How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials ( Version 7.00) – Redundant Networks Exam
1. What additional information is contained in the 12-bit extended system ID of a BPDU?
- MAC address
- VLAN ID
- IP address
- port ID
2. During the implementation of Spanning Tree Protocol, all switches are rebooted by the network administrator. What is the first step of the spanning-tree election process?
- Each switch with a lower root ID than its neighbor will not send BPDUs.
- All the switches send out BPDUs advertising themselves as the root bridge.
- Each switch determines the best path to forward traffic.
- Each switch determines what port to block to prevent a loop from occurring.
3. Which STP port role is adopted by a switch port if there is no other port with a lower cost to the root bridge?
- designated port
- root port
- alternate
- disabled port
Explanation: The root port is the port with the lowest cost to reach the root bridge.
4. Which two concepts relate to a switch port that is intended to have only end devices attached and intended never to be used to connect to another switch? (Choose two.)
- bridge ID
- edge port
- extended system ID
- PortFast
- PVST+
5. Which three components are combined to form a bridge ID?
- extended system ID
- cost
- IP address
- bridge priority
- MAC address
- port ID
Explanation: The three components that are combined to form a bridge ID are bridge priority, extended system ID, and MAC address.
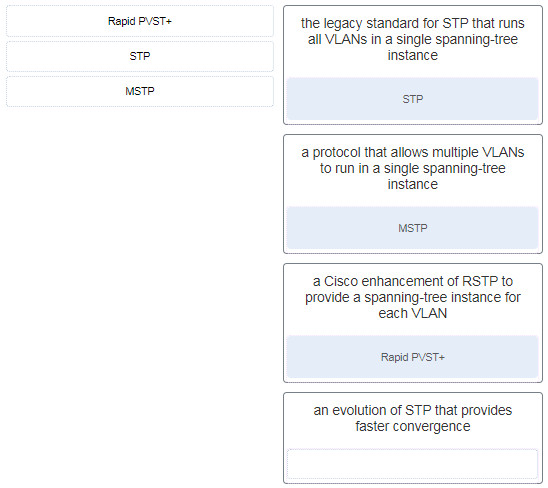
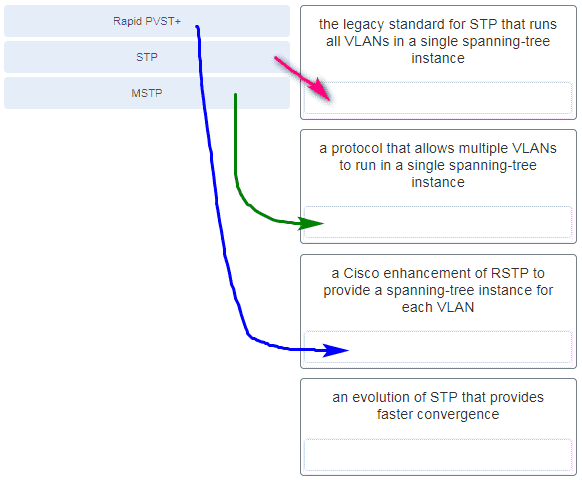
6. Match the STP protocol with the correct description. (Not all options are used.)
7. In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network? (Choose two.)
- disabled
- forwarding
- listening
- blocking
- learning
Explanation: Switches learn MAC addresses at the learning and forwarding port states. They receive and process BPDUs at the blocking, listening, learning, and forwarding port states.
8. If no bridge priority is configured in PVST, which criteria is considered when electing the root bridge?
- lowest MAC address
- lowest IP address
- highest IP address
- highest MAC address
Explanation: Only one switch can be the root bridge for a VLAN. The root bridge is the switch with the lowest BID. The BID is determined by priority and the MAC address. If no priority is configured then all switches use the default priority and the election of the root bridge will be based on the lowest MAC address.
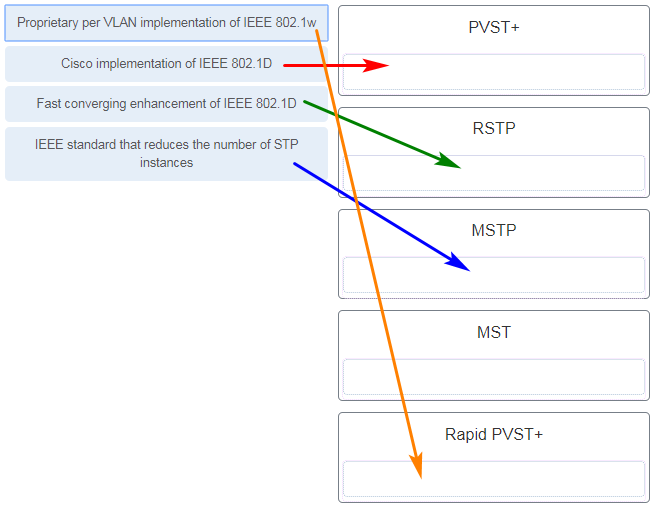
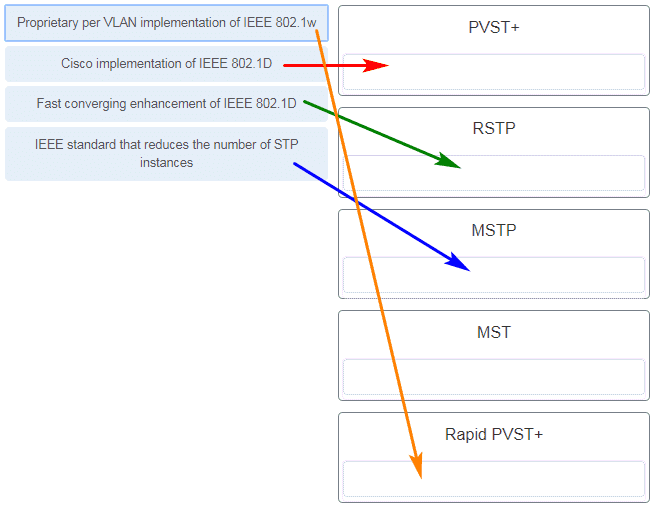
9. Match the spanning-tree feature with the protocol type. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP (IEEE 802.1s).
10. When the show spanning-tree vlan 33 command is issued on a switch, three ports are shown in the forwarding state. In which two port roles could these interfaces function while in the forwarding state? (Choose two.)
- alternate
- designated
- disabled
- blocked
- root
Explanation: The role of each of the three ports will be either designated port or root port. Ports in the disabled state are administratively disabled. Ports in the blocking state are alternate ports.
11. What is the function of STP in a scalable network?
- It decreases the size of the failure domain to contain the impact of failures.
- It protects the edge of the enterprise network from malicious activity.
- It combines multiple switch trunk links to act as one logical link for increased bandwidth.
- It disables redundant paths to eliminate Layer 2 loops.
Explanation: STP is an important component in a scalable network because it allows redundant physical connections between Layer 2 devices to be implemented without creating Layer 2 loops. STP prevents Layer 2 loops from forming by disabling interfaces on Layer 2 devices when they would create a loop.
12. What is a characteristic of spanning tree?
- It is enabled by default on Cisco switches.
- It is used to discover information about an adjacent Cisco device.
- It has a TTL mechanism that works at Layer 2.
- It prevents propagation of Layer 2 broadcast frames.
Explanation: Spanning tree does work at Layer 2 on Ethernet-based networks and is enabled by default, but it does not have a TTL mechanism. Spanning tree exists because Layer 2 frames do not have a TTL mechanism. Layer 2 frames are still broadcast when spanning tree is enabled, but the frames can only be transmitted through a single path through the Layer 2 network that was created by spanning tree. Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is used to discover information about an adjacent Cisco device.
13. Which spanning tree standard supports only one root bridge so that traffic from all VLANs flows over the same path?
- PVST+
- 802.1D
- MST
- Rapid PVST
Explanation: MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP, an IEEE standard protocol that provides up to 16 instances of RSTP. PVST+ provides a separate 802.1D spanning-tree instance for each VLAN that is configured in the network. 802.1D is the original STP standard defined by the IEEE and allows for only one root bridge for all VLANs. 802.1w, or RSTP, provides faster convergence but still uses only one STP instance for all VLANs.
14. What is the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
- creates smaller collision domains
- prevents routing loops on a router
- prevents Layer 2 loops
- allows Cisco devices to exchange routing table updates
- creates smaller broadcast domains
Explanation: The Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) creates one path through a switch network in order to prevent Layer 2 loops.
15. What is the value used to determine which port on a non-root bridge will become a root port in a STP network?
- the path cost
- the highest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
- the lowest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
- the VTP revision number
Explanation: STP establishes one root port on each non-root bridge. The root port is the lowest-cost path from the non-root bridge to the root bridge, indicating the direction of the best path to the root bridge. This is primarily based on the path cost to the root bridge.
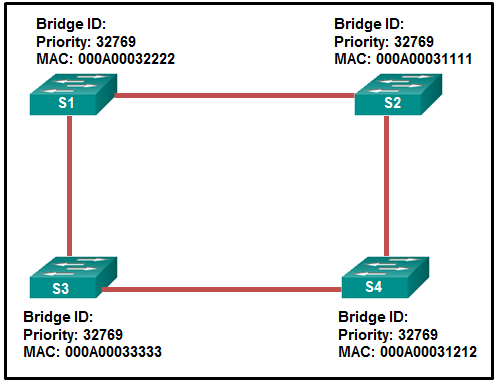
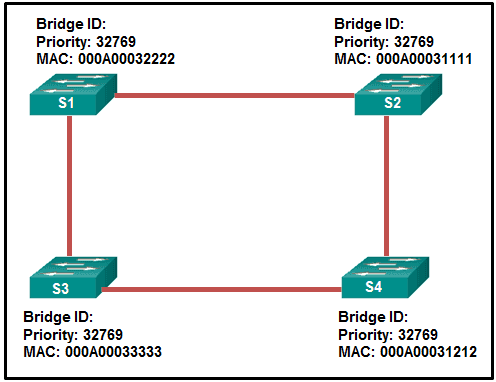
16. Refer to the exhibit. Which switch will be the root bridge after the election process is complete?
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
Explanation: The root bridge is determined by the lowest bridge ID, which consists of the priority value and the MAC address. Because the priority values of all of the switches are identical, the MAC address is used to determine the root bridge. Because S2 has the lowest MAC address, S2 becomes the root bridge.
17. What are two drawbacks to turning spanning tree off and having multiple paths through the Layer 2 switch network? (Choose two.)
- The MAC address table becomes unstable.
- The switch acts like a hub.
- Port security becomes unstable.
- Broadcast frames are transmitted indefinitely.
- Port security shuts down all of the ports that have attached devices.
Explanation: Spanning tree should never be disabled. Without it, the MAC address table becomes unstable, broadcast storms can render network clients and the switches unusable, and multiple copies of unicast frames can be delivered to the end devices.
18. A small company network has six interconnected Layer 2 switches. Currently all switches are using the default bridge priority value. Which value can be used to configure the bridge priority of one of the switches to ensure that it becomes the root bridge in this design?
- 1
- 28672
- 32768
- 34816
- 61440
Explanation: The default bridge priority value for all Cisco switches is 32768. The range is 0 to 61440 in increments of 4096. Thus, the values 1 and 34816 are invalid. Configuring one switch with the lower value of 28672 (and leaving the bridge priority value of all other switches unchanged) will make the switch become the root bridge.
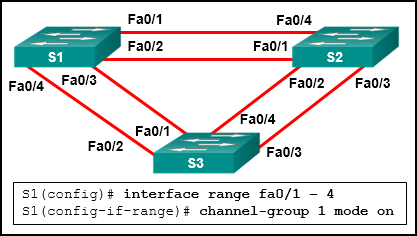
19. Refer to the exhibit. The administrator tried to create an EtherChannel between S1 and the other two switches via the commands that are shown, but was unsuccessful. What is the problem?
- Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches through the same EtherChannel link.
- Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches, but only to two different devices like an EtherChannel-enabled server and a switch.
- Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
- Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Layer 3 switches.
Explanation: An EtherChannel link can only be created between two switches or between an EtherChannel-enabled server and a switch. Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches through the same EtherChannel link.
20. Which statement is true regarding the use of PAgP to create EtherChannels?
- It requires full duplex.
- It increases the number of ports that are participating in spanning tree.
- It requires more physical links than LACP does.
- It mandates that an even number of ports (2, 4, 6, etc.) be used for aggregation.
- It is Cisco proprietary.
Explanation: PAgP is used to automatically aggregate multiple ports into an EtherChannel bundle, but it only works between Cisco devices. LACP can be used for the same purpose between Cisco and non-Cisco devices. PAgP must have the same duplex mode at both ends and can use two ports or more. The number of ports depends on the switch platform or module. An EtherChannel aggregated link is seen as one port by the spanning-tree algorithm.
21. What are two requirements to be able to configure an EtherChannel between two switches? (Choose two.)
- All the interfaces need to work at the same speed.
- All interfaces need to be assigned to different VLANs.
- Different allowed ranges of VLANs must exist on each end.
- All the interfaces need to be working in the same duplex mode.
- The interfaces that are involved need to be contiguous on the switch.
Explanation: All interfaces in the EtherChannel bundle must be assigned to the same VLAN or be configured as a trunk. If the allowed range of VLANs is not the same, the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel even when set to auto or desirable mode.
22. Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output that is shown, what can be determined about the EtherChannel bundle?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 22
- The EtherChannel bundle is down.
- Two Gigabit Ethernet ports are used to form the EtherChannel.
- A Cisco proprietary protocol was used to negotiate the EtherChannel link.
- The EtherChannel bundle is operating at both Layer 2 and Layer 3.
Explanation: Two protocols can be used to send negotiation frames that are used to try to establish an EtherChannel link: PAgP and LACP. PAgP is Cisco proprietary, and LACP adheres to the industry standard.
23. Which two parameters must match on the ports of two switches to create a PAgP EtherChannel between the switches? (Choose two.)
- port ID
- PAgP mode
- MAC address
- speed
- VLAN information
Explanation: For an EtherChannel to be created, the ports that are concerned on the two switches must match in terms of the speed, duplex, and VLAN information. The PAgP mode must be compatible but not necessarily equal. The port ID and the MAC addresses do not have to match.
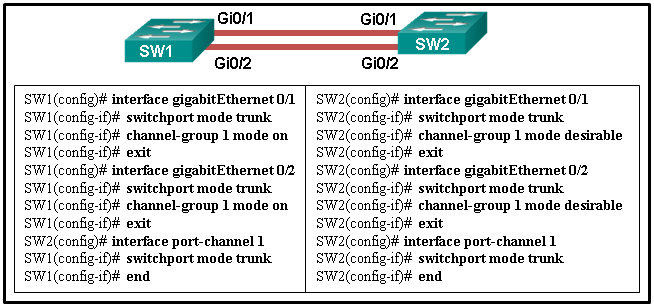
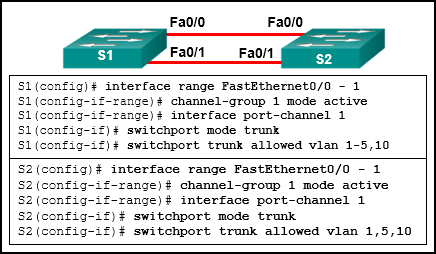
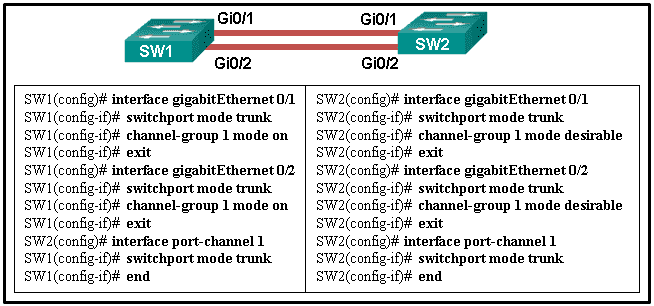
24. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two switches, SW1 and SW2. Which statement describes the effect after the commands are issued on SW1 and SW2?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 24
- The EtherChannel is established after SW2 initiates the link request.
- The EtherChannel is established after SW1 initiates the link request.
- The EtherChannel is established without negotiation.
- The EtherChannel fails to establish.
Explanation: The interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/1 and GigabitEthernet 0/2 are configured “on” for the EtherChannel link. This mode forces the interface to channel without PAgP or LACP. The EtherChannel will be established only if the other side is also set to “on”. However, the mode on SW2 side is set to PAgP desirable. Thus the EtherChannel link will not be established.
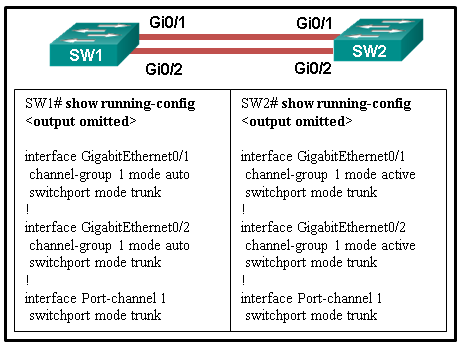
25. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two switches, SW1 and SW2. However, the EtherChannel link fails to establish. What change in configuration would correct the problem?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 25
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to desirable.
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to on.
- Configure SW1 EtherChannel mode to on.
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to auto.
Explanation: The EtherChannel mode must be compatible on each side for the link to work. The three modes from PAgP protocol are on, desirable, and auto. The three modes from LACP protocol are on, active, and passive. The compatible modes include on-on, auto-desirable, desirable-desirable, active-passive, and active-active. Any other combinations will not form an EtherChannel link.
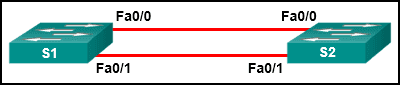
26. A network administrator configured an EtherChannel link with three interfaces between two switches. What is the result if one of the three interfaces is down?
- The remaining two interfaces continue to load balance traffic.
- The remaining two interfaces become separate links between the two switches.
- One interface becomes an active link for data traffic and the other becomes a backup link.
- The EtherChannel fails.
Explanation: EtherChannel creates an aggregation that is seen as one logical link. It provides redundancy because the overall link is one logical connection. The loss of one physical link within the channel does not create a change in the topology; the EtherChannel remains functional.
27. A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 by using the command SW1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode auto . Which command must be used on SW2 to enable this EtherChannel?
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode passive
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode on
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode active
Explanation: The possible combinations to establish an EtherChannel between SW1 and SW2 using LACP or PAgP are as follows:
PAgP
on on
auto desirable
desirable desirable
LACP
on on
active active
passive active
The EtherChannel mode chosen on each side of the EtherChannel must be compatible in order to enable it.
28. Which technology is an open protocol standard that allows switches to automatically bundle physical ports into a single logical link?
- PAgP
- LACP
- Multilink PPP
- DTP
Explanation: LACP, or Link Aggregation Control Protocol, is defined by IEEE 802.3ad and is an open standard protocol. LACP allows switches to automatically bundle switch ports into a single logical link to increase bandwidth. PAgP, or Port Aggregation Protocol, performs a similar function, but it is a Cisco proprietary protocol. DTP is Dynamic Trunking Protocol and is used to automatically and dynamically build trunks between switches. Multilink PPP is used to load-balance PPP traffic across multiple serial interfaces.
29. What is a requirement to configure a trunking EtherChannel between two switches?
- The allowed range of VLANs must be the same on both switches.
- The participating interfaces must be assigned the same VLAN number on both switches.
- The participating interfaces must be physically contiguous on a switch.
- The participating interfaces must be on the same module on a switch.
Explanation: To enable a trunking EtherChannel successfully, the range of VLANs allowed on all the interfaces must match; otherwise, the EtherChannel cannot be formed. The interfaces involved in an EtherChannel do not have to be physically contiguous, or on the same module. Because the EtherChannel is a trunking one, participating interfaces are configured as trunk mode, not access mode.
30. What are two advantages of using LACP? (Choose two.)
- It allows directly connected switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link.
- It eliminates the need for configuring trunk interfaces when deploying VLANs on multiple switches.
- It decreases the amount of configuration that is needed on a switch.
- It provides a simulated environment for testing link aggregation.
- It allows the use of multivendor devices.
- LACP allows Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces to be mixed within a single EtherChannel.
Explanation: The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) allows directly connected multivendor switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link. LACP helps create the EtherChannel link by detecting the configuration of each side and making sure that they are compatible so that the EtherChannel link can be enabled when needed.
31. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a non-root port that is permitted to forward traffic on the network?
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
- disabled
32. What are two advantages of EtherChannel? (Choose two.)
- Spanning Tree Protocol views the physical links in an EtherChannel as one logical connection.
- Load balancing occurs between links configured as different EtherChannels.
- Configuring the EtherChannel interface provides consistency in the configuration of the physical links.
- Spanning Tree Protocol ensures redundancy by transitioning failed interfaces in an EtherChannel to a forwarding state.
- EtherChannel uses upgraded physical links to provide increased bandwidth.
Explanation: EtherChannel configuration of one logical interface ensures configuration consistency across the physical links in the EtherChannel. The EtherChannel provides increased bandwidth using existing switch ports without requiring any upgrades to the physical interfaces. Load balancing methods are implemented between links that are part of the same Etherchannel. Because EtherChannel views the bundled physical links as one logical connection, spanning tree recalculation is not required if one of the bundled physical links fail. If a physical interface fails, STP cannot transition the failed interface into a forwarding state.
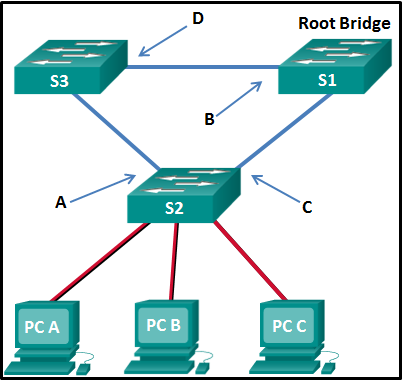
33. Refer to the exhibit. What are the possible port roles for ports A, B, C, and D in this RSTP-enabled network?
Modules 5 – 6: Redundant Networks Exam 33
- alternate, designated, root, root
- designated, alternate, root, root
- alternate, root, designated, root
- designated, root, alternate, root
Explanation: Because S1 is the root bridge, B is a designated port, and C and D root ports. RSTP supports a new port type, alternate port in discarding state, that can be port A in this scenario.
34. Refer to the exhibit. Which switching technology would allow each access layer switch link to be aggregated to provide more bandwidth between each Layer 2 switch and the Layer 3 switch?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 02
- trunking
- HSRP
- PortFast
- EtherChannel
Explanation: PortFast is used to reduce the amount of time that a port spends going through the spanning-tree algorithm, so that devices can start sending data sooner. Trunking can be implemented in conjunction with EtherChannel, but trunking alone does not aggregate switch links. HSRP is used to load-balance traffic across two different connections to Layer 3 devices for default gateway redundancy. HSRP does not aggregate links at either Layer 2 or Layer 3 as EtherChannel does.
35. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator wants to form an EtherChannel between the two switches by using the Port Aggregation Protocol. If switch S1 is configured to be in auto mode, which mode should be configured on S2 to form the EtherChannel?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 06
- auto
- on
- off
- desirable
Explanation: An EtherChannel will be formed via PAgP when both switches are in on mode or when one of them is in auto or desirable mode and the other is in desirable mode.
36. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which set of configuration commands issued on SW1 will successfully complete the EtherChannel link between SW1 and SW2?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 36
- interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no shutdown - interface Port-channel 1
no shutdown - interface GigabitEthernet0/2
channel-group 2 mode desirable - interface GigabitEthernet0/1
channel-group 1 mode desirable
Explanation: Issuing the show running-configuration command on SW1 shows that interface GigabitEthernet0/1 is missing the channel-group 1 mode desirable command which will compete the EtherChannel configuration for interface GigabitEthernet0/1 and interface GigabitEthernet0/2.
37. A set of switches is being connected in a LAN topology. Which STP bridge priority value will make it least likely for the switch to be selected as the root?
- 65535
- 4096
- 32768
- 61440
Explanation: The STP bridge priority is a two byte number, but it can only be customized in increments of 4096. The smaller number is preferred, but the largest usable priority value is 61440.
38. In which two PVST+ port states are MAC addresses learned? (Choose two.)
- learning
- forwarding
- disabled
- listening
- blocking
Explanation: The two PVST+ port states during which MAC addresses are learned and populate the MAC address table are the learning and the forwarding states.
39. Which port role is assigned to the switch port that has the lowest cost to reach the root bridge?
- designated port
- disabled port
- root port
- non-designated port
Explanation: The root port on a switch is the port with the lowest cost to reach the root bridge.
40. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the switch port closest, in terms of overall cost, to the root bridge?
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
- disabled
42. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field used to specify a VLAN ID?
- extended system ID
- port ID
- bridge priority
- bridge ID
43. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the reference point for all path calculations?
- root bridge
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
44. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field that has a default value of 32,768 and is the initial deciding factor when electing a root bridge?
- bridge priority
- MAC Address
- extended system ID
- bridge ID
45. Which statement describes an EtherChannel implementation?
- EtherChannel operates only at Layer 2.
- PAgP cannot be used in conjunction with EtherChannel.
- A trunked port can be part of an EtherChannel bundle.
- EtherChannel can support up to a maximum of ten separate links.
Explanation: Up to 16 links can be grouped in an EtherChannel by using the the PAgP or LACP protocol. EtherChannel can be configured as a Layer 2 bundle or a Layer 3 bundle. Configuring a Layer 3 bundle is beyond the scope of this course. If a trunked port is a part of the EtherChannel bundle, all ports in the bundle need to be trunk ports and the native VLAN must be the same on all of these ports. A best practice is to apply the configuration to the port channel interface. The configuration is then automatically applied to the individual ports.
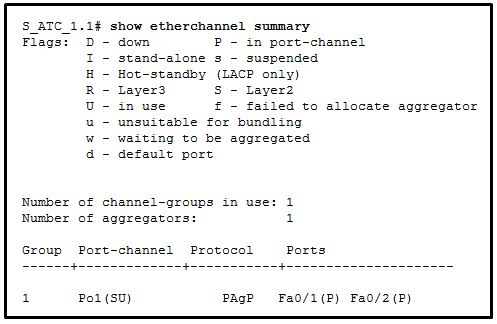
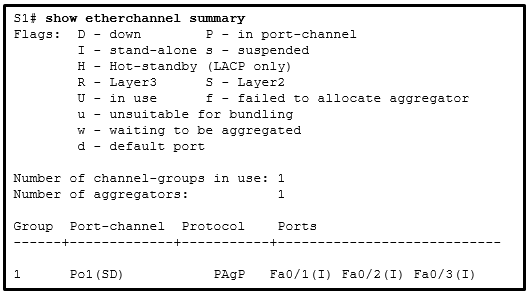
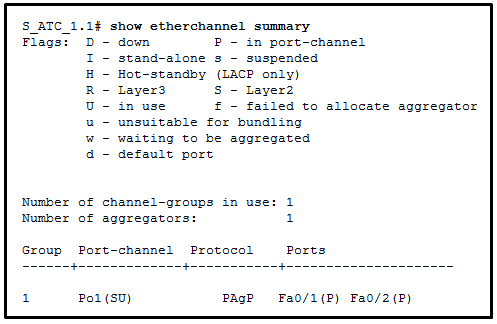
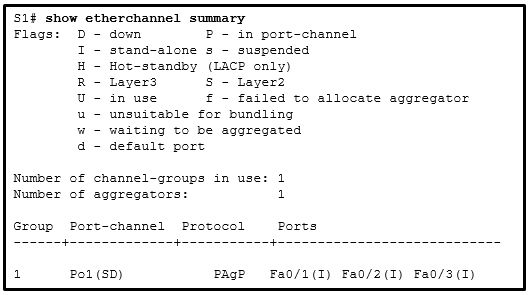
46. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issued the show etherchannel summary command on the switch S1. What conclusion can be drawn?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers
- The EtherChannel is suspended.
- The EtherChannel is not functional.
- The port aggregation protocol PAgP is misconfigured.
- FastEthernet ports Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 do not join the EtherChannel.
Explanation: The EtherChannel status shows as (SD), which means it is a Layer 2 EtherChannel with a status of D or down. Because the EtherChannel is down, the status of the interfaces in the channel group is stand-alone. PAgP is configured on S1, but there is no indication whether it is configured correctly on S1. The problem might also be the adjacent switch EtherChannel configuration.
47. Which statement describes a characteristic of EtherChannel?
- It can combine up to a maximum of 4 physical links.
- It can bundle mixed types of 100 Mb/s and 1Gb/s Ethernet links.
- It consists of multiple parallel links between a switch and a router.
- It is made by combining multiple physical links that are seen as one link between two switches.
Explanation: An EtherChannel is formed by combining multiple (same type) Ethernet physical links so they are seen and configured as one logical link. It provides an aggregated link between two switches. Currently each EtherChannel can consist of up to eight compatibly configured Ethernet ports.
48. Which two channel group modes would place an interface in a negotiating state using PAgP? (Choose two.)
- on
- desirable
- active
- auto
- passive
Explanation: There are three modes available when configuring an interface for PAgP: on, desirable, and auto. Only desirable and auto place the interface in a negotiating state. The active and passive states are used to configure LACP and not PAgP.
49. Which mode configuration setting would allow formation of an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 without sending negotiation traffic?
SW1: on
SW2: on
SW1: desirable
SW2: desirable
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
trunking enabled on both switches
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
PortFast enabled on both switches
SW1: passive
SW2: active
Explanation: The auto channel-group keyword enables PAgP only if a PAgP device is detected on the opposite side of the link. If the auto keyword is used, the only way to form an EtherChannel link is if the opposite connected device is configured with the desirable keyword. PortFast and trunking technologies are irrelevant to forming an EtherChannel link. Even though an EtherChannel can be formed if both sides are configured in desirable mode, PAgP is active and PAgP messages are being sent constantly across the link, decreasing the amount of bandwidth available for user traffic.
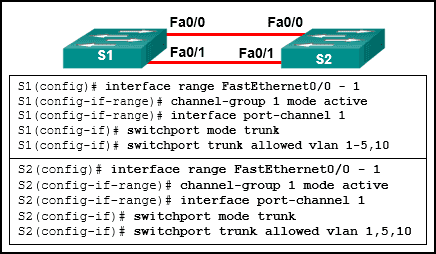
50. Refer to the exhibit. An EtherChannel was configured between switches S1 and S2, but the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel. What is the problem?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 50
- The interface port-channel number has to be different on each switch.
- The switch ports were not configured with speed and duplex mode.
- The switch ports have to be configured as access ports with each port having a VLAN assigned.
- The EtherChannel was not configured with the same allowed range of VLANs on each interface.
51. When EtherChannel is configured, which mode will force an interface into a port channel without exchanging aggregation protocol packets?
- active
- auto
- on
- desirable
Explanation: For both LACP and PAgP, the “on” mode will force an interface into an EtherChannel without exchanging protocol packets.
52. What are two load-balancing methods in the EtherChannel technology? (Choose two.)
- combination of source port and IP to destination port and IP
- source IP to destination IP
- source port to destination port
- combination of source MAC and IP to destination MAC and IP
- source MAC to destination MAC
Explanation: Depending on the hardware platform, one or more load-balancing methods can be implemented. These methods include source MAC to destination MAC load balancing or source IP to destination IP load balancing, across the physical links.
53. Which protocol provides up to 16 instances of RSTP, combines many VLANs with the same physical and logical topology into a common RSTP instance, and provides support for PortFast, BPDU guard, BPDU filter, root guard, and loop guard?
- STP
- Rapid PVST+
- PVST+
- MST
Explanation: MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP, an IEEE standard protocol that provides up to 16 instances of RSTP and combines many VLANs with the same physical and logical topology into a common RSTP instance. Each instance supports PortFast, BPDU guard, BPDU filter, root guard, and loop guard. STP and RSTP assume only one spanning-tree instance for the entire bridged network, regardless of the number of VLANs. PVST+ provides a separate 802.1D spanning-tree instance for each VLAN that is configured in the network.
54. What is the outcome of a Layer 2 broadcast storm?
- Routers will take over the forwarding of frames as switches become congested.
- New traffic is discarded by the switch because it is unable to be processed.
- CSMA/CD will cause each host to continue transmitting frames.
- ARP broadcast requests are returned to the transmitting host.
Explanation: When the network is saturated with broadcast traffic that is looping between switches, new traffic is discarded by each switch because it is unable to be processed.
55. Which two network design features require Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to ensure correct network operation? (Choose two.)
- static default routes
- implementing VLANs to contain broadcasts
- redundant links between Layer 2 switches
- link-state dynamic routing that provides redundant routes
- removing single points of failure with multiple Layer 2 switches
Explanation: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is required to ensure correct network operation when designing a network with multiple interconnected Layer 2 switches or using redundant links to eliminate single points of failure between Layer 2 switches. Routing is a Layer 3 function and does not relate to STP. VLANs do reduce the number of broadcast domains but relate to Layer 3 subnets, not STP.
56. A network administrator has configured an EtherChannel between two switches that are connected via four trunk links. If the physical interface for one of the trunk links changes to a down state, what happens to the EtherChannel?
- Spanning Tree Protocol will transition the failed physical interface into forwarding mode.
- Spanning Tree Protocol will recalculate the remaining trunk links.
- The EtherChannel will transition to a down state.
- The EtherChannel will remain functional.
Explanation: EtherChannel offers redundancy by bundling multiple trunk links into one logical connection. Failure of one physical link within the EtherChannel will not create a change in the topology and therefore a recalculation by Spanning Tree is unnecessary. Just one physical link must remain operational for the EtherChannel to continue to function.
Last Updated on February 1, 2021 by
CCNA 2 SRWE – Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials (Version 7.00) – Modules 5 – 6 – Redundant Networks Exam Answers
Cisco Netacad SRWE Version 7.00 CCNA 2 v7 Modules 5 – 6 – Redundant Networks Exam Answers 2020 2021 – Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essential
-
Which three components are combined to form a bridge ID?
- port ID
- IP address
- extended system ID
- MAC address
- bridge priority
- cost
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The three components that are combined to form a bridge ID are bridge priority, extended system ID, and MAC address.
-
Match the STP protocol with the correct description. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 001
-
In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network? (Choose two.)
- blocking
- disabled
- forwarding
- learning
- listening
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Switches learn MAC addresses at the learning and forwarding port states. They receive and process BPDUs at the blocking, listening, learning, and forwarding port states.
-
If no bridge priority is configured in PVST, which criteria is considered when electing the root bridge?
- lowest IP address
- lowest MAC address
- highest IP address
- highest MAC address
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Only one switch can be the root bridge for a VLAN. The root bridge is the switch with the lowest BID. The BID is determined by priority and the MAC address. If no priority is configured then all switches use the default priority and the election of the root bridge will be based on the lowest MAC address.
-
Which two network design features require Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to ensure correct network operation? (Choose two.)
- static default routes
- implementing VLANs to contain broadcasts
- redundant links between Layer 2 switches
- link-state dynamic routing that provides redundant routes
- removing single points of failure with multiple Layer 2 switches
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is required to ensure correct network operation when designing a network with multiple interconnected Layer 2 switches or using redundant links to eliminate single points of failure between Layer 2 switches. Routing is a Layer 3 function and does not relate to STP. VLANs do reduce the number of broadcast domains but relate to Layer 3 subnets, not STP.
-
What is the outcome of a Layer 2 broadcast storm?
- Routers will take over the forwarding of frames as switches become congested.
- New traffic is discarded by the switch because it is unable to be processed.
- CSMA/CD will cause each host to continue transmitting frames.
- ARP broadcast requests are returned to the transmitting host.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When the network is saturated with broadcast traffic that is looping between switches, new traffic is discarded by each switch because it is unable to be processed.
-
Match the spanning-tree feature with the protocol type. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 002
Answers Explanation & Hints:MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP (IEEE 802.1s).
-
When the show spanning-tree vlan 33 command is issued on a switch, three ports are shown in the forwarding state. In which two port roles could these interfaces function while in the forwarding state? (Choose two.)
- disabled
- designated
- root
- alternate
- blocked
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The role of each of the three ports will be either designated port or root port. Ports in the disabled state are administratively disabled. Ports in the blocking state are alternate ports.
-
A set of switches is being connected in a LAN topology. Which STP bridge priority value will make it least likely for the switch to be selected as the root?
- 4096
- 32768
- 61440
- 65535
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The STP bridge priority is a two byte number, but it can only be customized in increments of 4096. The smaller number is preferred, but the largest usable priority value is 61440.
-
What is the function of STP in a scalable network?
- It decreases the size of the failure domain to contain the impact of failures.
- It protects the edge of the enterprise network from malicious activity.
- It disables redundant paths to eliminate Layer 2 loops.
- It combines multiple switch trunk links to act as one logical link for increased bandwidth.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
STP is an important component in a scalable network because it allows redundant physical connections between Layer 2 devices to be implemented without creating Layer 2 loops. STP prevents Layer 2 loops from forming by disabling interfaces on Layer 2 devices when they would create a loop.
-
What is a characteristic of spanning tree?
- It is enabled by default on Cisco switches.
- It has a TTL mechanism that works at Layer 2.
- It prevents propagation of Layer 2 broadcast frames.
- It is used to discover information about an adjacent Cisco device.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Spanning tree does work at Layer 2 on Ethernet-based networks and is enabled by default, but it does not have a TTL mechanism. Spanning tree exists because Layer 2 frames do not have a TTL mechanism. Layer 2 frames are still broadcast when spanning tree is enabled, but the frames can only be transmitted through a single path through the Layer 2 network that was created by spanning tree. Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is used to discover information about an adjacent Cisco device.
-
Which spanning tree standard supports only one root bridge so that traffic from all VLANs flows over the same path?
- Rapid PVST
- 802.1D
- MST
- PVST+
Answers Explanation & Hints:
MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP, an IEEE standard protocol that provides up to 16 instances of RSTP. PVST+ provides a separate 802.1D spanning-tree instance for each VLAN that is configured in the network. 802.1D is the original STP standard defined by the IEEE and allows for only one root bridge for all VLANs. 802.1w, or RSTP, provides faster convergence but still uses only one STP instance for all VLANs.
-
What is the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
- prevents Layer 2 loops
- prevents routing loops on a router
- creates smaller collision domains
- creates smaller broadcast domains
- allows Cisco devices to exchange routing table updates
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) creates one path through a switch network in order to prevent Layer 2 loops.
-
Which protocol provides up to 16 instances of RSTP, combines many VLANs with the same physical and logical topology into a common RSTP instance, and provides support for PortFast, BPDU guard, BPDU filter, root guard, and loop guard?
- STP
- Rapid PVST+
- PVST+
- MST
Answers Explanation & Hints:
MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP, an IEEE standard protocol that provides up to 16 instances of RSTP and combines many VLANs with the same physical and logical topology into a common RSTP instance. Each instance supports PortFast, BPDU guard, BPDU filter, root guard, and loop guard. STP and RSTP assume only one spanning-tree instance for the entire bridged network, regardless of the number of VLANs. PVST+ provides a separate 802.1D spanning-tree instance for each VLAN that is configured in the network.
-
In which two PVST+ port states are MAC addresses learned? (Choose two.)
- forwarding
- disabled
- learning
- listening
- blocking
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The two PVST+ port states during which MAC addresses are learned and populate the MAC address table are the learning and the forwarding states.
-
What is the value used to determine which port on a non-root bridge will become a root port in a STP network?
- the highest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
- the lowest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
- the VTP revision number
- the path cost
Answers Explanation & Hints:
STP establishes one root port on each non-root bridge. The root port is the lowest-cost path from the non-root bridge to the root bridge, indicating the direction of the best path to the root bridge. This is primarily based on the path cost to the root bridge.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which switch will be the root bridge after the election process is complete?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 04
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The root bridge is determined by the lowest bridge ID, which consists of the priority value and the MAC address. Because the priority values of all of the switches are identical, the MAC address is used to determine the root bridge. Because S2 has the lowest MAC address, S2 becomes the root bridge.
-
What are two drawbacks to turning spanning tree off and having multiple paths through the Layer 2 switch network? (Choose two.)
- The switch acts like a hub.
- Port security becomes unstable.
- The MAC address table becomes unstable.
- Broadcast frames are transmitted indefinitely.
- Port security shuts down all of the ports that have attached devices.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Spanning tree should never be disabled. Without it, the MAC address table becomes unstable, broadcast storms can render network clients and the switches unusable, and multiple copies of unicast frames can be delivered to the end devices.
-
Which port role is assigned to the switch port that has the lowest cost to reach the root bridge?
- root port
- non-designated port
- designated port
- disabled port
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The root port on a switch is the port with the lowest cost to reach the root bridge.
-
A small company network has six interconnected Layer 2 switches. Currently all switches are using the default bridge priority value. Which value can be used to configure the bridge priority of one of the switches to ensure that it becomes the root bridge in this design?
- 1
- 28672
- 32768
- 34816
- 61440
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The default bridge priority value for all Cisco switches is 32768. The range is 0 to 61440 in increments of 4096. Thus, the values 1 and 34816 are invalid. Configuring one switch with the lower value of 28672 (and leaving the bridge priority value of all other switches unchanged) will make the switch become the root bridge.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The administrator tried to create an EtherChannel between S1 and the other two switches via the commands that are shown, but was unsuccessful. What is the problem?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 10
- Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
- Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Layer 3 switches.
- Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches through the same EtherChannel link.
- Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches, but only to two different devices like an EtherChannel-enabled server and a switch.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
An EtherChannel link can only be created between two switches or between an EtherChannel-enabled server and a switch. Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches through the same EtherChannel link.
-
Which statement is true regarding the use of PAgP to create EtherChannels?
- It requires full duplex.
- It is Cisco proprietary.
- It requires more physical links than LACP does.
- It increases the number of ports that are participating in spanning tree.
- It mandates that an even number of ports (2, 4, 6, etc.) be used for aggregation.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
PAgP is used to automatically aggregate multiple ports into an EtherChannel bundle, but it only works between Cisco devices. LACP can be used for the same purpose between Cisco and non-Cisco devices. PAgP must have the same duplex mode at both ends and can use two ports or more. The number of ports depends on the switch platform or module. An EtherChannel aggregated link is seen as one port by the spanning-tree algorithm.
-
What are two requirements to be able to configure an EtherChannel between two switches? (Choose two.)
- The interfaces that are involved need to be contiguous on the switch.
- All the interfaces need to work at the same speed.
- All the interfaces need to be working in the same duplex mode.
- All interfaces need to be assigned to different VLANs.
- Different allowed ranges of VLANs must exist on each end.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
All interfaces in the EtherChannel bundle must be assigned to the same VLAN or be configured as a trunk. If the allowed range of VLANs is not the same, the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel even when set to auto or desirable mode.
-
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output that is shown, what can be determined about the EtherChannel bundle?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 06
- The EtherChannel bundle is down.
- The EtherChannel bundle is operating at both Layer 2 and Layer 3.
- Two Gigabit Ethernet ports are used to form the EtherChannel.
- A Cisco proprietary protocol was used to negotiate the EtherChannel link.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Two protocols can be used to send negotiation frames that are used to try to establish an EtherChannel link: PAgP and LACP. PAgP is Cisco proprietary, and LACP adheres to the industry standard.
-
Which two parameters must match on the ports of two switches to create a PAgP EtherChannel between the switches? (Choose two.)
- MAC address
- speed
- VLAN information
- PAgP mode
- port ID
Answers Explanation & Hints:
For an EtherChannel to be created, the ports that are concerned on the two switches must match in terms of the speed, duplex, and VLAN information. The PAgP mode must be compatible but not necessarily equal. The port ID and the MAC addresses do not have to match.
-
What are two load-balancing methods in the EtherChannel technology? (Choose two.)
- combination of source port and IP to destination port and IP
- source IP to destination IP
- source port to destination port
- combination of source MAC and IP to destination MAC and IP
- source MAC to destination MAC
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Depending on the hardware platform, one or more load-balancing methods can be implemented. These methods include source MAC to destination MAC load balancing or source IP to destination IP load balancing, across the physical links.
-
When EtherChannel is configured, which mode will force an interface into a port channel without exchanging aggregation protocol packets?
- active
- auto
- on
- desirable
Answers Explanation & Hints:
For both LACP and PAgP, the “on” mode will force an interface into an EtherChannel without exchanging protocol packets.
-
Refer to the exhibit. An EtherChannel was configured between switches S1 and S2, but the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel. What is the problem?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 08
- The interface port-channel number has to be different on each switch.
- The switch ports were not configured with speed and duplex mode.
- The switch ports have to be configured as access ports with each port having a VLAN assigned.
- The EtherChannel was not configured with the same allowed range of VLANs on each interface.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The guidelines for configuring an EtherChannel link are:Interfaces which form an EtherChannel can be physically discontiguous, and on different modules.
Interfaces in an EtherChannel have to operate at the same speed and in the same duplex mode.
Interfaces in the EtherChannel must be assigned to the same VLAN, or be configured as a trunk.
Interfaces in the EtherChannel have to support the same allowed range of VLANs.
-
Which mode configuration setting would allow formation of an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 without sending negotiation traffic?
- SW1: on
SW2: on - SW1: desirable
SW2: desirable - SW1: auto
SW2: auto
trunking enabled on both switches - SW1: auto
SW2: auto
PortFast enabled on both switches - SW1: passive
SW2: activeAnswers Explanation & Hints:The auto channel-group keyword enables PAgP only if a PAgP device is detected on the opposite side of the link. If the auto keyword is used, the only way to form an EtherChannel link is if the opposite connected device is configured with the desirable keyword. PortFast and trunking technologies are irrelevant to forming an EtherChannel link. Even though an EtherChannel can be formed if both sides are configured in desirable mode, PAgP is active and PAgP messages are being sent constantly across the link, decreasing the amount of bandwidth available for user traffic.
- SW1: on
-
Which two channel group modes would place an interface in a negotiating state using PAgP? (Choose two.)
- on
- desirable
- active
- auto
- passive
Answers Explanation & Hints:
There are three modes available when configuring an interface for PAgP: on, desirable, and auto. Only desirable and auto place the interface in a negotiating state. The active and passive states are used to configure LACP and not PAgP.
-
A network administrator has configured an EtherChannel between two switches that are connected via four trunk links. If the physical interface for one of the trunk links changes to a down state, what happens to the EtherChannel?
- The EtherChannel will transition to a down state.
- Spanning Tree Protocol will recalculate the remaining trunk links.
- The EtherChannel will remain functional.
- Spanning Tree Protocol will transition the failed physical interface into forwarding mode.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
EtherChannel offers redundancy by bundling multiple trunk links into one logical connection. Failure of one physical link within the EtherChannel will not create a change in the topology and therefore a recalculation by Spanning Tree is unnecessary. Just one physical link must remain operational for the EtherChannel to continue to function.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two switches, SW1 and SW2. Which statement describes the effect after the commands are issued on SW1 and SW2?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 03
- The EtherChannel fails to establish.
- The EtherChannel is established without negotiation.
- The EtherChannel is established after SW1 initiates the link request.
- The EtherChannel is established after SW2 initiates the link request.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/1 and GigabitEthernet 0/2 are configured “on” for the EtherChannel link. This mode forces the interface to channel without PAgP or LACP. The EtherChannel will be established only if the other side is also set to “on”. However, the mode on SW2 side is set to PAgP desirable. Thus the EtherChannel link will not be established.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two switches, SW1 and SW2. However, the EtherChannel link fails to establish. What change in configuration would correct the problem?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 02
- Configure SW1 EtherChannel mode to on.
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to on.
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to auto.
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to desirable.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The EtherChannel mode must be compatible on each side for the link to work. The three modes from PAgP protocol are on, desirable, and auto. The three modes from LACP protocol are on, active, and passive. The compatible modes include on-on, auto-desirable, desirable-desirable, active-passive, and active-active. Any other combinations will not form an EtherChannel link.
-
A network administrator configured an EtherChannel link with three interfaces between two switches. What is the result if one of the three interfaces is down?
- The EtherChannel fails.
- The remaining two interfaces continue to load balance traffic.
- The remaining two interfaces become separate links between the two switches.
- One interface becomes an active link for data traffic and the other becomes a backup link.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
EtherChannel creates an aggregation that is seen as one logical link. It provides redundancy because the overall link is one logical connection. The loss of one physical link within the channel does not create a change in the topology; the EtherChannel remains functional.
-
Which statement describes a characteristic of EtherChannel?
- It can combine up to a maximum of 4 physical links.
- It can bundle mixed types of 100 Mb/s and 1Gb/s Ethernet links.
- It consists of multiple parallel links between a switch and a router.
- It is made by combining multiple physical links that are seen as one link between two switches.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
An EtherChannel is formed by combining multiple (same type) Ethernet physical links so they are seen and configured as one logical link. It provides an aggregated link between two switches. Currently each EtherChannel can consist of up to eight compatibly configured Ethernet ports.
-
A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 by using the command SW1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode auto . Which command must be used on SW2 to enable this EtherChannel?
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode on
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode active
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode passive
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The possible combinations to establish an EtherChannel between SW1 and SW2 using LACP or PAgP are as follows:
PAgP
on on
auto desirable
desirable desirableLACP
on on
active active
passive activeThe EtherChannel mode chosen on each side of the EtherChannel must be compatible in order to enable it.
-
Which technology is an open protocol standard that allows switches to automatically bundle physical ports into a single logical link?
- Multilink PPP
- DTP
- LACP
- PAgP
Answers Explanation & Hints:
LACP, or Link Aggregation Control Protocol, is defined by IEEE 802.3ad and is an open standard protocol. LACP allows switches to automatically bundle switch ports into a single logical link to increase bandwidth. PAgP, or Port Aggregation Protocol, performs a similar function, but it is a Cisco proprietary protocol. DTP is Dynamic Trunking Protocol and is used to automatically and dynamically build trunks between switches. Multilink PPP is used to load-balance PPP traffic across multiple serial interfaces.
-
What is a requirement to configure a trunking EtherChannel between two switches?
- The participating interfaces must be physically contiguous on a switch.
- The allowed range of VLANs must be the same on both switches.
- The participating interfaces must be on the same module on a switch.
- The participating interfaces must be assigned the same VLAN number on both switches.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
To enable a trunking EtherChannel successfully, the range of VLANs allowed on all the interfaces must match; otherwise, the EtherChannel cannot be formed. The interfaces involved in an EtherChannel do not have to be physically contiguous, or on the same module. Because the EtherChannel is a trunking one, participating interfaces are configured as trunk mode, not access mode.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issued the show etherchannel summary command on the switch S1. What conclusion can be drawn?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 01
- The EtherChannel is suspended.
- The EtherChannel is not functional.
- The port aggregation protocol PAgP is misconfigured.
- FastEthernet ports Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 do not join the EtherChannel.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The EtherChannel status shows as (SD), which means it is a Layer 2 EtherChannel with a status of D or down. Because the EtherChannel is down, the status of the interfaces in the channel group is stand-alone. PAgP is configured on S1, but there is no indication whether it is configured correctly on S1. The problem might also be the adjacent switch EtherChannel configuration.
-
Which statement describes an EtherChannel implementation?
- EtherChannel operates only at Layer 2.
- PAgP cannot be used in conjunction with EtherChannel.
- A trunked port can be part of an EtherChannel bundle.
- EtherChannel can support up to a maximum of ten separate links.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Up to 16 links can be grouped in an EtherChannel by using the the PAgP or LACP protocol. EtherChannel can be configured as a Layer 2 bundle or a Layer 3 bundle. Configuring a Layer 3 bundle is beyond the scope of this course. If a trunked port is a part of the EtherChannel bundle, all ports in the bundle need to be trunk ports and the native VLAN must be the same on all of these ports. A best practice is to apply the configuration to the port channel interface. The configuration is then automatically applied to the individual ports.
-
What are two advantages of using LACP? (Choose two.)
- LACP allows Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces to be mixed within a single EtherChannel.
- It eliminates the need for configuring trunk interfaces when deploying VLANs on multiple switches.
- It allows directly connected switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link.
- It provides a simulated environment for testing link aggregation.
- It decreases the amount of configuration that is needed on a switch.
- It allows the use of multivendor devices.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) allows directly connected multivendor switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link. LACP helps create the EtherChannel link by detecting the configuration of each side and making sure that they are compatible so that the EtherChannel link can be enabled when needed.
-
What are two advantages of EtherChannel? (Choose two.)
- Configuring the EtherChannel interface provides consistency in the configuration of the physical links.
- Load balancing occurs between links configured as different EtherChannels.
- EtherChannel uses upgraded physical links to provide increased bandwidth.
- Spanning Tree Protocol views the physical links in an EtherChannel as one logical connection.
- Spanning Tree Protocol ensures redundancy by transitioning failed interfaces in an EtherChannel to a forwarding state.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
EtherChannel configuration of one logical interface ensures configuration consistency across the physical links in the EtherChannel. The EtherChannel provides increased bandwidth using existing switch ports without requiring any upgrades to the physical interfaces. Load balancing methods are implemented between links that are part of the same Etherchannel. Because EtherChannel views the bundled physical links as one logical connection, spanning tree recalculation is not required if one of the bundled physical links fail. If a physical interface fails, STP cannot transition the failed interface into a forwarding state.
-
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field that has a default value of 32,768 and is the initial deciding factor when electing a root bridge?
- bridge priority
- BPDUs
- bridge ID
- extended system ID
-
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the reference point for all path calculations?
- root bridge
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
-
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field used to specify a VLAN ID?
- extended system ID
- port ID
- MAC Address
- bridge priority
-
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the switch port closest, in terms of overall cost, to the root bridge?
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
- disabled
-
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the switch port closest, in terms of overall cost, to the root bridge?
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
- root bridge
-
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the reference point for all path calculations?
- root bridge
- root port
- designated port
- disabled
-
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a non-root port that is permitted to forward traffic on the network?
- designated port
- alternate port
- disabled
- root port
-
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a non-root port that is permitted to forward traffic on the network?
- designated port
- alternate port
- disabled
- dedicated port
-
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field used to specify a VLAN ID?
- extended system ID
- port ID
- bridge priority
- bridge ID
-
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field that has a default value of 32,768 and is the initial deciding factor when electing a root bridge?
- bridge priority
- MAC Address
- extended system ID
- bridge ID
-
Refer to the exhibit. What are the possible port roles for ports A, B, C, and D in this RSTP-enabled network?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 05
- alternate, root, designated, root
- designated, root, alternate, root
- alternate, designated, root, root
- designated, alternate, root, root
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Because S1 is the root bridge, B is a designated port, and C and D root ports. RSTP supports a new port type, alternate port in discarding state, that can be port A in this scenario.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which switching technology would allow each access layer switch link to be aggregated to provide more bandwidth between each Layer 2 switch and the Layer 3 switch?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 07
- HSRP
- PortFast
- trunking
- EtherChannel
Answers Explanation & Hints:
PortFast is used to reduce the amount of time that a port spends going through the spanning-tree algorithm, so that devices can start sending data sooner. Trunking can be implemented in conjunction with EtherChannel, but trunking alone does not aggregate switch links. HSRP is used to load-balance traffic across two different connections to Layer 3 devices for default gateway redundancy. HSRP does not aggregate links at either Layer 2 or Layer 3 as EtherChannel does.
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator wants to form an EtherChannel between the two switches by using the Port Aggregation Protocol. If switch S1 is configured to be in auto mode, which mode should be configured on S2 to form the EtherChannel?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 09
- on
- auto
- desirable
- off
Answers Explanation & Hints:
An EtherChannel will be formed via PAgP when both switches are in on mode or when one of them is in auto or desirable mode and the other is in desirable mode.
-
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which set of configuration commands issued on SW1 will successfully complete the EtherChannel link between SW1 and SW2?
- interface Port-channel 1
no shutdown - interface GigabitEthernet0/1
channel-group 1 mode desirable - interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no shutdown - interface GigabitEthernet0/2
channel-group 2 mode desirableAnswers Explanation & Hints:Issuing the show running-configuration command on SW1 shows that interface GigabitEthernet0/1 is missing the channel-group 1 mode desirable command which will compete the EtherChannel configuration for interface GigabitEthernet0/1 and interface GigabitEthernet0/2.
- interface Port-channel 1
CCNA 2 v7 Modules 5 – 6: Redundant Networks Full Exam Answers
1. What additional information is contained in the 12-bit extended system ID of a BPDU?
MAC address
VLAN ID*
IP address
port ID
2. During the implementation of Spanning Tree Protocol, all switches are rebooted by the network administrator. What is the first step of the spanning-tree election process?
Each switch with a lower root ID than its neighbor will not send BPDUs.
All the switches send out BPDUs advertising themselves as the root bridge.*
Each switch determines the best path to forward traffic.
Each switch determines what port to block to prevent a loop from occurring.
3. Which STP port role is adopted by a switch port if there is no other port with a lower cost to the root bridge?
designated port
root port*
alternate
disabled port
4. Which two concepts relate to a switch port that is intended to have only end devices attached and intended never to be used to connect to another switch? (Choose two.)
bridge ID
edge port*
extended system ID
PortFast*
PVST+
5. Which three components are combined to form a bridge ID?
extended system ID*
cost
IP address
bridge priority*
MAC address*
port ID
Explanation: The three components that are combined to form a bridge ID are bridge priority, extended system ID, and MAC address.
6. Match the STP protocol with the correct description. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p6
7. In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network? (Choose two.)
disabled
forwarding*
listening
blocking
learning*
Explanation: Switches learn MAC addresses at the learning and forwarding port states. They receive and process BPDUs at the blocking, listening, learning, and forwarding port states.
8. If no bridge priority is configured in PVST, which criteria is considered when electing the root bridge?
lowest MAC address*
lowest IP address
highest IP address
highest MAC address
Explanation: Only one switch can be the root bridge for a VLAN. The root bridge is the switch with the lowest BID. The BID is determined by priority and the MAC address. If no priority is configured then all switches use the default priority and the election of the root bridge will be based on the lowest MAC address.
9. Match the spanning-tree feature with the protocol type. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p9
10. When the show spanning-tree vlan 33 command is issued on a switch, three ports are shown in the forwarding state. In which two port roles could these interfaces function while in the forwarding state? (Choose two.)
alternate
designated*
disabled
blocked
root*
Explanation: The role of each of the three ports will be either designated port or root port. Ports in the disabled state are administratively disabled. Ports in the blocking state are alternate ports.
11. What is the function of STP in a scalable network?
It decreases the size of the failure domain to contain the impact of failures.
It protects the edge of the enterprise network from malicious activity.
It combines multiple switch trunk links to act as one logical link for increased bandwidth.
It disables redundant paths to eliminate Layer 2 loops.*
12. What is a characteristic of spanning tree?
It is enabled by default on Cisco switches.*
It is used to discover information about an adjacent Cisco device.
It has a TTL mechanism that works at Layer 2.
It prevents propagation of Layer 2 broadcast frames.
13. Which spanning tree standard supports only one root bridge so that traffic from all VLANs flows over the same path?
PVST+
802.1D*
MST
Rapid PVST
Explanation: MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP, an IEEE standard protocol that provides up to 16 instances of RSTP. PVST+ provides a separate 802.1D spanning-tree instance for each VLAN that is configured in the network. 802.1D is the original STP standard defined by the IEEE and allows for only one root bridge for all VLANs. 802.1w, or RSTP, provides faster convergence but still uses only one STP instance for all VLANs.
14. What is the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
creates smaller collision domains
prevents routing loops on a router
prevents Layer 2 loops*
allows Cisco devices to exchange routing table updates
creates smaller broadcast domains
15. What is the value used to determine which port on a non-root bridge will become a root port in a STP network?
the path cost*
the highest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
the lowest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
the VTP revision number
16. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p16
Which switch will be the root bridge after the election process is complete?
S1
S2*
S3
S4
Explanation: The root bridge is determined by the lowest bridge ID, which consists of the priority value and the MAC address. Because the priority values of all of the switches are identical, the MAC address is used to determine the root bridge. Because S2 has the lowest MAC address, S2 becomes the root bridge.
17. What are two drawbacks to turning spanning tree off and having multiple paths through the Layer 2 switch network? (Choose two.)
The MAC address table becomes unstable.*
The switch acts like a hub.
Port security becomes unstable.
Broadcast frames are transmitted indefinitely.*
Port security shuts down all of the ports that have attached devices.
Explanation: Spanning tree should never be disabled. Without it, the MAC address table becomes unstable, broadcast storms can render network clients and the switches unusable, and multiple copies of unicast frames can be delivered to the end devices.
18. A small company network has six interconnected Layer 2 switches. Currently all switches are using the default bridge priority value. Which value can be used to configure the bridge priority of one of the switches to ensure that it becomes the root bridge in this design?
1
28672*
32768
34816
61440
Explanation: The default bridge priority value for all Cisco switches is 32768. The range is 0 to 61440 in increments of 4096. Thus, the values 1 and 34816 are invalid. Configuring one switch with the lower value of 28672 (and leaving the bridge priority value of all other switches unchanged) will make the switch become the root bridge.
19. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p19
The administrator tried to create an EtherChannel between S1 and the other two switches via the commands that are shown, but was unsuccessful. What is the problem?
Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches through the same EtherChannel link.*
Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches, but only to two different devices like an EtherChannel-enabled server and a switch.
Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Layer 3 switches.
20. Which statement is true regarding the use of PAgP to create EtherChannels?
It requires full duplex.
It increases the number of ports that are participating in spanning tree.
It requires more physical links than LACP does.
It mandates that an even number of ports (2, 4, 6, etc.) be used for aggregation.
It is Cisco proprietary.*
Explanation: PAgP is used to automatically aggregate multiple ports into an EtherChannel bundle, but it only works between Cisco devices. LACP can be used for the same purpose between Cisco and non-Cisco devices. PAgP must have the same duplex mode at both ends and can use two ports or more. The number of ports depends on the switch platform or module. An EtherChannel aggregated link is seen as one port by the spanning-tree algorithm.
21. What are two requirements to be able to configure an EtherChannel between two switches? (Choose two.)
All the interfaces need to work at the same speed.*
All interfaces need to be assigned to different VLANs.
Different allowed ranges of VLANs must exist on each end.
All the interfaces need to be working in the same duplex mode.*
The interfaces that are involved need to be contiguous on the switch.
Explanation: All interfaces in the EtherChannel bundle must be assigned to the same VLAN or be configured as a trunk. If the allowed range of VLANs is not the same, the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel even when set to auto or desirable mode.
22. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p22
On the basis of the output that is shown, what can be determined about the EtherChannel bundle?
The EtherChannel bundle is down.
Two Gigabit Ethernet ports are used to form the EtherChannel.
A Cisco proprietary protocol was used to negotiate the EtherChannel link.*
The EtherChannel bundle is operating at both Layer 2 and Layer 3.
Explanation: Two protocols can be used to send negotiation frames that are used to try to establish an EtherChannel link: PAgP and LACP. PAgP is Cisco proprietary, and LACP adheres to the industry standard.
23. Which two parameters must match on the ports of two switches to create a PAgP EtherChannel between the switches? (Choose two.)
port ID
PAgP mode
MAC address
Speed*
VLAN information*
Explanation: For an EtherChannel to be created, the ports that are concerned on the two switches must match in terms of the speed, duplex, and VLAN information. The PAgP mode must be compatible but not necessarily equal. The port ID and the MAC addresses do not have to match.
24. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p24
A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two switches, SW1 and SW2. Which statement describes the effect after the commands are issued on SW1 and SW2?
The EtherChannel is established after SW2 initiates the link request.
The EtherChannel is established after SW1 initiates the link request.
The EtherChannel is established without negotiation.
The EtherChannel fails to establish.*
25. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p25
A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two switches, SW1 and SW2. However, the EtherChannel link fails to establish. What change in configuration would correct the problem?
Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to desirable.*
Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to on.
Configure SW1 EtherChannel mode to on.
Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to auto.
Explanation: The EtherChannel mode must be compatible on each side for the link to work. The three modes from PAgP protocol are on, desirable, and auto. The three modes from LACP protocol are on, active, and passive. The compatible modes include on-on, auto-desirable, desirable-desirable, active-passive, and active-active. Any other combinations will not form an EtherChannel link.
26. A network administrator configured an EtherChannel link with three interfaces between two switches. What is the result if one of the three interfaces is down?
The remaining two interfaces continue to load balance traffic.*
The remaining two interfaces become separate links between the two switches.
One interface becomes an active link for data traffic and the other becomes a backup link.
The EtherChannel fails.
Explanation: EtherChannel creates an aggregation that is seen as one logical link. It provides redundancy because the overall link is one logical connection. The loss of one physical link within the channel does not create a change in the topology; the EtherChannel remains functional.
27. A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 by using the command SW1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode auto . Which command must be used on SW2 to enable this EtherChannel?
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode passive
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable*
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode on
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode active
Explanation: The possible combinations to establish an EtherChannel between SW1 and SW2 using LACP or PAgP are as follows:
PAgP
on on
auto desirable
desirable desirable
LACP
on on
active active
passive active
The EtherChannel mode chosen on each side of the EtherChannel must be compatible in order to enable it.
28. Which technology is an open protocol standard that allows switches to automatically bundle physical ports into a single logical link?
PAgP
LACP*
Multilink PPP
DTP
Explanation: LACP, or Link Aggregation Control Protocol, is defined by IEEE 802.3ad and is an open standard protocol. LACP allows switches to automatically bundle switch ports into a single logical link to increase bandwidth. PAgP, or Port Aggregation Protocol, performs a similar function, but it is a Cisco proprietary protocol. DTP is Dynamic Trunking Protocol and is used to automatically and dynamically build trunks between switches. Multilink PPP is used to load-balance PPP traffic across multiple serial interfaces.
29. What is a requirement to configure a trunking EtherChannel between two switches?
The allowed range of VLANs must be the same on both switches.*
The participating interfaces must be assigned the same VLAN number on both switches.
The participating interfaces must be physically contiguous on a switch.
The participating interfaces must be on the same module on a switch.
Explanation: To enable a trunking EtherChannel successfully, the range of VLANs allowed on all the interfaces must match; otherwise, the EtherChannel cannot be formed. The interfaces involved in an EtherChannel do not have to be physically contiguous, or on the same module. Because the EtherChannel is a trunking one, participating interfaces are configured as trunk mode, not access mode.
30. What are two advantages of using LACP? (Choose two.)
It allows directly connected switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link.*
It eliminates the need for configuring trunk interfaces when deploying VLANs on multiple switches.
It decreases the amount of configuration that is needed on a switch.
It provides a simulated environment for testing link aggregation.
It allows the use of multivendor devices.*
LACP allows Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces to be mixed within a single EtherChannel.
Explanation: The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) allows directly connected multivendor switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link. LACP helps create the EtherChannel link by detecting the configuration of each side and making sure that they are compatible so that the EtherChannel link can be enabled when needed.
31. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a non-root port that is permitted to forward traffic on the network?
root port
designated port*
alternate port
disabled
32. What are two advantages of EtherChannel? (Choose two.)
Spanning Tree Protocol views the physical links in an EtherChannel as one logical connection.*
Load balancing occurs between links configured as different EtherChannels.
Configuring the EtherChannel interface provides consistency in the configuration of the physical links.*
Spanning Tree Protocol ensures redundancy by transitioning failed interfaces in an EtherChannel to a forwarding state.
EtherChannel uses upgraded physical links to provide increased bandwidth.
Explanation: EtherChannel configuration of one logical interface ensures configuration consistency across the physical links in the EtherChannel. The EtherChannel provides increased bandwidth using existing switch ports without requiring any upgrades to the physical interfaces. Load balancing methods are implemented between links that are part of the same Etherchannel. Because EtherChannel views the bundled physical links as one logical connection, spanning tree recalculation is not required if one of the bundled physical links fail. If a physical interface fails, STP cannot transition the failed interface into a forwarding state.
33. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p33
What are the possible port roles for ports A, B, C, and D in this RSTP-enabled network?
alternate, designated, root, root*
designated, alternate, root, root
alternate, root, designated, root
designated, root, alternate, root
Explanation: Because S1 is the root bridge, B is a designated port, and C and D root ports. RSTP supports a new port type, alternate port in discarding state, that can be port A in this scenario.
34. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p34
Which switching technology would allow each access layer switch link to be aggregated to provide more bandwidth between each Layer 2 switch and the Layer 3 switch?
trunking
HSRP
PortFast
EtherChannel*
Explanation: PortFast is used to reduce the amount of time that a port spends going through the spanning-tree algorithm, so that devices can start sending data sooner. Trunking can be implemented in conjunction with EtherChannel, but trunking alone does not aggregate switch links. HSRP is used to load-balance traffic across two different connections to Layer 3 devices for default gateway redundancy. HSRP does not aggregate links at either Layer 2 or Layer 3 as EtherChannel does.
35. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p35
An administrator wants to form an EtherChannel between the two switches by using the Port Aggregation Protocol. If switch S1 is configured to be in auto mode, which mode should be configured on S2 to form the EtherChannel?
auto
on
off
desirable*
Explanation: An EtherChannel will be formed via PAgP when both switches are in on mode or when one of them is in auto or desirable mode and the other is in desirable mode.
36. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p36
Which set of configuration commands issued on SW1 will successfully complete the EtherChannel link between SW1 and SW2?
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no shutdown
interface Port-channel 1
no shutdown
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
channel-group 2 mode desirable
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
channel-group 1 mode desirable**
Explanation: Issuing the show running-configuration command on SW1 shows that interface GigabitEthernet0/1 is missing the channel-group 1 mode desirable command which will compete the EtherChannel configuration for interface GigabitEthernet0/1 and interface GigabitEthernet0/2.
37. A set of switches is being connected in a LAN topology. Which STP bridge priority value will make it least likely for the switch to be selected as the root?
65535
4096
32768
61440*
38. In which two PVST+ port states are MAC addresses learned? (Choose two.)
Learning*
Forwarding*
disabled
listening
blocking
Explanation: The two PVST+ port states during which MAC addresses are learned and populate the MAC address table are the learning and the forwarding states.
39. Which port role is assigned to the switch port that has the lowest cost to reach the root bridge?
designated port
disabled port
root port*
non-designated port
40. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the switch port closest, in terms of overall cost, to the root bridge
root port*
designated port
alternate port
disabled
42. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field used to specify a VLAN ID?
extended system ID*
port ID
bridge priority
bridge ID
43. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the reference point for all path calculations?
root bridge*
root port
designated port
alternate port
44. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field that has a default value of 32,768 and is the initial deciding factor when
electing a root bridge?
bridge priority*
MAC Address
extended system ID
bridge ID
45. Which statement describes an EtherChannel implementation?
EtherChannel operates only at Layer 2.
PAgP cannot be used in conjunction with EtherChannel.
A trunked port can be part of an EtherChannel bundle.*
EtherChannel can support up to a maximum of ten separate links.
46. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p46
A network administrator issued the show etherchannel summary command on the switch S1. What conclusion can be drawn?
The EtherChannel is suspended.
The EtherChannel is not functional.*
The port aggregation protocol PAgP is misconfigured.
FastEthernet ports Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 do not join the EtherChannel.
47. Which statement describes a characteristic of EtherChannel?
It can combine up to a maximum of 4 physical links.
It can bundle mixed types of 100 Mb/s and 1Gb/s Ethernet links.
It consists of multiple parallel links between a switch and a router.
It is made by combining multiple physical links that are seen as one link between two switches.*
48. Which two channel group modes would place an interface in a negotiating state using PAgP? (Choose two.)
on
desirable*
active
auto
passive*
49. Which mode configuration setting would allow formation of an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 without sending negotiation traffic?
SW1: on
SW2: on**
SW1: desirable
SW2: desirable
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
trunking enabled on both switches
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
PortFast enabled on both switches
SW1: passive
SW2: active
50. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p50
An EtherChannel was configured between switches S1 and S2, but the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel. What is the problem?
The interface port-channel number has to be different on each switch.
The switch ports were not configured with speed and duplex mode.
The switch ports have to be configured as access ports with each port having a VLAN assigned.
The EtherChannel was not configured with the same allowed range of VLANs on each interface.*
51. When EtherChannel is configured, which mode will force an interface into a port channel without exchanging aggregation protocol packets?
active
auto
on*
desirable
52. What are two load-balancing methods in the EtherChannel technology? (Choose two.)
combination of source port and IP to destination port and IP
source IP to destination IP*
source port to destination port
combination of source MAC and IP to destination MAC and IP
source MAC to destination MAC*
53. Which protocol provides up to 16 instances of RSTP, combines many VLANs with the same physical and logical topology into a common RSTP instance, and provides support for PortFast, BPDU guard, BPDU filter, root guard, and loop guard?
STP
Rapid PVST+
PVST+
MST*
54. What is the outcome of a Layer 2 broadcast storm?
Routers will take over the forwarding of frames as switches become congested.
New traffic is discarded by the switch because it is unable to be processed.*
CSMA/CD will cause each host to continue transmitting frames.
ARP broadcast requests are returned to the transmitting host.
55. Which two network design features require Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to ensure correct network operation? (Choose two.)
static default routes
implementing VLANs to contain broadcasts
redundant links between Layer 2 switches*
link-state dynamic routing that provides redundant routes
removing single points of failure with multiple Layer 2 switches*
56. A network administrator has configured an EtherChannel between two switches that are connected via four trunk links. If the physical interface for one of the trunk links changes to a down state, what happens to the EtherChannel?
Spanning Tree Protocol will transition the failed physical interface into forwarding mode.
Spanning Tree Protocol will recalculate the remaining trunk links.
The EtherChannel will transition to a down state.
The EtherChannel will remain functional.*
1. What additional information is contained in the 12-bit extended system ID of a BPDU?
- MAC address
- VLAN ID
- IP address
- port ID
2. During the implementation of Spanning Tree Protocol, all switches are rebooted by the network administrator. What is the first step of the spanning-tree election process?
- Each switch with a lower root ID than its neighbor will not send BPDUs.
- All the switches send out BPDUs advertising themselves as the root bridge.
- Each switch determines the best path to forward traffic.
- Each switch determines what port to block to prevent a loop from occurring.
3. Which STP port role is adopted by a switch port if there is no other port with a lower cost to the root bridge?
- designated port
- root port
- alternate
- disabled port
4. Which two concepts relate to a switch port that is intended to have only end devices attached and intended never to be used to connect to another switch? (Choose two.)
- bridge ID
- edge port
- extended system ID
- PortFast
- PVST+
5. Which three components are combined to form a bridge ID?
- extended system ID
- cost
- IP address
- bridge priority
- MAC address
- port ID
Explanation: The three components that are combined to form a bridge ID are bridge priority, extended system ID, and MAC address.
6. Match the STP protocol with the correct description. (Not all options are used.)
7. In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network? (Choose two.)
- disabled
- forwarding
- listening
- blocking
- learning
Explanation: Switches learn MAC addresses at the learning and forwarding port states. They receive and process BPDUs at the blocking, listening, learning, and forwarding port states.
8. If no bridge priority is configured in PVST, which criteria is considered when electing the root bridge?
- lowest MAC address
- lowest IP address
- highest IP address
- highest MAC address
Explanation: Only one switch can be the root bridge for a VLAN. The root bridge is the switch with the lowest BID. The BID is determined by priority and the MAC address. If no priority is configured then all switches use the default priority and the election of the root bridge will be based on the lowest MAC address.
9. Match the spanning-tree feature with the protocol type. (Not all options are used.)
10. When the show spanning-tree vlan 33 command is issued on a switch, three ports are shown in the forwarding state. In which two port roles could these interfaces function while in the forwarding state? (Choose two.)
- alternate
- designated
- disabled
- blocked
- root
Explanation: The role of each of the three ports will be either designated port or root port. Ports in the disabled state are administratively disabled. Ports in the blocking state are alternate ports.
11. What is the function of STP in a scalable network?
- It decreases the size of the failure domain to contain the impact of failures.
- It protects the edge of the enterprise network from malicious activity.
- It combines multiple switch trunk links to act as one logical link for increased bandwidth.
- It disables redundant paths to eliminate Layer 2 loops.
Explanation: STP is an important component in a scalable network because it allows redundant physical connections between Layer 2 devices to be implemented without creating Layer 2 loops. STP prevents Layer 2 loops from forming by disabling interfaces on Layer 2 devices when they would create a loop.
12. What is a characteristic of spanning tree?
- It is enabled by default on Cisco switches.
- It is used to discover information about an adjacent Cisco device.
- It has a TTL mechanism that works at Layer 2.
- It prevents propagation of Layer 2 broadcast frames.
Explanation: Spanning tree does work at Layer 2 on Ethernet-based networks and is enabled by default, but it does not have a TTL mechanism. Spanning tree exists because Layer 2 frames do not have a TTL mechanism. Layer 2 frames are still broadcast when spanning tree is enabled, but the frames can only be transmitted through a single path through the Layer 2 network that was created by spanning tree. Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is used to discover information about an adjacent Cisco device.
13. Which spanning tree standard supports only one root bridge so that traffic from all VLANs flows over the same path?
- PVST+
- 802.1D
- MST
- Rapid PVST
Explanation: MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP, an IEEE standard protocol that provides up to 16 instances of RSTP. PVST+ provides a separate 802.1D spanning-tree instance for each VLAN that is configured in the network. 802.1D is the original STP standard defined by the IEEE and allows for only one root bridge for all VLANs. 802.1w, or RSTP, provides faster convergence but still uses only one STP instance for all VLANs.
14. What is the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
- creates smaller collision domains
- prevents routing loops on a router
- prevents Layer 2 loops
- allows Cisco devices to exchange routing table updates
- creates smaller broadcast domains
Explanation: The Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) creates one path through a switch network in order to prevent Layer 2 loops.
15. What is the value used to determine which port on a non-root bridge will become a root port in a STP network?
- the path cost
- the highest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
- the lowest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
- the VTP revision number
16. Refer to the exhibit. Which switch will be the root bridge after the election process is complete?
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
Explanation: The root bridge is determined by the lowest bridge ID, which consists of the priority value and the MAC address. Because the priority values of all of the switches are identical, the MAC address is used to determine the root bridge. Because S2 has the lowest MAC address, S2 becomes the root bridge.
17. What are two drawbacks to turning spanning tree off and having multiple paths through the Layer 2 switch network? (Choose two.)
- The MAC address table becomes unstable.
- The switch acts like a hub.
- Port security becomes unstable.
- Broadcast frames are transmitted indefinitely.
- Port security shuts down all of the ports that have attached devices.
Explanation: Spanning tree should never be disabled. Without it, the MAC address table becomes unstable, broadcast storms can render network clients and the switches unusable, and multiple copies of unicast frames can be delivered to the end devices.
18. A small company network has six interconnected Layer 2 switches. Currently all switches are using the default bridge priority value. Which value can be used to configure the bridge priority of one of the switches to ensure that it becomes the root bridge in this design?
- 1
- 28672
- 32768
- 34816
- 61440
Explanation: The default bridge priority value for all Cisco switches is 32768. The range is 0 to 61440 in increments of 4096. Thus, the values 1 and 34816 are invalid. Configuring one switch with the lower value of 28672 (and leaving the bridge priority value of all other switches unchanged) will make the switch become the root bridge.
19. Refer to the exhibit. The administrator tried to create an EtherChannel between S1 and the other two switches via the commands that are shown, but was unsuccessful. What is the problem?
- Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches through the same EtherChannel link.
- Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches, but only to two different devices like an EtherChannel-enabled server and a switch.
- Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
- Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Layer 3 switches.
Explanation: An EtherChannel link can only be created between two switches or between an EtherChannel-enabled server and a switch. Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches through the same EtherChannel link.
20. Which statement is true regarding the use of PAgP to create EtherChannels?
- It requires full duplex.
- It increases the number of ports that are participating in spanning tree.
- It requires more physical links than LACP does.
- It mandates that an even number of ports (2, 4, 6, etc.) be used for aggregation.
- It is Cisco proprietary.
Explanation: PAgP is used to automatically aggregate multiple ports into an EtherChannel bundle, but it only works between Cisco devices. LACP can be used for the same purpose between Cisco and non-Cisco devices. PAgP must have the same duplex mode at both ends and can use two ports or more. The number of ports depends on the switch platform or module. An EtherChannel aggregated link is seen as one port by the spanning-tree algorithm.
21. What are two requirements to be able to configure an EtherChannel between two switches? (Choose two.)
- All the interfaces need to work at the same speed.
- All interfaces need to be assigned to different VLANs.
- Different allowed ranges of VLANs must exist on each end.
- All the interfaces need to be working in the same duplex mode.
- The interfaces that are involved need to be contiguous on the switch.
Explanation: All interfaces in the EtherChannel bundle must be assigned to the same VLAN or be configured as a trunk. If the allowed range of VLANs is not the same, the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel even when set to auto or desirable mode.
22. Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output that is shown, what can be determined about the EtherChannel bundle?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 22
- The EtherChannel bundle is down.
- Two Gigabit Ethernet ports are used to form the EtherChannel.
- A Cisco proprietary protocol was used to negotiate the EtherChannel link.
- The EtherChannel bundle is operating at both Layer 2 and Layer 3.
Explanation: Two protocols can be used to send negotiation frames that are used to try to establish an EtherChannel link: PAgP and LACP. PAgP is Cisco proprietary, and LACP adheres to the industry standard.
23. Which two parameters must match on the ports of two switches to create a PAgP EtherChannel between the switches? (Choose two.)
- port ID
- PAgP mode
- MAC address
- speed
- VLAN information
Explanation: For an EtherChannel to be created, the ports that are concerned on the two switches must match in terms of the speed, duplex, and VLAN information. The PAgP mode must be compatible but not necessarily equal. The port ID and the MAC addresses do not have to match.
24. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two switches, SW1 and SW2. Which statement describes the effect after the commands are issued on SW1 and SW2?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 24
- The EtherChannel is established after SW2 initiates the link request.
- The EtherChannel is established after SW1 initiates the link request.
- The EtherChannel is established without negotiation.
- The EtherChannel fails to establish.
Explanation: The interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/1 and GigabitEthernet 0/2 are configured “on” for the EtherChannel link. This mode forces the interface to channel without PAgP or LACP. The EtherChannel will be established only if the other side is also set to “on”. However, the mode on SW2 side is set to PAgP desirable. Thus the EtherChannel link will not be established.
25. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two switches, SW1 and SW2. However, the EtherChannel link fails to establish. What change in configuration would correct the problem?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 25
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to desirable.
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to on.
- Configure SW1 EtherChannel mode to on.
- Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to auto.
Explanation: The EtherChannel mode must be compatible on each side for the link to work. The three modes from PAgP protocol are on, desirable, and auto. The three modes from LACP protocol are on, active, and passive. The compatible modes include on-on, auto-desirable, desirable-desirable, active-passive, and active-active. Any other combinations will not form an EtherChannel link.
26. A network administrator configured an EtherChannel link with three interfaces between two switches. What is the result if one of the three interfaces is down?
- The remaining two interfaces continue to load balance traffic.
- The remaining two interfaces become separate links between the two switches.
- One interface becomes an active link for data traffic and the other becomes a backup link.
- The EtherChannel fails.
Explanation: EtherChannel creates an aggregation that is seen as one logical link. It provides redundancy because the overall link is one logical connection. The loss of one physical link within the channel does not create a change in the topology; the EtherChannel remains functional.
27. A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 by using the command SW1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode auto . Which command must be used on SW2 to enable this EtherChannel?
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode passive
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode on
- SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode active
Explanation: The possible combinations to establish an EtherChannel between SW1 and SW2 using LACP or PAgP are as follows:
PAgP
on on
auto desirable
desirable desirable
LACP
on on
active active
passive active
The EtherChannel mode chosen on each side of the EtherChannel must be compatible in order to enable it.
28. Which technology is an open protocol standard that allows switches to automatically bundle physical ports into a single logical link?
- PAgP
- LACP
- Multilink PPP
- DTP
Explanation: LACP, or Link Aggregation Control Protocol, is defined by IEEE 802.3ad and is an open standard protocol. LACP allows switches to automatically bundle switch ports into a single logical link to increase bandwidth. PAgP, or Port Aggregation Protocol, performs a similar function, but it is a Cisco proprietary protocol. DTP is Dynamic Trunking Protocol and is used to automatically and dynamically build trunks between switches. Multilink PPP is used to load-balance PPP traffic across multiple serial interfaces.
29. What is a requirement to configure a trunking EtherChannel between two switches?
- The allowed range of VLANs must be the same on both switches.
- The participating interfaces must be assigned the same VLAN number on both switches.
- The participating interfaces must be physically contiguous on a switch.
- The participating interfaces must be on the same module on a switch.
Explanation: To enable a trunking EtherChannel successfully, the range of VLANs allowed on all the interfaces must match; otherwise, the EtherChannel cannot be formed. The interfaces involved in an EtherChannel do not have to be physically contiguous, or on the same module. Because the EtherChannel is a trunking one, participating interfaces are configured as trunk mode, not access mode.
30. What are two advantages of using LACP? (Choose two.)
- It allows directly connected switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link.
- It eliminates the need for configuring trunk interfaces when deploying VLANs on multiple switches.
- It decreases the amount of configuration that is needed on a switch.
- It provides a simulated environment for testing link aggregation.
- It allows the use of multivendor devices.
- LACP allows Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces to be mixed within a single EtherChannel.
Explanation: The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) allows directly connected multivendor switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link. LACP helps create the EtherChannel link by detecting the configuration of each side and making sure that they are compatible so that the EtherChannel link can be enabled when needed.
31. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a non-root port that is permitted to forward traffic on the network?
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
- disabled
32. What are two advantages of EtherChannel? (Choose two.)
- Spanning Tree Protocol views the physical links in an EtherChannel as one logical connection.
- Load balancing occurs between links configured as different EtherChannels.
- Configuring the EtherChannel interface provides consistency in the configuration of the physical links.
- Spanning Tree Protocol ensures redundancy by transitioning failed interfaces in an EtherChannel to a forwarding state.
- EtherChannel uses upgraded physical links to provide increased bandwidth.
Explanation: EtherChannel configuration of one logical interface ensures configuration consistency across the physical links in the EtherChannel. The EtherChannel provides increased bandwidth using existing switch ports without requiring any upgrades to the physical interfaces. Load balancing methods are implemented between links that are part of the same Etherchannel. Because EtherChannel views the bundled physical links as one logical connection, spanning tree recalculation is not required if one of the bundled physical links fail. If a physical interface fails, STP cannot transition the failed interface into a forwarding state.
33. Refer to the exhibit. What are the possible port roles for ports A, B, C, and D in this RSTP-enabled network?
Modules 5 – 6: Redundant Networks Exam 33
- alternate, designated, root, root
- designated, alternate, root, root
- alternate, root, designated, root
- designated, root, alternate, root
Explanation: Because S1 is the root bridge, B is a designated port, and C and D root ports. RSTP supports a new port type, alternate port in discarding state, that can be port A in this scenario.
34. Refer to the exhibit. Which switching technology would allow each access layer switch link to be aggregated to provide more bandwidth between each Layer 2 switch and the Layer 3 switch?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 02
- trunking
- HSRP
- PortFast
- EtherChannel
Explanation: PortFast is used to reduce the amount of time that a port spends going through the spanning-tree algorithm, so that devices can start sending data sooner. Trunking can be implemented in conjunction with EtherChannel, but trunking alone does not aggregate switch links. HSRP is used to load-balance traffic across two different connections to Layer 3 devices for default gateway redundancy. HSRP does not aggregate links at either Layer 2 or Layer 3 as EtherChannel does.
35. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator wants to form an EtherChannel between the two switches by using the Port Aggregation Protocol. If switch S1 is configured to be in auto mode, which mode should be configured on S2 to form the EtherChannel?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 06
- auto
- on
- off
- desirable
Explanation: An EtherChannel will be formed via PAgP when both switches are in on mode or when one of them is in auto or desirable mode and the other is in desirable mode.
36. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which set of configuration commands issued on SW1 will successfully complete the EtherChannel link between SW1 and SW2?
CCNA-2-v7-Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam 36
- interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no shutdown - interface Port-channel 1
no shutdown - interface GigabitEthernet0/2
channel-group 2 mode desirable - interface GigabitEthernet0/1
channel-group 1 mode desirable
Explanation: Issuing the show running-configuration command on SW1 shows that interface GigabitEthernet0/1 is missing the channel-group 1 mode desirable command which will compete the EtherChannel configuration for interface GigabitEthernet0/1 and interface GigabitEthernet0/2.
37. A set of switches is being connected in a LAN topology. Which STP bridge priority value will make it least likely for the switch to be selected as the root?
- 65535
- 4096
- 32768
- 61440
38. In which two PVST+ port states are MAC addresses learned? (Choose two.)
- learning
- forwarding
- disabled
- listening
- blocking
Explanation: The two PVST+ port states during which MAC addresses are learned and populate the MAC address table are the learning and the forwarding states.
39. Which port role is assigned to the switch port that has the lowest cost to reach the root bridge?
- designated port
- disabled port
- root port
- non-designated port
Explanation: The root port on a switch is the port with the lowest cost to reach the root bridge.
40. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the switch port closest, in terms of overall cost, to the root bridge
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
- disabled
42. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field used to specify a VLAN ID?
- extended system ID
- port ID
- bridge priority
- bridge ID
43. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the reference point for all path calculations?
- root bridge
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
44. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field that has a default value of 32,768 and is the initial deciding factor when electing a root bridge?
- bridge priority
- MAC Address
- extended system ID
- bridge ID
45. Which statement describes an EtherChannel implementation?
- EtherChannel operates only at Layer 2.
- PAgP cannot be used in conjunction with EtherChannel.
- A trunked port can be part of an EtherChannel bundle.
- EtherChannel can support up to a maximum of ten separate links.
Explanation: Up to 16 links can be grouped in an EtherChannel by using the the PAgP or LACP protocol. EtherChannel can be configured as a Layer 2 bundle or a Layer 3 bundle. Configuring a Layer 3 bundle is beyond the scope of this course. If a trunked port is a part of the EtherChannel bundle, all ports in the bundle need to be trunk ports and the native VLAN must be the same on all of these ports. A best practice is to apply the configuration to the port channel interface. The configuration is then automatically applied to the individual ports.
46. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issued the show etherchannel summary command on the switch S1. What conclusion can be drawn?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers
- The EtherChannel is suspended.
- The EtherChannel is not functional.
- The port aggregation protocol PAgP is misconfigured.
- FastEthernet ports Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 do not join the EtherChannel.
47. Which statement describes a characteristic of EtherChannel?
- It can combine up to a maximum of 4 physical links.
- It can bundle mixed types of 100 Mb/s and 1Gb/s Ethernet links.
- It consists of multiple parallel links between a switch and a router.
- It is made by combining multiple physical links that are seen as one link between two switches.
Explanation: An EtherChannel is formed by combining multiple (same type) Ethernet physical links so they are seen and configured as one logical link. It provides an aggregated link between two switches. Currently each EtherChannel can consist of up to eight compatibly configured Ethernet ports.
48. Which two channel group modes would place an interface in a negotiating state using PAgP? (Choose two.)
- on
- desirable
- active
- auto
- passive
Explanation: There are three modes available when configuring an interface for PAgP: on, desirable, and auto. Only desirable and auto place the interface in a negotiating state. The active and passive states are used to configure LACP and not PAgP.
49. Which mode configuration setting would allow formation of an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 without sending negotiation traffic?
SW1: on
SW2: on
SW1: desirable
SW2: desirable
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
trunking enabled on both switches
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
PortFast enabled on both switches
SW1: passive
SW2: active
Explanation: The auto channel-group keyword enables PAgP only if a PAgP device is detected on the opposite side of the link. If the auto keyword is used, the only way to form an EtherChannel link is if the opposite connected device is configured with the desirable keyword. PortFast and trunking technologies are irrelevant to forming an EtherChannel link. Even though an EtherChannel can be formed if both sides are configured in desirable mode, PAgP is active and PAgP messages are being sent constantly across the link, decreasing the amount of bandwidth available for user traffic.
50. Refer to the exhibit. An EtherChannel was configured between switches S1 and S2, but the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel. What is the problem?
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 5 – 6 Redundant Networks Exam Answers 50
- The interface port-channel number has to be different on each switch.
- The switch ports were not configured with speed and duplex mode.
- The switch ports have to be configured as access ports with each port having a VLAN assigned.
- The EtherChannel was not configured with the same allowed range of VLANs on each interface.
51. When EtherChannel is configured, which mode will force an interface into a port channel without exchanging aggregation protocol packets?
- active
- auto
- on
- desirable
Explanation: For both LACP and PAgP, the “on” mode will force an interface into an EtherChannel without exchanging protocol packets.
52. What are two load-balancing methods in the EtherChannel technology? (Choose two.)
- combination of source port and IP to destination port and IP
- source IP to destination IP
- source port to destination port
- combination of source MAC and IP to destination MAC and IP
- source MAC to destination MAC
Explanation: Depending on the hardware platform, one or more load-balancing methods can be implemented. These methods include source MAC to destination MAC load balancing or source IP to destination IP load balancing, across the physical links.
53. Which protocol provides up to 16 instances of RSTP, combines many VLANs with the same physical and logical topology into a common RSTP instance, and provides support for PortFast, BPDU guard, BPDU filter, root guard, and loop guard?
- STP
- Rapid PVST+
- PVST+
- MST
Explanation: MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP, an IEEE standard protocol that provides up to 16 instances of RSTP and combines many VLANs with the same physical and logical topology into a common RSTP instance. Each instance supports PortFast, BPDU guard, BPDU filter, root guard, and loop guard. STP and RSTP assume only one spanning-tree instance for the entire bridged network, regardless of the number of VLANs. PVST+ provides a separate 802.1D spanning-tree instance for each VLAN that is configured in the network.
54. What is the outcome of a Layer 2 broadcast storm?
- Routers will take over the forwarding of frames as switches become congested.
- New traffic is discarded by the switch because it is unable to be processed.
- CSMA/CD will cause each host to continue transmitting frames.
- ARP broadcast requests are returned to the transmitting host.
Explanation: When the network is saturated with broadcast traffic that is looping between switches, new traffic is discarded by each switch because it is unable to be processed.
55. Which two network design features require Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to ensure correct network operation? (Choose two.)
- static default routes
- implementing VLANs to contain broadcasts
- redundant links between Layer 2 switches
- link-state dynamic routing that provides redundant routes
- removing single points of failure with multiple Layer 2 switches
56. A network administrator has configured an EtherChannel between two switches that are connected via four trunk links. If the physical interface for one of the trunk links changes to a down state, what happens to the EtherChannel?
- Spanning Tree Protocol will transition the failed physical interface into forwarding mode.
- Spanning Tree Protocol will recalculate the remaining trunk links.
- The EtherChannel will transition to a down state.
- The EtherChannel will remain functional.
Explanation: EtherChannel offers redundancy by bundling multiple trunk links into one logical connection. Failure of one physical link within the EtherChannel will not create a change in the topology and therefore a recalculation by Spanning Tree is unnecessary. Just one physical link must remain operational for the EtherChannel to continue to function.
Which three components are combined to form a bridge ID?
Please select 3 correct answers
IP address
extended system ID
bridge priority
port ID
cost
MAC address
Which mode configuration setting would allow formation of an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 without sending negotiation traffic?
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
trunking enabled on both switches
SW1: passive
SW2: active
SW1: desirable
SW2: desirable
SW1: on
SW2: on
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
PortFast enabled on both switches
What is the outcome of a Layer 2 broadcast storm?
ARP broadcast requests are returned to the transmitting host.
New traffic is discarded by the switch because it is unable to be processed.
CSMA/CD will cause each host to continue transmitting frames.
Routers will take over the forwarding of frames as switches become congested.
What is the function of STP in a scalable network?
It disables redundant paths to eliminate Layer 2 loops.
It decreases the size of the failure domain to contain the impact of failures.
It combines multiple switch trunk links to act as one logical link for increased bandwidth.
It protects the edge of the enterprise network from malicious activity.
An EtherChannel link using LACP was formed between two switches, S1 and S2. While verifying the configuration, which mode combination could be utilized on both switches?
S1-on and S2-passive
S1-on and S2-active
S1-passive and S2-passive
S1-passive and S2-active
Which port state will switch ports immediately transition to when configured for PortFast?
learning
blocking
listening
forwarding
A network administrator has configured an EtherChannel between two switches that are connected via four trunk links. If the physical interface for one of the trunk links changes to a down state, what happens to the EtherChannel?
Spanning Tree Protocol will transition the failed physical interface into forwarding mode.
The EtherChannel will remain functional.
Spanning Tree Protocol will recalculate the remaining trunk links.
The EtherChannel will transition to a down state.
Which two statements describe a switch port that is configured with PortFast? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
The switch port immediately transitions from blocking to the forwarding state.
The switch port immediately processes any BPDUs before transitioning to the forwarding state.
The switch port should never receive BPDUs.
The switch port sends DHCP requests before transitioning to the forwarding state.
The switch port immediately transitions from the listening to the forwarding state.
Which two mode combinations would result in the successful negotiation of an EtherChannel? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
passive; auto
auto; auto
desirable; desirable
desirable; active
active; passive
active; on
Which statement describes an EtherChannel implementation?
A trunked port can be part of an EtherChannel bundle.
EtherChannel operates only at Layer 2.
PAgP cannot be used in conjunction with EtherChannel.
EtherChannel can support up to a maximum of ten separate links.
In which two PVST+ port states are MAC addresses learned? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
listening
learning
blocking
disabled
forwarding
A network administrator configured an EtherChannel link with three interfaces between two switches. What is the result if one of the three interfaces is down?
One interface becomes an active link for data traffic and the other becomes a backup link.
The remaining two interfaces become separate links between the two switches.
The remaining two interfaces continue to load balance traffic.
The EtherChannel fails.
A small company network has six interconnected Layer 2 switches. Currently all switches are using the default bridge priority value. Which value can be used to configure the bridge priority of one of the switches to ensure that it becomes the root bridge in this design?
1
32768
34816
61440
28672
When a range of ports is being configured for EtherChannel, which mode will configure PAgP so that it initiates the EtherChannel negotiation?
desirable
active
auto
passive
What is the value used to determine which port on a non-root bridge will become a root port in a STP network?
the lowest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
the VTP revision number
the path cost
the highest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
Which statement is true about EtherChannel technology?
Links must be upgraded to support EtherChannel.
All configuration tasks must be done on the individual ports in the EtherChannel link.
EtherChannel uses existing switch ports.
STP does not run on redundant EtherChannel links.
When a range of ports is being configured for EtherChannel by the use of PAgP, which mode will form the bundled channel only if the port receives PAgP packets from another device?
auto
passive
desirable
active
When EtherChannel is configured, which mode will force an interface into a port channel without exchanging aggregation protocol packets?
After the election of the root bridge has been completed, how will switches find the best paths to the root bridge?
Each switch will analyze the port states of all neighbors and use the designated ports to forward traffic to the root.
Each switch will analyze the sum of the hops to reach the root and use the path with the fewest hops.
Each switch will analyze the BID of all neighbors to reach the root and use the path through the lowest BID neighbors.
Each switch will analyze the sum of all port costs to reach the root and use the path with the lowest cost.
What is the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
creates smaller broadcast domains
allows Cisco devices to exchange routing table updates
creates smaller collision domains
prevents routing loops on a router
prevents Layer 2 loops
What are two advantages of using LACP? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
It eliminates the need for configuring trunk interfaces when deploying VLANs on multiple switches.
It provides a simulated environment for testing link aggregation.
It allows directly connected switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link.
It allows the use of multivendor devices.
LACP allows Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces to be mixed within a single EtherChannel.
It decreases the amount of configuration that is needed on a switch.
Which RSTP ports are connected to end devices?
root ports
trunk ports
designated ports
edge ports
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field that has a default value of 32,768 and is the initial deciding factor when electing a root bridge?
bridge priority
extended system ID
bridge ID
BPDUs
An administrator is troubleshooting a switch and wants to verify if it is a root bridge. What command can be used to do this?
show running-config
show startup-config
show spanning-tree
show vlan
A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 by using the command SW1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode auto . Which command must be used on SW2 to enable this EtherChannel?
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode passive
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode on
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode active
Which statement describes a characteristic of EtherChannel?
It consists of multiple parallel links between a switch and a router.
It is made by combining multiple physical links that are seen as one link between two switches.
It can bundle mixed types of 100 Mb/s and 1Gb/s Ethernet links.
It can combine up to a maximum of 4 physical links.
What are three advantages of using EtherChannel technology? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
Load balancing is not needed with EtherChannel.
The Spanning Tree Protocol shuts down the unused interfaces in the bundle to avoid loops.
Configuration tasks can be done on the EtherChannel interface.
A spanning tree recalculation is not required when a single link within the channel goes down.
EtherChannel uses multiple logical links to provide redundancy.
There is no need to upgrade links to faster connections to increase bandwidth.
During the implementation of Spanning Tree Protocol, all switches are rebooted by the network administrator. What is the first step of the spanning-tree election process?
Each switch determines what port to block to prevent a loop from occurring.
Each switch with a lower root ID than its neighbor will not send BPDUs.
All the switches send out BPDUs advertising themselves as the root bridge.
Each switch determines the best path to forward traffic.
What are two load-balancing methods in the EtherChannel technology? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
source IP to destination IP
combination of source MAC and IP to destination MAC and IP
source MAC to destination MAC
source port to destination port
combination of source port and IP to destination port and IP
Which function is provided by EtherChannel?
spreading traffic across multiple physical WAN links
dividing the bandwidth of a single link into separate time slots
enabling traffic from multiple VLANs to travel over a single Layer 2 link
creating one logical link by using multiple physical links between two LAN switches
If no bridge priority is configured in PVST, which criteria is considered when electing the root bridge?
lowest IP address
lowest MAC address
highest IP address
highest MAC address
What is a requirement to configure a trunking EtherChannel between two switches?
The participating interfaces must be physically contiguous on a switch.
The allowed range of VLANs must be the same on both switches.
The participating interfaces must be assigned the same VLAN number on both switches.
Which three port states are used by Rapid PVST+? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
blocking
trunking
discarding
listening
forwarding
learning
When a range of ports is being configured for EtherChannel, which mode will configure LACP on a port only if the port receives LACP packets from another device?
passive
active
auto
desirable
When PVST is running over a switched network, which port state can participate in BPDU frame forwarding based on BPDUs received, but does not forward data frames?
disabled
forwarding
listening
blocking
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a non-root port that is permitted to forward traffic on the network?
disabled
alternate port
root port
designated port
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field used to specify a VLAN ID?
bridge priority
extended system ID
port ID
MAC Address
Which port role is assigned to the switch port that has the lowest cost to reach the root bridge?
disabled port
non-designated port
root port
designated port
What additional information is contained in the 12-bit extended system ID of a BPDU?
VLAN ID
MAC address
IP address
port ID
When the show spanning-tree vlan 33 command is issued on a switch, three ports are shown in the forwarding state. In which two port roles could these interfaces function while in the forwarding state? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
root
alternate
disabled
designated
blocked
Which protocol provides up to 16 instances of RSTP, combines many VLANs with the same physical and logical topology into a common RSTP instance, and provides support for PortFast, BPDU guard, BPDU filter, root guard, and loop guard?
STP
PVST+
MST
Rapid PVST+
Which two load balancing methods can be implemented with EtherChannel technology? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
source MAC to destination MAC
destination MAC to destination IP
destination IP to destination MAC
source IP to destination IP
destination MAC to source MAC
destination IP to source IP
Which three interface parameters must match for an EtherChannel to form? (Choose three.)
Please select 3 correct answers
trunking mode
EtherChannel mode
allowed VLANs
native VLAN
PortFast mode
spanning-tree state
A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two physical ports on a switch. Which statement describes the result when one of the physical ports fails?
The EtherChannel stops transmitting data until it is restarted.
The EtherChannel continues transmitting data with reduced bandwidth.
The EtherChannel link fails.
An STP recalculation is needed.
Which two parameters must match on the ports of two switches to create a PAgP EtherChannel between the switches? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
port ID
MAC address
VLAN information
PAgP mode
speed
What are two requirements to be able to configure an EtherChannel between two switches? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
All the interfaces need to work at the same speed.
All interfaces need to be assigned to different VLANs.
Different allowed ranges of VLANs must exist on each end.
All the interfaces need to be working in the same duplex mode.
The interfaces that are involved need to be contiguous on the switch.
What value determines the root bridge when all switches connected by trunk links have default STP configurations?
extended system ID
bridge priority
VLAN ID
MAC address
When EtherChannel is implemented, multiple physical interfaces are bundled into which type of logical connection?
interface range
port channel
loopback
VLAN interface
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the switch port closest, in terms of overall cost, to the root bridge?
designated port
root port
disabled
alternate port
Which STP port role is adopted by a switch port if there is no other port with a lower cost to the root bridge?
alternate
root port
disabled port
designated port
What will happen if a network administrator puts a port that is part of an EtherChannel bundle into a different VLAN than the other ports in that bundle?
The EtherChannel bundle will stay up if the ports were configured with no negotiation between the switches to form the EtherChannel.
The EtherChannel bundle will stay up only if PAgP is used.
The EtherChannel bundle will stay up if either PAgP or LACP is used.
The EtherChannel bundle will stay up only if LACP is used.
The EtherChannel will fail.
Which spanning tree standard supports only one root bridge so that traffic from all VLANs flows over the same path?
MST
PVST+
802.1D
Rapid PVST
What is a characteristic of spanning tree?
It has a TTL mechanism that works at Layer 2.
It is used to discover information about an adjacent Cisco device.
It prevents propagation of Layer 2 broadcast frames.
It is enabled by default on Cisco switches.
Which statement is true regarding the use of PAgP to create EtherChannels?
It mandates that an even number of ports (2, 4, 6, etc.) be used for aggregation.
It is Cisco proprietary.
It increases the number of ports that are participating in spanning tree.
It requires more physical links than LACP does.
It requires full duplex.
A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the reference point for all path calculations?
root port
root bridge
alternate port
designated port
In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
listening
forwarding
disabled
blocking
learning
Which technology is an open protocol standard that allows switches to automatically bundle physical ports into a single logical link?
DTP
PAgP
LACP
Multilink PPP
What are two advantages of EtherChannel? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
Spanning Tree Protocol views the physical links in an EtherChannel as one logical connection.
Load balancing occurs between links configured as different EtherChannels.
EtherChannel uses upgraded physical links to provide increased bandwidth.
Spanning Tree Protocol ensures redundancy by transitioning failed interfaces in an EtherChannel to a forwarding state.
Configuring the EtherChannel interface provides consistency in the configuration of the physical links.
What are two drawbacks to turning spanning tree off and having multiple paths through the Layer 2 switch network? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
Port security becomes unstable.
Broadcast frames are transmitted indefinitely.
Port security shuts down all of the ports that have attached devices.
The MAC address table becomes unstable.
The switch acts like a hub.
Which two network design features require Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to ensure correct network operation? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
removing single points of failure with multiple Layer 2 switches
implementing VLANs to contain broadcasts
link-state dynamic routing that provides redundant routes
redundant links between Layer 2 switches
static default routes
Which two concepts relate to a switch port that is intended to have only end devices attached and intended never to be used to connect to another switch? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
edge port
extended system ID
PortFast
PVST+
bridge ID
What is an accurate description of redundancy?
configuring a switch with proper security to ensure that all traffic forwarded through an interface is filtered
configuring a router with a complete MAC address database to ensure that all frames can be forwarded to the correct destination
designing a network to use multiple paths between switches to ensure there is no single point of failure
designing a network to use multiple virtual devices to ensure that all traffic uses the best path through the internetwork
Which two channel group modes would place an interface in a negotiating state using PAgP? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
desirable
passive
on
auto
active
When a range of ports is being configured for EtherChannel, which mode will configure LACP so that it initiates the EtherChannel negotiation?
desirable
auto
passive
active
A set of switches is being connected in a LAN topology. Which STP bridge priority value will make it least likely for the switch to be selected as the root?
Which two protocols are link aggregation protocols? (Choose two.)
Please select 2 correct answers
PAgP
RSTP
802.3ad
EtherChannel
STP
CCNA 2 v7 Modules 5 – 6: Redundant Networks Exam Answers
1. What additional information is contained in the 12-bit extended system ID of a BPDU?
MAC address
VLAN ID*
IP address
port ID
2. During the implementation of Spanning Tree Protocol, all switches are rebooted by the network administrator. What is the first step of the spanning-tree election process?
Each switch with a lower root ID than its neighbor will not send BPDUs.
All the switches send out BPDUs advertising themselves as the root bridge.*
Each switch determines the best path to forward traffic.
Each switch determines what port to block to prevent a loop from occurring.
3. Which STP port role is adopted by a switch port if there is no other port with a lower cost to the root bridge?
designated port
root port*
alternate
disabled port
4. Which two concepts relate to a switch port that is intended to have only end devices attached and intended never to be used to connect to another switch? (Choose two.)
bridge ID
edge port*
extended system ID
PortFast*
PVST+
5. Which three components are combined to form a bridge ID?
extended system ID*
cost
IP address
bridge priority*
MAC address*
port ID
Explanation: The three components that are combined to form a bridge ID are bridge priority, extended system ID, and MAC address.
6. Match the STP protocol with the correct description. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p6
7. In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network? (Choose two.)
disabled
forwarding*
listening
blocking
learning*
Explanation: Switches learn MAC addresses at the learning and forwarding port states. They receive and process BPDUs at the blocking, listening, learning, and forwarding port states.
8. If no bridge priority is configured in PVST, which criteria is considered when electing the root bridge?
lowest MAC address*
lowest IP address
highest IP address
highest MAC address
Explanation: Only one switch can be the root bridge for a VLAN. The root bridge is the switch with the lowest BID. The BID is determined by priority and the MAC address. If no priority is configured then all switches use the default priority and the election of the root bridge will be based on the lowest MAC address.
9. Match the spanning-tree feature with the protocol type. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p9
10. When the show spanning-tree vlan 33 command is issued on a switch, three ports are shown in the forwarding state. In which two port roles could these interfaces function while in the forwarding state? (Choose two.)
alternate
designated*
disabled
blocked
root*
Explanation: The role of each of the three ports will be either designated port or root port. Ports in the disabled state are administratively disabled. Ports in the blocking state are alternate ports.
11. What is the function of STP in a scalable network?
It decreases the size of the failure domain to contain the impact of failures.
It protects the edge of the enterprise network from malicious activity.
It combines multiple switch trunk links to act as one logical link for increased bandwidth.
It disables redundant paths to eliminate Layer 2 loops.*
12. What is a characteristic of spanning tree?
It is enabled by default on Cisco switches.*
It is used to discover information about an adjacent Cisco device.
It has a TTL mechanism that works at Layer 2.
It prevents propagation of Layer 2 broadcast frames.
13. Which spanning tree standard supports only one root bridge so that traffic from all VLANs flows over the same path?
PVST+
802.1D*
MST
Rapid PVST
Explanation: MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP, an IEEE standard protocol that provides up to 16 instances of RSTP. PVST+ provides a separate 802.1D spanning-tree instance for each VLAN that is configured in the network. 802.1D is the original STP standard defined by the IEEE and allows for only one root bridge for all VLANs. 802.1w, or RSTP, provides faster convergence but still uses only one STP instance for all VLANs.
14. What is the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
creates smaller collision domains
prevents routing loops on a router
prevents Layer 2 loops*
allows Cisco devices to exchange routing table updates
creates smaller broadcast domains
15. What is the value used to determine which port on a non-root bridge will become a root port in a STP network?
the path cost*
the highest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
the lowest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
the VTP revision number
16. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p16
Which switch will be the root bridge after the election process is complete?
S1
S2*
S3
S4
Explanation: The root bridge is determined by the lowest bridge ID, which consists of the priority value and the MAC address. Because the priority values of all of the switches are identical, the MAC address is used to determine the root bridge. Because S2 has the lowest MAC address, S2 becomes the root bridge.
17. What are two drawbacks to turning spanning tree off and having multiple paths through the Layer 2 switch network? (Choose two.)
The MAC address table becomes unstable.*
The switch acts like a hub.
Port security becomes unstable.
Broadcast frames are transmitted indefinitely.*
Port security shuts down all of the ports that have attached devices.
Explanation: Spanning tree should never be disabled. Without it, the MAC address table becomes unstable, broadcast storms can render network clients and the switches unusable, and multiple copies of unicast frames can be delivered to the end devices.
18. A small company network has six interconnected Layer 2 switches. Currently all switches are using the default bridge priority value. Which value can be used to configure the bridge priority of one of the switches to ensure that it becomes the root bridge in this design?
1
28672*
32768
34816
61440
Explanation: The default bridge priority value for all Cisco switches is 32768. The range is 0 to 61440 in increments of 4096. Thus, the values 1 and 34816 are invalid. Configuring one switch with the lower value of 28672 (and leaving the bridge priority value of all other switches unchanged) will make the switch become the root bridge.
19. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p19
The administrator tried to create an EtherChannel between S1 and the other two switches via the commands that are shown, but was unsuccessful. What is the problem?
Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches through the same EtherChannel link.*
Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches, but only to two different devices like an EtherChannel-enabled server and a switch.
Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Layer 3 switches.
20. Which statement is true regarding the use of PAgP to create EtherChannels?
It requires full duplex.
It increases the number of ports that are participating in spanning tree.
It requires more physical links than LACP does.
It mandates that an even number of ports (2, 4, 6, etc.) be used for aggregation.
It is Cisco proprietary.*
Explanation: PAgP is used to automatically aggregate multiple ports into an EtherChannel bundle, but it only works between Cisco devices. LACP can be used for the same purpose between Cisco and non-Cisco devices. PAgP must have the same duplex mode at both ends and can use two ports or more. The number of ports depends on the switch platform or module. An EtherChannel aggregated link is seen as one port by the spanning-tree algorithm.
21. What are two requirements to be able to configure an EtherChannel between two switches? (Choose two.)
All the interfaces need to work at the same speed.*
All interfaces need to be assigned to different VLANs.
Different allowed ranges of VLANs must exist on each end.
All the interfaces need to be working in the same duplex mode.*
The interfaces that are involved need to be contiguous on the switch.
Explanation: All interfaces in the EtherChannel bundle must be assigned to the same VLAN or be configured as a trunk. If the allowed range of VLANs is not the same, the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel even when set to auto or desirable mode.
22. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p22
On the basis of the output that is shown, what can be determined about the EtherChannel bundle?
The EtherChannel bundle is down.
Two Gigabit Ethernet ports are used to form the EtherChannel.
A Cisco proprietary protocol was used to negotiate the EtherChannel link.*
The EtherChannel bundle is operating at both Layer 2 and Layer 3.
Explanation: Two protocols can be used to send negotiation frames that are used to try to establish an EtherChannel link: PAgP and LACP. PAgP is Cisco proprietary, and LACP adheres to the industry standard.
23. Which two parameters must match on the ports of two switches to create a PAgP EtherChannel between the switches? (Choose two.)
port ID
PAgP mode
MAC address
Speed*
VLAN information*
Explanation: For an EtherChannel to be created, the ports that are concerned on the two switches must match in terms of the speed, duplex, and VLAN information. The PAgP mode must be compatible but not necessarily equal. The port ID and the MAC addresses do not have to match.
24. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p24
A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two switches, SW1 and SW2. Which statement describes the effect after the commands are issued on SW1 and SW2?
The EtherChannel is established after SW2 initiates the link request.
The EtherChannel is established after SW1 initiates the link request.
The EtherChannel is established without negotiation.
The EtherChannel fails to establish.*
25. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p25
A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between two switches, SW1 and SW2. However, the EtherChannel link fails to establish. What change in configuration would correct the problem?
Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to desirable.*
Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to on.
Configure SW1 EtherChannel mode to on.
Configure SW2 EtherChannel mode to auto.
Explanation: The EtherChannel mode must be compatible on each side for the link to work. The three modes from PAgP protocol are on, desirable, and auto. The three modes from LACP protocol are on, active, and passive. The compatible modes include on-on, auto-desirable, desirable-desirable, active-passive, and active-active. Any other combinations will not form an EtherChannel link.
26. A network administrator configured an EtherChannel link with three interfaces between two switches. What is the result if one of the three interfaces is down?
The remaining two interfaces continue to load balance traffic.*
The remaining two interfaces become separate links between the two switches.
One interface becomes an active link for data traffic and the other becomes a backup link.
The EtherChannel fails.
Explanation: EtherChannel creates an aggregation that is seen as one logical link. It provides redundancy because the overall link is one logical connection. The loss of one physical link within the channel does not create a change in the topology; the EtherChannel remains functional.
27. A network administrator is configuring an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 by using the command SW1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode auto . Which command must be used on SW2 to enable this EtherChannel?
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode passive
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable*
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode on
SW2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode active
Explanation: The possible combinations to establish an EtherChannel between SW1 and SW2 using LACP or PAgP are as follows:
PAgP
on on
auto desirable
desirable desirable
LACP
on on
active active
passive active
The EtherChannel mode chosen on each side of the EtherChannel must be compatible in order to enable it.
28. Which technology is an open protocol standard that allows switches to automatically bundle physical ports into a single logical link?
PAgP
LACP*
Multilink PPP
DTP
Explanation: LACP, or Link Aggregation Control Protocol, is defined by IEEE 802.3ad and is an open standard protocol. LACP allows switches to automatically bundle switch ports into a single logical link to increase bandwidth. PAgP, or Port Aggregation Protocol, performs a similar function, but it is a Cisco proprietary protocol. DTP is Dynamic Trunking Protocol and is used to automatically and dynamically build trunks between switches. Multilink PPP is used to load-balance PPP traffic across multiple serial interfaces.
29. What is a requirement to configure a trunking EtherChannel between two switches?
The allowed range of VLANs must be the same on both switches.*
The participating interfaces must be assigned the same VLAN number on both switches.
The participating interfaces must be physically contiguous on a switch.
The participating interfaces must be on the same module on a switch.
Explanation: To enable a trunking EtherChannel successfully, the range of VLANs allowed on all the interfaces must match; otherwise, the EtherChannel cannot be formed. The interfaces involved in an EtherChannel do not have to be physically contiguous, or on the same module. Because the EtherChannel is a trunking one, participating interfaces are configured as trunk mode, not access mode.
30. What are two advantages of using LACP? (Choose two.)
It allows directly connected switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link.*
It eliminates the need for configuring trunk interfaces when deploying VLANs on multiple switches.
It decreases the amount of configuration that is needed on a switch.
It provides a simulated environment for testing link aggregation.
It allows the use of multivendor devices.*
LACP allows Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces to be mixed within a single EtherChannel.
Explanation: The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) allows directly connected multivendor switches to negotiate an EtherChannel link. LACP helps create the EtherChannel link by detecting the configuration of each side and making sure that they are compatible so that the EtherChannel link can be enabled when needed.
31. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a non-root port that is permitted to forward traffic on the network?
root port
designated port*
alternate port
disabled
32. What are two advantages of EtherChannel? (Choose two.)
Spanning Tree Protocol views the physical links in an EtherChannel as one logical connection.*
Load balancing occurs between links configured as different EtherChannels.
Configuring the EtherChannel interface provides consistency in the configuration of the physical links.*
Spanning Tree Protocol ensures redundancy by transitioning failed interfaces in an EtherChannel to a forwarding state.
EtherChannel uses upgraded physical links to provide increased bandwidth.
Explanation: EtherChannel configuration of one logical interface ensures configuration consistency across the physical links in the EtherChannel. The EtherChannel provides increased bandwidth using existing switch ports without requiring any upgrades to the physical interfaces. Load balancing methods are implemented between links that are part of the same Etherchannel. Because EtherChannel views the bundled physical links as one logical connection, spanning tree recalculation is not required if one of the bundled physical links fail. If a physical interface fails, STP cannot transition the failed interface into a forwarding state.
33. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p33
What are the possible port roles for ports A, B, C, and D in this RSTP-enabled network?
alternate, designated, root, root*
designated, alternate, root, root
alternate, root, designated, root
designated, root, alternate, root
Explanation: Because S1 is the root bridge, B is a designated port, and C and D root ports. RSTP supports a new port type, alternate port in discarding state, that can be port A in this scenario.
34. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p34
Which switching technology would allow each access layer switch link to be aggregated to provide more bandwidth between each Layer 2 switch and the Layer 3 switch?
trunking
HSRP
PortFast
EtherChannel*
Explanation: PortFast is used to reduce the amount of time that a port spends going through the spanning-tree algorithm, so that devices can start sending data sooner. Trunking can be implemented in conjunction with EtherChannel, but trunking alone does not aggregate switch links. HSRP is used to load-balance traffic across two different connections to Layer 3 devices for default gateway redundancy. HSRP does not aggregate links at either Layer 2 or Layer 3 as EtherChannel does.
35. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p35
An administrator wants to form an EtherChannel between the two switches by using the Port Aggregation Protocol. If switch S1 is configured to be in auto mode, which mode should be configured on S2 to form the EtherChannel?
auto
on
off
desirable*
Explanation: An EtherChannel will be formed via PAgP when both switches are in on mode or when one of them is in auto or desirable mode and the other is in desirable mode.
36. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p36
Which set of configuration commands issued on SW1 will successfully complete the EtherChannel link between SW1 and SW2?
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no shutdown
interface Port-channel 1
no shutdown
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
channel-group 2 mode desirable
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
channel-group 1 mode desirable**
Explanation: Issuing the show running-configuration command on SW1 shows that interface GigabitEthernet0/1 is missing the channel-group 1 mode desirable command which will compete the EtherChannel configuration for interface GigabitEthernet0/1 and interface GigabitEthernet0/2.
37. A set of switches is being connected in a LAN topology. Which STP bridge priority value will make it least likely for the switch to be selected as the root?
65535
4096
32768
61440*
38. In which two PVST+ port states are MAC addresses learned? (Choose two.)
Learning*
Forwarding*
disabled
listening
blocking
Explanation: The two PVST+ port states during which MAC addresses are learned and populate the MAC address table are the learning and the forwarding states.
39. Which port role is assigned to the switch port that has the lowest cost to reach the root bridge?
designated port
disabled port
root port*
non-designated port
40. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the switch port closest, in terms of overall cost, to the root bridge
root port*
designated port
alternate port
disabled
42. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field used to specify a VLAN ID?
extended system ID*
port ID
bridge priority
bridge ID
43. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes the reference point for all path calculations?
root bridge*
root port
designated port
alternate port
44. A switch is configured to run STP. What term describes a field that has a default value of 32,768 and is the initial deciding factor when
electing a root bridge?
bridge priority*
MAC Address
extended system ID
bridge ID
45. Which statement describes an EtherChannel implementation?
EtherChannel operates only at Layer 2.
PAgP cannot be used in conjunction with EtherChannel.
A trunked port can be part of an EtherChannel bundle.*
EtherChannel can support up to a maximum of ten separate links.
46. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p46
A network administrator issued the show etherchannel summary command on the switch S1. What conclusion can be drawn?
The EtherChannel is suspended.
The EtherChannel is not functional.*
The port aggregation protocol PAgP is misconfigured.
FastEthernet ports Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 do not join the EtherChannel.
47. Which statement describes a characteristic of EtherChannel?
It can combine up to a maximum of 4 physical links.
It can bundle mixed types of 100 Mb/s and 1Gb/s Ethernet links.
It consists of multiple parallel links between a switch and a router.
It is made by combining multiple physical links that are seen as one link between two switches.*
48. Which two channel group modes would place an interface in a negotiating state using PAgP? (Choose two.)
on
desirable*
active
auto*
passive
49. Which mode configuration setting would allow formation of an EtherChannel link between switches SW1 and SW2 without sending negotiation traffic?
SW1: on
SW2: on**
SW1: desirable
SW2: desirable
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
trunking enabled on both switches
SW1: auto
SW2: auto
PortFast enabled on both switches
SW1: passive
SW2: active
50. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 2 v7.0 Modules 5 – 6 Exam Answers p50
An EtherChannel was configured between switches S1 and S2, but the interfaces do not form an EtherChannel. What is the problem?
The interface port-channel number has to be different on each switch.
The switch ports were not configured with speed and duplex mode.
The switch ports have to be configured as access ports with each port having a VLAN assigned.
The EtherChannel was not configured with the same allowed range of VLANs on each interface.*
51. When EtherChannel is configured, which mode will force an interface into a port channel without exchanging aggregation protocol packets?
active
auto
on*
desirable
52. What are two load-balancing methods in the EtherChannel technology? (Choose two.)
combination of source port and IP to destination port and IP
source IP to destination IP*
source port to destination port
combination of source MAC and IP to destination MAC and IP
source MAC to destination MAC*
53. Which protocol provides up to 16 instances of RSTP, combines many VLANs with the same physical and logical topology into a common RSTP instance, and provides support for PortFast, BPDU guard, BPDU filter, root guard, and loop guard?
STP
Rapid PVST+
PVST+
MST*
54. What is the outcome of a Layer 2 broadcast storm?
Routers will take over the forwarding of frames as switches become congested.
New traffic is discarded by the switch because it is unable to be processed.*
CSMA/CD will cause each host to continue transmitting frames.
ARP broadcast requests are returned to the transmitting host.
55. Which two network design features require Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to ensure correct network operation? (Choose two.)
static default routes
implementing VLANs to contain broadcasts
redundant links between Layer 2 switches*
link-state dynamic routing that provides redundant routes
removing single points of failure with multiple Layer 2 switches*
56. A network administrator has configured an EtherChannel between two switches that are connected via four trunk links. If the physical interface for one of the trunk links changes to a down state, what happens to the EtherChannel?
Spanning Tree Protocol will transition the failed physical interface into forwarding mode.
Spanning Tree Protocol will recalculate the remaining trunk links.
The EtherChannel will transition to a down state.
The EtherChannel will remain functional.*
Правильные ответы отмечены знаком +
Компания добавляет в корпоративную сеть несколько отремонтированных компьютеров. Однако выясняется, что производительность отремонтированных компьютеров значительно ниже других подключенных к сети компьютеров. На других компьютерах приложения, требующие передачи данных по сети, выполняются значительно быстрее. Что следует сделать инженерам компании?
Проверить, не установлено ли для сетевых плат в отремонтированных компьютерах ограничение в 10 Мбит/с.
Проверить правильность маски подсети.
Проверить правильность адреса шлюза.
+Проверить, используется ли на отремонтированных компьютерах виртуальная частная сеть (VPN).
————
Пользователь может печатать с помощью принтера, подключенного к той же сети, однако трафик пользователя не достигает Интернета. Укажите возможную причину проблемы.
Компьютер имеет неверный IP-адрес.
К компьютеру подключен неисправный сетевой кабель.
+Адрес шлюза по умолчанию на компьютере не указан или указан неверно.
Сетевая плата компьютера неисправна.
———-
Какие три фактора являются достаточным основанием для выбора клиент-серверной модели корпоративной сети вместо одноранговой модели? (Выберите три варианта).
+Данные, собранные сотрудниками, важны для бизнеса, поэтому необходимо регулярно выполнять их резервное копирование.
Сеть является маленькой и насчитывает менее восьми пользователей.
+Корпоративной сети требуется защищенный доступ к конфиденциальной информации.
При приеме на работу все сотрудники проходят строгую проверку биографических данных.
Каждый пользователь знает правила безопасного совместного использования файлов в сети.
+Пользователям требуется централизованная база данных для хранения ресурсов и информации о продажах.
———-
Какое сетевое устройство принимает решения о пересылке на основании MAC-адреса назначения, содержащегося в кадре?
повторитель
концентратор
маршрутизатор
+коммутатор
————
В чем заключается недостаток настройки беспроводного маршрутизатора или точки доступа для работы только в соответствии со стандартом протокола 802.11g?
Использование только стандарта 802.11g приведет к широковещательной передаче нескольких имен сетей (SSID).
+Беспроводные устройства стандарта 802.11a не смогут подключаться к беспроводной сети.
Стандарт 802.11g не поддерживает усовершенствованные функции обеспечения безопасности сети.
Стандарт 802.11g не поддерживает статическую адресацию IP.
———-
Какой тип подключения к Интернету обеспечивает максимальную скорость передачи?
ISDN PRI
коммутируемый доступ
+кабельное подключение
ISDN BRI
———
Какие две характеристики описывают технологию Ethernet? (Выберите два варианта.)
Она, как правило, обеспечивает скорость передачи данных 16 Мбит/с.
В ней используется кольцевая топология.
+В ней используется способ контроля доступа CSMA/CD.
Она поддерживается стандартами IEEE 802.5.
+Она поддерживается стандартами IEEE 802.3.
——-
Когда принтер считается узлом сети?
+когда он подключен к коммутатору
когда он подключен к персональному компьютеру
когда он подключен к рабочей станции
когда он подключен к ноутбуку
——
Компании ABC требуется профилактическое обслуживание всех кабелей локальной сети раз в год. Какая задача должна входить в программу профилактического обслуживания?
Отключение и повторное подключение всех соединительных кабелей.
Замена всех кабельных опор во избежание неплотных точек подключения.
+Обследование всех соединительных кабелей на предмет обрывов.
Замена всех маркировок на кабелях.
———-
Клиент выбирает многоцелевое устройство для создания домашней сети. Какие три устройства, как правило, интегрируются в многоцелевое сетевое устройство? (Выберите три варианта).
+маршрутизатор
сервер печати
+точка беспроводного доступа
сервер электронной почты
+коммутатор
веб-сервер
———
Какие три уровня модели OSI соответствуют уровню приложений модели TCP/IP? (Выберите три варианта).
сетевой
+уровень представления
+ сеансовый
+прикладной
физический
транспортный
канальный
———-
Что характерно для протокола UDP?
исправление ошибок
+низкая дополнительная нагрузка
сквозное установление каналов перед передачей
гарантированная передача
———-
Устройство имеет адрес IPv6 «2001:0DB8:75a3:0214:0607:1234:aa10:ba01». Какой идентификатор интерфейса у этого устройства?
+0607:1234:aa10:ba01
2001:0DB8
2001:0DB8:75a3
ba01
——-
Какое утверждение характеризует логическую топологию для локальной сети?
Она перечисляет компьютеры, маршрутизаторы и коммутаторы локальной сети.
Она изображает местоположения основных маршрутизаторов и коммутаторов в локальной сети.
Она определяет способ подключения компьютеров к локальной сети.
+Она описывает способ доступа компьютеров к среде локальной сети.
——
Что обозначает число 100 в стандарте 100BASE-TX?
максимальное число сетевых узлов
+максимальную пропускную способность в Мбит/с
максимальную длину кабеля в метрах
серийный номер стандарта
———-
Инженер пытается решить проблему пользователя, который утверждает, что ему не получить доступ к Интернету, при том что за день до этого доступ имелся. После беседы с пользователем инженер устанавливает, что пользователю также не удается осуществить доступ к сетевому принтеру в офисе. Сетевой принтер подключен к той же сети, что и компьютер. Компьютеру назначен IP-адрес 169.254.100.88. В чем наиболее вероятная причина проблемы?
Произошел сбой маршрутизатора, подключающего данную сеть к другим сетям.
На компьютере указан неверный шлюз IP по умолчанию.
Необходим обновить драйвер сетевой платы.
+Компьютеру не удается связаться с сервером DHCP.
———
Пользователь устанавливает на компьютер новую гигабитную сетевую плату (NIC). Он замечает, что скорость передачи данных значительно ниже ожидаемой. Что следует сделать для решения этой проблемы?
Отключить режим гибернации.
Отключить режим сна.
+Изменить параметр режима дуплекса сетевой платы с полудуплексного на полнодуплексный.
Изменить значение настройки дистанционного включения по сети для сетевого адаптера.
—
Какова максимальная длина сегмента, определенная стандартом 1000BASE-T?
500 м
+100 м
1000 м
300 м
185 м
—-
Что из перечисленного ниже является примером технического обслуживания сети?
+обучение пользователей ИТ-политикам и процедурам
немедленное отключение сетевого устройства, производящего необычный звук
использование кабельных опор для определения устройств, к которым подключены кабели
невыполнение регулярного профилактического обслуживания, если оно нарушает работу сети
——
Какая технология чаще всего используется для подключения устройств к персональной сети?
беспроводная связь стандарта IEEE 802.11n
оптоволоконные кабели
коаксиальные кабели
+Bluetooth
——
Какое преимущество предоставляет компьютерная сеть данных?
усиленная защита
упрощенные поиск и устранение неисправностей
+совместное использование ресурсов
децентрализованное администрирование
—————
Какую технологию можно рекомендовать для организации, сотрудникам которой требуется предоставить доступ к Интернету при посещении заказчиков в разных местоположениях?
ADSL
VPN
ISDN
+сотовая сеть
—-
Когда для подключения к поставщику услуг Интернета используется связь по коммутируемой линии?
когда цифровое подключение предоставляется по сети ISDN
когда услуга предоставляется через сотовый телефон
+когда используется стандартная телефонная линия
когда высокоскоростное соединение предоставляется по сети кабельного ТВ