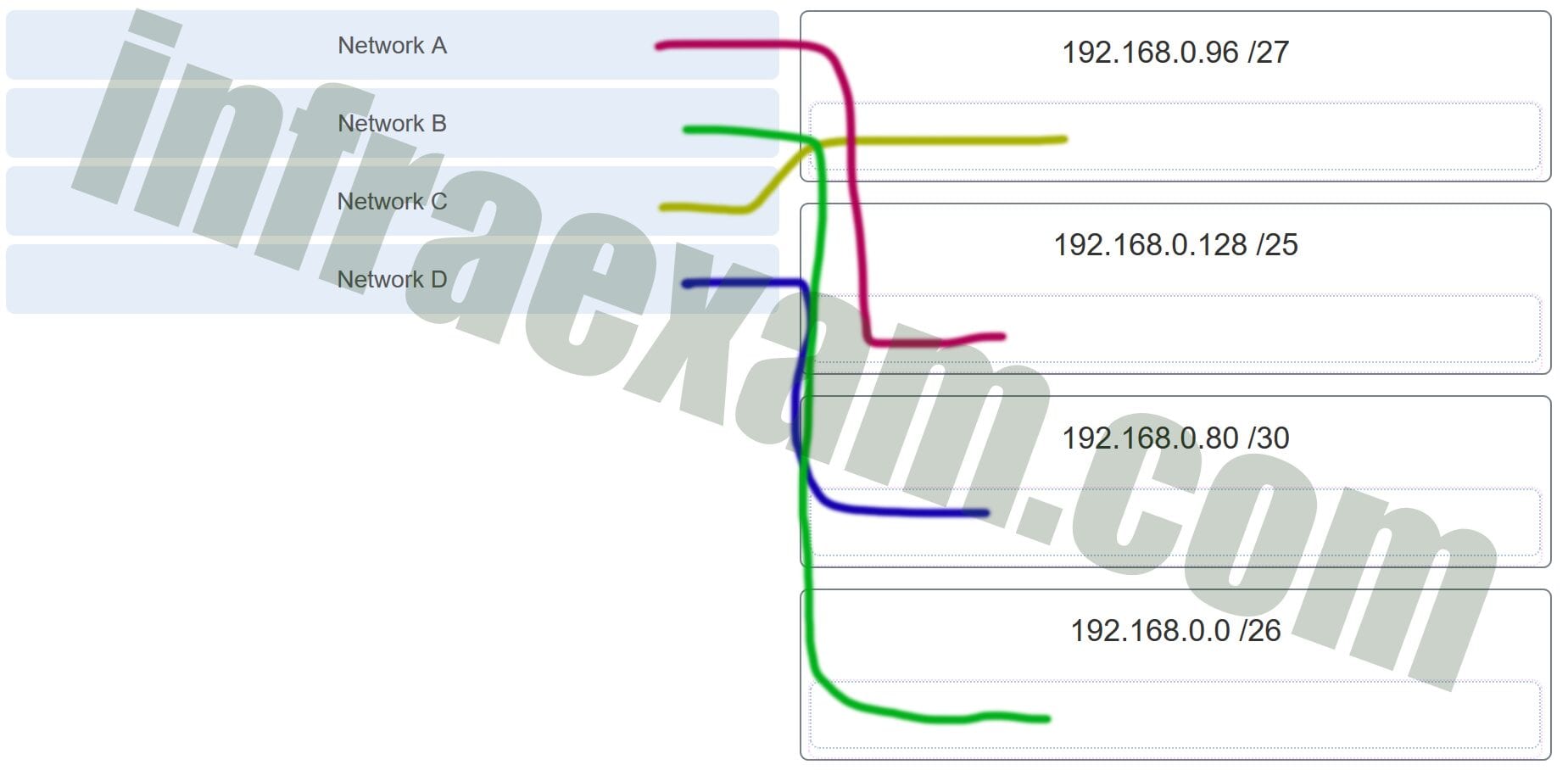
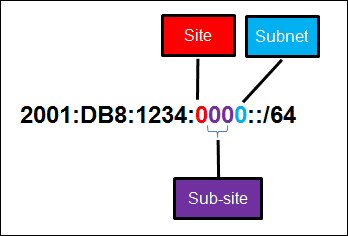
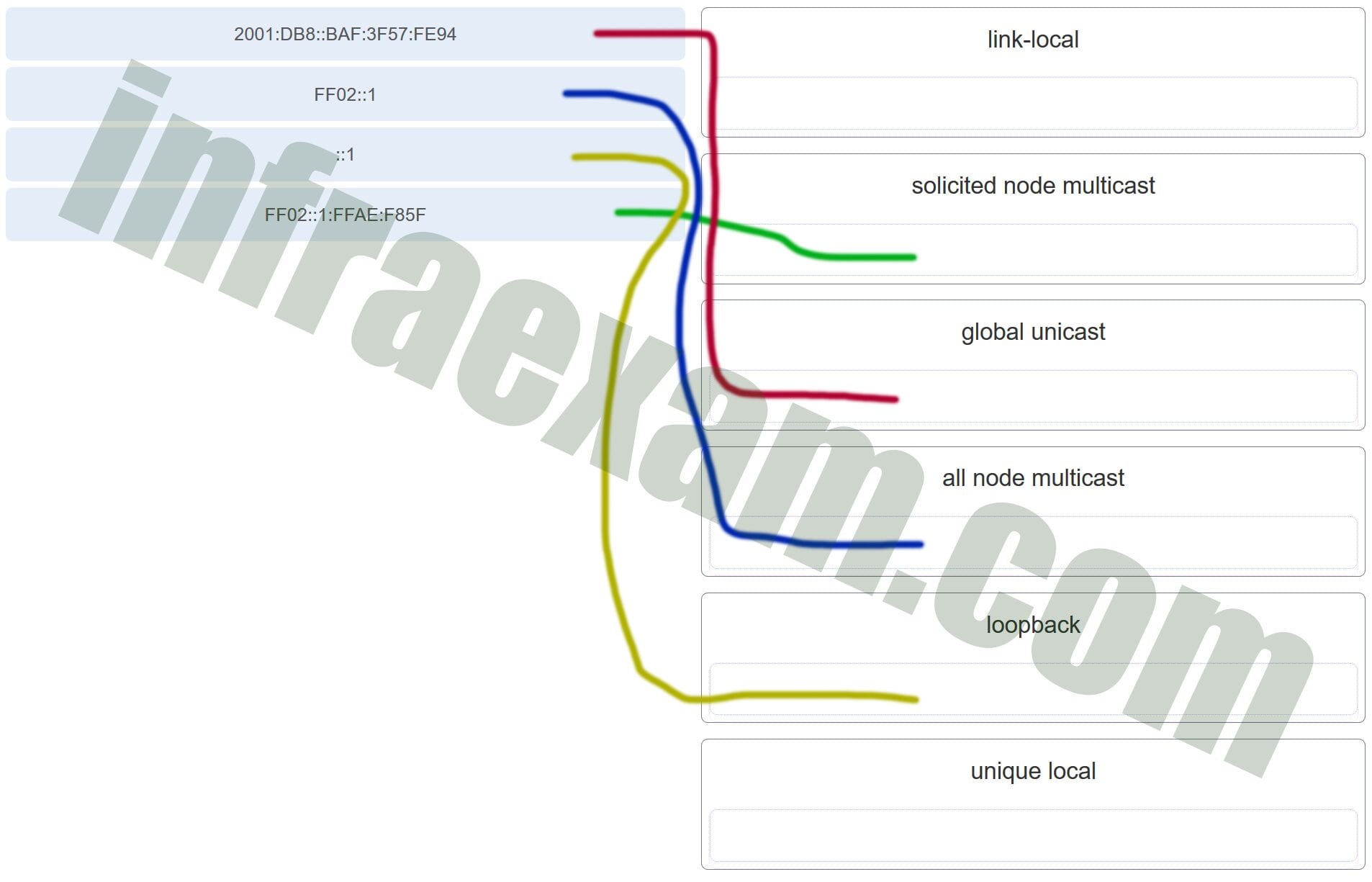
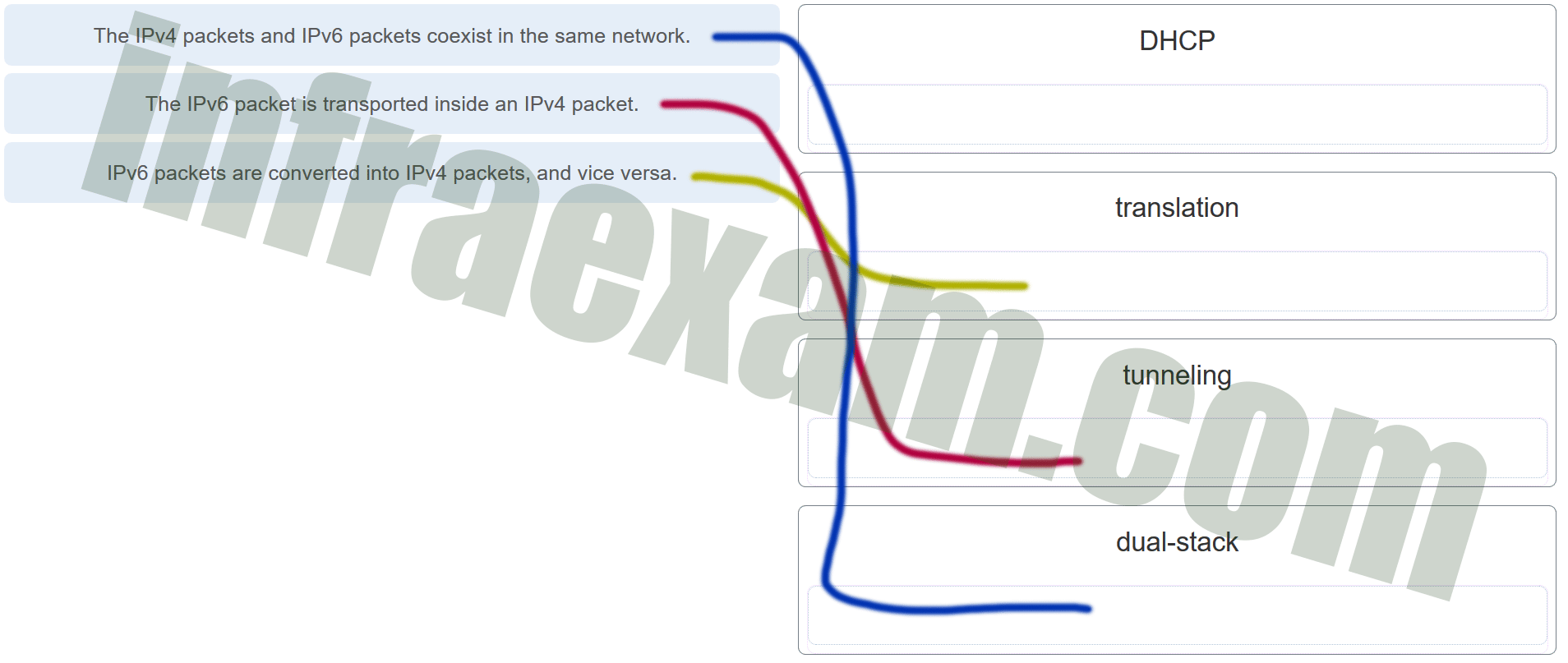
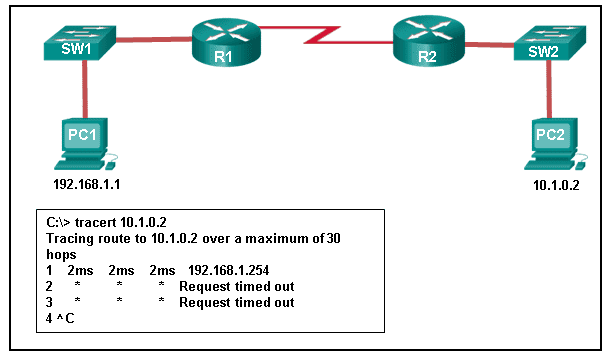
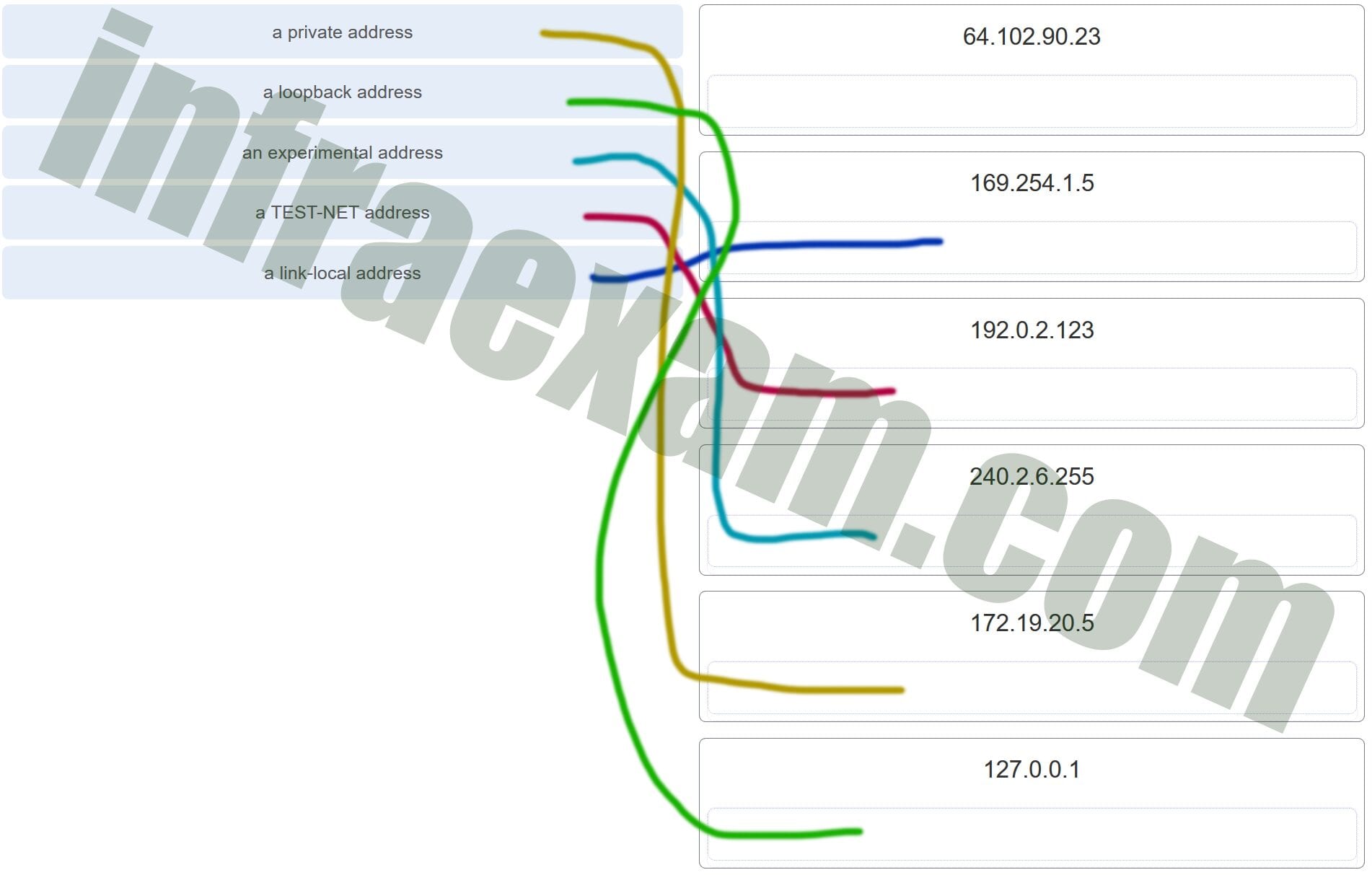















 можно использовать в адресе только один раз.
можно использовать в адресе только один раз.