How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
Introduction to Networks ( Version 7.00) – Modules 14 – 15: Network Application Communications Exam
1. Which action is performed by a client when establishing communication with a server via the use of UDP at the transport layer?
- The client sets the window size for the session.
- The client sends an ISN to the server to start the 3-way handshake.
- The client randomly selects a source port number.
- The client sends a synchronization segment to begin the session.
2. Which transport layer feature is used to guarantee session establishment?
- UDP ACK flag
- TCP 3-way handshake
- UDP sequence number
- TCP port number
3. What is the complete range of TCP and UDP well-known ports?
- 0 to 255
- 0 to 1023
- 256 – 1023
- 1024 – 49151
4. What is a socket?
- the combination of the source and destination IP address and source and destination Ethernet address
- the combination of a source IP address and port number or a destination IP address and port number
- the combination of the source and destination sequence and acknowledgment numbers
- the combination of the source and destination sequence numbers and port numbers
5. A PC is downloading a large file from a server. The TCP window is 1000 bytes. The server is sending the file using 100-byte segments. How many segments will the server send before it requires an acknowledgment from the PC?
- 1 segment
- 10 segments
- 100 segments
- 1000 segments
Explanation: With a window of 1000 bytes, the destination host accepts segments until all 1000 bytes of data have been received. Then the destination host sends an acknowledgment.
6. Which factor determines TCP window size?
- the amount of data to be transmitted
- the number of services included in the TCP segment
- the amount of data the destination can process at one time
- the amount of data the source is capable of sending at one time
Explanation: Window is the number of bytes that the sender will send prior to expecting an acknowledgement from the destination device. The initial window is agreed upon during the session startup via the three-way handshake between source and destination. It is determined by how much data the destination device of a TCP session is able to accept and process at one time.
7. What does a client do when it has UDP datagrams to send?
- It just sends the datagrams.
- It queries the server to see if it is ready to receive data.
- It sends a simplified three-way handshake to the server.
- It sends to the server a segment with the SYN flag set to synchronize the conversation.
Explanation: When a client has UDP datagrams to send, it just sends the datagrams.
8. Which three fields are used in a UDP segment header? (Choose three.)
- Window Size
- Length
- Source Port
- Acknowledgment Number
- Checksum
- Sequence Number
Explanation: A UDP header consists of only the Source Port, Destination Port, Length, and Checksum fields. Sequence Number, Acknowledgment Number, and Window Size are TCP header fields.
9. What are two roles of the transport layer in data communication on a network? (Choose two.)
- identifying the proper application for each communication stream
- tracking the individual communication between applications on the source and destination hosts
- providing frame delimiting to identify bits making up a frame
- performing a cyclic redundancy check on the frame for errors
- providing the interface between applications and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted
Explanation: The transport layer has several responsibilities. The primary responsibilities include the following:
- Tracking the individual communication streams between applications on the source and destination hosts
- Segmenting data at the source and reassembling the data at the destination
- Identifying the proper application for each communication stream through the use of port numbers
10. What information is used by TCP to reassemble and reorder received segments?
- port numbers
- sequence numbers
- acknowledgment numbers
- fragment numbers
Explanation: At the transport layer, TCP uses the sequence numbers in the header of each TCP segment to reassemble the segments into the correct order.
11. What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
- timing and synchronization
- destination and source port numbers
- destination and source physical addresses
- destination and source logical network addresses
12. Which two characteristics are associated with UDP sessions? (Choose two.)
- Destination devices receive traffic with minimal delay.
- Transmitted data segments are tracked.
- Destination devices reassemble messages and pass them to an application.
- Received data is unacknowledged.
- Unacknowledged data packets are retransmitted.
Explanation:
TCP:
- Provides tracking of transmitted data segments
- Destination devices will acknowledge received data.
- Source devices will retransmit unacknowledged data.
UDP
- Destination devices will not acknowledge received data
- Headers use very little overhead and cause minimal delay.
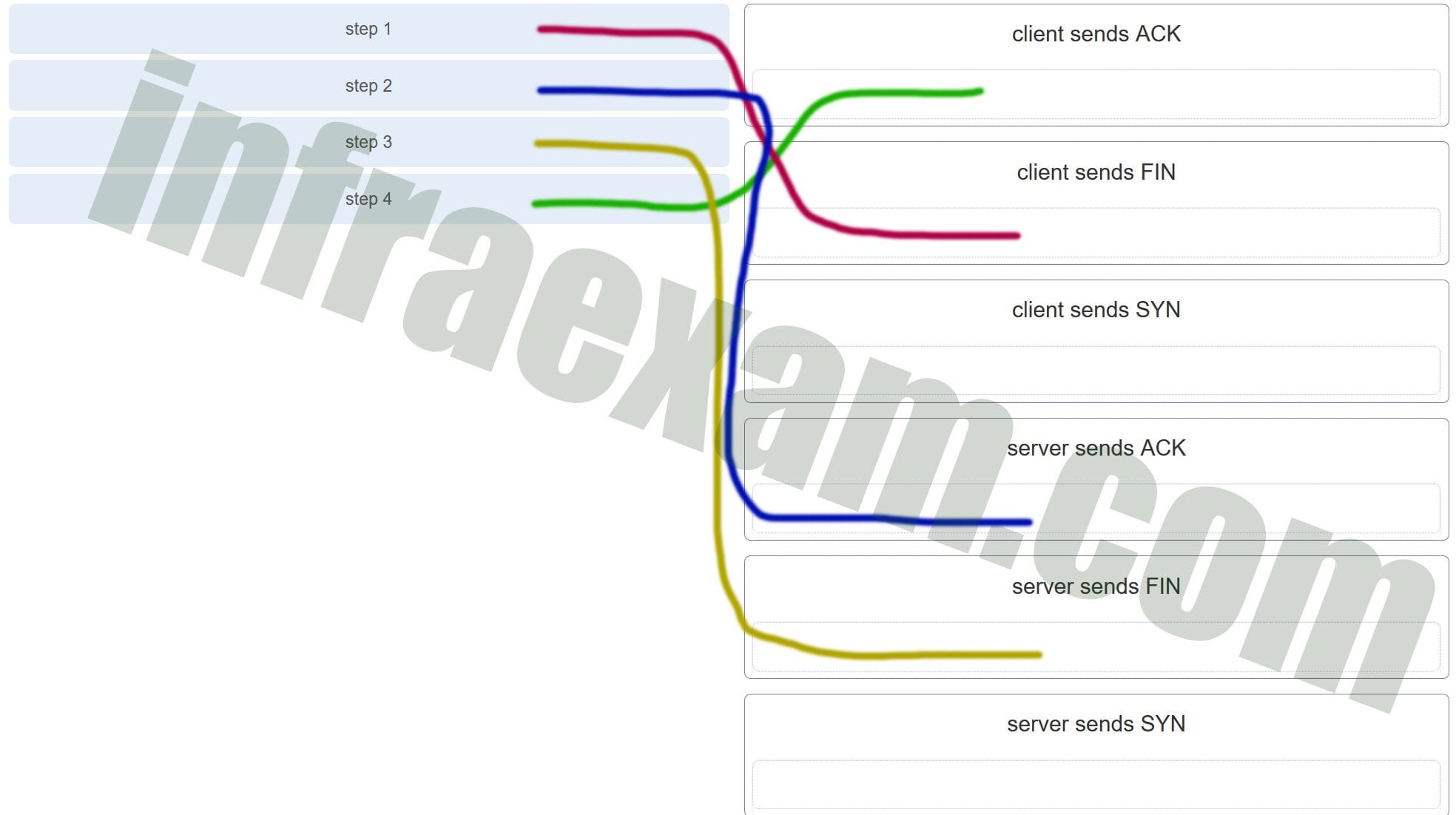
13. A client application needs to terminate a TCP communication session with a server. Place the termination process steps in the order that they will occur. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: In order to terminate a TCP session, the client sends to the server a segment with the FIN flag set. The server acknowledges the client by sending a segment with the ACK flag set. The server sends a FIN to the client to terminate the server to client session. The client acknowledges the termination by sending a segment with the ACK flag set.
14. Which flag in the TCP header is used in response to a received FIN in order to terminate connectivity between two network devices?
- FIN
- ACK
- SYN
- RST
Explanation: In a TCP session, when a device has no more data to send, it will send a segment with the FIN flag set. The connected device that receives the segment will respond with an ACK to acknowledge that segment. The device that sent the ACK will then send a FIN message to close the connection it has with the other device. The sending of the FIN should be followed with the receipt of an ACK from the other device.
15. Which protocol or service uses UDP for a client-to-server communication and TCP for server-to-server communication?
- HTTP
- FTP
- DNS
- SMTP
Explanation: Some applications may use both TCP and UDP. DNS uses UDP when clients send requests to a DNS server, and TCP when two DNS serves directly communicate.
16. What is a characteristic of UDP?
- UDP datagrams take the same path and arrive in the correct order at the destination.
- Applications that use UDP are always considered unreliable.
- UDP reassembles the received datagrams in the order they were received.
- UDP only passes data to the network when the destination is ready to receive the data.
Explanation: UDP has no way to reorder the datagrams into their transmission order, so UDP simply reassembles the data in the order it was received and forwards it to the application.
17. What kind of port must be requested from IANA in order to be used with a specific application?
- registered port
- private port
- dynamic port
- source port
Explanation: Registered ports (numbers 1024 to 49151) are assigned by IANA to a requesting entity to use with specific processes or applications. These processes are primarily individual applications that a user has chosen to install, rather than common applications that would receive a well-known port number. For example, Cisco has registered port 1985 for its Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP) process.
18. Which three application layer protocols use TCP? (Choose three.)
- SMTP
- FTP
- SNMP
- HTTP
- TFTP
- DHCP
Explanation: Some protocols require the reliable data transport that is provided by TCP. In addition, these protocols do not have real time communication requirements and can tolerate some data loss while minimizing protocol overhead. Examples of these protocols are SMTP, FTP, and HTTP.
19. Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
- UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.
- UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
- UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection.
- UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.
- UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
- UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
Explanation: UDP is a simple protocol that provides the basic transport layer functions. It has much lower overhead than TCP because it is not connection-oriented and does not offer the sophisticated retransmission, sequencing, and flow control mechanisms that provide reliability.
20. Which two fields are included in the TCP header but not in the UDP header? (Choose two.)
- window
- checksum
- source port
- destination port
- sequence number
Explanation: The sequence number and window fields are included in the TCP header but not in the UDP header.
21. Which field in the TCP header indicates the status of the three-way handshake process?
- window
- reserved
- checksum
- control bits
Explanation: The value in the control bits field of theTCP header indicates the progress and status of the connection.
22. Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
- to ensure the fastest possible download speed
- because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
- because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
- because HTTP requires reliable delivery
Explanation: When a host requests a web page, transmission reliability and completeness must be guaranteed. Therefore, HTTP uses TCP as its transport layer protocol.
23. Which two types of applications are best suited for UDP? (Choose two.)
- applications that need data flow control
- applications that require reliable delivery
- applications that handle reliability themselves
- applications that need the reordering of segments
- applications that can tolerate some data loss, but require little or no delay
Explanation: Applications that can tolerate some data loss, require a simple request and reply, and handle reliability themselves are best suited for UDP. UDP has low overhead and no requirement of reliability. TCP provides services for reliability, controlling data flow, and the reordering of segments.
24. How are port numbers used in the TCP/IP encapsulation process?
- Source port numbers and destination port numbers are not necessary when UDP is the transport layer protocol being used for the communication.
- Source port and destination port numbers are randomly generated.
- If multiple conversations occur that are using the same service, the source port number is used to track the separate conversations.
- Destination port numbers are assigned automatically and cannot be changed.
Explanation: Both UDP and TCP use port numbers to provide a unique identifier for each conversation. Source port numbers are randomly generated and are used to track different conversations. Destination port numbers identify specific services by using either a default port number for the service or a port number that is assigned manually by a system administrator.
25. In what two situations would UDP be better than TCP as the preferred transport protocol? (Choose two.)
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
Explanation: UDP is a very simple transport layer protocol that does not guarantee delivery. Devices on both ends of the conversation are not required to keep track of the conversation. UDP is used as the transport protocol for applications that need a speedy, best-effort delivery.
26. What are three responsibilities of the transport layer? (Choose three.)
- meeting the reliability requirements of applications, if any
- multiplexing multiple communication streams from many users or applications on the same network
- identifying the applications and services on the client and server that should handle transmitted data
- directing packets towards the destination network
- formatting data into a compatible form for receipt by the destination devices
- conducting error detection of the contents in frames
Explanation: The transport layer has several responsibilities. Some of the primary responsibilities include the following:
Tracking the individual communication streams between applications on the source and destination hosts
Segmenting data at the source and reassembling the data at the destination
Identifying the proper application for each communication stream through the use of port numbers
Multiplexing the communications of multiple users or applications over a single network
Managing the reliability requirements of applications
27. Which three statements describe a DHCP Discover message? (Choose three.)
- The source MAC address is 48 ones (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF).
- The destination IP address is 255.255.255.255.
- The message comes from a server offering an IP address.
- The message comes from a client seeking an IP address.
- All hosts receive the message, but only a DHCP server replies.
- Only the DHCP server receives the message.
Explanation: When a host configured to use DHCP powers up on a network it sends a DHCPDISCOVER message. FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF is the L2 broadcast address. A DHCP server replies with a unicast DHCPOFFER message back to the host.
28. Which two protocols may devices use in the application process that sends email? (Choose two.)
- HTTP
- SMTP
- POP
- IMAP
- DNS
- POP3
Explanation: POP, POP3, and IMAP are protocols that are used to retrieve email from servers. SMTP is the default protocol that is used to send email. DNS may be used by the sender email server to find the address of the destination email server.
29. What is true about the Server Message Block protocol?
- Different SMB message types have a different format.
- Clients establish a long term connection to servers.
- SMB messages cannot authenticate a session.
- SMB uses the FTP protocol for communication.
Explanation: The Server Message Block protocol is a protocol for file, printer, and directory sharing. Clients establish a long term connection to servers and when the connection is active, the resources can be accessed. Every SMB message has the same format. The use of SMB differs from FTP mainly in the length of the sessions. SMB messages can authenticate sessions.
30. What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
- to request an HTML page from a web server
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
Explanation: There are three common HTTP message types:
- GET – used by clients to request data from the web server
- POST – used by clients to upload data to a web server
- PUT – used by clients to upload data to a web server
31. Which OSI layer provides the interface between the applications used to communicate and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted?
- application
- presentation
- session
- transport
Explanation: The application layer is the layer that is closest to the end user and provides the interface between the underlying network and the applications used to communicate.
32. Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
- peer-to-peer
- master-slave
- client/server
- point-to-point
Explanation: In the client/server network model, a network device assumes the role of server in order to provide a particular service such as file transfer and storage. In the client/server network model, a dedicated server does not have to be used, but if one is present, the network model being used is the client/server model. In contrast, a peer-to-peer network does not have a dedicated server.
33. What do the client/server and peer-to-peer network models have in common?
- Both models have dedicated servers.
- Both models support devices in server and client roles.
- Both models require the use of TCP/IP-based protocols.
- Both models are used only in the wired network environment.
Explanation: In both the client/server and peer-to-peer network models, clients and servers exist. In peer-to-peer networks, no dedicated server exists, but a device can assume the server role to provide information to a device serving in the client role.
34. In what networking model would eDonkey, eMule, BitTorrent, Bitcoin, and LionShare be used?
- peer-to-peer
- client-based
- master-slave
- point-to-point
Explanation: In a peer-to-peer networking model, data is exchanged between two network devices without the use of a dedicated server. Peer-to-peer applications such as Shareaz, eDonkey, and Bitcoin allow one network device to assume the role of server, while one or more other network devices assume the role of client using the peer-to-peer application.
35. What is a common protocol that is used with peer-to-peer applications such as WireShare, Bearshare, and Shareaza?
- Ethernet
- Gnutella
- POP
- SMTP
Explanation: The Gnutella protocol is used when one user shares an entire file with another user. A person would load a Gnutella-based application such as gtk-gnutella or WireShare and use that application to locate and access resources shared by others.
36. What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
- wireless networking
- social networking without the Internet
- network printing using a print server
- resource sharing without a dedicated server
Explanation: The peer-to-peer (P2P) networking model allows data, printer, and resource sharing without a dedicated server.
37. The application layer of the TCP/IP model performs the functions of what three layers of the OSI model? (Choose three.)
- physical
- session
- network
- presentation
- data link
- transport
- application
Explanation: The network access layer of the TCP/IP model performs the same functions as the physical and data link layers of the OSI model. The internetwork layer equates to the network layer of the OSI model. The transport layers are the same in both models. The application layer of the TCP/IP model represents the session, presentation, and application layers of the OSI model.
38. What is an example of network communication that uses the client-server model?
- A user uses eMule to download a file that is shared by a friend after the file location is determined.
- A workstation initiates an ARP to find the MAC address of a receiving host.
- A user prints a document by using a printer that is attached to a workstation of a coworker.
- A workstation initiates a DNS request when the user types www.cisco.com in the address bar of a web browser.
Explanation: When a user types a domain name of a website into the address bar of a web browser, a workstation needs to send a DNS request to the DNS server for the name resolution process. This request is a client/server model application. The eMule application is P2P. Sharing a printer on a workstation is a peer-to-peer network. Using ARP is just a broadcast message sent by a host.
39. Which layer in the TCP/IP model is used for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data?
- internetwork
- session
- presentation
- application
- network access
Explanation: The application layer of the TCP/IP model performs the functions of three layers of the OSI model – application, presentation, and session. The application layer of the TCP/IP model is the layer that provides the interface between the applications, is responsible for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data, and is used to create and maintain dialogs between source and destination applications.
40. What is an advantage of SMB over FTP?
- Only with SMB can data transfers occur in both directions.
- Only SMB establishes two simultaneous connections with the client, making the data transfer faster.
- SMB is more reliable than FTP because SMB uses TCP and FTP uses UDP.
- SMB clients can establish a long-term connection to the server.
Explanation: SMB and FTP are client/server protocols that are used for file transfer. SMB allows the connecting device to access resources as if they were on the local client device. SMB and FTP use the TCP protocol for connection establishment and they can transfer data in both directions. FTP requires two connections between the client and the server, one for commands and replies, the other for the actual file transfer.
41. A manufacturing company subscribes to certain hosted services from its ISP. The services that are required include hosted world wide web, file transfer, and e-mail. Which protocols represent these three key applications? (Choose three.)
- FTP
- HTTP
- DNS
- SNMP
- DHCP
- SMTP
Explanation: The ISP uses the HTTP protocol in conjunction with hosting web pages, the FTP protocol with file transfers, and SMTP with e-mail. DNS is used to translate domain names to IP addresses. SNMP is used for network management traffic. DHCP ic commonly used to manage IP addressing.
42. Which application layer protocol uses message types such as GET, PUT, and POST?
- DNS
- DHCP
- SMTP
- HTTP
- POP3
Explanation: The GET command is a client request for data from a web server. A PUT command uploads resources and content, such as images, to a web server. A POST command uploads data files to a web server.
43. What type of information is contained in a DNS MX record?
- the FQDN of the alias used to identify a service
- the IP address for an FQDN entry
- the domain name mapped to mail exchange servers
- the IP address of an authoritative name server
Explanation: MX, or mail exchange messages, are used to map a domain name to several mail exchange servers that all belong to the same domain.
44. Which three protocols operate at the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- ARP
- TCP
- UDP
- FTP
- POP3
- DHCP
Explanation: FTP, DHCP, and POP3 are application layer protocols. TCP and UDP are transport layer protocols. ARP is a network layer protocol.
45. Which protocol is used by a client to communicate securely with a web server?
- SMTP
- SMB
- IMAP
- HTTPS
Explanation: HTTPS is a secure form of HTTP used to access web content hosted by a web server.
46. Which applications or services allow hosts to act as client and server at the same time?
- client/server applications
- email applications
- P2P applications
- authentication services
Explanation: P2P applications allow the clients to behave as servers if needed. When using authentication services, email exchange, and client/server applications, one host acts as server and the other acts as client at all times.
47. What are two characteristics of peer-to-peer networks? (Choose two.)
- scalability
- one way data flow
- decentralized resources
- centralized user accounts
- resource sharing without a dedicated server
Explanation: Peer-to-peer networks have decentralized resources because every computer can serve as both a server and a client. One computer might assume the role of server for one transaction while acting as a client for another transaction. Peer-to-peer networks can share resources among network devices without the use of a dedicated server.
48. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
Explanation: The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
49. Which three layers of the OSI model provide similar network services to those provided by the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- physical layer
- session layer
- transport layer
- application layer
- presentation layer
- data link layer
Explanation: The three upper layers of the OSI model, the session, presentation, and application layers, provide application services similar to those provided by the TCP/IP model application layer. Lower layers of the OSI model are more concerned with data flow.
50. A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received two packets of data from the PC?
- 3001
- 6001
- 4500
- 6000
51. A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received three packets of data from the PC?
- 4501
- 6001
- 6000
- 4500
52. A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received four packets of data from the PC?
- 6001
- 3001
- 1501
- 1500
60. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting TFTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 69
- 67
- 53
- 80
61. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting FTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 21
- 69
- 67
- 80
62. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SSH service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 22
- 69
- 67
- 80
63. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting HTTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 80
- 67
- 53
- 69
64. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting POP3 service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 110
- 67
- 53
- 69
- 443
- 161
- 80
65. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting telnet service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 23
- 443
- 161
- 110
67. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SNMP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 161
- 443
- 110
- 80
68. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SMTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 25
- 443
- 161
- 110
69. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting HTTPS service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 443
- 161
- 110
- 80
Last Updated on February 1, 2021 by
Cisco Netacad ITN Version 7.00 CCNA 1 v7 Modules 14 – 15: Network Application Communications Exam Answers 2020 2021 – Introduction to Networks
-
A PC is downloading a large file from a server. The TCP window is 1000 bytes. The server is sending the file using 100-byte segments. How many segments will the server send before it requires an acknowledgment from the PC?
- 1 segment
- 10 segments
- 100 segments
- 1000 segments
Answers Explanation & Hints:
With a window of 1000 bytes, the destination host accepts segments until all 1000 bytes of data have been received. Then the destination host sends an acknowledgment.
-
Which factor determines TCP window size?
- the amount of data to be transmitted
- the number of services included in the TCP segment
- the amount of data the destination can process at one time
- the amount of data the source is capable of sending at one time
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Window is the number of bytes that the sender will send prior to expecting an acknowledgement from the destination device. The initial window is agreed upon during the session startup via the three-way handshake between source and destination. It is determined by how much data the destination device of a TCP session is able to accept and process at one time.
-
What does a client do when it has UDP datagrams to send?
- It just sends the datagrams.
- It queries the server to see if it is ready to receive data.
- It sends a simplified three-way handshake to the server.
- It sends to the server a segment with the SYN flag set to synchronize the conversation.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a client has UDP datagrams to send, it just sends the datagrams.
-
Which three fields are used in a UDP segment header? (Choose three.)
- Window Size
- Length
- Source Port
- Acknowledgment Number
- Checksum
- Sequence Number
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A UDP header consists of only the Source Port, Destination Port, Length, and Checksum fields. Sequence Number, Acknowledgment Number, and Window Size are TCP header fields.
-
What are two roles of the transport layer in data communication on a network? (Choose two.)
- identifying the proper application for each communication stream
- tracking the individual communication between applications on the source and destination hosts
- providing frame delimiting to identify bits making up a frame
- performing a cyclic redundancy check on the frame for errors
- providing the interface between applications and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The transport layer has several responsibilities. The primary responsibilities include the following:
Tracking the individual communication streams between applications on the source and destination hosts
Segmenting data at the source and reassembling the data at the destination
Identifying the proper application for each communication stream through the use of port numbers
-
What information is used by TCP to reassemble and reorder received segments?
- port numbers
- sequence numbers
- acknowledgment numbers
- fragment numbers
Answers Explanation & Hints:
At the transport layer, TCP uses the sequence numbers in the header of each TCP segment to reassemble the segments into the correct order.
-
What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
- timing and synchronization
- destination and source port numbers
- destination and source physical addresses
- destination and source logical network addresses
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The destination and source port numbers are used to identify exactly which protocol and process is requesting or responding to a request.
-
Which two characteristics are associated with UDP sessions? (Choose two.)
- Destination devices receive traffic with minimal delay.
- Transmitted data segments are tracked.
- Destination devices reassemble messages and pass them to an application.
- Received data is unacknowledged.
- Unacknowledged data packets are retransmitted.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
TCP:
· Provides tracking of transmitted data segments
· Destination devices will acknowledge received data.
· Source devices will retransmit unacknowledged data.UDP
· Destination devices will not acknowledge received data
· Headers use very little overhead and cause minimal delay.
-
A client application needs to terminate a TCP communication session with a server. Place the termination process steps in the order that they will occur. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Modules 14 – 15 Network Application Communications Exam Answers 001
Answers Explanation & Hints:In order to terminate a TCP session, the client sends to the server a segment with the FIN flag set. The server acknowledges the client by sending a segment with the ACK flag set. The server sends a FIN to the client to terminate the server to client session. The client acknowledges the termination by sending a segment with the ACK flag set.
-
Which flag in the TCP header is used in response to a received FIN in order to terminate connectivity between two network devices?
- FIN
- ACK
- SYN
- RST
Answers Explanation & Hints:
In a TCP session, when a device has no more data to send, it will send a segment with the FIN flag set. The connected device that receives the segment will respond with an ACK to acknowledge that segment. The device that sent the ACK will then send a FIN message to close the connection it has with the other device. The sending of the FIN should be followed with the receipt of an ACK from the other device.
-
Which protocol or service uses UDP for a client-to-server communication and TCP for server-to-server communication?
- HTTP
- FTP
- DNS
- SMTP
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Some applications may use both TCP and UDP. DNS uses UDP when clients send requests to a DNS server, and TCP when two DNS serves directly communicate.
-
What is a characteristic of UDP?
- UDP datagrams take the same path and arrive in the correct order at the destination.
- Applications that use UDP are always considered unreliable.
- UDP reassembles the received datagrams in the order they were received.
- UDP only passes data to the network when the destination is ready to receive the data.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
UDP has no way to reorder the datagrams into their transmission order, so UDP simply reassembles the data in the order it was received and forwards it to the application.
-
What kind of port must be requested from IANA in order to be used with a specific application?
- registered port
- private port
- dynamic port
- source port
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Registered ports (numbers 1024 to 49151) are assigned by IANA to a requesting entity to use with specific processes or applications. These processes are primarily individual applications that a user has chosen to install, rather than common applications that would receive a well-known port number. For example, Cisco has registered port 1985 for its Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP) process.
-
Which three application layer protocols use TCP? (Choose three.)
- SMTP
- FTP
- SNMP
- HTTP
- TFTP
- DHCP
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Some protocols require the reliable data transport that is provided by TCP. In addition, these protocols do not have real time communication requirements and can tolerate some data loss while minimizing protocol overhead. Examples of these protocols are SMTP, FTP, and HTTP.
-
Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
- UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.
- UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
- UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection.
- UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.
- UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
- UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
UDP is a simple protocol that provides the basic transport layer functions. It has much lower overhead than TCP because it is not connection-oriented and does not offer the sophisticated retransmission, sequencing, and flow control mechanisms that provide reliability.
-
Which two fields are included in the TCP header but not in the UDP header? (Choose two.)
- window
- checksum
- source port
- destination port
- sequence number
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The sequence number and window fields are included in the TCP header but not in the UDP header.
-
Which field in the TCP header indicates the status of the three-way handshake process?
- window
- reserved
- checksum
- control bits
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The value in the control bits field of theTCP header indicates the progress and status of the connection.
-
Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
- to ensure the fastest possible download speed
- because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
- because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
- because HTTP requires reliable delivery
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a host requests a web page, transmission reliability and completeness must be guaranteed. Therefore, HTTP uses TCP as its transport layer protocol.
-
Which two types of applications are best suited for UDP? (Choose two.)
- applications that need data flow control
- applications that require reliable delivery
- applications that handle reliability themselves
- applications that need the reordering of segments
- applications that can tolerate some data loss, but require little or no delay
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Applications that can tolerate some data loss, require a simple request and reply, and handle reliability themselves are best suited for UDP. UDP has low overhead and no requirement of reliability. TCP provides services for reliability, controlling data flow, and the reordering of segments.
-
How are port numbers used in the TCP/IP encapsulation process?
- Source port numbers and destination port numbers are not necessary when UDP is the transport layer protocol being used for the communication.
- Source port and destination port numbers are randomly generated.
- If multiple conversations occur that are using the same service, the source port number is used to track the separate conversations.
- Destination port numbers are assigned automatically and cannot be changed.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Both UDP and TCP use port numbers to provide a unique identifier for each conversation. Source port numbers are randomly generated and are used to track different conversations. Destination port numbers identify specific services by using either a default port number for the service or a port number that is assigned manually by a system administrator.
-
In what two situations would UDP be better than TCP as the preferred transport protocol? (Choose two.)
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
Answers Explanation & Hints:
UDP is a very simple transport layer protocol that does not guarantee delivery. Devices on both ends of the conversation are not required to keep track of the conversation. UDP is used as the transport protocol for applications that need a speedy, best-effort delivery.
-
What are three responsibilities of the transport layer? (Choose three.)
- meeting the reliability requirements of applications, if any
- multiplexing multiple communication streams from many users or applications on the same network
- identifying the applications and services on the client and server that should handle transmitted data
- directing packets towards the destination network
- formatting data into a compatible form for receipt by the destination devices
- conducting error detection of the contents in frames
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The transport layer has several responsibilities. Some of the primary responsibilities include the following:
Tracking the individual communication streams between applications on the source and destination hosts
Segmenting data at the source and reassembling the data at the destination
Identifying the proper application for each communication stream through the use of port numbers
Multiplexing the communications of multiple users or applications over a single network
Managing the reliability requirements of applications
-
Which three statements describe a DHCP Discover message? (Choose three.)
- The source MAC address is 48 ones (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF).
- The destination IP address is 255.255.255.255.
- The message comes from a server offering an IP address.
- The message comes from a client seeking an IP address.
- All hosts receive the message, but only a DHCP server replies.
- Only the DHCP server receives the message.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a host configured to use DHCP powers up on a network it sends a DHCPDISCOVER message. FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF is the L2 broadcast address. A DHCP server replies with a unicast DHCPOFFER message back to the host.
-
Which two protocols may devices use in the application process that sends email? (Choose two.)
- HTTP
- SMTP
- POP
- IMAP
- DNS
- POP3
Answers Explanation & Hints:
POP, POP3, and IMAP are protocols that are used to retrieve email from servers. SMTP is the default protocol that is used to send email. DNS may be used by the sender email server to find the address of the destination email server.
-
What is true about the Server Message Block protocol?
- Different SMB message types have a different format.
- Clients establish a long term connection to servers.
- SMB messages cannot authenticate a session.
- SMB uses the FTP protocol for communication.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The Server Message Block protocol is a protocol for file, printer, and directory sharing. Clients establish a long term connection to servers and when the connection is active, the resources can be accessed. Every SMB message has the same format. The use of SMB differs from FTP mainly in the length of the sessions. SMB messages can authenticate sessions.
-
What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
- to request an HTML page from a web server
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
Answers Explanation & Hints:
There are three common HTTP message types:GET – used by clients to request data from the web server
POST – used by clients to upload data to a web server
PUT – used by clients to upload data to a web server
-
Which OSI layer provides the interface between the applications used to communicate and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted?
- application
- presentation
- session
- transport
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The application layer is the layer that is closest to the end user and provides the interface between the underlying network and the applications used to communicate.
-
Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
- peer-to-peer
- master-slave
- client/server
- point-to-point
Answers Explanation & Hints:
In the client/server network model, a network device assumes the role of server in order to provide a particular service such as file transfer and storage. In the client/server network model, a dedicated server does not have to be used, but if one is present, the network model being used is the client/server model. In contrast, a peer-to-peer network does not have a dedicated server.
-
What do the client/server and peer-to-peer network models have in common?
- Both models have dedicated servers.
- Both models support devices in server and client roles.
- Both models require the use of TCP/IP-based protocols.
- Both models are used only in the wired network environment.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
In both the client/server and peer-to-peer network models, clients and servers exist. In peer-to-peer networks, no dedicated server exists, but a device can assume the server role to provide information to a device serving in the client role.
-
In what networking model would eDonkey, eMule, BitTorrent, Bitcoin, and LionShare be used?
- peer-to-peer
- client-based
- master-slave
- point-to-point
Answers Explanation & Hints:
In a peer-to-peer networking model, data is exchanged between two network devices without the use of a dedicated server. Peer-to-peer applications such as Shareaz, eDonkey, and Bitcoin allow one network device to assume the role of server, while one or more other network devices assume the role of client using the peer-to-peer application.
-
What is a common protocol that is used with peer-to-peer applications such as WireShare, Bearshare, and Shareaza?
- Ethernet
- Gnutella
- POP
- SMTP
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The Gnutella protocol is used when one user shares an entire file with another user. A person would load a Gnutella-based application such as gtk-gnutella or WireShare and use that application to locate and access resources shared by others.
-
What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
- wireless networking
- social networking without the Internet
- network printing using a print server
- resource sharing without a dedicated server
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The peer-to-peer (P2P) networking model allows data, printer, and resource sharing without a dedicated server.
-
The application layer of the TCP/IP model performs the functions of what three layers of the OSI model? (Choose three.)
- physical
- session
- network
- presentation
- data link
- transport
- application
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The network access layer of the TCP/IP model performs the same functions as the physical and data link layers of the OSI model. The internetwork layer equates to the network layer of the OSI model. The transport layers are the same in both models. The application layer of the TCP/IP model represents the session, presentation, and application layers of the OSI model.
-
What is an example of network communication that uses the client-server model?
- A user uses eMule to download a file that is shared by a friend after the file location is determined.
- A workstation initiates an ARP to find the MAC address of a receiving host.
- A user prints a document by using a printer that is attached to a workstation of a coworker.
- A workstation initiates a DNS request when the user types www.cisco.com in the address bar of a web browser.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a user types a domain name of a website into the address bar of a web browser, a workstation needs to send a DNS request to the DNS server for the name resolution process. This request is a client/server model application. The eMule application is P2P. Sharing a printer on a workstation is a peer-to-peer network. Using ARP is just a broadcast message sent by a host.
-
Which layer in the TCP/IP model is used for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data?
- internetwork
- session
- presentation
- application
- network access
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The application layer of the TCP/IP model performs the functions of three layers of the OSI model – application, presentation, and session. The application layer of the TCP/IP model is the layer that provides the interface between the applications, is responsible for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data, and is used to create and maintain dialogs between source and destination applications.
-
What is an advantage of SMB over FTP?
- Only with SMB can data transfers occur in both directions.
- Only SMB establishes two simultaneous connections with the client, making the data transfer faster.
- SMB is more reliable than FTP because SMB uses TCP and FTP uses UDP.
- SMB clients can establish a long-term connection to the server.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
SMB and FTP are client/server protocols that are used for file transfer. SMB allows the connecting device to access resources as if they were on the local client device. SMB and FTP use the TCP protocol for connection establishment and they can transfer data in both directions. FTP requires two connections between the client and the server, one for commands and replies, the other for the actual file transfer.
-
A manufacturing company subscribes to certain hosted services from its ISP. The services that are required include hosted world wide web, file transfer, and e-mail. Which protocols represent these three key applications? (Choose three.)
- FTP
- HTTP
- DNS
- SNMP
- DHCP
- SMTP
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The ISP uses the HTTP protocol in conjunction with hosting web pages, the FTP protocol with file transfers, and SMTP with e-mail. DNS is used to translate domain names to IP addresses. SNMP is used for network management traffic. DHCP ic commonly used to manage IP addressing.
-
Which application layer protocol uses message types such as GET, PUT, and POST?
- DNS
- DHCP
- SMTP
- HTTP
- POP3
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The GET command is a client request for data from a web server. A PUT command uploads resources and content, such as images, to a web server. A POST command uploads data files to a web server.
-
What type of information is contained in a DNS MX record?
- the FQDN of the alias used to identify a service
- the IP address for an FQDN entry
- the domain name mapped to mail exchange servers
- the IP address of an authoritative name server
Answers Explanation & Hints:
MX, or mail exchange messages, are used to map a domain name to several mail exchange servers that all belong to the same domain.
-
Which three protocols operate at the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- ARP
- TCP
- UDP
- FTP
- POP3
- DHCP
Answers Explanation & Hints:
FTP, DHCP, and POP3 are application layer protocols. TCP and UDP are transport layer protocols. ARP is a network layer protocol.
-
Which protocol is used by a client to communicate securely with a web server?
- SMTP
- SMB
- IMAP
- HTTPS
Answers Explanation & Hints:
HTTPS is a secure form of HTTP used to access web content hosted by a web server.
-
Which applications or services allow hosts to act as client and server at the same time?
- client/server applications
- email applications
- P2P applications
- authentication services
Answers Explanation & Hints:
P2P applications allow the clients to behave as servers if needed. When using authentication services, email exchange, and client/server applications, one host acts as server and the other acts as client at all times.
-
What are two characteristics of peer-to-peer networks? (Choose two.)
- scalability
- one way data flow
- decentralized resources
- centralized user accounts
- resource sharing without a dedicated server
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Peer-to-peer networks have decentralized resources because every computer can serve as both a server and a client. One computer might assume the role of server for one transaction while acting as a client for another transaction. Peer-to-peer networks can share resources among network devices without the use of a dedicated server.
-
Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
-
Which three layers of the OSI model provide similar network services to those provided by the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- physical layer
- session layer
- transport layer
- application layer
- presentation layer
- data link layer
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The three upper layers of the OSI model, the session, presentation, and application layers, provide application services similar to those provided by the TCP/IP model application layer. Lower layers of the OSI model are more concerned with data flow.
-
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received two packets of data from the PC?
- 3001
- 6001
- 4500
- 6000
-
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received three packets of data from the PC?
- 4501
- 6001
- 6000
- 4500
-
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received four packets of data from the PC?
- 6001
- 3001
- 1501
- 1500
-
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received four packets of data from the PC?
- 6001
- 3001
- 3000
- 1500
-
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received two packets of data from the PC?
- 3001
- 4501
- 3000
- 1500
-
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received two packets of data from the PC?
- 3001
- 4501
- 4500
- 1500
-
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received two packets of data from the PC?
- 3001
- 6001
- 4500
- 3000
-
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received two packets of data from the PC?
- 3001
- 6001
- 6000
- 3000
-
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received three packets of data from the PC?
- 4501
- 6001
- 6000
- 3000
-
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received three packets of data from the PC?
- 4501
- 6001
- 1500
- 4500
-
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting TFTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 69
- 67
- 53
- 80
-
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting FTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 21
- 69
- 67
- 80
-
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SSH service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 22
- 69
- 67
- 80
-
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting HTTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 80
- 67
- 53
- 69
-
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting POP3 service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 110
- 67
- 53
- 69
-
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting telnet service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 23
- 443
- 161
- 110
-
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting POP3 service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 110
- 443
- 161
- 80
-
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SNMP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 161
- 443
- 110
- 80
-
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SMTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 25
- 443
- 161
- 110
-
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting HTTPS service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
- 443
- 161
- 110
- 80
Which two protocols may devices use in the application process that sends email? (Choose two.)
Please select 3 correct answers
POP
IMAP
DNS
HTTP
SMTP
POP3
What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
to send error information from a web server to a web client
to upload content to a web server from a web client
to request an HTML page from a web server
What is the complete range of TCP and UDP well-known ports?
0 to 255
256 – 1023
0 to 1023
1024 – 49151
Which three fields are used in a UDP segment header? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
Sequence Number
Acknowledgment Number
Source Port
Length
Checksum
Window Size
What is an example of network communication that uses the client-server model?
A user prints a document by using a printer that is attached to a workstation of a coworker.
A workstation initiates an ARP to find the MAC address of a receiving host.
A user uses eMule to download a file that is shared by a friend after the file location is determined.
A workstation initiates a DNS request when the user types www.cisco.com in the address bar of a web browser.
Which protocol or service uses UDP for a client-to-server communication and TCP for server-to-server communication?
Which flag in the TCP header is used in response to a received FIN in order to terminate connectivity between two network devices?
Which two flags in the TCP header are used in a TCP three-way handshake to establish connectivity between two network devices? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SMTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
What is a socket?
the combination of the source and destination IP address and source and destination Ethernet address
the combination of the source and destination sequence numbers and port numbers
the combination of a source IP address and port number or a destination IP address and port number
the combination of the source and destination sequence and acknowledgment numbers
Network congestion has resulted in the source learning of the loss of TCP segments that were sent to the destination. What is one way that the TCP protocol addresses this?
The source decreases the window size to decrease the rate of transmission from the destination.
The destination sends fewer acknowledgement messages in order to conserve bandwidth.
The source decreases the amount of data that it transmits before it receives an acknowledgement from the destination.
The destination decreases the window size.
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SSH service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
Which three layers of the OSI model provide similar network services to those provided by the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
physical layer
transport layer
application layer
session layer
presentation layer
data link layer
Which two fields are included in the TCP header but not in the UDP header? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
checksum
window
destination port
source port
sequence number
What happens if part of an FTP message is not delivered to the destination?
The message is lost because FTP does not use a reliable delivery method.
The part of the FTP message that was lost is re-sent.
The entire FTP message is re-sent.
The FTP source host sends a query to the destination host.
Which three protocols or standards are used at the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
What is an advantage of SMB over FTP?
SMB clients can establish a long-term connection to the server.
Only with SMB can data transfers occur in both directions.
Only SMB establishes two simultaneous connections with the client, making the data transfer faster.
SMB is more reliable than FTP because SMB uses TCP and FTP uses UDP.
Which protocol can be used to transfer messages from an email server to an email client?
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting HTTPS service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
In what two situations would UDP be better than TCP as the preferred transport protocol? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data
when destination port numbers are dynamic
when delivery overhead is not an issue
when a faster delivery mechanism is needed
when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
What message type is used by an HTTP client to request data from a web server?
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SNMP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
Which two operations are provided by TCP but not by UDP? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
retransmitting any unacknowledged data
reconstructing data in the order received
tracking individual conversations
identifying the applications
acknowledging received data
How are port numbers used in the TCP/IP encapsulation process?
Source port numbers and destination port numbers are not necessary when UDP is the transport layer protocol being used for the communication.
If multiple conversations occur that are using the same service, the source port number is used to track the separate conversations.
Destination port numbers are assigned automatically and cannot be changed.
Source port and destination port numbers are randomly generated.
What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
network printing using a print server
wireless networking
resource sharing without a dedicated server
social networking without the Internet
An author is uploading one chapter document from a personal computer to a file server of a book publisher. What role is the personal computer assuming in this network model?
server
master
client
slave
transient
What information is used by TCP to reassemble and reorder received segments?
acknowledgment numbers
port numbers
sequence numbers
fragment numbers
What is the purpose of using a source port number in a TCP communication?
to notify the remote device that the conversation is over
to keep track of multiple conversations between devices
to assemble the segments that arrived out of order
to inquire for a nonreceived segment
What is the TCP mechanism used in congestion avoidance ?
three-way handshake
socket pair
two-way handshake
sliding window
What are two characteristics of peer-to-peer networks? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
decentralized resources
one way data flow
resource sharing without a dedicated server
scalability
centralized user accounts
Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.
UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection.
UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting FTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
Which two characteristics are associated with UDP sessions? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
Transmitted data segments are tracked.
Unacknowledged data packets are retransmitted.
Destination devices receive traffic with minimal delay.
Received data is unacknowledged.
Destination devices reassemble messages and pass them to an application.
What does a client do when it has UDP datagrams to send?
It just sends the datagrams.
It queries the server to see if it is ready to receive data.
It sends to the server a segment with the SYN flag set to synchronize the conversation.
It sends a simplified three-way handshake to the server.
Which three statements describe a DHCP Discover message? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
Only the DHCP server receives the message.
The destination IP address is 255.255.255.255.
The message comes from a client seeking an IP address.
All hosts receive the message, but only a DHCP server replies.
The source MAC address is 48 ones (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF).
The message comes from a server offering an IP address.
Which two services or protocols use the preferred UDP protocol for fast transmission and low overhead? (Choose two)
Please select 2 correct answers
Which factor determines TCP window size?
the amount of data the destination can process at one time
the number of services included in the TCP segment
the amount of data the source is capable of sending at one time
the amount of data to be transmitted
What type of applications are best suited for using UDP?
applications that need reliable delivery
applications that are sensitive to delay
applications that require retransmission of lost segments
applications that are sensitive to packet loss
When retrieving email messages, which protocol allows for easy, centralized storage and backup of emails that would be desirable for a small- to medium-sized business?
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting HTTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
A PC is downloading a large file from a server. The TCP window is 1000 bytes. The server is sending the file using 100-byte segments. How many segments will the server send before it requires an acknowledgment from the PC?
100 segments
1 segment
10 segments
1000 segments
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received two packets of data from the PC?
What type of information is contained in a DNS MX record?
the FQDN of the alias used to identify a service
the IP address for an FQDN entry
the domain name mapped to mail exchange servers
the IP address of an authoritative name server
What is true about the Server Message Block protocol?
Different SMB message types have a different format.
SMB uses the FTP protocol for communication.
SMB messages cannot authenticate a session.
Clients establish a long term connection to servers.
Why is DHCP preferred for use on large networks?
Large networks send more requests for domain to IP address resolution than do smaller networks.
It prevents sharing of files that are copyrighted.
It is a more efficient way to manage IP addresses than static address assignment.
DHCP uses a reliable transport layer protocol.
Hosts on large networks require more IP addressing configuration settings than hosts on small networks.
Which two types of applications are best suited for UDP? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
applications that need the reordering of segments
applications that can tolerate some data loss, but require little or no delay
applications that need data flow control
applications that handle reliability themselves
applications that require reliable delivery
Which three application layer protocols use TCP? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
FTP
DHCP
HTTP
SNMP
SMTP
TFTP
What part of the URL, http://www.cisco.com/index.html, represents the top-level DNS domain?
Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting telnet service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
Which application layer protocol uses message types such as GET, PUT, and POST?
Which statement is true about FTP?
The client can choose if FTP is going to establish one or two connections with the server.
FTP is a peer-to-peer application.
FTP does not provide reliability during data transmission.
The client can download data from or upload data to the server.
A manufacturing company subscribes to certain hosted services from its ISP. The services that are required include hosted world wide web, file transfer, and e-mail. Which protocols represent these three key applications? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
SNMP
DHCP
HTTP
DNS
FTP
SMTP
Which field in the TCP header indicates the status of the three-way handshake process?
reserved
checksum
window
control bits
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received three packets of data from the PC?
A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received four packets of data from the PC?
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting POP3 service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting TFTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
to ensure the fastest possible download speed
because HTTP requires reliable delivery
What are two characteristics of the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
responsibility for logical addressing
responsibility for physical addressing
the creation and maintenance of dialogue between source and destination applications
closest to the end user
Which application layer protocol is used to provide file-sharing and print services to Microsoft applications?
Which applications or services allow hosts to act as client and server at the same time?
client/server applications
email applications
P2P applications
authentication services
Which transport layer feature is used to guarantee session establishment?
TCP 3-way handshake
UDP ACK flag
UDP sequence number
TCP port number
Which layer in the TCP/IP model is used for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data?
presentation
session
network access
internetwork
application
In what networking model would eDonkey, eMule, BitTorrent, Bitcoin, and LionShare be used?
master-slave
point-to-point
client-based
peer-to-peer
How does a networked server manage requests from multiple clients for different services?
Each request is tracked through the physical address of the client.
The server uses IP addresses to identify different services.
The server sends all requests through a default gateway.
Each request is assigned source and destination port numbers.
What is a responsibility of transport layer protocols?
translating private IP addresses to public IP addresses
providing network access
determining the best path to forward a packet
tracking individual conversations
Which protocol is used by a client to communicate securely with a web server?
A wireless host needs to request an IP address. What protocol would be used to process the request?
The application layer of the TCP/IP model performs the functions of what three layers of the OSI model? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
physical
application
session
transport
network
presentation
data link
Which number or set of numbers represents a socket?
10.1.1.15
21
192.168.1.1:80
01-23-45-67-89-AB
What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
destination and source logical network addresses
timing and synchronization
destination and source physical addresses
destination and source port numbers
Which three protocols operate at the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
POP3
TCP
ARP
UDP
DHCP
FTP
What is a characteristic of UDP?
UDP datagrams take the same path and arrive in the correct order at the destination.
UDP reassembles the received datagrams in the order they were received.
UDP only passes data to the network when the destination is ready to receive the data.
Applications that use UDP are always considered unreliable.
Which OSI layer provides the interface between the applications used to communicate and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted?
transport
presentation
session
application
Which TCP/IP model layer is closest to the end user?
internet
transport
network access
application
Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
master-slave
client/server
peer-to-peer
point-to-point
What kind of port must be requested from IANA in order to be used with a specific application?
private port
registered port
dynamic port
source port
What do the client/server and peer-to-peer network models have in common?
Both models require the use of TCP/IP-based protocols.
Both models support devices in server and client roles.
Both models have dedicated servers.
Both models are used only in the wired network environment.
What is a common protocol that is used with peer-to-peer applications such as WireShare, Bearshare, and Shareaza?
POP
SMTP
Gnutella
Ethernet
Which action is performed by a client when establishing communication with a server via the use of UDP at the transport layer?
The client randomly selects a source port number.
The client sets the window size for the session.
The client sends an ISN to the server to start the 3-way handshake.
The client sends a synchronization segment to begin the session.
On a home network, which device is most likely to provide dynamic IP addressing to clients on the home network?
a home router
a dedicated file server
an ISP DHCP server
a DNS server
Which protocol uses encryption?
What are two roles of the transport layer in data communication on a network? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
providing frame delimiting to identify bits making up a frame
performing a cyclic redundancy check on the frame for errors
identifying the proper application for each communication stream
tracking the individual communication between applications on the source and destination hosts
providing the interface between applications and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted
What are three responsibilities of the transport layer? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
multiplexing multiple communication streams from many users or applications on the same network
meeting the reliability requirements of applications, if any
identifying the applications and services on the client and server that should handle transmitted data
directing packets towards the destination network
conducting error detection of the contents in frames
formatting data into a compatible form for receipt by the destination devices
Which two tasks can be performed by a local DNS server? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
forwarding name resolution requests between servers
mapping name-to-IP addresses for internal hosts
allowing data transfer between two network devices
providing IP addresses to local hosts
retrieving email messages
Подборка по базе: Контрольная работа _Разделительные вопросы_ (1).doc, Самые популярные вопросы о Чичикове из поэмы.docx, Примерные вопросы к дифференцированному зачету_Психология общени, Политология. Ответы на тест 1.pdf, Тестовые вопросы к разделу 5_ просмотр попытки.pdf, ОИ рк1 ответы.pdf, Тестовые вопросы к разделу 8_ просмотр попытки.pdf, Экзамен вопросы СП ОМ_англ_ok.docx, 2.2 Вопросы к экзамену Смета+Финансы.docx, РК-1 вопросы каз, русс 1 курс.docx
Хост передает многоадресную рассылку.Какой хост или хосты его получат?
- специально определенная группа хостов
- один конкретный хост
- все хосты с одинаковым IP-адресом
- ближайший сосед в той же сети
- специально определенная группа хостов
- один конкретный хост
- напрямую подключенные сетевые устройства
- ближайший сосед в той же сети
- специально определенная группа хостов
- один конкретный хост
- все хосты с одинаковым IP-адресом
- все хосты в Интернете
- специально определенная группа хостов
- один конкретный хост
- напрямую подключенные сетевые устройства
- все хосты в Интернете
- специально определенная группа хостов
- все хосты в одной подсети
- напрямую подключенные сетевые устройства
- ближайший сосед в той же сети
- все хосты в одной подсети
- один конкретный хост
- ближайший сосед в той же сети
- напрямую подключенные сетевые устройства
- все хосты в одной подсети
- один конкретный хост
- все хосты в Интернете
- напрямую подключенные сетевые устройства
- 2001: db8 :: a0b0: 8: 1
- 2001: db8 :: ab8: 1: 0: 1000
- 2001: db80: 0: 1 :: 80: 1
- 2001: db80 ::: 1 :: 80: 1
- fe80: 9ea: 0: 2200 :: fe0: 290
- fe80: 9: 20 :: b000: 290
- fe80: 9ea0 :: 2020: 0: bf: e0: 9290
- fe80: 9ea0 :: 2020 :: bf: e0: 9290
- 2002: 42: 10: c400 :: 909
- 200: 420: 110: c4b :: 910: 0: 90
- 2002: 4200 :: 25: 1090: 0: 99
- 2002: 42 :: 25: 1090: 0: 99
- 2001: db8 :: ab8: 1: 0: 1000
- 2001: db8 :: a0b0: 8: 1
- 2001: db8: 1 :: ab8: 0: 1
- 2001: db8: 0: 1 :: 8: 1
- 2002: 420: c4: 1008: 25: 190 :: 990
- 2002: 42: 10: c400 :: 909
- 2002: 4200 :: 25: 1090: 0: 99
- 2002: 42 :: 25: 1090: 0: 99
- 2001: db8 :: a0b0: 8: 1
- 2001: db8: 1 :: ab8: 0: 1
- 2001: db8 :: ab8: 1: 0: 1000
- 2001: db8: 0: 1 :: 8: 1
- fe80 :: 220: b3f: f0e0: 29
- fe80: 9ea: 0: 2200 :: fe0: 290
- fe80: 9ea0 :: 2020: 0: bf: e0: 9290
- fe80: 9ea0 :: 2020 :: bf: e0: 9290
- 2001: db8 :: a0b0: 8: 1
- 2001: db8 :: ab8: 1: 0: 1000
- 2001: db80: 0: 1 :: 80: 1
- 2001: db8: 0: 1 :: 8: 1
- 2002: 42: 10: c400 :: 909
- 2002: 4200 :: 25: 1090: 0: 99
- 2002: 420: c4: 1008: 25: 190 :: 990
- 2002: 42 :: 25: 1090: 0: 99
- fe80: 9ea: 0: 2200 :: fe0: 290
- fe80: 9ea0 :: 2020: 0: bf: e0: 9290
- fe80 :: 220: b3f: f0e0: 29
- fe80 :: 0220: 0b3f: f0e0: 0029
- за пределами исходного адреса
- сообщение с местом назначения запрещено в административном порядке
- адрес недоступен
- нет маршрута к месту назначения
- хост недоступен
- за пределами исходного адреса
- адрес недоступен
- сообщение с местом назначения запрещено в административном порядке
- адрес недоступен
- сообщение с местом назначения запрещено в административном порядке
- за пределами исходного адреса
- нет маршрута к месту назначения
- сеть недоступна
- протокол недоступен
- порт недоступен
- хост недоступен
- порт недоступен
- хост недоступен
- протокол недоступен
- сеть недоступна
- сеть недоступна
- протокол недоступен
- порт недоступен
- хост недоступен
- порт недоступен
- хост недоступен
- протокол недоступен
- сеть недоступна
- за пределами исходного адреса
- хост недоступен
- протокол недоступен
- сеть недоступна
- хост недоступен
- протокол недоступен
- порт недоступен
- сеть недоступна
- адрес недоступен
- сеть недоступна
- хост недоступен
- протокол недоступен
- 1 сегмент
- 10 сегментов
- 100 сегментов
- 1000 сегментов
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: С окном в 1000 байтов целевой хост принимает сегменты до тех пор, пока не будут получены все 1000 байтов данных. Затем хост-адресат отправляет подтверждение.
- объем передаваемых данных
- количество сервисов, включенных в сегмент TCP
- объем данных, которые адресат может обработать за один раз
- количество данных, которые источник может отправить за один раз
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Окно — это количество байтов, которое отправитель отправит до ожидания подтверждения от устройства назначения. Первоначальное окно согласовывается во время запуска сеанса посредством трехстороннего рукопожатия между источником и местом назначения. Он определяется тем, сколько данных устройство назначения сеанса TCP может принять и обработать за один раз.
- Он просто отправляет дейтаграммы.
- Он запрашивает у сервера, готов ли он к приему данных.
- Он отправляет на сервер упрощенное трехстороннее рукопожатие.
- Он отправляет на сервер сегмент с установленным флагом SYN для синхронизации разговора.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Когда у клиента есть дейтаграммы UDP для отправки, он просто отправляет дейтаграммы.
- Размер окна
- Длина
- Исходный порт
- Номер подтверждения
- Контрольная сумма
- Последовательность чисел
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Заголовок UDP состоит только из полей Source Port, Destination Port, Length и Checksum. Порядковый номер, номер подтверждения и размер окна являются полями заголовка TCP.
- определение подходящего приложения для каждого коммуникационного потока
- отслеживание индивидуальной связи между приложениями на исходном и целевом хостах
- обеспечение разграничения кадров для идентификации битов, составляющих кадр
- выполнение циклического контроля избыточности кадра на наличие ошибок
- обеспечение интерфейса между приложениями и базовой сетью, по которой передаются сообщения
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Транспортный уровень выполняет несколько задач. В основные обязанности входит следующее:
Отслеживание отдельных потоков обмена данными между приложениями на исходном и целевом хостах.
Сегментация данных в источнике и повторная сборка данных в месте назначения.
Определение надлежащего приложения для каждого потока обмена данными с помощью номеров портов.
- номера портов
- порядковые номера
- номера подтверждения
- номера фрагментов
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: На транспортном уровне TCP использует порядковые номера в заголовке каждого сегмента TCP для повторной сборки сегментов в правильном порядке.
- хронометраж и синхронизация
- номера портов назначения и источника
- физические адреса назначения и источника
- логические сетевые адреса назначения и источника
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Номера портов назначения и источника используются для точной идентификации того, какой протокол и процесс запрашивает или отвечает на запрос.
- Целевые устройства получают трафик с минимальной задержкой.
- Переданные сегменты данных отслеживаются.
- Целевые устройства повторно собирают сообщения и передают их приложению.
- Полученные данные не подтверждаются.
- Неподтвержденные пакеты данных передаются повторно.
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: TCP:
· Обеспечивает отслеживание переданных сегментов данных
· Целевые устройства подтверждают полученные данные.
· Устройства-источники будут повторно передавать неподтвержденные данные.UDP
· Целевые устройства не подтверждают полученные данные
· Заголовки используют очень мало служебных данных и вызывают минимальную задержку.

| Ответы, объяснения и подсказки:
Чтобы завершить сеанс TCP, клиент отправляет на сервер сегмент с установленным флагом FIN. Сервер подтверждает клиента, отправляя сегмент с установленным флагом ACK. Сервер отправляет клиенту FIN, чтобы завершить сеанс между сервером и клиентом. Клиент подтверждает завершение, отправляя сегмент с установленным флагом ACK. |
- Какой флаг в заголовке TCP используется в ответ на полученный FIN, чтобы разорвать соединение между двумя сетевыми устройствами?
- ПЛАВНИК
- ACK
- SYN
- RST
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: В сеансе TCP, когда у устройства больше нет данных для отправки, оно отправляет сегмент с установленным флагом FIN. Подключенное устройство, которое получает сегмент, ответит ACK, чтобы подтвердить этот сегмент. Устройство, отправившее ACK, затем отправит сообщение FIN, чтобы закрыть соединение, которое оно имеет с другим устройством. Отправка FIN должна сопровождаться получением ACK от другого устройства.
- Какой протокол или служба использует UDP для связи между клиентом и сервером и TCP для связи между серверами?
- HTTP
- FTP
- DNS
- SMTP
Ответы, объяснения и подсказки: Некоторые приложения могут использовать как TCP, так и UDP. DNS использует UDP, когда клиенты отправляют запросы на DNS-сервер, и TCP, когда два DNS-сервера напрямую взаимодействуют.
На чтение 6 мин. Просмотров 579 Опубликовано 18.03.2014
Ответы на на все вопросы (все модули) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
Ответы на 1 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 1) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Какие три утверждения относительно протокола IP являются верными? (Выберите три варианта.)
IP является протоколом без установления соединения.
Протокол IP не предлагает функции восстановления.
Протокол IP осуществляет негарантированную доставку данных
2) Какие компоненты модели OSI и стека протоколов TCP/IP расходятся сильнее всего?
Канальный уровень
3) Сколько бит содержит IPv4 адрес?
32
4) Каково назначение маршрутизатора?
соединение сетей между собой и выбор наилучшего пути между ними
5) Какие два утверждения о цели модели OSI являются верными? (Выберите два варианта.)
Эталонная модель OSI определяет функции сети, реализуемые на каждом уровне.
Модель OSI облегчает понимание передачи данных по сети.
6) Укажите неправильную характеристику сети с коммутацией пакетов
Трафик реального времени передается без задержек
7) Какое утверждение относительно логических топологий сети является верным?
Логическая топология описывает пути, по которым сигналы передаются из одной точки сети в другую.

Физическая топология определяет способ соединения компьютеров, принтеров, сетевых и прочих устройств.
9) Какое из этих событий произошло позже других:
изобретение Web;
10) Каково назначение коммутатора?
подключение сети к конечным системам и интеллектуальная коммутация данных внутри локальной сети
Ответы на 2 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 2) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Укажите неправильное описание методов кодирования
метод NRZ обладает свойством самосинхронизации
2) Какой принцип лежит в основе методов обнаружения и коррекции ошибок?
избыточность
3) Укажите правильный вариант
Символьное подавление — способ сжатия информации, при котором длинные последовательности из идентичных данных заменяются более короткими.
4) Укажите неправильный вариант ответа
Кодовое расстояние в коде Хемминга dmin = 2
5) Укажите неправильный ответ о преимуществах синхронных каналов передачи данных
Невысокая цена оборудования
6) Во сколько раз увеличится ширина спектра кода NRZ при увеличении тактовой частоты передатчика в 2 раза?
2
7) Какой из вариантов является признаком синхронного канала в отличие от асинхронного
данные передаются блоками. Для синхронизации работы приемника и передатчика в начале блока передаются биты синхронизации

B8ZC используется в потоках E1 (2.044 Мбит/с)
9) Укажите неправильный вариант ответа
Текстовые документы, базы данных, принято сжимать с потерей качества
10) Укажите неправильный вариант скорости COM порта в компьютере
2048000
Ответы на 3 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 3) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Каковы два главных преимущества добавления моста к сети? (Выберите два варианта.)
расширение ЛВС для охвата больших расстояний путем соединения нескольких сегментов
изоляция потенциальных проблем сети в отдельных сегментах
2) Какой разъем не используется для подключения сетевой платы к локальной сети
DB -9
3) Укажите неправильный вариант ответа
Хаб может проверить физический адрес (источник и пункт назначения), содержащиеся в пакете.
4) Какова максимальная длина сегмента 10BASE-2 в метрах
185
5) Какой стандарт не предусматривает использование витой пары?
10BASE-2
6) На каком уровне OSI работают мост и коммутатор
2
7) Какой стандарт не предусматривает использование разделяемой среды:
10GBASE-T

мосты ведут таблицу маршрутизации, что позволяет им передавать выбрать оптимальный путь из одной сети в другую.
9) Укажите неверную запись стандарта
1GBACE –T
10) На каком уровне OSI работают репитер и хаб
1
Ответы на 4 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 4) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Укажите неправильный вариант – размер поля Data (данные) в кадре Ethernet 802.3
1530
2) Чем объясняется, что минимальный размер поля данных кадра Ethernet выбран равным 46 байт?
для устойчивого распознавания коллизий;
3) На какой скорости работает Fast Ethetnet
100М
4) Как скорость передачи данных технологии Ethernet на разделяемой среде влияет на максимальный диаметр сети?
чем выше скорость передачи, тем меньше максимальный диаметр сети;
5) В каких средах не работает Ethernet на физическом уровне
Акустический канал
6) К какому типу относится МАС-адрес 01:С2:00:00:08?
индивидуальный
7) Из каких соображений выбирается длительность слота в режиме DCF?
длительность слота должна превосходить время распространения сигнала между любыми станциями сети плюс время, затрачиваемое станцией на распознавание

OUI
9) Выберите утверждения, корректно описывающие особенности метода доступа технологии Ethernet:
если в течение времени передачи кадра коллизия не произошла, то кадр считается переданным успешно.
10) Какое количество бит в MAC адресе
48
Ответы на 5 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 5) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Как вы считаете, протоколы транспортного уровня устанавливаются
и там, и там.
2) Какие параметры сети учитывают метрики, поддерживаемые протоколом OSPF
пропускная способность
3) Данные каких трех типов предоставляются DHCP-клиенту сервером DHCP? (Выберите три варианта.)
IP-адреса DNS-серверов
маска подсети
основной шлюз
4) Какое утверждение наилучшим образом описывает статические и динамические маршруты
Статические маршруты вручную задаются администратором сети, динамические маршруты автоматически добавляются и настраиваются протоколом маршрутизации.
5) Какие три утверждения относительно протокола IP являются верными? (Выберите три варианта.)
IP является протоколом без установления соединения.
Протокол IP осуществляет негарантированную доставку данных.
Протокол IP не предлагает функции восстановления.
6) В студенческом общежитии живет 200 студентов и каждый из них имеет собственный ноутбук. В общежитии оборудована специальная комната, в которой развернута компьютерная сеть, имеющая 25 коннекторов для подключения компьютеров. Время от времени студенты работают в этом компьютерном классе, подключая свои ноутбуки к сети. Каким количеством IP-адресов должен располагать администратор этой компьютерной сети, чтобы все студенты могли подключаться к сети, не выполняя процедуру конфигурирования своих ноутбуков при каждом посещении компьютерного класса не используя DHCP?
254
7) К какому типу стандартов могут относиться современные документы RFC
к международным стандартам.

решение проблемы дефицита адресов в протоколе IPv4;
Ответы на 6 модуль (Тестирование по Разделу 6) по предмету «СЕТИ И ТЕЛЕКОММУНИКАЦИИ»
1) Какой из протоколов предназначен для пересылки электронной почты
SMTP
2) Какие три утверждения точно описывают распределенные сети WAN ? (Выберите три варианта)
В распределенных сетях последовательные соединения различных типов используются для предоставления доступа к полосе пропускания.
В распределенных сетях используются услуги таких операторов, как телефонные компании, компании, предоставляющие услуги кабельной связи, спутниковые системы и поставщики сетевых услуг.
Распределенные сети связывают устройства, разделенные обширными географическими областями.
3) Каков размер ячейки ATM
53
4) Какая из атак осуществляется отправкой подложного ARP ответа?
Перенаправление трафика
5) Какая из функций IPsec может выполняться алгоритмом AES?
Конфиденциальность
6) Какая из сетевых технологий появилась раньше?
X.25
7) В чем заключаются преимущества услуг виртуальных частных сетей по сравнению с услугами выделенных каналов с точки зрения поставщика этих услуг?
можно обслужить большее число клиентов, имея ту же инфраструктуру физических каналов связи

21
9) Какая разновидность облачных технологий предоставляет программное обеспечение как услугу
SaaS
10) Укажите назначение сервера DNS
Преобразует имя компьютера или домена в ассоциированный IP-адрес.
Русский язык
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Литература
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Иностранный язык
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Математика
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
История
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Физическая культура
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Основы безопасности жизнедеятельности
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Астрономия
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Физика
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Химия
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Биология
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Обществознание
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Информатика
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Эффективное поведение на рынке труда/Психология/Духовное краеведение Подмосковья/Введение в специальность/Основы духовно-нравственной культуры народов России
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Общий гуманитарный и социально-экономический цикл
Основы философии
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
История
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Иностранный язык в профессиональной деятельности
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Физическая культура
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Психология общения
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Математический и общий естественнонаучный цикл
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Математика
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Компьютерное моделирование
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Физика
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Общепрофессиональный цикл
Теория электрических цепей
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Электронная техника
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Теория электросвязи
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Вычислительная техника
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Электрорадиоизмерения
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Основы телекоммуникаций
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Энергоснабжение телекоммуникационных систем
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Прикладное программное обеспечение профессиональной деятельности
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Безопасность жизнедеятельности
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Способы поиска работы, рекомендации по трудоустройству, планирование карьеры
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Основы предпринимательства, открытие собственного дела
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Адаптационная дисциплина «Адаптивные информационные и коммуникационные технологии»
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Адаптационная дисциплина «Психология личности и профессиональное самоопределение»
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
Адаптационная дисциплина «Социальная адаптация и основы социально-правовых знаний»
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
ПМ.01 Техническая эксплуатация информационно-коммуникационных сетей связи
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
ПМ.02 Техническая эксплуатация инфокоммуникационных систем связи
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
ПМ.03 Обеспечение информационной безопасности инфокоммуникационных сетей и систем связи
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
ПМ.04 Участие в организации производственной деятельности малого структурного подразделения
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
ПМ.05 Адаптация конвергентных технологий и систем к потребностям заказчика
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы
ПМ.06 Выполнение работ по одной или нескольким профессиям рабочих, должностям служащих
Программы
Календарно-тематические планы
Методические указания к лабораторным и практическим работам
Методические указания к внеаудиторной самостоятельной работе
Методические рекомендации по выполнению курсового проектирования
Контрольно-оценочные средства
Техническая экспертиза программы
Содержательная экспертиза программы