Last Updated on December 12, 2022 by
Cisco Netacad ITN Version 7.00 CCNA 1 v7 Final Exam Answers 2021 2022 2023 – Introduction to Networks
-
Recommend
ITN (Version 7.00 & v7.02) – ITNv7 Final Exam Answers 2021 2022 2023 Full 100%
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 143. What service is the client requesting?
- Telnet
- SSH
- IMAP
- FTP
-
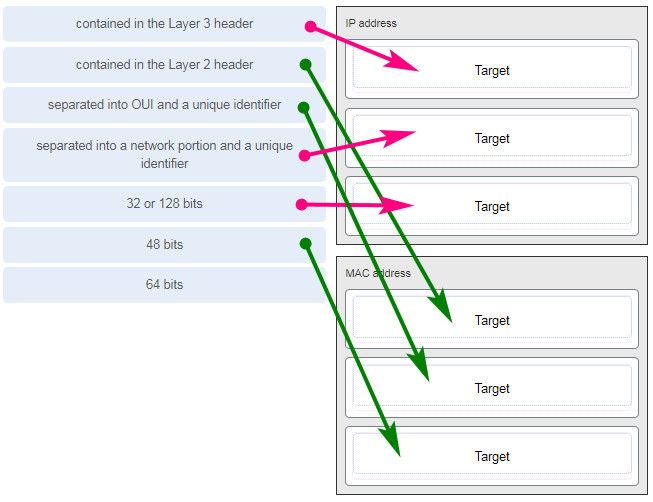
Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.) —> Case A
-
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
- implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- applies delimiting of Ethernet frame fields to synchronize communication between nodes
-
Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.) —> Case B
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
-
Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.) —> Case C
- implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
- implements a process to delimit fields within an Ethernet 2 frame
-
-
A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
- Enter CTRL-Z at the privileged mode prompt.
- Power cycle the device.
- Exit privileged EXEC mode and press Enter.
- Exit global configuration mode.
- Reboot the device.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
While at the privileged mode prompt such as Router#, type exit ,press Enter , and the banner message appears. Power cycling a network device that has had the banner motd command issued will also display the banner message, but this is not a quick way to test the configuration.
-
What happens when the transport input ssh command is entered on the switch vty lines?
- The switch requires a username/password combination for remote access.
- The SSH client on the switch is enabled.
- Communication between the switch and remote users is encrypted.
- The switch requires remote connections via a proprietary client software.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The transport input ssh command when entered on the switch vty (virtual terminal lines) will encrypt all inbound controlled telnet connections.
-
What is the subnet ID associated with the IPv6 address 2001:DA48:FC5:A4:3D1B::1/64?
- 2001:DA48::/64
- 2001::/64
- 2001:DA48:FC5:A4::/64
- 2001:DA48:FC5::A4:/64
Explanation:
-
A client is using SLAAC to obtain an IPv6 address for its interface. After an address has been generated and applied to the interface, what must the client do before it can begin to use this IPv6 address?
- It must send an ICMPv6 Router Solicitation message to determine what default gateway it should use.
- It must send a DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST message to request the address of the DNS server.
- It must send a DHCPv6 REQUEST message to the DHCPv6 server to request permission to use this address.
- It must send an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message to ensure that the address is not already in use on the network.
Explanation:
Stateless DHCPv6 or stateful DHCPv6 uses a DHCP server, but Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) does not. A SLAAC client can automatically generate an address that is based on information from local routers via Router Advertisement (RA) messages. Once an address has been assigned to an interface via SLAAC, the client must ensure via Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) that the address is not already in use. It does this by sending out an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message and listening for a response. If a response is received, then it means that another device is already using this address.
-
Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FE80::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FF00::/8
- FEC0::/10
Explanation:
Link-local addresses are in the range of FE80::/10 to FEBF::/10. The original IPv6 specification defined site-local addresses and used the prefix range FEC0::/10, but these addresses were deprecated by the IETF in favor of unique local addresses. FDEE::/7 is a unique local address because it is in the range of FC00::/7 to FDFF::/7. IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8.
-
What mechanism is used by a router to prevent a received IPv4 packet from traveling endlessly on a network?
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It increments the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Parameter Problem message to the source host.
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It decrements the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Time Exceeded message to the source host.
-
A network administrator is designing the layout of a new wireless network. Which three areas of concern should be accounted for when building a wireless network? (Choose three.)
- mobility options
- security
- interference
- coverage area
- packet collision
- extensive cabling
Explanation:
The three areas of concern for wireless networks focus on the size of the coverage area, any nearby interference, and providing network security. Extensive cabling is not a concern for wireless networks, as a wireless network will require minimal cabling for providing wireless access to hosts. Mobility options are not a component of the areas of concern for wireless networks.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What is wrong with the displayed termination?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 07 - The untwisted length of each wire is too long.
- The woven copper braid should not have been removed.
- The wrong type of connector is being used.
- The wires are too thick for the connector that is used.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a cable to an RJ-45 connector is terminated, it is important to ensure that the untwisted wires are not too long and that the flexible plastic sheath surrounding the wires is crimped down and not the bare wires. None of the colored wires should be visible from the bottom of the jack.
-
A network administrator notices that some newly installed Ethernet cabling is carrying corrupt and distorted data signals. The new cabling was installed in the ceiling close to fluorescent lights and electrical equipment. Which two factors may interfere with the copper cabling and result in signal distortion and data corruption? (Choose two.)
- EMI
- signal attenuation
- crosstalk
- RFI
- extended length of cabling
Explanation:
EMI and RFI signals can distort and corrupt data signals that are carried by copper media. These distortions usually come from radio waves and electromagnetic devices such as motors and florescent lights. Crosstalk is a disturbance that is caused by adjacent wires bundled too close together with the magnetic field of one wire affecting another. Signal attenuation is caused when an electrical signal begins to deteriorate over the length of a copper cable.
-
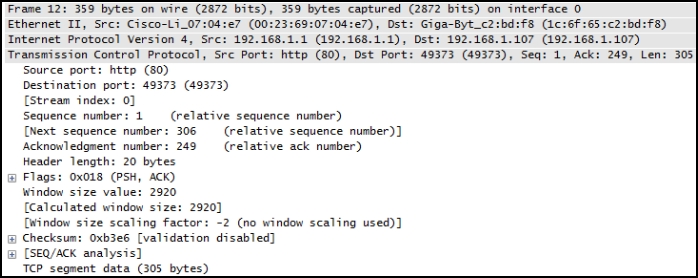
Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function of TCP or UDP in this situation? (Choose three.)
- TCP is the preferred protocol when a function requires lower network overhead.
- The source port field identifies the running application or service that will handle data returning to the PC.
- The TCP source port number identifies the sending host on the network.
- UDP segments are encapsulated within IP packets for transport across the network.
- The UDP destination port number identifies the application or service on the server which will handle the data.
- The TCP process running on the PC randomly selects the destination port when establishing a session with the server.
Explanation:
Layer 4 port numbers identify the application or service which will handle the data. The source port number is added by the sending device and will be the destination port number when the requested information is returned. Layer 4 segments are encapsulated within IP packets. UDP, not TCP, is used when low overhead is needed. A source IP address, not a TCP source port number, identifies the sending host on the network. Destination port numbers are specific ports that a server application or service monitors for requests.
-
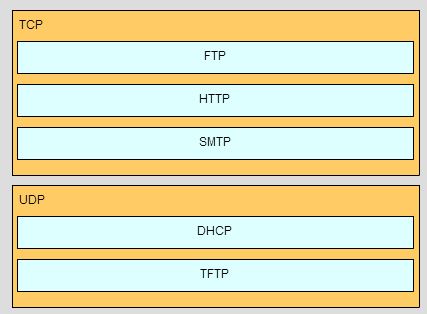
Match the application protocols to the correct transport protocols.
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 01 -
A group of Windows PCs in a new subnet has been added to an Ethernet network. When testing the connectivity, a technician finds that these PCs can access local network resources but not the Internet resources. To troubleshoot the problem, the technician wants to initially confirm the IP address and DNS configurations on the PCs, and also verify connectivity to the local router. Which three Windows CLI commands and utilities will provide the necessary information? (Choose three.)
- netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor
- arp -a
- tracert
- ping
- ipconfig
- nslookup
- telnet
Explanation:
The ipconfig and nslookup commands will provide initial IP address and DNS configuration information to the technicians and determine if DHCP is assigning correct information to the PCs. The ping utility would be used to verify, or not, connectivity to the default gateway (router) using the configured default gateway address, or using the known correct default gateway address if these are found to be different. The arp -a or netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor commands could be used if the problem is then suspected to be an IP address to MAC address mapping issue. The telnet and tracert utilities could be used to determine where the problem was located in the network if the default gateway configuration was found to be correct.
-
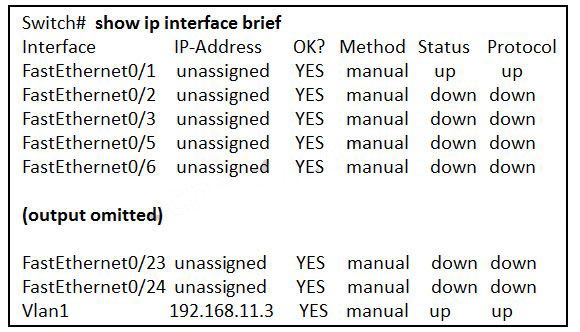
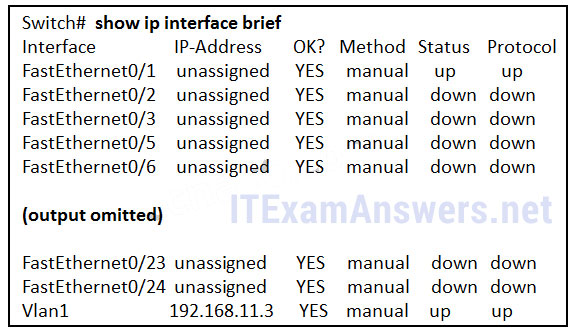
What two pieces of information are displayed in the output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose two.)
- speed and duplex settings
- MAC addresses
- next-hop addresses
- interface descriptions
- IP addresses
- Layer 1 statuses
Explanation:
The command show ip interface brief shows the IP address of each interface, as well as the operational status of the interfaces at both Layer 1 and Layer 2. In order to see interface descriptions and speed and duplex settings, use the command show running-config interface. Next-hop addresses are displayed in the routing table with the command show ip route, and the MAC address of an interface can be seen with the command show interfaces.
-
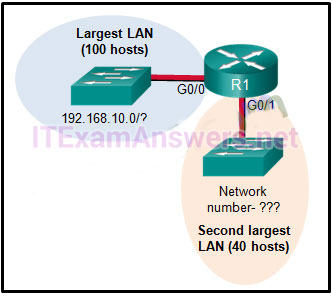
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 25 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.128
-
Which frame field is created by a source node and used by a destination node to ensure that a transmitted data signal has not been altered by interference, distortion, or signal loss?
- transport layer error check field
- error correction process field
- flow control field
- User Datagram Protocol field
- frame check sequence field
-
What is a function of the data link layer?
- provides delivery of data between two applications
- provides for the exchange of frames over a common local media
- provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
- provides the formatting of data
-
What are three characteristics of the CSMA/CD process? (Choose three.)
- After detecting a collision, hosts can attempt to resume transmission after a random time delay has expired.
- A jam signal indicates that the collision has cleared and the media is not busy.
- All of the devices on a segment see data that passes on the network medium.
- The device with the electronic token is the only one that can transmit after a collision.
- Devices can be configured with a higher transmission priority.
- A device listens and waits until the media is not busy before transmitting.
-
What characteristic describes a Trojan horse?
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- malicious software or code running on an end device
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
-
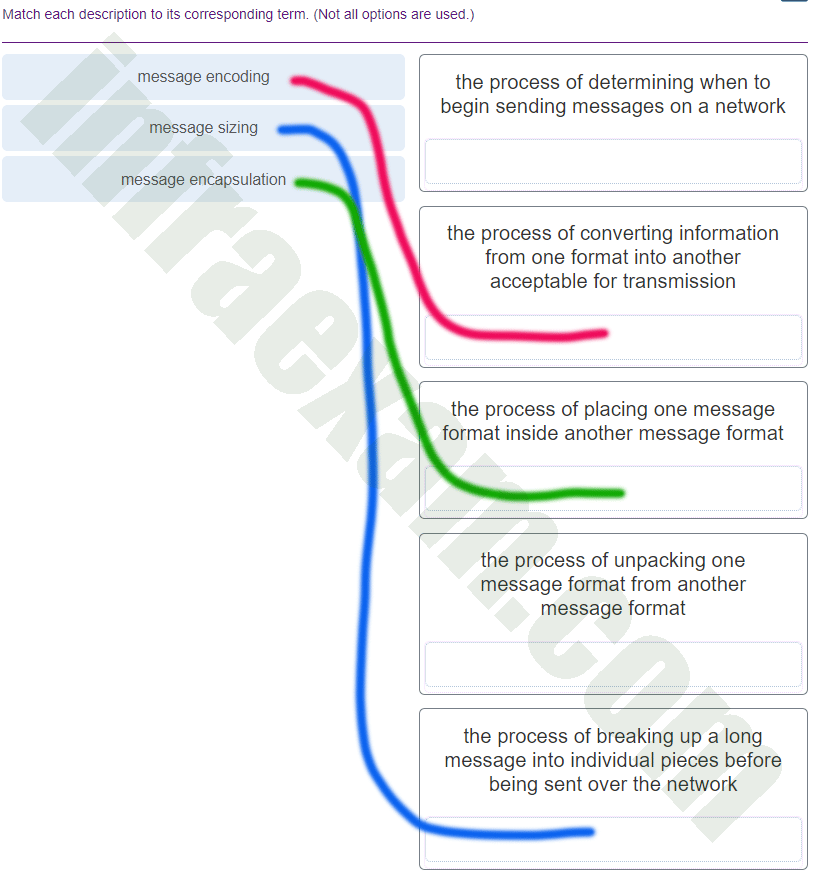
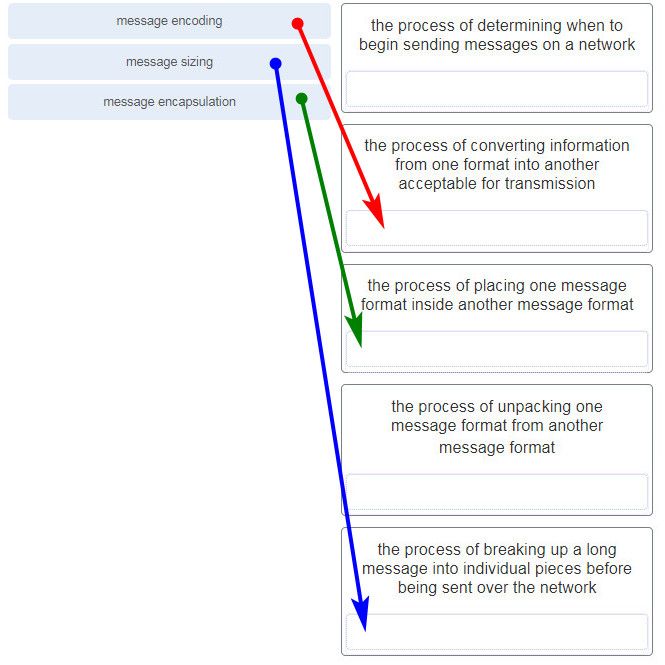
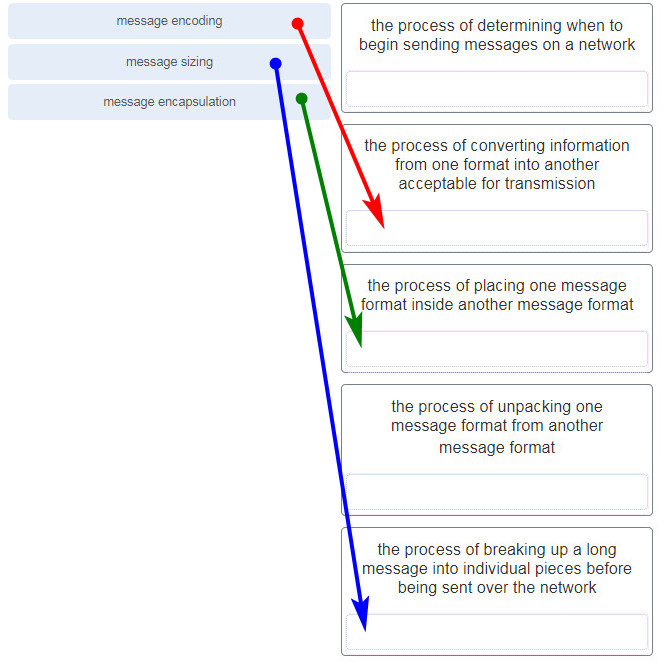
What three requirements are defined by the protocols used in network communcations to allow message transmission across a network? (Choose three.)
- end-device installation
- media selection
- message encoding
- delivery options
- connector specifications
- message size
-
What are two features of ARP? (Choose two.)
- If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.
- When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
- If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
- An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
- If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.
Explanation:
When a node encapsulates a data packet into a frame, it needs the destination MAC address. First it determines if the destination device is on the local network or on a remote network. Then it checks the ARP table (not the MAC table) to see if a pair of IP address and MAC address exists for either the destination IP address (if the destination host is on the local network) or the default gateway IP address (if the destination host is on a remote network). If the match does not exist, it generates an ARP broadcast to seek the IP address to MAC address resolution. Because the destination MAC address is unknown, the ARP request is broadcast with the MAC address FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. Either the destination device or the default gateway will respond with its MAC address, which enables the sending node to assemble the frame. If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will discard the packet because a frame cannot be created.
-
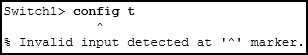
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 06 - The entire command, configure terminal , must be used.
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
In order to enter global configuration mode, the command configure terminal , or a shortened version such as config t , must be entered from privileged EXEC mode. In this scenario the administrator is in user EXEC mode, as indicated by the > symbol after the hostname. The administrator would need to use the enable command to move into privileged EXEC mode before entering the configure terminal command.
-
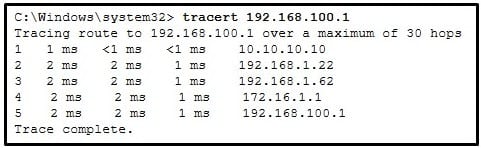
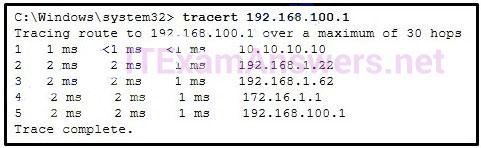
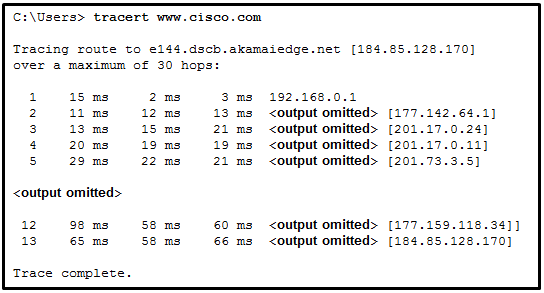
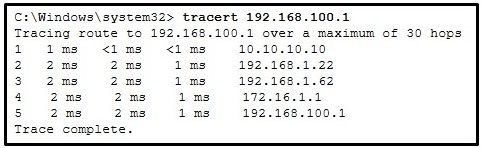
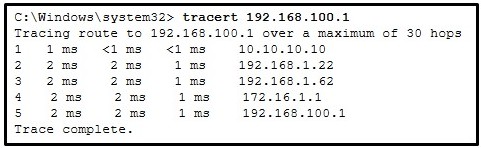
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 05 - This host does not have a default gateway configured.
- There are 4 hops between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
- There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
Explanation:
The output displays a successful Layer 3 connection between a host computer and a host at 19.168.100.1. It can be determined that 4 hops exist between them and the average transmission time is 1 milliseconds. Layer 3 connectivity does not necessarily mean that an application can run between the hosts.
-
What are two characteristics of IP? (Choose two.)
- retransmits packets if errors occur
- guarantees delivery of packets
- does not require a dedicated end-to-end connection
- operates independently of the network media
- re-assembles out of order packets into the correct order at the receiver end
Explanation:
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a connectionless, best effort protocol. This means that IP requires no end-to-end connection nor does it guarantee delivery of packets. IP is also media independent, which means it operates independently of the network media carrying the packets.
-
What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a host needs to send a message to another host located on the same network, it can forward the message directly. However, when a host needs to send a message to a remote network, it must use the router, also known as the default gateway. This is because the data link frame address of the remote destination host cannot be used directly. Instead, the IP packet has to be sent to the router (default gateway) and the router will forward the packet toward its destination. Therefore, if the default gateway is incorrectly configured, the host can communicate with other hosts on the same network, but not with hosts on remote networks.
-
Users report that the network access is slow. After questioning the employees, the network administrator learned that one employee downloaded a third-party scanning program for the printer. What type of malware might be introduced that causes slow performance of the network?
- spam
- virus
- worm
- phishing
Explanation:
-
A company has a file server that shares a folder named Public. The network security policy specifies that the Public folder is assigned Read-Only rights to anyone who can log into the server while the Edit rights are assigned only to the network admin group. Which component is addressed in the AAA network service framework?
- automation
- authorization
- accounting
- authentication
Explanation:
After a user is successfully authenticated (logged into the server), the authorization is the process of determining what network resources the user can access and what operations (such as read or edit) the user can perform.
-
What are two common causes of signal degradation when using UTP cabling? (Choose two.)
- loss of light over long distances
- low-quality cable or connectors
- low-quality shielding in cable
- installing cables in conduit
- improper termination
-
Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
Explanation:
The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
-
What is the consequence of configuring a router with the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command?
- Each router interface will generate an IPv6 link-local address.
- The IPv6 enabled router interfaces begin sending ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages.
- It statically creates a global unicast address on this router.
- All router interfaces will be automatically activated.
-
Which two protocols operate at the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose two.)
- POP
- DNS
- IP
- TCP
- Ethernet
- UDP
-
An employee of a large corporation remotely logs into the company using the appropriate username and password. The employee is attending an important video conference with a customer concerning a large sale. It is important for the video quality to be excellent during the meeting. The employee is unaware that after a successful login, the connection to the company ISP failed. The secondary connection, however, activated within seconds. The disruption was not noticed by the employee or other employees.
What three network characteristics are described in this scenario? (Choose three.)- integrity
- scalability
- quality of service
- fault tolerance
- powerline networking
- security
-
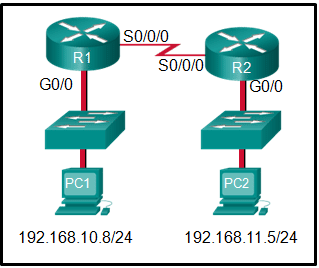
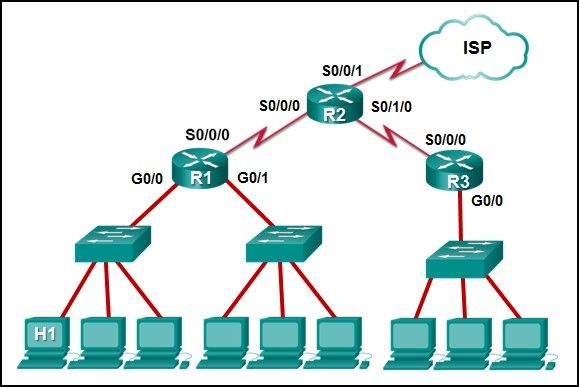
Refer to the exhibit. If PC1 is sending a packet to PC2 and routing has been configured between the two routers, what will R1 do with the Ethernet frame header attached by PC1?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 04 - open the header and use it to determine whether the data is to be sent out S0/0/0
- open the header and replace the destination MAC address with a new one
- nothing, because the router has a route to the destination network
- remove the Ethernet header and configure a new Layer 2 header before sending it out S0/0/0
Explanation:
When PC1 forms the various headers attached to the data one of those headers is the Layer 2 header. Because PC1 connects to an Ethernet network, an Ethernet header is used. The source MAC address will be the MAC address of PC1 and the destination MAC address will be that of G0/0 on R1. When R1 gets that information, the router removes the Layer 2 header and creates a new one for the type of network the data will be placed onto (the serial link).
-
Which three layers of the OSI model map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- transport
- application
- network
- session
- data link
- presentation
Explanation:
-
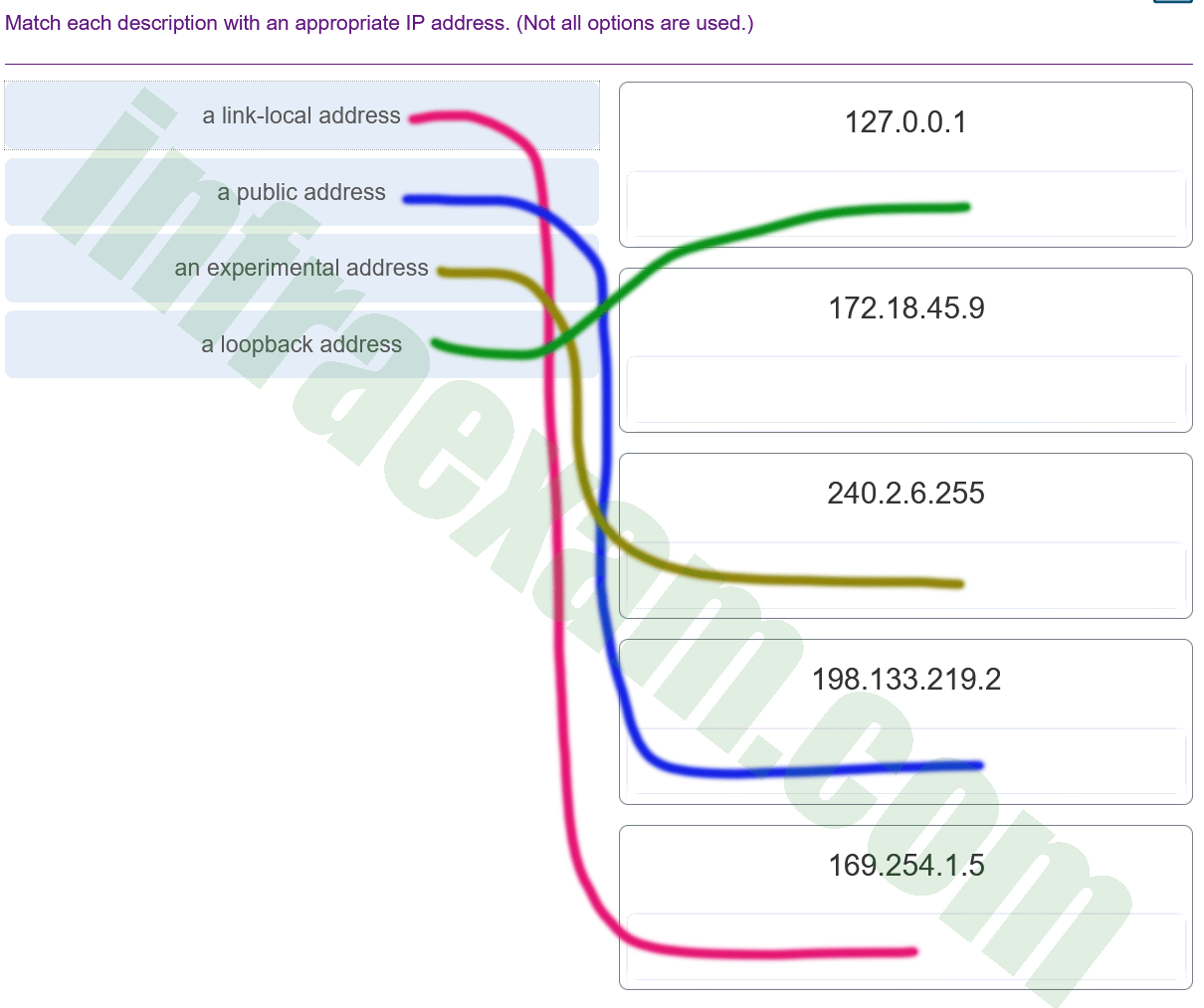
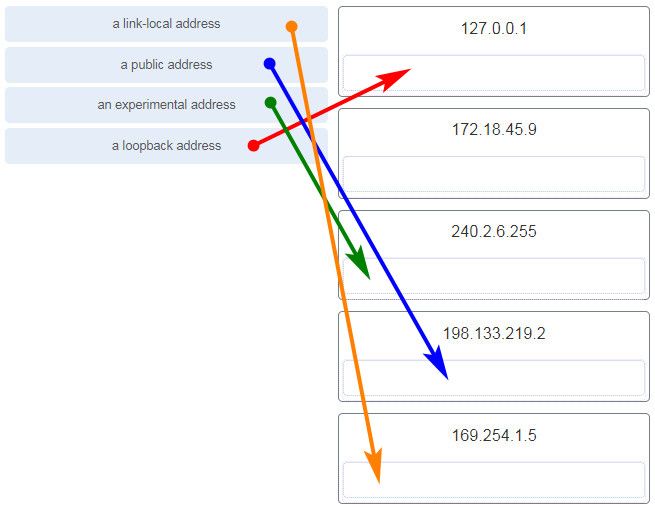
Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 02 Explanation:
Link-Local addresses are assigned automatically by the OS environment and are located in the block 169.254.0.0/16. The private addresses ranges are 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, and 192.168.0.0/16. TEST-NET addresses belong to the range 192.0.2.0/24. The addresses in the block 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.254 are reserved as experimental addresses. Loopback addresses belong to the block 127.0.0.0/8.
-
What does the term “attenuation” mean in data communication?
- strengthening of a signal by a networking device
- leakage of signals from one cable pair to another
- loss of signal strength as distance increases
- time for a signal to reach its destination
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Data is transmitted on copper cables as electrical pulses. A detector in the network interface of a destination device must receive a signal that can be successfully decoded to match the signal sent. However, the farther the signal travels, the more it deteriorates. This is referred to as signal attenuation.
-
Which two statements describe how to assess traffic flow patterns and network traffic types using a protocol analyzer? (Choose two.)
- Capture traffic during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types.
- Perform the capture on different network segments.
- Only capture WAN traffic because traffic to the web is responsible for the largest amount of traffic on a network.
- Only capture traffic in the areas of the network that receive most of the traffic such as the data center.
- Capture traffic on the weekends when most employees are off work.
Explanation:
Traffic flow patterns should be gathered during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types. The capture should also be performed on different network segments because some traffic will be local to a particular segment.
-
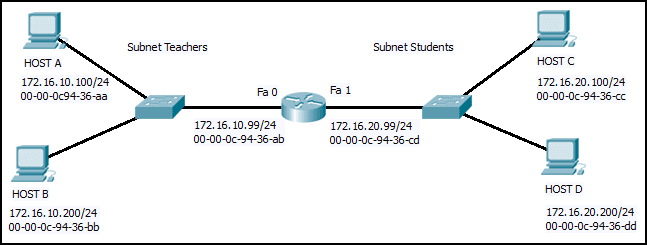
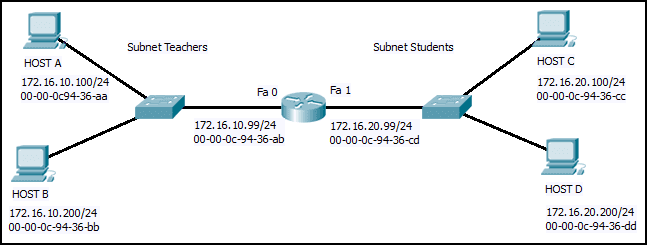
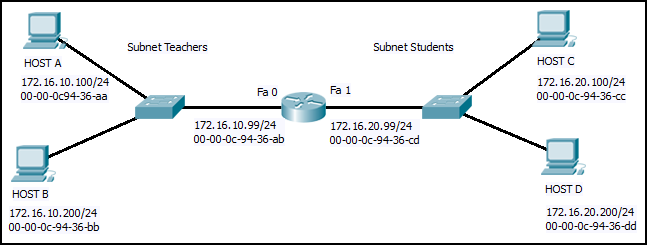
Refer to the exhibit. Host B on subnet Teachers transmits a packet to host D on subnet Students. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 addresses are contained in the PDUs that are transmitted from host B to the router?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 03 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-dd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.100.200 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200 - Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-cd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.99
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
- Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-dd
-
Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
- 192.168.1.64/26
Explanation:
For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
-
What are two problems that can be caused by a large number of ARP request and reply messages? (Choose two.)
- A large number of ARP request and reply messages may slow down the switching process, leading the switch to make many changes in its MAC table.
- The ARP request is sent as a broadcast, and will flood the entire subnet.
- Switches become overloaded because they concentrate all the traffic from the attached subnets.
- All ARP request messages must be processed by all nodes on the local network.
- The network may become overloaded because ARP reply messages have a very large payload due to the 48-bit MAC address and 32-bit IP address that they contain.
-
Why would a Layer 2 switch need an IP address?
- to enable the switch to be managed remotely
- to enable the switch to receive frames from attached PCs
- to enable the switch to send broadcast frames to attached PCs
- to enable the switch to function as a default gateway
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A switch, as a Layer 2 device, does not need an IP address to transmit frames to attached devices. However, when a switch is accessed remotely through the network, it must have a Layer 3 address. The IP address must be applied to a virtual interface rather than to a physical interface. Routers, not switches, function as default gateways.
-
How does the service password-encryption command enhance password security on Cisco routers and switches?
- It requires encrypted passwords to be used when connecting remotely to a router or switch with Telnet.
- It encrypts passwords that are stored in router or switch configuration files.
- It requires that a user type encrypted passwords to gain console access to a router or switch.
- It encrypts passwords as they are sent across the network.
Explanation:
The service password-encryption command encrypts plaintext passwords in the configuration file so that they cannot be viewed by unauthorized users.
-
Which two statements are correct in a comparison of IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers? (Choose two.)
- The Destination Address field is new in IPv6.
- The Source Address field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
- The Version field from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6.
- The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6.
- The Header Checksum field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
-
Which two statements accurately describe an advantage or a disadvantage when deploying NAT for IPv4 in a network? (Choose two.)
- NAT will impact negatively on switch performance.
- NAT causes routing tables to include more information.
- NAT improves packet handling.
- NAT adds authentication capability to IPv4.
- NAT provides a solution to slow down the IPv4 address depletion.
- NAT introduces problems for some applications that require end-to-end connectivity.
-
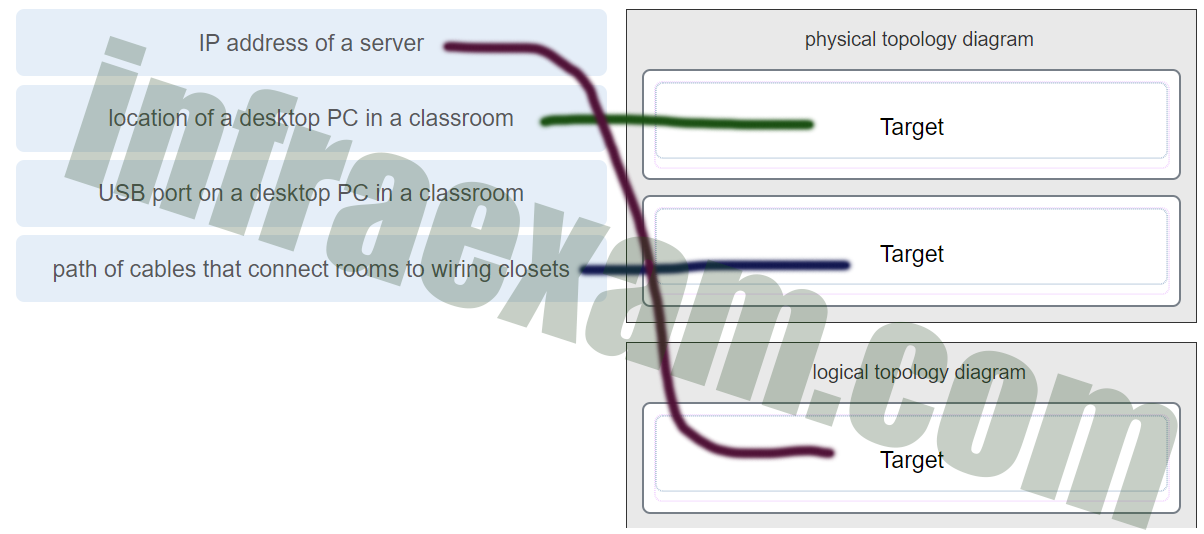
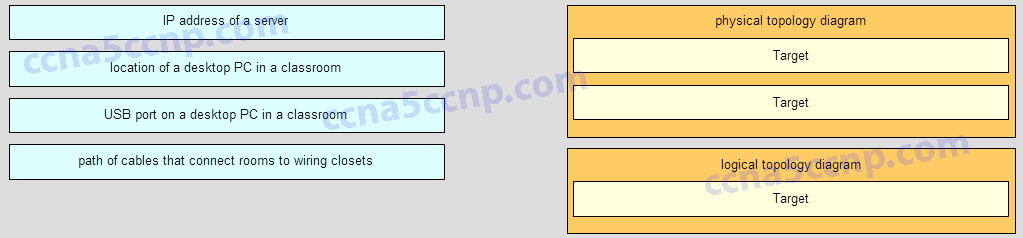
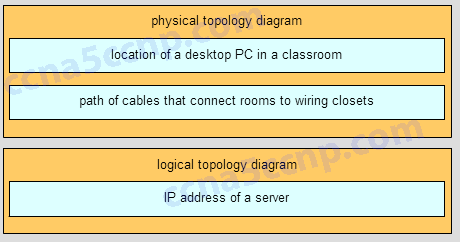
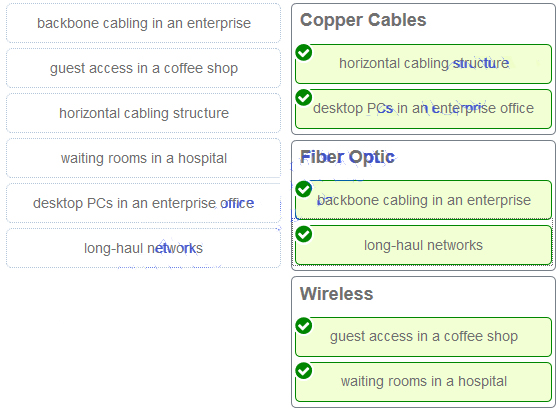
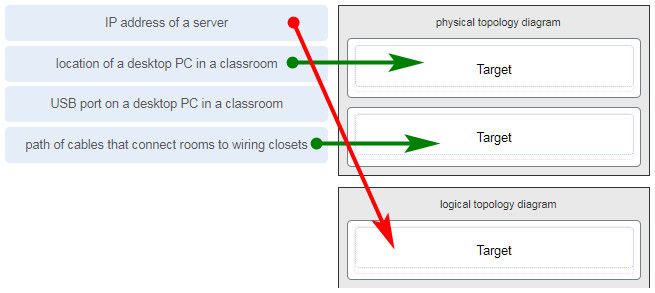
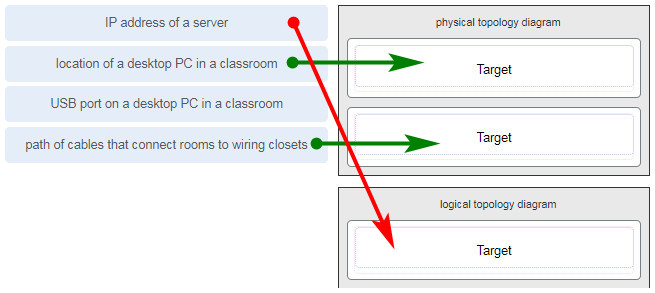
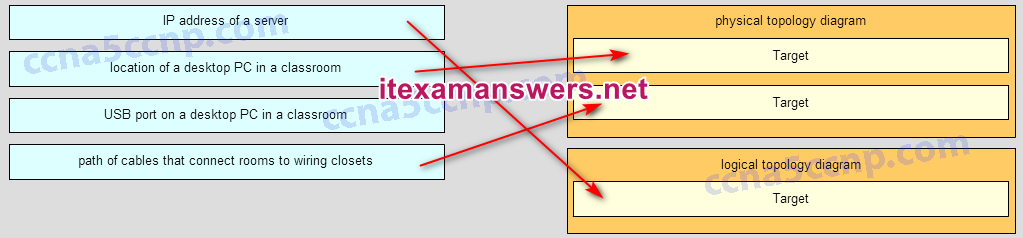
Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 003 Explanation:
A logical topology diagram typically depicts the IP addressing scheme and groupings of devices and ports. A physical topology diagram shows how those devices are connected to each other and the network, focusing on the physical locations of intermediary devices, configured ports, and cabling.
-
What service is provided by HTTP?
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 67. What service is the client requesting?
- Telnet
- FTP
- SSH
- DHCP
-
What are the two most effective ways to defend against malware? (Choose two.)
- Implement strong passwords.
- Update the operating system and other application software.
- Install and update antivirus software.
- Implement RAID.
- Implement a VPN.
- Implement network firewalls.
Explanation:
-
An administrator defined a local user account with a secret password on router R1 for use with SSH. Which three additional steps are required to configure R1 to accept only encrypted SSH connections? (Choose three.)
- Configure the IP domain name on the router.
- Enable inbound vty Telnet sessions.
- Configure DNS on the router.
- Generate the SSH keys.
- Generate two-way pre-shared keys.
- Enable inbound vty SSH sessions.
Explanation:
There are four steps to configure SSH support on a Cisco router:
Step 1: Set the domain name.
Step 2: Generate one-way secret keys.
Step 3: Create a local username and password.
Step 4: Enable SSH inbound on a vty line.
-
A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in its ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
- It will send the frame and use its own MAC address as the destination.
- It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
- It will send a request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.
-
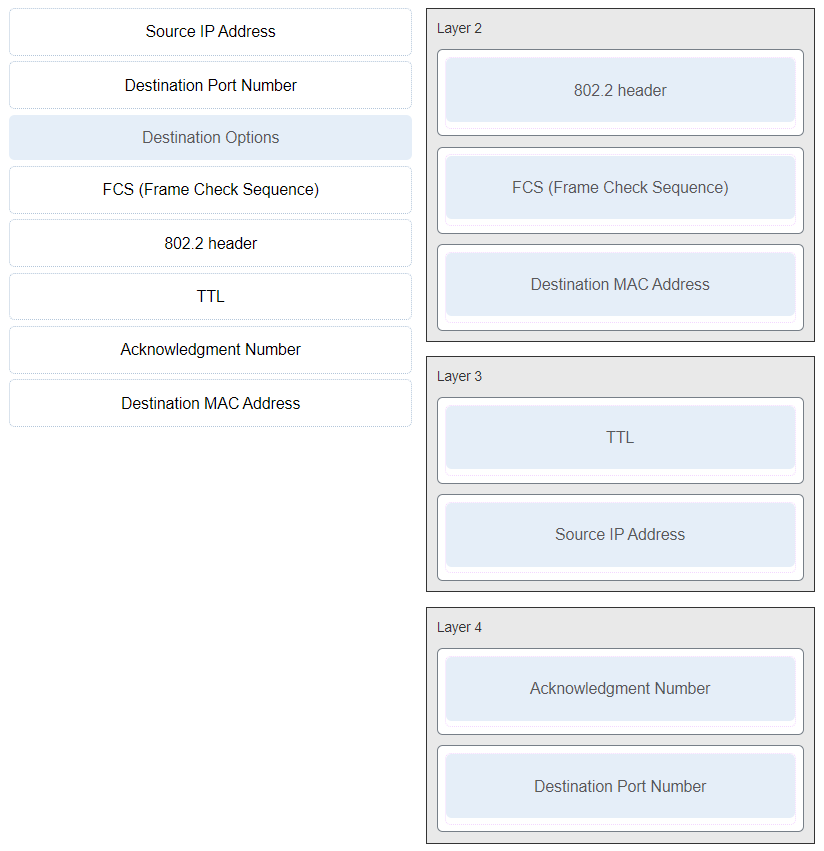
Match the header field with the appropriate layer of the OSI model. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 03 -
When a switch configuration includes a user-defined error threshold on a per-port basis, to which switching method will the switch revert when the error threshold is reached?
- fast-forward
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
-
What are proprietary protocols?
- protocols that can be freely used by any organization or vendor
- protocols developed by private organizations to operate on any vendor hardware
- a collection of protocols known as the TCP/IP protocol suite
- protocols developed by organizations who have control over their definition and operation
Explanation:
Proprietary protocols have their definition and operation controlled by one company or vendor. Some of them can be used by different organizations with permission from the owner. The TCP/IP protocol suite is an open standard, not a proprietary protocol.
-
What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- A company can monopolize the market.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
Explanation:
A monopoly by one company is not a good idea from a user point of view. If a protocol can only be run on one brand, it makes it difficult to have mixed equipment in a network. A proprietary protocol is not free to use. An open standard protocol will in general be implemented by a wide range of vendors.
-
Which type of server relies on record types such as A, NS, AAAA, and MX in order to provide services?
- file
- web
- DNS
Explanation:
-
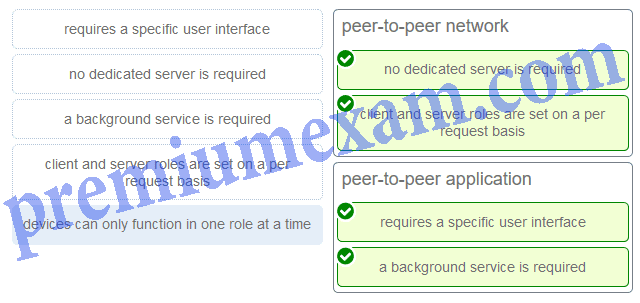
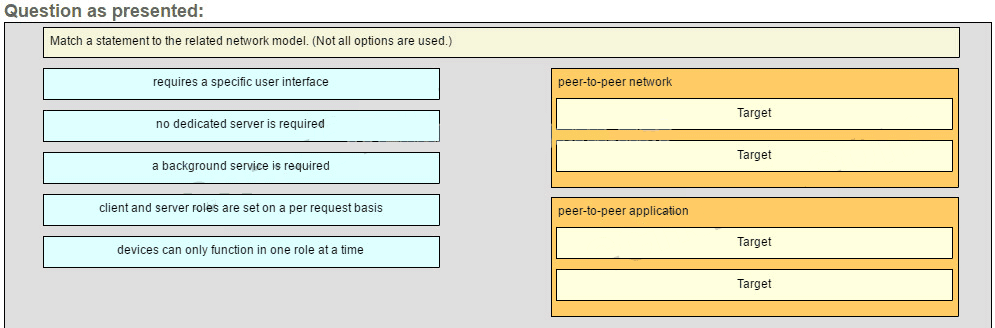
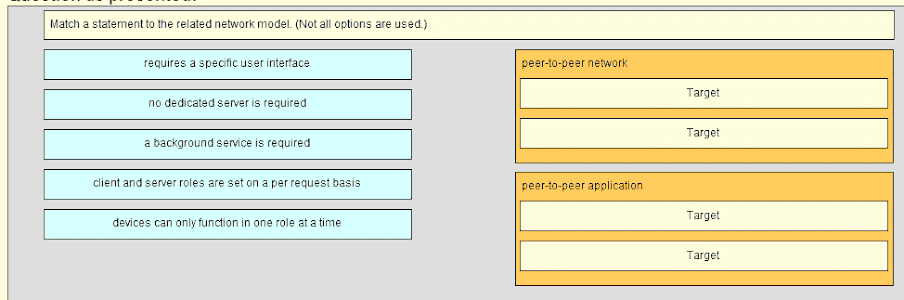
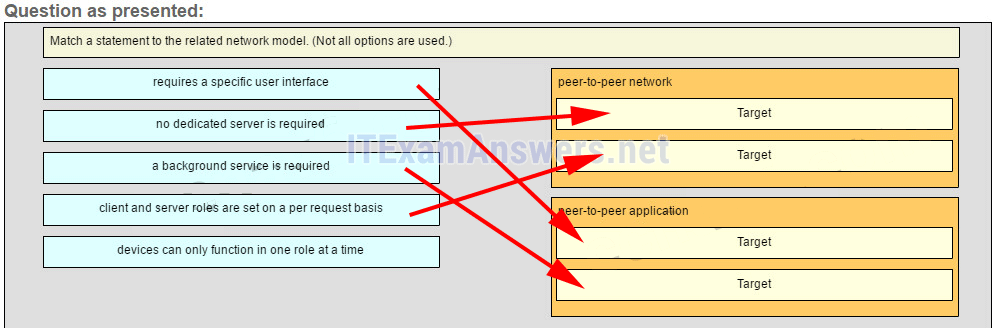
Match a statement to the related network model. (Not all options are used.)
ITN Chapter 10 Exam Answers 02 Explanation:
Peer-to-peer networks do not require the use of a dedicated server, and devices can assume both client and server roles simultaneously on a per request basis. Because they do not require formalized accounts or permissions, they are best used in limited situations. Peer-to-peer applications require a user interface and background service to be running, and can be used in more diverse situations.
-
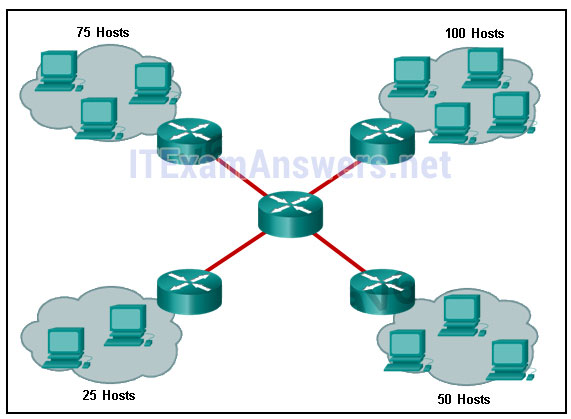
A network administrator wants to have the same network mask for all networks at a particular small site. The site has the following networks and number of devices:
IP phones – 22 addresses
PCs – 20 addresses needed
Printers – 2 addresses needed
Scanners – 2 addresses neededThe network administrator has deemed that 192.168.10.0/24 is to be the network used at this site. Which single subnet mask would make the most efficient use of the available addresses to use for the four subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
-
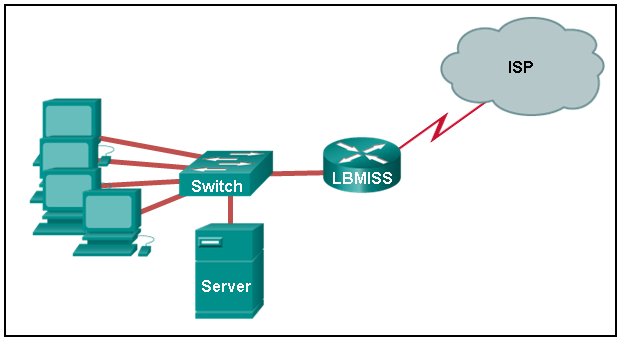
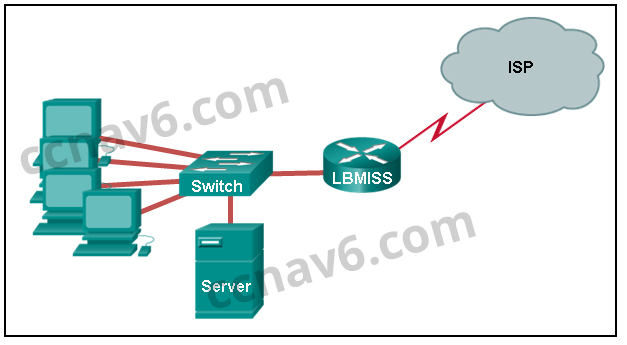
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has assigned the LAN of LBMISS an address range of 192.168.10.0. This address range has been subnetted using a /29 prefix. In order to accommodate a new building, the technician has decided to use the fifth subnet for configuring the new network (subnet zero is the first subnet). By company policies, the router interface is always assigned the first usable host address and the workgroup server is given the last usable host address. Which configuration should be entered into the properties of the workgroup server to allow connectivity to the Internet?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 02 - IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
- IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
- IP address: 192.168.10.254 subnet mask: 255.255.255.0, default gateway: 192.168.10.1
- IP address: 192.168.10.41 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.46
- IP address: 192.168.10.65 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.76
Explanation:
-
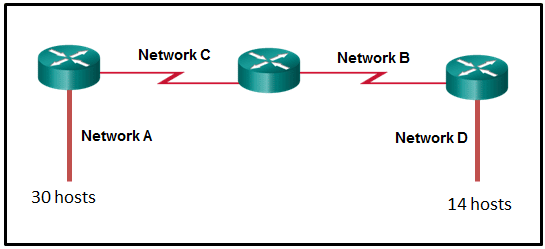
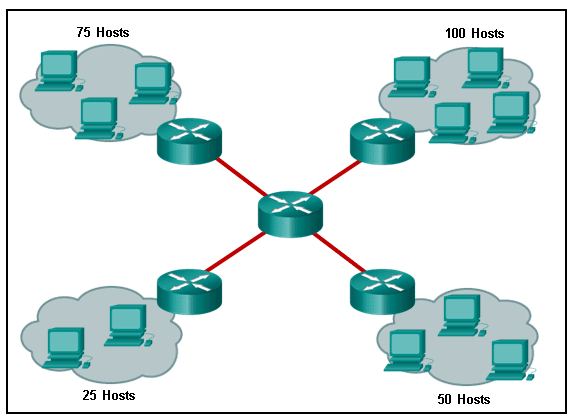
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer has been given the network address of 192.168.99.0 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192 to subnet across the four networks shown. How many total host addresses are unused across all four subnets?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 01 - 158
- 200
- 224
- 88
- 72
Explanation:
-
What would be the interface ID of an IPv6 enabled interface with a MAC address of 1C-6F-65-C2-BD-F8 when the interface ID is generated by using the EUI-64 process?
- 1E6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- C16F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 0C6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 106F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
-
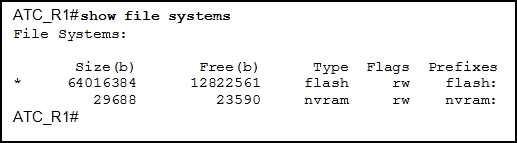
Which information does the show startup-config command display?
- the IOS image copied into RAM
- the bootstrap program in the ROM
- the contents of the saved configuration file in the NVRAM
- the contents of the current running configuration file in the RAM
-
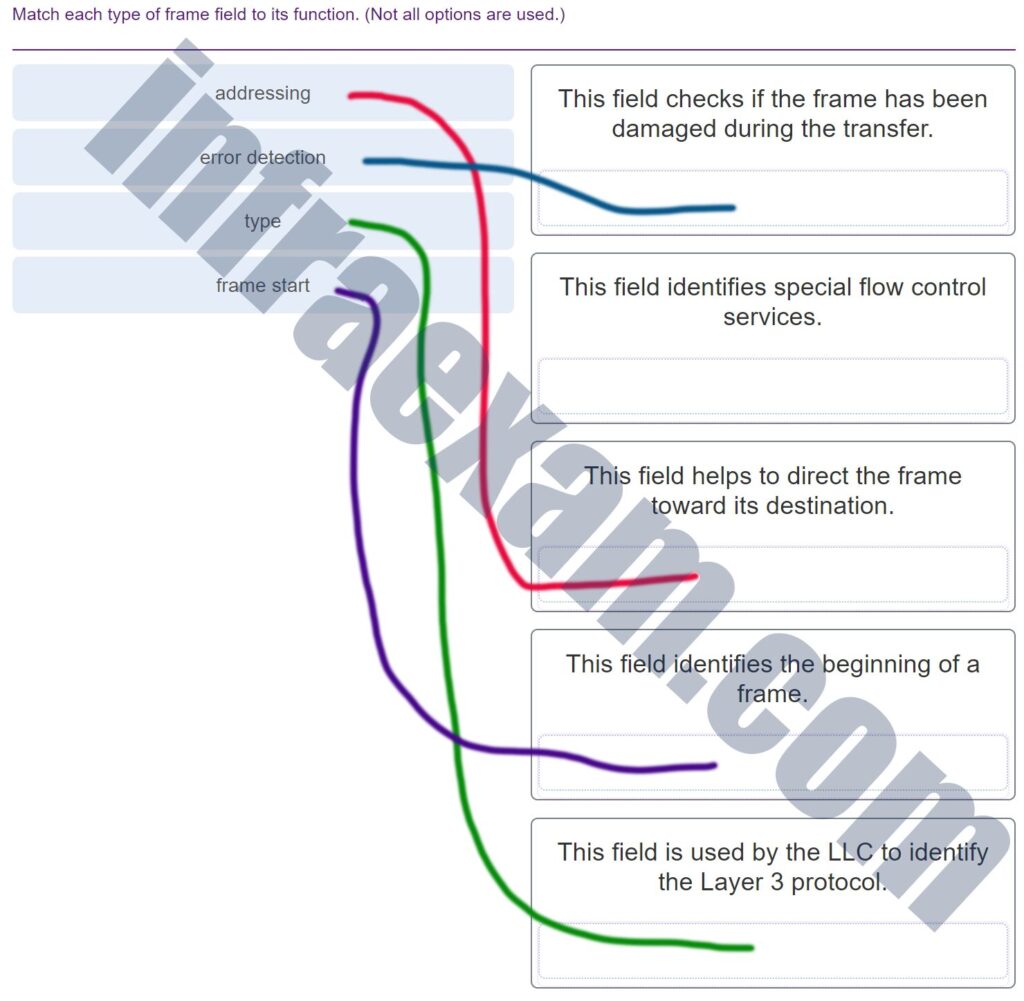
Match each type of frame field to its function. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 004 -
What are two primary responsibilities of the Ethernet MAC sublayer? (Choose two.)
- accessing the media
- data encapsulation
- logical addressing
- error detection
- frame delimiting
-
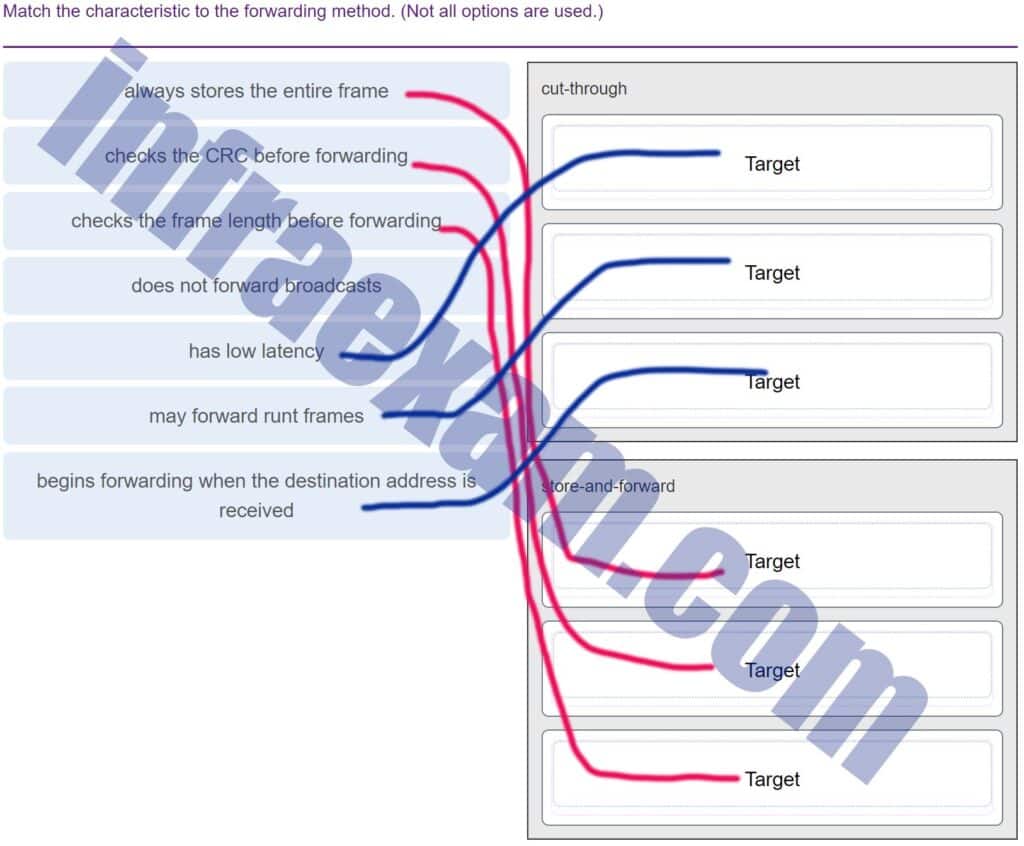
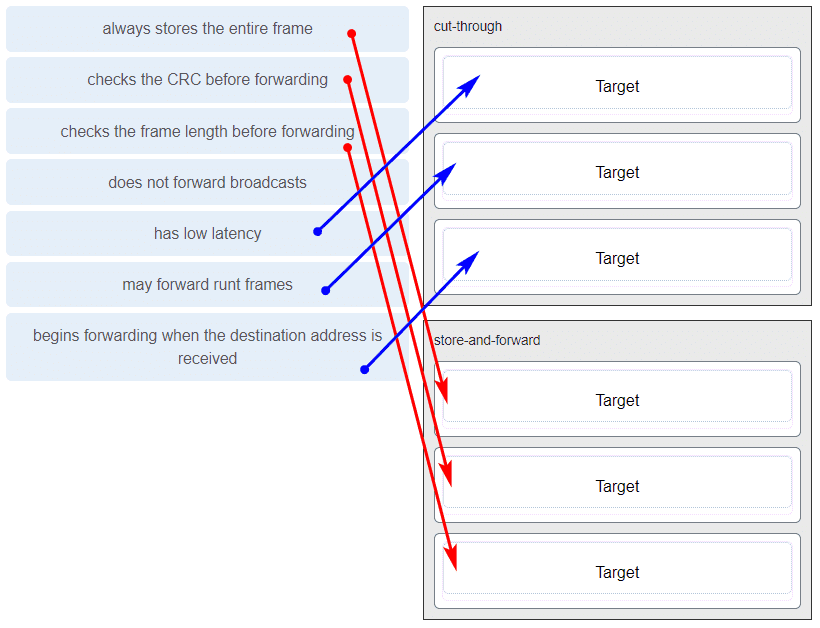
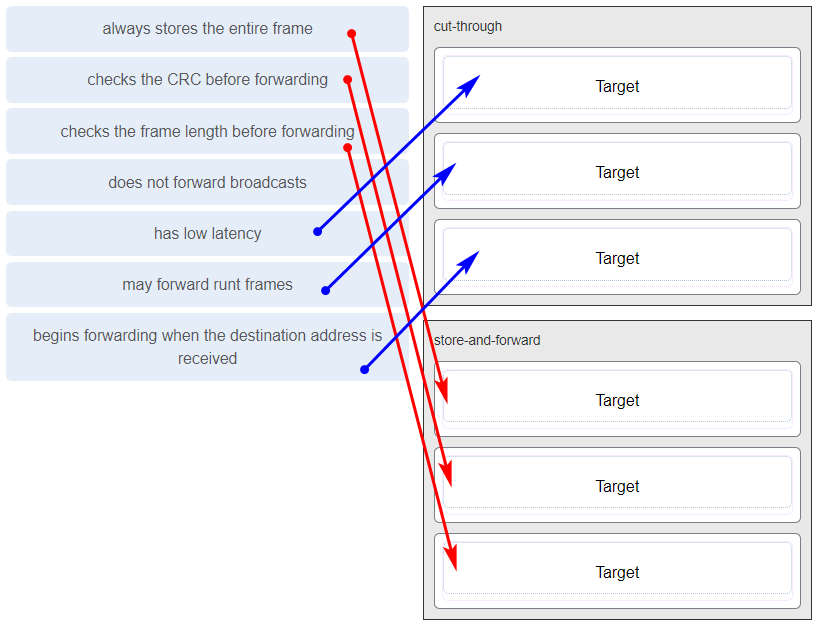
Match the characteristic to the forwarding method. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 005 -
Which switching method drops frames that fail the FCS check?
- store-and-forward switching
- ingress port buffering
- cut-through switching
- borderless switching
-
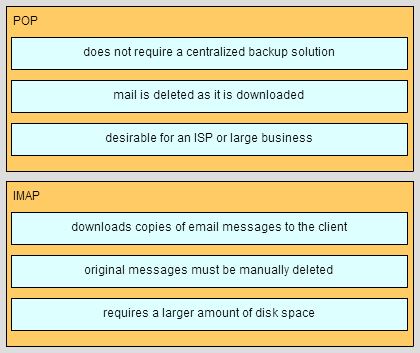
What is an advantage for small organizations of adopting IMAP instead of POP?
- IMAP sends and retrieves email, but POP only retrieves email.
- POP only allows the client to store messages in a centralized way, while IMAP allows distributed storage.
- Messages are kept in the mail servers until they are manually deleted from the email client.
- When the user connects to a POP server, copies of the messages are kept in the mail server for a short time, but IMAP keeps them for a long time.
Explanation:
-
A wired laser printer is attached to a home computer. That printer has been shared so that other computers on the home network can also use the printer. What networking model is in use?
- point-to-point
- client-based
- peer-to-peer (P2P)
- master-slave
Explanation:
-
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 200 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
-
Which wireless technology has low-power and data rate requirements making it popular in home automation applications?
- ZigBee
- 5G
- Wi-Fi
- LoRaWAN
-
What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- 3-way handshake
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering
- use of checksum
Explanation:
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 69. What service is the client requesting?
- DHCP
- SMTP
- TFTP
- DNS
-
What service is provided by Internet Messenger?
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
-
What characteristic describes antispyware?
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- applications that protect end devices from becoming infected with malicious software
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
-
A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses
Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses
Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
-
Refer to the exhibit. A company uses the address block of 128.107.0.0/16 for its network. What subnet mask would provide the maximum number of equal size subnets while providing enough host addresses for each subnet in the exhibit?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 08 - 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240
-
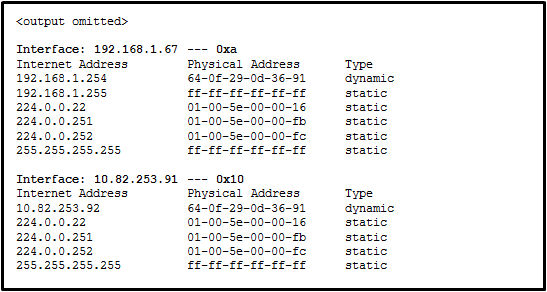
Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol was responsible for building the table that is shown?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 09 - ARP
- DNS
- DHCP
- ICMP
-
Which two traffic types use the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP)? (Choose two.)
- web
- peer to peer
- file transfer
- video
- voice
-
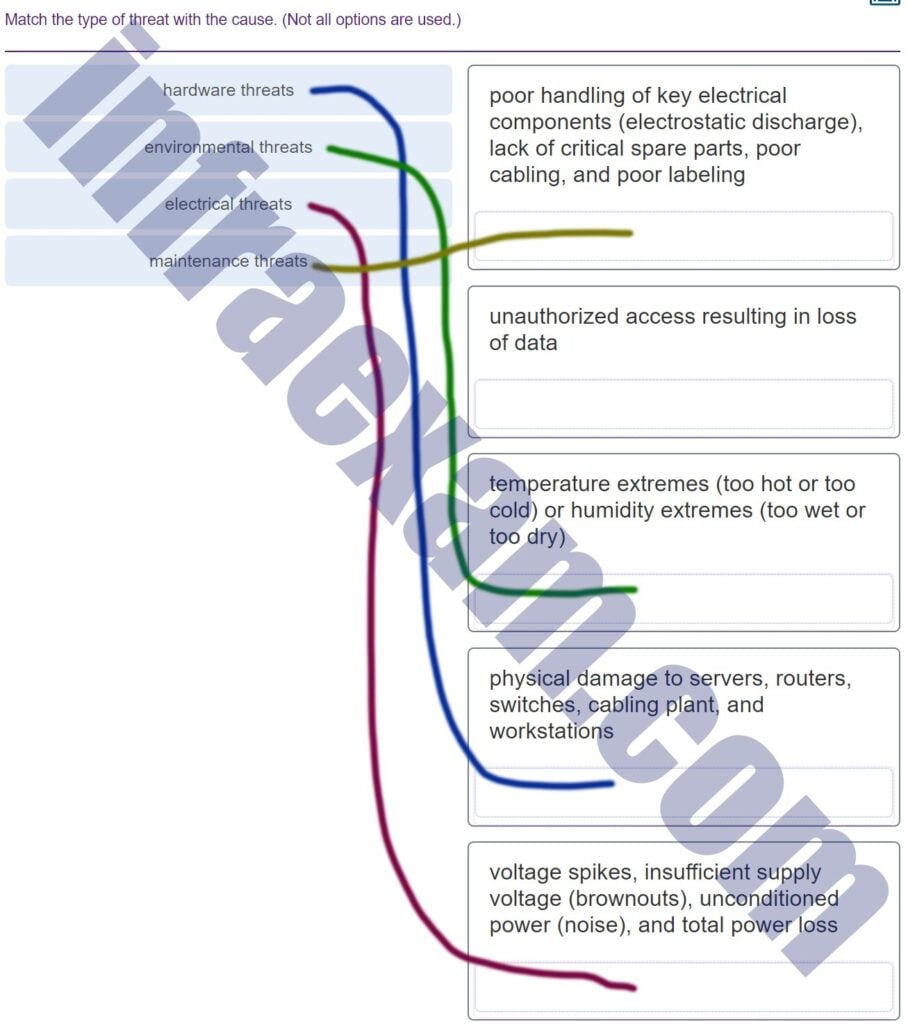
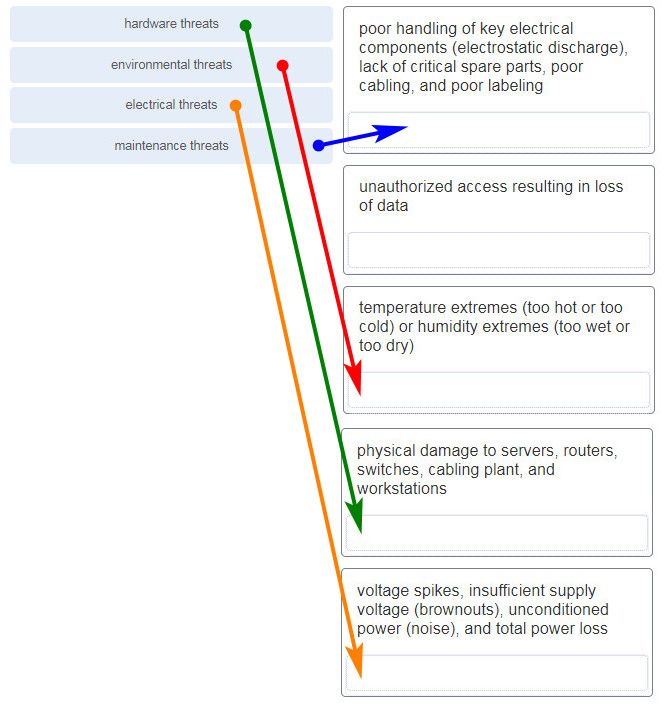
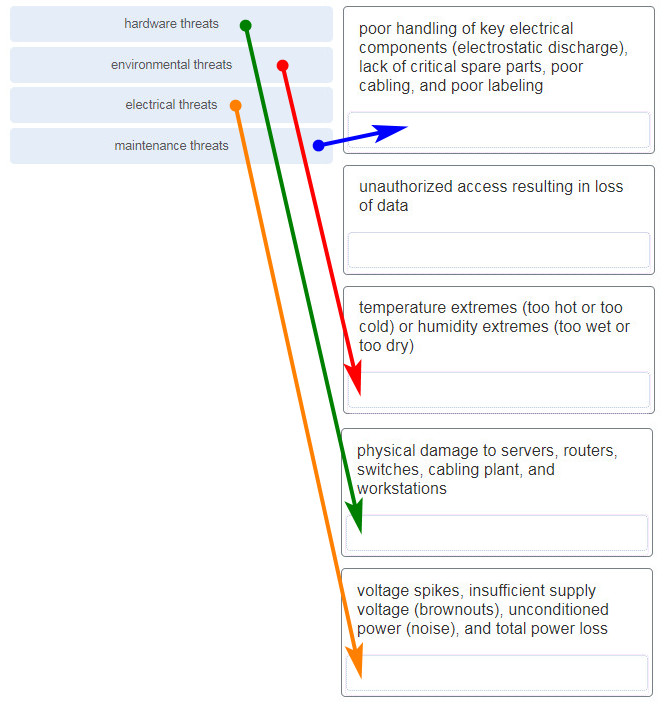
Match the type of threat with the cause. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 006 -
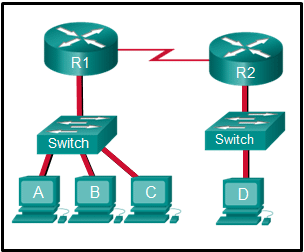
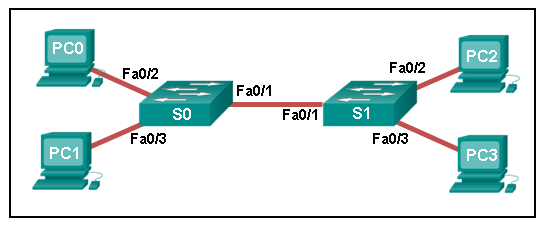
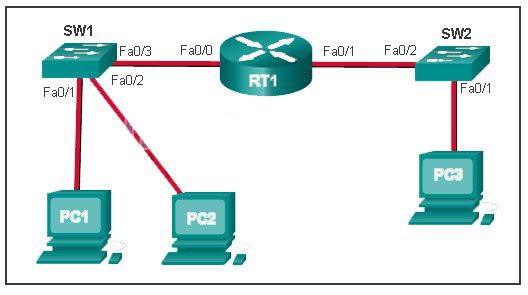
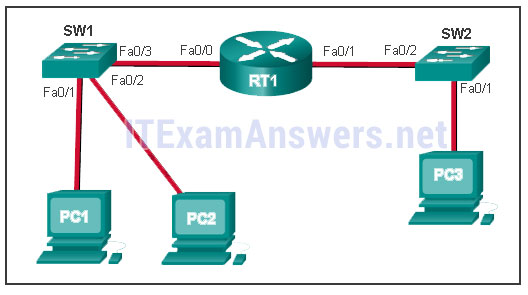
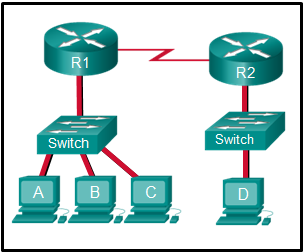
Refer to the exhibit. The switches are in their default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for its default gateway. Which network hosts will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 10 - only hosts A, B, C, and D
- only router R1
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only hosts B and C
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
- only host D
Explanation:
-
Which value, that is contained in an IPv4 header field, is decremented by each router that receives a packet?
- Differentiated Services
- Fragment Offset
- Header Length
- Time-to-Live
-
Refer to the exhibit. The IP address of which device interface should be used as the default gateway setting of host H1?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 11 - R2: S0/0/1
- R1: G0/0
- R2: S0/0/0
- R1: S0/0/0
-
Which two statements describe features of an IPv4 routing table on a router? (Choose two.)
- Directly connected interfaces will have two route source codes in the routing table: C and S .
- The netstat -r command can be used to display the routing table of a router.
- If there are two or more possible routes to the same destination, the route associated with the higher metric value is included in the routing table.
- The routing table lists the MAC addresses of each active interface.
- If a default static route is configured in the router, an entry will be included in the routing table with source code S .
- It stores information about routes derived from the active router interfaces.
-
Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
Explanation:
-
What is the consequence of configuring a router with the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command?
- All router interfaces will be automatically activated.
- Each router interface will generate an IPv6 link-local address.
- The IPv6 enabled router interfaces begin sending ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages.
- It statically creates a global unicast address on this router.
-
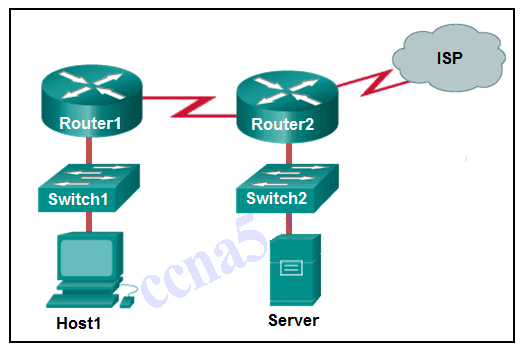
Refer to the exhibit. If Host1 were to transfer a file to the server, what layers of the TCP/IP model would be used?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 12 - only application, Internet, and network access layers
- only application, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
- application, session, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
- only application and Internet layers
- application, transport, Internet, and network access layers
- only Internet and network access layers
Explanation:
-
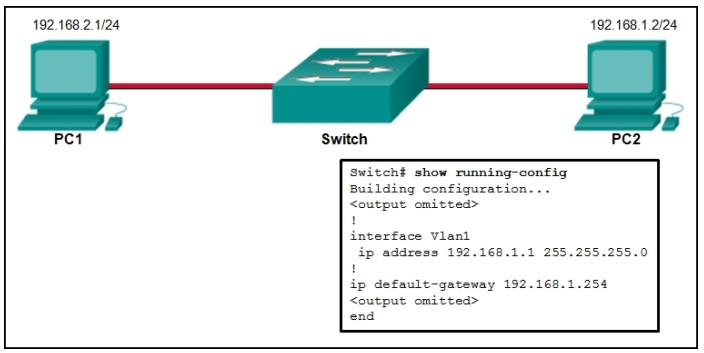
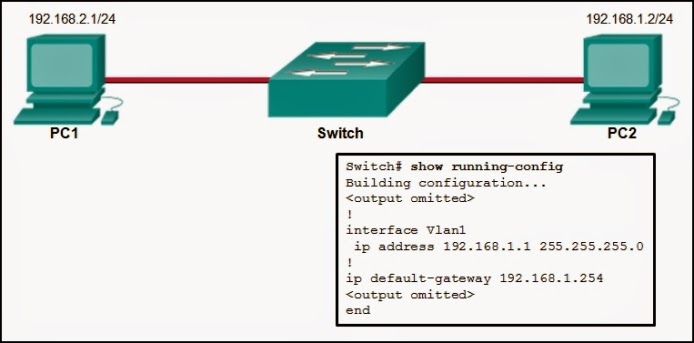
The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
Explanation:
-
What characteristic describes adware?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
-
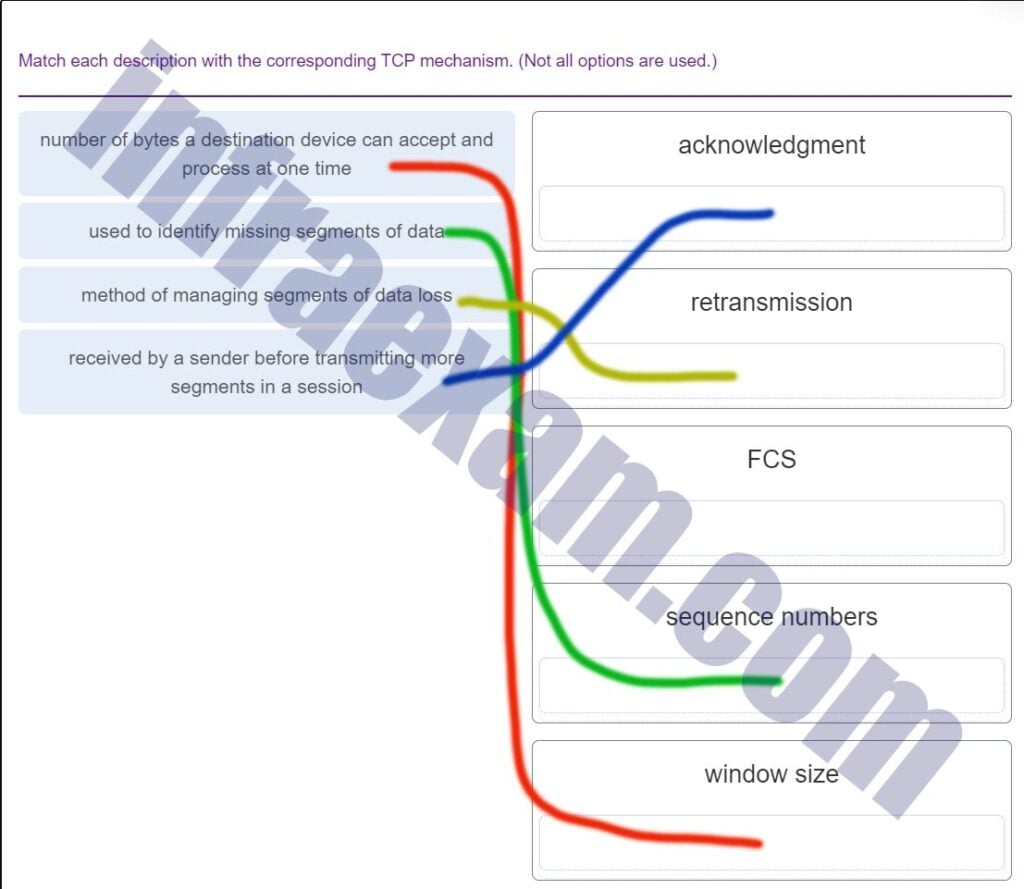
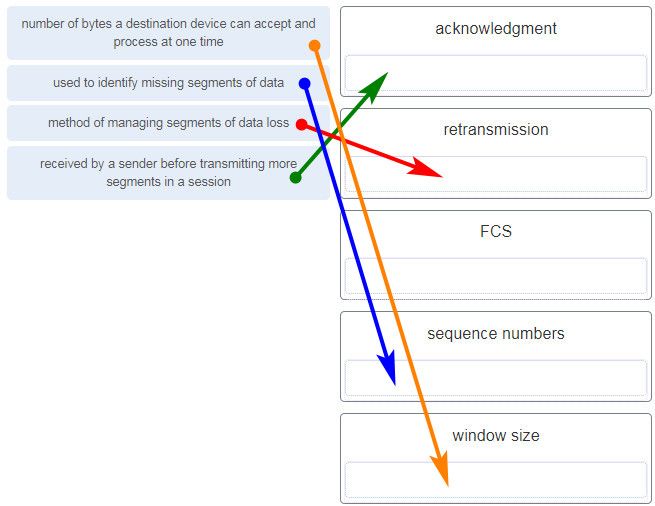
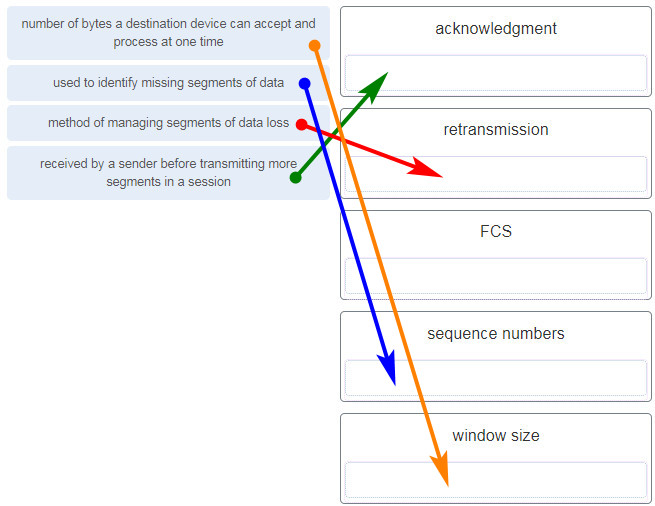
Match each description with the corresponding TCP mechanism. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 007 -
What is the purpose of the TCP sliding window?
- to ensure that segments arrive in order at the destination
- to request that a source decrease the rate at which it transmits data
- to inform a source to retransmit data from a specific point forward
- to end communication when data transmission is complete
-
What technique is used with UTP cable to help protect against signal interference from crosstalk?
- terminating the cable with special grounded connectors
- twisting the wires together into pairs
- wrapping a foil shield around the wire pairs
- encasing the cables within a flexible plastic sheath
Explanation:
To help prevent the effects of crosstalk, UTP cable wires are twisted together into pairs. Twisting the wires together causes the magnetic fields of each wire to cancel each other out.
-
A network technician is researching the use of fiber optic cabling in a new technology center. Which two issues should be considered before implementing fiber optic media? (Choose two.)
- Fiber optic cabling requires different termination and splicing expertise from what copper cabling requires.
- Fiber optic cabling requires specific grounding to be immune to EMI.
- Fiber optic cabling is susceptible to loss of signal due to RFI.
- Fiber optic provides higher data capacity but is more expensive than copper cabling.
- Fiber optic cable is able to withstand rough handling.
-
Users are reporting longer delays in authentication and in accessing network resources during certain time periods of the week. What kind of information should network engineers check to find out if this situation is part of a normal network behavior?
- syslog records and messages
- debug output and packet captures
- network configuration files
- the network performance baseline
-
A user is complaining that an external web page is taking longer than normal to load.The web page does eventually load on the user machine. Which tool should the technician use with administrator privileges in order to locate where the issue is in the network?
- ipconfig /displaydns
- nslookup
- tracert
- ping
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 53. What service is the client requesting?
- SSH
- FTP
- Telnet
- DNS
-
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 issues an ARP request because it needs to send a packet to PC2. In this scenario, what will happen next?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 13 - RT1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/0 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/1 MAC address.
- PC2 will send an ARP reply with its MAC address.
Explanation:
When a network device wants to communicate with another device on the same network, it sends a broadcast ARP request. In this case, the request will contain the IP address of PC2. The destination device (PC2) sends an ARP reply with its MAC address.
-
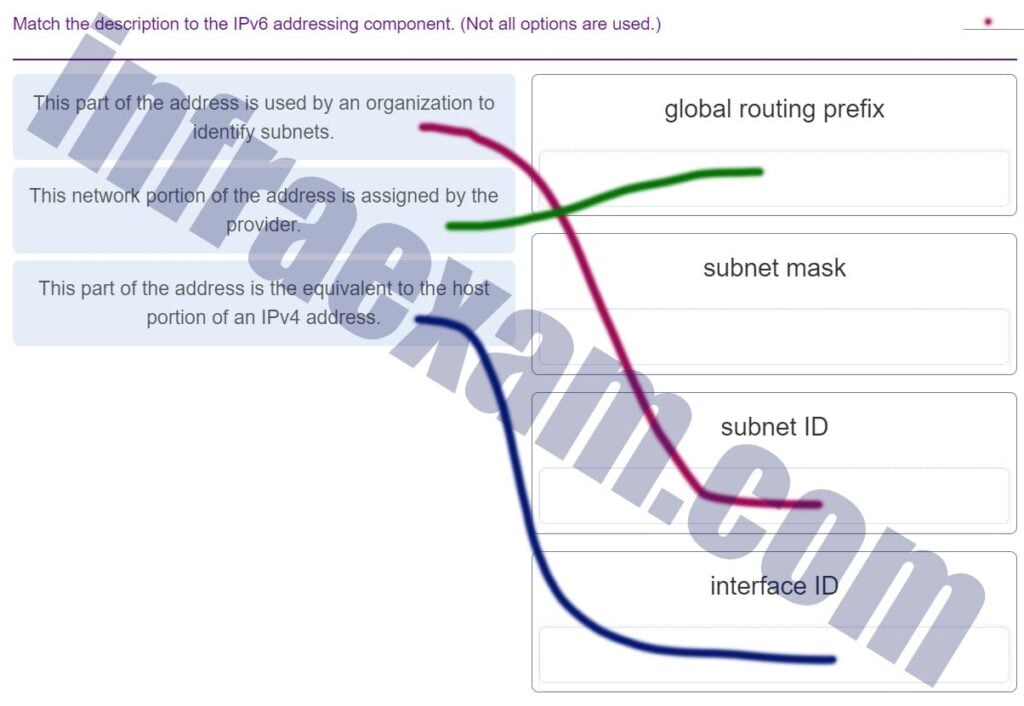
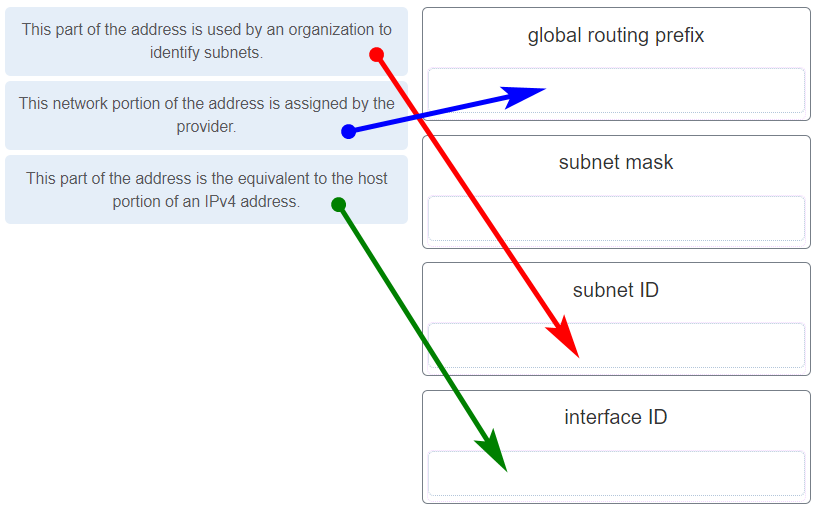
Match the description to the IPv6 addressing component. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 008 -
An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::2. What is the target of this packet?
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link
- all IPv6 DHCP servers
- all IPv6 enabled devices across the network
- all IPv6 configured routers on the local link
-
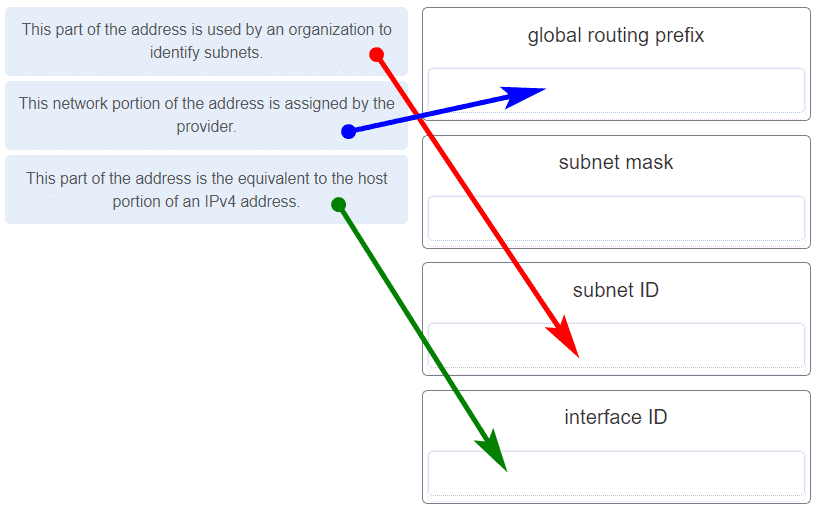
What are the three parts of an IPv6 global unicast address? (Choose three.)
- subnet ID
- global routing prefix
- interface ID
- subnet mask
- broadcast address
-
What is one main characteristic of the data link layer?
- It generates the electrical or optical signals that represent the 1 and 0 on the media.
- It converts a stream of data bits into a predefined code.
- It shields the upper layer protocol from being aware of the physical medium to be used in the communication.
- It accepts Layer 3 packets and decides the path by which to forward the packet to a remote network.
-
Which type of security threat would be responsible if a spreadsheet add-on disables the local software firewall?
- Trojan horse
- brute-force attack
- DoS
- buffer overflow
Explanation:
A Trojan horse is software that does something harmful, but is hidden in legitimate software code. A denial of service (DoS) attack results in interruption of network services to users, network devices, or applications. A brute-force attack commonly involves trying to access a network device. A buffer overflow occurs when a program attempts to store more data in a memory location than it can hold.
-
What service is provided by HTTPS?
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
-
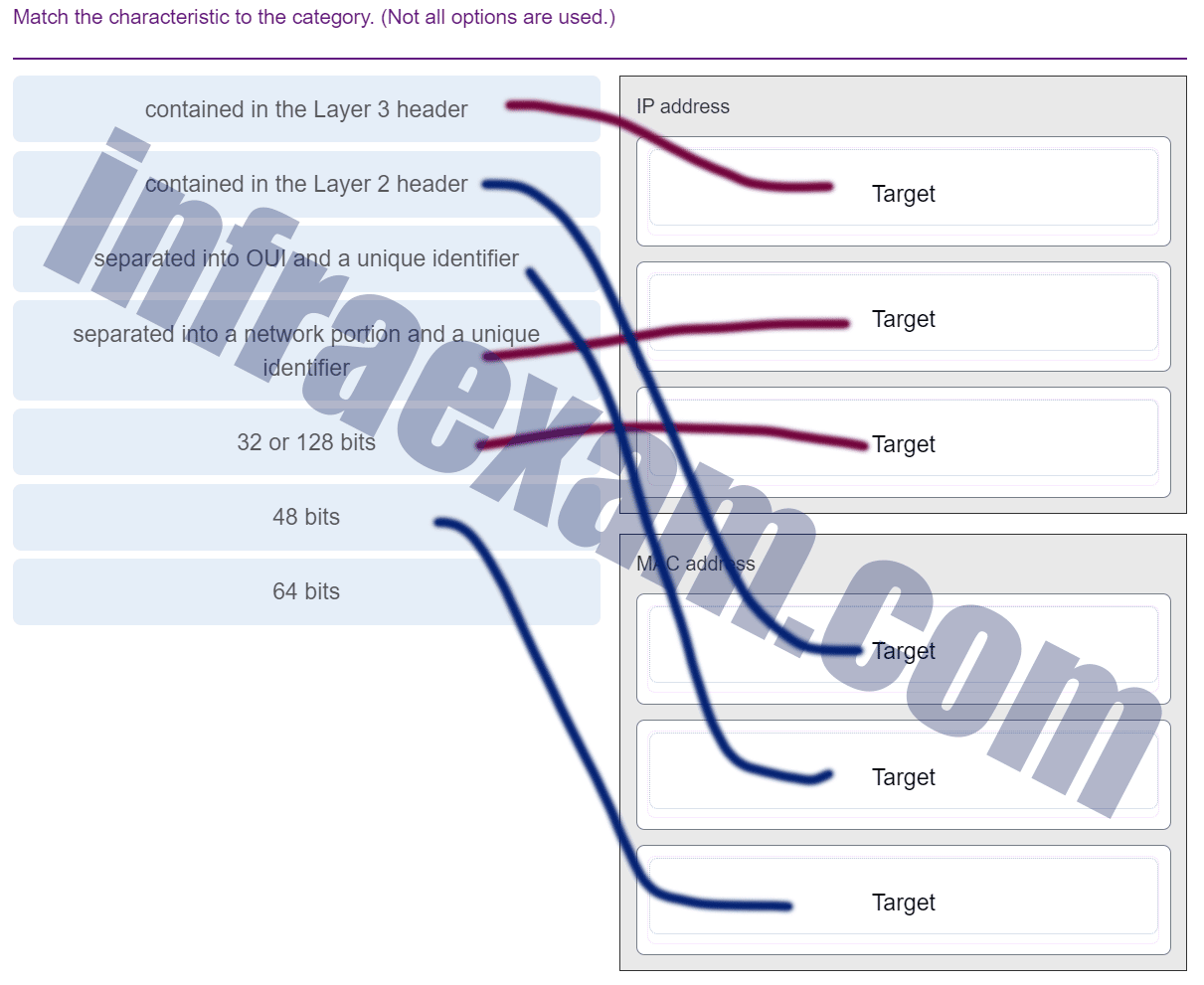
Match the characteristic to the category. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 Final Exam Answers 009 -
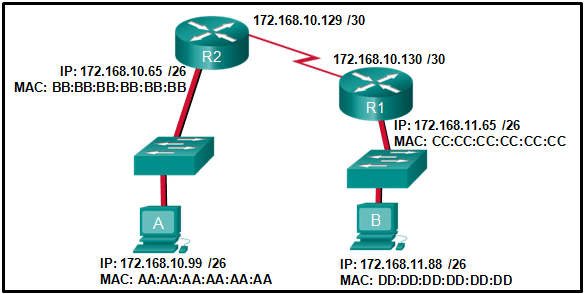
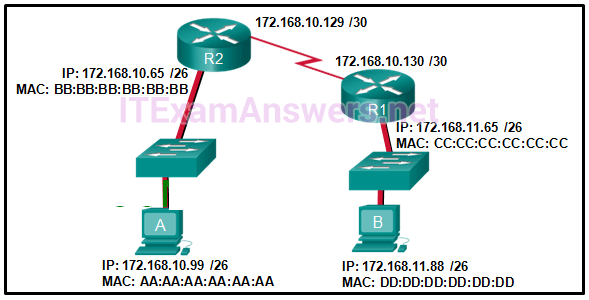
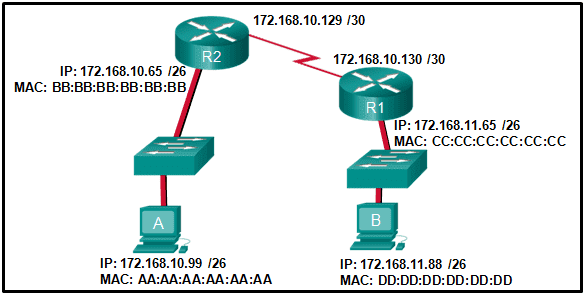
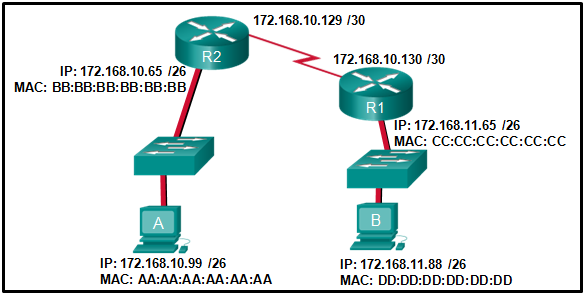
Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 14 - 172.168.10.65
- 172.168.10.99
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
-
Which two statements are correct about MAC and IP addresses during data transmission if NAT is not involved? (Choose two.)
- Destination MAC addresses will never change in a frame that goes across seven routers.
- A packet that has crossed four routers has changed the destination IP address four times.
- Every time a frame is encapsulated with a new destination MAC address, a new destination IP address is needed.
- Destination and source MAC addresses have local significance and change every time a frame goes from one LAN to another.
- Destination IP addresses in a packet header remain constant along the entire path to a target host.
-
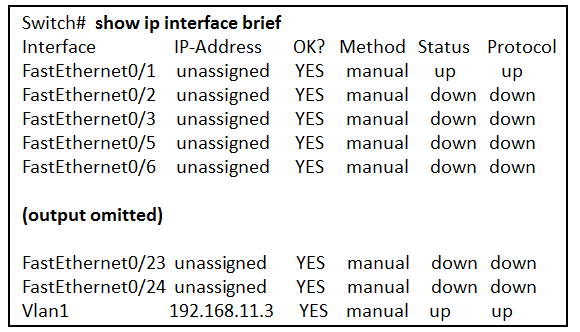
Refer to the exhibit. What three facts can be determined from the viewable output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose three.)
CCNA1 v7 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 15 - Two devices are attached to the switch.
- The default SVI has been configured.
- The switch can be remotely managed.
- Two physical interfaces have been configured.
- Passwords have been configured on the switch.
- One device is attached to a physical interface.
-
A user is executing a tracert to a remote device. At what point would a router, which is in the path to the destination device, stop forwarding the packet?
- when the values of both the Echo Request and Echo Reply messages reach zero
- when the value in the TTL field reaches zero
- when the router receives an ICMP Time Exceeded message
- when the host responds with an ICMP Echo Reply message
- when the RTT value reaches zero
Explanation:
When a router receives a traceroute packet, the value in the TTL field is decremented by 1. When the value in the field reaches zero, the receiving router will not forward the packet, and will send an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source.
-
What are two functions that are provided by the network layer? (Choose two.)
- carrying data between processes that are running on source and destination hosts
- directing data packets to destination hosts on other networks
- providing dedicated end-to-end connections
- placing data on the network medium
- providing end devices with a unique network identifier
-
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 61 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.128
-
What characteristic describes spyware?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
-
What are three commonly followed standards for constructing and installing cabling? (Choose three.)
- pinouts
- tensile strength of plastic insulator
- cable lengths
- connector types
- cost per meter (foot)
- connector color
-
Which connector is used with twisted-pair cabling in an Ethernet LAN?
-
What attribute of a NIC would place it at the data link layer of the OSI model?
- attached Ethernet cable
- TCP/IP protocol stack
- IP address
- RJ-45 port
- MAC address
-
A network administrator needs to keep the user ID, password, and session contents private when establishing remote CLI connectivity with a switch to manage it. Which access method should be chosen?
- AUX
- Telnet
- SSH
- Console
-
A user sends an HTTP request to a web server on a remote network. During encapsulation for this request, what information is added to the address field of a frame to indicate the destination?
- the network domain of the destination host
- the MAC address of the default gateway
- the IP address of the default gateway
- the MAC address of the destination host
-
Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- route print
- show ip route
- netstat -r
- netstat -s
- tracert
Answers Explanation & Hints:
On a Windows host, the route print or netstat -r commands can be used to display the host routing table. Both commands generate the same output. On a router, the show ip route command is used to display the routing table. The netstat –s command is used to display per-protocol statistics. The tracert command is used to display the path that a packet travels to its destination.
-
Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 001 -
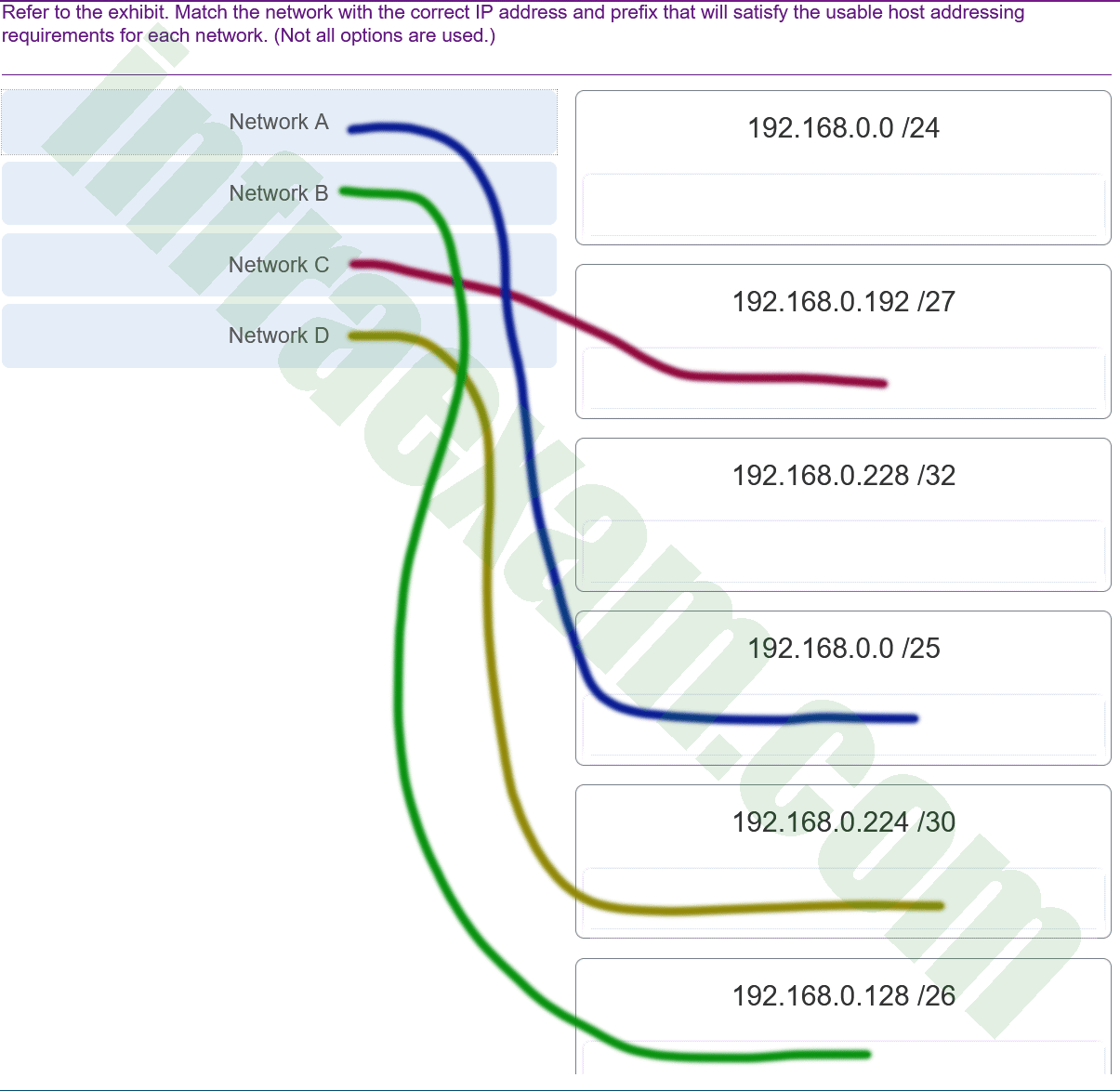
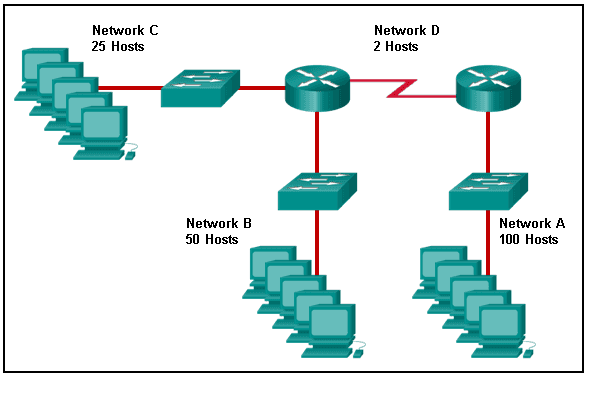
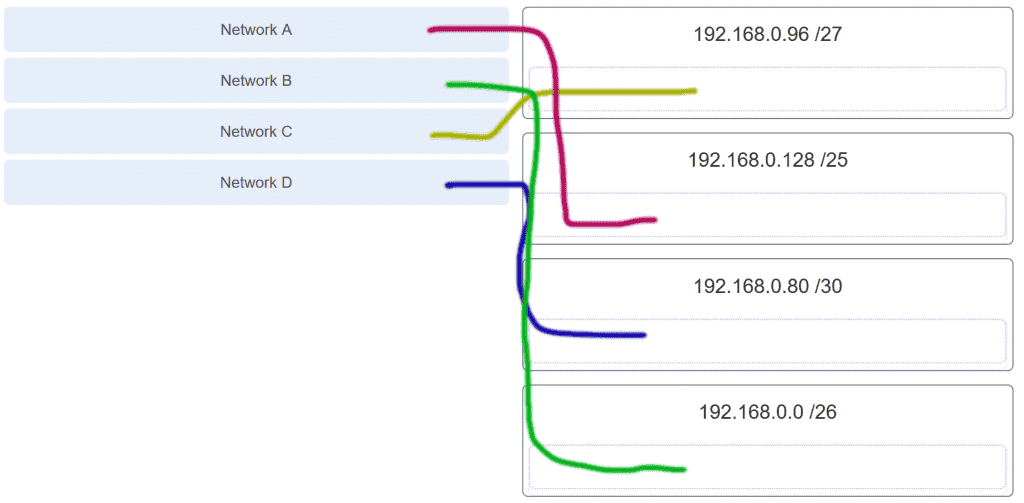
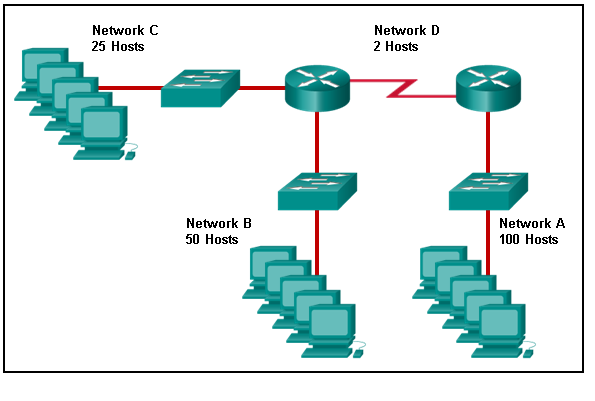
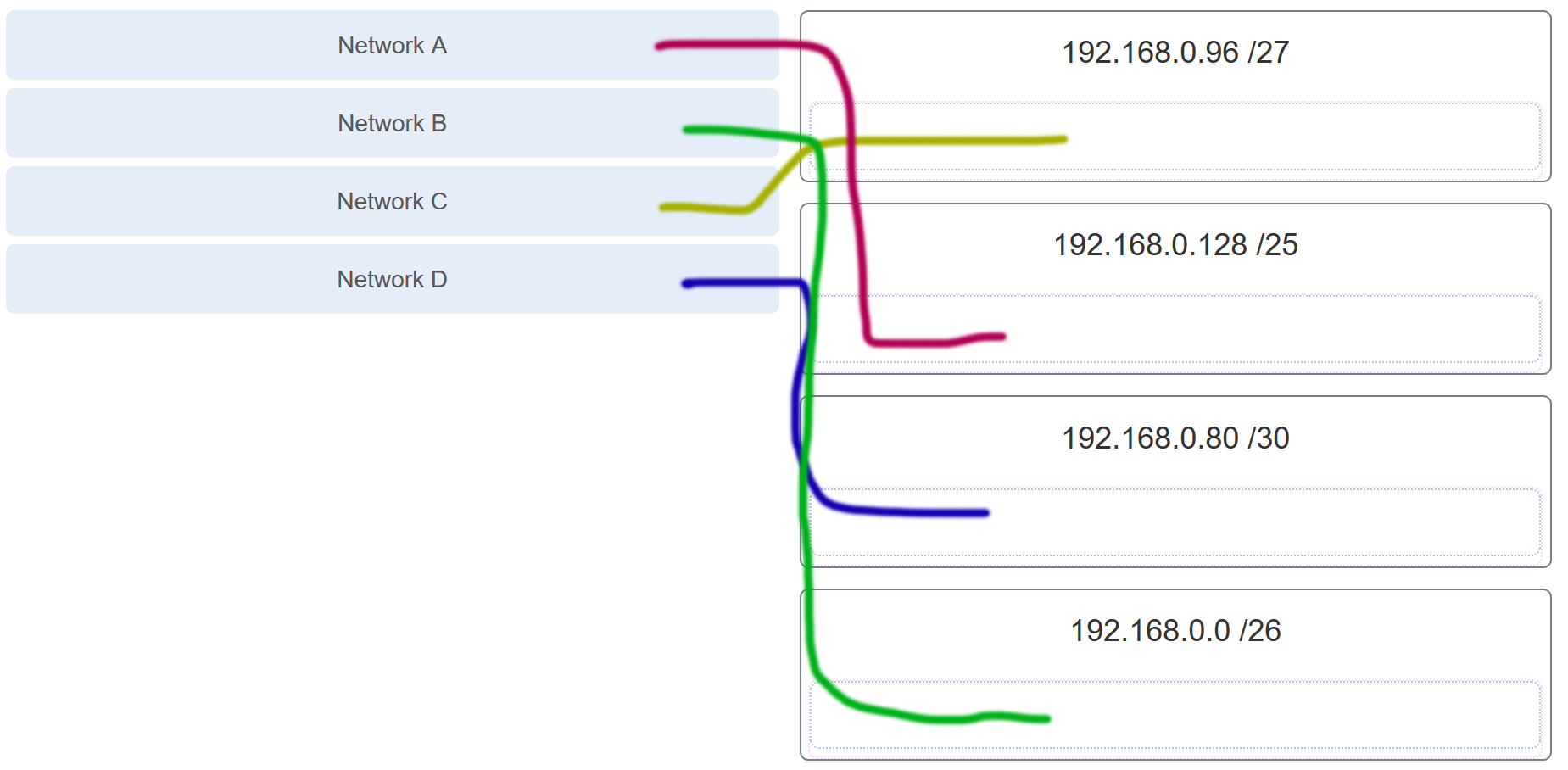
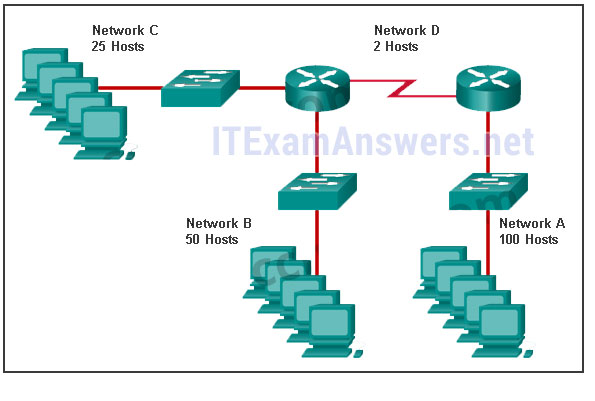
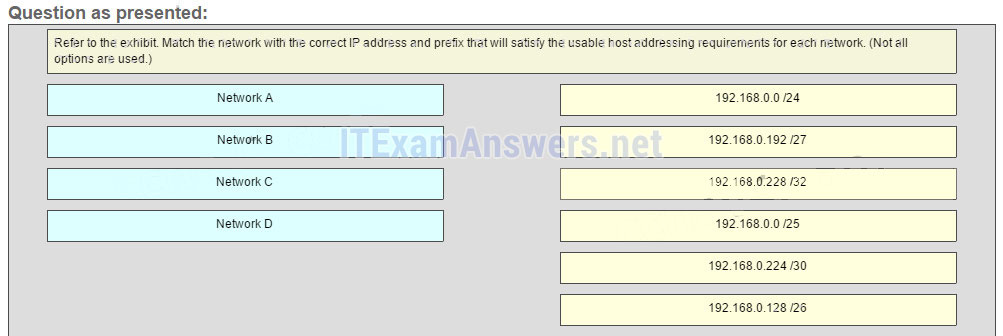
Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 01 CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 002 Explanation:
Network A needs to use 192.168.0.0 /25 which yields 128 host addresses.
Network B needs to use 192.168.0.128 /26 which yields 64 host addresses.
Network C needs to use 192.168.0.192 /27 which yields 32 host addresses.
Network D needs to use 192.168.0.224 /30 which yields 4 host addresses. -
A technician with a PC is using multiple applications while connected to the Internet. How is the PC able to keep track of the data flow between multiple application sessions and have each application receive the correct packet flows?
- The data flow is being tracked based on the source port number that is used by each application.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the destination IP address that is used by the PC of the technician.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the source IP address that is used by the PC of the technician.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the destination MAC address of the technician PC.
Explanation:
The source port number of an application is randomly generated and used to individually keep track of each session connecting out to the Internet. Each application will use a unique source port number to provide simultaneous communication from multiple applications through the Internet.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 80. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- HTTP
- DHCP
- SMTP
-
A user is attempting to access http://www.cisco.com/ without success. Which two configuration values must be set on the host to allow this access? (Choose two.)
- source port number
- HTTP server
- source MAC address
- DNS server
- default gateway
-
What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA
- token passing
-
What are two ICMPv6 messages that are not present in ICMP for IPv4? (Choose two.)
- Router Advertisement
- Destination Unreachable
- Neighbor Solicitation
- Route Redirection
- Host Confirmation
- Time Exceeded
-
An organization is assigned an IPv6 address block of 2001:db8:0:ca00::/56. How many subnets can be created without using bits in the interface ID space?
- 4096
- 256
- 512
- 1024
-
What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
-
A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in the ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
- It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
- It will send the frame and use the device MAC address as the destination.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.
- It will send an ARP request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
-
What characteristic describes a virus?
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- malicious software or code running on an end device
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
-
A disgruntled employee is using some free wireless networking tools to determine information about the enterprise wireless networks. This person is planning on using this information to hack the wireless network. What type of attack is this?
- access
- DoS
- Trojan horse
- reconnaissance
-
What service is provided by POP3?
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Retrieves email from the server by downloading the email to the local mail application of the client.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
-
What command can be used on a Windows PC to see the IP configuration of that computer?
- ipconfig
- show interfaces
- ping
- show ip interface brief
-
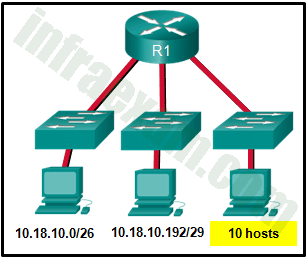
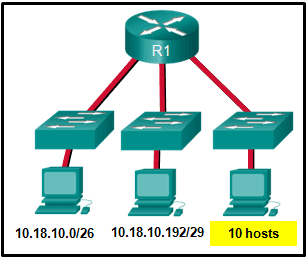
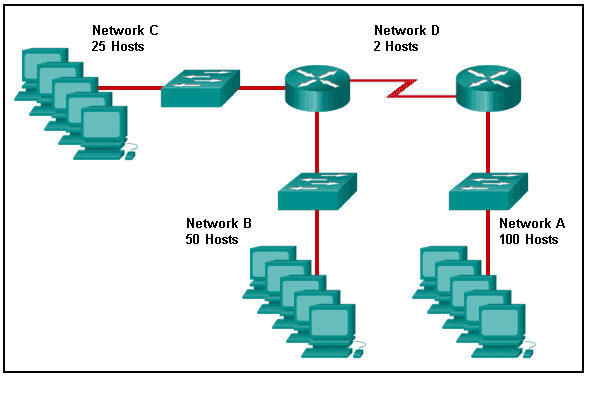
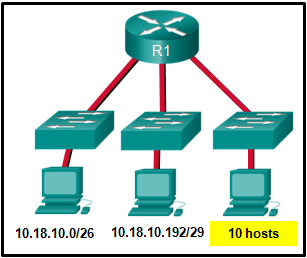
Refer to the exhibit. Which two network addresses can be assigned to the network containing 10 hosts? Your answers should waste the fewest addresses, not reuse addresses that are already assigned, and stay within the 10.18.10.0/24 range of addresses. (Choose two.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 02 - 10.18.10.224/27
- 10.18.10.208/28
- 10.18.10.200/27
- 10.18.10.200/28
- 10.18.10.224/28
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Addresses 10.18.10.0 through 10.18.10.63 are taken for the leftmost network. Addresses 192 through 199 are used by the center network. Because 4 host bits are needed to accommodate 10 hosts, a /28 mask is needed. 10.18.10.200/28 is not a valid network number. Two subnets that can be used are 10.18.10.208/28 and 10.18.10.224/28.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 110. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- DHCP
- POP3
- SMTP
-
Which layer of the TCP/IP model provides a route to forward messages through an internetwork?
- transport
- application
- network access
- internet
-
What characteristic describes identity theft?
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- software that identifies fast-spreading threats
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
-
What two security solutions are most likely to be used only in a corporate environment? (Choose two.)
- intrusion prevention systems
- antivirus software
- antispyware
- strong passwords
- virtual private networks
-
What service is provided by DNS?
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
-
Which wireless technology has low-power and low-data rate requirements making it popular in IoT environments?
- Bluetooth
- Zigbee
- WiMAX
- Wi-Fi
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Zigbee is a specification used for low-data rate, low-power communications. It is intended for applications that require short-range, low data-rates and long battery life. Zigbee is typically used for industrial and Internet of Things (IoT) environments such as wireless light switches and medical device data collection.
-
What characteristic describes a VPN?
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that identifies fast-spreading threats
-
A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 4 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.224
-
During the process of forwarding traffic, what will the router do immediately after matching the destination IP address to a network on a directly connected routing table entry?
- switch the packet to the directly connected interface
- discard the traffic after consulting the route table
- look up the next-hop address for the packet
- analyze the destination IP address
-
What service is provided by BOOTP?
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- Legacy application that enables a diskless workstation to discover its own IP address and find a BOOTP server on the network.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 21. What service is the client requesting?
- DHCP
- FTP
- TFTP
- DNS
-
Match each description to its corresponding term. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 003 -
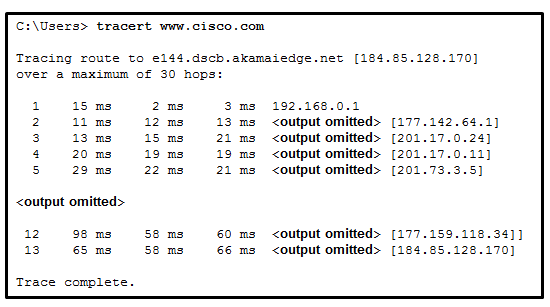
A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- netstat
- nslookup
- ipconfig
Explanation:
-
What two ICMPv6 message types must be permitted through IPv6 access control lists to allow resolution of Layer 3 addresses to Layer 2 MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
- echo requests
- router solicitations
- router advertisements
- neighbor advertisements
- echo replies
- neighbor solicitations
-
Refer to the exhibit. The switches have a default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for the default gateway. Which network devices will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 03 - only hosts A, B, C, and D
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only host D
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
- only router R1
- only hosts B and C
-
Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
- implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
- applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
-
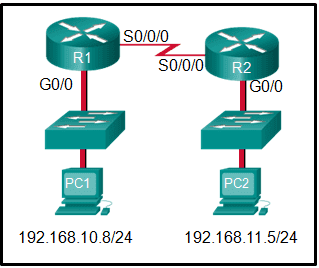
Two pings were issued from a host on a local network. The first ping was issued to the IP address of the default gateway of the host and it failed. The second ping was issued to the IP address of a host outside the local network and it was successful. What is a possible cause for the failed ping?
- The default gateway is not operational.
- The default gateway device is configured with the wrong IP address.
- The TCP/IP stack on the default gateway is not working properly.
- Security rules are applied to the default gateway device, preventing it from processing ping requests.
-
What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
-
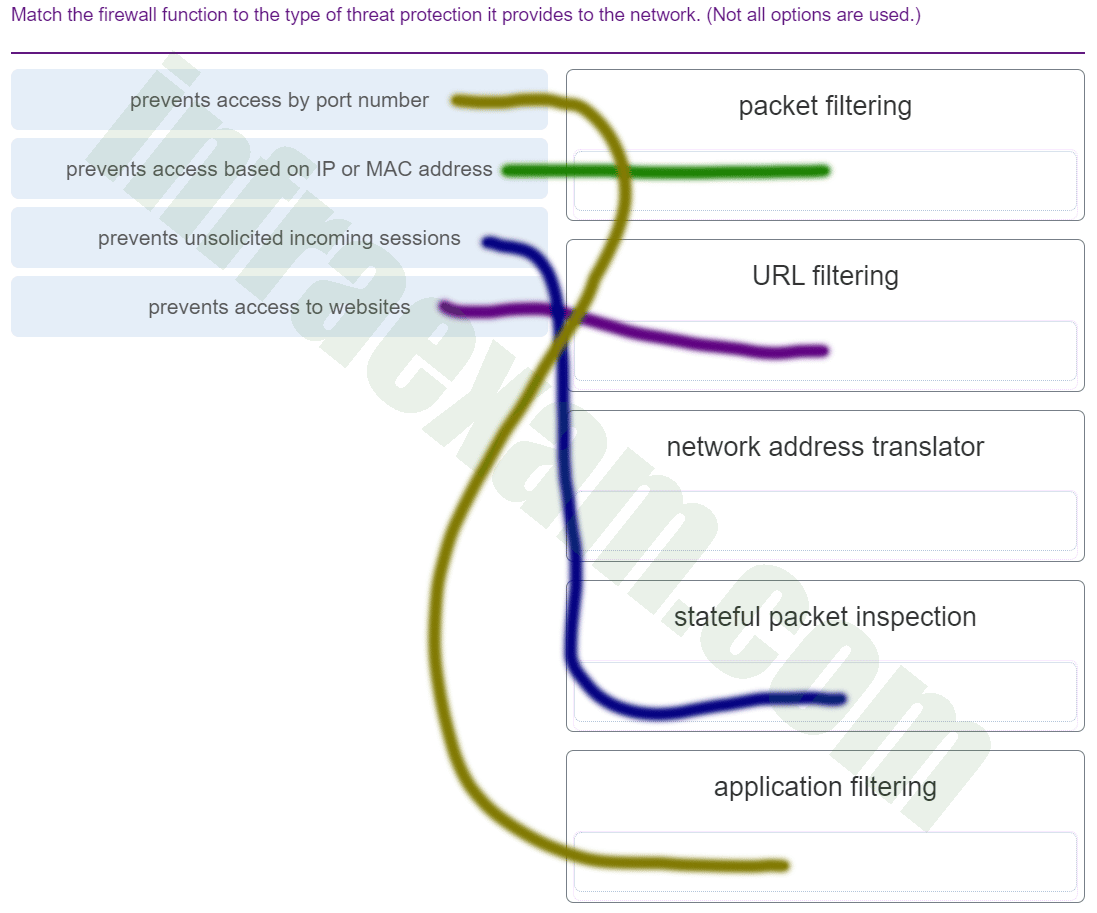
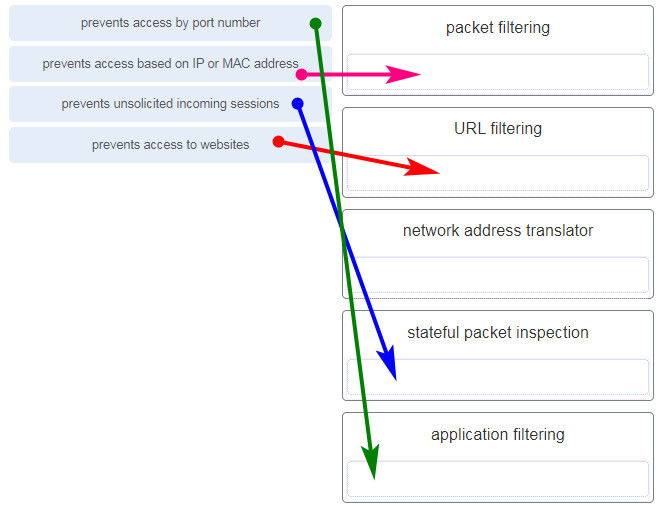
Match the firewall function to the type of threat protection it provides to the network. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA1 v7 & v7.02 – ITNv7 – Final Exam Answers 004 Answers Explanation & Hints:
Application filters prevent access based on Layer 4 port numbers.
Packet filters prevent access based on IP or MAC address.
URL filters prevent access to web site URLs or content.
Stateful packet inspection prevents unsolicited incoming sessions.
Network address translators translate internal IP addresses to to outside IP addresses and do not prevent network attacks. -
What service is provided by SMTP?
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Allows clients to send email to a mail server and the servers to send email to other servers.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 22. What service is the client requesting?
- SSH
- DNS
- DHCP
- TFTP
-
Recommend
4.4
43
votes
Article Rating
New Version: Final Exam Answers v6.0
- What is a characteristic of a fault tolerant network?
- a network that protects confidential information from unauthorized access
- a network that can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service delivered to existing users
- a network that supports a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users
- a network that recovers quickly when a failure occurs and depends on redundancy to limit the impact of a failure*
- Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page*
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.*
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
- What is the function of the shell in an OS?
- It interacts with the device hardware.
- It interfaces between the users and the kernel.*
- It provides dedicated firewall services.
- It provides the intrusion protection services for the device.
- Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco switch?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection*
- A network technician is attempting to configure an interface by entering the following command: SanJose(config)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0. The command is rejected by the device. What is the reason for this?
- The command is being entered from the wrong mode of operation.*
- The command syntax is wrong.
- The subnet mask information is incorrect.
- The interface is shutdown and must be enabled before the switch will accept the IP address.
- An administrator uses the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination on a switch after issuing the ping command. What is the purpose of using these keystrokes?
- to restart the ping process
- to interrupt the ping process*
- to exit to a different configuration mode
- to allow the user to complete the command
- Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses a console connection to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?
- letmein
- secretin
- linevtyin
- lineconin*
- On which switch interface would an administrator configure an IP address so that the switch can be managed remotely?
- FastEthernet0/1
- VLAN 1*
- vty 0
- console 0
- What protocol is responsible for controlling the size of segments and the rate at which segments are exchanged between a web client and a web server?
- TCP*
- IP
- HTTP
- Ethernet
- What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- A company can monopolize the market.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.*
- What are two benefits of using a layered network model? (Choose two.)
- It assists in protocol design. *
- It speeds up packet delivery.
- It prevents designers from creating their own model.
- It prevents technology in one layer from affecting other layers.*
- It ensures a device at one layer can function at the next higher layer.
- Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- data link
- network*
- physical
- session
- transport*
- Which name is assigned to the transport layer PDU?
- bits
- data
- frame
- packet
- segment*
- A network engineer is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical database application. The engineer notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network*
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network*
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
- A network administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues on a server. Using a tester, the administrator notices that the signals generated by the server NIC are distorted and not usable. In which layer of the OSI model is the error categorized?
- presentation layer
- network layer
- physical layer*
- data link layer
- Which type of UTP cable is used to connect a PC to a switch port?
- console
- rollover
- crossover
- straight-through**
- A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network*
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network *
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
- What is a characteristic of UTP cabling?
- cancellation*
- cladding
- immunity to electrical hazards
- woven copper braid or metallic foil
- What are two characteristics of fiber-optic cable? (Choose two.)
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.*
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding, and twisting to protect data.
- It typically contains 4 pairs of fiber-optic wires.
- It is more expensive than UTP cabling is.*
- What is a characteristic of the LLC sublayer?
- It provides the logical addressing required that identifies the device.
- It provides delimitation of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium.
- It places information in the frame allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to use the same network interface and media.*
- It defines software processes that provide services to the physical layer.
- A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies for connecting remote sites to a headquarters building. Which topology provides high availability and connects some, but not all, remote sites?
- mesh
- partial mesh*
- hub and spoke
- point-to-point
- What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA*
- token passing
- What are the three primary functions provided by Layer 2 data encapsulation? (Choose three.)
- error correction through a collision detection method
- session control using port numbers
- data link layer addressing*
- placement and removal of frames from the media
- detection of errors through CRC calculations *
- delimiting groups of bits into frames*
- conversion of bits into data signals
- What will a host on an Ethernet network do if it receives a frame with a destination MAC address that does not match its own MAC address?
- It will discard the frame.*
- It will forward the frame to the next host.
- It will remove the frame from the media.
- It will strip off the data-link frame to check the destination IP address.
- What are two examples of the cut-through switching method? (Choose two.)
- store-and-forward switching
- fast-forward switching*
- CRC switching
- fragment-free switching*
- QOS switching
- What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table*
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address*
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
- Which frame forwarding method receives the entire frame and performs a CRC check to detect errors before forwarding the frame?
- cut-through switching
- store-and-forward switching*
- fragment-free switching
- fast-forward switching
- Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- 172.168.10.99
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- 172.168.10.65
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB*
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
- What addresses are mapped by ARP?
- destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address*
- destination IPv4 address to the source MAC address
- destination IPv4 address to the destination host name
- destination MAC address to the source IPv4 address
- What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
- source and destination MAC
- source and destination application protocol
- source and destination port number
- source and destination IP address*
- What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination *
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer*
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
- Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?
- subnet mask
- DNS address
- host IP address
- default gateway address*
- Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
- to identify the broadcast address of the destination network
- to identify the host address of the destination host
- to identify faulty frames
- to identify the network address of the destination network*
- What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed *
- to store the startup configuration file*
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
Refer to the exhibit. What will be the result of entering this configuration the next time a network administrator connects a console cable to the router and no additional commands have been entered?- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco123.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco234.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco789.
- The administrator will be presented with the R1> prompt.*
- What is the dotted decimal representation of the IPv4 address 11001011.00000000.01110001.11010011?
- 192.0.2.199
- 198.51.100.201
- 203.0.113.211*
- 209.165.201.223
- What are three characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose three.)
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts. *
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information. *
- Routers will not forward multicast addresses in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.*
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses.
- What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8*
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 127.16.0.0/12
- 172.16.0.0/12*
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 192.168.0.0/16*
- What purpose does NAT64 serve in IPv6?
- It converts IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.*
- It translates private IPv6 addresses into public IPv6 addresses.
- It enables companies to use IPv6 unique local addresses in the network.
- It converts regular IPv6 addresses into 64-bit addresses that can be used on the Internet.
- It converts the 48-bit MAC address into a 64-bit host address that can be used for automatic host addressing.
- What is the most compressed representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001?
- 2001:0:abcd::1
- 2001:0:0:abcd::1*
- 2001::abcd::1
- 2001:0000:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd:0:1
- Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FEC0::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FE80::/10*
- FF00::/8
- Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17*
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117*
- 192.15.301.240
- 64.104.78.227 *
- Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
- There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.*
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
- There are 4 hops b**etween this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.*
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
- This host does not have a default gateway configured.
- What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local*
- multicast
- global unicast
- How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
- 254
- 190
- 192
- 62*
- 64
- A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128*
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses
Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses
Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240*
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
- How many hosts are addressable on a network that has a mask of 255.255.255.248?
- 2
- 6*
- 8
- 14
- 16
- 254
- Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26*
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
- What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192*
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering*
- 3-way handshake
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- use of checksum*
- Why are port numbers included in the TCP header of a segment?
- to indicate the correct router interface that should be used to forward a segment
- to identify which switch ports should receive or forward the segment
- to determine which Layer 3 protocol should be used to encapsulate the data
- to enable a receiving host to forward the data to the appropriate application*
- to allow the receiving host to assemble the packet in the proper order
- Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address of 192.168.10.0/24 that has been assigned to a high school building. The largest network in this building has 100 devices. If 192.168.10.0 is the network number for the largest network, what would be the network number for the next largest network, which has 40 devices?
- 192.168.10.0
- 192.168.10.128*
- 192.168.10.192
- 192.168.10.224
- 192.168.10.240
- Which statement is true about variable-length subnet masking?
- Each subnet is the same size.
- The size of each subnet may be different, depending on requirements.*
- Subnets may only be subnetted one additional time.
- Bits are returned, rather than borrowed, to create additional subnets.
- In what two situations would UDP be the preferred transport protocol over TCP? (Choose two.)
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed*
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data*
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
- What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
- timing and synchronization
- destination and source port numbers*
- destination and source physical addresses
- destination and source logical network addresses
- What is the TCP mechanism used in congestion avoidance?
- three-way handshake
- socket pair
- two-way handshake
- sliding window*
- Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.*
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
- A user opens three browsers on the same PC to access www.cisco.com to search for certification course information. The Cisco web server sends a datagram as a reply to the request from one of the web browsers. Which information is used by the TCP/IP protocol stack in the PC to identify which of the three web browsers should receive the reply?
- the destination IP address
- the destination port number*
- the source IP address
- the source port number
- What are two ways that TCP uses the sequence numbers in a segment? (Choose two.)
- to identify missing segments at the destination *
- to reassemble the segments at the remote location*
- to specify the order in which the segments travel from source to destination
- to limit the number of segments that can be sent out of an interface at one time
- to determine if the packet changed during transit
- Which two tasks are functions of the presentation layer? (Choose two.)
- compression*
- addressing
- encryption*
- session control
- authentication
- Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
- UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.*
- UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
- UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection. *
- UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.*
- UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
- UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
- What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
- wireless networking
- social networking without the Internet
- network printing using a print server
- resource sharing without a dedicated server*
- A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- ipconfig
- netstat
- nslookup*
- Which domain name would be an example of a top-level domain?
- www.cisco.com
- cisco.com
- .com*
- root.cisco.com
- A PC obtains its IP address from a DHCP server. If the PC is taken off the network for repair, what happens to the IP address configuration?
- The configuration is permanent and nothing changes.
- The address lease is automatically renewed until the PC is returned.
- The address is returned to the pool for reuse when the lease expires.*
- The configuration is held by the server to be reissued when the PC is returned.
- When planning for network growth, where in the network should packet captures take place to assess network traffic?
- on as many different network segments as possible*
- only at the edge of the network
- between hosts and the default gateway
- only on the busiest network segment
- A wireless host needs to request an IP address. What protocol would be used to process the request?
- FTP
- HTTP
- DHCP*
- ICMP
- SNMP
- Which example of malicious code would be classified as a Trojan horse?
- malware that was written to look like a video game*
- malware that requires manual user intervention to spread between systems
- malware that attaches itself to a legitimate program and spreads to other programs when launched
- malware that can automatically spread from one system to another by exploiting a vulnerability in the target
- When applied to a router, which command would help mitigate brute-force password attacks against the router?
- exec-timeout 30
- service password-encryption
- banner motd $Max failed logins = 5$
- login block-for 60 attempts 5 within 60*
- A network technician suspects that a particular network connection between two Cisco switches is having a duplex mismatch. Which command would the technician use to see the Layer 1 and Layer 2 details of a switch port?
- show mac-address-table
- show ip interface brief
- show interfaces*
- show running-config
- Where are Cisco IOS debug output messages sent by default?
- Syslog server
- console line*
- memory buffers
- vty lines
- Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (not all options are used.)
- Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
- Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is testing connectivity to a remote device with the IP address 10.1.1.1. What does the output of this command indicate?
- Connectivity to the remote device was successful.
- A router along the path did not have a route to the destination.*
- A ping packet is being blocked by a security device along the path.
- The connection timed out while waiting for a reply from the remote device.
- A user is unable to reach the web site when typing http://www.cisco.com in a web browser, but can reach the same site by typing http://72.163.4.161. What is the issue?
- default gateway
- DHCP
- TCP/IP protocol stack
- DNS *
- A company is expanding its business to other countries. All branch offices must remain connected to corporate headquarters at all times. Which network technology is required to support this requirement?
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN*
- WLAN
- A home user is looking for an ISP connection that provides high speed digital transmission over regular phone lines. What ISP connection type should be used?
- DSL*
- dial-up
- satellite
- cell modem
- cable modem
- How does quality of service help a network support a wide range of applications and services?
- by limiting the impact of a network failure
- by allowing quick recovery from network failures
- by providing mechanisms to manage congested network traffic*
- by providing the ability for the network to grow to accommodate new users
- What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface*
- After making configuration changes on a Cisco switch, a network administrator issues a copy running-config startup-config command. What is the result of issuing this command?
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.*
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
- Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator has already logged into a Telnet session on the switch, which password is needed to access privileged EXEC mode?
- letmein
- secretin*
- lineconin
- linevtyin
- Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
- Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco network device?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection*
- What function does pressing the Tab key have when entering a command in IOS?
- It aborts the current command and returns to configuration mode.
- It exits configuration mode and returns to user EXEC mode.
- It moves the cursor to the beginning of the next line.
- It completes the remainder of a partially typed word in a command.*
- What layer is responsible for routing messages through an internetwork in the TCP/IP model?
- internet*
- transport
- network access
- session
- Which statement accurately describes a TCP/IP encapsulation process when a PC is sending data to the network?
- Data is sent from the internet layer to the network access layer.
- Packets are sent from the network access layer to the transport layer.
- Segments are sent from the transport layer to the internet layer.*
- Frames are sent from the network access layer to the internet layer.
- What unique address is embedded in an Ethernet NIC and used for communication on an Ethernet network?
- host address
- IP address
- MAC address*
- network address
- k layer
- Which procedure is used to reduce the effect of crosstalk in copper cables?
- requiring proper grounding connections
- twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together*
- wrapping the bundle of wires with metallic shielding
- designing a cable infrastructure to avoid crosstalk interference
- avoiding sharp bends during installation
- During the encapsulation process, what occurs at the data link layer for a PC connected to an Ethernet network?
- An IP address is added.
- The logical address is added.
- The physical address is added.*
- The process port number is added.
- What are two characteristics of Ethernet MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
- They are globally unique.*
- They are routable on the Internet.
- They are expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits.*
- MAC addresses use a flexible hierarchical structure.
- MAC addresses must be unique for both Ethernet and serial interfaces on a device.
- If a device receives an Ethernet frame of 60 bytes, what will it do?
- drop the frame*
- process the frame as it is
- send an error message to the sending device
- add random data bytes to make it 64 bytes long and then forward it
- Under which two circumstances will a switch flood a frame out of every port except the port that the frame was received on? (Choose two.)
- The frame has the broadcast address as the destination address. *
- The destination address is unknown to the switch.*
- The source address in the frame header is the broadcast address.
- The source address in the frame is a multicast address.
- The destination address in the frame is a known unicast address.
- Which switching method has the lowest level of latency?
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
- fast-forward*
- Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- netstat -s
- route print*
- show ip route
- netstat -r*
- tracert
- Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet forwarding*
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection*
- flow control
- What is the binary representation of 0xCA?
- 10111010
- 11010101
- 11001010*
- 11011010
- At a minimum, which address is required on IPv6-enabled interfaces?
- link-local*
- unique local
- site local
- global unicast
- Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC*
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
- What is the purpose of the command ping ::1?
- It tests the internal configuration of an IPv6 host.*
- It tests the broadcast capability of all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the multicast connectivity to all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the reachability of the default gateway for the network.
- How many usable IP addresses are available on the 192.168.1.0/27 network?
- 256
- 254
- 62
- 30*
- 16
- 32
- What is the process of dividing a data stream into smaller pieces before transmission?
- segmentation*
- encapsulation
- encoding
- flow control
- When IPv4 addressing is manually configured on a web server, which property of the IPv4 configuration identifies the network and host portion for an IPv4 address?
- DNS server address
- subnet mask*
- default gateway
- DHCP server address
- Which two roles can a computer assume in a peer-to-peer network where a file is being shared between two computers? (Choose two.)
- client*
- master
- server*
- slave
- transient
- Which two protocols operate at the highest layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack? (Choose two.)
- DNS*
- Ethernet
- IP
- POP*
- TCP
- UDP
- What is one difference between the client-server and peer-to-peer network models?
- Only in the client-server model can file transfers occur.
- Every device in a peer-to-peer network can function as a client or a server.*
- A peer-to-peer network transfers data faster than a transfer using a client-server network.
- A data transfer that uses a device serving in a client role requires that a dedicated server be present.
- What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
- to request an HTML page from a web server*
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
- Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
- peer-to-peer
- master-slave
- client/server*
- point-to-point
- What network service resolves the URL entered on a PC to the IP address of the destination server?
- DNS*
- DHCP
- FTP
- SNMP
- A network engineer is analyzing reports from a recently performed network baseline. Which situation would depict a possible latency issue?
- a change in the bandwidth according to the show interfaces output
- a next-hop timeout from a traceroute
- an increase in host-to-host ping response times*
- a change in the amount of RAM according to the show version output
- Which firewall feature is used to ensure that packets coming into a network are legitimate responses to requests initiated from internal hosts?
- stateful packet inspection*
- URL filtering
- application filtering
- packet filtering
- What is one indication that a Windows computer did not receive an IPv4 address from a DHCP server?The computer cannot ping 127.0.0.1.
Windows displays a DHCP timeout message.
The computer receives an IP address that starts with 169.254*
The computer cannot ping other devices on the same network with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 range. - Which command can an administrator issue on a Cisco router to send debug messages to the vty lines?terminal monitor*
logging console
logging buffered
logging synchronous - Fill in the blank.
During data communications, a host may need to send a single message to a specific group of destination hosts simultaneously. This message is in the form of a Multicast *message. - A medium-sized business is researching available options for connecting to the Internet. The company is looking for a high speed option with dedicated, symmetric access. Which connection type should the company choose?
- DSL
- dialup
- satellite
- leased line*
- cable modem
- What is the purpose of having a converged network?
- to provide high speed connectivity to all end devices
- to make sure that all types of data packets will be treated equally
- to achieve fault tolerance and high availability of data network infrastructure devices
- to reduce the cost of deploying and maintaining the communication infrastructure*
- What characteristic of a network enables it to quickly grow to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users?
- reliability
- scalability*
- quality of service
- accessibility
- After several configuration changes are made to a router, the copy running-configuration startup-configuration command is issued. Where will the changes be stored?
- flash
- ROM
- NVRAM*
- RAM
- the configuration register
- a TFTP server
- Refer to the exhibit. From global configuration mode, an administrator is attempting to create a message-of-the-day banner by using the command banner motd V Authorized access only! Violators will be prosecuted! V When users log in using Telnet, the banner does not appear correctly. What is the problem?
- The banner message is too long.
- The delimiting character appears in the banner message.*
- The symbol “!” signals the end of a banner message.
- Message-of-the-day banners will only appear when a user logs in through the console port.
- What are three characteristics of an SVI? (Choose three.)
- It is designed as a security protocol to protect switch ports.
- It is not associated with any physical interface on a switch.*
- It is a special interface that allows connectivity by different types of media.
- It is required to allow connectivity by any device at any location.
- It provides a means to remotely manage a switch. *
- It is associated with VLAN1 by default.*
- A technician configures a switch with these commands:SwitchA(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
SwitchA(config-if)# no shutdownWhat is the technician configuring?- Telnet access
- SVI*
- password encryption
- physical switchport access
- In computer communication, what is the purpose of message encoding?
- to convert information to the appropriate form for transmission*
- to interpret information
- to break large messages into smaller frames
- to negotiate correct timing for successful communication
Older Version: CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers v5.1
- What is a function of the data link layer?
- provides the formatting of data
- provides for the exchange of data over a common local media*
- provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
- provides delivery of data between two applications
- Which communication tool allows real-time collaboration?
- wiki
- weblog
- instant messaging*
- A host is accessing a Web server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals*
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data *
- notifying other devices when errors occur*
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
- Refer to the exhibit. From which location did this router load the IOS?
- flash memory*
- NVRAM?
- RAM
- ROM
- a TFTP server?
- Refer to the exhibit. Which action will be successful?
- PC1 can send a ping to 192.168.1.1?.
- PC1 can send a ping to 192.168.1.254?.
- PC2 can send a ping to 192.168.1.1.*
- PC2 can send a ping to 192.168.1.254?.
- Fill in the blank.
Port numbers ranging from 0 to 1023 are considered to be Well Known ports. - Fill in the blank.
ISOC, IANA, EIA, and IEEE represent standards organizations which help to promote and maintain an open Internet. - Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?
- The entire command, configure terminal, must be used.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.*
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
- A company is expanding its business to other countries. All branch offices must remain connected to corporate headquarters at all times. Which network technology is required to support this requirement?
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN*
- WLAN
- A network administrator is upgrading a small business network to give high priority to real-time applications traffic. What two types of network services is the network administrator trying to accommodate? (Choose two.)
- SNMP
- instant messaging
- voice*
- FTP
- video*
- Match the situation with the appropriate use of network media.
- Which IPv4 address can be pinged to test the internal TCP/IP operation of a host?
- 0.0.0.0
- 0.0.0.1
- 127.0.0.1*
- 192.168.1.1
- 255.255.255.255
- What three application layer protocols are part of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose three.)
- ARP
- DHCP*
- DNS*
- FTP*
- NAT
- PPP
- Which two protocols function at the internet layer? (Choose two)
- ARP
- BOOTP
- ICMP*
- IP*
- PPP
- Which publicly available resources describe protocols, processes, and technologies for the Internet but do not give implementation details?
- Request for Comments*
- IRTF research papers
- protocol models
- IEEE standards
- Which address on a PC does not change, even if the PC is moved to a different network?
- IP address
- default gateway address
- MAC address*
- logical address
- What is the protocol that is used to discover a physical address from a known logical address and what message type does it use?
- ARP, multicast
- DNS, unicast
- DNS, broadcast
- ARP, broadcast*
- PING, multicast
- PING, broadcast
- What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.*
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- What is an important function of the physical layer of the OSI model?
- It accepts frames from the physical media.
- It encapsulates upper layer data into frames.
- It defines the media access method performed by the hardware interface.
- It encodes frames into electrical, optical, or radio wave signals.*
- Which two statements describe the characteristics of fiber-optic cabling? (Choose two.)
- Fiber-optic cabling does not conduct electricity.*
- Fiber-optic cabling has high signal loss.
- Fiber-optic cabling is primarily used as backbone cabling.*
- Multimode fiber-optic cabling carries signals from multiple sending devices.
- Fiber-optic cabling uses LEDs for single-mode cab?les and laser technology for multimode cables.
- What is contained in the trailer of a data-link frame?
- logical address
- physical address
- data
- error detection*
- Refer to the exhibit. A ping to PC3 is issued from PC0, PC1, and PC2 in this exact order. Which MAC addresses will be contained in the S1 MAC address table that is associated with the Fa0/1 port?
- just PC0 and PC1 MAC addresses*
- just the PC0 MAC address
- PC0, PC1, and PC2 MAC addresses
- just the PC1 MAC address
- just the PC2 MAC address?
- How does a Layer 3 switch differ from a Layer 2 switch?
- A Layer 3 switch supports VLANs, but a Layer 2 switch does not.
- An IP address can be assigned to a physical port of a Layer 3 switch. However, this is not supported in Layer 2 switches.*
- A Layer 3 switch maintains an IP address table instead of a MAC address table.
- A Layer 3 switch learns the MAC addresses that are associated with each of its ports. However, a Layer 2 switch does not.
- What is the purpose of the routing process?
- to encapsulate data that is used to communicate across a network
- to select the paths that are used to direct traffic to destination networks*
- to convert a URL name into an IP address
- to provide secure Internet file transfer
- to forward traffic on the basis of MAC addresses
- Which technology provides a solution to IPv4 address depletion by allowing multiple devices to share one public IP address?
- ARP
- DNS
- NAT*
- SMB
- DHCP
- HTTP
- Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address configuration shown from PC1. What is a description of the default gateway address?
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the company to the Internet.
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the PC1 LAN to Router1.*
- It is the IP address of Switch1 that connects PC1 to other devices on the same LAN.
- It is the IP address of the ISP network device located in the cloud.
- Which of the following are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet switching*
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection*
- flow control
- Which two statements correctly describe a router memory type and its contents? (Choose two.)
- ROM is nonvolatile and contains basic diagnostic software.*
- FLASH is nonvolatile and contains a limited portion of the IOS.
- ROM is nonvolatile and stores the running IOS.
- RAM is volatile and stores the IP routing table.*
- NVRAM is nonvolatile and stores other system files.
- In which default order will a router search for startup configuration information?
- NVRAM, RAM, TFTP
- NVRAM, TFTP, setup mode*
- setup mode, NVRAM, TFTP
- TFTP, ROM, NVRAM
- flash, ROM, setup mode
- What happens when part of an Internet VoIP transmission is not delivered to the destination?
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the VoIP transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.*
- Which three IP addresses are private ? (Choose three.)
- 10.172.168.1*
- 172.32.5.2
- 192.167.10.10
- 172.20.4.4 *
- 192.168.5.254*
- 224.6.6.6
- How many bits make up the single IPv6 hextet :10CD:?
- 4
- 8
- 16*
- 32
- What is the effect of configuring the ipv6 unicast-routing command on a router?
- to assign the router to the all-nodes multicast group
- to enable the router as an IPv6 router*
- to permit only unicast packets on the router
- to prevent the router from joining the all-routers multicast group
- Which group of IPv6 addresses cannot be allocated as a host source address?
- FEC0::/10?
- FDFF::/7?
- FEBF::/10?
- FF00::/8*
- What is the purpose of ICMP messages?
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions*
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
- Refer to the exhibit. A technician has configured a user workstation with the IP address and default subnet masks that are shown. Although the user can access all local LAN resources, the user cannot access any Internet sites by using either FQDN or IP addresses. Based upon the exhibit, what could account for this failure?
- The DNS server addresses are incorrect.
- The default gateway address in incorrect.*
- The wrong subnet mask was assigned to the workstation.
- The workstation is not in the same network as the DNS servers.
- A network administrator needs to monitor network traffic to and from servers in a data center. Which features of an IP addressing scheme should be applied to these devices?
- random static addresses to improve security
- addresses from different subnets for redundancy
- predictable static IP addresses for easier identification*
- dynamic addresses to reduce the probability of duplicate addresses
- Refer to the exhibit. Which IP addressing scheme should be changed?
- Site 1
- Site 2*
- Site 3
- Site 4
- Which two notations are useable nibble boundaries when subnetting in IPv6? (Choose two.)
- /62
- /64*
- /66
- /68*
- /70
- A host PC has just booted and is attempting to lease an address through DHCP. Which two messages will the client typically broadcast on the network? (Choose two.)
- DHCPDISCOVER*
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST*
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
- What is the purpose of the network security accounting function?
- to require users to prove who they are
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to keep track of the actions of a user*
- to provide challenge and response questions
- Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router:
R1# copy running-config tftp
Address or name of remote host [ ]?
When the router prompts for an address or remote host name, what IP address should the administrator enter at the prompt?- 192.168.9.254
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.10.2
- 192.168.11.252*
- 192.168.11.254
- Match the IPv6 address to the IPv6 address type. (Not all options are used.)
- What two preconfigured settings that affect security are found on most new wireless routers? (Choose two.)
- broadcast SSID*
- MAC filtering enabled
- WEP encryption enabled
- PSK authentication required
- default administrator password*
- Which type of wireless security generates dynamic encryption keys each time a client associates with an AP?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA*
- Fill in the blank.
TFTP* is a best-effort, connectionless application layer protocol that is used to transfer files. - Which two components are necessary for a wireless client to be installed on a WLAN? (Choose two.)
- media
- wireless NIC*
- custom adapter
- crossover cable
- wireless bridge
- wireless client software*
- Consider the following range of addresses:
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000::
…
2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::
The prefix-length for the range of addresses is /60* . - Match the phases to their correct stage in the router bootup process. (Not all options are used.)
- A host is accessing an FTP server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals*
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data*
- notifying other devices when errors occur*
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
- When is a dial-up connection used to connect to an ISP?
- when a cellular telephone provides the service
- when a high-speed connection is provided over a cable TV network
- when a satellite dish is used
- when a regular telephone line is used*
- On a school network, students are surfing the web, searching the library database, and attending an audio conference with their sister school in Japan. If network traffic is prioritized with QoS, how will the traffic be classified from highest priority to lowest priority?
- audio conference, database, HTTP*
- database, HTTP, audio conference
- audio conference, HTTP, database
- database, audio conference, HTTP
- During normal operation, from which location do most Cisco routers run the IOS?
- RAM*
- flash
- NVRAM
- disk drive
- Which keys act as a hot key combination that is used to interrupt an IOS process?
- Ctrl-Shift-X
- Ctrl-Shift-6*
- Ctrl-Z
- Ctrl-C
- Refer to the exhibit. An administrator wants to change the name of a brand new switch, using the hostname command as shown. What prompt will display after the command is issued??
- HR Switch(config)#?
- Switch(config)#?*
- HRSwitch(config)#?
- HR(config)#?
- Switch#
- A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?
- the TCP/IP stack on a network host*
- connectivity between two adjacent Cisco devices
- connectivity between a PC and the default gateway
- connectivity between two PCs on the same network
- physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network
- What is the correct order for PDU encapsulation?
- Which device should be used for enabling a host to communicate with another host on a different network?
- switch
- hub
- router*
- host
- A network technician is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical application. The technician notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network*
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network*
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
- Which characteristics describe fiber optic cable? (Choose two.)
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.*
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding and twisting to protect data.
- It has a maximum speed of 100 Mbps.
- It is the most expensive type of LAN cabling*
- What are two features of a physical, star network topology? (Choose two.)
- It is straightforward to troubleshoot.*
- End devices are connected together by a bus.
- It is easy to add and remove end devices.*
- All end devices are connected in a chain to each other.
- Each end system is connected to its respective neighbor.
- A frame is transmitted from one networking device to another. Why does the receiving device check the FCS field in the frame?
- to determine the physical address of the sending device
- to verify the network layer protocol information
- to compare the interface media type between the sending and receiving ends
- to check the frame for possible transmission errors*
- to verify that the frame destination matches the MAC address of the receiving device
- What will a Layer 2 switch do when the destination MAC address of a received frame is not in the MAC table?
- It initiates an ARP request.
- It broadcasts the frame out of all ports on the switch.
- It notifies the sending host that the frame cannot be delivered.
- It forwards the frame out of all ports except for the port at which the frame was received.*
- Which parameter does the router use to choose the path to the destination when there are multiple routes available?
- the lower metric value that is associated with the destination network*
- the lower gateway IP address to get to the destination network
- the higher metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the higher gateway IP address to get to the destination network
- Which two statements describe the functions or characteristics of ROM in a router? (Choose two.)
- stores routing tables
- allows software to be updated without replacing pluggable chips on the motherboard
- maintains instructions for POST diagnostics*
- holds ARP cache
- stores bootstrap program*
- Which statement describes a characteristic of the Cisco router management ports?
- A console port is used for remote management of the router.
- A console port is not used for packet forwarding.*
- Serial and DSL interfaces are types of management ports.
- Each Cisco router has a LED indicator to provide information about the status of the management ports.
- What happens when part of an Internet radio transmission is not delivered to the destination?
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the radio transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.*
- What types of addresses make up the majority of addresses within the /8 block IPv4 bit space?
- private addresses
- public addresses*
- multicast addresses
- experimental addresses
- Refer to the exhibit. What is the maximum TTL value that is used to reach the destination www.cisco.com??
- 11
- 12
- 13*
- 14
- A company has a network address of 192.168.1.64 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192. The company wants to create two subnetworks that would contain 10 hosts and 18 hosts respectively. Which two networks would achieve that? (Choose two.)
- 192.168.1.16/28
- 192.168.1.64/27*
- 192.168.1.128/27
- 192.168.1.96/28*
- 192.168.1.192/28
- In a network that uses IPv4, what prefix would best fit a subnet containing 100 hosts?
- /23
- /24
- /25*
- /26
- Which protocol supports rapid delivery of streaming media?
- Transmission Control Protocol
- Real-Time Transport Protocol*
- Secure File Transfer Protocol
- Video over Internet Protocol
- Why would a network administrator use the tracert utility?
- to determine the active TCP connections on a PC
- to check information about a DNS name in the DNS server
- to identify where a packet was lost or delayed on a network*
- to display the IP address, default gateway, and DNS server address for a PC
- Refer to the exhibit. What is the significance of the asterisk (*) in the exhibited output?
- The asterisk shows which file system was used to boot the system.
- The asterisk designates which file system is the default file system.*
- An asterisk indicates that the file system is bootable.
- An asterisk designates that the file system has at least one file that uses that file system.
- Which WLAN security protocol generates a new dynamic key each time a client establishes a connection with the AP?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA*
- Fill in the blank.
Point-to-point communications where both devices can transmit and receive on the medium at the same time are known as full-duplex* - Match each characteristic to the appropriate email protocol. (Not all options are used.)
- A host is accessing a Telnet server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals*
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data*
- notifying other devices when errors occur*
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
- Refer to the exhibit. Which area would most likely be an extranet for the company network that is shown?
- area A
- area B
- area C*
- area D
- Three office workers are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other office workers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page*
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
- During normal operation, from which location do most Cisco switches and routers run the IOS?
- RAM*
- flash
- NVRAM
- disk drive
- A network administrator is making changes to the configuration of a router. After making the changes and verifying the results, the administrator issues the copy running-config startup-config command. What will happen after this command executes?
- The configuration will be copied to flash.
- The configuration will load when the router is restarted.*
- The new configuration file will replace the IOS file.
- The changes will be lost when the router restarts.
- What information does the loopback test provide?
- The TCP/IP stack on the device is working correctly.*
- The device has end-to-end connectivity.
- DHCP is working correctly.
- The Ethernet cable is working correctly.
- The device has the correct IP address on the network.
- What happens when a switch receives a frame and the calculated CRC value is different than the value that is in the FCS field?
- The switch places the new CRC value in the FCS field and forwards the frame.
- The switch notifies the source of the bad frame.
- The switch drops the frame.*
- The switch floods the frame to all ports except the port through which the frame arrived to notify the hosts of the error.
- Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame?
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF*
- 127.0.0.1
- 01-00-5E-00-AA-23
- What is the auto-MDIX feature on a switch?
- the automatic configuration of an interface for 10/100/1000 Mb/s operation
- the automatic configuration of an interface for a straight-through or a crossover Ethernet cable connection*
- the automatic configuration of full-duplex operation over a single Ethernet copper or optical cable
- the ability to turn a switch interface on or off accordingly if an active connection is detected
- What are the two main components of Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)? (Choose two.)
- adjacency tables*
- MAC-address tables
- routing tables
- ARP tables
- forwarding information base (FIB)*
- Which statement describes the sequence of processes executed by a router when it receives a packet from a host to be delivered to a host on another network?
- It receives the packet and forwards it directly to the destination host.
- It de-encapsulates the packet, selects the appropriate path, and encapsulates the packet to forward it toward the destination host*
- It de-encapsulates the packet and forwards it toward the destination host.
- It selects the path and forwards it toward the destination host.
- Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 has two interfaces that were configured with correct IP addresses and subnet masks. Why does the show ip route command output not display any information about the directly connected networks??
- The directly connected networks have to be created manually to be displayed in the routing table.
- The routing table will only display information about these networks when the router receives a packet.
- The no shutdown command was not issued on these interfaces.*
- The gateway of last resort was not configured.
- What happens when part of an Internet television transmission is not delivered to the destination?
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the television transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.*
- Which three statements characterize the transport layer protocols? (Choose three.)
- TCP and UDP port numbers are used by application layer protocols.*
- TCP uses port numbers to provide reliable transportation of IP packets.
- UDP uses windowing and acknowledgments for reliable transfer of data.
- TCP uses windowing and sequencing to provide reliable transfer of data.*
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. UDP is a connectionless protocol.*
- Which statement is true regarding the UDP client process during a session with a server?
- Datagrams that arrive in a different order than that in which they were sent are not placed in order.*
- A session must be established before datagrams can be exchanged.
- A three-way handshake takes place before the transmission of data begins.
- Application servers have to use port numbers above 1024 in order to be UDP capable.
- Which two components are configured via software in order for a PC to participate in a network environment? (Choose two.)
- MAC address
- IP address*
- kernel
- shell
- subnet mask*
- Which two reasons generally make DHCP the preferred method of assigning IP addresses to hosts on large networks? (Choose two.)
- It eliminates most address configuration errors.*
- It ensures that addresses are only applied to devices that require a permanent address.
- It guarantees that every device that needs an address will get one.
- It provides an address only to devices that are authorized to be connected to the network.
- It reduces the burden on network support staff.*
- What is the subnet address for the address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
- 2001:DB8:BC15::0
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A::0*
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1::1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12::0
- What is the purpose of the network security authentication function?
- to require users to prove who they are*
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to keep track of the actions of a user
- to provide challenge and response questions
- Which type of wireless security makes use of dynamic encryption keys each time a client associates with an AP?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA*
- Launch PT – Hide and Save PT.
Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then fill in the blank.
The Server0 message is . ” winner ” - Which field in an IPv4 packet header will typically stay the same during its transmission?
Packet Length
Destination Address*
Flag
Time-to-Live - Launch PT – Hide and Save PT
- Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which IPv6 address is assigned to the Serial0/0/0 interface on RT2?
2001:db8:abc:1::1
2001:db8:abc:5::1 *
2001:db8:abc:5::2
2001:db8:abc:10::15 - What must be configured to enable Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) on most Cisco devices that perform Layer 3 switching?
- Manually configure next-hop Layer 2 addresses.
- Issue the no shutdown command on routed ports.
- CEF is enabled by default, so no configuration is necessary.*
- Manually map Layer 2 addresses to Layer 3 addresses to populate the forwarding information base (FIB).
- What is the purpose of adjacency tables as used in Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)?
- to populate the forwarding information base (FIB)
- to maintain Layer 2 next-hop addresses*
- to allow the separation of Layer 2 and Layer 3 decision making
- to update the forwarding information base (FIB)
- Which statement describes a characteristic of the network layer in the OSI model?
- It manages the data transport between the processes running on each host.
- In the encapsulation process, it adds source and destination port numbers to the IP header.
- When a packet arrives at the destination host, its IP header is checked by the network layer to determine where the packet has to be routed.
- Its protocols specify the packet structure and processing used to carry the data from one host to another.*
- A user gets an IP address of 192.168.0.1 from the company network administrator. A friend of the user at a different company gets the same IP address on another PC. How can two PCs use the same IP address and still reach the Internet, send and receive email, and search the web?
- Both users must be using the same Internet Service Provider.
- ISPs use Network Address Translation to change a user IP address into an address that can be used on the Internet.*
- ISPs use Domain Name Service to change a user IP address into a public IP address that can be used on the Internet.
- Both users must be on the same network.
- Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
- to ensure the fastest possible download speed
- because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
- because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
- because HTTP requires reliable delivery*
- What is the valid most compressed format possible of the IPv6 address 2001:0DB8:0000:AB00:0000:0000:0000:1234?
- 2001:DB8:0:AB00::1234*
- 2001:DB8:0:AB::1234
- 2001:DB8::AB00::1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB:0:1234
- What field content is used by ICMPv6 to determine that a packet has expired?
- TTL field
- CRC field
- Hop Limit field*
- Time Exceeded field
- Which firewall technique blocks incoming packets unless they are responses to internal requests?
- port filtering
- stateful packet inspection*
- URL filtering
- application filtering
- A network technician is investigating network connectivity from a PC to a remote host with the address 10.1.1.5. Which command issued on the PC will return to the technician the complete path to the remote host?
- trace 10.1.1.5
- traceroute 10.1.1.5
- tracert 10.1.1.5*
- ping 10.1.1.5
- Fill in the blank.
To prevent faulty network devices from carrying dangerous voltage levels, equipment must be grounded *correctly - What is a possible hazard that can be caused by network cables in a fire?
- The cable insulation could be flammable.*
- Users could be exposed to excessive voltage.
- Network cables could be exposed to water.
- The network cable could explode.
- What device is commonly used to verify a UTP cable?
- a multimeter
- an Optical Time Domain Reflectometer
- a cable tester*
- an ohmmeter
- What needs to be checked when testing a UTP network cable?
- capacitance
- wire map*
- inductance
- flexibility
- Refer to the exhibit. A ping to PC2 is issued from PC0, PC1, and PC3 in this exact order. Which MAC addresses will be contained in the S1 MAC address table that is associated with the Fa0/1 port?
- just PC0 and PC1 MAC addresses*
- just the PC0 MAC address
- PC0, PC1, and PC2 MAC addresses
- just the PC1 MAC address
- just the PC2 MAC address
- Which function is provided by TCP?
- data encapsulation
- detection of missing packets*
- communication session control
- path determination for data packets
- What does a router use to determine where to send data it receives from the network?
- an ARP table
- a routing table*
- the destination PC physical address
- a switching table
- Which router interface should be used for direct remote access to the router via a modem?
- an inband router interface
- a console port
- a serial WAN interface
- an AUX port*
- A technician is configuring a router to allow for all forms of management access. As part of each different type of access, the technician is trying to type the command login. Which configuration mode should be entered to do this task?
- user executive mode
- global configuration mode
- any line configuration mode*
- privileged EXEC mode
- Which three statements characterize the transport layer protocols? (Choose three.)
- TCP and UDP port numbers are used by application layer protocols.*
- TCP uses port numbers to provide reliable transportation of IP packets.
- UDP uses windowing and acknowledgments for reliable transfer of data.
- TCP uses windowing and sequencing to provide reliable transfer of data.*
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. UDP is a connectionless protocol.*
- Refer to the exhibit. A TCP segment from a server has been captured by Wireshark, which is running on a host. What acknowledgement number will the host return for the TCP segment that has been received?
- 2
- 21
- 250
- 306*
- 2921
- Which statement is true about an interface that is configured with the IPv6 address command?
- IPv6 traffic-forwarding is enabled on the interface.
- A link-local IPv6 address is automatically configured on the interface.*
- A global unicast IPv6 address is dynamically configured on the interface.
- Any IPv4 addresses that are assigned to the interface are replaced with an IPv6 address.
- Refer to the exhibit. An administrator must send a message to everyone on the router A network. What is the broadcast address for network 172.16.16.0/22?
- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255*
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
- A network administrator is variably subnetting a given block of IPv4 addresses. Which combination of network addresses and prefix lengths will make the most efficient use of addresses when the need is for 2 subnets capable of supporting 10 hosts and 1 subnet that can support 6 hosts?
- 10.1.1.128/28*
10.1.1.144/28*
10.1.1.160/29* - 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.144/28
10.1.1.160/28 - 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.140/28
10.1.1.158/26 - 10.1.1.128/26
10.1.1.144/26
10.1.1.160/26 - 10.1.1.128/26
10.1.1.140/26
10.1.1.158/28
- 10.1.1.128/28*
- How many additional bits should be borrowed from a /26 subnet mask in order to create subnets for WAN links that need only 2 useable addresses?
- 2
- 3
- 4*
- 5
- 6
- A network administrator requires access to manage routers and switches locally and remotely. Match the description to the access method. (Not all options are used.)
240. Refer to the exhibit. The administrator configured the access to the console and the vty lines of a router. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?
- Unauthorized individuals can connect to the router via Telnet without entering a password.
- Because the IOS includes the login command on the vty lines by default, access to the device via Telnet will require authentication.*
- Access to the vty lines will not be allowed via Telnet by anyone.
- Because the login command was omitted, the password cisco command is not applied to the vty lines.
- An administrator issued the service password-encryption command to apply encryption to the passwords configured for enable password, vty, and console lines. What will be the consequences if the administrator later issues the no service password-encryption command?
- It will remove encryption from all passwords.
- It will reverse only the vty and console password encryptions.
- It will not reverse any encryption.*
- It will reverse only the enable password encryption.
- After making configuration changes, a network administrator issues a copy running-config startup-config command in a Cisco switch. What is the result of issuing this command?
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.*
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
- What are two features of ARP? (Choose two.)
- If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.*
- An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
- When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
- If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
- If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.*
- A network administrator is enabling services on a newly installed server. Which two statements describe how services are used on a server? (Choose two.)
- Data sent with a service that uses TCP is received in the order the data was sent.
- A port is considered to be open when it has an active server application that is assigned to it.*
- An individual server can have two services that are assigned to the same port number.
- An individual server cannot have multiple services running at the same time.
- Server security can be improved by closing ports that are associated with unused services.*
- Given the binary address of 11101100 00010001 00001100 00001010, which address does this represent in dotted decimal format?
- 234.17.10.9
- 234.16.12.10
- 236.17.12.6
- 236.17.12.10*
- A particular telnet site does not appear to be responding on a Windows 7 computer. What command could the technician use to show any cached DNS entries for this web page?
- ipconfig /all
- arp -a
- ipconfig /displaydns*
- nslookup
- Fill in the blank.
Network devices come in two physical configurations. Devices that have expansion slots that provide the flexibility to add new modules have a Modular * configuration.
Refer to the exhibit. What is the maximum TIL value that is used to reach the destination www.cisco.com?- 11
- 12
- 13*
- 14
- Which statement is true about DHCP operation?
- When a device that is configured to use DHCP boots, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network.*
- A client must wait for lease expiration before it sends another DHCPREOUEST message.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the IP address and sub net masK to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway.
- If the client receives several DHCPOFFER messages from different servers, it sends a unicast DHCPREOUEST message to the server from which it chooses to obtain the IP information.
- Which type of wireless security is easily compromised?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP*
- WPA
- A network administrator notices that the throughput on the network appears lower than expected when compared to the end-to-end network bandwidth. Which three factors can explain this difference? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic*
- the type of data encapsulation in use
- the type of traffic*
- the number and type of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the connection to the ISP
- the reliability of the network backbone
- A host PC is attempting to lease an address through DHCP. What message is sent by the server to the client know it is able to use the provided IP information?
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER*
- DHCPPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
- A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses console line to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?
- letmein
- secretin
- lineconin*
- linevtyin
- How many bits would need to be borrowed if a network admin were given the IP addressing scheme of 172.16.0.0/16 and needed no more than 16 subnet with equal number of hosts?
- 10
- 12
- 2
- 4*
- 8
- Question:
It will give 4 options about ping, the correct one is:
The PC2 will be able to ping 192.168.1.1* - Which statement best describes the operation of the File Transfer Protocol?
An FTP client uses a source port number of 21 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP Server.
An FTP client uses a source port number of 20 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of data traffic with an FTP Server.
An FTP server uses a source port number of 20 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP client.*
An FTP server uses a source port number of 21 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP client. - A client is establishing a TCP session with a server. How is the acknowledgment number in the response segment to the client determined?
The acknowledgment number field is modified by adding 1 to the randomly chosen initial sequence number in response to the client.*
The acknowledgment number is set to 11 to signify an acknowledgment packet and synchronization packet back to the client.
The acknowledgment number field uses a random source port number in response to the client.
The acknowledgment number is set to 1 to signify an acknowledgment packet back to the client. - Why does layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP and subnet Mask?
to identify host address and destination host;
to identify network address of destination host;*
to identify faulty frames;
to identify broadcast address of destination network; - There was also a question about if you activated service password encryption in the past and you prompt “no service password encryption” what password are modified ?
no password at all;*
password of the lines are in clear;
login password;
? - What type of communication rule would best describe CSMA/CD?
message encapsulation
flow control
message encoding
access method* - What is the primary reason to subnet IPv6 prefixes?
to conserve IPv6 addresses
to avoid wasting IPv6 addresses
to conserve IPv6 prefixes
to create a hierarchical Layer 3 network design* - Which statement describes data throughput?
It is the measure of the bits transferred across the media under perfect conditions.
It is the measure of the bits transferred across the media over a given period of time.*
It indicates the capacity of a particular medium to carry data.
It is the guaranteed data transfer rate offered by an ISP. - Fill in the blank. Use a number.
IPv4 multicast addresses are directly mapped to IEEE 802 (Ethernet) MAC addresses using the last ___4___ of the 28 available bits in the IPv4 multicast group address. - How could a faulty network device create a source of hazard for a user? (Choose two.)
It could stop functioning.*
It could apply dangerous voltage to other pieces of equipment.
It could explode.*
It could produce an unsafe electromagnetic field.
It could apply dangerous voltage to itself. - What are three important considerations when planning the structure of an IP addressing scheme? (Choose three.)
preventing duplication of addresses*
providing and controlling access*
documenting the network
monitoring security and performance
conserving addresses*
implementing new services - What is the metric value that is used to reach the 10.1.1.0 network in the following routing table entry? D 10.1.1.0/24 [90/2170112] via 209.165.200.226, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/0
24
90
05
2170112* - Which two services or protocols use the preferred UDP protocol for fast transmission and low overhead? (Choose two)
VoIP*
DNS*
HTTP
FTP
POP3 - What action does a DHCPv4 client take if it receives more than one DHCPOFFER from multiple DHCP servers?
It sends a DHCPREQUEST that identifies which lease offer the client is accepting.*
It sends a DHCPNAK and begins the DHCP process over again.
It discards both offers and sends a new DHCPDISCOVER.
It accepts both DHCPOFFER messages and sends a DHCPACK. - To what legacy address class does the address 10.0.0.0 belong?
Class B
Class D
Class A*
Class C
Class E - What type of communication medium is used with a wireless LAN connection?
radio waves*
fiber
microwave
UTP - Which method of IPv6 prefix assignment relies on the prefix contained in RA messages?
EUI-64
static
SLAAC*
stateful DHCPv6 - What is a characteristic of DNS?
DNS servers can cache recent queries to reduce DNS query traffic.*
DNS servers are programmed to drop requests for name translations that are not within their zone.
All DNS servers must maintain mappings for the entire DNS structure.
DNS relies on a hub-and-spoke topology with centralized servers. - What is the prefix for the host address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
2001:DB8:BC15
2001:DB8:BC15:A*
2001:DB8:BC15:A:1
2001:DB8:BC15:A:12 - What information is maintained in the CEF adjacency table?
Layer 2 next hops
MAC address to IPv4 address mappings*
IP address to interface mappings
the IP addresses of all neighboring routers - Which command can an administrator issue on a Cisco router to send debug messages to the vty lines?terminal monitor*
logging console
logging buffered
logging synchronous -
-
How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
Version 6.0:
1. What is a characteristic of a fault tolerant network?
- a network that protects confidential information from unauthorized access
- a network that can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service delivered to existing users
- a network that supports a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users
- a network that recovers quickly when a failure occurs and depends on redundancy to limit the impact of a failure
Explain:
Fault tolerant networks limit the impact of a failure because the networks are built in a way that allows for quick recovery when such a failure occurs. These networks depend on multiple or redundant paths between the source and destination of a message.
A scalable network can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users.
Quality of service (QoS) is a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users.
2. Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
Explain:
QoS mechanisms enable the establishment of queue management strategies that enforce priorities for different categories of application data. Thus, this queuing enables voice data to have priority over transaction data, which has priority over web data.
3. What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
Explain:
Cloud computing extends IT’s capabilities without requiring investment in new infrastructure, training new personnel, or licensing new software. These services are available on-demand and delivered economically to any device anywhere in the world without compromising security or function. BYOD is about end users having the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business or campus network. Smart home technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated. Powerline networking is a trend for home networking that uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
4. What is the function of the shell in an OS?
- It interacts with the device hardware.
- It interfaces between the users and the kernel.
- It provides dedicated firewall services.
- It provides the intrusion protection services for the device.
Explain:
Most operating systems contain a shell and a kernel. The kernel interacts with the hardware and the shell interfaces between the kernel and the users.
5. Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco switch?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection
Explain:
A CLI session using Secure Shell (SSH) provides enhanced security because SSH supports strong passwords and encryption during the transport of session data. The other methods support authentication but not encryption.
6. A network technician is attempting to configure an interface by entering the following command: SanJose(config)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0. The command is rejected by the device. What is the reason for this?
- The command is being entered from the wrong mode of operation.
- The command syntax is wrong.
- The subnet mask information is incorrect.
- The interface is shutdown and must be enabled before the switch will accept the IP address.
Explain:
The wrong mode of operation is being used. The CLI prompt indicates that the mode of operation is global configuration. IP addresses must be configured from interface configuration mode, as indicated by the SanJose(config-if)# prompt.
7. An administrator uses the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination on a switch after issuing the ping command. What is the purpose of using these keystrokes?
- to restart the ping process
- to interrupt the ping process
- to exit to a different configuration mode
- to allow the user to complete the command
Explain:
To interrupt an IOS process such as ping or traceroute, a user enters the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination. Tab completes the remainder of parameters or arguments within a command. To exit from configuration mode to privileged mode use the Ctrl-Z keystroke. CTRL-R will redisplay the line just typed, thus making it easier for the user to press Enter and reissue the ping command.
8. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses a console connection to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?
- letmein
- secretin
- linevtyin
- lineconin
Explain:
Telnet accesses a network device through the virtual interface configured with the line VTY command. The password configured under this is required to access the user EXEC mode. The password configured under the line console 0 command is required to gain entry through the console port, and the enable and enable secret passwords are used to allow entry into the privileged EXEC mode.
9. On which switch interface would an administrator configure an IP address so that the switch can be managed remotely?
- FastEthernet0/1
- VLAN 1
- vty 0
- console 0
Explain:
Interface VLAN 1 is a virtual interface on a switch, called SVI (switch virtual interface). Configuring an IP address on the default SVI, interface VLAN 1, will allow a switch to be accessed remotely. The VTY line must also be configured to allow remote access, but an IP address cannot be configured on this line.
10. What protocol is responsible for controlling the size of segments and the rate at which segments are exchanged between a web client and a web server?
- TCP
- IP
- HTTP
- Ethernet
Explain:
TCP is a Layer 4 protocol of the OSI model. TCP has several responsibilities in the network communication process. It divides large messages into smaller segments which are more efficient to send across the network. It also controls the size and rate of segments exchanged between clients and servers.
11. What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- A company can monopolize the market.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.
Explain:
A monopoly by one company is not a good idea from a user point of view. If a protocol can only be run on one brand, it makes it difficult to have mixed equipment in a network. A proprietary protocol is not free to use. An open standard protocol will in general be implemented by a wide range of vendors.
12. What are two benefits of using a layered network model? (Choose two.)
- It assists in protocol design.
- It speeds up packet delivery.
- It prevents designers from creating their own model.
- It prevents technology in one layer from affecting other layers.
- It ensures a device at one layer can function at the next higher layer.
Explain:
Some vendors have developed their own reference models and protocols. Today, if a device is to communicate on the Internet, the device must use the TCP/IP model. The benefits of using a layered model are as follows:
assists in protocol design
fosters competition between vendors
prevents a technology that functions at one layer from affecting any other layer
provides a common language for describing network functionality
helps in visualizing the interaction between each layer and protocols between each layer
13. Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- data link
- network
- physical
- session
- transport
Explain:
The OSI transport layer is functionally equivalent to the TCP/IP transport layer, and the OSI network layer is equivalent to the TCP/IP internet layer. The OSI data link and physical layers together are equivalent to the TCP/IP network access layer. The OSI session layer (with the presentation layer) is included within the TCP/IP application layer.
14. Which name is assigned to the transport layer PDU?
- bits
- data
- frame
- packet
- segment
Explain:
Application data is passed down the protocol stack on its way to be transmitted across the network media. During the process, various protocols add information to it at each level. At each stage of the process, a PDU (protocol data unit) has a different name to reflect its new functions. The PDUs are named according to the protocols of the TCP/IP suite:
Data – The general term for the PDU used at the application layer.
Segment – transport layer PDU
Packet – network layer PDU
Frame – data link layer PDU
Bits – A physical layer PDU used when physically transmitting data over the medium
15. A network engineer is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical database application. The engineer notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
Explain:
Throughput usually does not match the specified bandwidth of physical links due to multiple factors. These factors include, the amount of traffic, type of traffic, and latency created by the network devices the data has to cross.
16. A network administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues on a server. Using a tester, the administrator notices that the signals generated by the server NIC are distorted and not usable. In which layer of the OSI model is the error categorized?
- presentation layer
- network layer
- physical layer
- data link layer
Explain:
The NIC has responsibilities in both Layer 1 and Layer 2. The NIC encodes the frame as a series of signals that are transmitted onto the local media. This is the responsibility of the physical layer of the OSI model. The signal could be in the form of electrical, optical, or radio waves.
17. Which type of UTP cable is used to connect a PC to a switch port?
- console
- rollover
- crossover
- straight-through
Explain:
A rollover cable is a Cisco proprietary cable used to connect to a router or switch console port. A straight-through (also called patch) cable is usually used to interconnect a host to a switch and a switch to a router. A crossover cable is used to interconnect similar devices together, for example, between two switches, two routers, and two hosts.
18. A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
Explain:
Throughput usually does not match the specified bandwidth of physical links due to multiple factors. These factors include, the amount of traffic, type of traffic, and latency created by the network devices the data has to cross.
19. What is a characteristic of UTP cabling?
- cancellation
- cladding
- immunity to electrical hazards
- woven copper braid or metallic foil
Explain:
Cladding and immunization from electrical hazards are characteristics for fiber-optic cabling. A woven copper braid or metallic foil is used as a shield for the inner coaxial cable conductor. Cancellation is a property of UTP cabling where two wires are located adjacent to one another so each magnetic field cancels out the adjacent magnetic field.
20. What are two characteristics of fiber-optic cable? (Choose two.)
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding, and twisting to protect data.
- It typically contains 4 pairs of fiber-optic wires.
- It is more expensive than UTP cabling is.
Explain:
Fiber-optic cabling supports higher bandwidth than UTP for longer distances. Fiber is immune to EMI and RFI, but costs more, requires more skill to install, and requires more safety precautions.
21. What is a characteristic of the LLC sublayer?
- It provides the logical addressing required that identifies the device.
- It provides delimitation of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium.
- It places information in the frame allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to use the same network interface and media.
- It defines software processes that provide services to the physical layer.
Explain:
The Logical Link Control (LLC) defines the software processes that provide services to the network layer protocols. The information is placed by LLC in the frame and identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame. This information allows multiple Layer 3 protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6, to utilize the same network interface and media.
22. A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies for connecting remote sites to a headquarters building. Which topology provides high availability and connects some, but not all, remote sites?
- mesh
- partial mesh
- hub and spoke
- point-to-point
Explain:
Partial mesh topologies provide high availability by interconnecting multiple remote sites, but do not require a connection between all remote sites. A mesh topology requires point-to-point links with every system being connected to every other system. A point-to-point topology is where each device is connected to one other device. A hub and spoke uses a central device in a star topology that connects to other point-to-point devices.
23. What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA
- token passing
Explain:
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) is used with wireless networking technology to mediate media contention. Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is used with wired Ethernet technology to mediate media contention. Priority ordering and token passing are not used (or not a method) for media access control.
24. What are the three primary functions provided by Layer 2 data encapsulation? (Choose three.)
- error correction through a collision detection method
- session control using port numbers
- data link layer addressing
- placement and removal of frames from the media
- detection of errors through CRC calculations
- delimiting groups of bits into frames
- conversion of bits into data signals
Explain:
Through the framing process, delimiters are used to identify the start and end of the sequence of bits that make up a frame. Data link layer addressing is added to enable a frame to be delivered to a destination node. A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) field is calculated on every bit and added to the frame. If the CRC value contained in the arriving frame is the same as the one the receiving node creates, the frame will be processed.
25. What will a host on an Ethernet network do if it receives a frame with a destination MAC address that does not match its own MAC address?
- It will discard the frame.
- It will forward the frame to the next host.
- It will remove the frame from the media.
- It will strip off the data-link frame to check the destination IP address.
Explain:
In an Ethernet network, each NIC in the network checks every arriving frame to see if the destination MAC address in the frame matches its own MAC address. If there is no match, the device discards the frame. If there is a match, the NIC passes the frame up to the next OSI layer.
26. What are two examples of the cut-through switching method? (Choose two.)
- store-and-forward switching
- fast-forward switching
- CRC switching
- fragment-free switching
- QOS switching
Explain:
Store-and forward switching accepts the entire frame and performs error checking using CRC before forwarding the frame. Store-and-forward is often required for QOS analysis. Fast-forward and fragment-free are both variations of the cut-through switching method where only part of the frame is received before the switch begins to forward it.
27. What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
Explain:
Important actions that a switch performs are as follows:
When a frame comes in, the switch examines the Layer 2 source address to build and maintain the Layer 2 MAC address table.
It examines the Layer 2 destination address to determine how to forward the frame. When the destination address is in the MAC address table, then the frame is sent out a particular port. When the address is unknown, the frame is sent to all ports that have devices connected to that network.
28. Which frame forwarding method receives the entire frame and performs a CRC check to detect errors before forwarding the frame?
- cut-through switching
- store-and-forward switching
- fragment-free switching
- fast-forward switching
Explain:
Fast-forward and fragment-free switching are variations of cut-through switching, which begins to forward the frame before the entire frame is received.
29. Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- 172.168.10.99
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- 172.168.10.65
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
Explain:
When a host sends information to a distant network, the Layer 2 frame header will contain a source and destination MAC address. The source address will be the originating host device. The destination address will be the router interface that connects to the same network. In the case of host A sending information to host B, the source address is AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA and the destination address is the MAC address assigned to the R2 Ethernet interface, BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB.
30. What addresses are mapped by ARP?
- destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address
- destination IPv4 address to the source MAC address
- destination IPv4 address to the destination host name
- destination MAC address to the source IPv4 address
Explain:
ARP, or the Address Resolution Protocol, works by mapping a destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address. The host knows the destination IPv4 address and uses ARP to resolve the corresponding destination MAC address.
31. What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
- source and destination MAC
- source and destination application protocol
- source and destination port number
- source and destination IP address
Explain:
IP is a Layer 3 protocol. Layer 3 devices can open the Layer 3 header to inspect the Layer 3 header which contains IP-related information including the source and destination IP addresses.
32. What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
Explain:
The OSI network layer provides several services to allow communication between devices:
addressing
encapsulation
routing
de-encapsulation
Error detection, placing frames on the media, and collision detection are all functions of the data ink layer.
33. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?
- subnet mask
- DNS address
- host IP address
- default gateway address
Explain:
When a 255.255.255.224 subnet mask is used, the first three bits of the last octet are part of the network portion for an IPv4 address in the subnet. For the 192.168.5.96/27 network, valid host addresses are 192.168.5.97 through 192.168.5.126. The default gateway address is for the Layer 3 device on the same network and it must contain an IP address within the valid IP address range.
34. Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
- to identify the broadcast address of the destination network
- to identify the host address of the destination host
- to identify faulty frames
- to identify the network address of the destination network
Explain:
ANDing allows us to identify the network address from the IP address and the network mask.
35. What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed
- to store the startup configuration file
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
Explain:
NVRAM is permanent memory storage, so the startup configuration file is preserved even if the router loses power.
36. Refer to the exhibit. What will be the result of entering this configuration the next time a network administrator connects a console cable to the router and no additional commands have been entered?
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco123.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco234.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco789.
- The administrator will be presented with the R1> prompt.
Explain:
Until both the password password and the login commands are entered in console line configuration mode, no password is required to gain access to enable mode.
37. What is the dotted decimal representation of the IPv4 address 11001011.00000000.01110001.11010011?
- 192.0.2.199
- 198.51.100.201
- 203.0.113.211
- 209.165.201.223
Explain:
Each section (octet) contains eight binary digits. Each digit represents a specific value (128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1). Everywhere there is a 1, the specific value is relevant. Add all relevant values in a particular octet to obtain the decimal value. For example binary 11001011 equals 203 in decimal.
38. What are three characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose three.)
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts.
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information.
- Routers will not forward multicast addresses in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses.
Explain:
Broadcast messages consist of single packets that are sent to all hosts on a network segment. These types of messages are used to request IPv4 addresses, and map upper layer addresses to lower layer addresses. A multicast transmission is a single packet sent to a group of hosts and is used by routing protocols, such as OSPF and RIPv2, to exchange routes. The address range 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 is reserved for link-local addresses to reach multicast groups on a local network.
39. What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 127.16.0.0/12
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 192.168.0.0/16
Explain:
The private IP address blocks that are used inside companies are as follows:
10.0.0.0 /8 (any address that starts with 10 in the first octet)
172.16.0.0 /12 (any address that starts with 172.16 in the first two octets through 172.31.255.255)
192.168.0.0 /16 (any address that starts with 192.168 in the first two octets)
40. What purpose does NAT64 serve in IPv6?
- It converts IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
- It translates private IPv6 addresses into public IPv6 addresses.
- It enables companies to use IPv6 unique local addresses in the network.
- It converts regular IPv6 addresses into 64-bit addresses that can be used on the Internet.
- It converts the 48-bit MAC address into a 64-bit host address that can be used for automatic host addressing.
Explain:
NAT64 is typically used in IPv6 when networks are being transitioned from IPv4 to IPv6. It allows the IPv6 networks to connect to IPv4 networks (such as the Internet), and works by translating the IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
41. What is the most compressed representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001?
- 2001:0:abcd::1
- 2001:0:0:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd::1
- 2001:0000:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd:0:1
Explain:
The IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001 in its most compressed format would be 2001:0:0:abcd::1. The first two hextets of zeros would each compress to a single zero. The three consecutive hextets of zeros can be compressed to a double colon ::. The three leading zeros in the last hextet can be removed. The double colon :: can only be used once in an address.
42. Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FEC0::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FE80::/10
- FF00::/8
Explain:
Link-local addresses are in the range of FE80::/10 to FEBF::/10. The original IPv6 specification defined site-local addresses and used the prefix range FEC0::/10, but these addresses were deprecated by the IETF in favor of unique local addresses. FDEE::/7 is a unique local address because it is in the range of FC00::/7 to FDFF::/7. IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8.
43. Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117
- 192.15.301.240
- 64.104.78.227
44. Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
- There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
- There are 4 hops between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
- This host does not have a default gateway configured.
Explain:
The output displays a successful Layer 3 connection between a host computer and a host at 19.168.100.1. It can be determined that 4 hops exist between them and the average transmission time is 1 milliseconds. Layer 3 connectivity does not necessarily mean that an application can run between the hosts.
45. What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local
- multicast
- global unicast
Explain:
Link-local IPv6 addresses start with FE80::/10, which is any address from FE80:: to FEBF::. Link-local addresses are used extensively in IPv6 and allow directly connected devices to communicate with each other on the link they share.
46. How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
- 254
- 190
- 192
- 62
- 64
Explain:
When a /26 mask is used, 6 bits are used as host bits. With 6 bits, 64 addresses are possible, but one address is for the subnet number and one address is for a broadcast. This leaves 62 addresses that can be assigned to network devices.
47. A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
Explain:
The subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 has 8 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.128 results in 7 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.224 has 5 host bits. Finally, 255.255.255.240 represents 4 host bits.
48. A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses
Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses
Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
Explain:
If the same mask is to be used, then the network with the most hosts must be examined for number of hosts. Because this is 10 hosts, 4 host bits are needed. The /28 or 255.255.255.240 subnet mask would be appropriate to use for these networks.
49. How many hosts are addressable on a network that has a mask of 255.255.255.248?
- 2
- 6
- 8
- 14
- 16
- 254
Explain:
The subnet mask of 255.255.255.248 is the same as /29. This means the network portion of the address is 29 of the 32 bits in the address. Only 3 bits remain for host bits. 2^3 = 8, but one of these addresses has to be used for the network number and one address must be used as the broadcast address to reach all of the hosts on this network. That leaves only 6 usable IP addresses that can be assigned to hosts in this network. Don’t forget that the default gateway must be one of these devices if this network is to communicate with other networks.
50. Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
Explain:
For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
51. What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
Explain:
In order to accommodate 40 devices, 6 host bits are needed. With 6 bits, 64 addresses are possible, but one address is for the subnet number and one address is for a broadcast. This leaves 62 addresses that can be assigned to network devices. The mask associated with leaving 6 host bits for addressing is 255.255.255.192.
52. What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering
- 3-way handshake
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- use of checksum
Explain:
Both TCP and UDP use source and destination port numbers to distinguish different data streams and to forward the right data segments to the right applications. Error checking the header and data is done by both protocols by using a checksum calculation to determine the integrity of the data that is received. TCP is connection-oriented and uses a 3-way handshake to establish an initial connection. TCP also uses window to regulate the amount of traffic sent before receiving an acknowledgment. UDP is connectionless and is the best protocol for carry digitized VoIP signals.
53. Why are port numbers included in the TCP header of a segment?
- to indicate the correct router interface that should be used to forward a segment
- to identify which switch ports should receive or forward the segment
- to determine which Layer 3 protocol should be used to encapsulate the data
- to enable a receiving host to forward the data to the appropriate application
- to allow the receiving host to assemble the packet in the proper order
54. Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address of 192.168.10.0/24 that has been assigned to a high school building. The largest network in this building has 100 devices. If 192.168.10.0 is the network number for the largest network, what would be the network number for the next largest network, which has 40 devices?
- 192.168.10.0
- 192.168.10.128
- 192.168.10.192
- 192.168.10.224
- 192.168.10.240
Explain:
The first thing to calculate is what IP addresses are used by the largest LAN. Because the LAN has 100 hosts, 7 bits must be left for host bits. This would be a subnet mask of 255.255.255.128 for the largest LAN (192.168.10.0/25). The IP addresses range from 192.168.10.0 through 192.168.10.127. 192.168.10.0 is the network number (all 0s in the host bits) and 192.168.10.127 is the broadcast for this Ethernet LAN (all 1s in the host bits). The next available IP address is the next network number – 192.168.10.128.
55. Which statement is true about variable-length subnet masking?
- Each subnet is the same size.
- The size of each subnet may be different, depending on requirements.
- Subnets may only be subnetted one additional time.
- Bits are returned, rather than borrowed, to create additional subnets.
Explain:
In variable-length subnet masking, bits are borrowed to create subnets. Additional bits may be borrowed to create additional subnets within the original subnets. This may continue until there are no bits available to borrow.
56. In what two situations would UDP be the preferred transport protocol over TCP? (Choose two.)
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
Explain:
UDP is a stateless protocol, which means that neither device on either end of the conversation must keep track of the conversation. As a stateless protocol, UDP is used as the Layer 4 protocol for applications that need speedy (best-effort) delivery. An example of such traffic is the transport of digitized voice or video.
57. What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
- timing and synchronization
- destination and source port numbers
- destination and source physical addresses
- destination and source logical network addresses
Explain:
The destination and source port numbers are used to identify exactly which protocol and process is requesting or responding to a request.
58. What is the TCP mechanism used in congestion avoidance?
- three-way handshake
- socket pair
- two-way handshake
- sliding window
Explain:
TCP uses windows to attempt to manage the rate of transmission to the maximum flow that the network and destination device can support while minimizing loss and retransmissions. When overwhelmed with data, the destination can send a request to reduce the of the window. This congestion avoidance is called sliding windows.
59. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
Explain:
The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
60. A user opens three browsers on the same PC to access www.cisco.com to search for certification course information. The Cisco web server sends a datagram as a reply to the request from one of the web browsers. Which information is used by the TCP/IP protocol stack in the PC to identify which of the three web browsers should receive the reply?
- the destination IP address
- the destination port number
- the source IP address
- the source port number
Explain:
Each web browser client application opens a randomly generated port number in the range of the registered ports and uses this number as the source port number in the datagram that it sends to a server. The server then uses this port number as the destination port number in the reply datagram that it sends to the web browser. The PC that is running the web browser application receives the datagram and uses the destination port number that is contained in this datagram to identify the client application.
61. What are two ways that TCP uses the sequence numbers in a segment? (Choose two.)
- to identify missing segments at the destination
- to reassemble the segments at the remote location
- to specify the order in which the segments travel from source to destination
- to limit the number of segments that can be sent out of an interface at one time
- to determine if the packet changed during transit
62. Which two tasks are functions of the presentation layer? (Choose two.)
- compression
- addressing
- encryption
- session control
- authentication
Explain:
The presentation layer deals with common data format. Encryption, formatting, and compression are some of the functions of the layer. Addressing occurs in the network layer, session control occurs in the session layer, and authentication takes place in the application or session layer.
63. Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
- UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.
- UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
- UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection.
- UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.
- UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
- UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
Explain:
UDP is a simple protocol that provides the basic transport layer functions. It has much lower overhead than TCP because it is not connection-oriented and does not offer the sophisticated retransmission, sequencing, and flow control mechanisms that provide reliability.
64. What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
- wireless networking
- social networking without the Internet
- network printing using a print server
- resource sharing without a dedicated server
Explain:
The peer-to-peer (P2P) networking model allows data, printer, and resource sharing without a dedicated server.
65. A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- ipconfig
- netstat
- nslookup
Explain:
Traceroute (tracert) is a utility that generates a list of hops that were successfully reached along the path from source to destination.This list can provide important verification and troubleshooting information. The ipconfig utility is used to display the IP configuration settings on a Windows PC. The Netstat utility is used to identify which active TCP connections are open and running on a networked host. Nslookup is a utility that allows the user to manually query the name servers to resolve a given host name. This utility can also be used to troubleshoot name resolution issues and to verify the current status of the name servers.
66. Which domain name would be an example of a top-level domain?
- www.cisco.com
- cisco.com
- .com
- root.cisco.com
Explain:
Top-level domains represent a country or type of organization, such as .com or .edu.
67. A PC obtains its IP address from a DHCP server. If the PC is taken off the network for repair, what happens to the IP address configuration?
- The configuration is permanent and nothing changes.
- The address lease is automatically renewed until the PC is returned.
- The address is returned to the pool for reuse when the lease expires.
- The configuration is held by the server to be reissued when the PC is returned.
Explain:
When a DCHP address is issued to a host, it is for a specific lease time. Once the lease expires, the address is returned to the DHCP pool.
68. When planning for network growth, where in the network should packet captures take place to assess network traffic?
- on as many different network segments as possible
- only at the edge of the network
- between hosts and the default gateway
- only on the busiest network segment
Explain:
Because some types of traffic will be only on specific network segments, packet captures for analysis should be performed on as many segments as possible.
69. A wireless host needs to request an IP address. What protocol would be used to process the request?
- FTP
- HTTP
- DHCP
- ICMP
- SNMP
Explain:
The DHCP protocol is used to request, issue, and manage IP addressing information. CSMA/CD is the access method used with wired Ethernet. ICMP is used to test connectivity. SNMP is used with network management and FTP is used for file transfer.
70. Which example of malicious code would be classified as a Trojan horse?
- malware that was written to look like a video game
- malware that requires manual user intervention to spread between systems
- malware that attaches itself to a legitimate program and spreads to other programs when launched
- malware that can automatically spread from one system to another by exploiting a vulnerability in the target
Explain:
A Trojan horse is malicious code that has been written specifically to look like a legitimate program. This is in contrast to a virus, which simply attaches itself to an actual legitimate program. Viruses require manual intervention from a user to spread from one system to another, while a worm is able to spread automatically between systems by exploiting vulnerabilities on those devices.
71. When applied to a router, which command would help mitigate brute-force password attacks against the router?
- exec-timeout 30
- service password-encryption
- banner motd $Max failed logins = 5$
- login block-for 60 attempts 5 within 60
Explain:
The login block-for command sets a limit on the maximum number of failed login attempts allowed within a defined period of time. If this limit is exceeded, no further logins are allowed for the specified period of time. This helps to mitigate brute-force password cracking since it will significantly increase the amount of time required to crack a password. The exec-timeout command specifies how long the session can be idle before the user is disconnected. The service password-encryption command encrypts the passwords in the running configuration. The banner motd command displays a message to users who are logging in to the device.
72. A network technician suspects that a particular network connection between two Cisco switches is having a duplex mismatch. Which command would the technician use to see the Layer 1 and Layer 2 details of a switch port?
- show mac-address-table
- show ip interface brief
- show interfaces
- show running-config
Explain:
The show interfaces command can be used on both routers and switches to see speed, duplex, media type, MAC address, port type, and other Layer 1/Layer 2-related information.
73. Where are Cisco IOS debug output messages sent by default?
- Syslog server
- console line
- memory buffers
- vty lines
Explain:
Debug messages, like other IOS log messages, are sent to the console line by default. Sending these messages to the terminal lines requires the terminal monitor command.
74. Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (not all options are used.)
Question
Answer
user EXEC mode
limited number of basic monitoring commands
the first entrance intro the CLI of an IOS device
privileged EXEC mode
accessed by entering the enable command
identified by a prompt ending with the # character
global configuration mode
changes made affect the operation of the device as a whole
accessed by entering the configure terminal command
75. Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all options are used.)
- FastEthernet0/0 -> packets with destination of 172.17.6.15
- FastEthernet0/1 -> packets with destination of 172.17.14.8
- FastEthernet1/0 -> packets with destination of 172.17.12.10
- FastEthernet1/1 -> packets with destination of 172.17.10.5
- Serial0/0/0 -> packets with destination of 172.17.8.20
76. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is testing connectivity to a remote device with the IP address 10.1.1.1. What does the output of this command indicate?
- Connectivity to the remote device was successful.
- A router along the path did not have a route to the destination.
- A ping packet is being blocked by a security device along the path.
- The connection timed out while waiting for a reply from the remote device.
Explain:
In the output of the ping command, an exclamation mark (!) indicates a response was successfully received, a period (.) indicates that the connection timed out while waiting for a reply, and the letter “U” indicates that a router along the path did not have a route to the destination and sent an ICMP destination unreachable message back to the source.
77. A user is unable to reach the web site when typing http://www.cisco.com in a web browser, but can reach the same site by typing http://72.163.4.161. What is the issue?
- default gateway
- DHCP
- TCP/IP protocol stack
- DNS
Explain:
Domain Name Service (DNS) is used to translate a web address to an IP address. The address of the DNS server is provided via DHCP to host computers.
78. A company is expanding its business to other countries. All branch offices must remain connected to corporate headquarters at all times. Which network technology is required to support this requirement?
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN
- WLAN
Explain:
A local-area network (LAN) normally connects end users and network resources over a limited geographic area using Ethernet technology. A wireless LAN (WLAN) serves the same purpose as a LAN but uses wireless technologies. A metropolitan-area network (MAN) spans a larger geographic area such as a city, and a wide-area network (WAN) connects networks together over a large geographic area. WANs can span cities, countries, or the globe.
79. A home user is looking for an ISP connection that provides high speed digital transmission over regular phone lines. What ISP connection type should be used?
- DSL
- dial-up
- satellite
- cell modem
- cable modem
80. How does quality of service help a network support a wide range of applications and services?
- by limiting the impact of a network failure
- by allowing quick recovery from network failures
- by providing mechanisms to manage congested network traffic
- by providing the ability for the network to grow to accommodate new users
Explain:
Quality of service (QoS), is a vital component of the architecture of a network. With QoS, network administrators can provide applications with predictable and measurable service guarantees through mechanisms that manage congested network traffic.
81. What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface
Explain:
When sending an echo request message, a router will use the IP address of the exit interface as the source IP address. This default behavior can be changed by using an extended ping and specifying a specific source IP address.
82. After making configuration changes on a Cisco switch, a network administrator issues a copy running-config startup-config command. What is the result of issuing this command?
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
Explain:
With the copy running-config startup-config command, the content of the current operating configuration replaces the startup configuration file stored in NVRAM. The configuration file saved in NVRAM will be loaded when the device is restarted.
83. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator has already logged into a Telnet session on the switch, which password is needed to access privileged EXEC mode?
- letmein
- secretin
- lineconin
- linevtyin
Explain:
Telnet accesses a network device through the virtual interface configured with the line VTY command. The password configured under this is required to access the user EXEC mode. The password configured under the line console 0 command is required to gain entry through the console port, and the enable and enable secret passwords are used to allow entry into the privileged EXEC mode.
84. Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
Question
Answer
- physical topology diagram
location of a desktop PC in a classroom
path of cables that connect rooms to wiring closets - logical topology diagram
IP address of a server
Explain:
A logical topology diagram typically depicts the IP addressing scheme and groupings of devices and ports. A physical topology diagram shows how those devices are connected to each other and the network, focusing on the physical locations of intermediary devices, configured ports, and cabling.
85. Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco network device?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection
Explain:
A CLI session using Secure Shell (SSH) provides enhanced security because SSH supports strong passwords and encryption during the transport of session data. The other methods support authentication but not encryption.
86. What function does pressing the Tab key have when entering a command in IOS?
- It aborts the current command and returns to configuration mode.
- It exits configuration mode and returns to user EXEC mode.
- It moves the cursor to the beginning of the next line.
- It completes the remainder of a partially typed word in a command.
Explain:
Pressing the Tab key after a command has been partially typed will cause the IOS to complete the rest of the command.
87. What layer is responsible for routing messages through an internetwork in the TCP/IP model?
- internet
- transport
- network access
- session
Explain:
The TCP/IP model consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and network access. Of these four layers, it is the internet layer that is responsible for routing messages. The session layer is not part of the TCP/IP model but is rather part of the OSI model.
88. Which statement accurately describes a TCP/IP encapsulation process when a PC is sending data to the network?
- Data is sent from the internet layer to the network access layer.
- Packets are sent from the network access layer to the transport layer.
- Segments are sent from the transport layer to the internet layer.
- Frames are sent from the network access layer to the internet layer.
Explain:
When the data is traveling from the PC to the network, the transport layer sends segments to the internet layer. The internet layer sends packets to the network access layer, which creates frames and then converts the frames to bits. The bits are released to the network media.
89. What unique address is embedded in an Ethernet NIC and used for communication on an Ethernet network?
- host address
- IP address
- MAC address
- network address
- k layer
Explain:
The MAC address is a 48-bit address that is burned into every Ethernet NIC. Each MAC address is unique throughout the world.
90. Which procedure is used to reduce the effect of crosstalk in copper cables?
- requiring proper grounding connections
- twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together
- wrapping the bundle of wires with metallic shielding
- designing a cable infrastructure to avoid crosstalk interference
- avoiding sharp bends during installation
Explain:
In copper cables, crosstalk is a disturbance caused by the electric or magnetic fields of a signal on one wire interfering with the signal in an adjacent wire. Twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together can effectively cancel the crosstalk. The other options are effective measures to counter the negative effects of EMI and RFI, but not crosstalk.
91. During the encapsulation process, what occurs at the data link layer for a PC connected to an Ethernet network?
- An IP address is added.
- The logical address is added.
- The physical address is added.
- The process port number is added.
Explain:
The Ethernet frame includes the source and destination physical address. The trailer includes a CRC value in the Frame Check Sequence field to allow the receiving device to determine if the frame has been changed (has errors) during the transmission.
92. What are two characteristics of Ethernet MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
- They are globally unique.
- They are routable on the Internet.
- They are expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits.
- MAC addresses use a flexible hierarchical structure.
- MAC addresses must be unique for both Ethernet and serial interfaces on a device.
Explain:
An Ethernet MAC address is a 48-bit binary value expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits. MAC addresses must be globally unique by design. MAC addresses are in flat structure and thus they are not routable on the Internet. Serial interfaces do not use MAC addresses.
93. If a device receives an Ethernet frame of 60 bytes, what will it do?
- drop the frame
- process the frame as it is
- send an error message to the sending device
- add random data bytes to make it 64 bytes long and then forward it
Explain:
Ethernet standards define the minimum frame size as 64 bytes. A frame less than 64 bytes is considered a “collision fragment” or “runt frame” and is automatically discarded by receiving devices.
94. Under which two circumstances will a switch flood a frame out of every port except the port that the frame was received on? (Choose two.)
- The frame has the broadcast address as the destination address.
- The destination address is unknown to the switch.
- The source address in the frame header is the broadcast address.
- The source address in the frame is a multicast address.
- The destination address in the frame is a known unicast address.
Explain:
A switch will flood a frame out of every port, except the one that the frame was received from, under two circumstances. Either the frame has the broadcast address as the destination address, or the destination address is unknown to the switch.
95. Which switching method has the lowest level of latency?
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
- fast-forward
Explain:
Fast-forward switching begins to forward a frame after reading the destination MAC address, resulting in the lowest latency. Fragment-free reads the first 64 bytes before forwarding. Store-and-forward has the highest latency because it reads the entire frame before beginning to forward it. Both fragment-free and fast-forward are types of cut-through switching.
96. Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- netstat -s
- route print
- show ip route
- netstat -r
- tracert
Explain:
On a Windows host, the route print or netstat -r commands can be used to display the host routing table. Both commands generate the same output. On a router, the show ip route command is used to display the routing table. The netstat –scommand is used to display per-protocol statistics. The tracert command is used to display the path that a packet travels to its destination.
97. Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet forwarding
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection
- flow control
98. What is the binary representation of 0xCA?
- 10111010
- 11010101
- 11001010
- 11011010
Explain:
When converted, CA in hex is equivalent to 11011010 in binary. One way to do the conversion is one nibble at a time, C = 1100 and A = 1010. Combine the two nibbles gives 11001010.
99. At a minimum, which address is required on IPv6-enabled interfaces?
- link-local
- unique local
- site local
- global unicast
Explain:
All IPv6 enabled interfaces must at minimum have a link-local address. Other IPv6 addresses can be assigned to the interface as required.
100. Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
Explain:
Using stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC), a PC can solicit a router and receive the prefix length of the network. From this information the PC can then create its own IPv6 global unicast address.
101. What is the purpose of the command ping ::1?
- It tests the internal configuration of an IPv6 host.
- It tests the broadcast capability of all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the multicast connectivity to all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the reachability of the default gateway for the network.
Explain:
The address ::1 is an IPv6 loopback address. Using the command ping ::1 tests the internal IP stack to ensure that it is configured and functioning correctly. It does not test reachability to any external device, nor does it confirm that IPv6 addresses are properly configured on the host.
102. How many usable IP addresses are available on the 192.168.1.0/27 network?
- 256
- 254
- 62
- 30
- 16
- 32
Explain:
A /27 mask is the same as 255.255.255.224. This leaves 5 host bits. With 5 host bits, 32 IP addresses are possible, but one address represents the subnet number and one address represents the broadcast address. Thus, 30 addresses can then be used to assign to network devices.
103. What is the process of dividing a data stream into smaller pieces before transmission?
- segmentation
- encapsulation
- encoding
- flow control
Explain:
Data streams would cause significant network congestion if they were transmitted as a single large stream of bits. To increase efficiency, data streams are segmented into smaller more manageable pieces which are then transmitted over the network.
104. When IPv4 addressing is manually configured on a web server, which property of the IPv4 configuration identifies the network and host portion for an IPv4 address?
- DNS server address
- subnet mask
- default gateway
- DHCP server address
Explain:
There are several components that need to be entered when configuring IPv4 for an end device:
IPv4 address – uniquely identifies an end device on the network
Subnet mask – determines the network address portion and host portion for an IPv4 address
Default gateway – the IP address of the router interface used for communicating with hosts in another network
DNS server address – the IP address of the Domain Name System (DNS) server
DHCP server address (if DHCP is used) is not configured manually on end devices. It will be provided by a DHCP server when an end device requests an IP address.
105. Which two roles can a computer assume in a peer-to-peer network where a file is being shared between two computers? (Choose two.)
- client
- master
- server
- slave
- transient
Explain:
In a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, two or more computers are connected and can share resources without the use of a dedicated server. The computer that has the file acts as a server for the device (the client) that requests the file.
106. Which two protocols operate at the highest layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack? (Choose two.)
- DNS
- Ethernet
- IP
- POP
- TCP
- UDP
Explain:
The application layer is the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack. Application layer protocols include HTTP, DNS, HTML, TFTP, POP, IMAP, FTP, and SMTP.
107. What is one difference between the client-server and peer-to-peer network models?
- Only in the client-server model can file transfers occur.
- Every device in a peer-to-peer network can function as a client or a server.
- A peer-to-peer network transfers data faster than a transfer using a client-server network.
- A data transfer that uses a device serving in a client role requires that a dedicated server be present.
Explain:
Data transfer speeds depend on a number of factors including the amount of traffic, the quality of service imposed, and the network media. Transfer speeds are not dependent on the network model type. File transfers can occur using the client-server model or the peer-to-peer model. A data transfer between a device acting in the client role and a device acting in the server role can occur in both peer-to-peer and client-server networks.
108. What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
- to request an HTML page from a web server
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
Explain:
There are three common HTTP message types:
GET – used by clients to request data from the web server
POST – used by clients to upload data to a web server
PUT – used by clients to upload data to a web server
109. Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
- peer-to-peer
- master-slave
- client/server
- point-to-point
Explain:
In the client/server network model, a network device assumes the role of server in order to provide a particular service such as file transfer and storage. In the client/server network model, a dedicated server does not have to be used, but if one is present, the network model being used is the client/server model. In contrast, a peer-to-peer network does not have a dedicated server.
110. What network service resolves the URL entered on a PC to the IP address of the destination server?
- DNS
- DHCP
- FTP
- SNMP
Explain:
When a client attempts to connect to a website, the destination URL must be resolved to an IP address. To do this the client queries a Domain Name System (DNS) server.
111. A network engineer is analyzing reports from a recently performed network baseline. Which situation would depict a possible latency issue?
- a change in the bandwidth according to the show interfaces output
- a next-hop timeout from a traceroute
- an increase in host-to-host ping response times
- a change in the amount of RAM according to the show version output
Explain:
While analyzing historical reports an administrator can compare host-to-host timers from the ping command and depict possible latency issues.
112. Which firewall feature is used to ensure that packets coming into a network are legitimate responses to requests initiated from internal hosts?
- stateful packet inspection
- URL filtering
- application filtering
- packet filtering
Explain:
Stateful packet inspection on a firewall checks that incoming packets are actually legitimate responses to requests originating from hosts inside the network. Packet filtering can be used to permit or deny access to resources based on IP or MAC address. Application filtering can permit or deny access based on port number. URL filtering is used to permit or deny access based on URL or on keywords.
113. What is one indication that a Windows computer did not receive an IPv4 address from a DHCP server?
- The computer cannot ping 127.0.0.1.
- Windows displays a DHCP timeout message.
- The computer receives an IP address that starts with 169.254
- The computer cannot ping other devices on the same network with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 range.
Explain:
When a Windows PC cannot communicate with an IPv4 DHCP server, the computer automatically assigns an IP address in the 169.254.0.0/16 range. Any other device on the same network that receives an address in the same range is reachable.
114. Which command can an administrator issue on a Cisco router to send debug messages to the vty lines?
- terminal monitor
- logging console
- logging buffered
- logging synchronous
Explain:
Debug messages, like other IOS log messages, are sent to the console line by default. Sending these messages to the terminal lines requires the terminal monitor command.
115. Fill in the blank.
During data communications, a host may need to send a single message to a specific group of destination hosts simultaneously. This message is in the form of a Multicast message.
116. A medium-sized business is researching available options for connecting to the Internet. The company is looking for a high speed option with dedicated, symmetric access. Which connection type should the company choose?
- DSL
- dialup
- satellite
- leased line
- cable modem
117. What is the purpose of having a converged network?
- to provide high speed connectivity to all end devices
- to make sure that all types of data packets will be treated equally
- to achieve fault tolerance and high availability of data network infrastructure devices
- to reduce the cost of deploying and maintaining the communication infrastructure
Explain:
With the development of technology, companies can now consolidate disparate networks onto one platform called a converged network. In a converged network, voice, video, and data travel over the same network, thus eliminating the need to create and maintain separate networks. This also reduces the costs associated with providing and maintaining the communication network infrastructure.
118. What characteristic of a network enables it to quickly grow to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users?
- reliability
- scalability
- quality of service
- accessibility
Explain:
Networks must be able to quickly grow to support new users and services, without impacting existing users and services. This ability to grow is known as scalability.
119. After several configuration changes are made to a router, the copy running-configuration startup-configuration command is issued. Where will the changes be stored?
- flash
- ROM
- NVRAM
- RAM
- the configuration register
- a TFTP server
120. Refer to the exhibit. From global configuration mode, an administrator is attempting to create a message-of-the-day banner by using the command banner motd V Authorized access only! Violators will be prosecuted! V When users log in using Telnet, the banner does not appear correctly. What is the problem?
- The banner message is too long.
- The delimiting character appears in the banner message.
- The symbol “!” signals the end of a banner message.
- Message-of-the-day banners will only appear when a user logs in through the console port.
121. What are three characteristics of an SVI? (Choose three.)
- It is designed as a security protocol to protect switch ports.
- It is not associated with any physical interface on a switch.
- It is a special interface that allows connectivity by different types of media.
- It is required to allow connectivity by any device at any location.
- It provides a means to remotely manage a switch.
- It is associated with VLAN1 by default.
Explain:
Switches have one or more switch virtual interfaces (SVIs). SVIs are created in software since there is no physical hardware associated with them. Virtual interfaces provide a means to remotely manage a switch over a network that is using IP. Each switch comes with one SVI appearing in the default configuration “out-of-the-box.” The default SVI interface is VLAN1.
122. A technician configures a switch with these commands:SwitchA(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
SwitchA(config-if)# no shutdownWhat is the technician configuring?
- Telnet access
- SVI
- password encryption
- physical switchport access
Explain:
For a switch to have an IP address, a switch virtual interface must be configured. This allows the switch to be managed remotely over the network.
123. In computer communication, what is the purpose of message encoding?
- to convert information to the appropriate form for transmission
- to interpret information
- to break large messages into smaller frames
- to negotiate correct timing for successful communication
Explain:
Before a message is sent across a network it must first be encoded. Encoding is the process of converting the data message into another format suitable for transmission across the physical medium. Each bit of the message is encoded into a pattern of sounds, light waves, or electrical impulses depending on the network media over which the bits are transmitted. The destination host receives and decodes the signals in order to interpret the message.
124. What is a characteristic of multicast messages?
- They are sent to a select group of hosts.
- They must be acknowledged.
- They are sent to a single destination.
- They are sent to all hosts on a network.
Explain:
Multicast is a one-to-many type of communication. Multicast messages are addressed to a specific multicast group.
125. A large corporation has modified its network to allow users to access network resources from their personal laptops and smart phones. Which networking trend does this describe?
- bring your own device
- video conferencing
- online collaboration
- cloud computing
126. True or False.
A dedicated server is not needed when implementing a peer-to-peer network.
- true
- false
127. Which term refers to a network that provides secure access to the corporate offices by suppliers, customers and collaborators?
- Internet
- intranet
- extranet
- extendednet
Explain:
The term Internet refers to the worldwide collection of connected networks. Intranet refers to a private connection of LANs and WANS that belong to an organization and is designed to be accessible to the members of the organization, employees, or others with authorization. Extranets provide secure and safe access to suppliers, customers, and collaborators. Extendednet is not a type of network.
128. What subnet mask is required to support 512 subnets on networks 172.28.0.0/16?
- 255.255.240.0
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.252.0
129. A DHCP server is used to IP addresses dynamically to the hosts on a network. The address pool is configured with 10.29.244.0/25. There are 19 printers on this network that need to use reserve static IP addresses from the pool. How many IP address in the pool are left to be assign to other hosts?
- 210
- 60
- 109
- 107
- 146
Version 5:
130. What is a function of the data link layer?
- provides the formatting of data
- provides for the exchange of data over a common local media
- provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
- provides delivery of data between two applications
131. Which communication tool allows real-time collaboration?
- wiki
- weblog
- instant messaging
132. A host is accessing a Web server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data
- notifying other devices when errors occur
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
133. Refer to the exhibit. From which location did this router load the IOS?
- flash memory
- NVRAM?
- RAM
- ROM
- a TFTP server?
134. Refer to the exhibit. Which action will be successful?
- PC1 can send a ping to 192.168.1.1?.
- PC1 can send a ping to 192.168.1.254?.
- PC2 can send a ping to 192.168.1.1.
- PC2 can send a ping to 192.168.1.254?.
135. Fill in the blank.
Port numbers ranging from 0 to 1023 are considered to be Well Known ports.
136. Fill in the blank.
ISOC, IANA, EIA, and IEEE represent standards organizations which help to promote and maintain an open Internet.
137. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?
- The entire command, configure terminal, must be used.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
138. A company is expanding its business to other countries. All branch offices must remain connected to corporate headquarters at all times. Which network technology is required to support this requirement?
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN
- WLAN
Explain:
A local-area network (LAN) normally connects end users and network resources over a limited geographic area using Ethernet technology. A wireless LAN (WLAN) serves the same purpose as a LAN but uses wireless technologies. A metropolitan-area network (MAN) spans a larger geographic area such as a city, and a wide-area network (WAN) connects networks together over a large geographic area. WANs can span cities, countries, or the globe.
139. A network administrator is upgrading a small business network to give high priority to real-time applications traffic. What two types of network services is the network administrator trying to accommodate? (Choose two.)
- SNMP
- instant messaging
- voice
- FTP
- video
140. Match the situation with the appropriate use of network media.
- Copper Cables
horizontal cabling structure
desktop PCs in an enterprise office - Fiber Optic
backbone cabling in an enterprise
long-haul networks - Wireless
guest access in a coffee shop
waiting rooms in a hospital
Explain:
Copper Cables – horizontal cabling structure and desktop PCs in offices in an enterprise
Fiber optic – backbone cabling in an enterprise and long-haul networks
Wireless – coffee shops and waiting rooms in a hospital
141. Which IPv4 address can be pinged to test the internal TCP/IP operation of a host?
- 0.0.0.0
- 0.0.0.1
- 127.0.0.1
- 192.168.1.1
- 255.255.255.255
142. What three application layer protocols are part of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose three.)
ARP
- DHCP
- DNS
- FTP
- NAT
- PPP
143. Which two protocols function at the internet layer? (Choose two)
- ARP
- BOOTP
- ICMP
- IP
- PPP
144. Which publicly available resources describe protocols, processes, and technologies for the Internet but do not give implementation details?
- Request for Comments
- IRTF research papers
- protocol models
- IEEE standards
145. Which address on a PC does not change, even if the PC is moved to a different network?
- IP address
- default gateway address
- MAC address
- logical address
146. What is the protocol that is used to discover a physical address from a known logical address and what message type does it use?
- ARP, multicast
- DNS, unicast
- DNS, broadcast
- ARP, broadcast
- PING, multicast
- PING, broadcast
147. What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
148. What is an important function of the physical layer of the OSI model?
- It accepts frames from the physical media.
- It encapsulates upper layer data into frames.
- It defines the media access method performed by the hardware interface.
- It encodes frames into electrical, optical, or radio wave signals.
149. Which two statements describe the characteristics of fiber-optic cabling? (Choose two.)
- Fiber-optic cabling does not conduct electricity.
- Fiber-optic cabling has high signal loss.
- Fiber-optic cabling is primarily used as backbone cabling.
- Multimode fiber-optic cabling carries signals from multiple sending devices.
- Fiber-optic cabling uses LEDs for single-mode cab?les and laser technology for multimode cables.
150. What is contained in the trailer of a data-link frame?
- logical address
- physical address
- data
- error detection
151. Refer to the exhibit. A ping to PC3 is issued from PC0, PC1, and PC2 in this exact order. Which MAC addresses will be contained in the S1 MAC address table that is associated with the Fa0/1 port?
- just PC0 and PC1 MAC addresses
- just the PC0 MAC address
- PC0, PC1, and PC2 MAC addresses
- just the PC1 MAC address
- just the PC2 MAC address
152. How does a Layer 3 switch differ from a Layer 2 switch?
- A Layer 3 switch supports VLANs, but a Layer 2 switch does not.
- An IP address can be assigned to a physical port of a Layer 3 switch. However, this is not supported in Layer 2 switches.
- A Layer 3 switch maintains an IP address table instead of a MAC address table.
- A Layer 3 switch learns the MAC addresses that are associated with each of its ports. However, a Layer 2 switch does not.
153. What is the purpose of the routing process?
- to encapsulate data that is used to communicate across a network
- to select the paths that are used to direct traffic to destination networks
- to convert a URL name into an IP address
- to provide secure Internet file transfer
- to forward traffic on the basis of MAC addresses
154. Which technology provides a solution to IPv4 address depletion by allowing multiple devices to share one public IP address?
- ARP
- DNS
- NAT
- SMB
- DHCP
- HTTP
155. Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address configuration shown from PC1. What is a description of the default gateway address?
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the company to the Internet.
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the PC1 LAN to Router1.
- It is the IP address of Switch1 that connects PC1 to other devices on the same LAN.
- It is the IP address of the ISP network device located in the cloud.
156. Which of the following are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet switching
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection
- flow control
157. Which two statements correctly describe a router memory type and its contents? (Choose two.)
- ROM is nonvolatile and contains basic diagnostic software.
- FLASH is nonvolatile and contains a limited portion of the IOS.
- ROM is nonvolatile and stores the running IOS.
- RAM is volatile and stores the IP routing table.
- NVRAM is nonvolatile and stores other system files.
158. In which default order will a router search for startup configuration information?
- NVRAM, RAM, TFTP
- NVRAM, TFTP, setup mode
- setup mode, NVRAM, TFTP
- TFTP, ROM, NVRAM
- flash, ROM, setup mode
159. What happens when part of an Internet VoIP transmission is not delivered to the destination?
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the VoIP transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.
160. Which three IP addresses are private ? (Choose three.)
- 10.172.168.1
- 172.32.5.2
- 192.167.10.10
- 172.20.4.4
- 192.168.5.254
- 224.6.6.6
161. How many bits make up the single IPv6 hextet :10CD:?
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 32
162. What is the effect of configuring the ipv6 unicast-routing command on a router?
- to assign the router to the all-nodes multicast group
- to enable the router as an IPv6 router
- to permit only unicast packets on the router
- to prevent the router from joining the all-routers multicast group
163. Which group of IPv6 addresses cannot be allocated as a host source address?
- FEC0::/10?
- FDFF::/7?
- FEBF::/10?
- FF00::/8
164. What is the purpose of ICMP messages?
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
165. Refer to the exhibit. A technician has configured a user workstation with the IP address and default subnet masks that are shown. Although the user can access all local LAN resources, the user cannot access any Internet sites by using either FQDN or IP addresses. Based upon the exhibit, what could account for this failure?
- The DNS server addresses are incorrect.
- The default gateway address in incorrect.
- The wrong subnet mask was assigned to the workstation.
- The workstation is not in the same network as the DNS servers.
166. A network administrator needs to monitor network traffic to and from servers in a data center. Which features of an IP addressing scheme should be applied to these devices?
- random static addresses to improve security
- addresses from different subnets for redundancy
- predictable static IP addresses for easier identification
- dynamic addresses to reduce the probability of duplicate addresses
167. Refer to the exhibit. Which IP addressing scheme should be changed?
- Site 1
- Site 2
- Site 3
- Site 4
168. Which two notations are useable nibble boundaries when subnetting in IPv6? (Choose two.)
- /62
- /64
- /66
- /68
- /70
169. A host PC has just booted and is attempting to lease an address through DHCP. Which two messages will the client typically broadcast on the network? (Choose two.)
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
170. What is the purpose of the network security accounting function?
- to require users to prove who they are
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to keep track of the actions of a user
- to provide challenge and response questions
171. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router:
R1# copy running-config tftp
Address or name of remote host [ ]?
When the router prompts for an address or remote host name, what IP address should the administrator enter at the prompt?
- 192.168.9.254
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.10.2
- 192.168.11.252
- 192.168.11.254
172. Match the IPv6 address to the IPv6 address type. (Not all options are used.)
173. What two preconfigured settings that affect security are found on most new wireless routers? (Choose two.)
- broadcast SSID
- MAC filtering enabled
- WEP encryption enabled
- PSK authentication required
- default administrator password
174. Which type of wireless security generates dynamic encryption keys each time a client associates with an AP?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA
175. Fill in the blank.
TFTP is a best-effort, connectionless application layer protocol that is used to transfer files.
176. Which two components are necessary for a wireless client to be installed on a WLAN? (Choose two.)
- media
- wireless NIC
- custom adapter
- crossover cable
- wireless bridge
- wireless client software
177. Consider the following range of addresses:
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000:: 2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000:: 2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000:: … 2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::
The prefix-length for the range of addresses is /60
178. Match the phases to their correct stage in the router bootup process. (Not all options are used.)
179. A host is accessing an FTP server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data
- notifying other devices when errors occur
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
180. When is a dial-up connection used to connect to an ISP?
- when a cellular telephone provides the service
- when a high-speed connection is provided over a cable TV network
- when a satellite dish is used
- when a regular telephone line is used
181. On a school network, students are surfing the web, searching the library database, and attending an audio conference with their sister school in Japan. If network traffic is prioritized with QoS, how will the traffic be classified from highest priority to lowest priority?
- audio conference, database, HTTP
- database, HTTP, audio conference
- audio conference, HTTP, database
- database, audio conference, HTTP
182. During normal operation, from which location do most Cisco routers run the IOS?
- RAM
- flash
- NVRAM
- disk drive
183. Which keys act as a hot key combination that is used to interrupt an IOS process?
- Ctrl-Shift-X
- Ctrl-Shift-6
- Ctrl-Z
- Ctrl-C
184. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator wants to change the name of a brand new switch, using the hostname command as shown. What prompt will display after the command is issued??
- HR Switch(config)#?
- Switch(config)#?
- HRSwitch(config)#?
- HR(config)#?
- Switch#
185. A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?
- the TCP/IP stack on a network host
- connectivity between two adjacent Cisco devices
- connectivity between a PC and the default gateway
- connectivity between two PCs on the same network
- physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network
186. What is the correct order for PDU encapsulation?
187. Which device should be used for enabling a host to communicate with another host on a different network?
- switch
- hub
- router
- host
188. A network technician is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical application. The technician notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
189. Which characteristics describe fiber optic cable? (Choose two.)
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding and twisting to protect data.
- It has a maximum speed of 100 Mbps.
- It is the most expensive type of LAN cabling
190. What are two features of a physical, star network topology? (Choose two.)
- It is straightforward to troubleshoot.
- End devices are connected together by a bus.
- It is easy to add and remove end devices.
- All end devices are connected in a chain to each other.
- Each end system is connected to its respective neighbor.
191. A frame is transmitted from one networking device to another. Why does the receiving device check the FCS field in the frame?
- to determine the physical address of the sending device
- to verify the network layer protocol information
- to compare the interface media type between the sending and receiving ends
- to check the frame for possible transmission errors
- to verify that the frame destination matches the MAC address of the receiving device
192. What will a Layer 2 switch do when the destination MAC address of a received frame is not in the MAC table?
- It initiates an ARP request.
- It broadcasts the frame out of all ports on the switch.
- It notifies the sending host that the frame cannot be delivered.
- It forwards the frame out of all ports except for the port at which the frame was received.
193. Which parameter does the router use to choose the path to the destination when there are multiple routes available?
- the lower metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the lower gateway IP address to get to the destination network
- the higher metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the higher gateway IP address to get to the destination network
194. Which two statements describe the functions or characteristics of ROM in a router? (Choose two.)
- stores routing tables
- allows software to be updated without replacing pluggable chips on the motherboard
- maintains instructions for POST diagnostics
- holds ARP cache
- stores bootstrap program
195. Which statement describes a characteristic of the Cisco router management ports?
- A console port is used for remote management of the router.
- A console port is not used for packet forwarding.
- Serial and DSL interfaces are types of management ports.
- Each Cisco router has a LED indicator to provide information about the status of the management ports.
196. What happens when part of an Internet radio transmission is not delivered to the destination?
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the radio transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.
197. What types of addresses make up the majority of addresses within the /8 block IPv4 bit space?
- private addresses
- public addresses
- multicast addresses
- experimental addresses
198. Refer to the exhibit. What is the maximum TTL value that is used to reach the destination www.cisco.com??
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
199. A company has a network address of 192.168.1.64 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192. The company wants to create two subnetworks that would contain 10 hosts and 18 hosts respectively. Which two networks would achieve that? (Choose two.)
- 192.168.1.16/28
- 192.168.1.64/27
- 192.168.1.128/27
- 192.168.1.96/28
- 192.168.1.192/28
200. In a network that uses IPv4, what prefix would best fit a subnet containing 100 hosts?
- /23
- /24
- /25
- /26
201. Which protocol supports rapid delivery of streaming media?
- Transmission Control Protocol
- Real-Time Transport Protocol
- Secure File Transfer Protocol
- Video over Internet Protocol
202. Why would a network administrator use the tracert utility?
- to determine the active TCP connections on a PC
- to check information about a DNS name in the DNS server
- to identify where a packet was lost or delayed on a network
- to display the IP address, default gateway, and DNS server address for a PC
203. Refer to the exhibit. What is the significance of the asterisk (*) in the exhibited output?
- The asterisk shows which file system was used to boot the system.
- The asterisk designates which file system is the default file system.
- An asterisk indicates that the file system is bootable.
- An asterisk designates that the file system has at least one file that uses that file system.
204. Which WLAN security protocol generates a new dynamic key each time a client establishes a connection with the AP?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA
205. Fill in the blank.
Point-to-point communications where both devices can transmit and receive on the medium at the same time are known as full-duplex
206. Match each characteristic to the appropriate email protocol. (Not all options are used.)
207. A host is accessing a Telnet server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data
- notifying other devices when errors occur
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
208. Refer to the exhibit. Which area would most likely be an extranet for the company network that is shown?
- area A
- area B
- area C
- area D
209. Three office workers are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other office workers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
Explain:
QoS mechanisms enable the establishment of queue management strategies that enforce priorities for different categories of application data. Thus, this queuing enables voice data to have priority over transaction data, which has priority over web data.
210. During normal operation, from which location do most Cisco switches and routers run the IOS?
- RAM
- flash
- NVRAM
- disk drive
211. A network administrator is making changes to the configuration of a router. After making the changes and verifying the results, the administrator issues the copy running-config startup-config command. What will happen after this command executes?
- The configuration will be copied to flash.
- The configuration will load when the router is restarted.
- The new configuration file will replace the IOS file.
- The changes will be lost when the router restarts.
212. What information does the loopback test provide?
- The TCP/IP stack on the device is working correctly.
- The device has end-to-end connectivity.
- DHCP is working correctly.
- The Ethernet cable is working correctly.
- The device has the correct IP address on the network.
213. What happens when a switch receives a frame and the calculated CRC value is different than the value that is in the FCS field?
- The switch places the new CRC value in the FCS field and forwards the frame.
- The switch notifies the source of the bad frame.
- The switch drops the frame.
- The switch floods the frame to all ports except the port through which the frame arrived to notify the hosts of the error.
214. Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame?
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF
- 127.0.0.1
- 01-00-5E-00-AA-23
215. What is the auto-MDIX feature on a switch?
- the automatic configuration of an interface for 10/100/1000 Mb/s operation
- the automatic configuration of an interface for a straight-through or a crossover Ethernet cable connection
- the automatic configuration of full-duplex operation over a single Ethernet copper or optical cable
- the ability to turn a switch interface on or off accordingly if an active connection is detected
216. What are the two main components of Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)? (Choose two.)
- adjacency tables
- MAC-address tables
- routing tables
- ARP tables
- forwarding information base (FIB)
217. Which statement describes the sequence of processes executed by a router when it receives a packet from a host to be delivered to a host on another network?
- It receives the packet and forwards it directly to the destination host.
- It de-encapsulates the packet, selects the appropriate path, and encapsulates the packet to forward it toward the destination host
- It de-encapsulates the packet and forwards it toward the destination host.
- It selects the path and forwards it toward the destination host.
218. Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 has two interfaces that were configured with correct IP addresses and subnet masks. Why does the show ip route command output not display any information about the directly connected networks??
- The directly connected networks have to be created manually to be displayed in the routing table.
- The routing table will only display information about these networks when the router receives a packet.
- The no shutdown command was not issued on these interfaces.
- The gateway of last resort was not configured.
219. What happens when part of an Internet television transmission is not delivered to the destination?
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the television transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.
220. Which three statements characterize the transport layer protocols? (Choose three.)
- TCP and UDP port numbers are used by application layer protocols.
- TCP uses port numbers to provide reliable transportation of IP packets.
- UDP uses windowing and acknowledgments for reliable transfer of data.
- TCP uses windowing and sequencing to provide reliable transfer of data.
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. UDP is a connectionless protocol.
221. Which statement is true regarding the UDP client process during a session with a server?
- Datagrams that arrive in a different order than that in which they were sent are not placed in order.
- A session must be established before datagrams can be exchanged.
- A three-way handshake takes place before the transmission of data begins.
- Application servers have to use port numbers above 1024 in order to be UDP capable.
222. Which two components are configured via software in order for a PC to participate in a network environment? (Choose two.)
- MAC address
- IP address
- kernel
- shell
- subnet mask
223. Which two reasons generally make DHCP the preferred method of assigning IP addresses to hosts on large networks? (Choose two.)
- It eliminates most address configuration errors.
- It ensures that addresses are only applied to devices that require a permanent address.
- It guarantees that every device that needs an address will get one.
- It provides an address only to devices that are authorized to be connected to the network.
- It reduces the burden on network support staff.
224. What is the subnet address for the address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
- 2001:DB8:BC15::0
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A::0
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1::1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12::0
225. What is the purpose of the network security authentication function?
- to require users to prove who they are
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to keep track of the actions of a user
- to provide challenge and response questions
226. Which type of wireless security makes use of dynamic encryption keys each time a client associates with an AP?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA
227. Launch PT – Hide and Save PT.
Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then fill in the blank.
The Server0 message isb ”winner”
228. Which field in an IPv4 packet header will typically stay the same during its transmission?
- Packet Length
- Destination Address
- Flag
- Time-to-Live
229. Launch PT – Hide and Save PT
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. Which IPv6 address is assigned to the Serial0/0/0 interface on RT2?
- 2001:db8:abc:1::1
- 2001:db8:abc:5::1
- 2001:db8:abc:5::2
- 2001:db8:abc:10::15
230. What must be configured to enable Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) on most Cisco devices that perform Layer 3 switching?
- Manually configure next-hop Layer 2 addresses.
- Issue the no shutdown command on routed ports.
- CEF is enabled by default, so no configuration is necessary.
- Manually map Layer 2 addresses to Layer 3 addresses to populate the forwarding information base (FIB).
231. What is the purpose of adjacency tables as used in Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)?
- to populate the forwarding information base (FIB)
- to maintain Layer 2 next-hop addresses
- to allow the separation of Layer 2 and Layer 3 decision making
- to update the forwarding information base (FIB)
232. Which statement describes a characteristic of the network layer in the OSI model?
- It manages the data transport between the processes running on each host.
- In the encapsulation process, it adds source and destination port numbers to the IP header.
- When a packet arrives at the destination host, its IP header is checked by the network layer to determine where the packet has to be routed.
- Its protocols specify the packet structure and processing used to carry the data from one host to another.
233. A user gets an IP address of 192.168.0.1 from the company network administrator. A friend of the user at a different company gets the same IP address on another PC. How can two PCs use the same IP address and still reach the Internet, send and receive email, and search the web?
- Both users must be using the same Internet Service Provider.
- ISPs use Network Address Translation to change a user IP address into an address that can be used on the Internet.
- ISPs use Domain Name Service to change a user IP address into a public IP address that can be used on the Internet.
- Both users must be on the same network.
234. Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
- to ensure the fastest possible download speed
- because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
- because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
- because HTTP requires reliable delivery
235. What is the valid most compressed format possible of the IPv6 address 2001:0DB8:0000:AB00:0000:0000:0000:1234?
- 2001:DB8:0:AB00::1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB::1234
- 2001:DB8::AB00::1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB:0:1234
236. What field content is used by ICMPv6 to determine that a packet has expired?
- TTL field
- CRC field
- Hop Limit field
- Time Exceeded field
237. Which firewall technique blocks incoming packets unless they are responses to internal requests?
- port filtering
- stateful packet inspection
- URL filtering
- application filtering
238. A network technician is investigating network connectivity from a PC to a remote host with the address 10.1.1.5. Which command issued on the PC will return to the technician the complete path to the remote host?
- trace 10.1.1.5
- traceroute 10.1.1.5
- tracert 10.1.1.5
- ping 10.1.1.5
239. Fill in the blank.
To prevent faulty network devices from carrying dangerous voltage levels, equipment must be grounded correctly
240. What is a possible hazard that can be caused by network cables in a fire?
- The cable insulation could be flammable.
- Users could be exposed to excessive voltage.
- Network cables could be exposed to water.
- The network cable could explode.
241. What device is commonly used to verify a UTP cable?
- a multimeter
- an Optical Time Domain Reflectometer
- a cable tester
- an ohmmeter
242. What needs to be checked when testing a UTP network cable?
- capacitance
- wire map
- inductance
- flexibility
243. Refer to the exhibit. A ping to PC2 is issued from PC0, PC1, and PC3 in this exact order. Which MAC addresses will be contained in the S1 MAC address table that is associated with the Fa0/1 port?
- just PC0 and PC1 MAC addresses
- just the PC0 MAC address
- PC0, PC1, and PC2 MAC addresses
- just the PC1 MAC address
- just the PC2 MAC address
244. Which function is provided by TCP?
- data encapsulation
- detection of missing packets
- communication session control
- path determination for data packets
245. What does a router use to determine where to send data it receives from the network?
- an ARP table
- a routing table
- the destination PC physical address
- a switching table
246. Which router interface should be used for direct remote access to the router via a modem?
- an inband router interface
- a console port
- a serial WAN interface
- an AUX port
247. A technician is configuring a router to allow for all forms of management access. As part of each different type of access, the technician is trying to type the command login. Which configuration mode should be entered to do this task?
- user executive mode
- global configuration mode
- any line configuration mode
- privileged EXEC mode
248. Which three statements characterize the transport layer protocols? (Choose three.)
- TCP and UDP port numbers are used by application layer protocols.
- TCP uses port numbers to provide reliable transportation of IP packets.
- UDP uses windowing and acknowledgments for reliable transfer of data.
- TCP uses windowing and sequencing to provide reliable transfer of data.
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. UDP is a connectionless protocol.
249. Refer to the exhibit. A TCP segment from a server has been captured by Wireshark, which is running on a host. What acknowledgement number will the host return for the TCP segment that has been received?
- 2
- 21
- 250
- 306
- 2921
250. Which statement is true about an interface that is configured with the IPv6 address command?
- IPv6 traffic-forwarding is enabled on the interface.
- A link-local IPv6 address is automatically configured on the interface.
- A global unicast IPv6 address is dynamically configured on the interface.
- Any IPv4 addresses that are assigned to the interface are replaced with an IPv6 address.
251. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator must send a message to everyone on the router A network. What is the broadcast address for network 172.16.16.0/22?
- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
252. A network administrator is variably subnetting a given block of IPv4 addresses. Which combination of network addresses and prefix lengths will make the most efficient use of addresses when the need is for 2 subnets capable of supporting 10 hosts and 1 subnet that can support 6 hosts?
- 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.144/28
10.1.1.160/29 - 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.144/28
10.1.1.160/28 - 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.140/28
10.1.1.158/26 - 10.1.1.128/26
10.1.1.144/26
10.1.1.160/26 - 10.1.1.128/26
10.1.1.140/26
10.1.1.158/28
253. How many additional bits should be borrowed from a /26 subnet mask in order to create subnets for WAN links that need only 2 useable addresses?
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
254. A network administrator requires access to manage routers and switches locally and remotely. Match the description to the access method. (Not all options are used.)
255. Refer to the exhibit. The administrator configured the access to the console and the vty lines of a router. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?
- Unauthorized individuals can connect to the router via Telnet without entering a password.
- Because the IOS includes the login command on the vty lines by default, access to the device via Telnet will require authentication.
- Access to the vty lines will not be allowed via Telnet by anyone.
- Because the login command was omitted, the password cisco command is not applied to the vty lines.
256. An administrator issued the service password-encryption command to apply encryption to the passwords configured for enable password, vty, and console lines. What will be the consequences if the administrator later issues the no service password-encryption command?
- It will remove encryption from all passwords.
- It will reverse only the vty and console password encryptions.
- It will not reverse any encryption.
- It will reverse only the enable password encryption.
257. After making configuration changes, a network administrator issues a copy running-config startup-config command in a Cisco switch. What is the result of issuing this command?
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
258. What are two features of ARP? (Choose two.)
- If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.
- An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
- When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
- If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
- If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.
259. A network administrator is enabling services on a newly installed server. Which two statements describe how services are used on a server? (Choose two.)
- Data sent with a service that uses TCP is received in the order the data was sent.
- A port is considered to be open when it has an active server application that is assigned to it.
- An individual server can have two services that are assigned to the same port number.
- An individual server cannot have multiple services running at the same time.
- Server security can be improved by closing ports that are associated with unused services.
260. Given the binary address of 11101100 00010001 00001100 00001010, which address does this represent in dotted decimal format?
- 234.17.10.9
- 234.16.12.10
- 236.17.12.6
- 236.17.12.10
261. A particular telnet site does not appear to be responding on a Windows 7 computer. What command could the technician use to show any cached DNS entries for this web page?
- ipconfig /all
- arp -a
- ipconfig /displaydns
- nslookup
262. Fill in the blank.
Network devices come in two physical configurations. Devices that have expansion slots that provide the flexibility to add new modules have a Modular configuration.
263. Refer to the exhibit. What is the maximum TIL value that is used to reach the destination www.cisco.com?
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
264. Which statement is true about DHCP operation?
- When a device that is configured to use DHCP boots, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network.
- A client must wait for lease expiration before it sends another DHCPREOUEST message.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the IP address and sub net masK to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway.
- If the client receives several DHCPOFFER messages from different servers, it sends a unicast DHCPREOUEST message to the server from which it chooses to obtain the IP information.
265. Which type of wireless security is easily compromised?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA
266. A network administrator notices that the throughput on the network appears lower than expected when compared to the end-to-end network bandwidth. Which three factors can explain this difference? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic
- the type of data encapsulation in use
- the type of traffic
- the number and type of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the connection to the ISP
- the reliability of the network backbone
267. A host PC is attempting to lease an address through DHCP. What message is sent by the server to the client know it is able to use the provided IP information?
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
268. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses console line to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?
- letmein
- secretin
- lineconin
- linevtyin
Explain:
Telnet accesses a network device through the virtual interface configured with the line VTY command. The password configured under this is required to access the user EXEC mode. The password configured under the line console 0 command is required to gain entry through the console port, and the enable and enable secret passwords are used to allow entry into the privileged EXEC mode.
269. How many bits would need to be borrowed if a network admin were given the IP addressing scheme of 172.16.0.0/16 and needed no more than 16 subnet with equal number of hosts?
- 10
- 12
- 2
- 4
- 8
270. Question:
It will give 4 options about ping, the correct one is:
The PC2 will be able to ping 192.168.1.1
271. Which statement best describes the operation of the File Transfer Protocol?
- An FTP client uses a source port number of 21 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP Server.
- An FTP client uses a source port number of 20 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of data traffic with an FTP Server.
- An FTP server uses a source port number of 20 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP client.
- An FTP server uses a source port number of 21 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP client.
272. A client is establishing a TCP session with a server. How is the acknowledgment number in the response segment to the client determined?
- The acknowledgment number field is modified by adding 1 to the randomly chosen initial sequence number in response to the client.
- The acknowledgment number is set to 11 to signify an acknowledgment packet and synchronization packet back to the client.
- The acknowledgment number field uses a random source port number in response to the client.
- The acknowledgment number is set to 1 to signify an acknowledgment packet back to the client.
273. Why does layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP and subnet Mask?
- to identify host address and destination host;
- to identify network address of destination host;
- to identify faulty frames;
- to identify broadcast address of destination network;
274. There was also a question about if you activated service password encryption in the past and you prompt “no service password encryption” what password are modified ?
- no password at all;
- password of the lines are in clear;
- login password;
- ?
275. What type of communication rule would best describe CSMA/CD?
- message encapsulation
- flow control
- message encoding
- access method
276. What is the primary reason to subnet IPv6 prefixes?
- to conserve IPv6 addresses
- to avoid wasting IPv6 addresses
- to conserve IPv6 prefixes
- to create a hierarchical Layer 3 network design
277. Which statement describes data throughput?
- It is the measure of the bits transferred across the media under perfect conditions.
- It is the measure of the bits transferred across the media over a given period of time.
- It indicates the capacity of a particular medium to carry data.
- It is the guaranteed data transfer rate offered by an ISP.
278. Fill in the blank. Use a number.
IPv4 multicast addresses are directly mapped to IEEE 802 (Ethernet) MAC addresses using the last ___4___ of the 28 available bits in the IPv4 multicast group address.
279. How could a faulty network device create a source of hazard for a user? (Choose two.)
- It could stop functioning.
- It could apply dangerous voltage to other pieces of equipment.
- It could explode.
- It could produce an unsafe electromagnetic field.
- It could apply dangerous voltage to itself.
280. What are three important considerations when planning the structure of an IP addressing scheme? (Choose three.)
- preventing duplication of addresses
- providing and controlling access
- documenting the network
- monitoring security and performance
- conserving addresses
- implementing new services
281. What is the metric value that is used to reach the 10.1.1.0 network in the following routing table entry? D 10.1.1.0/24 [90/2170112] via 209.165.200.226, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/0
- 24
- 90
- 05
- 2170112
282. Which two services or protocols use the preferred UDP protocol for fast transmission and low overhead? (Choose two)
- VoIP
- DNS
- HTTP
- FTP
- POP3
New Questions (v6.0):
283. What action does a DHCPv4 client take if it receives more than one DHCPOFFER from multiple DHCP servers?
- It sends a DHCPREQUEST that identifies which lease offer the client is accepting.
- It sends a DHCPNAK and begins the DHCP process over again.
- It discards both offers and sends a new DHCPDISCOVER.
- It accepts both DHCPOFFER messages and sends a DHCPACK.
284. To what legacy address class does the address 10.0.0.0 belong?
- Class B
- Class D
- Class A
- Class C
- Class E
285. How many IPv4 addresses are available to be assigned to hosts on a network that has a mask of 255.255.255.248?
- 16
- 14
- 8
- 254
- 6
- 2
286. What type of communication medium is used with a wireless LAN connection?
- radio waves
- fiber
- microwave
- UTP
287. Which method of IPv6 prefix assignment relies on the prefix contained in RA messages?
- EUI-64
- static
- SLAAC
- stateful DHCPv6
288. What is a characteristic of DNS?
- DNS servers can cache recent queries to reduce DNS query traffic.
- DNS servers are programmed to drop requests for name translations that are not within their zone.
- All DNS servers must maintain mappings for the entire DNS structure.
- DNS relies on a hub-and-spoke topology with centralized servers.
289. What is the prefix for the host address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
- 2001:DB8:BC15
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12
290. What information is maintained in the CEF adjacency table?
- Layer 2 next hops
- MAC address to IPv4 address mappings
- IP address to interface mappings
- the IP addresses of all neighboring routers
291. Which command can an administrator issue on a Cisco router to send debug messages to the vty lines?
- terminal monitor
- logging console
- logging buffered
- logging synchronous
Explain:
Debug messages, like other IOS log messages, are sent to the console line by default. Sending these messages to the terminal lines requires the terminal monitor command.
292. What is an example of a top-level domain?
- root.cisco.com
- http://www.cisco.com
- .com
- cisco.com
Explain:
Top-level domains represent a country or type of organization, such as .com or .edu.
293. Which protocol requires the establishment of a session between sender and receiver hosts prior to transmitting data?
- UDP
- TCP
- IP
- ICMP
294. Which two protocols operate at the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose two.)
- TCP
- IP
- UDP
- POP
- DNS
- Ethernet
295. What does a client do when it has UDP datagrams to send?
- It sends to the server a segment with the SYN flag set to synchronize the conversation.
- It just sends the datagrams.
- It queries the server to see if it is ready to receive data.
- It sends a simplified three-way handshake to the server.
296. What is a characteristic of multicast messages?
- They are sent to all hosts on a network.
- They must be acknowledged.
- They are sent to a select group of hosts.
- They are sent to a single destination.
297. Which protocol or service uses UDP for a client-to-server communication and TCP for server-to-server communication?
- FTP
- HTTP
- DNS
- SMTP
298. In what networking model would eDonkey, eMule, BitTorrent, Bitcoin, and LionShare be used?
- master-slave
- client-based
- peer-to-peer
- point-to-point
299. A network technician is attempting to configure an interface by entering the following command: SanJose(config)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 . The command is rejected by the device. What is the reason for this?
- The interface is shutdown and must be enabled before the switch will accept the IP address.
- The subnet mask information is incorrect.
- The command syntax is wrong.
- The command is being entered from the wrong mode of operation.
300. Refer to the exhibit. A company uses the address block of 128.107.0.0/16 for its network. What subnet mask would provide the maximum number of equal size subnets while providing enough host addresses for each subnet in the exhibit?
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.224
Explanation: The largest subnet in the topology has 100 hosts in it so the subnet mask must have at least 7 host bits in it (27-2=126). 255.255.255.0 has 8 hosts bits, but this does not meet the requirement of providing the maximum number of subnets.
CCNA 1 v7 ITN Final Exam Answers INTRODUCTION TO NETWORKS 2021
1. What two ICMPv6 message types must be permitted through IPv6 access control lists to allow resolution of Layer 3 addresses to Layer 2 MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
neighbor solicitations*
echo requests
neighbor advertisements*
echo replies
router solicitations
router advertisements
2. Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
FEC0::/10
FDEE::/7
FE80::/10*
FF00::/8
Explanation:
Link-local addresses are in the range of FE80::/10 to FEBF::/10. The original IPv6 specification defined site-local addresses and used the prefix range FEC0::/10, but these addresses were deprecated by the IETF in favor of unique local addresses. FDEE::/7 is a unique local address because it is in the range of FC00::/7 to FDFF::/7. IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8.
3. What would be the interface ID of an IPv6 enabled interface with a MAC address of 1C-6F-65-C2-BD-F8 when the interface ID is generated by using the EUI-64 process?
0C6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
1E6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8*
C16F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
106F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
4. An organization is assigned an IPv6 address block of 2001:db8:0:ca00::/56. How many subnets can be created without using bits in the interface ID space?
256*
512
1024
4096
5. Refer to the exhibit.
If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
172.168.10.99
CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
172.168.10.65
BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB*
AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
Explanation:
When a host sends information to a distant network, the Layer 2 frame header will contain a source and destination MAC address. The source address will be the originating host device. The destination address will be the router interface that connects to the same network. In the case of host A sending information to host B, the source address is AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA and the destination address is the MAC address assigned to the R2 Ethernet interface, BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB.
6. When a switch configuration includes a user-defined error threshold on a per-port basis, to which switching method will the switch revert when the error threshold is reached?
cut-through
store-and-forward*
fast-forward
fragment-free
7. Which two statements are correct about MAC and IP addresses during data transmission if NAT is not involved? (Choose two.)
Destination IP addresses in a packet header remain constant along the entire path to a target host.*
Destination MAC addresses will never change in a frame that goes across seven routers.
Every time a frame is encapsulated with a new destination MAC address, a new destination IP address is needed.
Destination and source MAC addresses have local significance and change every time a frame goes from one LAN to another.*
A packet that has crossed four routers has changed the destination IP address four times.
8. What is one main characteristic of the data link layer?
It generates the electrical or optical signals that represent the 1 and 0 on the media.
It converts a stream of data bits into a predefined code.
It shields the upper layer protocol from being aware of the physical medium to be used in the communication.*
It accepts Layer 3 packets and decides the path by which to forward the packet to a remote network.
9. What are three characteristics of the CSMA/CD process? (Choose three.)
The device with the electronic token is the only one that can transmit after a collision.
A device listens and waits until the media is not busy before transmitting.*
After detecting a collision, hosts can attempt to resume transmission after a random time delay has expired.*
All of the devices on a segment see data that passes on the network medium.*
A jam signal indicates that the collision has cleared and the media is not busy.
Devices can be configured with a higher transmission priority.
10. What are two primary responsibilities of the Ethernet MAC sublayer? (Choose two.)
error detection
frame delimiting
accessing the media*
data encapsulation*
logical addressing
11. Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
netstat -s
route print*
show ip route
netstat –r*
tracert
Explanation:
On a Windows host, the route print or netstat -r commands can be used to display the host routing table. Both commands generate the same output. On a router, the show ip route command is used to display the routing table. The netstat –s command is used to display per-protocol statistics. The tracert command is used to display the path that a packet travels to its destination.
12. What are two functions that are provided by the network layer? (Choose two.)
directing data packets to destination hosts on other networks*
placing data on the network medium
carrying data between processes that are running on source and destination hosts
providing dedicated end-to-end connections
providing end devices with a unique network identifier*
13. Which two statements describe features of an IPv4 routing table on a router? (Choose two.)
Directly connected interfaces will have two route source codes in the routing table: C and S.
If there are two or more possible routes to the same destination, the route associated with the higher metric value is included in the routing table.*
The netstat -r command can be used to display the routing table of a router.
The routing table lists the MAC addresses of each active interface.
It stores information about routes derived from the active router interfaces.
If a default static route is configured in the router, an entry will be included in the routing table with source code S.*
14. How does the service password-encryption command enhance password security on Cisco routers and switches?
It requires encrypted passwords to be used when connecting remotely to a router or switch with Telnet.
It encrypts passwords that are stored in router or switch configuration files.*
It requires that a user type encrypted passwords to gain console access to a router or switch.
It encrypts passwords as they are sent across the network.
Explanation: The service password-encryption command encrypts plaintext passwords in the configuration file so that they cannot be viewed by unauthorized users.
15. Why would a Layer 2 switch need an IP address?
to enable the switch to send broadcast frames to attached PCs
to enable the switch to function as a default gateway
to enable the switch to be managed remotely*
to enable the switch to receive frames from attached PCs
Explanation: A switch, as a Layer 2 device, does not need an IP address to transmit frames to attached devices. However, when a switch is accessed remotely through the network, it must have a Layer 3 address. The IP address must be applied to a virtual interface rather than to a physical interface. Routers, not switches, function as default gateways.
16. What characteristic describes identity theft?
the use of stolen credentials to access private data*
software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
software that identifies fast-spreading threats
a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
17. Match each description to its corresponding term. (Not all options are used.)
18. A user sends an HTTP request to a web server on a remote network. During encapsulation for this request, what information is added to the address field of a frame to indicate the destination?
the network domain of the destination host
the IP address of the default gateway
the MAC address of the destination host
the MAC address of the default gateway*
19. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function of TCP or UDP in this situation? (Choose three.)
The source port field identifies the running application or service that will handle data returning to the PC.*
The TCP process running on the PC randomly selects the destination port when establishing a session with the server.
UDP segments are encapsulated within IP packets for transport across the network.*
The UDP destination port number identifies the application or service on the server which will handle the data.*
TCP is the preferred protocol when a function requires lower network overhead.
The TCP source port number identifies the sending host on the network.
Explanation: Layer 4 port numbers identify the application or service which will handle the data. The source port number is added by the sending device and will be the destination port number when the requested information is returned. Layer 4 segments are encapsulated within IP packets. UDP, not TCP, is used when low overhead is needed. A source IP address, not a TCP source port number, identifies the sending host on the network. Destination port numbers are specific ports that a server application or service monitors for requests.
20. Match each description with the corresponding TCP mechanism. (Not all options are used.)
21. Refer to the exhibit.
Which two network addresses can be assigned to the network containing 10 hosts? Your answers should waste the fewest addresses, not reuse addresses that are already assigned, and stay within the 10.18.10.0/24 range of addresses. (Choose two.)
10.18.10.200/28
10.18.10.208/28*
10.18.10.240/27
10.18.10.200/27
10.18.10.224/27
10.18.10.224/28*
Explanation: Addresses 10.18.10.0 through 10.18.10.63 are taken for the leftmost network. Addresses 192 through 199 are used by the center network. Because 4 host bits are needed to accommodate 10 hosts, a /28 mask is needed. 10.18.10.200/28 is not a valid network number. Two subnets that can be used are 10.18.10.208/28 and 10.18.10.224/28.
22. Refer to the exhibit.
A company uses the address block of 128.107.0.0/16 for its network. What subnet mask would provide the maximum number of equal size subnets while providing enough host addresses for each subnet in the exhibit?
255.255.255.192
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.128*
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.224
Explanation: The largest subnet in the topology has 100 hosts in it so the subnet mask must have at least 7 host bits in it (27-2=126). 255.255.255.0 has 8 hosts bits, but this does not meet the requirement of providing the maximum number of subnets.
23. A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.240*
255.255.255.248
255.255.255.252
Explanation:
If the same mask is to be used, then the network with the most hosts must be examined for number of hosts. Because this is 10 hosts, 4 host bits are needed. The /28 or 255.255.255.240 subnet mask would be appropriate to use for these networks.
24. Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
25. What two pieces of information are displayed in the output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose two.)
IP addresses*
interface descriptions
MAC addresses
next-hop addresses
Layer 1 statuses*
speed and duplex settings
Explanation: The command show ip interface brief shows the IP address of each interface, as well as the operational status of the interfaces at both Layer 1 and Layer 2. In order to see interface descriptions and speed and duplex settings, use the command show running-config interface. Next-hop addresses are displayed in the routing table with the command show ip route, and the MAC address of an interface can be seen with the command show interfaces.
26. A user is complaining that an external web page is taking longer than normal to load.The web page does eventually load on the user machine. Which tool should the technician use with administrator privileges in order to locate where the issue is in the network?
ping
nslookup
tracert*
ipconfig /displaydns
27. A network technician is researching the use of fiber optic cabling in a new technology center. Which two issues should be considered before implementing fiber optic media? (Choose two.)
Fiber optic cabling requires different termination and splicing expertise from what copper cabling requires.*
Fiber optic cabling requires specific grounding to be immune to EMI.
Fiber optic cabling is susceptible to loss of signal due to RFI.
Fiber optic cable is able to withstand rough handling.
Fiber optic provides higher data capacity but is more expensive than copper cabling.*
28. What technique is used with UTP cable to help protect against signal interference from crosstalk?
wrapping a foil shield around the wire pairs
twisting the wires together into pairs*
terminating the cable with special grounded connectors
encasing the cables within a flexible plastic sheath
Explanation: To help prevent the effects of crosstalk, UTP cable wires are twisted together into pairs. Twisting the wires together causes the magnetic fields of each wire to cancel each other out.
29. A network administrator is designing the layout of a new wireless network. Which three areas of concern should be accounted for when building a wireless network? (Choose three.)
extensive cabling
mobility options
packet collision
interference*
security*
coverage área*
Explanation: The three areas of concern for wireless networks focus on the size of the coverage area, any nearby interference, and providing network security. Extensive cabling is not a concern for wireless networks, as a wireless network will require minimal cabling for providing wireless access to hosts. Mobility options are not a component of the areas of concern for wireless networks.
30. Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
31. Users report that the network access is slow. After questioning the employees, the network administrator learned that one employee downloaded a third-party scanning program for the printer. What type of malware might be introduced that causes slow performance of the network?
virus
worm*
phishing
spam
Explanation: A cybersecurity specialist needs to be familiar with the characteristics of the different types of malware and attacks that threaten an organization.
32. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.*
A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
Explanation:
The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
33. Refer to the exhibit.
Host B on subnet Teachers transmits a packet to host D on subnet Students. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 addresses are contained in the PDUs that are transmitted from host B to the router?
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200****
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-dd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-cd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.99
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.100.200
34. What does the term “attenuation” mean in data communication?
strengthening of a signal by a networking device
leakage of signals from one cable pair to another
time for a signal to reach its destination
loss of signal strength as distance increases*
35. Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?
The entire command, configure terminal, must be used.
The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.*
The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
36. Which two protocols operate at the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose two.)
TCP
IP
UDP
POP*
DNS*
Ethernet
37. A company has a file server that shares a folder named Public. The network security policy specifies that the Public folder is assigned Read-Only rights to anyone who can log into the server while the Edit rights are assigned only to the network admin group. Which component is addressed in the AAA network service framework?
automation
accounting
authentication
authorization*
Explanation:
After a user is successfully authenticated (logged into the server), the authorization is the process of determining what network resources the user can access and what operations (such as read or edit) the user can perform.
38. What three requirements are defined by the protocols used in network communcations to allow message transmission across a network? (Choose three.)
message size*
message encoding*
connector specifications
media selection
delivery options*
end-device installation
39. What are two characteristics of IP? (Choose two.)
does not require a dedicated end-to-end connection*
operates independently of the network media*
retransmits packets if errors occur
re-assembles out of order packets into the correct order at the receiver end
guarantees delivery of packets
Explanation:
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a connectionless, best effort protocol. This means that IP requires no end-to-end connection nor does it guarantee delivery of packets. IP is also media independent, which means it operates independently of the network media carrying the packets.
40. An employee of a large corporation remotely logs into the company using the appropriate username and password. The employee is attending an important video conference with a customer concerning a large sale. It is important for the video quality to be excellent during the meeting. The employee is unaware that after a successful login, the connection to the company ISP failed. The secondary connection, however, activated within seconds. The disruption was not noticed by the employee or other employees. What three network characteristics are described in this scenario? (Choose three.)
security*
quality of service*
scalability
powerline networking
integrity
fault tolerance*
41. What are two common causes of signal degradation when using UTP cabling? (Choose two.)
improper termination*
low-quality shielding in cable
installing cables in conduit
low-quality cable or connectors*
loss of light over long distances
42. Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
192.168.1.64/26*
192.168.1.32/27
192.168.1.32/28
192.168.1.64/29
Explanation: For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
43. Refer to the exhibit.
On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
This host does not have a default gateway configured.
There are 4 hops between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.*
There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.*
The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
Explanation:
The output displays a successful Layer 3 connection between a host computer and a host at 19.168.100.1. It can be determined that 4 hops exist between them and the average transmission time is 1 milliseconds. Layer 3 connectivity does not necessarily mean that an application can run between the hosts.
44. Which two statements describe how to assess traffic flow patterns and network traffic types using a protocol analyzer? (Choose two.)
Capture traffic on the weekends when most employees are off work.
Capture traffic during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types.*
Only capture traffic in the areas of the network that receive most of the traffic such as the data center.
Perform the capture on different network segments.*
Only capture WAN traffic because traffic to the web is responsible for the largest amount of traffic on a network.
Explanation: Traffic flow patterns should be gathered during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types. The capture should also be performed on different network segments because some traffic will be local to a particular segment.
45. What is the consequence of configuring a router with the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command?
All router interfaces will be automatically activated.
The IPv6 enabled router interfaces begin sending ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages.*
Each router interface will generate an IPv6 link-local address.
It statically creates a global unicast address on this router.
46. Which three layers of the OSI model map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
Application*
network
data link
sesión*
presentation*
transport
Explanation: The TCP/IP model consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and network access. The OSI model consists of seven layers: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical. The top three layers of the OSI model: application, presentation, and session map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model.
47. Refer to the exhibit.
If PC1 is sending a packet to PC2 and routing has been configured between the two routers, what will R1 do with the Ethernet frame header attached by PC1?
nothing, because the router has a route to the destination network
open the header and use it to determine whether the data is to be sent out S0/0/0
open the header and replace the destination MAC address with a new one
remove the Ethernet header and configure a new Layer 2 header before sending it out S0/0/0*
Explanation: When PC1 forms the various headers attached to the data one of those headers is the Layer 2 header. Because PC1 connects to an Ethernet network, an Ethernet header is used. The source MAC address will be the MAC address of PC1 and the destination MAC address will be that of G0/0 on R1. When R1 gets that information, the router removes the Layer 2 header and creates a new one for the type of network the data will be placed onto (the serial link).
48. What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.*
A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
49. What are two features of ARP? (Choose two.)
When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.*
If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.*
50. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 90 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
255.255.255.128*
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.248
255.255.255.224
51. What are two ICMPv6 messages that are not present in ICMP for IPv4? (Choose two.)
Neighbor Solicitation*
Destination Unreachable
Host Confirmation
Time Exceeded
Router Advertisement*
Route Redirection
52. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 80. What service is the client requesting?
DHCP
SMTP
DNS
HTTP*
53. What is an advantage for small organizations of adopting IMAP instead of POP?
POP only allows the client to store messages in a centralized way, while IMAP allows distributed storage.
Messages are kept in the mail servers until they are manually deleted from the email client.*
When the user connects to a POP server, copies of the messages are kept in the mail server for a short time, but IMAP keeps them for a long time.
IMAP sends and retrieves email, but POP only retrieves email.
Explanation: IMAP and POP are protocols that are used to retrieve email messages. The advantage of using IMAP instead of POP is that when the user connects to an IMAP-capable server, copies of the messages are downloaded to the client application. IMAP then stores the email messages on the server until the user manually deletes those messages.
54. A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
tracert
ipconfig
netstat
nslookup*
Explanation:
Traceroute (tracert) is a utility that generates a list of hops that were successfully reached along the path from source to destination.This list can provide important verification and troubleshooting information. The ipconfig utility is used to display the IP configuration settings on a Windows PC. The Netstat utility is used to identify which active TCP connections are open and running on a networked host. Nslookup is a utility that allows the user to manually query the name servers to resolve a given host name. This utility can also be used to troubleshoot name resolution issues and to verify the current status of the name servers.
55. Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media
enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium*
integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
implements a process to delimit fields within an Ethernet 2 frame
places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame*
Explanation: The data link layer is actually divided into two sublayers:
+ Logical Link Control (LLC): This upper sublayer defines the software processes that provide services to the network layer protocols. It places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame. This information allows multiple Layer 3 protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6, to utilize the same network interface and media.
+ Media Access Control (MAC): This lower sublayer defines the media access processes performed by the hardware. It provides data link layer addressing and delimiting of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium and the type of data link layer protocol in use.
56. The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.*
The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
Explanation: A default gateway address is typically configured on all devices to allow them to communicate beyond just their local network.In a switch this is achieved using the command ip default-gateway .
57. What happens when the transport input ssh command is entered on the switch vty lines?
The SSH client on the switch is enabled.
The switch requires a username/password combination for remote access.
Communication between the switch and remote users is encrypted.*
The switch requires remote connections via a proprietary client software.
Explanation: The transport input ssh command when entered on the switch vty (virtual terminal lines) will encrypt all inbound controlled telnet connections.
58. Match the type of threat with the cause. (Not all options are used.)
59. A disgruntled employee is using some free wireless networking tools to determine information about the enterprise wireless networks. This person is planning on using this information to hack the wireless network. What type of attack is this?
DoS
access
reconnaissance*
Trojan horse
60. What service is provided by HTTP?
Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.*
61. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 67. What service is the client requesting?
FTP
DHCP*
Telnet
SSH
62. What are two problems that can be caused by a large number of ARP request and reply messages? (Choose two.)
Switches become overloaded because they concentrate all the traffic from the attached subnets.
The ARP request is sent as a broadcast, and will flood the entire subnet.*
The network may become overloaded because ARP reply messages have a very large payload due to the 48-bit MAC address and 32-bit IP address that they contain.
A large number of ARP request and reply messages may slow down the switching process, leading the switch to make many changes in its MAC table.*
All ARP request messages must be processed by all nodes on the local network.
63. A group of Windows PCs in a new subnet has been added to an Ethernet network. When testing the connectivity, a technician finds that these PCs can access local network resources but not the Internet resources. To troubleshoot the problem, the technician wants to initially confirm the IP address and DNS configurations on the PCs, and also verify connectivity to the local router. Which three Windows CLI commands and utilities will provide the necessary information? (Choose three.)
netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor
arp -a
tracert
ping*
ipconfig*
nslookup*
telnet
64. During the process of forwarding traffic, what will the router do immediately after matching the destination IP address to a network on a directly connected routing table entry?
analyze the destination IP address
switch the packet to the directly connected interface*
look up the next-hop address for the packet
discard the traffic after consulting the route table
65. What characteristic describes antispyware?
applications that protect end devices from becoming infected with malicious software*
a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
66. A network administrator needs to keep the user ID, password, and session contents private when establishing remote CLI connectivity with a switch to manage it. Which access method should be chosen?
Telnet
AUX
SSH*
Console
67. What are the two most effective ways to defend against malware? (Choose two.)
Implement a VPN.
Implement network firewalls.
Implement RAID.
Implement strong passwords.
Update the operating system and other application software.*
Install and update antivirus software.*
Explanation: A cybersecurity specialist must be aware of the technologies and measures that are used as countermeasures to protect the organization from threats and vulnerabilities.
68. Which type of security threat would be responsible if a spreadsheet add-on disables the local software firewall?
brute-force attack
Trojan horse*
DoS
buffer overflow
Explanation: A Trojan horse is software that does something harmful, but is hidden in legitimate software code. A denial of service (DoS) attack results in interruption of network services to users, network devices, or applications. A brute-force attack commonly involves trying to access a network device. A buffer overflow occurs when a program attempts to store more data in a memory location than it can hold.
69. Match the header field with the appropriate layer of the OSI model. (Not all options are used.)
70. Which frame field is created by a source node and used by a destination node to ensure that a transmitted data signal has not been altered by interference, distortion, or signal loss?
User Datagram Protocol field
transport layer error check field
flow control field
frame check sequence field*
error correction process field
71. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 4 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
255.255.255.248*
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.128
255.255.255.192
72. What service is provided by POP3?
Retrieves email from the server by downloading the email to the local mail application of the client.*
An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
73. What two security solutions are most likely to be used only in a corporate environment? (Choose two.)
antispyware
virtual private networks*
intrusion prevention systems*
strong passwords
antivirus software
74. What characteristic describes antivirus software?
applications that protect end devices from becoming infected with malicious software*
a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
75. What mechanism is used by a router to prevent a received IPv4 packet from traveling endlessly on a network?
It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
It decrements the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Time Exceeded message to the source host.*
It increments the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Parameter Problem message to the source host.
76. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 69. What service is the client requesting?
DNS
DHCP
SMTP
TFTP*
77. An administrator defined a local user account with a secret password on router R1 for use with SSH. Which three additional steps are required to configure R1 to accept only encrypted SSH connections? (Choose three.)
Configure DNS on the router.
Generate two-way pre-shared keys.
Configure the IP domain name on the router.*
Generate the SSH keys.*
Enable inbound vty SSH sessions.*
Enable inbound vty Telnet sessions.
78. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame*
adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
responsible for internal structure of Ethernet frame
enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection*
79. An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::2. What is the target of this packet?
all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link
all IPv6 DHCP servers
all IPv6 enabled devices across the network
all IPv6 configured routers on the local link*
80. What are the three parts of an IPv6 global unicast address? (Choose three.)
subnet ID*
subnet mask
broadcast address
global routing prefix*
interface ID*
81. A client is using SLAAC to obtain an IPv6 address for its interface. After an address has been generated and applied to the interface, what must the client do before it can begin to use this IPv6 address?
It must send a DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST message to request the address of the DNS server.
It must send a DHCPv6 REQUEST message to the DHCPv6 server to request permission to use this address.
It must send an ICMPv6 Router Solicitation message to determine what default gateway it should use.
It must send an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message to ensure that the address is not already in use on the network.*
82. A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
Enter CTRL-Z at the privileged mode prompt.
Exit global configuration mode.
Power cycle the device.
Reboot the device.
Exit privileged EXEC mode and press Enter.*
83. What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
token passing
CSMA/CA*
priority ordering
CSMA/CD
84. What is a function of the data link layer?
provides the formatting of data
provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
provides delivery of data between two applications
provides for the exchange of frames over a common local media*
85. What is the purpose of the TCP sliding window?
to ensure that segments arrive in order at the destination
to end communication when data transmission is complete
to inform a source to retransmit data from a specific point forward
to request that a source decrease the rate at which it transmits data*
86. What characteristic describes spyware?
a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user*
an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
the use of stolen credentials to access private data
87. Which switching method drops frames that fail the FCS check?
store-and-forward switching*
borderless switching
ingress port buffering
cut-through switching
88. Two pings were issued from a host on a local network. The first ping was issued to the IP address of the default gateway of the host and it failed. The second ping was issued to the IP address of a host outside the local network and it was successful. What is a possible cause for the failed ping?
The default gateway is not operational.
The default gateway device is configured with the wrong IP address.
Security rules are applied to the default gateway device, preventing it from processing ping requests.*
The TCP/IP stack on the default gateway is not working properly.
89. What service is provided by FTP?
A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.*
Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
90. A user is attempting to access http://www.cisco.com/ without success. Which two configuration values must be set on the host to allow this access? (Choose two.)
DNS server*
source port number
HTTP server
source MAC address
default Gateway*
91. Which two statements accurately describe an advantage or a disadvantage when deploying NAT for IPv4 in a network? (Choose two.)
NAT adds authentication capability to IPv4.
NAT introduces problems for some applications that require end-to-end connectivity.*
NAT will impact negatively on switch performance.
NAT provides a solution to slow down the IPv4 address depletion.*
NAT improves packet handling.
NAT causes routing tables to include more information.
92. What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.128
255.255.255.192*
255.255.255.224
93. Refer to the exhibit.
PC1 issues an ARP request because it needs to send a packet to PC2. In this scenario, what will happen next?
PC2 will send an ARP reply with its MAC address.*
RT1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/0 MAC address.
RT1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
SW1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
SW1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/1 MAC address.
Explanation:
When a network device wants to communicate with another device on the same network, it sends a broadcast ARP request. In this case, the request will contain the IP address of PC2. The destination device (PC2) sends an ARP reply with its MAC address.
94. What service is provided by BOOTP?
Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
Legacy application that enables a diskless workstation to discover its own IP address and find a BOOTP server on the network.*
A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
95. What characteristic describes adware?
a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user*
the use of stolen credentials to access private data
an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
96. What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.*
End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
97. Match a statement to the related network model. (Not all options are used.)
Place the options in the following order:
peer-to-peer network
[+] no dedicated server is required
[+] client and server roles are set on a per request basis
peer-to-peer aplication
[#] requires a specific user interface
[#] a background service is required
Explanation:
Peer-to-peer networks do not require the use of a dedicated server, and devices can assume both client and server roles simultaneously on a per request basis. Because they do not require formalized accounts or permissions, they are best used in limited situations. Peer-to-peer applications require a user interface and background service to be running, and can be used in more diverse situations.
98. Which information does the show startup-config command display?
the IOS image copied into RAM
the bootstrap program in the ROM
the contents of the current running configuration file in the RAM
the contents of the saved configuration file in the NVRAM*
Explanation:
The show startup-config command displays the saved configuration located in NVRAM. The show running-config command displays the contents of the currently running configuration file located in RAM.
99. Refer to the exhibit.
What three facts can be determined from the viewable output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose three.)
Two physical interfaces have been configured.
The switch can be remotely managed.*
One device is attached to a physical interface.*
Passwords have been configured on the switch.
Two devices are attached to the switch.
The default SVI has been configured.*
Explanation:
Vlan1 is the default SVI. Because an SVI has been configured, the switch can be configured and managed remotely. FastEthernet0/0 is showing up and up, so a device is connected.
100. Match each type of frame field to its function. (Not all options are used.)
101. What is the subnet ID associated with the IPv6 address 2001:DA48:FC5:A4:3D1B::1/64?
2001:DA48::/64
2001:DA48:FC5::A4:/64
2001:DA48:FC5:A4::/64*
2001::/64
102. Match the firewall function to the type of threat protection it provides to the network. (Not all options are used.)
packet filtering – prevents access based on IP or MAC address
URL filtering – prevents access to websites
network address translator – (none)
stateful packet inspection – prevents unsolicited incoming sessions
application filtering – prevents access by port number
Explanation:Firewall products come packaged in various forms. These products use different techniques for determining what will be permitted or denied access to a network. They include the following:
+ Packet filtering – Prevents or allows access based on IP or MAC addresses
+ Application filtering – Prevents or allows access by specific application types based on port numbers
+ URL filtering – Prevents or allows access to websites based on specific URLs or keywords
+ Stateful packet inspection (SPI) – Incoming packets must be legitimate responses to requests from internal hosts. Unsolicited packets are blocked unless permitted specifically. SPI can also include the capability to recognize and filter out specific types of attacks, such as denial of service (DoS)
103. Users are reporting longer delays in authentication and in accessing network resources during certain time periods of the week. What kind of information should network engineers check to find out if this situation is part of a normal network behavior?
syslog records and messages
the network performance baseline*
debug output and packet captures
network configuration files
104. What characteristic describes a VPN?
software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
software that identifies fast-spreading threats
a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization*
a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
105. Which two statements are correct in a comparison of IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers? (Choose two.)
The Source Address field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.*
The Version field from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6.
The Destination Address field is new in IPv6.
The Header Checksum field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6.*
106. A network administrator wants to have the same network mask for all networks at a particular small site. The site has the following networks and number of devices:
IP phones – 22 addresses PCs – 20 addresses needed Printers – 2 addresses needed Scanners – 2 addresses needed
The network administrator has deemed that 192.168.10.0/24 is to be the network used at this site. Which single subnet mask would make the most efficient use of the available addresses to use for the four subnetworks?
255.255.255.192
255.255.255.252
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.248
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.224*
107. What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
A company can monopolize the market.
The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
It encourages competition and promotes choices.*
Explanation:
A monopoly by one company is not a good idea from a user point of view. If a protocol can only be run on one brand, it makes it difficult to have mixed equipment in a network. A proprietary protocol is not free to use. An open standard protocol will in general be implemented by a wide range of vendors.
108. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 200 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.0*
255.255.255.248
255.255.255.224
109. What are three commonly followed standards for constructing and installing cabling? (Choose three.)
cost per meter (foot)
cable lengths*
connector color
pinouts*
connector types*
tensile strength of plastic insulator
110. Refer to the exhibit.
What is wrong with the displayed termination?
The woven copper braid should not have been removed.
The wrong type of connector is being used.
The untwisted length of each wire is too long.*
The wires are too thick for the connector that is used.
Explanation: When a cable to an RJ-45 connector is terminated, it is important to ensure that the untwisted wires are not too long and that the flexible plastic sheath surrounding the wires is crimped down and not the bare wires. None of the colored wires should be visible from the bottom of the jack.
111. Match the characteristic to the category. (Not all options are used.)
112. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 143. What service is the client requesting?
IMAP*
FTP
SSH
Telnet
113. What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
default window size
connectionless communication
port numbering*
3-way handshake
ability to to carry digitized voice
use of checksum*
Explanation:
Both TCP and UDP use source and destination port numbers to distinguish different data streams and to forward the right data segments to the right applications. Error checking the header and data is done by both protocols by using a checksum calculation to determine the integrity of the data that is received. TCP is connection-oriented and uses a 3-way handshake to establish an initial connection. TCP also uses window to regulate the amount of traffic sent before receiving an acknowledgment. UDP is connectionless and is the best protocol for carry digitized VoIP signals.
114. Which value, that is contained in an IPv4 header field, is decremented by each router that receives a packet?
Header Length
Differentiated Services
Time-to-Live*
Fragment Offset
115. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 21. What service is the client requesting?
FTP*
LDAP
SLP
SNMP
116. What attribute of a NIC would place it at the data link layer of the OSI model?
attached Ethernet cable
IP address
MAC address*
RJ-45 port
TCP/IP protocol stack
117. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 10 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
255.255.255.192
255.255.255.248
255.255.255.224
255.255.255.240*
118. A user is executing a tracert to a remote device. At what point would a router, which is in the path to the destination device, stop forwarding the packet?
when the router receives an ICMP Time Exceeded message
when the RTT value reaches zero
when the host responds with an ICMP Echo Reply message
when the value in the TTL field reaches zero*
when the values of both the Echo Request and Echo Reply messages reach zero
Explanation:
When a router receives a traceroute packet, the value in the TTL field is decremented by 1. When the value in the field reaches zero, the receiving router will not forward the packet, and will send an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source.
119. Refer to the exhibit.
The network administrator has assigned the LAN of LBMISS an address range of 192.168.10.0. This address range has been subnetted using a /29 prefix. In order to accommodate a new building, the technician has decided to use the fifth subnet for configuring the new network (subnet zero is the first subnet). By company policies, the router interface is always assigned the first usable host address and the workgroup server is given the last usable host address. Which configuration should be entered into the properties of the workgroup server to allow connectivity to the Internet?
IP address: 192.168.10.65 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.76
IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.33*
IP address: 192.168.10.41 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.46
IP address: 192.168.10.254 subnet mask: 255.255.255.0, default gateway: 192.168.10.1
Explanation:
Using a /29 prefix to subnet 192.168.10.0 results in subnets that increment by 8:
192.168.10.0 (1)
192.168.10.8 (2)
192.168.10.16 (3)
192.168.10.24 (4)
192.168.10.32 (5)
120. Refer to the exhibit.
The switches are in their default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for its default gateway. Which network hosts will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
only host D
only router R1
only hosts A, B, and C
only hosts A, B, C, and D
only hosts B and C
only hosts B, C, and router R1*
Explanation:
Since host A does not have the MAC address of the default gateway in its ARP table, host A sends an ARP broadcast. The ARP broadcast would be sent to every device on the local network. Hosts B, C, and router R1 would receive the broadcast. Router R1 would not forward the message.
121. Which two traffic types use the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP)? (Choose two.)
video*
web
file transfer
voice*
peer to peer
122. Which wireless technology has low-power and data rate requirements making it popular in home automation applications?
ZigBee*
LoRaWAN
5G
Wi-Fi
123. Which layer of the TCP/IP model provides a route to forward messages through an internetwork?
application
network access
internet*
transport
Explanation:
The OSI model network layer corresponds directly to the internet layer of the TCP/IP model and is used to describe protocols that address and route messages through an internetwork.
124. Which type of server relies on record types such as A, NS, AAAA, and MX in order to provide services?
DNS*
email
file
web
Explanation:
A DNS server stores records that are used to resolve IP addresses to host names. Some DNS record types include the following:
A – an end device IPv4 address
NS – an authoritative name server
AAAA – an end device IPv6 address
MX – a mail exchange record
125. What are proprietary protocols?
protocols developed by private organizations to operate on any vendor hardware
protocols that can be freely used by any organization or vendor
protocols developed by organizations who have control over their definition and operation*
a collection of protocols known as the TCP/IP protocol suite
Explanation:
Proprietary protocols have their definition and operation controlled by one company or vendor. Some of them can be used by different organizations with permission from the owner. The TCP/IP protocol suite is an open standard, not a proprietary protocol.
126. What service is provided by DNS?
Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.*
A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
127. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 110. What service is the client requesting?
DNS
DHCP
SMTP
POP3*
128. What command can be used on a Windows PC to see the IP configuration of that computer?
show ip interface brief
ping
show interfaces
ipconfig*
129. A wired laser printer is attached to a home computer. That printer has been shared so that other computers on the home network can also use the printer. What networking model is in use?
client-based
master-slave
point-to-point
peer-to-peer (P2P)*
Explanation: Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks have two or more network devices that can share resources such as printers or files without having a dedicated server.
130. What characteristic describes a virus?
a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
the use of stolen credentials to access private data
an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
malicious software or code running on an end device*
131. Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
financial transactions, web page, audio conference
audio conference, financial transactions, web page
financial transactions, audio conference, web page*
audio conference, web page, financial transactions
132. Match the description to the IPv6 addressing component. (Not all options are used.)
133. Refer to the exhibit.
If Host1 were to transfer a file to the server, what layers of the TCP/IP model would be used?
only application and Internet layers
only Internet and network access layers
only application, Internet, and network access layers
application, transport, Internet, and network access layers*
only application, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
application, session, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
Explanation: The TCP/IP model contains the application, transport, internet, and network access layers. A file transfer uses the FTP application layer protocol. The data would move from the application layer through all of the layers of the model and across the network to the file server.
134. Match the characteristic to the forwarding method. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: A store-and-forward switch always stores the entire frame before forwarding, and checks its CRC and frame length. A cut-through switch can forward frames before receiving the destination address field, thus presenting less latency than a store-and-forward switch. Because the frame can begin to be forwarded before it is completely received, the switch may transmit a corrupt or runt frame. All forwarding methods require a Layer 2 switch to forward broadcast frames.
135. Refer to the exhibit.
The IP address of which device interface should be used as the default gateway setting of host H1?
R1: S0/0/0
R2: S0/0/1
R1: G0/0*
R2: S0/0/0
136. What service is provided by Internet Messenger?
An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.*
Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
137. Refer to the exhibit.
Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network.
Explanation: Network A needs to use 192.168.0.128 /25, which yields 128 host addresses.
Network B needs to use 192.168.0.0 /26, which yields 64 host addresses.
Network C needs to use 192.168.0.96 /27, which yields 32 host addresses.
Network D needs to use 192.168.0.80/30, which yields 4 host addresses.
138. Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol was responsible for building the table that is shown?
interface: 192.168.1.67 — 0xa internet address physical address type 192.168.1.254 64-0f-29-0d-36-91 dynamic . . . interface: 10.82.253.91 —- 0x10
DHCP
ARP*
DNS
ICMP
139. A network administrator notices that some newly installed Ethernet cabling is carrying corrupt and distorted data signals. The new cabling was installed in the ceiling close to fluorescent lights and electrical equipment. Which two factors may interfere with the copper cabling and result in signal distortion and data corruption? (Choose two.)
crosstalk
extended length of cabling
RFI*
EMI*
signal attenuation
140. A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in its ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
It will send the frame and use its own MAC address as the destination.
It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
It will send a request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.*
141. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication?
integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper*
enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media*
142. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 53. What service is the client requesting?
DNS*
NetBIOS (NetBT)
POP3
IMAP
143. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 25 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
255.255.255.128
255.255.255.192
255.255.255.224*
255.255.255.240
144. What characteristic describes a Trojan horse?
malicious software or code running on an end device*
an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
the use of stolen credentials to access private data
a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
145. What service is provided by HTTPS?
Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.*
Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
146. A technician with a PC is using multiple applications while connected to the Internet. How is the PC able to keep track of the data flow between multiple application sessions and have each application receive the correct packet flows?
The data flow is being tracked based on the destination MAC address of the technician PC.
The data flow is being tracked based on the source port number that is used by each application.*
The data flow is being tracked based on the source IP address that is used by the PC of the technician.
The data flow is being tracked based on the destination IP address that is used by the PC of the technician.
Explanation:
The source port number of an application is randomly generated and used to individually keep track of each session connecting out to the Internet. Each application will use a unique source port number to provide simultaneous communication from multiple applications through the Internet.
147. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 61 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.224
255.255.255.192*
255.255.255.128
148. Refer to the exhibit.
Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation:
Network A needs to use 192.168.0.0 /25 which yields 128 host addresses.
Network B needs to use 192.168.0.128 /26 which yields 64 host addresses.
Network C needs to use 192.168.0.192 /27 which yields 32 host addresses.
Network D needs to use 192.168.0.224 /30 which yields 4 host addresses.
149. What characteristic describes a DoS attack?
the use of stolen credentials to access private data
a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service*
150. Match the application protocols to the correct transport protocols
151. What service is provided by SMTP?
Allows clients to send email to a mail server and the servers to send email to other servers.*
Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
152. Match a statement to the related network model. (Not all options are used.)
Place the options in the following order:
peer-to-peer network
[+] no dedicated server is required
[+] client and server roles are set on a per request basis
peer-to-peer aplication
[#] requires a specific user interface
[#] a background service is required
Explanation:
Peer-to-peer networks do not require the use of a dedicated server, and devices can assume both client and server roles simultaneously on a per request basis. Because they do not require formalized accounts or permissions, they are best used in limited situations. Peer-to-peer applications require a user interface and background service to be running, and can be used in more diverse situations.
153. Match the application protocols to the correct transport protocols.
Answer.
TCP
FTP
HTTP
SMTP
UDP
DHCP
TFTP
154. Refer to the exhibit.
A network engineer has been given the network address of 192.168.99.0 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192 to subnet across the four networks shown. How many total host addresses are unused across all four subnets?
88
200*
72
224
158
155. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame*
handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame*
applies delimiting of Ethernet frame fields to synchronize communication between nodes
156. Which connector is used with twisted-pair cabling in an Ethernet LAN?
LC conector
SC conector
BNC
RJ 11
RJ 45 (TRUE ANSWERS)*
157. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 22. What service is the client requesting?
SSH*
SMB/CIFS
HTTPS
SLP
158. What characteristic describes an IPS?
a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
software that identifies fast-spreading threats*
software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
159. What service is provided by DHCP?
Dynamically assigns IP addresses to end and intermediary devices.*
160. Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
responsible for internal structure of Ethernet frame
applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame
integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium*
handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware*
161. Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data*
responsible for internal structure of Ethernet frame
implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium*
applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame
162. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media*
enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper*
163. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame*
handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame*
applies delimiting of Ethernet frame fields to synchronize communication between nodes
CCNA 1 – ITN Introduction to Networks (Version 7.00) – ITNv7 Final Exam Answers Full
Number of questions: 60; Passed score: 80-100%
1. What two ICMPv6 message types must be permitted through IPv6 access control lists to allow resolution of Layer 3 addresses to Layer 2 MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
- neighbor solicitations
- echo requests
- neighbor advertisements
- echo replies
- router solicitations
- router advertisements
2. Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FEC0::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FE80::/10
- FF00::/8
Explain:
Link-local addresses are in the range of FE80::/10 to FEBF::/10. The original IPv6 specification defined site-local addresses and used the prefix range FEC0::/10, but these addresses were deprecated by the IETF in favor of unique local addresses. FDEE::/7 is a unique local address because it is in the range of FC00::/7 to FDFF::/7. IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8.
3. What would be the interface ID of an IPv6 enabled interface with a MAC address of 1C-6F-65-C2-BD-F8 when the interface ID is generated by using the EUI-64 process?
- 0C6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 1E6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- C16F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 106F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
Explanation: To derive the EUI-64 interface ID by using the MAC address 1C-6F-65-C2-BD-F8, three steps are taken.
- Change the seventh bit of the MAC address from a binary 0 to a binary 1 which changes the hex C, into a hex E.
- Insert hex digits FFFE into the middle of the address.
- Rewrite the address in IPv6 format.
The three steps, when complete, give the interface ID of 1E6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8.
4. An organization is assigned an IPv6 address block of 2001:db8:0:ca00::/56. How many subnets can be created without using bits in the interface ID space?
- 256
- 512
- 1024
- 4096
5. Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- 172.168.10.99
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- 172.168.10.65
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
Explain:
When a host sends information to a distant network, the Layer 2 frame header will contain a source and destination MAC address. The source address will be the originating host device. The destination address will be the router interface that connects to the same network. In the case of host A sending information to host B, the source address is AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA and the destination address is the MAC address assigned to the R2 Ethernet interface, BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB.
6. When a switch configuration includes a user-defined error threshold on a per-port basis, to which switching method will the switch revert when the error threshold is reached?
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fast-forward
- fragment-free
7. Which two statements are correct about MAC and IP addresses during data transmission if NAT is not involved? (Choose two.)
- Destination IP addresses in a packet header remain constant along the entire path to a target host.
- Destination MAC addresses will never change in a frame that goes across seven routers.
- Every time a frame is encapsulated with a new destination MAC address, a new destination IP address is needed.
- Destination and source MAC addresses have local significance and change every time a frame goes from one LAN to another.
- A packet that has crossed four routers has changed the destination IP address four times.
8. What is one main characteristic of the data link layer?
- It generates the electrical or optical signals that represent the 1 and 0 on the media.
- It converts a stream of data bits into a predefined code.
- It shields the upper layer protocol from being aware of the physical medium to be used in the communication.
- It accepts Layer 3 packets and decides the path by which to forward the packet to a remote network.
9. What are three characteristics of the CSMA/CD process? (Choose three.)
- The device with the electronic token is the only one that can transmit after a collision.
- A device listens and waits until the media is not busy before transmitting.
- After detecting a collision, hosts can attempt to resume transmission after a random time delay has expired.
- All of the devices on a segment see data that passes on the network medium.
- A jam signal indicates that the collision has cleared and the media is not busy.
- Devices can be configured with a higher transmission priority.
Explanation: The Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) process is a contention-based media access control mechanism used on shared media access networks, such as Ethernet. When a device needs to transmit data, it listens and waits until the media is available (quiet), then it will send data. If two devices transmit at the same time, a collision will occur. Both devices will detect the collision on the network. When a device detects a collision, it will stop the data transmission process, wait for a random amount of time, then try again.
10. What are two primary responsibilities of the Ethernet MAC sublayer? (Choose two.)
- error detection
- frame delimiting
- accessing the media
- data encapsulation
- logical addressing
11. Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- netstat -s
- route print
- show ip route
- netstat -r
- tracert
Explain:
On a Windows host, the route print or netstat -r commands can be used to display the host routing table. Both commands generate the same output. On a router, the show ip route command is used to display the routing table. The netstat –s command is used to display per-protocol statistics. The tracert command is used to display the path that a packet travels to its destination.
12. What are two functions that are provided by the network layer? (Choose two.)
- directing data packets to destination hosts on other networks
- placing data on the network medium
- carrying data between processes that are running on source and destination hosts
- providing dedicated end-to-end connections
- providing end devices with a unique network identifier
13. Which two statements describe features of an IPv4 routing table on a router? (Choose two.)
- Directly connected interfaces will have two route source codes in the routing table: C and S.
- If there are two or more possible routes to the same destination, the route associated with the higher metric value is included in the routing table.
- The netstat -r command can be used to display the routing table of a router.
- The routing table lists the MAC addresses of each active interface.
- It stores information about routes derived from the active router interfaces.
- If a default static route is configured in the router, an entry will be included in the routing table with source code S.
14. How does the service password-encryption command enhance password security on Cisco routers and switches?
- It requires encrypted passwords to be used when connecting remotely to a router or switch with Telnet.
- It encrypts passwords that are stored in router or switch configuration files.
- It requires that a user type encrypted passwords to gain console access to a router or switch.
- It encrypts passwords as they are sent across the network.
Explain: The service password-encryption command encrypts plaintext passwords in the configuration file so that they cannot be viewed by unauthorized users.
15. Why would a Layer 2 switch need an IP address?
- to enable the switch to send broadcast frames to attached PCs
- to enable the switch to function as a default gateway
- to enable the switch to be managed remotely
- to enable the switch to receive frames from attached PCs
Explanation: A switch, as a Layer 2 device, does not need an IP address to transmit frames to attached devices. However, when a switch is accessed remotely through the network, it must have a Layer 3 address. The IP address must be applied to a virtual interface rather than to a physical interface. Routers, not switches, function as default gateways.
16. What characteristic describes identity theft?
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
- software that identifies fast-spreading threats
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
17. Match each description to its corresponding term. (Not all options are used.)
18. A user sends an HTTP request to a web server on a remote network. During encapsulation for this request, what information is added to the address field of a frame to indicate the destination?
- the network domain of the destination host
- the IP address of the default gateway
- the MAC address of the destination host
- the MAC address of the default gateway
Explanation: A frame is encapsulated with source and destination MAC addresses. The source device will not know the MAC address of the remote host. An ARP request will be sent by the source and will be responded to by the router. The router will respond with the MAC address of its interface, the one which is connected to the same network as the source.
19. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function of TCP or UDP in this situation? (Choose three.)
- The source port field identifies the running application or service that will handle data returning to the PC.
- The TCP process running on the PC randomly selects the destination port when establishing a session with the server.
- UDP segments are encapsulated within IP packets for transport across the network.
- The UDP destination port number identifies the application or service on the server which will handle the data.
- TCP is the preferred protocol when a function requires lower network overhead.
- The TCP source port number identifies the sending host on the network.
Explanation: Layer 4 port numbers identify the application or service which will handle the data. The source port number is added by the sending device and will be the destination port number when the requested information is returned. Layer 4 segments are encapsulated within IP packets. UDP, not TCP, is used when low overhead is needed. A source IP address, not a TCP source port number, identifies the sending host on the network. Destination port numbers are specific ports that a server application or service monitors for requests.
20. Match each description with the corresponding TCP mechanism. (Not all options are used.)
21. Refer to the exhibit. Which two network addresses can be assigned to the network containing 10 hosts? Your answers should waste the fewest addresses, not reuse addresses that are already assigned, and stay within the 10.18.10.0/24 range of addresses. (Choose two.)
- 10.18.10.200/28
- 10.18.10.208/28
- 10.18.10.240/27
- 10.18.10.200/27
- 10.18.10.224/27
- 10.18.10.224/28
Explanation: Addresses 10.18.10.0 through 10.18.10.63 are taken for the leftmost network. Addresses 192 through 199 are used by the center network. Because 4 host bits are needed to accommodate 10 hosts, a /28 mask is needed. 10.18.10.200/28 is not a valid network number. Two subnets that can be used are 10.18.10.208/28 and 10.18.10.224/28.
22. Refer to the exhibit. A company uses the address block of 128.107.0.0/16 for its network. What subnet mask would provide the maximum number of equal size subnets while providing enough host addresses for each subnet in the exhibit?
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.224
Explanation: The largest subnet in the topology has 100 hosts in it so the subnet mask must have at least 7 host bits in it (27-2=126). 255.255.255.0 has 8 hosts bits, but this does not meet the requirement of providing the maximum number of subnets.
23. A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
Explain:
If the same mask is to be used, then the network with the most hosts must be examined for number of hosts. Because this is 10 hosts, 4 host bits are needed. The /28 or 255.255.255.240 subnet mask would be appropriate to use for these networks.
24. Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
25. What two pieces of information are displayed in the output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose two.)
- IP addresses
- interface descriptions
- MAC addresses
- next-hop addresses
- Layer 1 statuses
- speed and duplex settings
Explanation: The command show ip interface brief shows the IP address of each interface, as well as the operational status of the interfaces at both Layer 1 and Layer 2. In order to see interface descriptions and speed and duplex settings, use the command show running-config interface. Next-hop addresses are displayed in the routing table with the command show ip route, and the MAC address of an interface can be seen with the command show interfaces.
26. A user is complaining that an external web page is taking longer than normal to load.The web page does eventually load on the user machine. Which tool should the technician use with administrator privileges in order to locate where the issue is in the network?
- ping
- nslookup
- tracert
- ipconfig /displaydns
27. A network technician is researching the use of fiber optic cabling in a new technology center. Which two issues should be considered before implementing fiber optic media? (Choose two.)
- Fiber optic cabling requires different termination and splicing expertise from what copper cabling requires.
- Fiber optic cabling requires specific grounding to be immune to EMI.
- Fiber optic cabling is susceptible to loss of signal due to RFI.
- Fiber optic cable is able to withstand rough handling.
- Fiber optic provides higher data capacity but is more expensive than copper cabling.
28. What technique is used with UTP cable to help protect against signal interference from crosstalk?
- wrapping a foil shield around the wire pairs
- twisting the wires together into pairs
- terminating the cable with special grounded connectors
- encasing the cables within a flexible plastic sheath
Explanation: To help prevent the effects of crosstalk, UTP cable wires are twisted together into pairs. Twisting the wires together causes the magnetic fields of each wire to cancel each other out.
29. A network administrator is designing the layout of a new wireless network. Which three areas of concern should be accounted for when building a wireless network? (Choose three.)
- extensive cabling
- mobility options
- packet collision
- interference
- security
- coverage area
Explanation: The three areas of concern for wireless networks focus on the size of the coverage area, any nearby interference, and providing network security. Extensive cabling is not a concern for wireless networks, as a wireless network will require minimal cabling for providing wireless access to hosts. Mobility options are not a component of the areas of concern for wireless networks.
30. Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
31. Users report that the network access is slow. After questioning the employees, the network administrator learned that one employee downloaded a third-party scanning program for the printer. What type of malware might be introduced that causes slow performance of the network?
- virus
- worm
- phishing
- spam
Explanation: A cybersecurity specialist needs to be familiar with the characteristics of the different types of malware and attacks that threaten an organization.
32. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
Explain:
The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
33.Refer to the exhibit. Host B on subnet Teachers transmits a packet to host D on subnet Students. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 addresses are contained in the PDUs that are transmitted from host B to the router?
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-dd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-cd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.99
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.100.200
34. What does the term “attenuation” mean in data communication?
- strengthening of a signal by a networking device
- leakage of signals from one cable pair to another
- time for a signal to reach its destination
- loss of signal strength as distance increases
35. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?
- The entire command, configure terminal, must be used.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
36. Which two protocols operate at the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose two.)
- TCP
- IP
- UDP
- POP
- DNS
- Ethernet
37. A company has a file server that shares a folder named Public. The network security policy specifies that the Public folder is assigned Read-Only rights to anyone who can log into the server while the Edit rights are assigned only to the network admin group. Which component is addressed in the AAA network service framework?
- automation
- accounting
- authentication
- authorization
After a user is successfully authenticated (logged into the server), the authorization is the process of determining what network resources the user can access and what operations (such as read or edit) the user can perform.
38. What three requirements are defined by the protocols used in network communcations to allow message transmission across a network? (Choose three.)
- message size
- message encoding
- connector specifications
- media selection
- delivery options
- end-device installation
39. What are two characteristics of IP? (Choose two.)
- does not require a dedicated end-to-end connection
- operates independently of the network media
- retransmits packets if errors occur
- re-assembles out of order packets into the correct order at the receiver end
- guarantees delivery of packets
Explain:
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a connectionless, best effort protocol. This means that IP requires no end-to-end connection nor does it guarantee delivery of packets. IP is also media independent, which means it operates independently of the network media carrying the packets.
40. An employee of a large corporation remotely logs into the company using the appropriate username and password. The employee is attending an important video conference with a customer concerning a large sale. It is important for the video quality to be excellent during the meeting. The employee is unaware that after a successful login, the connection to the company ISP failed. The secondary connection, however, activated within seconds. The disruption was not noticed by the employee or other employees.
What three network characteristics are described in this scenario? (Choose three.)
- security
- quality of service
- scalability
- powerline networking
- integrity
- fault tolerance
41. What are two common causes of signal degradation when using UTP cabling? (Choose two.)
- improper termination
- low-quality shielding in cable
- installing cables in conduit
- low-quality cable or connectors
- loss of light over long distances
42. Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
Explanation: For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
43. Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
- This host does not have a default gateway configured.
- There are 4 hops between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
Explain:
The output displays a successful Layer 3 connection between a host computer and a host at 19.168.100.1. It can be determined that 4 hops exist between them and the average transmission time is 1 milliseconds. Layer 3 connectivity does not necessarily mean that an application can run between the hosts.
44. Which two statements describe how to assess traffic flow patterns and network traffic types using a protocol analyzer? (Choose two.)
- Capture traffic on the weekends when most employees are off work.
- Capture traffic during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types.
- Only capture traffic in the areas of the network that receive most of the traffic such as the data center.
- Perform the capture on different network segments.
- Only capture WAN traffic because traffic to the web is responsible for the largest amount of traffic on a network.
Explanation: Traffic flow patterns should be gathered during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types. The capture should also be performed on different network segments because some traffic will be local to a particular segment.
45. What is the consequence of configuring a router with the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command?
- All router interfaces will be automatically activated.
- The IPv6 enabled router interfaces begin sending ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages.
- Each router interface will generate an IPv6 link-local address.
- It statically creates a global unicast address on this router.
46. Which three layers of the OSI model map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- application
- network
- data link
- session
- presentation
- transport
Explanation: The TCP/IP model consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and network access. The OSI model consists of seven layers: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical. The top three layers of the OSI model: application, presentation, and session map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model.
47. Refer to the exhibit. If PC1 is sending a packet to PC2 and routing has been configured between the two routers, what will R1 do with the Ethernet frame header attached by PC1?
- nothing, because the router has a route to the destination network
- open the header and use it to determine whether the data is to be sent out S0/0/0
- open the header and replace the destination MAC address with a new one
- remove the Ethernet header and configure a new Layer 2 header before sending it out S0/0/0
Explanation: When PC1 forms the various headers attached to the data one of those headers is the Layer 2 header. Because PC1 connects to an Ethernet network, an Ethernet header is used. The source MAC address will be the MAC address of PC1 and the destination MAC address will be that of G0/0 on R1. When R1 gets that information, the router removes the Layer 2 header and creates a new one for the type of network the data will be placed onto (the serial link).
48. What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
49. What are two features of ARP? (Choose two.)
- When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
- An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
- If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.
- If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
- If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.
50. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 90 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.224
51. What are two ICMPv6 messages that are not present in ICMP for IPv4? (Choose two.)
- Neighbor Solicitation
- Destination Unreachable
- Host Confirmation
- Time Exceeded
- Router Advertisement
- Route Redirection
52. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 80. What service is the client requesting?
- DHCP
- SMTP
- DNS
- HTTP
53. What is an advantage for small organizations of adopting IMAP instead of POP?
- POP only allows the client to store messages in a centralized way, while IMAP allows distributed storage.
- Messages are kept in the mail servers until they are manually deleted from the email client.
- When the user connects to a POP server, copies of the messages are kept in the mail server for a short time, but IMAP keeps them for a long time.
- IMAP sends and retrieves email, but POP only retrieves email.
Explanation: IMAP and POP are protocols that are used to retrieve email messages. The advantage of using IMAP instead of POP is that when the user connects to an IMAP-capable server, copies of the messages are downloaded to the client application. IMAP then stores the email messages on the server until the user manually deletes those messages.
54. A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- ipconfig
- netstat
- nslookup
Explain:
Traceroute (tracert) is a utility that generates a list of hops that were successfully reached along the path from source to destination.This list can provide important verification and troubleshooting information. The ipconfig utility is used to display the IP configuration settings on a Windows PC. The Netstat utility is used to identify which active TCP connections are open and running on a networked host. Nslookup is a utility that allows the user to manually query the name servers to resolve a given host name. This utility can also be used to troubleshoot name resolution issues and to verify the current status of the name servers.
55. Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
- implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- implements a process to delimit fields within an Ethernet 2 frame
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
Other case:
- responsible for internal structure of Ethernet frame
- applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
Other case:
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
- implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame
Other case:
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame
- responsible for the internal structure of Ethernet frame
- implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
Other case:
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
- applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- responsible for internal structure of Ethernet frame
Explanation: The data link layer is actually divided into two sublayers:
+ Logical Link Control (LLC): This upper sublayer defines the software processes that provide services to the network layer protocols. It places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame. This information allows multiple Layer 3 protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6, to utilize the same network interface and media.
+ Media Access Control (MAC): This lower sublayer defines the media access processes performed by the hardware. It provides data link layer addressing and delimiting of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium and the type of data link layer protocol in use.
56. The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
Explanation: A default gateway address is typically configured on all devices to allow them to communicate beyond just their local network.In a switch this is achieved using the command ip default-gateway .
57. What happens when the transport input ssh command is entered on the switch vty lines?
- The SSH client on the switch is enabled.
- The switch requires a username/password combination for remote access.
- Communication between the switch and remote users is encrypted.
- The switch requires remote connections via a proprietary client software.
Explanation: The transport input ssh command when entered on the switch vty (virtual terminal lines) will encrypt all inbound controlled telnet connections.
58. Match the type of threat with the cause. (Not all options are used.)
59. A disgruntled employee is using some free wireless networking tools to determine information about the enterprise wireless networks. This person is planning on using this information to hack the wireless network. What type of attack is this?
- DoS
- access
- reconnaissance
- Trojan horse
60. What service is provided by HTTP?
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
61. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 67. What service is the client requesting?
- FTP
- DHCP
- Telnet
- SSH
62. What are two problems that can be caused by a large number of ARP request and reply messages? (Choose two.)
- Switches become overloaded because they concentrate all the traffic from the attached subnets.
- The ARP request is sent as a broadcast, and will flood the entire subnet.
- The network may become overloaded because ARP reply messages have a very large payload due to the 48-bit MAC address and 32-bit IP address that they contain.
- A large number of ARP request and reply messages may slow down the switching process, leading the switch to make many changes in its MAC table.
- All ARP request messages must be processed by all nodes on the local network.
Explanation: ARP requests are sent as broadcasts:
(1) All nodes will receive them, and they will be processed by software, interrupting the CPU.
(2) The switch forwards (floods) Layer 2 broadcasts to all ports.
A switch does not change its MAC table based on ARP request or reply messages. The switch populates the MAC table using the source MAC address of all frames. The ARP payload is very small and does not overload the switch.
63. A group of Windows PCs in a new subnet has been added to an Ethernet network. When testing the connectivity, a technician finds that these PCs can access local network resources but not the Internet resources. To troubleshoot the problem, the technician wants to initially confirm the IP address and DNS configurations on the PCs, and also verify connectivity to the local router. Which three Windows CLI commands and utilities will provide the necessary information? (Choose three.)
- netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor
- arp -a
- tracert
- ping
- ipconfig
- nslookup
- telnet
64. During the process of forwarding traffic, what will the router do immediately after matching the destination IP address to a network on a directly connected routing table entry?
- analyze the destination IP address
- switch the packet to the directly connected interface
- look up the next-hop address for the packet
- discard the traffic after consulting the route table
65. What characteristic describes antispyware?
- applications that protect end devices from becoming infected with malicious software
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
66. A network administrator needs to keep the user ID, password, and session contents private when establishing remote CLI connectivity with a switch to manage it. Which access method should be chosen?
- Telnet
- AUX
- SSH
- Console
67. What are the two most effective ways to defend against malware? (Choose two.)
- Implement a VPN.
- Implement network firewalls.
- Implement RAID.
- Implement strong passwords.
- Update the operating system and other application software.
- Install and update antivirus software.
Explanation: A cybersecurity specialist must be aware of the technologies and measures that are used as countermeasures to protect the organization from threats and vulnerabilities.
68. Which type of security threat would be responsible if a spreadsheet add-on disables the local software firewall?
- brute-force attack
- Trojan horse
- DoS
- buffer overflow
Explanation: A Trojan horse is software that does something harmful, but is hidden in legitimate software code. A denial of service (DoS) attack results in interruption of network services to users, network devices, or applications. A brute-force attack commonly involves trying to access a network device. A buffer overflow occurs when a program attempts to store more data in a memory location than it can hold.
69. Which frame field is created by a source node and used by a destination node to ensure that a transmitted data signal has not been altered by interference, distortion, or signal loss?
- User Datagram Protocol field
- transport layer error check field
- flow control field
- frame check sequence field
- error correction process field
70. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 4 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192
71. What service is provided by POP3?
- Retrieves email from the server by downloading the email to the local mail application of the client.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
72. What two security solutions are most likely to be used only in a corporate environment? (Choose two.)
- antispyware
- virtual private networks
- intrusion prevention systems
- strong passwords
- antivirus software
73. What characteristic describes antivirus software?
- applications that protect end devices from becoming infected with malicious software
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
74. What mechanism is used by a router to prevent a received IPv4 packet from traveling endlessly on a network?
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It decrements the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Time Exceeded message to the source host.
- It increments the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Parameter Problem message to the source host.
75. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 69. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- DHCP
- SMTP
- TFTP
76. An administrator defined a local user account with a secret password on router R1 for use with SSH. Which three additional steps are required to configure R1 to accept only encrypted SSH connections? (Choose three.)
- Configure DNS on the router.
- Generate two-way pre-shared keys.
- Configure the IP domain name on the router.
- Generate the SSH keys.
- Enable inbound vty SSH sessions.
- Enable inbound vty Telnet sessions.
77. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- responsible for internal structure of Ethernet frame
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
- implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
Other case
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media
- applies source and destination MAC addresses to Ethernet frame
- applies delimiting of Ethernet frame fields to synchronize communication between nodes
78. An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::2. What is the target of this packet?
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link
- all IPv6 DHCP servers
- all IPv6 enabled devices across the network
- all IPv6 configured routers on the local link
79. What are the three parts of an IPv6 global unicast address? (Choose three.)
- subnet ID
- subnet mask
- broadcast address
- global routing prefix
- interface ID
80. A client is using SLAAC to obtain an IPv6 address for its interface. After an address has been generated and applied to the interface, what must the client do before it can begin to use this IPv6 address?
- It must send a DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST message to request the address of the DNS server.
- It must send a DHCPv6 REQUEST message to the DHCPv6 server to request permission to use this address.
- It must send an ICMPv6 Router Solicitation message to determine what default gateway it should use.
- It must send an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message to ensure that the address is not already in use on the network.
81. A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
- Enter CTRL-Z at the privileged mode prompt.
- Exit global configuration mode.
- Power cycle the device.
- Reboot the device.
- Exit privileged EXEC mode and press Enter .
82. What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- token passing
- CSMA/CA
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CD
83. What is a function of the data link layer?
- provides the formatting of data
- provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
- provides delivery of data between two applications
- provides for the exchange of frames over a common local media
84. What is the purpose of the TCP sliding window?
- to ensure that segments arrive in order at the destination
- to end communication when data transmission is complete
- to inform a source to retransmit data from a specific point forward
- to request that a source decrease the rate at which it transmits data
85. What characteristic describes spyware?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
86. Which switching method drops frames that fail the FCS check?
- store-and-forward switching
- borderless switching
- ingress port buffering
- cut-through switching
87. Two pings were issued from a host on a local network. The first ping was issued to the IP address of the default gateway of the host and it failed. The second ping was issued to the IP address of a host outside the local network and it was successful. What is a possible cause for the failed ping?
- The default gateway is not operational.
- The default gateway device is configured with the wrong IP address.
- Security rules are applied to the default gateway device, preventing it from processing ping requests.
- The TCP/IP stack on the default gateway is not working properly.
88. What service is provided by FTP?
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
89. A user is attempting to access http://www.cisco.com/ without success. Which two configuration values must be set on the host to allow this access? (Choose two.)
- DNS server
- source port number
- HTTP server
- source MAC address
- default gateway
90. Which two statements accurately describe an advantage or a disadvantage when deploying NAT for IPv4 in a network? (Choose two.)
- NAT adds authentication capability to IPv4.
- NAT introduces problems for some applications that require end-to-end connectivity.
- NAT will impact negatively on switch performance.
- NAT provides a solution to slow down the IPv4 address depletion.
- NAT improves packet handling.
- NAT causes routing tables to include more information.
91. What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.224
92. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 issues an ARP request because it needs to send a packet to PC2. In this scenario, what will happen next?
- PC2 will send an ARP reply with its MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/0 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/1 MAC address.
Explain:
When a network device wants to communicate with another device on the same network, it sends a broadcast ARP request. In this case, the request will contain the IP address of PC2. The destination device (PC2) sends an ARP reply with its MAC address.
93. What service is provided by BOOTP?
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- Legacy application that enables a diskless workstation to discover its own IP address and find a BOOTP server on the network.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
94. What characteristic describes adware?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
95. What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
96. Match a statement to the related network model. (Not all options are used.)
Place the options in the following order:peer-to-peer network
[+] no dedicated server is required
[+] client and server roles are set on a per request basis
peer-to-peer aplication
[#] requires a specific user interface
[#] a background service is required
Explain:
Peer-to-peer networks do not require the use of a dedicated server, and devices can assume both client and server roles simultaneously on a per request basis. Because they do not require formalized accounts or permissions, they are best used in limited situations. Peer-to-peer applications require a user interface and background service to be running, and can be used in more diverse situations.
97. Which information does the show startup-config command display?
- the IOS image copied into RAM
- the bootstrap program in the ROM
- the contents of the current running configuration file in the RAM
- the contents of the saved configuration file in the NVRAM
Explain:
The show startup-config command displays the saved configuration located in NVRAM. The show running-config command displays the contents of the currently running configuration file located in RAM.
98. Refer to the exhibit. What three facts can be determined from the viewable output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose three.)
- Two physical interfaces have been configured.
- The switch can be remotely managed.
- One device is attached to a physical interface.
- Passwords have been configured on the switch.
- Two devices are attached to the switch.
- The default SVI has been configured.
Explain:
Vlan1 is the default SVI. Because an SVI has been configured, the switch can be configured and managed remotely. FastEthernet0/0 is showing up and up, so a device is connected.
99. Match each type of frame field to its function. (Not all options are used.)
100. What is the subnet ID associated with the IPv6 address 2001:DA48:FC5:A4:3D1B::1/64?
- 2001:DA48::/64
- 2001:DA48:FC5::A4:/64
- 2001:DA48:FC5:A4::/64
- 2001::/64
101. Match the firewall function to the type of threat protection it provides to the network. (Not all options are used.)
- packet filtering – prevents access based on IP or MAC address
- URL filtering – prevents access to websites
- network address translator – (none)
- stateful packet inspection – prevents unsolicited incoming sessions
- application filtering – prevents access by port number
Explain:Firewall products come packaged in various forms. These products use different techniques for determining what will be permitted or denied access to a network. They include the following:
+ Packet filtering – Prevents or allows access based on IP or MAC addresses
+ Application filtering – Prevents or allows access by specific application types based on port numbers
+ URL filtering – Prevents or allows access to websites based on specific URLs or keywords
+ Stateful packet inspection (SPI) – Incoming packets must be legitimate responses to requests from internal hosts. Unsolicited packets are blocked unless permitted specifically. SPI can also include the capability to recognize and filter out specific types of attacks, such as denial of service (DoS)
102. Users are reporting longer delays in authentication and in accessing network resources during certain time periods of the week. What kind of information should network engineers check to find out if this situation is part of a normal network behavior?
- syslog records and messages
- the network performance baseline
- debug output and packet captures
- network configuration files
103. What characteristic describes a VPN?
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
- software that identifies fast-spreading threats
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
104. Which two statements are correct in a comparison of IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers? (Choose two.)
- The Source Address field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
- The Version field from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6.
- The Destination Address field is new in IPv6.
- The Header Checksum field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
- The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6.
105. A network administrator wants to have the same network mask for all networks at a particular small site. The site has the following networks and number of devices:
IP phones – 22 addresses
PCs – 20 addresses needed
Printers – 2 addresses needed
Scanners – 2 addresses needed
The network administrator has deemed that 192.168.10.0/24 is to be the network used at this site. Which single subnet mask would make the most efficient use of the available addresses to use for the four subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.252
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.224
106. What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- A company can monopolize the market.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.
Explain:
A monopoly by one company is not a good idea from a user point of view. If a protocol can only be run on one brand, it makes it difficult to have mixed equipment in a network. A proprietary protocol is not free to use. An open standard protocol will in general be implemented by a wide range of vendors.
107. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 200 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.224
108. What are three commonly followed standards for constructing and installing cabling? (Choose three.)
- cost per meter (foot)
- cable lengths
- connector color
- pinouts
- connector types
- tensile strength of plastic insulator
109. Refer to the exhibit. What is wrong with the displayed termination?
- The woven copper braid should not have been removed.
- The wrong type of connector is being used.
- The untwisted length of each wire is too long.
- The wires are too thick for the connector that is used.
Explanation: When a cable to an RJ-45 connector is terminated, it is important to ensure that the untwisted wires are not too long and that the flexible plastic sheath surrounding the wires is crimped down and not the bare wires. None of the colored wires should be visible from the bottom of the jack.
110. Match the characteristic to the category. (Not all options are used.)
111. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 143. What service is the client requesting?
- IMAP
- FTP
- SSH
- Telnet
112. What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering
- 3-way handshake
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- use of checksum
Explain:
Both TCP and UDP use source and destination port numbers to distinguish different data streams and to forward the right data segments to the right applications. Error checking the header and data is done by both protocols by using a checksum calculation to determine the integrity of the data that is received. TCP is connection-oriented and uses a 3-way handshake to establish an initial connection. TCP also uses window to regulate the amount of traffic sent before receiving an acknowledgment. UDP is connectionless and is the best protocol for carry digitized VoIP signals.
113. Which value, that is contained in an IPv4 header field, is decremented by each router that receives a packet?
- Header Length
- Differentiated Services
- Time-to-Live
- Fragment Offset
Explanation: When a router receives a packet, the router will decrement the Time-to-Live (TTL) field by one. When the field reaches zero, the receiving router will discard the packet and will send an ICMP Time Exceeded message to the sender.
114. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 21. What service is the client requesting?
- FTP
- LDAP
- SLP
- SNMP
115. What attribute of a NIC would place it at the data link layer of the OSI model?
- attached Ethernet cable
- IP address
- MAC address
- RJ-45 port
- TCP/IP protocol stack
116. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 10 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
117. A user is executing a tracert to a remote device. At what point would a router, which is in the path to the destination device, stop forwarding the packet?
- when the router receives an ICMP Time Exceeded message
- when the RTT value reaches zero
- when the host responds with an ICMP Echo Reply message
- when the value in the TTL field reaches zero
- when the values of both the Echo Request and Echo Reply messages reach zero
Explain:
When a router receives a traceroute packet, the value in the TTL field is decremented by 1. When the value in the field reaches zero, the receiving router will not forward the packet, and will send an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source.
118. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has assigned the LAN of LBMISS an address range of 192.168.10.0. This address range has been subnetted using a /29 prefix. In order to accommodate a new building, the technician has decided to use the fifth subnet for configuring the new network (subnet zero is the first subnet). By company policies, the router interface is always assigned the first usable host address and the workgroup server is given the last usable host address. Which configuration should be entered into the properties of the workgroup server to allow connectivity to the Internet?
- IP address: 192.168.10.65 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.76
- IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
- IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
- IP address: 192.168.10.41 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.46
- IP address: 192.168.10.254 subnet mask: 255.255.255.0, default gateway: 192.168.10.1
Explain:
Using a /29 prefix to subnet 192.168.10.0 results in subnets that increment by 8:
192.168.10.0 (1)
192.168.10.8 (2)
192.168.10.16 (3)
192.168.10.24 (4)
192.168.10.32 (5)
119. Refer to the exhibit. The switches are in their default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for its default gateway. Which network hosts will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
- only host D
- only router R1
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only hosts A, B, C, and D
- only hosts B and C
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
Explain:
Since host A does not have the MAC address of the default gateway in its ARP table, host A sends an ARP broadcast. The ARP broadcast would be sent to every device on the local network. Hosts B, C, and router R1 would receive the broadcast. Router R1 would not forward the message.
120. Which two traffic types use the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP)? (Choose two.)
- video
- web
- file transfer
- voice
- peer to peer
121. Which wireless technology has low-power and data rate requirements making it popular in home automation applications?
- ZigBee
- LoRaWAN
- 5G
- Wi-Fi
122. Which layer of the TCP/IP model provides a route to forward messages through an internetwork?
- application
- network access
- internet
- transport
Explain:
The OSI model network layer corresponds directly to the internet layer of the TCP/IP model and is used to describe protocols that address and route messages through an internetwork.
123. Which type of server relies on record types such as A, NS, AAAA, and MX in order to provide services?
- DNS
- file
- web
Explain:
A DNS server stores records that are used to resolve IP addresses to host names. Some DNS record types include the following:
A – an end device IPv4 address
NS – an authoritative name server
AAAA – an end device IPv6 address
MX – a mail exchange record
124. What are proprietary protocols?
- protocols developed by private organizations to operate on any vendor hardware
- protocols that can be freely used by any organization or vendor
- protocols developed by organizations who have control over their definition and operation
- a collection of protocols known as the TCP/IP protocol suite
Explain:
Proprietary protocols have their definition and operation controlled by one company or vendor. Some of them can be used by different organizations with permission from the owner. The TCP/IP protocol suite is an open standard, not a proprietary protocol.
125. What service is provided by DNS?
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
126. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 110. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- DHCP
- SMTP
- POP3
127. What command can be used on a Windows PC to see the IP configuration of that computer?
- show ip interface brief
- ping
- show interfaces
- ipconfig
128. A wired laser printer is attached to a home computer. That printer has been shared so that other computers on the home network can also use the printer. What networking model is in use?
- client-based
- master-slave
- point-to-point
- peer-to-peer (P2P)
Explanation: Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks have two or more network devices that can share resources such as printers or files without having a dedicated server.
129. What characteristic describes a virus?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- malicious software or code running on an end device
130. Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
Explanation: QoS mechanisms enable the establishment of queue management strategies that enforce priorities for different categories of application data. Thus, this queuing enables voice data to have priority over transaction data, which has priority over web data.
131. Match the description to the IPv6 addressing component. (Not all options are used.)
132. Refer to the exhibit. If Host1 were to transfer a file to the server, what layers of the TCP/IP model would be used?
- only application and Internet layers
- only Internet and network access layers
- only application, Internet, and network access layers
- application, transport, Internet, and network access layers
- only application, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
- application, session, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
Explanation: The TCP/IP model contains the application, transport, internet, and network access layers. A file transfer uses the FTP application layer protocol. The data would move from the application layer through all of the layers of the model and across the network to the file server.
133. Match the characteristic to the forwarding method. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: A store-and-forward switch always stores the entire frame before forwarding, and checks its CRC and frame length. A cut-through switch can forward frames before receiving the destination address field, thus presenting less latency than a store-and-forward switch. Because the frame can begin to be forwarded before it is completely received, the switch may transmit a corrupt or runt frame. All forwarding methods require a Layer 2 switch to forward broadcast frames.
134. Refer to the exhibit. The IP address of which device interface should be used as the default gateway setting of host H1?
- R1: S0/0/0
- R2: S0/0/1
- R1: G0/0
- R2: S0/0/0
135. What service is provided by Internet Messenger?
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
136. Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network.
Explanation: Network A needs to use 192.168.0.128 /25, which yields 128 host addresses.
Network B needs to use 192.168.0.0 /26, which yields 64 host addresses.
Network C needs to use 192.168.0.96 /27, which yields 32 host addresses.
Network D needs to use 192.168.0.80/30, which yields 4 host addresses.
137. Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol was responsible for building the table that is shown?
- DHCP
- ARP
- DNS
- ICMP
138. A network administrator notices that some newly installed Ethernet cabling is carrying corrupt and distorted data signals. The new cabling was installed in the ceiling close to fluorescent lights and electrical equipment. Which two factors may interfere with the copper cabling and result in signal distortion and data corruption? (Choose two.)
- crosstalk
- extended length of cabling
- RFI
- EMI
- signal attenuation
139. A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in its ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in the ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
- It will send the frame and use its own MAC address as the destination.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
- It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
- It will send a request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.
140. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication?
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media
141. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 53. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- NetBIOS (NetBT)
- POP3
- IMAP
142. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 25 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
143. What characteristic describes a Trojan horse?
- malicious software or code running on an end device
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
144. What service is provided by HTTPS?
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
145. A technician with a PC is using multiple applications while connected to the Internet. How is the PC able to keep track of the data flow between multiple application sessions and have each application receive the correct packet flows?
- The data flow is being tracked based on the destination MAC address of the technician PC.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the source port number that is used by each application.*
- The data flow is being tracked based on the source IP address that is used by the PC of the technician.
- The data flow is being tracked based on the destination IP address that is used by the PC of the technician.
Explanation:
The source port number of an application is randomly generated and used to individually keep track of each session connecting out to the Internet. Each application will use a unique source port number to provide simultaneous communication from multiple applications through the Internet.
146. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 61 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.128
147. Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network. (Not all options are used.)
Question
Answer
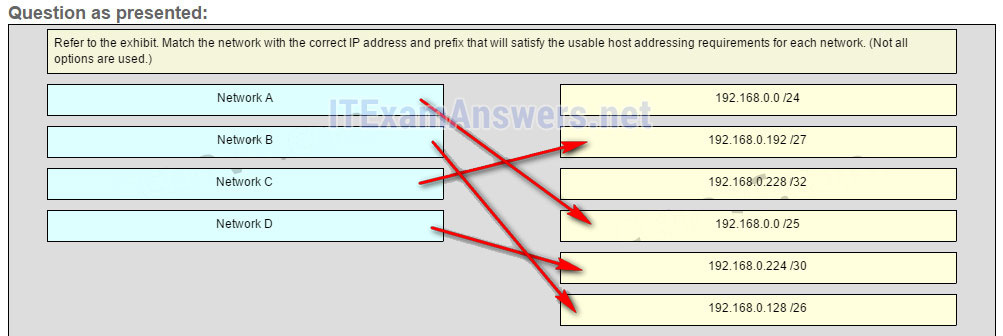
Explanation:
Network A needs to use 192.168.0.0 /25 which yields 128 host addresses.
Network B needs to use 192.168.0.128 /26 which yields 64 host addresses.
Network C needs to use 192.168.0.192 /27 which yields 32 host addresses.
Network D needs to use 192.168.0.224 /30 which yields 4 host addresses.
148. What characteristic describes a DoS attack?
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
149. Match the application protocols to the correct transport protocols
150. What service is provided by SMTP?
- Allows clients to send email to a mail server and the servers to send email to other servers.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
151. Match a statement to the related network model. (Not all options are used.)
Place the options in the following order:peer-to-peer network
[+] no dedicated server is required
[+] client and server roles are set on a per request basis
peer-to-peer aplication
[#] requires a specific user interface
[#] a background service is required
Explain:
Peer-to-peer networks do not require the use of a dedicated server, and devices can assume both client and server roles simultaneously on a per request basis. Because they do not require formalized accounts or permissions, they are best used in limited situations. Peer-to-peer applications require a user interface and background service to be running, and can be used in more diverse situations.
152. Match the application protocols to the correct transport protocols.
153. Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer has been given the network address of 192.168.99.0 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192 to subnet across the four networks shown. How many total host addresses are unused across all four subnets?
- 88
- 200
- 72
- 224
- 158
154. Which connector is used with twisted-pair cabling in an Ethernet LAN?
True Answer:
155. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 22. What service is the client requesting?
- SSH
- SMB/CIFS
- HTTPS
- SLP
156. What characteristic describes an IPS?
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that identifies fast-spreading threats
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
157. What service is provided by DHCP?
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Dynamically assigns IP addresses to end and intermediary devices.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
158. Match the header field with the appropriate layer of the OSI model. (Not all options are used.)
159. Refer to the exhibit. The switches have a default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for the default gateway. Which network devices will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
- only host D
- only hosts A, B, C, and D
- only hosts B and C
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only router R1
160. Which wireless technology has low-power and low-data rate requirements making it popular in IoT environments?
- Bluetooth
- Zigbee
- WiMAX
- Wi-Fi
Explanation: Zigbee is a specification used for low-data rate, low-power communications. It is intended for applications that require short-range, low data-rates and long battery life. Zigbee is typically used for industrial and Internet of Things (IoT) environments such as wireless light switches and medical device data collection.
161. The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
Explanation: A default gateway address is typically configured on all devices to allow them to communicate beyond just their local network.In a switch this is achieved using the command ip default-gateway <ip address>.
Last Updated on May 20, 2021 by
Cisco CCNA 1 ITN v6.0 final Exam Answers Routing and Switching (R&S) Introduction to Networks (ITN) (Version 6.00) collection year 2017, 2018 and 2019 Full 100%. CCNA 1 has been know as ITN. The following are the questions exam answers. Guarantee Passed 100%. CCNA 1 v6.0 final exam answers has some new update from the old version 5.1. You can review all final Exam Answers. You will get passed scored 100% with this version 6.0. Good Luck for Cisco Netacad ITN v6.0 Exam!
Noted: There are 3 forms of Final Exam. In this page we have collected all 3 forms. You will random from these question which 55 to 60 questions.
-
Recommend
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to «Online Test» link below.
| Version 5.02 | Version 5.1 | Version 6.0 | Online Assessment |
| Final Exam | Final Exam | Final Exam | Online A, Online B, Online C |
| CCNA2 Pretest Exam | |||
| Pretest Exam | Pretest Exam | Pretest Exam | Online Test |
March, 2019 New Update for CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam
-
What is an example of a top-level domain?
- www.cisco.com
- cisco.com
- .com
- root.cisco.com
Explanation:
Top-level domains represent a country or type of organization, such as .com or .edu.
-
What is a characteristic of multicast messages?
- They are sent to a select group of hosts.
- They are sent to all hosts on a network.
- They must be acknowledged.
- They are sent to a single destination.
Explanation:
Multicast is a one-to-many type of communication. Multicast messages are addressed to a specific multicast group.
-
A network technician suspects that a particular network connection between two Cisco switches is having a duplex mismatch. Which command would the technician use to see the Layer 1 and Layer 2 details of a switch port?
- show interfaces
- show running-config
- show ip interface brief
- show mac-address-table
Explanation:
The show interfaces command can be used on both routers and switches to see speed, duplex, media type, MAC address, port type, and other Layer 1/Layer 2-related information.
-
Where are Cisco IOS debug output messages sent by default?
- memory buffers
- vty lines
- Syslog server
- console line
Explanation:
Debug messages, like other IOS log messages, are sent to the console line by default. Sending these messages to the terminal lines requires the terminal monitor command.
-
Which command can an administrator issue on a Cisco router to send debug messages to the vty lines?
- terminal monitor
- logging console
- logging buffered
- logging synchronous
Explanation:
Debug messages, like other IOS log messages, are sent to the console line by default. Sending these messages to the terminal lines requires the terminal monitor command.
-
What is one indication that a Windows computer did not receive an IPv4 address from a DHCP server?
- The computer cannot ping 127.0.0.1.
- Windows displays a DHCP timeout message.
- The computer receives an IP address that starts with 169.254.
- The computer cannot ping other devices on the same network with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 range.
Explanation:
When a Windows PC cannot communicate with an IPv4 DHCP server, the computer automatically assigns an IP address in the 169.254.0.0/16 range. Any other device on the same network that receives an address in the same range is reachable.
-
What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
Explanation:
When sending an echo request message, a router will use the IP address of the exit interface as the source IP address. This default behavior can be changed by using an extended ping and specifying a specific source IP address.
-
A user is unable to reach the web site when typing http://www.cisco.com in a web browser, but can reach the same site by typing http://72.163.4.161. What is the issue?
- default gateway
- DHCP
- DNS
- TCP/IP protocol stack
Explanation:
Domain Name Service (DNS) is used to translate a web address to an IP address. The address of the DNS server is provided via DHCP to host computers.
-
What is a characteristic of a fault tolerant network?
- a network that protects confidential information from unauthorized access
- a network that can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service delivered to existing users
- a network that supports a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users
- a network that recovers quickly when a failure occurs and depends on redundancy to limit the impact of a failure
Explanation:
Fault tolerant networks limit the impact of a failure because the networks are built in a way that allows for quick recovery when such a failure occurs. These networks depend on multiple or redundant paths between the source and destination of a message.
A scalable network can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users.
Quality of service (QoS) is a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users.
-
Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
Explanation:
QoS mechanisms enable the establishment of queue management strategies that enforce priorities for different categories of application data. Thus, this queuing enables voice data to have priority over transaction data, which has priority over web data.
-
What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
Explanation:
Cloud computing extends IT’s capabilities without requiring investment in new infrastructure, training new personnel, or licensing new software. These services are available on-demand and delivered economically to any device anywhere in the world without compromising security or function. BYOD is about end users having the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business or campus network. Smart home technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated. Powerline networking is a trend for home networking that uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
-
What is the function of the shell in an OS?
- It interacts with the device hardware.
- It interfaces between the users and the kernel.
- It provides dedicated firewall services.
- It provides the intrusion protection services for the device.
Explanation:
Most operating systems contain a shell and a kernel. The kernel interacts with the hardware and the shell interfaces between the kernel and the users.
-
Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco switch?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection
Explanation:
A CLI session using Secure Shell (SSH) provides enhanced security because SSH supports strong passwords and encryption during the transport of session data. The other methods support authentication but not encryption.
-
A network technician is attempting to configure an interface by entering the following command: SanJose(config)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0. The command is rejected by the device. What is the reason for this?
- The command is being entered from the wrong mode of operation.
- The command syntax is wrong.
- The subnet mask information is incorrect.
- The interface is shutdown and must be enabled before the switch will accept the IP address.
Explanation:
The wrong mode of operation is being used. The CLI prompt indicates that the mode of operation is global configuration. IP addresses must be configured from interface configuration mode, as indicated by the SanJose(config-if)# prompt.
-
An administrator uses the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination on a switch after issuing the ping command. What is the purpose of using these keystrokes?
- to restart the ping process
- to interrupt the ping process
- to exit to a different configuration mode
- to allow the user to complete the command
Explanation:
To interrupt an IOS process such as ping or traceroute, a user enters the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination. Tab completes the remainder of parameters or arguments within a command. To exit from configuration mode to privileged mode use the Ctrl-Z keystroke. CTRL-R will redisplay the line just typed, thus making it easier for the user to press Enter and reissue the ping command.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses a console connection to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 001 - letmein
- secretin
- lineconin
- linevtyin
Explanation:
Telnet accesses a network device through the virtual interface configured with the line VTY command. The password configured under this is required to access the user EXEC mode. The password configured under the line console 0 command is required to gain entry through the console port, and the enable and enable secret passwords are used to allow entry into the privileged EXEC mode.
-
On which switch interface would an administrator configure an IP address so that the switch can be managed remotely?
- FastEthernet0/1
- VLAN 1
- vty 0
- console 0
Explanation:
Interface VLAN 1 is a virtual interface on a switch, called SVI (switch virtual interface). Configuring an IP address on the default SVI, interface VLAN 1, will allow a switch to be accessed remotely. The VTY line must also be configured to allow remote access, but an IP address cannot be configured on this line.
-
What protocol is responsible for controlling the size of segments and the rate at which segments are exchanged between a web client and a web server?
- TCP
- IP
- HTTP
- Ethernet
Explanation:
TCP is a Layer 4 protocol of the OSI model. TCP has several responsibilities in the network communication process. It divides large messages into smaller segments which are more efficient to send across the network. It also controls the size and rate of segments exchanged between clients and servers.
-
What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- A company can monopolize the market.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.
Explanation:
A monopoly by one company is not a good idea from a user point of view. If a protocol can only be run on one brand, it makes it difficult to have mixed equipment in a network. A proprietary protocol is not free to use. An open standard protocol will in general be implemented by a wide range of vendors.
-
What are two benefits of using a layered network model? (Choose two.)
- It assists in protocol design.
- It speeds up packet delivery.
- It prevents designers from creating their own model.
- It prevents technology in one layer from affecting other layers.
- It ensures a device at one layer can function at the next higher layer.
Explanation:
Some vendors have developed their own reference models and protocols. Today, if a device is to communicate on the Internet, the device must use the TCP/IP model. The benefits of using a layered model are as follows:
- assists in protocol design
- fosters competition between vendors
- prevents a technology that functions at one layer from affecting any other layer
- provides a common language for describing network functionality
- helps in visualizing the interaction between each layer and protocols between each layer
-
Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- data link
- network
- physical
- session
- transport
Explanation:
The OSI transport layer is functionally equivalent to the TCP/IP transport layer, and the OSI network layer is equivalent to the TCP/IP internet layer. The OSI data link and physical layers together are equivalent to the TCP/IP network access layer. The OSI session layer (with the presentation layer) is included within the TCP/IP application layer.
-
Which name is assigned to the transport layer PDU?
- bits
- data
- frame
- packet
- segment
Explanation:
Application data is passed down the protocol stack on its way to be transmitted across the network media. During the process, various protocols add information to it at each level. At each stage of the process, a PDU (protocol data unit) has a different name to reflect its new functions. The PDUs are named according to the protocols of the TCP/IP suite:
- Data – The general term for the PDU used at the application layer.
- Segment – transport layer PDU
- Packet – network layer PDU
- Frame – data link layer PDU
- Bits – A physical layer PDU used when physically transmitting data over the medium
-
A network administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues on a server. Using a tester, the administrator notices that the signals generated by the server NIC are distorted and not usable. In which layer of the OSI model is the error categorized?
- presentation layer
- network layer
- physical layer
- data link layer
Explanation:
The NIC has responsibilities in both Layer 1 and Layer 2. The NIC encodes the frame as a series of signals that are transmitted onto the local media. This is the responsibility of the physical layer of the OSI model. The signal could be in the form of electrical, optical, or radio waves.
-
A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
Explanation:
Throughput usually does not match the specified bandwidth of physical links due to multiple factors. These factors include, the amount of traffic, type of traffic, and latency created by the network devices the data has to cross.
-
What is a characteristic of UTP cabling?
- cancellation
- cladding
- immunity to electrical hazards
- woven copper braid or metallic foil
Explanation:
Cladding and immunization from electrical hazards are characteristics for fiber-optic cabling. A woven copper braid or metallic foil is used as a shield for the inner coaxial cable conductor. Cancellation is a property of UTP cabling where two wires are located adjacent to one another so each magnetic field cancels out the adjacent magnetic field.
-
What are two characteristics of fiber-optic cable? (Choose two.)
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding, and twisting to protect data.
- It typically contains 4 pairs of fiber-optic wires.
- It is more expensive than UTP cabling is.
Explanation:
Fiber-optic cabling supports higher bandwidth than UTP for longer distances. Fiber is immune to EMI and RFI, but costs more, requires more skill to install, and requires more safety precautions.
-
What is a characteristic of the LLC sublayer?
- It provides the logical addressing required that identifies the device.
- It provides delimitation of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium.
- It places information in the frame allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to use the same network interface and media.
- It defines software processes that provide services to the physical layer.
Explanation:
The Logical Link Control (LLC) defines the software processes that provide services to the network layer protocols. The information is placed by LLC in the frame and identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame. This information allows multiple Layer 3 protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6, to utilize the same network interface and media.
-
A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies for connecting remote sites to a headquarters building. Which topology provides high availability and connects some, but not all, remote sites?
- mesh
- partial mesh
- hub and spoke
- point-to-point
Explanation:
Partial mesh topologies provide high availability by interconnecting multiple remote sites, but do not require a connection between all remote sites. A mesh topology requires point-to-point links with every system being connected to every other system. A point-to-point topology is where each device is connected to one other device. A hub and spoke uses a central device in a star topology that connects to other point-to-point devices.
-
What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA
- token passing
Explanation:
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) is used with wireless networking technology to mediate media contention. Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is used with wired Ethernet technology to mediate media contention. Priority ordering and token passing are not used (or not a method) for media access control.
-
What are the three primary functions provided by Layer 2 data encapsulation? (Choose three.)
- error correction through a collision detection method
- session control using port numbers
- data link layer addressing
- placement and removal of frames from the media
- detection of errors through CRC calculations
- delimiting groups of bits into frames
- conversion of bits into data signals
Explanation:
Through the framing process, delimiters are used to identify the start and end of the sequence of bits that make up a frame. Data link layer addressing is added to enable a frame to be delivered to a destination node. A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) field is calculated on every bit and added to the frame. If the CRC value contained in the arriving frame is the same as the one the receiving node creates, the frame will be processed.
-
What will a host on an Ethernet network do if it receives a frame with a destination MAC address that does not match its own MAC address?
- It will discard the frame.
- It will forward the frame to the next host.
- It will remove the frame from the media.
- It will strip off the data-link frame to check the destination IP address.
Explanation:
In an Ethernet network, each NIC in the network checks every arriving frame to see if the destination MAC address in the frame matches its own MAC address. If there is no match, the device discards the frame. If there is a match, the NIC passes the frame up to the next OSI layer.
-
Which frame forwarding method receives the entire frame and performs a CRC check to detect errors before forwarding the frame?
- cut-through switching
- store-and-forward switching
- fragment-free switching
- fast-forward switching
Explanation:
Fast-forward and fragment-free switching are variations of cut-through switching, which begins to forward the frame before the entire frame is received.
-
Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 002 - DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- 172.168.10.99
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- 172.168.10.65
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
Explanation:
When a host sends information to a distant network, the Layer 2 frame header will contain a source and destination MAC address. The source address will be the originating host device. The destination address will be the router interface that connects to the same network. In the case of host A sending information to host B, the source address is AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA and the destination address is the MAC address assigned to the R2 Ethernet interface, BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB.
-
What addresses are mapped by ARP?
- destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address
- destination IPv4 address to the source MAC address
- destination IPv4 address to the destination host name
- destination MAC address to the source IPv4 address
Explanation:
ARP, or the Address Resolution Protocol, works by mapping a destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address. The host knows the destination IPv4 address and uses ARP to resolve the corresponding destination MAC address.
-
What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
Explanation:
The OSI network layer provides several services to allow communication between devices:
- addressing
- encapsulation
- routing
- de-encapsulation
Error detection, placing frames on the media, and collision detection are all functions of the data ink layer.
-
What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed
- to store the startup configuration file
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
Explanation:
NVRAM is permanent memory storage, so the startup configuration file is preserved even if the router loses power.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What will be the result of entering this configuration the next time a network administrator connects a console cable to the router and no additional commands have been entered?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 003 - The administrator will be required to enter Cisco123.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco234.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco789.
- The administrator will be presented with the R1> prompt.
Explanation:
Until both the password password and the login commands are entered in console line configuration mode, no password is required to gain access to enable mode.
-
What is the dotted decimal representation of the IPv4 address 11001011.00000000.01110001.11010011?
- 192.0.2.199
- 198.51.100.201
- 203.0.113.211
- 209.165.201.223
Explanation:
Each section (octet) contains eight binary digits. Each digit represents a specific value (128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1). Everywhere there is a 1, the specific value is relevant. Add all relevant values in a particular octet to obtain the decimal value. For example binary 11001011 equals 203 in decimal.
-
What are three characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose three.)
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts.
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information.
- Routers will not forward multicast addresses in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses.
Explanation:
Broadcast messages consist of single packets that are sent to all hosts on a network segment. These types of messages are used to request IPv4 addresses, and map upper layer addresses to lower layer addresses. A multicast transmission is a single packet sent to a group of hosts and is used by routing protocols, such as OSPF and RIPv2, to exchange routes. The address range 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 is reserved for link-local addresses to reach multicast groups on a local network.
-
What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 127.16.0.0/12
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 192.168.0.0/16
Explanation:
The private IP address blocks that are used inside companies are as follows:
- 10.0.0.0 /8 (any address that starts with 10 in the first octet)
- 172.16.0.0 /12 (any address that starts with 172.16 in the first two octets through 172.31.255.255)
- 192.168.0.0 /16 (any address that starts with 192.168 in the first two octets)
-
What purpose does NAT64 serve in IPv6?
- It converts IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
- It translates private IPv6 addresses into public IPv6 addresses.
- It enables companies to use IPv6 unique local addresses in the network.
- It converts regular IPv6 addresses into 64-bit addresses that can be used on the Internet.
- It converts the 48-bit MAC address into a 64-bit host address that can be used for automatic host addressing.
Explanation:
NAT64 is typically used in IPv6 when networks are being transitioned from IPv4 to IPv6. It allows the IPv6 networks to connect to IPv4 networks (such as the Internet), and works by translating the IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
-
What is the most compressed representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001?
- 2001:0:abcd::1
- 2001:0:0:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd::1
- 2001:0000:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd:0:1
Explanation:
The IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001 in its most compressed format would be 2001:0:0:abcd::1. The first two hextets of zeros would each compress to a single zero. The three consecutive hextets of zeros can be compressed to a double colon ::. The three leading zeros in the last hextet can be removed. The double colon :: can only be used once in an address.
-
Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FEC0::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FE80::/10
- FF00::/8
Explanation:
Link-local addresses are in the range of FE80::/10 to FEBF::/10. The original IPv6 specification defined site-local addresses and used the prefix range FEC0::/10, but these addresses were deprecated by the IETF in favor of unique local addresses. FDEE::/7 is a unique local address because it is in the range of FC00::/7 to FDFF::/7. IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8.
-
How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
- 254
- 190
- 192
- 62
- 64
Explanation:
When a /26 mask is used, 6 bits are used as host bits. With 6 bits, 64 addresses are possible, but one address is for the subnet number and one address is for a broadcast. This leaves 62 addresses that can be assigned to network devices.
-
A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
Explanation:
The subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 has 8 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.128 results in 7 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.224 has 5 host bits. Finally, 255.255.255.240 represents 4 host bits.
-
Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
Explanation:
For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
-
Which statement is true about variable-length subnet masking?
- Each subnet is the same size.
- The size of each subnet may be different, depending on requirements.
- Subnets may only be subnetted one additional time.
- Bits are returned, rather than borrowed, to create additional subnets.
Explanation:
In variable-length subnet masking, bits are borrowed to create subnets. Additional bits may be borrowed to create additional subnets within the original subnets. This may continue until there are no bits available to borrow.
-
Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
Explanation:
The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
-
A user opens three browsers on the same PC to access www.cisco.com to search for certification course information. The Cisco web server sends a datagram as a reply to the request from one of the web browsers. Which information is used by the TCP/IP protocol stack in the PC to identify which of the three web browsers should receive the reply?
- the destination IP address
- the destination port number
- the source IP address
- the source port number
Explanation:
Each web browser client application opens a randomly generated port number in the range of the registered ports and uses this number as the source port number in the datagram that it sends to a server. The server then uses this port number as the destination port number in the reply datagram that it sends to the web browser. The PC that is running the web browser application receives the datagram and uses the destination port number that is contained in this datagram to identify the client application.
-
What are two ways that TCP uses the sequence numbers in a segment? (Choose two.)
- to identify missing segments at the destination
- to reassemble the segments at the remote location
- to specify the order in which the segments travel from source to destination
- to limit the number of segments that can be sent out of an interface at one time
- to determine if the packet changed during transit
-
Which two tasks are functions of the presentation layer? (Choose two.)
- compression
- addressing
- encryption
- session control
- authentication
Explanation:
The presentation layer deals with common data format. Encryption, formatting, and compression are some of the functions of the layer. Addressing occurs in the network layer, session control occurs in the session layer, and authentication takes place in the application or session layer.
-
What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
- wireless networking
- social networking without the Internet
- network printing using a print server
- resource sharing without a dedicated server
Explanation:
The peer-to-peer (P2P) networking model allows data, printer, and resource sharing without a dedicated server.
-
A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- ipconfig
- netstat
- nslookup
Explanation:
Traceroute (tracert) is a utility that generates a list of hops that were successfully reached along the path from source to destination.This list can provide important verification and troubleshooting information. The ipconfig utility is used to display the IP configuration settings on a Windows PC. The Netstat utility is used to identify which active TCP connections are open and running on a networked host. Nslookup is a utility that allows the user to manually query the name servers to resolve a given host name. This utility can also be used to troubleshoot name resolution issues and to verify the current status of the name servers.
-
Which domain name would be an example of a top-level domain?
- www.cisco.com
- cisco.com
- .com
- root.cisco.com
-
Explanation:
Top-level domains represent a country or type of organization, such as .com or .edu.
-
A PC obtains its IP address from a DHCP server. If the PC is taken off the network for repair, what happens to the IP address configuration?
- The configuration is permanent and nothing changes.
- The address lease is automatically renewed until the PC is returned.
- The address is returned to the pool for reuse when the lease expires.
- The configuration is held by the server to be reissued when the PC is returned.
Explanation:
When a DCHP address is issued to a host, it is for a specific lease time. Once the lease expires, the address is returned to the DHCP pool.
-
A wireless host needs to request an IP address. What protocol would be used to process the request?
- FTP
- HTTP
- DHCP
- ICMP
- SNMP
Explanation:
The DHCP protocol is used to request, issue, and manage IP addressing information. CSMA/CD is the access method used with wired Ethernet. ICMP is used to test connectivity. SNMP is used with network management and FTP is used for file transfer.
-
Which example of malicious code would be classified as a Trojan horse?
- malware that was written to look like a video game
- malware that requires manual user intervention to spread between systems
- malware that attaches itself to a legitimate program and spreads to other programs when launched
- malware that can automatically spread from one system to another by exploiting a vulnerability in the target
Explanation:
A Trojan horse is malicious code that has been written specifically to look like a legitimate program. This is in contrast to a virus, which simply attaches itself to an actual legitimate program. Viruses require manual intervention from a user to spread from one system to another, while a worm is able to spread automatically between systems by exploiting vulnerabilities on those devices.
-
When applied to a router, which command would help mitigate brute-force password attacks against the router?
- exec-timeout 30
- service password-encryption
- banner motd $Max failed logins = 5$
- login block-for 60 attempts 5 within 60
Explanation:
The login block-for command sets a limit on the maximum number of failed login attempts allowed within a defined period of time. If this limit is exceeded, no further logins are allowed for the specified period of time. This helps to mitigate brute-force password cracking since it will significantly increase the amount of time required to crack a password. The exec-timeout command specifies how long the session can be idle before the user is disconnected. The service password-encryption command encrypts the passwords in the running configuration. The banner motd command displays a message to users who are logging in to the device.
-
Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (not all options are used.)
- Question
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 004 - Answer
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 005
- Question
-
Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 006 - Question
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 007 - Answer
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 008 Explanation:
Packets with a destination of 172.17.6.15 are forwarded through Fa0/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.10.5 are forwarded through Fa1/1. Packets with a destination of 172.17.12.10 are forwarded through Fa1/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.14.8 are forwarded through Fa0/1. Because network 172.17.8.0 has no entry in the routing table, it will take the gateway of last resort, which means that packets with a destination of 172.17.8.20 are forwarded through Serial0/0/0. Because a gateway of last resort exists, no packets will be dropped.
- Question
-
A company is expanding its business to other countries. All branch offices must remain connected to corporate headquarters at all times. Which network technology is required to support this requirement?
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN
- WLAN
Explanation:
A local-area network (LAN) normally connects end users and network resources over a limited geographic area using Ethernet technology. A wireless LAN (WLAN) serves the same purpose as a LAN but uses wireless technologies. A metropolitan-area network (MAN) spans a larger geographic area such as a city, and a wide-area network (WAN) connects networks together over a large geographic area. WANs can span cities, countries, or the globe.
-
A home user is looking for an ISP connection that provides high speed digital transmission over regular phone lines. What ISP connection type should be used?
- DSL
- dial-up
- satellite
- cell modem
- cable modem
-
How does quality of service help a network support a wide range of applications and services?
- by limiting the impact of a network failure
- by allowing quick recovery from network failures
- by providing mechanisms to manage congested network traffic
- by providing the ability for the network to grow to accommodate new users
Explanation:
Quality of service (QoS), is a vital component of the architecture of a network. With QoS, network administrators can provide applications with predictable and measurable service guarantees through mechanisms that manage congested network traffic.
-
After making configuration changes on a Cisco switch, a network administrator issues a copy running-config startup-config command. What is the result of issuing this command?
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
Explanation:
With the copy running-config startup-config command, the content of the current operating configuration replaces the startup configuration file stored in NVRAM. The configuration file saved in NVRAM will be loaded when the device is restarted.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator has already logged into a Telnet session on the switch, which password is needed to access privileged EXEC mode?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 009 - letmein
- secretin
- lineconin
- linevtyin
Explanation:
Telnet accesses a network device through the virtual interface configured with the line VTY command. The password configured under this is required to access the user EXEC mode. The password configured under the line console 0 command is required to gain entry through the console port, and the enable and enable secret passwords are used to allow entry into the privileged EXEC mode.
- letmein
-
What function does pressing the Tab key have when entering a command in IOS?
- It aborts the current command and returns to configuration mode.
- It exits configuration mode and returns to user EXEC mode.
- It moves the cursor to the beginning of the next line.
- It completes the remainder of a partially typed word in a command.
Explanation:
Pressing the Tab key after a command has been partially typed will cause the IOS to complete the rest of the command.
-
What layer is responsible for routing messages through an internetwork in the TCP/IP model?
- internet
- transport
- network access
- session
Explanation:
The TCP/IP model consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and network access. Of these four layers, it is the internet layer that is responsible for routing messages. The session layer is not part of the TCP/IP model but is rather part of the OSI model.
-
Which statement accurately describes a TCP/IP encapsulation process when a PC is sending data to the network?
- Data is sent from the internet layer to the network access layer.
- Packets are sent from the network access layer to the transport layer.
- Segments are sent from the transport layer to the internet layer.
- Frames are sent from the network access layer to the internet layer.
Explanation:
When the data is traveling from the PC to the network, the transport layer sends segments to the internet layer. The internet layer sends packets to the network access layer, which creates frames and then converts the frames to bits. The bits are released to the network media.
-
What unique address is embedded in an Ethernet NIC and used for communication on an Ethernet network?
- host address
- IP address
- MAC address
- network address
Explanation:
The MAC address is a 48-bit address that is burned into every Ethernet NIC. Each MAC address is unique throughout the world.
-
Which procedure is used to reduce the effect of crosstalk in copper cables?
- requiring proper grounding connections
- twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together
- wrapping the bundle of wires with metallic shielding
- designing a cable infrastructure to avoid crosstalk interference
- avoiding sharp bends during installation
Explanation:
In copper cables, crosstalk is a disturbance caused by the electric or magnetic fields of a signal on one wire interfering with the signal in an adjacent wire. Twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together can effectively cancel the crosstalk. The other options are effective measures to counter the negative effects of EMI and RFI, but not crosstalk.
-
During the encapsulation process, what occurs at the data link layer for a PC connected to an Ethernet network?
- An IP address is added.
- The logical address is added.
- The physical address is added.
- The process port number is added.
Explanation:
The Ethernet frame includes the source and destination physical address. The trailer includes a CRC value in the Frame Check Sequence field to allow the receiving device to determine if the frame has been changed (has errors) during the transmission.
-
What are two characteristics of Ethernet MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
- They are globally unique.
- They are routable on the Internet.
- They are expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits.
- MAC addresses use a flexible hierarchical structure.
- MAC addresses must be unique for both Ethernet and serial interfaces on a device.
Explanation:
An Ethernet MAC address is a 48-bit binary value expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits. MAC addresses must be globally unique by design. MAC addresses are in flat structure and thus they are not routable on the Internet. Serial interfaces do not use MAC addresses.
-
If a device receives an Ethernet frame of 60 bytes, what will it do?
- drop the frame
- process the frame as it is
- send an error message to the sending device
- add random data bytes to make it 64 bytes long and then forward it
Explanation:
Ethernet standards define the minimum frame size as 64 bytes. A frame less than 64 bytes is considered a “collision fragment” or “runt frame” and is automatically discarded by receiving devices.
-
Under which two circumstances will a switch flood a frame out of every port except the port that the frame was received on? (Choose two.)
- The frame has the broadcast address as the destination address.
- The destination address is unknown to the switch.
- The source address in the frame header is the broadcast address.
- The source address in the frame is a multicast address.
- The destination address in the frame is a known unicast address.
Explanation:
A switch will flood a frame out of every port, except the one that the frame was received from, under two circumstances. Either the frame has the broadcast address as the destination address, or the destination address is unknown to the switch.
-
Which switching method has the lowest level of latency?
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
- fast-forward
Explanation:
Fast-forward switching begins to forward a frame after reading the destination MAC address, resulting in the lowest latency. Fragment-free reads the first 64 bytes before forwarding. Store-and-forward has the highest latency because it reads the entire frame before beginning to forward it. Both fragment-free and fast-forward are types of cut-through switching.
-
Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- netstat -s
- route print
- show ip route
- netstat -r
- tracert
Explanation:
On a Windows host, the route print or netstat -r commands can be used to display the host routing table. Both commands generate the same output. On a router, the show ip route command is used to display the routing table. The netstat –scommand is used to display per-protocol statistics. The tracert command is used to display the path that a packet travels to its destination.
-
Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet forwarding
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection
- flow control
-
What is the binary representation of 0xCA?
- 10111010
- 11010101
- 11001010
- 11011010
Explanation:
When converted, CA in hex is equivalent to 11011010 in binary. One way to do the conversion is one nibble at a time, C = 1100 and A = 1010. Combine the two nibbles gives 11001010.
-
At a minimum, which address is required on IPv6-enabled interfaces?
- link-local
- unique local
- site local
- global unicast
Explanation:
All IPv6 enabled interfaces must at minimum have a link-local address. Other IPv6 addresses can be assigned to the interface as required.
-
Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
Explanation:
Using stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC), a PC can solicit a router and receive the prefix length of the network. From this information the PC can then create its own IPv6 global unicast address.
-
What is the purpose of the command ping ::1?
- It tests the internal configuration of an IPv6 host.
- It tests the broadcast capability of all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the multicast connectivity to all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the reachability of the default gateway for the network.
Explanation:
The address ::1 is an IPv6 loopback address. Using the command ping ::1 tests the internal IP stack to ensure that it is configured and functioning correctly. It does not test reachability to any external device, nor does it confirm that IPv6 addresses are properly configured on the host.
-
How many usable IP addresses are available on the 192.168.1.0/27 network?
- 256
- 254
- 62
- 30
- 16
- 32
Explanation:
A /27 mask is the same as 255.255.255.224. This leaves 5 host bits. With 5 host bits, 32 IP addresses are possible, but one address represents the subnet number and one address represents the broadcast address. Thus, 30 addresses can then be used to assign to network devices.
-
A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses
Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses
Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addressesWhat single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
If the same mask is to be used, then the network with the most hosts must be examined for number of hosts. Because this is 10 hosts, 4 host bits are needed. The /28 or 255.255.255.240 subnet mask would be appropriate to use for these networks.
-
What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
Explanation:
In order to accommodate 40 devices, 6 host bits are needed. With 6 bits, 64 addresses are possible, but one address is for the subnet number and one address is for a broadcast. This leaves 62 addresses that can be assigned to network devices. The mask associated with leaving 6 host bits for addressing is 255.255.255.192.
-
What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering
- 3-way handshake
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- use of checksum
Explanation:
Both TCP and UDP use source and destination port numbers to distinguish different data streams and to forward the right data segments to the right applications. Error checking the header and data is done by both protocols by using a checksum calculation to determine the integrity of the data that is received. TCP is connection-oriented and uses a 3-way handshake to establish an initial connection. TCP also uses window to regulate the amount of traffic sent before receiving an acknowledgment. UDP is connectionless and is the best protocol for carry digitized VoIP signals.
-
Why are port numbers included in the TCP header of a segment?
- to indicate the correct router interface that should be used to forward a segment
- to identify which switch ports should receive or forward the segment
- to determine which Layer 3 protocol should be used to encapsulate the data
- to enable a receiving host to forward the data to the appropriate application
- to allow the receiving host to assemble the packet in the proper order
-
Which two protocols operate at the highest layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack? (Choose two.)
- DNS
- Ethernet
- IP
- POP
- TCP
- UDP
Explanation:
The application layer is the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack. Application layer protocols include HTTP, DNS, HTML, TFTP, POP, IMAP, FTP, and SMTP.
-
What is one difference between the client-server and peer-to-peer network models?
- Only in the client-server model can file transfers occur.
- Every device in a peer-to-peer network can function as a client or a server.
- A peer-to-peer network transfers data faster than a transfer using a client-server network.
- A data transfer that uses a device serving in a client role requires that a dedicated server be present.
Explanation:
Data transfer speeds depend on a number of factors including the amount of traffic, the quality of service imposed, and the network media. Transfer speeds are not dependent on the network model type. File transfers can occur using the client-server model or the peer-to-peer model. A data transfer between a device acting in the client role and a device acting in the server role can occur in both peer-to-peer and client-server networks.
-
Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
- peer-to-peer
- master-slave
- client/server
- point-to-point
Explanation:
In the client/server network model, a network device assumes the role of server in order to provide a particular service such as file transfer and storage. In the client/server network model, a dedicated server does not have to be used, but if one is present, the network model being used is the client/server model. In contrast, a peer-to-peer network does not have a dedicated server.
-
What network service resolves the URL entered on a PC to the IP address of the destination server?
- DNS
- DHCP
- FTP
- SNMP
Explanation:
When a client attempts to connect to a website, the destination URL must be resolved to an IP address. To do this the client queries a Domain Name System (DNS) server.
-
A network engineer is analyzing reports from a recently performed network baseline. Which situation would depict a possible latency issue?
- a change in the bandwidth according to the show interfaces output
- a next-hop timeout from a traceroute
- an increase in host-to-host ping response times
- a change in the amount of RAM according to the show version output
Explanation:
While analyzing historical reports an administrator can compare host-to-host timers from the ping command and depict possible latency issues.
-
Which firewall feature is used to ensure that packets coming into a network are legitimate responses to requests initiated from internal hosts?
- stateful packet inspection
- URL filtering
- application filtering
- packet filtering
Explanation:
Stateful packet inspection on a firewall checks that incoming packets are actually legitimate responses to requests originating from hosts inside the network. Packet filtering can be used to permit or deny access to resources based on IP or MAC address. Application filtering can permit or deny access based on port number. URL filtering is used to permit or deny access based on URL or on keywords.
-
Fill in the blank.
During data communications, a host may need to send a single message to a specific group of destination hosts simultaneously. This message is in the form of a Multicast message.
-
A medium-sized business is researching available options for connecting to the Internet. The company is looking for a high speed option with dedicated, symmetric access. Which connection type should the company choose?
- DSL
- dialup
- satellite
- leased line
- cable modem
-
What is the purpose of having a converged network?
- to provide high speed connectivity to all end devices
- to make sure that all types of data packets will be treated equally
- to achieve fault tolerance and high availability of data network infrastructure devices
- to reduce the cost of deploying and maintaining the communication infrastructure
Explanation:
With the development of technology, companies can now consolidate disparate networks onto one platform called a converged network. In a converged network, voice, video, and data travel over the same network, thus eliminating the need to create and maintain separate networks. This also reduces the costs associated with providing and maintaining the communication network infrastructure.
-
What characteristic of a network enables it to quickly grow to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users?
- reliability
- scalability
- quality of service
- accessibility
Explanation:
Networks must be able to quickly grow to support new users and services, without impacting existing users and services. This ability to grow is known as scalability.
-
After several configuration changes are made to a router, the copy running-configuration startup-configuration command is issued. Where will the changes be stored?
- flash
- ROM
- NVRAM
- RAM
- the configuration register
- a TFTP server
-
Refer to the exhibit. From global configuration mode, an administrator is attempting to create a message-of-the-day banner by using the command banner motd V Authorized access only! Violators will be prosecuted! V When users log in using Telnet, the banner does not appear correctly. What is the problem?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 015 - The banner message is too long.
- The delimiting character appears in the banner message.
- The symbol “!” signals the end of a banner message.
- Message-of-the-day banners will only appear when a user logs in through the console port.
-
What are three characteristics of an SVI? (Choose three.)
- It is designed as a security protocol to protect switch ports.
- It is not associated with any physical interface on a switch.
- It is a special interface that allows connectivity by different types of media.
- It is required to allow connectivity by any device at any location.
- It provides a means to remotely manage a switch.
- It is associated with VLAN1 by default.
Explanation:
Switches have one or more switch virtual interfaces (SVIs). SVIs are created in software since there is no physical hardware associated with them. Virtual interfaces provide a means to remotely manage a switch over a network that is using IP. Each switch comes with one SVI appearing in the default configuration “out-of-the-box.” The default SVI interface is VLAN1.
-
A technician configures a switch with these commands:SwitchA(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
SwitchA(config-if)# no shutdownWhat is the technician configuring?
- Telnet access
- SVI
- password encryption
- physical switchport access
Explanation:
For a switch to have an IP address, a switch virtual interface must be configured. This allows the switch to be managed remotely over the network.
-
In computer communication, what is the purpose of message encoding?
- to convert information to the appropriate form for transmission
- to interpret information
- to break large messages into smaller frames
- to negotiate correct timing for successful communication
Explanation:
Before a message is sent across a network it must first be encoded. Encoding is the process of converting the data message into another format suitable for transmission across the physical medium. Each bit of the message is encoded into a pattern of sounds, light waves, or electrical impulses depending on the network media over which the bits are transmitted. The destination host receives and decodes the signals in order to interpret the message.
-
What is the process of dividing a data stream into smaller pieces before transmission?
- segmentation
- encapsulation
- encoding
- flow control
Explanation:
Data streams would cause significant network congestion if they were transmitted as a single large stream of bits. To increase efficiency, data streams are segmented into smaller more manageable pieces which are then transmitted over the network.
-
When IPv4 addressing is manually configured on a web server, which property of the IPv4 configuration identifies the network and host portion for an IPv4 address?
- DNS server address
- subnet mask
- default gateway
- DHCP server address
Explanation:
There are several components that need to be entered when configuring IPv4 for an end device:
- IPv4 address – uniquely identifies an end device on the network
- Subnet mask – determines the network address portion and host portion for an IPv4 address
- Default gateway – the IP address of the router interface used for communicating with hosts in another network
- DNS server address – the IP address of the Domain Name System (DNS) server
DHCP server address (if DHCP is used) is not configured manually on end devices. It will be provided by a DHCP server when an end device requests an IP address.
-
A network engineer is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical database application. The engineer notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
Explanation:
Throughput usually does not match the specified bandwidth of physical links due to multiple factors. These factors include, the amount of traffic, type of traffic, and latency created by the network devices the data has to cross.
-
Which type of UTP cable is used to connect a PC to a switch port?
- console
- rollover
- crossover
- straight-through
Explanation:
A rollover cable is a Cisco proprietary cable used to connect to a router or switch console port. A straight-through (also called patch) cable is usually used to interconnect a host to a switch and a switch to a router. A crossover cable is used to interconnect similar devices together, for example, between two switches, two routers, and two hosts.
-
What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
Explanation:
Important actions that a switch performs are as follows:
- When a frame comes in, the switch examines the Layer 2 source address to build and maintain the Layer 2 MAC address table.
- It examines the Layer 2 destination address to determine how to forward the frame. When the destination address is in the MAC address table, then the frame is sent out a particular port. When the address is unknown, the frame is sent to all ports that have devices connected to that network.
-
What are two examples of the cut-through switching method? (Choose two.)
- store-and-forward switching
- fast-forward switching
- CRC switching
- fragment-free switching
- QOS switching
Explanation:
Store-and forward switching accepts the entire frame and performs error checking using CRC before forwarding the frame. Store-and-forward is often required for QOS analysis. Fast-forward and fragment-free are both variations of the cut-through switching method where only part of the frame is received before the switch begins to forward it.
-
What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
- source and destination MAC
- source and destination application protocol
- source and destination port number
- source and destination IP address
Explanation:
IP is a Layer 3 protocol. Layer 3 devices can open the Layer 3 header to inspect the Layer 3 header which contains IP-related information including the source and destination IP addresses.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 016 - subnet mask
- DNS address
- host IP address
- default gateway address
Explanation:
When a 255.255.255.224 subnet mask is used, the first three bits of the last octet are part of the network portion for an IPv4 address in the subnet. For the 192.168.5.96/27 network, valid host addresses are 192.168.5.97 through 192.168.5.126. The default gateway address is for the Layer 3 device on the same network and it must contain an IP address within the valid IP address range.
-
Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
- to identify the broadcast address of the destination network
- to identify the host address of the destination host
- to identify faulty frames
- to identify the network address of the destination network
Explanation:
ANDing allows us to identify the network address from the IP address and the network mask.
-
Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117
- 192.15.301.240
- 64.104.78.227
-
What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local
- multicast
- global unicast
Explanation:
Link-local IPv6 addresses start with FE80::/10, which is any address from FE80:: to FEBF::. Link-local addresses are used extensively in IPv6 and allow directly connected devices to communicate with each other on the link they share.
-
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 017 - There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
- There are 4 hops between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
- This host does not have a default gateway configured.
Explanation:
The output displays a successful Layer 3 connection between a host computer and a host at 19.168.100.1. It can be determined that 4 hops exist between them and the average transmission time is 1 milliseconds. Layer 3 connectivity does not necessarily mean that an application can run between the hosts.
-
How many hosts are addressable on a network that has a mask of 255.255.255.248?
- 2
- 6
- 8
- 14
- 16
- 254
Explanation:
The subnet mask of 255.255.255.248 is the same as /29. This means the network portion of the address is 29 of the 32 bits in the address. Only 3 bits remain for host bits. 2^3 = 8, but one of these addresses has to be used for the network number and one address must be used as the broadcast address to reach all of the hosts on this network. That leaves only 6 usable IP addresses that can be assigned to hosts in this network. Don’t forget that the default gateway must be one of these devices if this network is to communicate with other networks.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address of 192.168.10.0/24 that has been assigned to a high school building. The largest network in this building has 100 devices. If 192.168.10.0 is the network number for the largest network, what would be the network number for the next largest network, which has 40 devices?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 018 - 192.168.10.0
- 192.168.10.128
- 192.168.10.192
- 192.168.10.224
- 192.168.10.240
Explanation:
The first thing to calculate is what IP addresses are used by the largest LAN. Because the LAN has 100 hosts, 7 bits must be left for host bits. This would be a subnet mask of 255.255.255.128 for the largest LAN (192.168.10.0/25). The IP addresses range from 192.168.10.0 through 192.168.10.127. 192.168.10.0 is the network number (all 0s in the host bits) and 192.168.10.127 is the broadcast for this Ethernet LAN (all 1s in the host bits). The next available IP address is the next network number – 192.168.10.128.
-
In what two situations would UDP be the preferred transport protocol over TCP? (Choose two.)
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
Explanation:
UDP is a stateless protocol, which means that neither device on either end of the conversation must keep track of the conversation. As a stateless protocol, UDP is used as the Layer 4 protocol for applications that need speedy (best-effort) delivery. An example of such traffic is the transport of digitized voice or video.
-
What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
- timing and synchronization
- destination and source port numbers
- destination and source physical addresses
- destination and source logical network addresses
Explanation:
The destination and source port numbers are used to identify exactly which protocol and process is requesting or responding to a request.
-
What is the TCP mechanism used in congestion avoidance?
- three-way handshake
- socket pair
- two-way handshake
- sliding window
Explanation:
TCP uses windows to attempt to manage the rate of transmission to the maximum flow that the network and destination device can support while minimizing loss and retransmissions. When overwhelmed with data, the destination can send a request to reduce the of the window. This congestion avoidance is called sliding windows.
-
Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
- UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.
- UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
- UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection.
- UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.
- UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
- UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
Explanation:
UDP is a simple protocol that provides the basic transport layer functions. It has much lower overhead than TCP because it is not connection-oriented and does not offer the sophisticated retransmission, sequencing, and flow control mechanisms that provide reliability.
-
Which two roles can a computer assume in a peer-to-peer network where a file is being shared between two computers? (Choose two.)
- client
- master
- server
- slave
- transient
Explanation:
In a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, two or more computers are connected and can share resources without the use of a dedicated server. The computer that has the file acts as a server for the device (the client) that requests the file.
-
What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
- to request an HTML page from a web server
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
Explanation:
There are three common HTTP message types:
- GET – used by clients to request data from the web server
- POST – used by clients to upload data to a web server
- PUT – used by clients to upload data to a web server
-
When planning for network growth, where in the network should packet captures take place to assess network traffic?
- on as many different network segments as possible
- only at the edge of the network
- between hosts and the default gateway
- only on the busiest network segment
Explanation:
Because some types of traffic will be only on specific network segments, packet captures for analysis should be performed on as many segments as possible.
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is testing connectivity to a remote device with the IP address 10.1.1.1. What does the output of this command indicate?
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 019 - Connectivity to the remote device was successful.
- A router along the path did not have a route to the destination.
- A ping packet is being blocked by a security device along the path.
- The connection timed out while waiting for a reply from the remote device.
Explanation:
In the output of the ping command, an exclamation mark (!) indicates a response was successfully received, a period (.) indicates that the connection timed out while waiting for a reply, and the letter “U” indicates that a router along the path did not have a route to the destination and sent an ICMP destination unreachable message back to the source.
-
Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
- Question
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 020 - Answer
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 021 Explanation:A logical topology diagram typically depicts the IP addressing scheme and groupings of devices and ports. A physical topology diagram shows how those devices are connected to each other and the network, focusing on the physical locations of intermediary devices, configured ports, and cabling.
- Question
-
Match the situation with the appropriate use of network media.
- Question
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 024 - Answer
Cisco ITN CCNA 1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer R&S 2018 2019 025 Explanation:Copper Cables – horizontal cabling structure and desktop PCs in offices in an enterprise
Fiber optic – backbone cabling in an enterprise and long-haul networks
Wireless – coffee shops and waiting rooms in a hospital
- Question
-
Recommend
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to «Online Test» link below.
| Version 5.02 | Version 5.1 | Version 6.0 | Online Assessment |
| Final Exam | Final Exam | Final Exam | Online A, Online B, Online C |
| CCNA2 Pretest Exam | |||
| Pretest Exam | Pretest Exam | Pretest Exam | Online Test |
1. What is a characteristic of a fault tolerant network?
- a network that protects confidential information from unauthorized access
- a network that can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service delivered to existing users
- a network that supports a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users
- a network that recovers quickly when a failure occurs and depends on redundancy to limit the impact of a failure*
2. Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page*
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
3. What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.*
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
4. What is the function of the shell in an OS?
- It interacts with the device hardware.
- It interfaces between the users and the kernel.*
- It provides dedicated firewall services.
- It provides the intrusion protection services for the device.
5. Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco switch?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection*
6. A network technician is attempting to configure an interface by entering the following command: SanJose(config)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0. The command is rejected by the device. What is the reason for this?
- The command is being entered from the wrong mode of operation.*
- The command syntax is wrong.
- The subnet mask information is incorrect.
- The interface is shutdown and must be enabled before the switch will accept the IP address.
7. An administrator uses the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination on a switch after issuing the ping command. What is the purpose of using these keystrokes?
- to restart the ping process
- to interrupt the ping process*
- to exit to a different configuration mode
- to allow the user to complete the command
8. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses a console connection to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?
- letmein
- secretin
- linevtyin
- lineconin*
9. On which switch interface would an administrator configure an IP address so that the switch can be managed remotely?
- FastEthernet0/1
- VLAN 1*
- vty 0
- console 0
10. What protocol is responsible for controlling the size of segments and the rate at which segments are exchanged between a web client and a web server?
- TCP*
- IP
- HTTP
- Ethernet
11. What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- A company can monopolize the market.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.*
12. What are two benefits of using a layered network model? (Choose two.)
- It assists in protocol design. *
- It speeds up packet delivery.
- It prevents designers from creating their own model.
- It prevents technology in one layer from affecting other layers.*
- It ensures a device at one layer can function at the next higher layer.
13. Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- data link
- network*
- physical
- session
- transport*
14. Which name is assigned to the transport layer PDU?
- bits
- data
- frame
- packet
- segment*
15. A network engineer is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical database application. The engineer notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network*
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network*
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
16. A network administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues on a server. Using a tester, the administrator notices that the signals generated by the server NIC are distorted and not usable. In which layer of the OSI model is the error categorized?
- presentation layer
- network layer
- physical layer*
- data link layer
17. Which type of UTP cable is used to connect a PC to a switch port?
- console
- rollover
- crossover
- straight-through**
18. A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network*
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network *
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
19. What is a characteristic of UTP cabling?
- cancellation*
- cladding
- immunity to electrical hazards
- woven copper braid or metallic foil
20. What are two characteristics of fiber-optic cable? (Choose two.)
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.*
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding, and twisting to protect data.
- It typically contains 4 pairs of fiber-optic wires.
- It is more expensive than UTP cabling is.*
21. What is a characteristic of the LLC sublayer?
- It provides the logical addressing required that identifies the device.
- It provides delimitation of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium.
- It places information in the frame allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to use the same network interface and media.*
- It defines software processes that provide services to the physical layer.
22. A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies for connecting remote sites to a headquarters building. Which topology provides high availability and connects some, but not all, remote sites?
- mesh
- partial mesh*
- hub and spoke
- point-to-point
23. What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA*
- token passing
24. What are the three primary functions provided by Layer 2 data encapsulation? (Choose three.)
- error correction through a collision detection method
- session control using port numbers
- data link layer addressing*
- placement and removal of frames from the media
- detection of errors through CRC calculations *
- delimiting groups of bits into frames*
- conversion of bits into data signals
25. What will a host on an Ethernet network do if it receives a frame with a destination MAC address that does not match its own MAC address?
- It will discard the frame.*
- It will forward the frame to the next host.
- It will remove the frame from the media.
- It will strip off the data-link frame to check the destination IP address.
26. What are two examples of the cut-through switching method? (Choose two.)
- store-and-forward switching
- fast-forward switching*
- CRC switching
- fragment-free switching*
- QOS switching
27. What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table*
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address*
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
28. Which frame forwarding method receives the entire frame and performs a CRC check to detect errors before forwarding the frame?
- cut-through switching
- store-and-forward switching*
- fragment-free switching
- fast-forward switching
29. Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- 172.168.10.99
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- 172.168.10.65
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB*
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
30. What addresses are mapped by ARP?
- destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address*
- destination IPv4 address to the source MAC address
- destination IPv4 address to the destination host name
- destination MAC address to the source IPv4 address
31. What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
- source and destination MAC
- source and destination application protocol
- source and destination port number
- source and destination IP address*
32. What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination *
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer*
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
33. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?
- subnet mask
- DNS address
- host IP address
- default gateway address*
34. Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
- to identify the broadcast address of the destination network
- to identify the host address of the destination host
- to identify faulty frames
- to identify the network address of the destination network*
35. What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed *
- to store the startup configuration file*
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
36. Refer to the exhibit. What will be the result of entering this configuration the next time a network administrator connects a console cable to the router and no additional commands have been entered?
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco123.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco234.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco789.
- The administrator will be presented with the R1> prompt.*
37. What is the dotted decimal representation of the IPv4 address 11001011.00000000.01110001.11010011?
- 192.0.2.199
- 198.51.100.201
- 203.0.113.211*
- 209.165.201.223
38. What are three characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose three.)
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts. *
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information. *
- Routers will not forward multicast addresses in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.*
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses.
39. What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8*
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 127.16.0.0/12
- 172.16.0.0/12*
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 192.168.0.0/16*
40. What purpose does NAT64 serve in IPv6?
- It converts IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.*
- It translates private IPv6 addresses into public IPv6 addresses.
- It enables companies to use IPv6 unique local addresses in the network.
- It converts regular IPv6 addresses into 64-bit addresses that can be used on the Internet.
- It converts the 48-bit MAC address into a 64-bit host address that can be used for automatic host addressing.
41. What is the most compressed representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001?
- 2001:0:abcd::1
- 2001:0:0:abcd::1*
- 2001::abcd::1
- 2001:0000:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd:0:1
42. Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FEC0::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FE80::/10*
- FF00::/8
43. Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17*
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117*
- 192.15.301.240
- 64.104.78.227 *
44. Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
- There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.*
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
- There are 4 hops b**etween this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.*
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
- This host does not have a default gateway configured.
45. What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local*
- multicast
- global unicast
46. How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
- 254
- 190
- 192
- 62*
- 64
47. A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128*
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
48. A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses
Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses
Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240*
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
49. How many hosts are addressable on a network that has a mask of 255.255.255.248?
- 2
- 6*
- 8
- 14
- 16
- 254
50. Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26*
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
51. What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192*
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
52. What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering*
- 3-way handshake
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- use of checksum*
53. Why are port numbers included in the TCP header of a segment?
- to indicate the correct router interface that should be used to forward a segment
- to identify which switch ports should receive or forward the segment
- to determine which Layer 3 protocol should be used to encapsulate the data
- to enable a receiving host to forward the data to the appropriate application*
- to allow the receiving host to assemble the packet in the proper order
54. Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address of 192.168.10.0/24 that has been assigned to a high school building. The largest network in this building has 100 devices. If 192.168.10.0 is the network number for the largest network, what would be the network number for the next largest network, which has 40 devices?
- 192.168.10.0
- 192.168.10.128*
- 192.168.10.192
- 192.168.10.224
- 192.168.10.240
55. Which statement is true about variable-length subnet masking?
- Each subnet is the same size.
- The size of each subnet may be different, depending on requirements.*
- Subnets may only be subnetted one additional time.
- Bits are returned, rather than borrowed, to create additional subnets.
56. In what two situations would UDP be the preferred transport protocol over TCP? (Choose two.)
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed*
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data*
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
57. What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
- timing and synchronization
- destination and source port numbers*
- destination and source physical addresses
- destination and source logical network addresses
58. What is the TCP mechanism used in congestion avoidance?
- three-way handshake
- socket pair
- two-way handshake
- sliding window*
59. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.*
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
60. A user opens three browsers on the same PC to access www.cisco.com to search for certification course information. The Cisco web server sends a datagram as a reply to the request from one of the web browsers. Which information is used by the TCP/IP protocol stack in the PC to identify which of the three web browsers should receive the reply?
- the destination IP address
- the destination port number*
- the source IP address
- the source port number
61. What are two ways that TCP uses the sequence numbers in a segment? (Choose two.)
- to identify missing segments at the destination *
- to reassemble the segments at the remote location*
- to specify the order in which the segments travel from source to destination
- to limit the number of segments that can be sent out of an interface at one time
- to determine if the packet changed during transit
62. Which two tasks are functions of the presentation layer? (Choose two.)
- compression*
- addressing
- encryption*
- session control
- authentication
63. Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
- UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.*
- UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
- UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection. *
- UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.*
- UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
- UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
64. What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
- wireless networking
- social networking without the Internet
- network printing using a print server
- resource sharing without a dedicated server*
65. A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- ipconfig
- netstat
- nslookup*
66. Which domain name would be an example of a top-level domain?
- www.cisco.com
- cisco.com
- .com*
- root.cisco.com
67. A PC obtains its IP address from a DHCP server. If the PC is taken off the network for repair, what happens to the IP address configuration?
- The configuration is permanent and nothing changes.
- The address lease is automatically renewed until the PC is returned.
- The address is returned to the pool for reuse when the lease expires.*
- The configuration is held by the server to be reissued when the PC is returned.
68. When planning for network growth, where in the network should packet captures take place to assess network traffic?
- on as many different network segments as possible*
- only at the edge of the network
- between hosts and the default gateway
- only on the busiest network segment
69. A wireless host needs to request an IP address. What protocol would be used to process the request?
- FTP
- HTTP
- DHCP*
- ICMP
- SNMP
70. Which example of malicious code would be classified as a Trojan horse?
- malware that was written to look like a video game*
- malware that requires manual user intervention to spread between systems
- malware that attaches itself to a legitimate program and spreads to other programs when launched
- malware that can automatically spread from one system to another by exploiting a vulnerability in the target
71. When applied to a router, which command would help mitigate brute-force password attacks against the router?
- exec-timeout 30
- service password-encryption
- banner motd $Max failed logins = 5$
- login block-for 60 attempts 5 within 60*
72. A network technician suspects that a particular network connection between two Cisco switches is having a duplex mismatch. Which command would the technician use to see the Layer 1 and Layer 2 details of a switch port?
- show mac-address-table
- show ip interface brief
- show interfaces*
- show running-config
73. Where are Cisco IOS debug output messages sent by default?
- Syslog server
- console line*
- memory buffers
- vty lines
74. Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (not all options are used.)
Question
Answer
75. Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
Question
Answer
76. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is testing connectivity to a remote device with the IP address 10.1.1.1. What does the output of this command indicate?
- Connectivity to the remote device was successful.
- A router along the path did not have a route to the destination.*
- A ping packet is being blocked by a security device along the path.
- The connection timed out while waiting for a reply from the remote device.
77. A user is unable to reach the web site when typing http://www.cisco.com in a web browser, but can reach the same site by typing http://72.163.4.161. What is the issue?
- default gateway
- DHCP
- TCP/IP protocol stack
- DNS *
78. A company is expanding its business to other countries. All branch offices must remain connected to corporate headquarters at all times. Which network technology is required to support this requirement?
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN*
- WLAN
79. A home user is looking for an ISP connection that provides high speed digital transmission over regular phone lines. What ISP connection type should be used?
- DSL*
- dial-up
- satellite
- cell modem
- cable modem
80. How does quality of service help a network support a wide range of applications and services?
- by limiting the impact of a network failure
- by allowing quick recovery from network failures
- by providing mechanisms to manage congested network traffic*
- by providing the ability for the network to grow to accommodate new users
81. What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface*
82. After making configuration changes on a Cisco switch, a network administrator issues a copy running-config startup-config command. What is the result of issuing this command?
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.*
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
83. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator has already logged into a Telnet session on the switch, which password is needed to access privileged EXEC mode?
- letmein
- secretin*
- lineconin
- linevtyin
84. Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
Question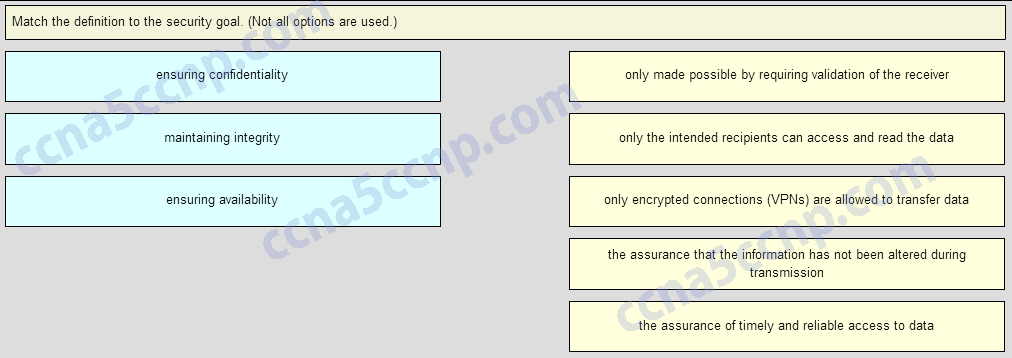
85. Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco network device?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection*
86. What function does pressing the Tab key have when entering a command in IOS?
- It aborts the current command and returns to configuration mode.
- It exits configuration mode and returns to user EXEC mode.
- It moves the cursor to the beginning of the next line.
- It completes the remainder of a partially typed word in a command.*
87. What layer is responsible for routing messages through an internetwork in the TCP/IP model?
- internet*
- transport
- network access
- session
88. Which statement accurately describes a TCP/IP encapsulation process when a PC is sending data to the network?
- Data is sent from the internet layer to the network access layer.
- Packets are sent from the network access layer to the transport layer.
- Segments are sent from the transport layer to the internet layer.*
- Frames are sent from the network access layer to the internet layer.
89. What unique address is embedded in an Ethernet NIC and used for communication on an Ethernet network?
- host address
- IP address
- MAC address*
- network address
- k layer
90. Which procedure is used to reduce the effect of crosstalk in copper cables?
- requiring proper grounding connections
- twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together*
- wrapping the bundle of wires with metallic shielding
- designing a cable infrastructure to avoid crosstalk interference
- avoiding sharp bends during installation
91. During the encapsulation process, what occurs at the data link layer for a PC connected to an Ethernet network?
- An IP address is added.
- The logical address is added.
- The physical address is added.*
- The process port number is added.
92. What are two characteristics of Ethernet MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
- They are globally unique.*
- They are routable on the Internet.
- They are expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits.*
- MAC addresses use a flexible hierarchical structure.
- MAC addresses must be unique for both Ethernet and serial interfaces on a device.
93. If a device receives an Ethernet frame of 60 bytes, what will it do?
- drop the frame*
- process the frame as it is
- send an error message to the sending device
- add random data bytes to make it 64 bytes long and then forward it
94. Under which two circumstances will a switch flood a frame out of every port except the port that the frame was received on? (Choose two.)
- The frame has the broadcast address as the destination address. *
- The destination address is unknown to the switch.*
- The source address in the frame header is the broadcast address.
- The source address in the frame is a multicast address.
- The destination address in the frame is a known unicast address.
95. Which switching method has the lowest level of latency?
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
- fast-forward*
96. Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- netstat -s
- route print*
- show ip route
- netstat -r*
- tracert
97. Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet forwarding*
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection*
- flow control
98. What is the binary representation of 0xCA?
- 10111010
- 11010101
- 11001010*
- 11011010
99. At a minimum, which address is required on IPv6-enabled interfaces?
- link-local*
- unique local
- site local
- global unicast
100. Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC*
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
101. What is the purpose of the command ping ::1?
- It tests the internal configuration of an IPv6 host.*
- It tests the broadcast capability of all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the multicast connectivity to all hosts on the subnet.
- It tests the reachability of the default gateway for the network.
102. How many usable IP addresses are available on the 192.168.1.0/27 network?
- 256
- 254
- 62
- 30*
- 16
- 32
103. What is the process of dividing a data stream into smaller pieces before transmission?
- segmentation*
- encapsulation
- encoding
- flow control
104. When IPv4 addressing is manually configured on a web server, which property of the IPv4 configuration identifies the network and host portion for an IPv4 address?
- DNS server address
- subnet mask*
- default gateway
- DHCP server address
105. Which two roles can a computer assume in a peer-to-peer network where a file is being shared between two computers? (Choose two.)
- client*
- master
- server*
- slave
- transient
106. Which two protocols operate at the highest layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack? (Choose two.)
- DNS*
- Ethernet
- IP
- POP*
- TCP
- UDP
107. What is one difference between the client-server and peer-to-peer network models?
- Only in the client-server model can file transfers occur.
- Every device in a peer-to-peer network can function as a client or a server.*
- A peer-to-peer network transfers data faster than a transfer using a client-server network.
- A data transfer that uses a device serving in a client role requires that a dedicated server be present.
108. What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
- to request an HTML page from a web server*
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
109. Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
- peer-to-peer
- master-slave
- client/server*
- point-to-point
110. What network service resolves the URL entered on a PC to the IP address of the destination server?
- DNS*
- DHCP
- FTP
- SNMP
111. A network engineer is analyzing reports from a recently performed network baseline. Which situation would depict a possible latency issue?
- a change in the bandwidth according to the show interfaces output
- a next-hop timeout from a traceroute
- an increase in host-to-host ping response times*
- a change in the amount of RAM according to the show version output
112. Which firewall feature is used to ensure that packets coming into a network are legitimate responses to requests initiated from internal hosts?
- stateful packet inspection*
- URL filtering
- application filtering
- packet filtering
113. What is one indication that a Windows computer did not receive an IPv4 address from a DHCP server?
- The computer cannot ping 127.0.0.1.
- Windows displays a DHCP timeout message.
- The computer receives an IP address that starts with 169.254*
- The computer cannot ping other devices on the same network with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 range.
114. Which command can an administrator issue on a Cisco router to send debug messages to the vty lines?
- terminal monitor*
- logging console
- logging buffered
- logging synchronous
115. Fill in the blank.
During data communications, a host may need to send a single message to a specific group of destination hosts simultaneously. This message is in the form of a Multicast *message.
116. A medium-sized business is researching available options for connecting to the Internet. The company is looking for a high speed option with dedicated, symmetric access. Which connection type should the company choose?
- DSL
- dialup
- satellite
- leased line*
- cable modem
117. What is the purpose of having a converged network?
- to provide high speed connectivity to all end devices
- to make sure that all types of data packets will be treated equally
- to achieve fault tolerance and high availability of data network infrastructure devices
- to reduce the cost of deploying and maintaining the communication infrastructure*
118. What characteristic of a network enables it to quickly grow to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users?
- reliability
- scalability*
- quality of service
- accessibility
119. After several configuration changes are made to a router, the copy running-configuration startup-configuration command is issued. Where will the changes be stored?
- flash
- ROM
- NVRAM*
- RAM
- the configuration register
- a TFTP server
120. Refer to the exhibit. From global configuration mode, an administrator is attempting to create a message-of-the-day banner by using the command banner motd V Authorized access only! Violators will be prosecuted! V When users log in using Telnet, the banner does not appear correctly. What is the problem?
- The banner message is too long.
- The delimiting character appears in the banner message.*
- The symbol “!” signals the end of a banner message.
- Message-of-the-day banners will only appear when a user logs in through the console port.
121. What are three characteristics of an SVI? (Choose three.)
- It is designed as a security protocol to protect switch ports.
- It is not associated with any physical interface on a switch.*
- It is a special interface that allows connectivity by different types of media.
- It is required to allow connectivity by any device at any location.
- It provides a means to remotely manage a switch. *
- It is associated with VLAN1 by default.*
122. A technician configures a switch with these commands:SwitchA(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
SwitchA(config-if)# no shutdownWhat is the technician configuring?
- Telnet access
- SVI*
- password encryption
- physical switchport access
123. In computer communication, what is the purpose of message encoding?
- to convert information to the appropriate form for transmission*
- to interpret information
- to break large messages into smaller frames
- to negotiate correct timing for successful communication
124. What is a characteristic of multicast messages?
- They are sent to a select group of hosts.*
- They must be acknowledged.
- They are sent to a single destination.
- They are sent to all hosts on a network.
125. A large corporation has modified its network to allow users to access network resources from their personal laptops and smart phones. Which networking trend does this describe?
- bring your own device*
- video conferencing
- online collaboration
- cloud computing
126. True or False.
A dedicated server is not needed when implementing a peer-to-peer network.
- true*
- false
127. Which term refers to a network that provides secure access to the corporate offices by suppliers, customers and collaborators?
- Internet
- intranet
- extranet*
- extendednet
Explain:
The term Internet refers to the worldwide collection of connected networks. Intranet refers to a private connection of LANs and WANS that belong to an organization and is designed to be accessible to the members of the organization, employees, or others with authorization. Extranets provide secure and safe access to suppliers, customers, and collaborators. Extendednet is not a type of network.
128. What subnet mask is required to support 512 subnets on networks 172.28.0.0/16?
- 255.255.240.0
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.128*
- 255.255.252.0
129. A DHCP server is used to IP addresses dynamically to the hosts on a network. The address pool is configured with 10.29.244.0/25. There are 19 printers on this network that need to use reserve static IP addresses from the pool. How many IP address in the pool are left to be assign to other hosts?
- 210
- 60
- 109
- 107*
- 146
Older Version:
130. What is a function of the data link layer?
- provides the formatting of data
- provides for the exchange of data over a common local media*
- provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
- provides delivery of data between two applications
131. Which communication tool allows real-time collaboration?
- wiki
- weblog
- instant messaging*
132. A host is accessing a Web server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals*
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data *
- notifying other devices when errors occur*
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
133. Refer to the exhibit. From which location did this router load the IOS?
- flash memory*
- NVRAM?
- RAM
- ROM
- a TFTP server?
134. Refer to the exhibit. Which action will be successful?
- PC1 can send a ping to 192.168.1.1?.
- PC1 can send a ping to 192.168.1.254?.
- PC2 can send a ping to 192.168.1.1.*
- PC2 can send a ping to 192.168.1.254?.
135. Fill in the blank.
Port numbers ranging from 0 to 1023 are considered to be Well Known ports.
136. Fill in the blank.
ISOC, IANA, EIA, and IEEE represent standards organizations which help to promote and maintain an open Internet.
137. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?
- The entire command, configure terminal, must be used.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.*
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
138. A company is expanding its business to other countries. All branch offices must remain connected to corporate headquarters at all times. Which network technology is required to support this requirement?
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN*
- WLAN
139. A network administrator is upgrading a small business network to give high priority to real-time applications traffic. What two types of network services is the network administrator trying to accommodate? (Choose two.)
- SNMP
- instant messaging
- voice*
- FTP
- video*
140. Match the situation with the appropriate use of network media.
Question
Answer
141. Which IPv4 address can be pinged to test the internal TCP/IP operation of a host?
- 0.0.0.0
- 0.0.0.1
- 127.0.0.1*
- 192.168.1.1
- 255.255.255.255
142. What three application layer protocols are part of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose three.)
ARP
- DHCP*
- DNS*
- FTP*
- NAT
- PPP
143. Which two protocols function at the internet layer? (Choose two)
- ARP
- BOOTP
- ICMP*
- IP*
- PPP
144. Which publicly available resources describe protocols, processes, and technologies for the Internet but do not give implementation details?
- Request for Comments*
- IRTF research papers
- protocol models
- IEEE standards
145. Which address on a PC does not change, even if the PC is moved to a different network?
- IP address
- default gateway address
- MAC address*
- logical address
146. What is the protocol that is used to discover a physical address from a known logical address and what message type does it use?
- ARP, multicast
- DNS, unicast
- DNS, broadcast
- ARP, broadcast*
- PING, multicast
- PING, broadcast
147. What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.*
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
148. What is an important function of the physical layer of the OSI model?
- It accepts frames from the physical media.
- It encapsulates upper layer data into frames.
- It defines the media access method performed by the hardware interface.
- It encodes frames into electrical, optical, or radio wave signals.*
149. Which two statements describe the characteristics of fiber-optic cabling? (Choose two.)
- Fiber-optic cabling does not conduct electricity.*
- Fiber-optic cabling has high signal loss.
- Fiber-optic cabling is primarily used as backbone cabling.*
- Multimode fiber-optic cabling carries signals from multiple sending devices.
- Fiber-optic cabling uses LEDs for single-mode cab?les and laser technology for multimode cables.
150. What is contained in the trailer of a data-link frame?
- logical address
- physical address
- data
- error detection*
151. Refer to the exhibit. A ping to PC3 is issued from PC0, PC1, and PC2 in this exact order. Which MAC addresses will be contained in the S1 MAC address table that is associated with the Fa0/1 port?
- just PC0 and PC1 MAC addresses*
- just the PC0 MAC address
- PC0, PC1, and PC2 MAC addresses
- just the PC1 MAC address
- just the PC2 MAC address
152. How does a Layer 3 switch differ from a Layer 2 switch?
- A Layer 3 switch supports VLANs, but a Layer 2 switch does not.
- An IP address can be assigned to a physical port of a Layer 3 switch. However, this is not supported in Layer 2 switches.*
- A Layer 3 switch maintains an IP address table instead of a MAC address table.
- A Layer 3 switch learns the MAC addresses that are associated with each of its ports. However, a Layer 2 switch does not.
153. What is the purpose of the routing process?
- to encapsulate data that is used to communicate across a network
- to select the paths that are used to direct traffic to destination networks*
- to convert a URL name into an IP address
- to provide secure Internet file transfer
- to forward traffic on the basis of MAC addresses
154. Which technology provides a solution to IPv4 address depletion by allowing multiple devices to share one public IP address?
- ARP
- DNS
- NAT*
- SMB
- DHCP
- HTTP
155. Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address configuration shown from PC1. What is a description of the default gateway address?
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the company to the Internet.
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the PC1 LAN to Router1.*
- It is the IP address of Switch1 that connects PC1 to other devices on the same LAN.
- It is the IP address of the ISP network device located in the cloud.
156. Which of the following are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- packet switching*
- microsegmentation
- domain name resolution
- path selection*
- flow control
157. Which two statements correctly describe a router memory type and its contents? (Choose two.)
- ROM is nonvolatile and contains basic diagnostic software.*
- FLASH is nonvolatile and contains a limited portion of the IOS.
- ROM is nonvolatile and stores the running IOS.
- RAM is volatile and stores the IP routing table.*
- NVRAM is nonvolatile and stores other system files.
158. In which default order will a router search for startup configuration information?
- NVRAM, RAM, TFTP
- NVRAM, TFTP, setup mode*
- setup mode, NVRAM, TFTP
- TFTP, ROM, NVRAM
- flash, ROM, setup mode
159. What happens when part of an Internet VoIP transmission is not delivered to the destination?
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the VoIP transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.*
160. Which three IP addresses are private ? (Choose three.)
- 10.172.168.1*
- 172.32.5.2
- 192.167.10.10
- 172.20.4.4 *
- 192.168.5.254*
- 224.6.6.6
161. How many bits make up the single IPv6 hextet :10CD:?
- 4
- 8
- 16*
- 32
162. What is the effect of configuring the ipv6 unicast-routing command on a router?
- to assign the router to the all-nodes multicast group
- to enable the router as an IPv6 router*
- to permit only unicast packets on the router
- to prevent the router from joining the all-routers multicast group
163. Which group of IPv6 addresses cannot be allocated as a host source address?
- FEC0::/10?
- FDFF::/7?
- FEBF::/10?
- FF00::/8*
164. What is the purpose of ICMP messages?
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions*
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
165. Refer to the exhibit. A technician has configured a user workstation with the IP address and default subnet masks that are shown. Although the user can access all local LAN resources, the user cannot access any Internet sites by using either FQDN or IP addresses. Based upon the exhibit, what could account for this failure?
- The DNS server addresses are incorrect.
- The default gateway address in incorrect.*
- The wrong subnet mask was assigned to the workstation.
- The workstation is not in the same network as the DNS servers.
166. A network administrator needs to monitor network traffic to and from servers in a data center. Which features of an IP addressing scheme should be applied to these devices?
- random static addresses to improve security
- addresses from different subnets for redundancy
- predictable static IP addresses for easier identification*
- dynamic addresses to reduce the probability of duplicate addresses
167. Refer to the exhibit. Which IP addressing scheme should be changed?
- Site 1
- Site 2*
- Site 3
- Site 4
168. Which two notations are useable nibble boundaries when subnetting in IPv6? (Choose two.)
- /62
- /64*
- /66
- /68*
- /70
169. A host PC has just booted and is attempting to lease an address through DHCP. Which two messages will the client typically broadcast on the network? (Choose two.)
- DHCPDISCOVER*
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST*
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
170. What is the purpose of the network security accounting function?
- to require users to prove who they are
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to keep track of the actions of a user*
- to provide challenge and response questions
171. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router:
R1# copy running-config tftp
Address or name of remote host [ ]?
When the router prompts for an address or remote host name, what IP address should the administrator enter at the prompt?
- 192.168.9.254
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.10.2
- 192.168.11.252*
- 192.168.11.254
172. Match the IPv6 address to the IPv6 address type. (Not all options are used.)
173. What two preconfigured settings that affect security are found on most new wireless routers? (Choose two.)
- broadcast SSID*
- MAC filtering enabled
- WEP encryption enabled
- PSK authentication required
- default administrator password*
174. Which type of wireless security generates dynamic encryption keys each time a client associates with an AP?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA*
175. Fill in the blank.
TFTP* is a best-effort, connectionless application layer protocol that is used to transfer files.
176. Which two components are necessary for a wireless client to be installed on a WLAN? (Choose two.)
- media
- wireless NIC*
- custom adapter
- crossover cable
- wireless bridge
- wireless client software*
177. Consider the following range of addresses:
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000:: 2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000:: 2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000:: … 2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::
The prefix-length for the range of addresses is /60*
178. Match the phases to their correct stage in the router bootup process. (Not all options are used.)
179. A host is accessing an FTP server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals*
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data*
- notifying other devices when errors occur*
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
180. When is a dial-up connection used to connect to an ISP?
- when a cellular telephone provides the service
- when a high-speed connection is provided over a cable TV network
- when a satellite dish is used
- when a regular telephone line is used*
181. On a school network, students are surfing the web, searching the library database, and attending an audio conference with their sister school in Japan. If network traffic is prioritized with QoS, how will the traffic be classified from highest priority to lowest priority?
- audio conference, database, HTTP*
- database, HTTP, audio conference
- audio conference, HTTP, database
- database, audio conference, HTTP
182. During normal operation, from which location do most Cisco routers run the IOS?
- RAM*
- flash
- NVRAM
- disk drive
183. Which keys act as a hot key combination that is used to interrupt an IOS process?
- Ctrl-Shift-X
- Ctrl-Shift-6*
- Ctrl-Z
- Ctrl-C
184. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator wants to change the name of a brand new switch, using the hostname command as shown. What prompt will display after the command is issued??
- HR Switch(config)#?
- Switch(config)#?*
- HRSwitch(config)#?
- HR(config)#?
- Switch#
185. A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?
- the TCP/IP stack on a network host*
- connectivity between two adjacent Cisco devices
- connectivity between a PC and the default gateway
- connectivity between two PCs on the same network
- physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network
186. What is the correct order for PDU encapsulation?
187. Which device should be used for enabling a host to communicate with another host on a different network?
- switch
- hub
- router*
- host
188. A network technician is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical application. The technician notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network*
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network*
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
189. Which characteristics describe fiber optic cable? (Choose two.)
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.*
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding and twisting to protect data.
- It has a maximum speed of 100 Mbps.
- It is the most expensive type of LAN cabling*
190. What are two features of a physical, star network topology? (Choose two.)
- It is straightforward to troubleshoot.*
- End devices are connected together by a bus.
- It is easy to add and remove end devices.*
- All end devices are connected in a chain to each other.
- Each end system is connected to its respective neighbor.
191. A frame is transmitted from one networking device to another. Why does the receiving device check the FCS field in the frame?
- to determine the physical address of the sending device
- to verify the network layer protocol information
- to compare the interface media type between the sending and receiving ends
- to check the frame for possible transmission errors*
- to verify that the frame destination matches the MAC address of the receiving device
192. What will a Layer 2 switch do when the destination MAC address of a received frame is not in the MAC table?
- It initiates an ARP request.
- It broadcasts the frame out of all ports on the switch.
- It notifies the sending host that the frame cannot be delivered.
- It forwards the frame out of all ports except for the port at which the frame was received.*
193. Which parameter does the router use to choose the path to the destination when there are multiple routes available?
- the lower metric value that is associated with the destination network*
- the lower gateway IP address to get to the destination network
- the higher metric value that is associated with the destination network
- the higher gateway IP address to get to the destination network
194. Which two statements describe the functions or characteristics of ROM in a router? (Choose two.)
- stores routing tables
- allows software to be updated without replacing pluggable chips on the motherboard
- maintains instructions for POST diagnostics*
- holds ARP cache
- stores bootstrap program*
195. Which statement describes a characteristic of the Cisco router management ports?
- A console port is used for remote management of the router.
- A console port is not used for packet forwarding.*
- Serial and DSL interfaces are types of management ports.
- Each Cisco router has a LED indicator to provide information about the status of the management ports.
196. What happens when part of an Internet radio transmission is not delivered to the destination?
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the radio transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.*
197. What types of addresses make up the majority of addresses within the /8 block IPv4 bit space?
- private addresses
- public addresses*
- multicast addresses
- experimental addresses
198. Refer to the exhibit. What is the maximum TTL value that is used to reach the destination www.cisco.com??
- 11
- 12
- 13*
- 14
199. A company has a network address of 192.168.1.64 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192. The company wants to create two subnetworks that would contain 10 hosts and 18 hosts respectively. Which two networks would achieve that? (Choose two.)
- 192.168.1.16/28
- 192.168.1.64/27*
- 192.168.1.128/27
- 192.168.1.96/28*
- 192.168.1.192/28
200. In a network that uses IPv4, what prefix would best fit a subnet containing 100 hosts?
- /23
- /24
- /25*
- /26
201. Which protocol supports rapid delivery of streaming media?
- Transmission Control Protocol
- Real-Time Transport Protocol*
- Secure File Transfer Protocol
- Video over Internet Protocol
202. Why would a network administrator use the tracert utility?
- to determine the active TCP connections on a PC
- to check information about a DNS name in the DNS server
- to identify where a packet was lost or delayed on a network*
- to display the IP address, default gateway, and DNS server address for a PC
203. Refer to the exhibit. What is the significance of the asterisk (*) in the exhibited output?
- The asterisk shows which file system was used to boot the system.
- The asterisk designates which file system is the default file system.*
- An asterisk indicates that the file system is bootable.
- An asterisk designates that the file system has at least one file that uses that file system.
204. Which WLAN security protocol generates a new dynamic key each time a client establishes a connection with the AP?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA*
205. Fill in the blank.
Point-to-point communications where both devices can transmit and receive on the medium at the same time are known as full-duplex
206. Match each characteristic to the appropriate email protocol. (Not all options are used.)
207. A host is accessing a Telnet server on a remote network. Which three functions are performed by intermediary network devices during this conversation? (Choose three.)
- regenerating data signals*
- acting as a client or a server
- providing a channel over which messages travel
- applying security settings to control the flow of data*
- notifying other devices when errors occur*
- serving as the source or destination of the messages
208. Refer to the exhibit. Which area would most likely be an extranet for the company network that is shown?
- area A
- area B
- area C*
- area D
209. Three office workers are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other office workers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page*
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
210. During normal operation, from which location do most Cisco switches and routers run the IOS?
- RAM*
- flash
- NVRAM
- disk drive
211. A network administrator is making changes to the configuration of a router. After making the changes and verifying the results, the administrator issues the copy running-config startup-config command. What will happen after this command executes?
- The configuration will be copied to flash.
- The configuration will load when the router is restarted.*
- The new configuration file will replace the IOS file.
- The changes will be lost when the router restarts.
212. What information does the loopback test provide?
- The TCP/IP stack on the device is working correctly.*
- The device has end-to-end connectivity.
- DHCP is working correctly.
- The Ethernet cable is working correctly.
- The device has the correct IP address on the network.
213. What happens when a switch receives a frame and the calculated CRC value is different than the value that is in the FCS field?
- The switch places the new CRC value in the FCS field and forwards the frame.
- The switch notifies the source of the bad frame.
- The switch drops the frame.*
- The switch floods the frame to all ports except the port through which the frame arrived to notify the hosts of the error.
214. Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame?
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF*
- 127.0.0.1
- 01-00-5E-00-AA-23
215. What is the auto-MDIX feature on a switch?
- the automatic configuration of an interface for 10/100/1000 Mb/s operation
- the automatic configuration of an interface for a straight-through or a crossover Ethernet cable connection*
- the automatic configuration of full-duplex operation over a single Ethernet copper or optical cable
- the ability to turn a switch interface on or off accordingly if an active connection is detected
216. What are the two main components of Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)? (Choose two.)
- adjacency tables*
- MAC-address tables
- routing tables
- ARP tables
- forwarding information base (FIB)*
217. Which statement describes the sequence of processes executed by a router when it receives a packet from a host to be delivered to a host on another network?
- It receives the packet and forwards it directly to the destination host.
- It de-encapsulates the packet, selects the appropriate path, and encapsulates the packet to forward it toward the destination host*
- It de-encapsulates the packet and forwards it toward the destination host.
- It selects the path and forwards it toward the destination host.
218. Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 has two interfaces that were configured with correct IP addresses and subnet masks. Why does the show ip route command output not display any information about the directly connected networks??
- The directly connected networks have to be created manually to be displayed in the routing table.
- The routing table will only display information about these networks when the router receives a packet.
- The no shutdown command was not issued on these interfaces.*
- The gateway of last resort was not configured.
219. What happens when part of an Internet television transmission is not delivered to the destination?
- A delivery failure message is sent to the source host.
- The part of the television transmission that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire transmission is re-sent.
- The transmission continues without the missing portion.*
220. Which three statements characterize the transport layer protocols? (Choose three.)
- TCP and UDP port numbers are used by application layer protocols.*
- TCP uses port numbers to provide reliable transportation of IP packets.
- UDP uses windowing and acknowledgments for reliable transfer of data.
- TCP uses windowing and sequencing to provide reliable transfer of data.*
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. UDP is a connectionless protocol.*
221. Which statement is true regarding the UDP client process during a session with a server?
- Datagrams that arrive in a different order than that in which they were sent are not placed in order.*
- A session must be established before datagrams can be exchanged.
- A three-way handshake takes place before the transmission of data begins.
- Application servers have to use port numbers above 1024 in order to be UDP capable.
222. Which two components are configured via software in order for a PC to participate in a network environment? (Choose two.)
- MAC address
- IP address*
- kernel
- shell
- subnet mask*
223. Which two reasons generally make DHCP the preferred method of assigning IP addresses to hosts on large networks? (Choose two.)
- It eliminates most address configuration errors.*
- It ensures that addresses are only applied to devices that require a permanent address.
- It guarantees that every device that needs an address will get one.
- It provides an address only to devices that are authorized to be connected to the network.
- It reduces the burden on network support staff.*
224. What is the subnet address for the address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
- 2001:DB8:BC15::0
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A::0*
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1::1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12::0
225. What is the purpose of the network security authentication function?
- to require users to prove who they are*
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to keep track of the actions of a user
- to provide challenge and response questions
226. Which type of wireless security makes use of dynamic encryption keys each time a client associates with an AP?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP
- WPA*
227. Launch PT – Hide and Save PT.
Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then fill in the blank.
The Server0 message isb ”winner”
228. Which field in an IPv4 packet header will typically stay the same during its transmission?
- Packet Length
- Destination Address*
- Flag
- Time-to-Live
229. Launch PT – Hide and Save PT
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. Which IPv6 address is assigned to the Serial0/0/0 interface on RT2?
- 2001:db8:abc:1::1
- 2001:db8:abc:5::1*
- 2001:db8:abc:5::2
- 2001:db8:abc:10::15
230. What must be configured to enable Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) on most Cisco devices that perform Layer 3 switching?
- Manually configure next-hop Layer 2 addresses.
- Issue the no shutdown command on routed ports.
- CEF is enabled by default, so no configuration is necessary.*
- Manually map Layer 2 addresses to Layer 3 addresses to populate the forwarding information base (FIB).
231. What is the purpose of adjacency tables as used in Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)?
- to populate the forwarding information base (FIB)
- to maintain Layer 2 next-hop addresses*
- to allow the separation of Layer 2 and Layer 3 decision making
- to update the forwarding information base (FIB)
232. Which statement describes a characteristic of the network layer in the OSI model?
- It manages the data transport between the processes running on each host.
- In the encapsulation process, it adds source and destination port numbers to the IP header.
- When a packet arrives at the destination host, its IP header is checked by the network layer to determine where the packet has to be routed.
- Its protocols specify the packet structure and processing used to carry the data from one host to another.*
233. A user gets an IP address of 192.168.0.1 from the company network administrator. A friend of the user at a different company gets the same IP address on another PC. How can two PCs use the same IP address and still reach the Internet, send and receive email, and search the web?
- Both users must be using the same Internet Service Provider.
- ISPs use Network Address Translation to change a user IP address into an address that can be used on the Internet.*
- ISPs use Domain Name Service to change a user IP address into a public IP address that can be used on the Internet.
- Both users must be on the same network.
234. Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
- to ensure the fastest possible download speed
- because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
- because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
- because HTTP requires reliable delivery*
235. What is the valid most compressed format possible of the IPv6 address 2001:0DB8:0000:AB00:0000:0000:0000:1234?
- 2001:DB8:0:AB00::1234*
- 2001:DB8:0:AB::1234
- 2001:DB8::AB00::1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB:0:1234
236. What field content is used by ICMPv6 to determine that a packet has expired?
- TTL field
- CRC field
- Hop Limit field*
- Time Exceeded field
237. Which firewall technique blocks incoming packets unless they are responses to internal requests?
- port filtering
- stateful packet inspection*
- URL filtering
- application filtering
238. A network technician is investigating network connectivity from a PC to a remote host with the address 10.1.1.5. Which command issued on the PC will return to the technician the complete path to the remote host?
- trace 10.1.1.5
- traceroute 10.1.1.5
- tracert 10.1.1.5*
- ping 10.1.1.5
239. Fill in the blank.
To prevent faulty network devices from carrying dangerous voltage levels, equipment must be grounded *correctly
240. What is a possible hazard that can be caused by network cables in a fire?
- The cable insulation could be flammable.*
- Users could be exposed to excessive voltage.
- Network cables could be exposed to water.
- The network cable could explode.
241. What device is commonly used to verify a UTP cable?
- a multimeter
- an Optical Time Domain Reflectometer
- a cable tester*
- an ohmmeter
242. What needs to be checked when testing a UTP network cable?
- capacitance
- wire map*
- inductance
- flexibility
243. Refer to the exhibit. A ping to PC2 is issued from PC0, PC1, and PC3 in this exact order. Which MAC addresses will be contained in the S1 MAC address table that is associated with the Fa0/1 port?
- just PC0 and PC1 MAC addresses*
- just the PC0 MAC address
- PC0, PC1, and PC2 MAC addresses
- just the PC1 MAC address
- just the PC2 MAC address
244. Which function is provided by TCP?
- data encapsulation
- detection of missing packets*
- communication session control
- path determination for data packets
245. What does a router use to determine where to send data it receives from the network?
- an ARP table
- a routing table*
- the destination PC physical address
- a switching table
246. Which router interface should be used for direct remote access to the router via a modem?
- an inband router interface
- a console port
- a serial WAN interface
- an AUX port*
247. A technician is configuring a router to allow for all forms of management access. As part of each different type of access, the technician is trying to type the command login. Which configuration mode should be entered to do this task?
- user executive mode
- global configuration mode
- any line configuration mode*
- privileged EXEC mode
248. Which three statements characterize the transport layer protocols? (Choose three.)
- TCP and UDP port numbers are used by application layer protocols.*
- TCP uses port numbers to provide reliable transportation of IP packets.
- UDP uses windowing and acknowledgments for reliable transfer of data.
- TCP uses windowing and sequencing to provide reliable transfer of data.*
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. UDP is a connectionless protocol.*
249. Refer to the exhibit. A TCP segment from a server has been captured by Wireshark, which is running on a host. What acknowledgement number will the host return for the TCP segment that has been received?
- 2
- 21
- 250
- 306*
- 2921
250. Which statement is true about an interface that is configured with the IPv6 address command?
- IPv6 traffic-forwarding is enabled on the interface.
- A link-local IPv6 address is automatically configured on the interface.*
- A global unicast IPv6 address is dynamically configured on the interface.
- Any IPv4 addresses that are assigned to the interface are replaced with an IPv6 address.
251. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator must send a message to everyone on the router A network. What is the broadcast address for network 172.16.16.0/22?
- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255*
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
252. A network administrator is variably subnetting a given block of IPv4 addresses. Which combination of network addresses and prefix lengths will make the most efficient use of addresses when the need is for 2 subnets capable of supporting 10 hosts and 1 subnet that can support 6 hosts?
- 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.144/28
10.1.1.160/29* - 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.144/28
10.1.1.160/28 - 10.1.1.128/28
10.1.1.140/28
10.1.1.158/26 - 10.1.1.128/26
10.1.1.144/26
10.1.1.160/26 - 10.1.1.128/26
10.1.1.140/26
10.1.1.158/28
253. How many additional bits should be borrowed from a /26 subnet mask in order to create subnets for WAN links that need only 2 useable addresses?
- 2
- 3
- 4*
- 5
- 6
254. A network administrator requires access to manage routers and switches locally and remotely. Match the description to the access method. (Not all options are used.)
255. Refer to the exhibit. The administrator configured the access to the console and the vty lines of a router. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?
- Unauthorized individuals can connect to the router via Telnet without entering a password.
- Because the IOS includes the login command on the vty lines by default, access to the device via Telnet will require authentication.*
- Access to the vty lines will not be allowed via Telnet by anyone.
- Because the login command was omitted, the password cisco command is not applied to the vty lines.
256. An administrator issued the service password-encryption command to apply encryption to the passwords configured for enable password, vty, and console lines. What will be the consequences if the administrator later issues the no service password-encryption command?
- It will remove encryption from all passwords.
- It will reverse only the vty and console password encryptions.
- It will not reverse any encryption.*
- It will reverse only the enable password encryption.
257. After making configuration changes, a network administrator issues a copy running-config startup-config command in a Cisco switch. What is the result of issuing this command?
- The new configuration will be stored in flash memory.
- The new configuration will be loaded if the switch is restarted.*
- The current IOS file will be replaced with the newly configured file.
- The configuration changes will be removed and the original configuration will be restored.
258. What are two features of ARP? (Choose two.)
- If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.*
- An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
- When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
- If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
- If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.*
259. A network administrator is enabling services on a newly installed server. Which two statements describe how services are used on a server? (Choose two.)
- Data sent with a service that uses TCP is received in the order the data was sent.
- A port is considered to be open when it has an active server application that is assigned to it.*
- An individual server can have two services that are assigned to the same port number.
- An individual server cannot have multiple services running at the same time.
- Server security can be improved by closing ports that are associated with unused services.*
260. Given the binary address of 11101100 00010001 00001100 00001010, which address does this represent in dotted decimal format?
- 234.17.10.9
- 234.16.12.10
- 236.17.12.6
- 236.17.12.10*
261. A particular telnet site does not appear to be responding on a Windows 7 computer. What command could the technician use to show any cached DNS entries for this web page?
- ipconfig /all
- arp -a
- ipconfig /displaydns*
- nslookup
262. Fill in the blank.
Network devices come in two physical configurations. Devices that have expansion slots that provide the flexibility to add new modules have a Modular * configuration.
263. Refer to the exhibit. What is the maximum TIL value that is used to reach the destination www.cisco.com?
- 11
- 12
- 13*
- 14
264. Which statement is true about DHCP operation?
- When a device that is configured to use DHCP boots, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network.*
- A client must wait for lease expiration before it sends another DHCPREOUEST message.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the IP address and sub net masK to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway.
- If the client receives several DHCPOFFER messages from different servers, it sends a unicast DHCPREOUEST message to the server from which it chooses to obtain the IP information.
265. Which type of wireless security is easily compromised?
- EAP
- PSK
- WEP*
- WPA
266. A network administrator notices that the throughput on the network appears lower than expected when compared to the end-to-end network bandwidth. Which three factors can explain this difference? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic*
- the type of data encapsulation in use
- the type of traffic*
- the number and type of network devices that the data is crossing*
- the bandwidth of the connection to the ISP
- the reliability of the network backbone
267. A host PC is attempting to lease an address through DHCP. What message is sent by the server to the client know it is able to use the provided IP information?
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER*
- DHCPPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
268. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses console line to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?
- letmein
- secretin
- lineconin*
- linevtyin
269. How many bits would need to be borrowed if a network admin were given the IP addressing scheme of 172.16.0.0/16 and needed no more than 16 subnet with equal number of hosts?
- 10
- 12
- 2
- 4*
- 8
270. Question:
It will give 4 options about ping, the correct one is:
The PC2 will be able to ping 192.168.1.1*
271. Which statement best describes the operation of the File Transfer Protocol?
- An FTP client uses a source port number of 21 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP Server.
- An FTP client uses a source port number of 20 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of data traffic with an FTP Server.
- An FTP server uses a source port number of 20 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP client.*
- An FTP server uses a source port number of 21 and a randomly generated destination port number during the establishment of control traffic with an FTP client.
272. A client is establishing a TCP session with a server. How is the acknowledgment number in the response segment to the client determined?
- The acknowledgment number field is modified by adding 1 to the randomly chosen initial sequence number in response to the client.*
- The acknowledgment number is set to 11 to signify an acknowledgment packet and synchronization packet back to the client.
- The acknowledgment number field uses a random source port number in response to the client.
- The acknowledgment number is set to 1 to signify an acknowledgment packet back to the client.
273. Why does layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP and subnet Mask?
- to identify host address and destination host;
- to identify network address of destination host;*
- to identify faulty frames;
- to identify broadcast address of destination network;
274. There was also a question about if you activated service password encryption in the past and you prompt “no service password encryption” what password are modified ?
- no password at all;*
- password of the lines are in clear;
- login password;
- ?
275. What type of communication rule would best describe CSMA/CD?
- message encapsulation
- flow control
- message encoding
- access method*
276. What is the primary reason to subnet IPv6 prefixes?
- to conserve IPv6 addresses
- to avoid wasting IPv6 addresses
- to conserve IPv6 prefixes
- to create a hierarchical Layer 3 network design*
277. Which statement describes data throughput?
- It is the measure of the bits transferred across the media under perfect conditions.
- It is the measure of the bits transferred across the media over a given period of time.*
- It indicates the capacity of a particular medium to carry data.
- It is the guaranteed data transfer rate offered by an ISP.
278. Fill in the blank. Use a number.
IPv4 multicast addresses are directly mapped to IEEE 802 (Ethernet) MAC addresses using the last ___4___ of the 28 available bits in the IPv4 multicast group address.
279. How could a faulty network device create a source of hazard for a user? (Choose two.)
- It could stop functioning.*
- It could apply dangerous voltage to other pieces of equipment.
- It could explode.*
- It could produce an unsafe electromagnetic field.
- It could apply dangerous voltage to itself.
280. What are three important considerations when planning the structure of an IP addressing scheme? (Choose three.)
- preventing duplication of addresses*
- providing and controlling access*
- documenting the network
- monitoring security and performance
- conserving addresses*
- implementing new services
281. What is the metric value that is used to reach the 10.1.1.0 network in the following routing table entry? D 10.1.1.0/24 [90/2170112] via 209.165.200.226, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/0
- 24
- 90
- 05
- 2170112*
282. Which two services or protocols use the preferred UDP protocol for fast transmission and low overhead? (Choose two)
- VoIP*
- DNS*
- HTTP
- FTP
- POP3
283. What action does a DHCPv4 client take if it receives more than one DHCPOFFER from multiple DHCP servers?
- It sends a DHCPREQUEST that identifies which lease offer the client is accepting.*
- It sends a DHCPNAK and begins the DHCP process over again.
- It discards both offers and sends a new DHCPDISCOVER.
- It accepts both DHCPOFFER messages and sends a DHCPACK.
284. To what legacy address class does the address 10.0.0.0 belong?
- Class B
- Class D
- Class A*
- Class C
- Class E
285. How many IPv4 addresses are available to be assigned to hosts on a network that has a mask of 255.255.255.248?
- 16
- 14
- 8
- 254
- 6*
- 2
286. What type of communication medium is used with a wireless LAN connection?
- radio waves*
- fiber
- microwave
- UTP
287. Which method of IPv6 prefix assignment relies on the prefix contained in RA messages?
- EUI-64
- static
- SLAAC*
- stateful DHCPv6
288. What is a characteristic of DNS?
- DNS servers can cache recent queries to reduce DNS query traffic.*
- DNS servers are programmed to drop requests for name translations that are not within their zone.
- All DNS servers must maintain mappings for the entire DNS structure.
- DNS relies on a hub-and-spoke topology with centralized servers.
289. What is the prefix for the host address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
- 2001:DB8:BC15
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A*
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12
290. What information is maintained in the CEF adjacency table?
- Layer 2 next hops
- MAC address to IPv4 address mappings*
- IP address to interface mappings
- the IP addresses of all neighboring routers
291. Which command can an administrator issue on a Cisco router to send debug messages to the vty lines?
- terminal monitor*
- logging console
- logging buffered
- logging synchronous
292. What is an example of a top-level domain?
- root.cisco.com
- http://www.cisco.com
- .com*
- cisco.com
293. Which protocol requires the establishment of a session between sender and receiver hosts prior to transmitting data?
- UDP
- TCP*
- IP
- ICMP
294. Which two protocols operate at the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose two.)
- TCP
- IP
- UDP
- POP
- DNS
- Ethernet
295. What does a client do when it has UDP datagrams to send?
- It sends to the server a segment with the SYN flag set to synchronize the conversation.
- It just sends the datagrams.*
- It queries the server to see if it is ready to receive data.
- It sends a simplified three-way handshake to the server.
296. What is a characteristic of multicast messages?
- They are sent to all hosts on a network.
- They must be acknowledged.
- They are sent to a select group of hosts.*
- They are sent to a single destination.
297. Which protocol or service uses UDP for a client-to-server communication and TCP for server-to-server communication?
- FTP
- HTTP
- DNS *
- SMTP
298. In what networking model would eDonkey, eMule, BitTorrent, Bitcoin, and LionShare be used?
- master-slave
- client-based
- peer-to-peer *
- point-to-point